Chapter 2 Molecular Interactions単語カード | Quizlet
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
C (backbone), H, O, N
What are the building blocks of large organic molecules?
anabolic reactions
What type of reaction is used to build macromolecules?
catabolic reactions
What type of reaction is used to break down macromolecules?
monosaccharides
monomers of carbohydrates
fatty acids
monomer of lipids
amino acids
monomers of proteins
nucleotides
monomers of nucleic acids
mono - 1 sugar
di - 2 sugars
poly - many sugars
What is the difference between a monosaccharide, disaccharide, and a polysaccharide?
monomer/monosaccharides
pentose sugar (5 carbons)
hexose sugar (6 carbons)
glucose
disaccharidases
sucrose, maltose, lactose
Polysaccharides
glycogen
triglycerides - lipids/fat (true lipid)
phopholipids - contains a phosphate group in molecule
steroids - derived from cholesterol
What are the structural and functional differences between triglycerides, phospholipids, and steroids?
glycerol
back bone of lipid
side chain (R group)
attached to amino acids
differ in size, shape, and ability to form hydrogen bonds or ions - helps amino acid react with other molecules in a unique way
primary structure of protein
the amino acid sequence of the polypeptide chain
secondary structure of protein
protein structure is formed by folding and twisting of amino acid chain
covalent bond angles between amino acid
alpha helix and beta strands form sheets
tertiary structure of protein
3D shape of protein
quaternary structure of a protein
multiple subunits combine with noncovalent bonds
hemoglobin molecules are made from 4 globular protein subunits
A = adenine
T = tri
D= di
M= mono
P = phosphate group
* the more phosphate, the more energy is stored in that nucleotide
What is the difference between ATP, ADP, and AMP?
adenine + ribose (sugar)+ (1, 2, 3) phosphates
What is the basic make up of a nucleotide?
deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
double helix nucleic acid structure
with nitrogenous bases
T - thymine
A - adenine
G - guanine
C - cytosine
T = A
C = G
What are the complementary base pairs in DNA?
A = U
C = G
What are the complementary base pairs in RNA?
Ribose Nucleic Acid (RNA)
single linear strand of nucleic acid
protons
charge: +
located in nucleus
neutrons
no charge
located in nucleus
electrons
charge: -
located in orbital
covalent bond
A chemical bond formed when two atoms share electrons
ex: H2O
ions
atoms that have gained or lost electrons (transfer)
nonpolar molecule - hydrophobic (hating)
molecule that shares\ electrons equally and does not have oppositely charged ends
