Human Anatomy Exam 3
1/144
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
145 Terms
keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
What specific tissue type is characteristic of the epidermis?
stomach
What digestive organ is found between the esophagus and the small intestine?
tongue
highly muscularized
taste-special senses
digestion- initial, mechanical, chemical
speech
lingual papillae
a variety of types on the tongue
lingual frenulum
tether that keeps our tongue in place so we dont swallow it.
clinical: ankyloglossia (being tongue tied)
intrinsic
_____ salivary glands are found on the tongue
32, 20
adults have ___ permanent teeth
baby/toddler has ___ deciduous (baby) teeth
incisors, premolars, molars
teeth:
2 ___
1 canine
2 ____ (bicuspids)
3 ____ (adults)
wisdom tooth
1. 2. 3 of homosapiens
tooth enamel
hard hydroxyapatite
dentin
firm, supportive, inorganic and organic throughout all levels of the teeth
cementum
anchors the root of a tooth into its socket
periodontal
____________ ligaments = gomphosis
gums
gingiva= _____
pulp cavity and root canal
what part of the tooth contains pulp, blood vessels, nerves, and lymphatics
saliva
what substance contains H2O, digestive enzymes, lysozymes, mucus, and opiorphin
parotid, submandibular, sublingual
what are the 3 extrinsic salivary glands:
____ glands & ducts,
____ glands,
____ glands
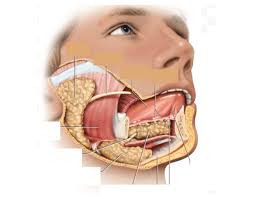
parotid gland and duct
what extrinsic gland is located anterior to the ear,
along ramus of mandible; its duct runs along masseter muscle and pierces buccinator muscle, open across from 2nd maxillary muscle
mumps
what is the clinical disease connected to the parotid gland
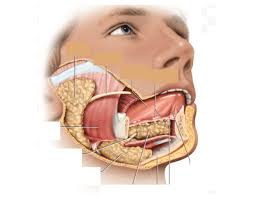
submandibular gland and ducts
what extrinsic gland lies under the medial body of mandible, ducts open on floor of oral cavity, adjacent to lingual frenulum
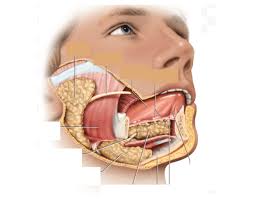
sublingual gland and smaller ducts
what extrinsic gland lies along inferior tongue
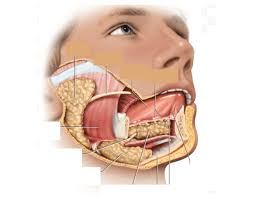
palate, breathe, nurse
anterior hard palate (maxilla)- palatine bone. separates oral and nasal cavity.
allows mammals to ____ and chew/___ at the same time
cleft palate and lip
what is the clinical complication with palates
pharynx
what is apart of the respiratory and digestive systems and is posterior to oral cavity. Has 3 parts.

nasopharynx, oropharynx, laryngopharynx
list in order from most superior to inferior the 3 parts of the pharynx
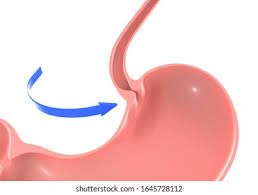
lower esophageal sphincter
what controls opening into the stomach
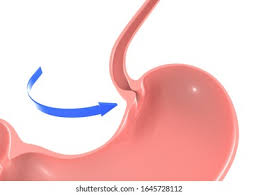
heartburn, gastroesophageal reflux
what is the clinical problem with the lower esophageal sphincter
____/acid reflux and _____ disease
abdominopelvic cavity
space where viscera are found
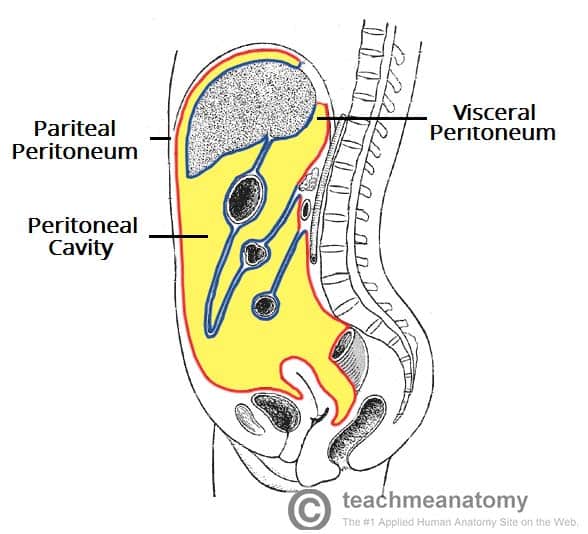
peritoneum
serous membrane of abdominopelvic cavity that is double layered, epithelial tissue lining, produces serous fluid
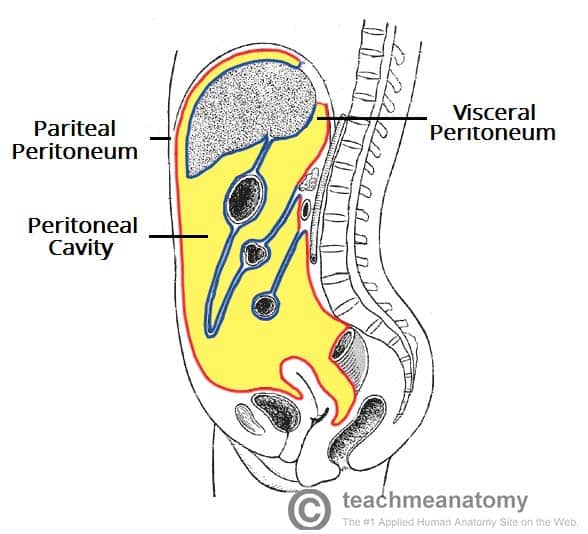
