(Anatomy) Bones of the Upper Limb Diagram | Quizlet
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
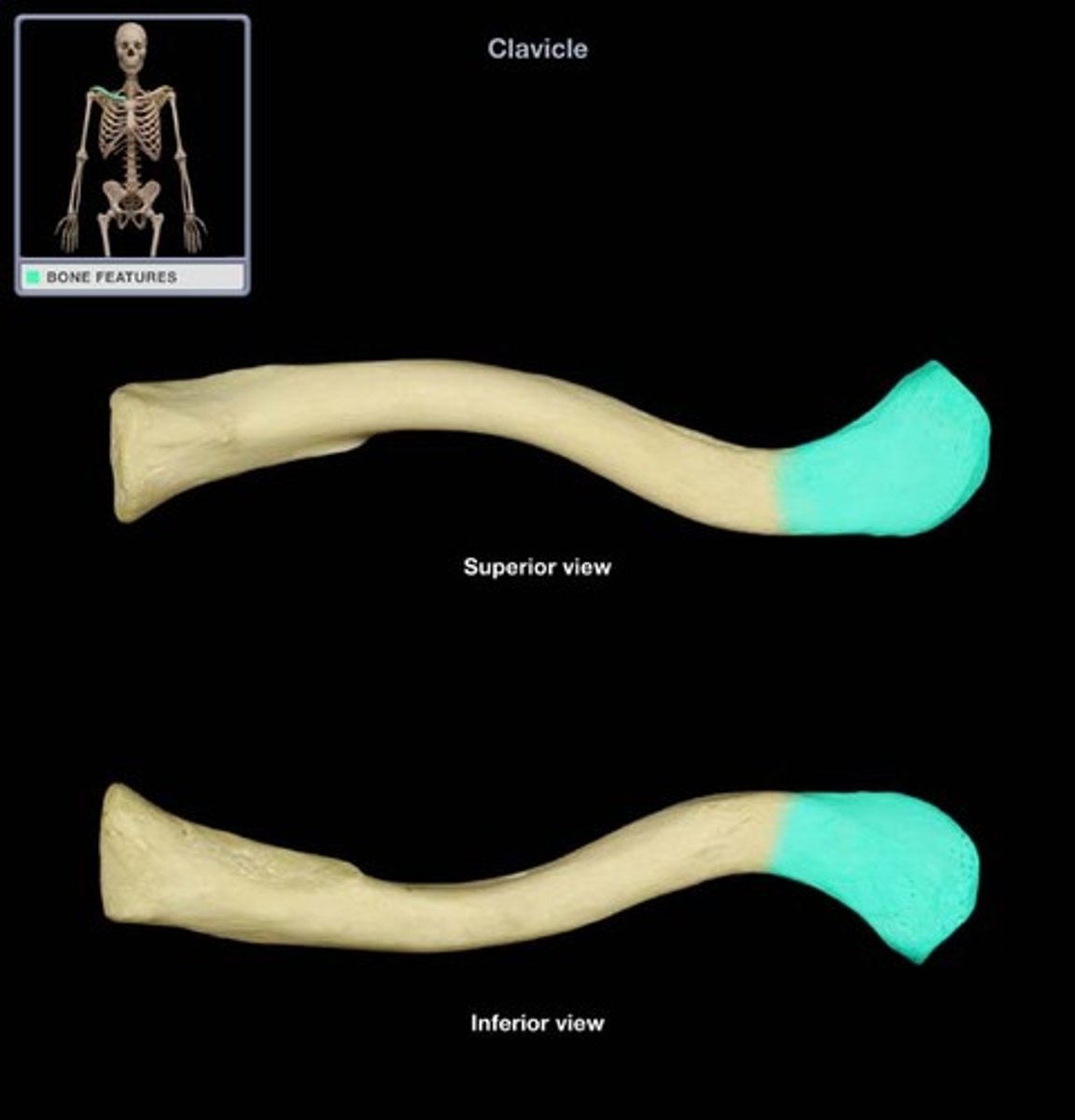
Clavicle
The Collar bone, connects the upper limb to the trunk
Sternal End of Clavicle
Enlarged and triangular
Articulates with the manubrium of the sternum at the sternoclavicular joint
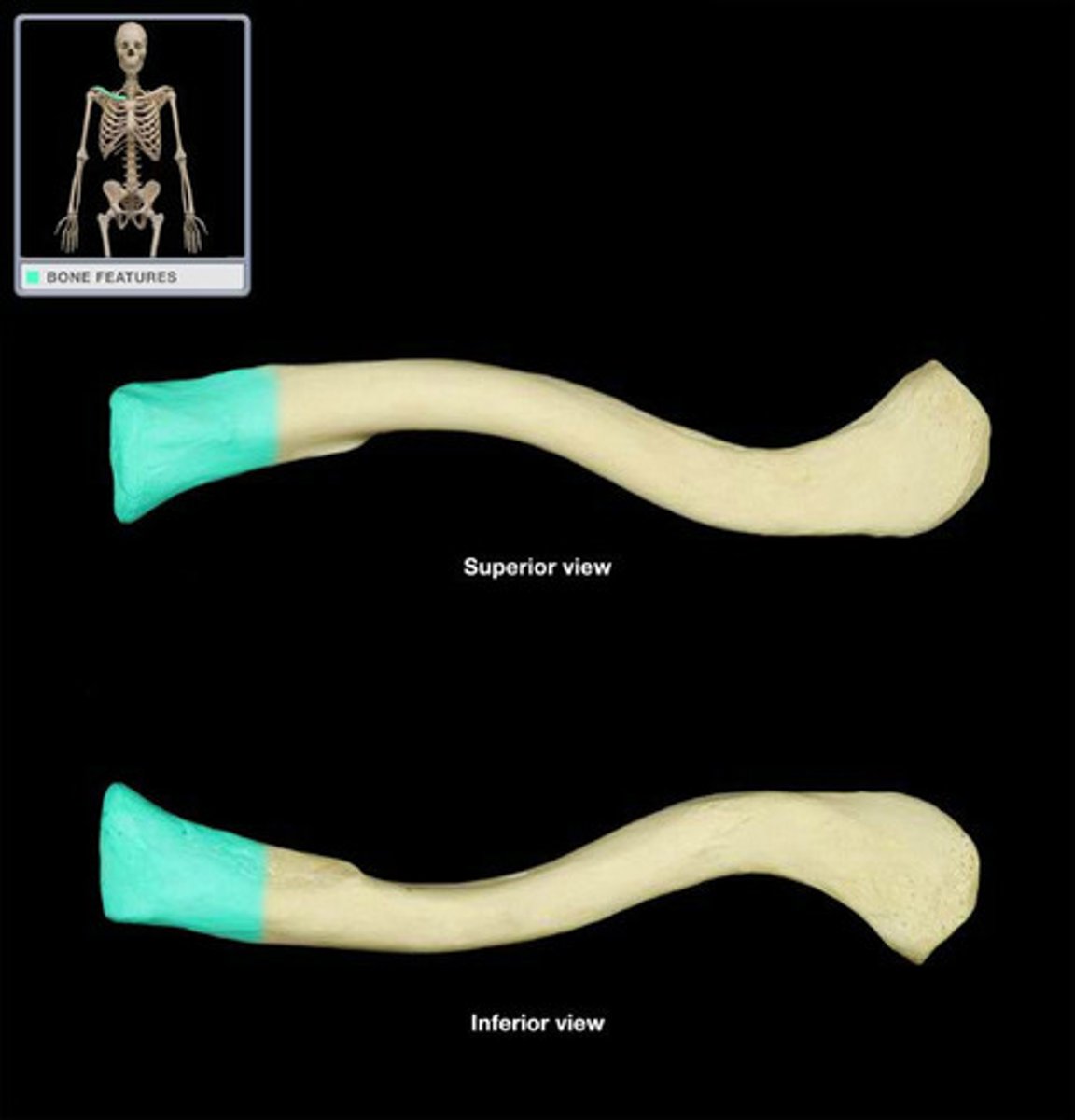
Acromial End of Clavicle
Flat where it articulates with the acromion of the scapula at the acromioclavicular joint
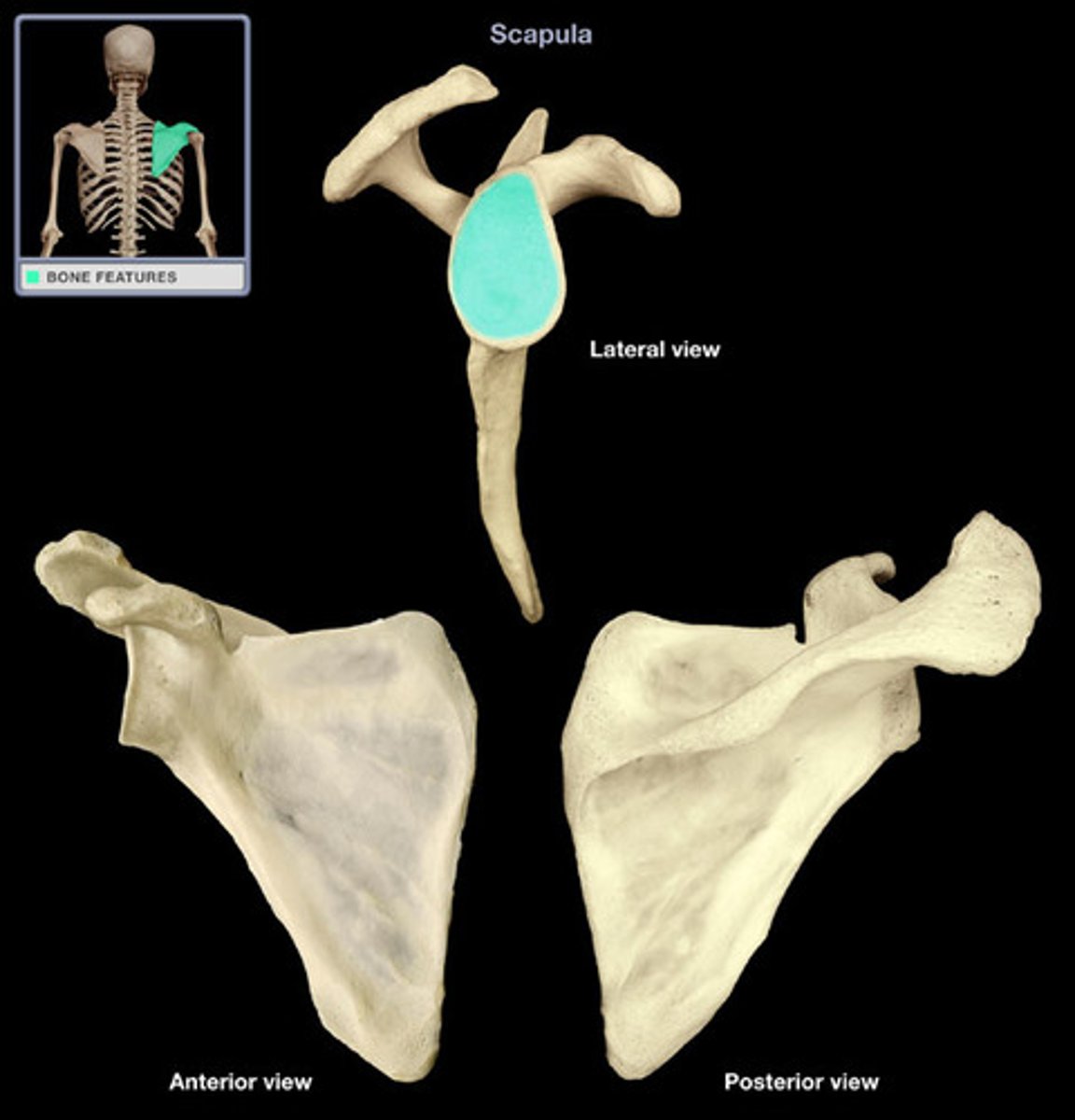
Scapula