CO2
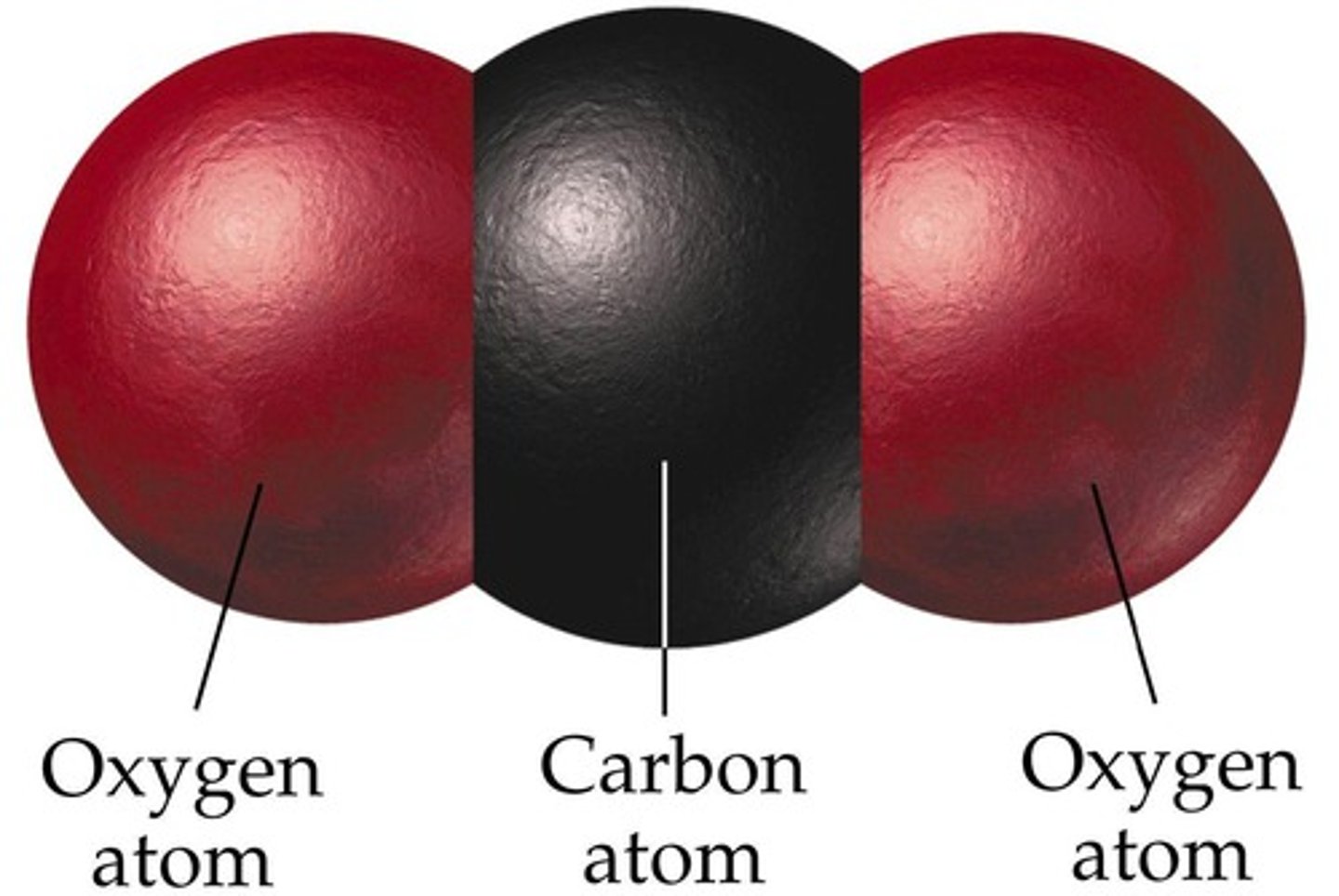
polar molecule - hydrophilic (loving)
a molecule in which one side of the molecule is slightly negative and the opposite side is slightly positive
H2O
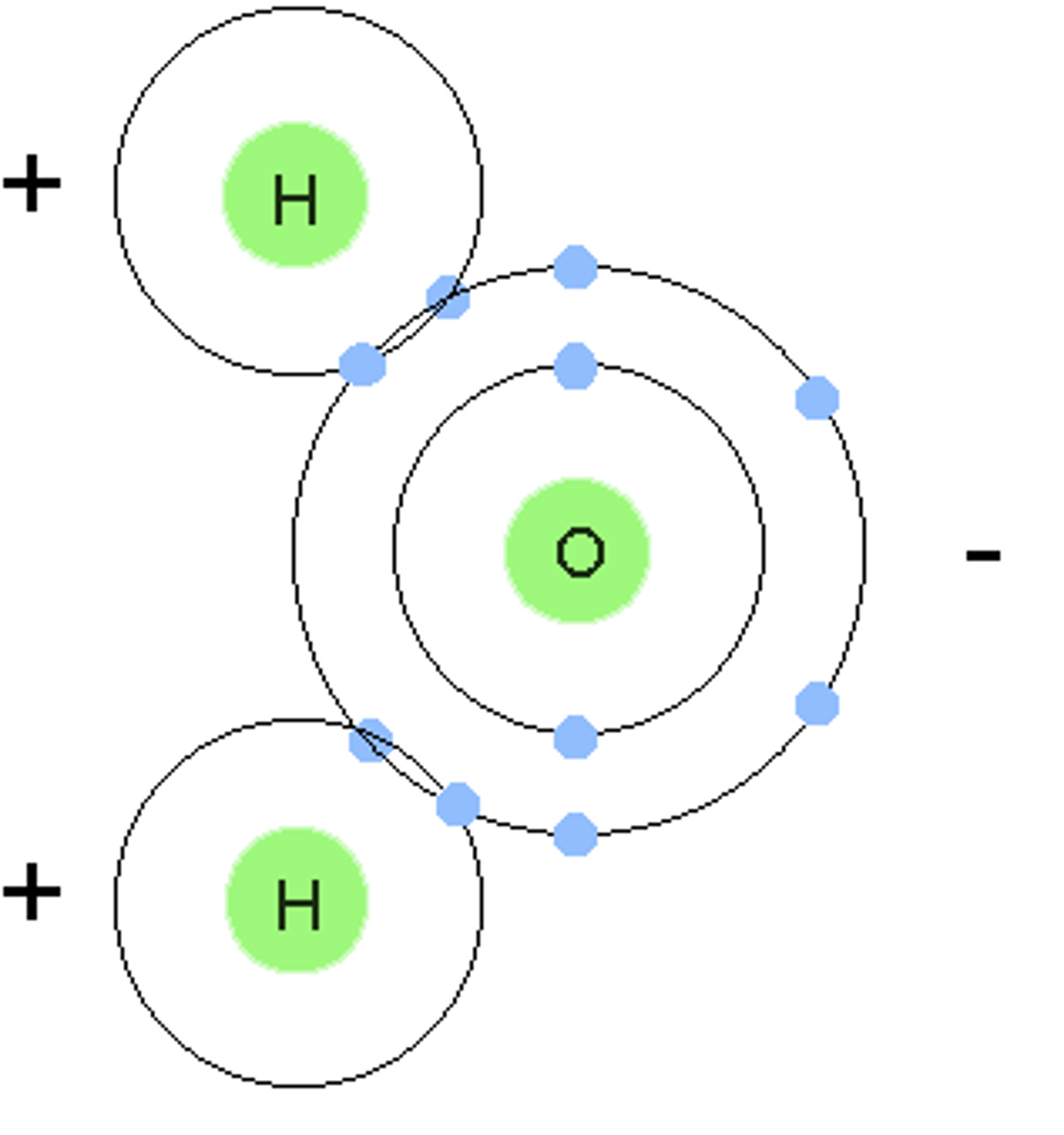
polarity
Molecules having uneven distribution of charges
positive on one end and negative on another
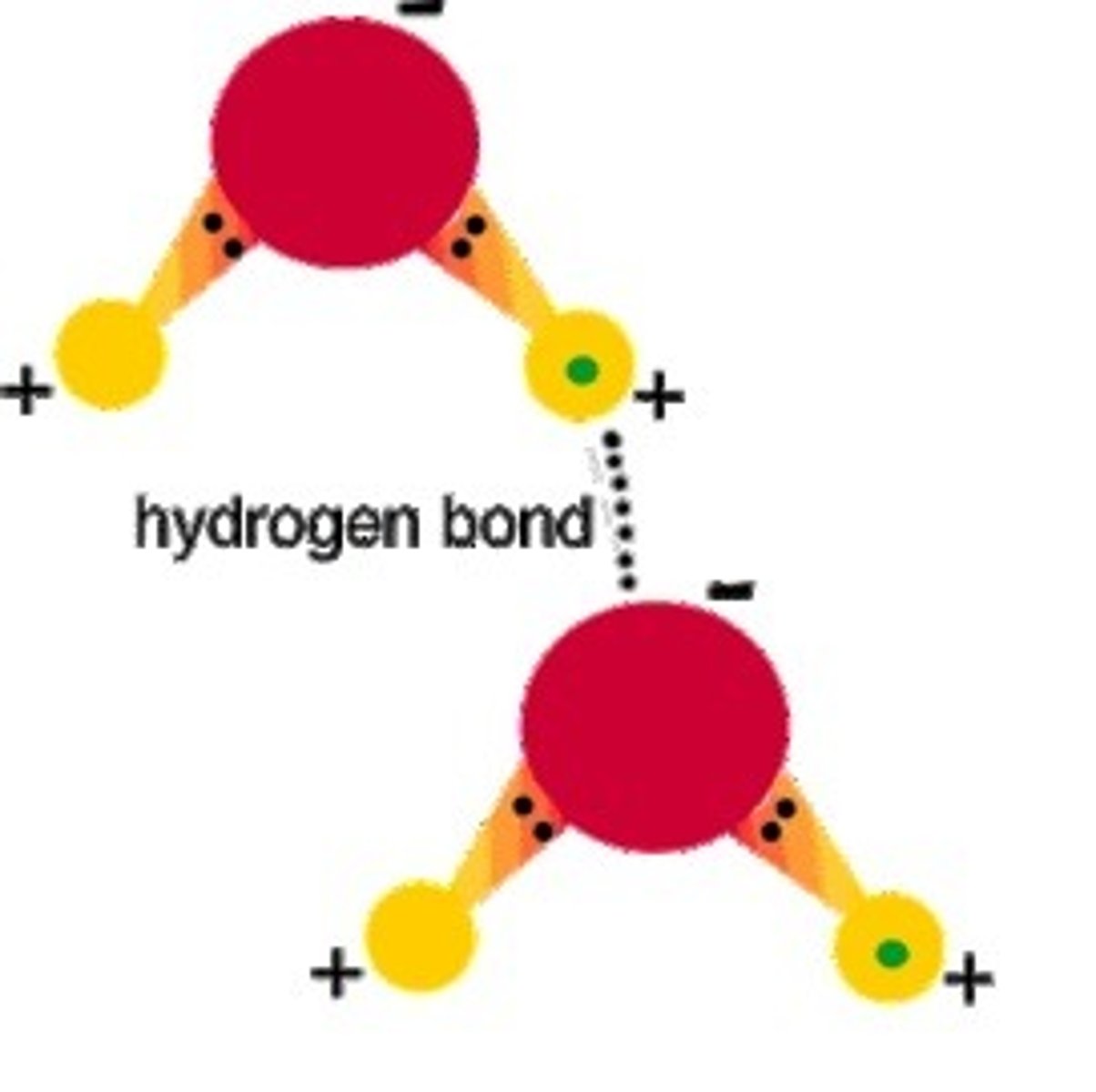
hydrogen bonds
weak attraction (temporary bonds) between a hydrogen atom and another atom
H2O attracted to another H2O
(hydrogen attracted to a different oxygen)
van der Waals forces
non-specific attraction between one atom's nucleus and another atom's electrons
solvent
A liquid substance capable of dissolving other substances
solute
A substance that is dissolved in a solution.
Solubility
The ability to dissolve in another substance
Hydrophobic
Water fearing
nonpolar - does not separate in water
Hydrophilic
water loving
polar - separates in water
amphipathic
having both a hydrophilic region and a hydrophobic region
concentration = amount of solute / unit solvent
What is concentration a measure of?
Yes - it is water loving and polar meaning it will dissolve in water
Would a hydrophilic molecule be soluble in water?
No - it hates water and is nonpolar meaning it will not dissolve in water
Would a hydrophobic molecule be soluble in water?
% solution
X g/100 mL
5% solution = 5 g solute per 100 mL solution
molarity
moles/Liter
3 Mole solution = 3 mol/L
mole
atomic mass of an atom
gram molecular weight of a molecule
(sum of atomic mass of all atoms in a molecule expressed as grams)
below 7
acidic pH
above 7
basic pH
7-7.7
neutral pH
acids
releases a H+ in water
bases
release OH- or accept H+
enzymes
membrane transport
signal molecules
receptors
binding
immunoglobulins
regulatory
What are some functions of proteins?
binding site
binds ligand or substrate
specificity
molecular complementarity
reversible binding
can be unbound; affinity = how likely/well it binds
competition
agonist VS. antagonist
mimics each others actions VS. working against/inhibiting
isoforms
slightly different versions of the same protein
function is similar
Protelysis
change structure of polypeptide
allosteric modulation
a modulator that binds to protein to activate a binding site for a ligand
covalent modulation
binds covalently to protein to change activity (phosphates)
cofactors
nonprotein enzyme helpers - assist with function
denaturing
the breakdown or unfolding of protein (becomes inactive)
up regulation
production of more proteins - more activity
down regulation
removal of proteins - less activity