parietal
_________ peritoneum: 2 layers
lines the posterior cavity
retroperitoneal
when an organ is held against posterior wall of cavity: an example is the kidneys
visceral
_________ peritoneum= serosa: intra peritoneal
mesenteries
____________-layer sheets of peritoneum: encloses blood vessels, adipose connective tissue, nervous tissue endocrine cells
greater omentum
mesentery that drapes down from greater curvature of the stomach, covers majority of small intestine
visceral peritoneum
The serosa that covers much of the digestive tract is part of the ________________ of the abdominopelvic cavity.
nasopharynx
Which region of the pharynx is lined with ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium?
lesser omentum
mesentery that lies between the base of liver and lesser curvature of stomach
mesentary proper
which mesentery cover all of the small intestine
LU, pancreas, spleen, bolus, gastric rugae
Stomach: lies in the ___Q
anterior to ________ and ________
receives ________ from esophagus
lining of stomach= ________ (wrinkles)
gastric rugae
lining of stomach (wrinkles)
gastric juice, chyme
gastric glands --> _______
bolus --> __________
2-4 hours, mechanical and chemical
how long does it take to turn bolus to chyme? what kind of digestion takes place?
chyme
acidic soupy mix that enters the small intestine from the stomach
chief, pepsin
__ cells produce digestive enzymes (ex: ___)
HCL (acid)
PARIETAL cells produce __
endocrine
__ cells produce hormones (ex: GASTRIN)
columnar, gastric, gastric juice
Mucosa:
simple ___________ epithelium
find ___________ pits and glands that produce "________"
mucin
mucous neck cells produce ________
3-4 L
a 1L bolus when churned with gastric juice produces how many L of chyme
pyloric orifice, absorption, duodenum, jejunum, ileum
Small Intestine: 2-8m= 20ft/ Present in all quadrants/ receives chyme from _________.
functions: continued digestion, ________ of nutrients from chyme
3 sections: __________, _________, __________
duodenum
what part of the small intestine is a short, u shape that receives chyme from the stomach, bile from liver and gallbladder, and pancreatic juice from pancreas. Glands secrete more mucin
jejunum
what part of the small intestine contains mucosa
ileum
what part of the small intestine contains pyers patches and is the longest of the 3 sections
duodenum
Which region of the small intestine is the first to receive chyme from the stomach?
simple columnar epithelium
What type of epithelium is characteristic of the mucosa of the small intestine?
pyres patches
lymphatic nodules=
blood vessels, lipids
________ pickup nutrients and lacteals pickup __________
brush border
microvilli form the ____ of the mucosa
6,8, 16, H2O, absorption, compaction
Large Intestine:
___-___ hours from ingestion to enter cecum
In large intestine for ___hrs to several days
Functions: _______ and mineral __________
____________= feces formation
cecum
processed matter (processed chyme) from ileum via ileocecal valve.