Shoulder/ Wing bone
Etymology:
Originally meaning shovels
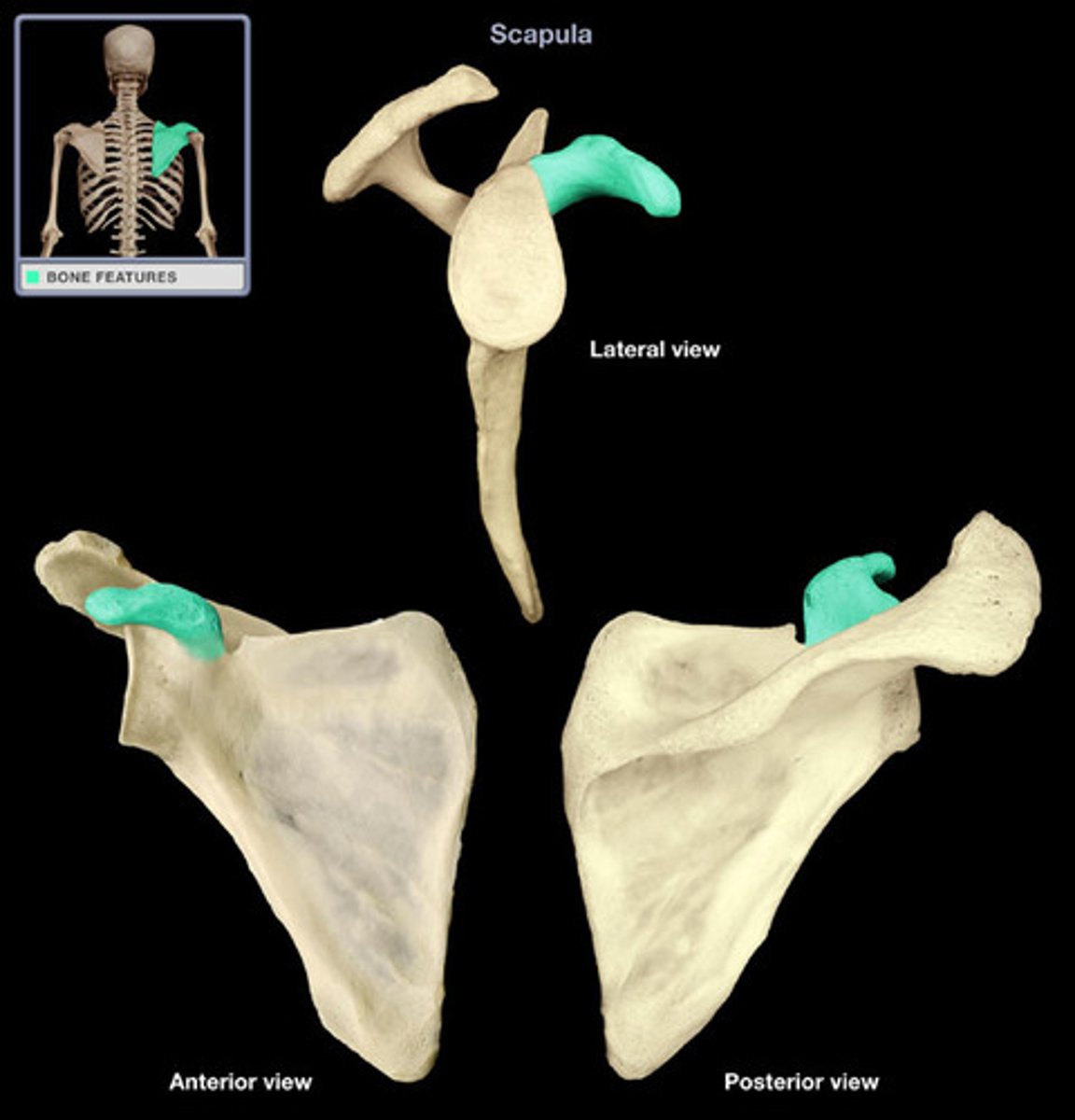
Coracoid Process
Serves to stabilize the shoulder joint.
Helps to anchor the biceps muscle of the arm
Etymology:
- Corac: like a raven's beak
- Process: a natural appendage/outgrowth
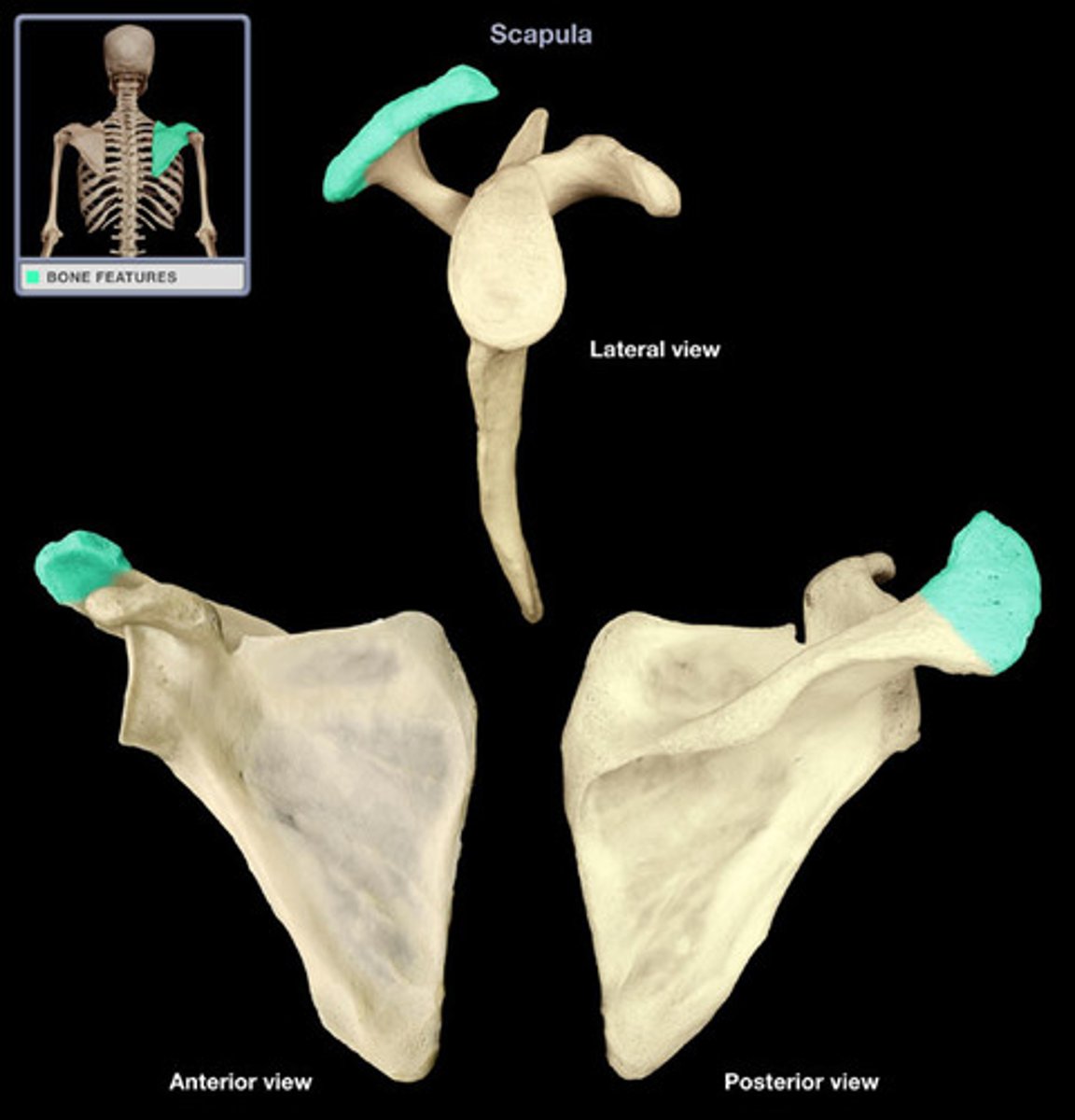
Acromion
Articulates with the acromial end of the clavicle, forms the acromioclavicular joint
Etymology:
- Akros: Highest
- Omos: Shoulder
The highest point in the shoulder
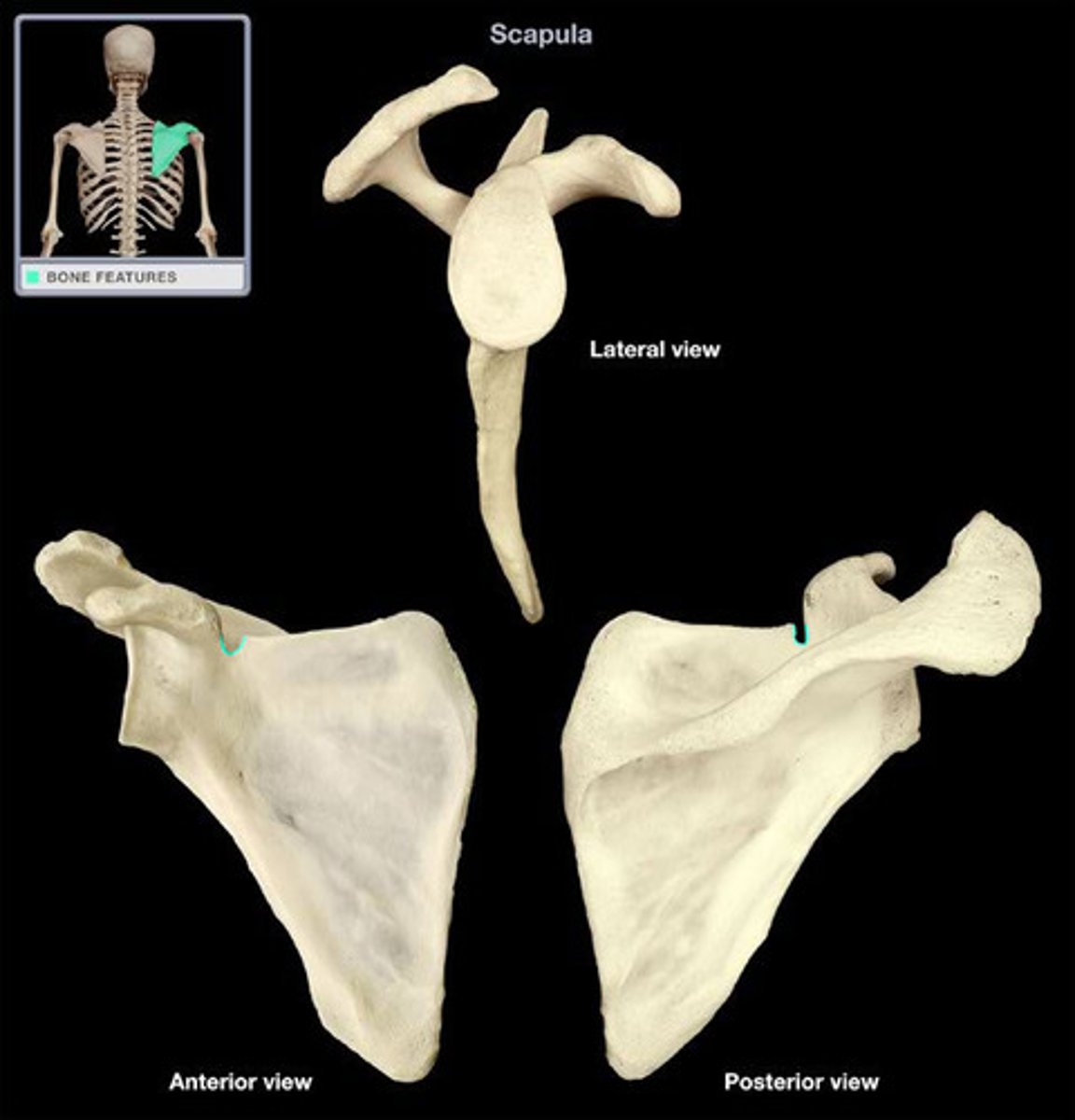
