Volumetric Muscle Loss
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
muscle injury
loss of muscle function caused by physical disruption of muscle structures involved in producing/transmitting force
muscle
bundle of fascicles
fascicle
bundle of muscle fibers
muscle cells/fibers
bundle of myofibrils; multinucleated cells
myofibril
bundle of sarcomeres
sarcomere
contains a lattice of thick myosin and thin actin protein filaments
neuromuscular junction
synapse formed by contact between motor neuron and muscle fiber; site of signal exchange
muscle contraction
1. neurotransmitter causes release of calcium
2. calcium binds to actin
3. mysosin attaches to actin and pulls toward M-line
3 types of contractions
concentric, eccentric, isometric
most common type of contraction-induced injury
eccentric
concentric contraction
muscle contracts
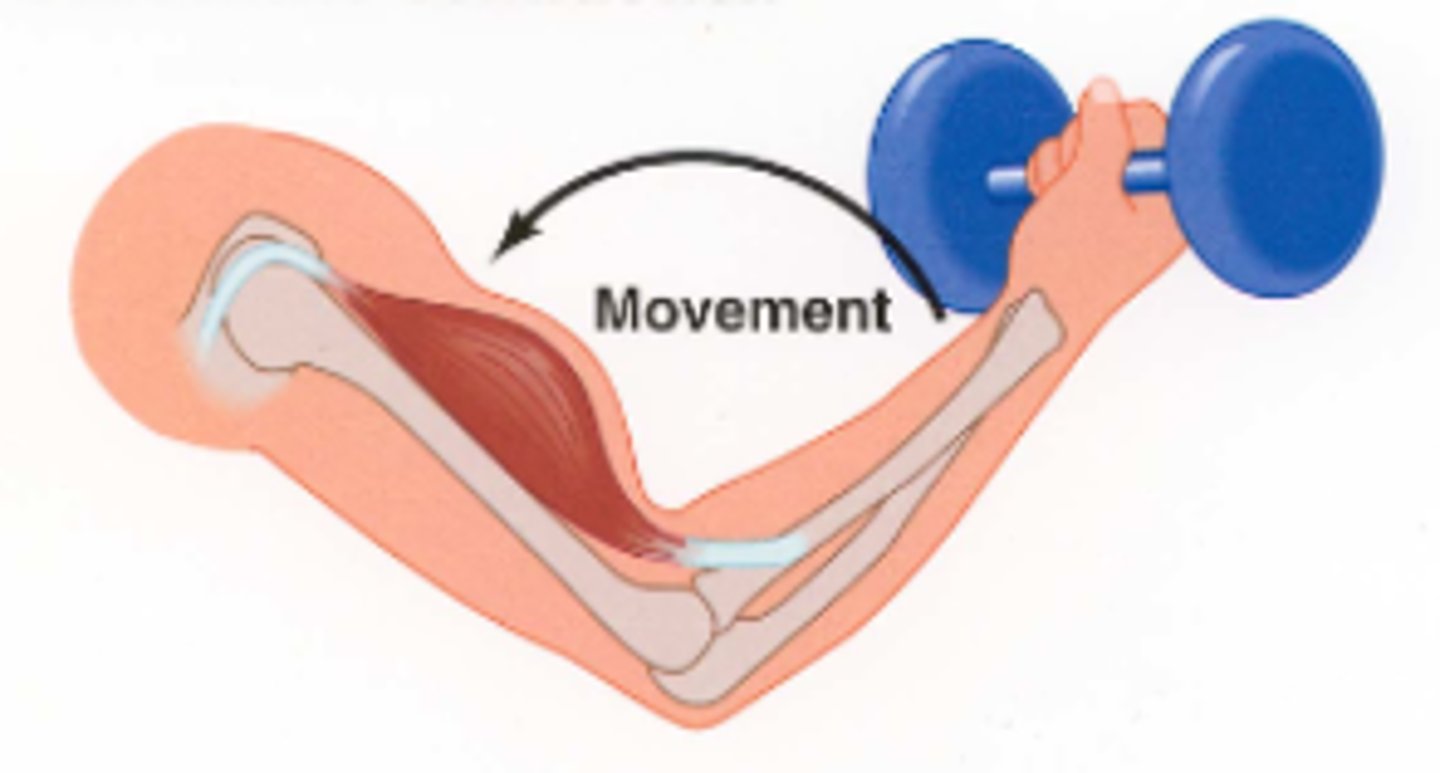
eccentric contraction
muscle elongates
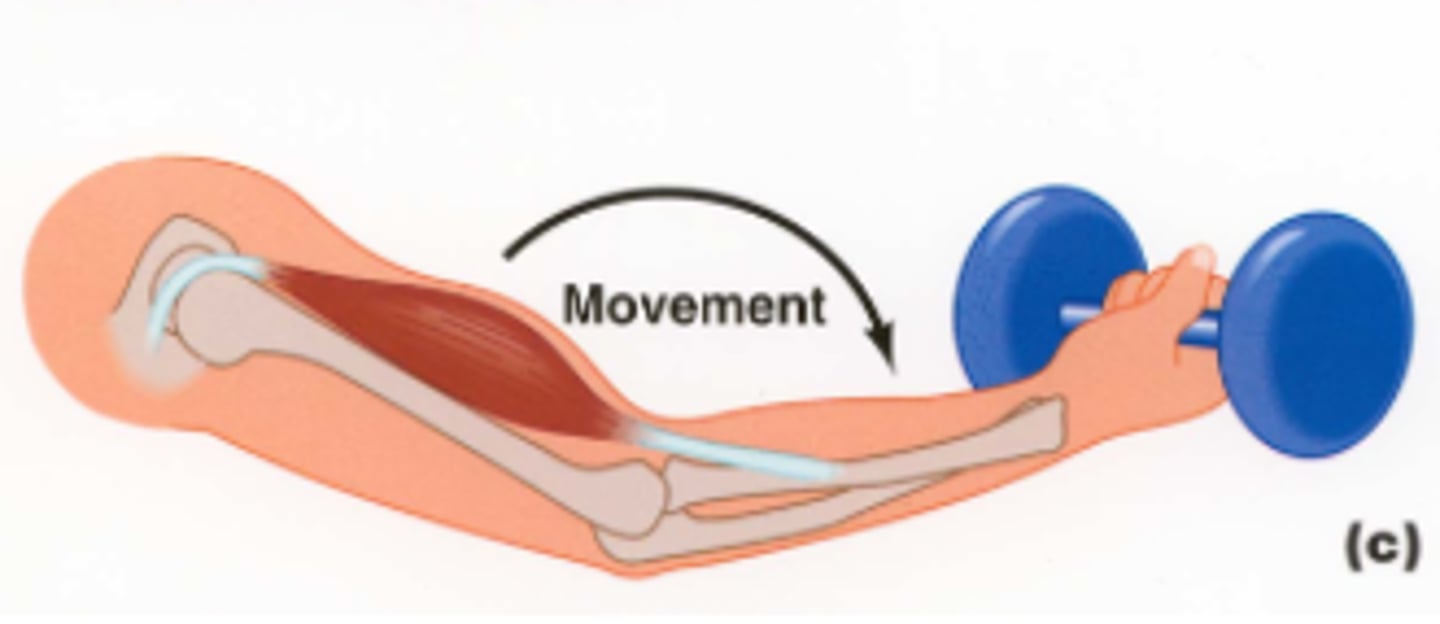
isometric contraction
muscle contraction

delayed-onset muscle soreness
exercise damages sarcomeres and sarcoplasmic reticulum -> Ca+ leaks out of sarcoplasmic reticulum and collects in mitochondria -> reduced ability of muscles to produce ATP and contract -> membrane damage -> inflammation and pain
neutrophils
immune cells that promote inflammation and degrade and phagocytize damaged myofibers
macrophages
immune cells that
- phagocytize hematoma and damaged tissue
- assist with ECM modeling
fibroblasts
promote ECM modeling and provide scaffold for muscle regeneration
satellite cells
muscle stem cells that
- differentiate into myoblasts
- fuse to form myotubes
- regenerate damaged muscle fibers
chemotaxis
migration of cells toward or away from a concentration gradient of a soluble chemical attractant
volumetric muscle loss injury
surgical or traumatic loss of muscle tissue; loss of at least 20% of a given muscle's mass
causes of VML injuries
excessive exercise, contusions, lacerations, surgical resection or reconstruction, combat injuries
main characteristics of VML injury
- persistent inflammation
- ECM breakdown/stiffening
- fibrosis
- regenerative progenitors inhibited
functional outcomes of VML
- muscle weakness
- loss of range of motion
- gait impairments
- late amputations due to functional deficits of the limb
surgical intervention for VML
suture muscle tissue
autologous muscle transfer
graft healthy muscle and skin from a donor site
long term outcomes of autologous muscle transfer
- scar tissue formation
- loss of muscle strength and function