cecum
_____
a POUCH full of good bacteria', fermentation, plant matter, lymphatic tissue
appendix
cecum:
____- lymphatic function
clinical: appendicitis
appendix
what comes off of the cecum
appendicitis, Mcburney’s point
what is the clinical diagnosis and landmark of the appendix
tenia coli
what are the ribbons of muscle on the colon
ascending, sigmoid
Colon:
_____ → transverse → descending → ____
omental appendages
fatty tags on the colon
colonoscopy
clinical diagnosis of colon
sigmoid, stretch receptors, rectal valves
Rectum: receives feces from _________ colon
___________= signal nervous system urge to defecate
_________= control and allow gas to pass
hemorrhoids, mucous, nonkeratinized, internal anal sphincter, skeletal, constipation
Anal Canal:
Along walls entering anal region
hemorrhoidal veins
clinical: ____________
anal columns and sinuses= more ______ production
return to a ____________ stratified squamous epithelium
___________= smooth muscle and exterior anal sphincter= __________ muscle
clinical: _____________
RU, LU, diaphragm, thoracic, bile, vitamins, minerals, synthesis
Liver: Mostly in ____Q and partially in ____Q
inferior to _____________, protected partly by _____________ cage
highly vascularized
largest gland!!
Functions: produces ________, detoxification, storage of ___________ and ___________, protein _____________
hepatic lobule
structural functional unit of liver and is made up of hepatocyte
cirrhosis of the liver
clinical diagnosis of liver
gallbladder
accessory to liver collects and concentrates bile
common bile, gallstones
___________ duct: through head of pancreas, joins pancreatic duct, into duodenum
clinical: ____
non keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
What type of epithelium lines the last region of the large intestine?
lacteals
What are the lymphatic vessels that absorb dietary fats (lipids) from within the intestinal villi of the small intestine?
pancreas, pancreatic juice, retroperitoneal, gallstones
_____:
both an endocrine and exocrine gland
__________: H2O, digestive enzymes, bicarbonate
mostly ________ in LUQ
clinical: _____
hormones, salivary glands
how the pancreas is endocrine or exocrine:
endocrine- secretes ____ via circulatory system (ex: insuline)
exocrine- secretes product into space/surface (ex: ____)
gas, homeostasis
what are the functions of the respiratory system:
___ exchange, communication, ____, conduction/filtering air, and smell
bronchioles and alveoli, everything else
respiratory division: includes?
conducting division: includes?
upper and lower
Respiratory system is divided into 2 parts:
ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium
what kind of histology is in the conducting division? _____ with goblet cells
nasal, trachea
upper respiratory system includes:
____ cavity, pharynx, larynx, ____
vestibules, vibrissae, nasal septum, ethmoid, vomer
Nose and Nasal Cavity:
Features- external nose, nares, nasal __________, nasal cartilages, ________(nose hair)
R and L sides are divided by ____________
Septum= perpendicular plate of __________ bone and _______
palate
what separates the digestive and respiratory system
nasal meatus
__________ = spaces/channels created by conchae
posterior nasal choana
the space that enters into nasopharynx
nasopharynx
which part of the pharynx is lined by nasal mucosa
larynx, epiglottis, thyroid, circoid, glottis
_____________= the "voice box" and receives air from the laryngopharynx
3 large cartilages and smaller paired cartilages : _______________, ______________,_____________
space= _____________
hyaline cartilage
what cartilage is the thyroid and cricoid
trachea
firm tube between larynx and brachial tree
mucociliary escalator
_____________: helps capture and move out debris
main bronchus, lobar bronchi, segmental bronchi
list in order the brachial tree from most medial to lateral
thoracic cage, superior, middle, inferior, superior, inferior, mediastinum, serous
Lungs:
protected by _________
3 Lobes of R lung: __________, _________, __________
2 Lobes of L lung: ___________ and ___________
________________= space between lungs/ post. to sternum
lungs covered with pleura= double layered _________membrane
cystic duct
Name the duct that is both an entrance to and exit from the gallbladder:
epiglottis
What structure has a foundation of elastic cartilage?
alveoli
clusters of connected spheres
between them there is gas exchange
simple squamous cells
what cells are responsible for gas exchange
(CO2 enters alveoli & leaves body)
(O2 moves from alveoli into RBC then back to heart)
asthma, lung, pneumonia
list some clinical problems with the lungs:
___, bronchitis, ___ cancer, ____
arteries, veins
Circulatory System:
away=
return=