Suprascapular Notch
Supra: above
Suprascapular nerve passes through the notch
Superior transverse scapular ligament passes over the notch and attaches to the base of the coracoid process
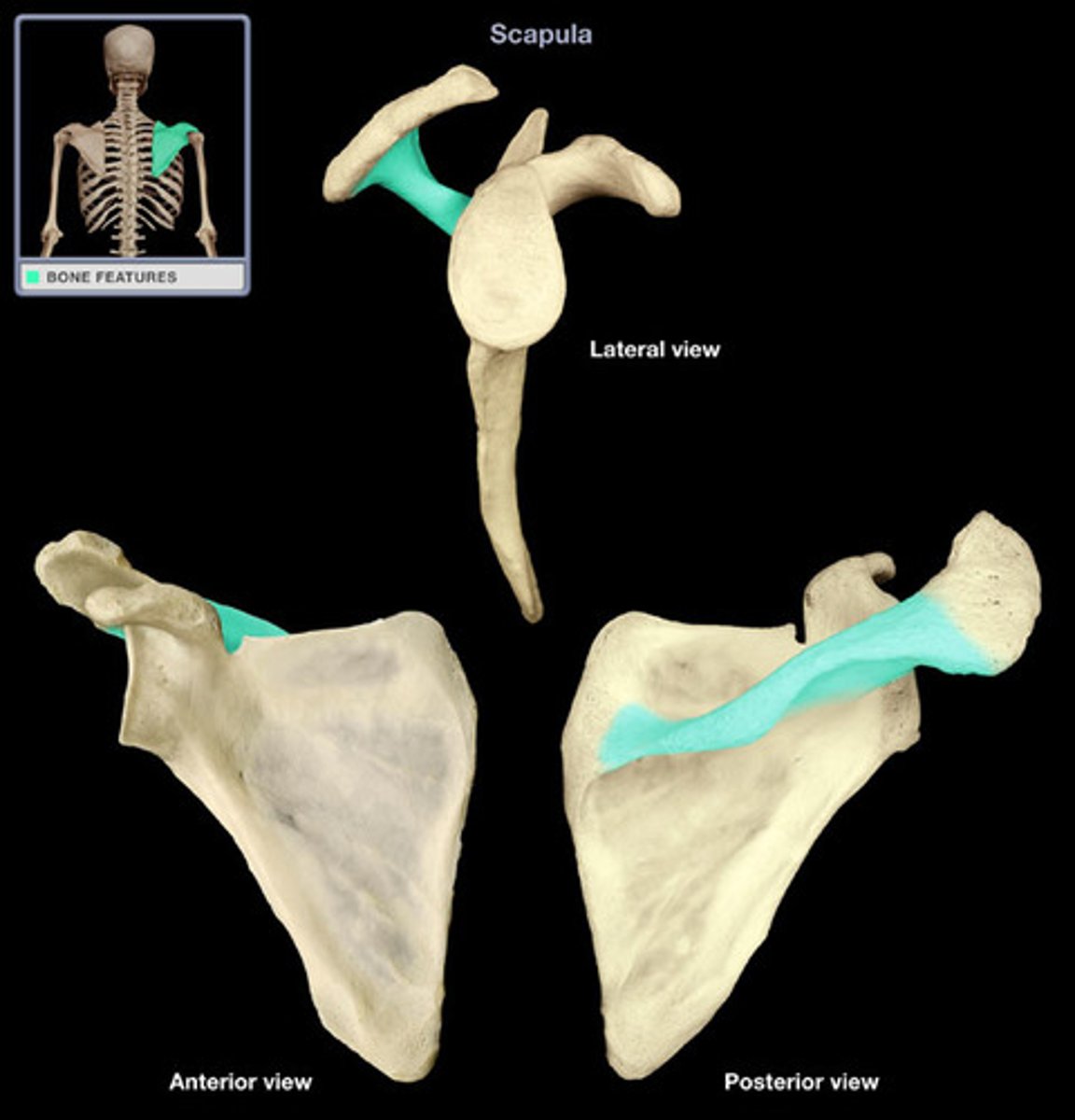
Spine of Scapula
Separates the supraspinous fossa from the infraspinous fossa
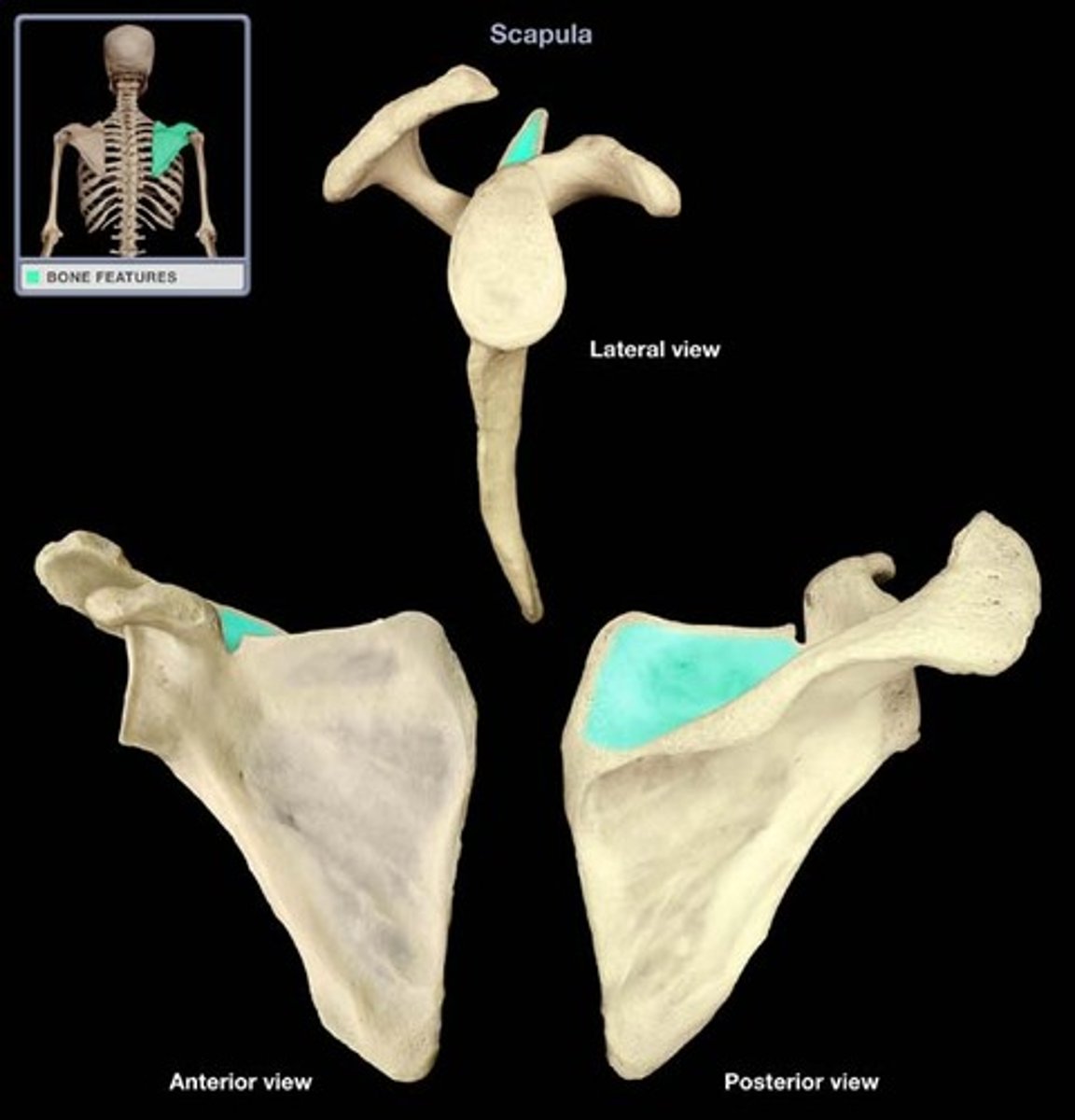
Supraspinous Fossa
Supra: above
Fossa: a shallow depression or hollow
Gives origin to the supraspinatus muscle
Insertion for levator scapulae ventralis muscle
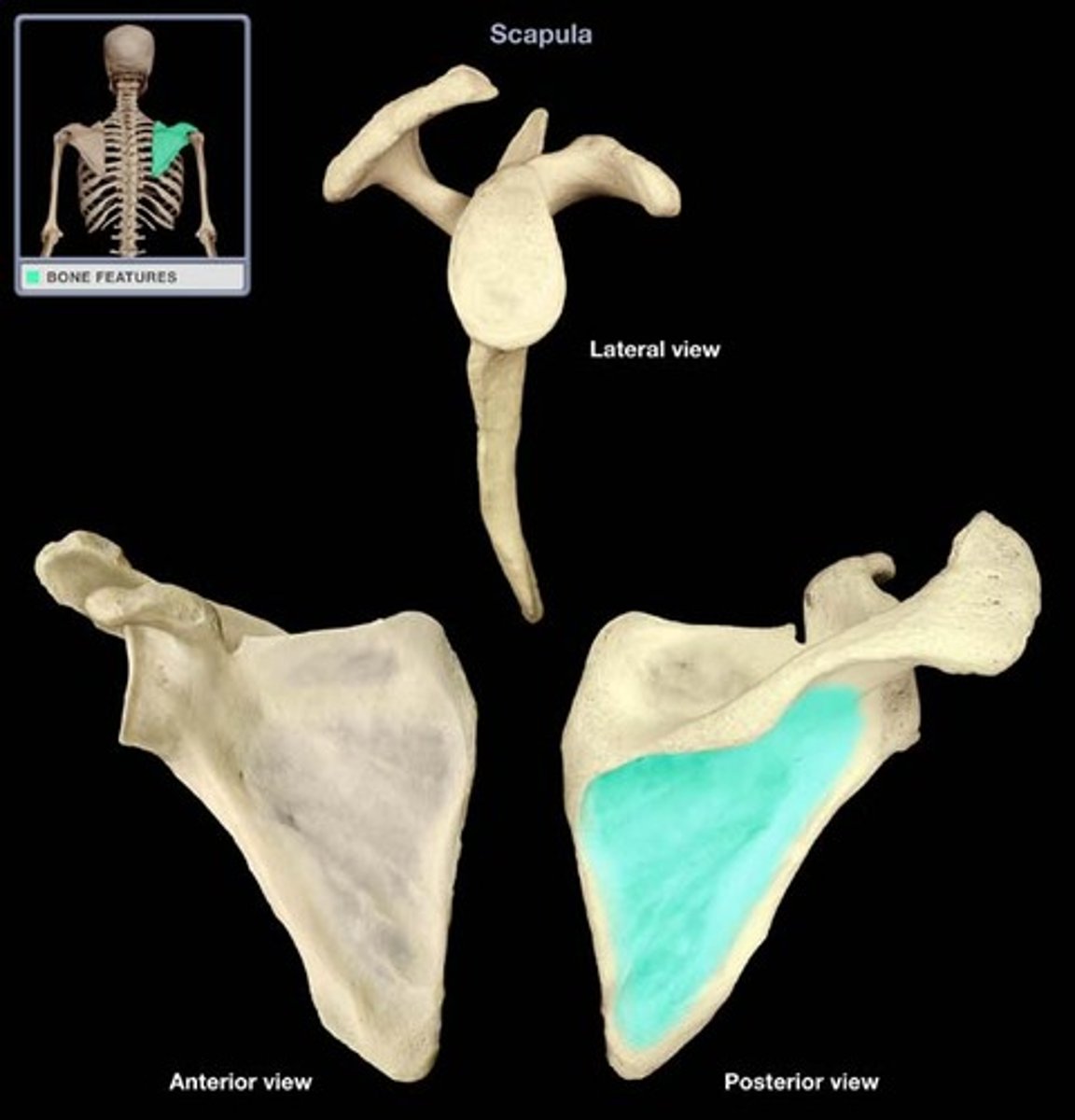