- graft failure (10% of surgeries)
ultrasound
tool that uses high-frequency sound waves to generate an image
sonogram
the image the ultrasound generates
T1W imaging for VML
fibrosis is hypointense
disruptions in muscle tissue are hyperintense
How is VML indicated on MRI and CT?
decrease in muscle volume
dynameter
measures isokinetic exercises; for any forces exerted, machine produces equivalent resistance
dynametric evaluation
measures isokinetic exercises; patient performs multiple repetitions of flexion and extension; assesses strength, work done, and endurance ratio
dorsiflexion
tilt ankle up
plantarflexion
tilt ankle down
effect of VML on isometric strength and range of motion?
reduced
why are endogenous repair mechanisms impaired after VML?
loss/dysfunction of satellite cells and loss/dysfunction of ECM
ECM function
provides structure and modulates behavior and communication of endogenous cells
ECM scaffold
transplantation of decellularized ECM provides a scaffold for repair and regeneration
functions of ECM scaffold
- provides structural support
- recruits endogenous cells
- provides trophic factor support
ECM scaffold preclinical findings
- improvements in muscle activation
- defect site filled with granulation in non-treated animals
- cellularized with host cells
ECM scaffold clinical findings
- promotes angiogenesis and recruitment of perivascular stem cells
- leads to formation of new skeletal muscle cells
- increases force production and muscle strength
3 ATP generator systems
glycolysis, krebs cycle, electron transport chain
molecule used to generate ATP in glycolysis
glucose
by-products of glycolysis
2 pyruvate, 2 NADH
anaerobic respiration systems
glycolysis
aerobic respiration systems
krebs cycle, electron transport chain
effect of mitochondrial damage due to VML injury
- reduced oxidative capacity
- less ATP produced in muscle cell that can be used for contraction
mitochondrial biogenesis
the process by which new mitochondria are formed in the cell
fissioned mitochondria -> fusion -> fused mitochondria -> fission
PGC1-a
protein that regulates mitochondrial biogenesis; inhibits protein degradation pathways in mitochondria
effect of VML on mitochondrial structure and function
impair function and disruipts mitochondrial networks
effect of treatment with PGC1-a?
improved mitochondrial function and muscle strength
What does PGC1-a upregulation promote?
fusion > fission
isometric exercise
muscle contracts without changing length or visible joint movement
isokinetic exercise
muscle contracts while joint moves at constant speed