Infraspinous Fossa
Much larger than the supraspinatus fossa
Gives origin to the infraspinatus muscle
Etymology:
- Infra: below
- Fossa: a shallow depression or hollow
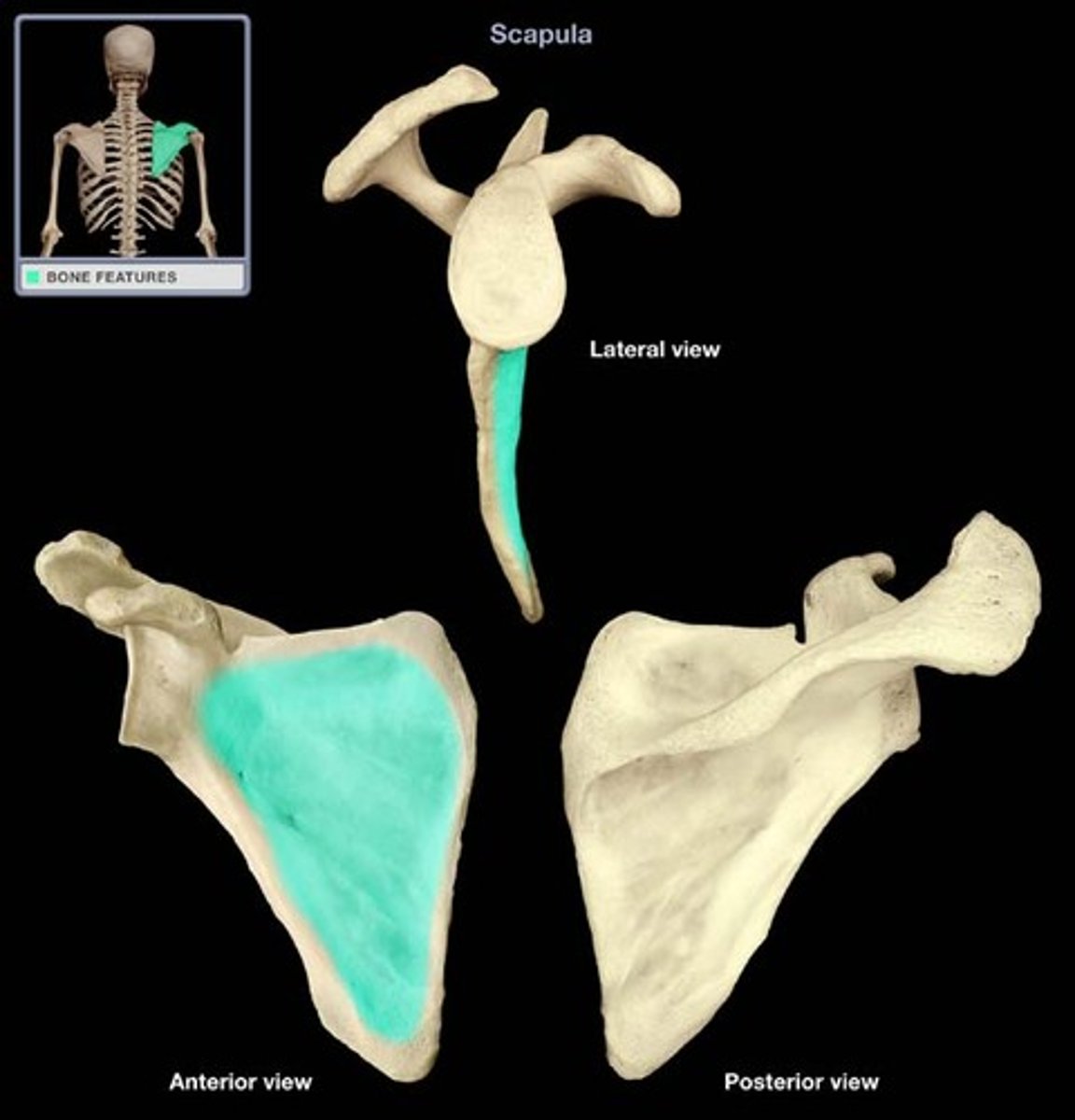
Subscapular Fossa
Gives origin to subscapularis muscle
Insertion for serratus anterior muscle
Etymology:
- Sub: below
- Fossa: a shallow depression or hollow
Glenoid Cavity
Articulates with humerus of the arm, forming the glenohumeral joint
Etymology:
- Glenoid, from the the Greek glene, socket, eyeball, or mirror, and eidus, shape.
Humerus
The only bone of the arm. The largest and longest bone of the upper limb.
Articulates with the scapula, radius and ulna.
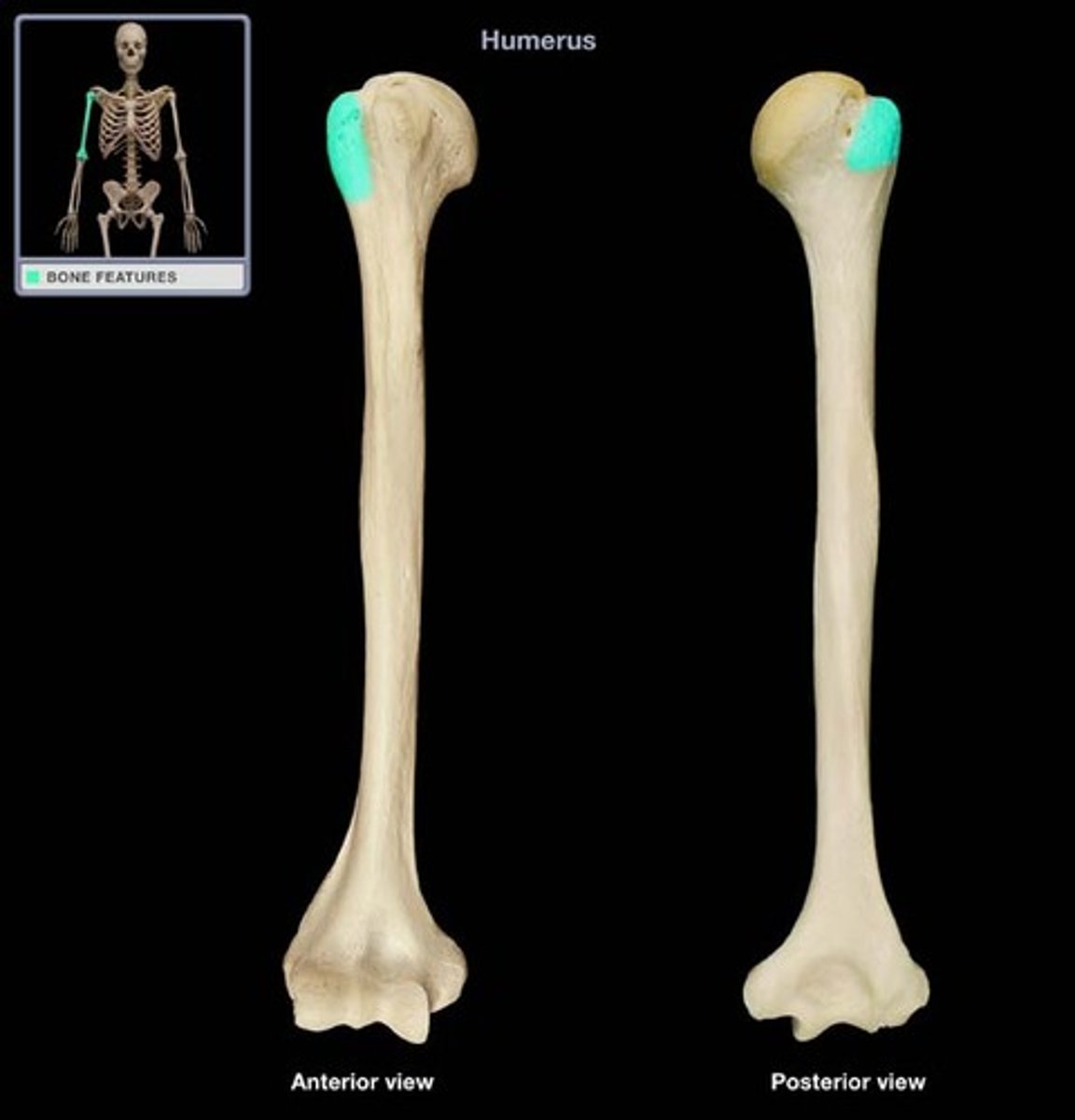
Greater Tubercle
Lies lateral to the head of the humerus.
Superior facet provides attachment for supraspinatus muscle
Middle facet provides attachment for infraspinatus muscle
Inferior facet provides attachment for teres minor muscle
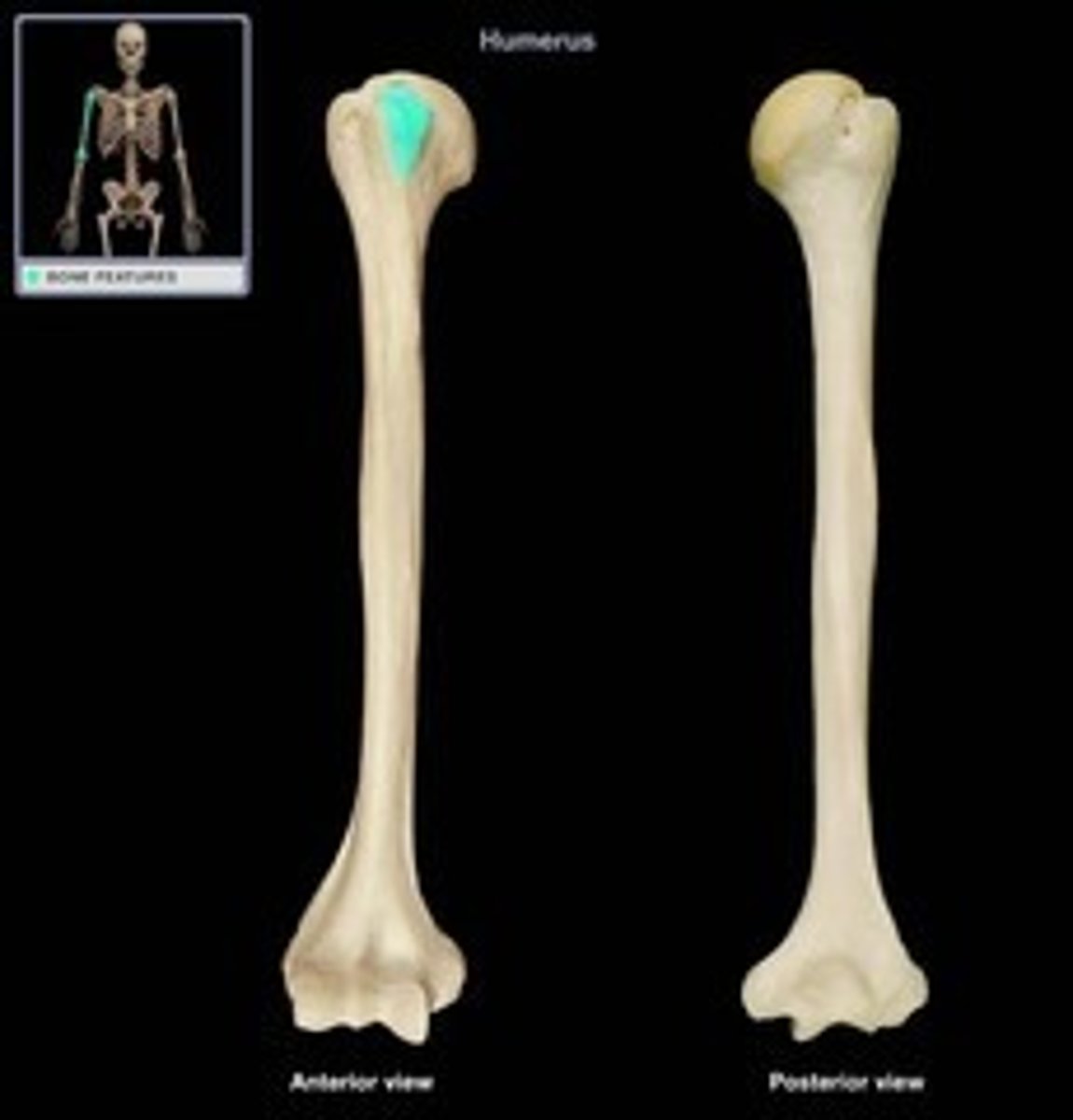
Lesser Tubercule
Provides attachment for the subscapularis muscle
Intertubercular Groove
Guides tendon of the (long head of) biceps to its attachment point at the rim of the glenoid cavity.
Latissimus dorsi insertion on floor of intertubercular groove
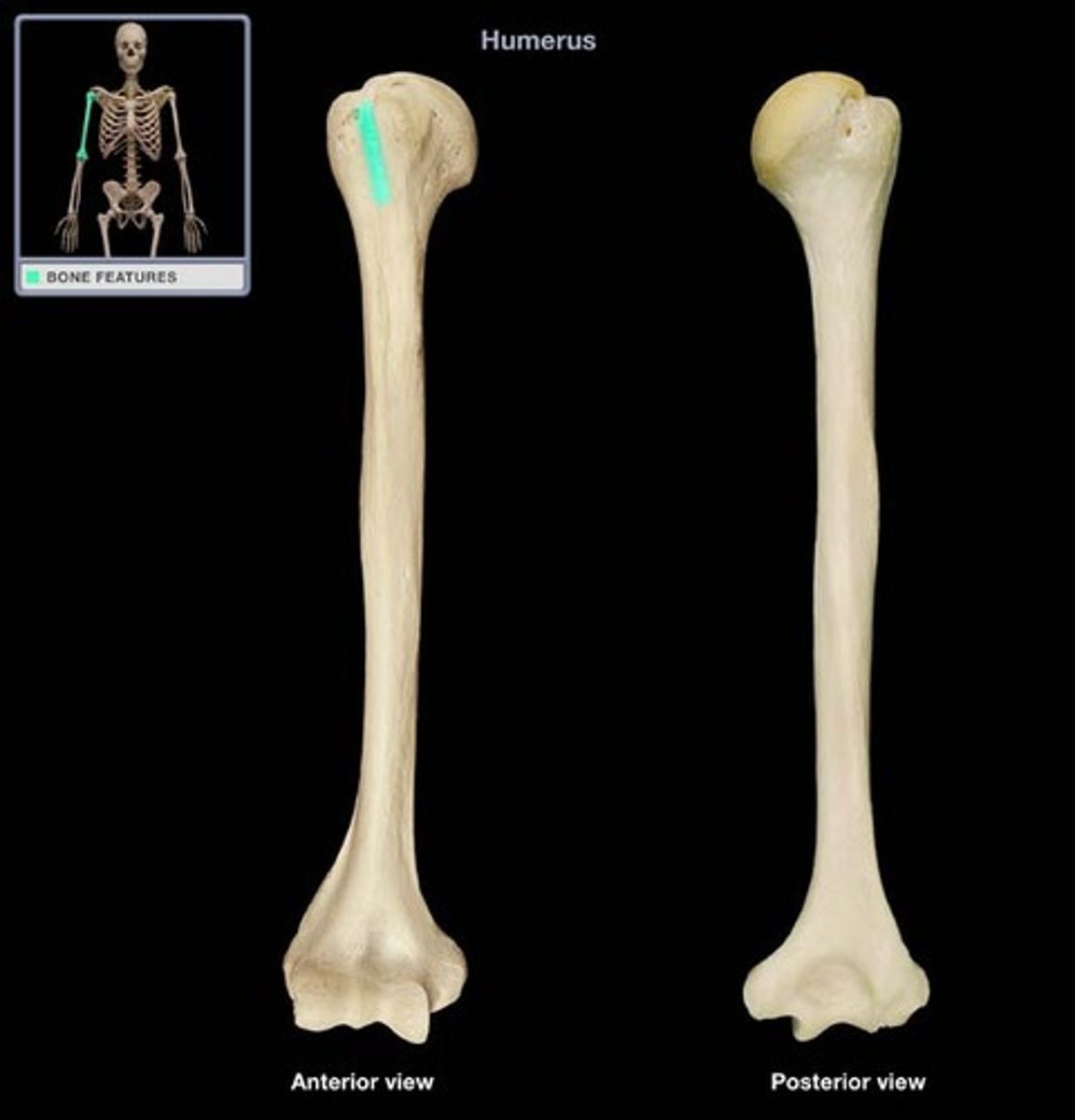
Anatomical Neck of Humerus
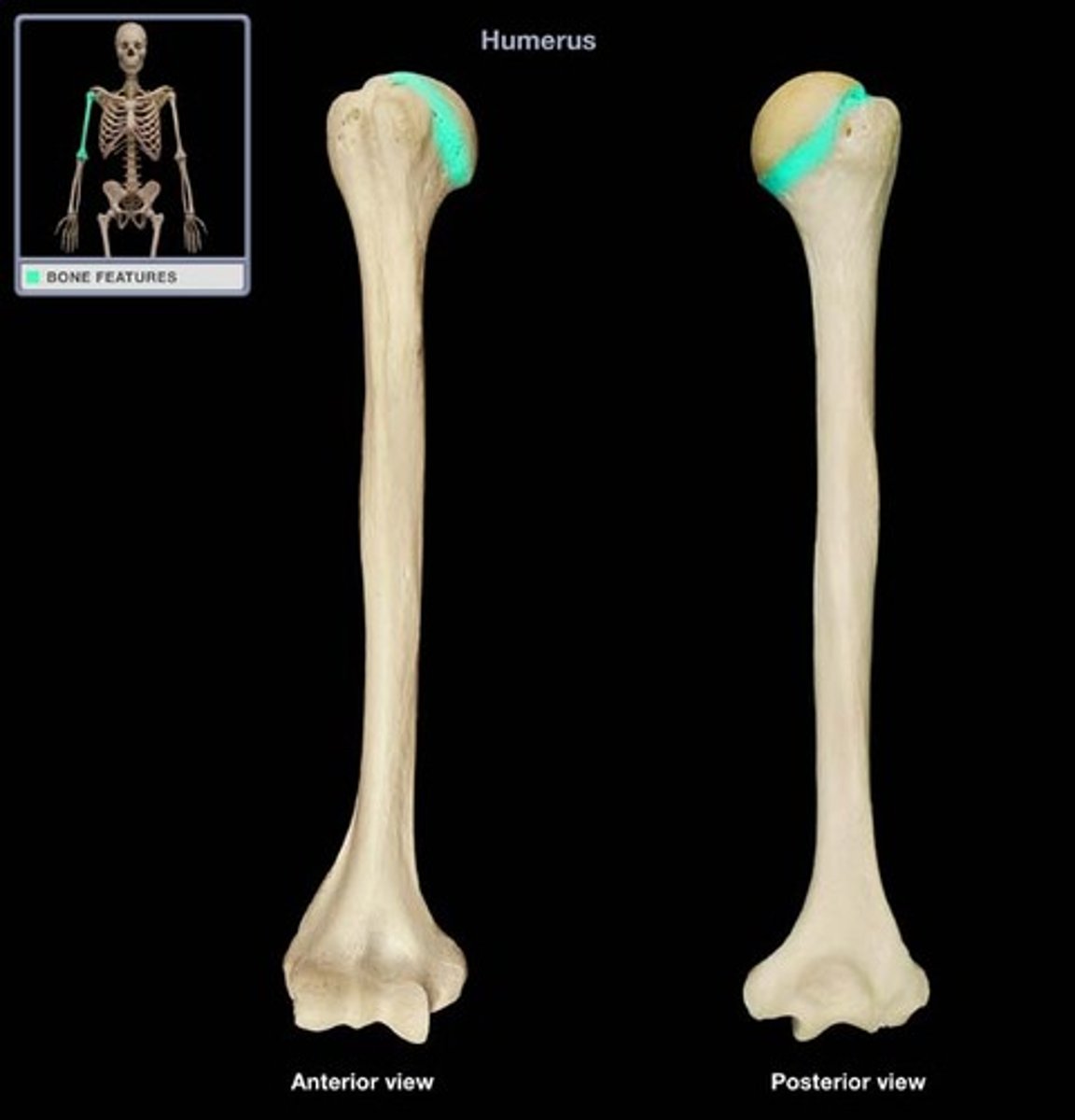
Surgical Neck of Humerus
Named due to it being the most commonly fractured site on the humerus.
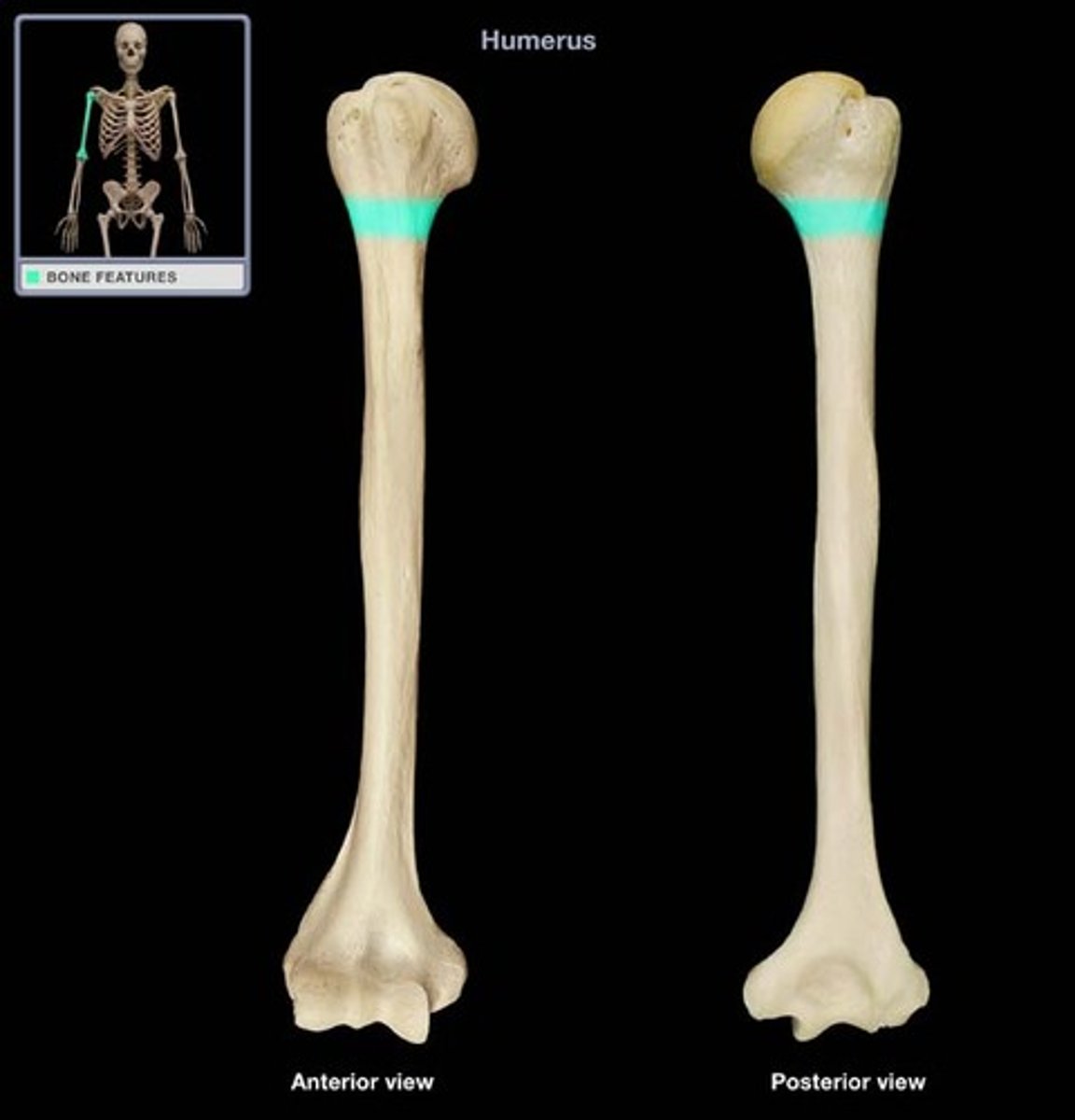
Deltoid Tuberosity
Midway down the shaft on the lateral side.
Attachment site for deltoid muscle.
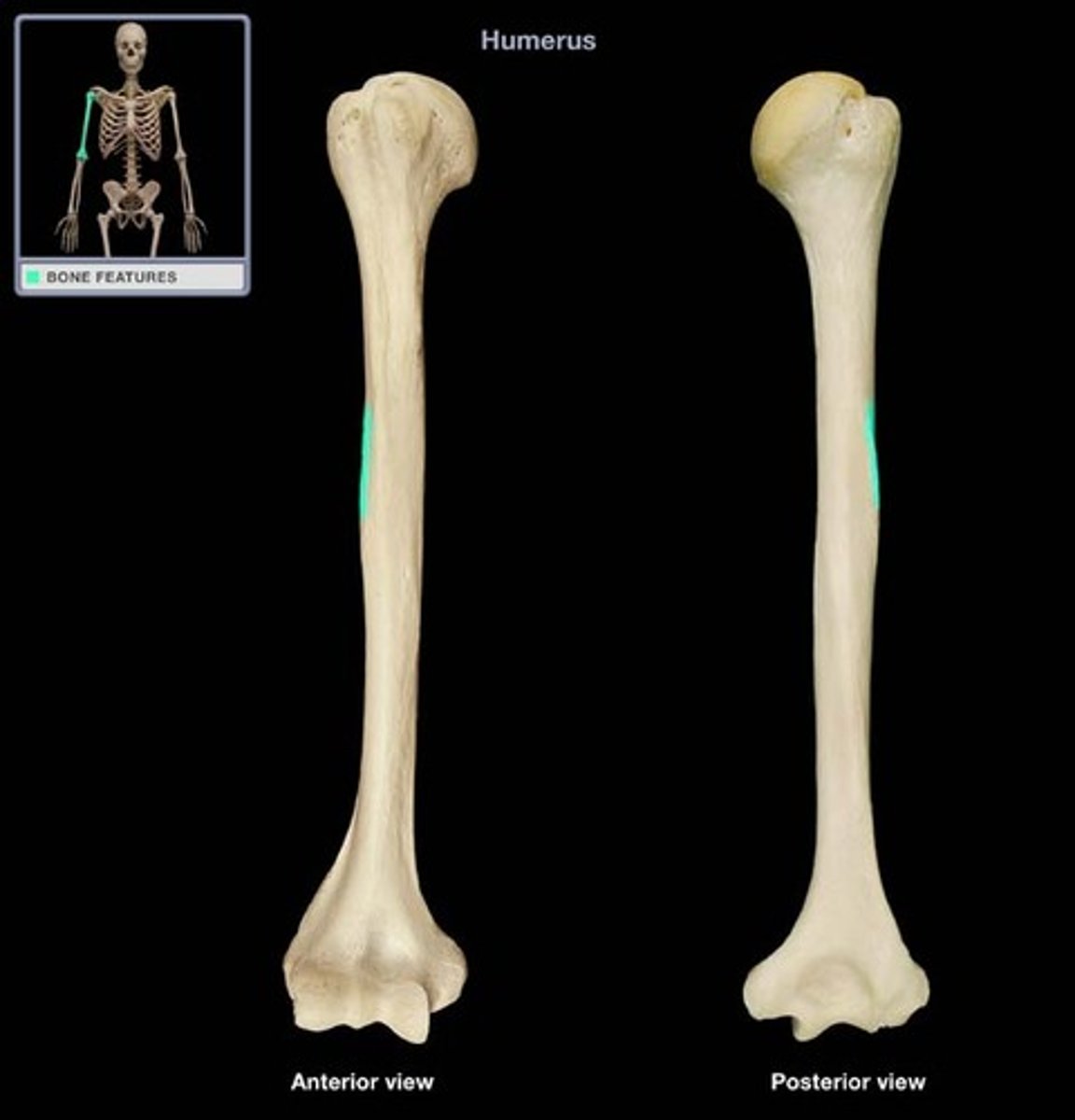
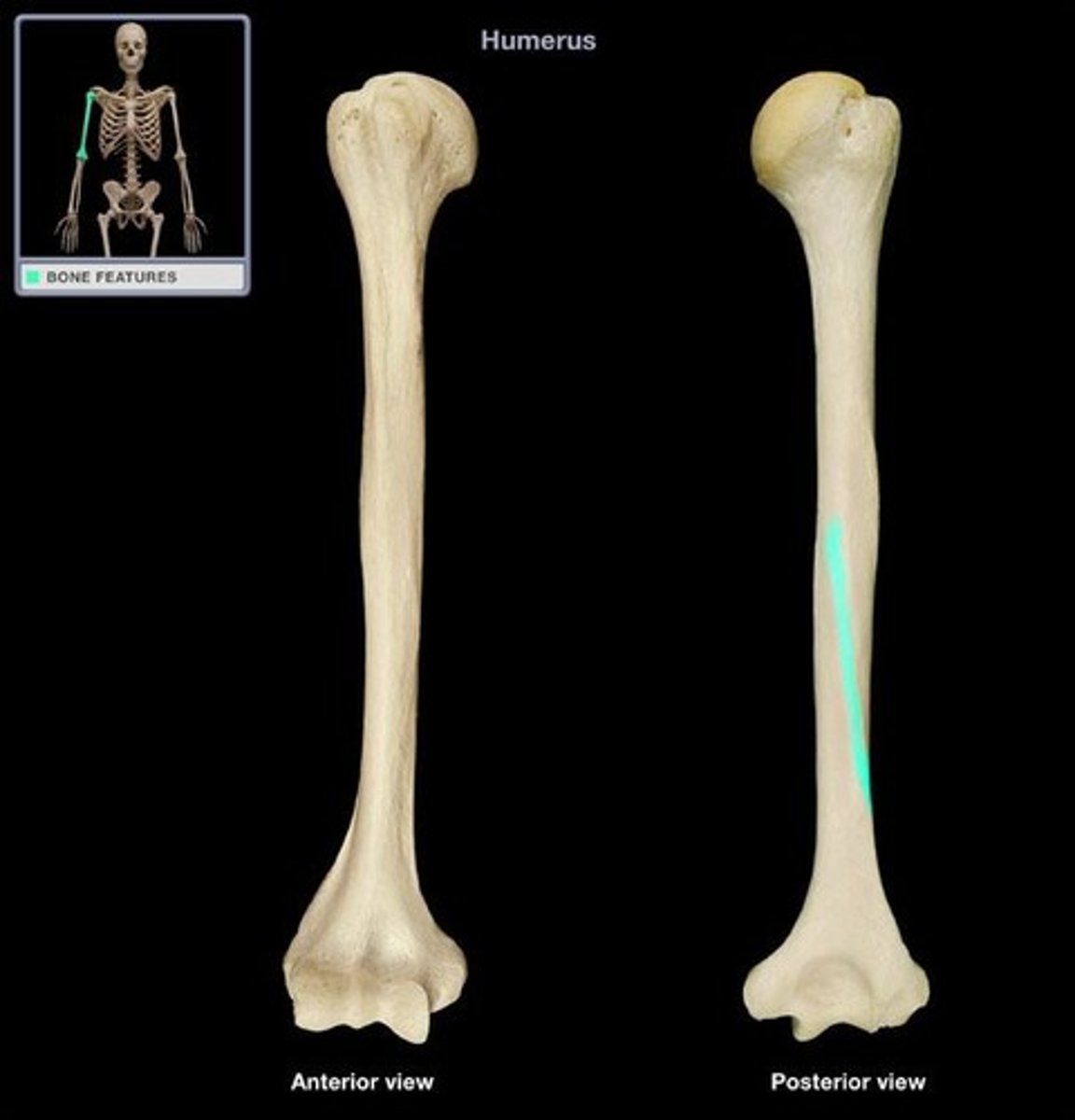
Radial Groove
Runs obliquely down the posterior aspect of the shaft.
Marks course of the radial nerve
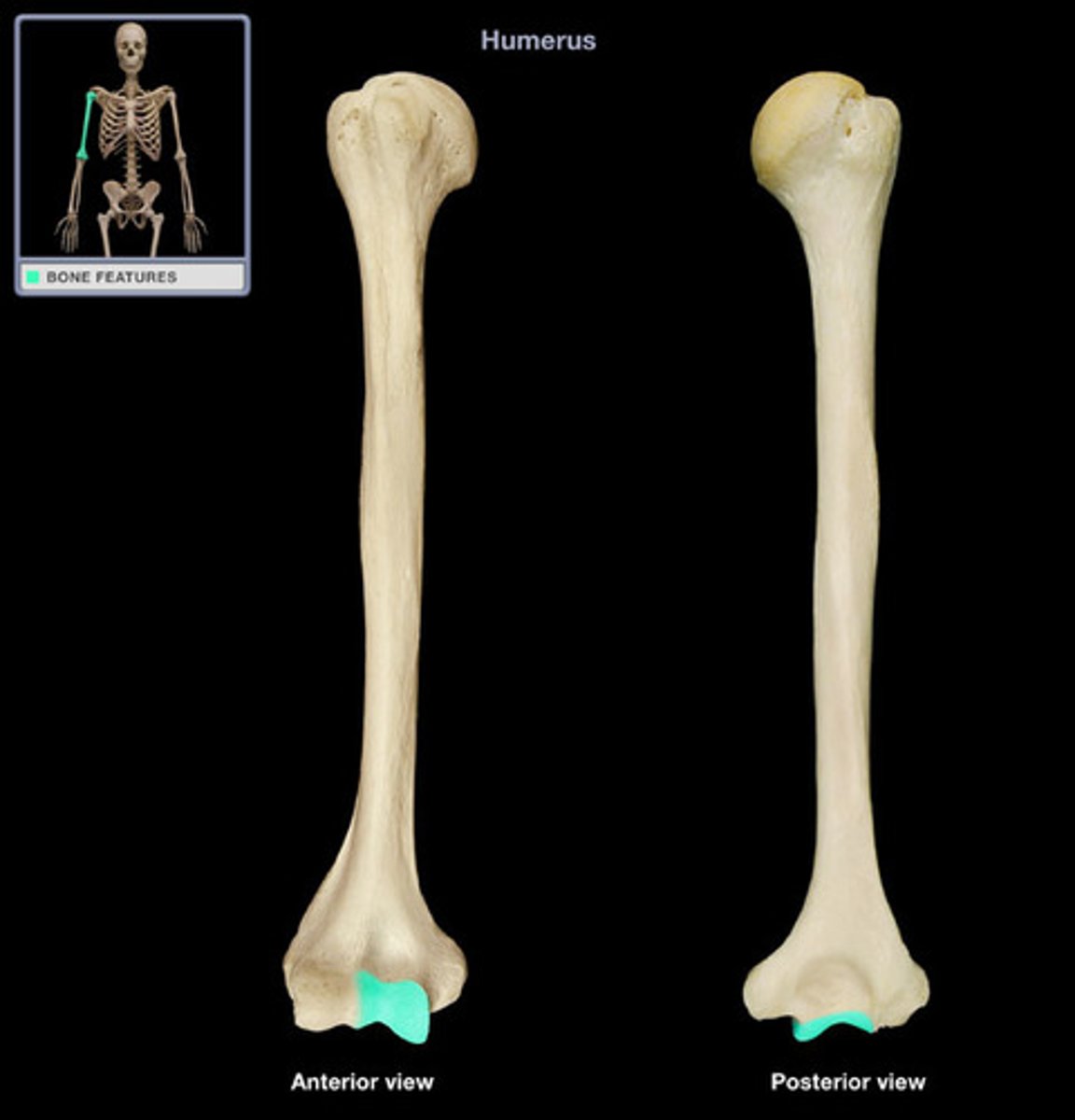
Trochlea (Condyle)
Located medially, sideways hourglass
Articulates with the ulna
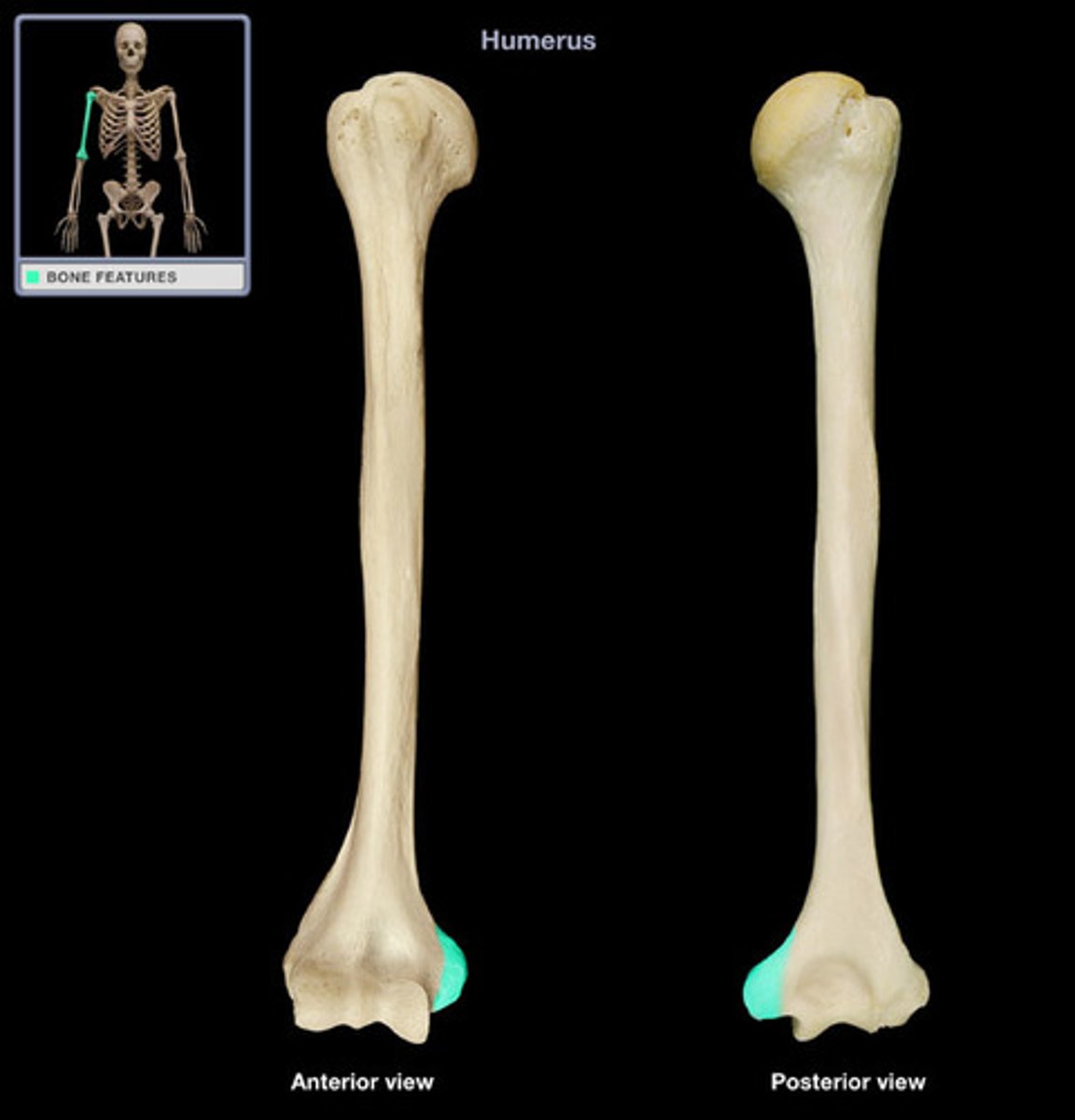
Capitulum (Condyle)
Located laterally, ball shaped
Articulates with the radius
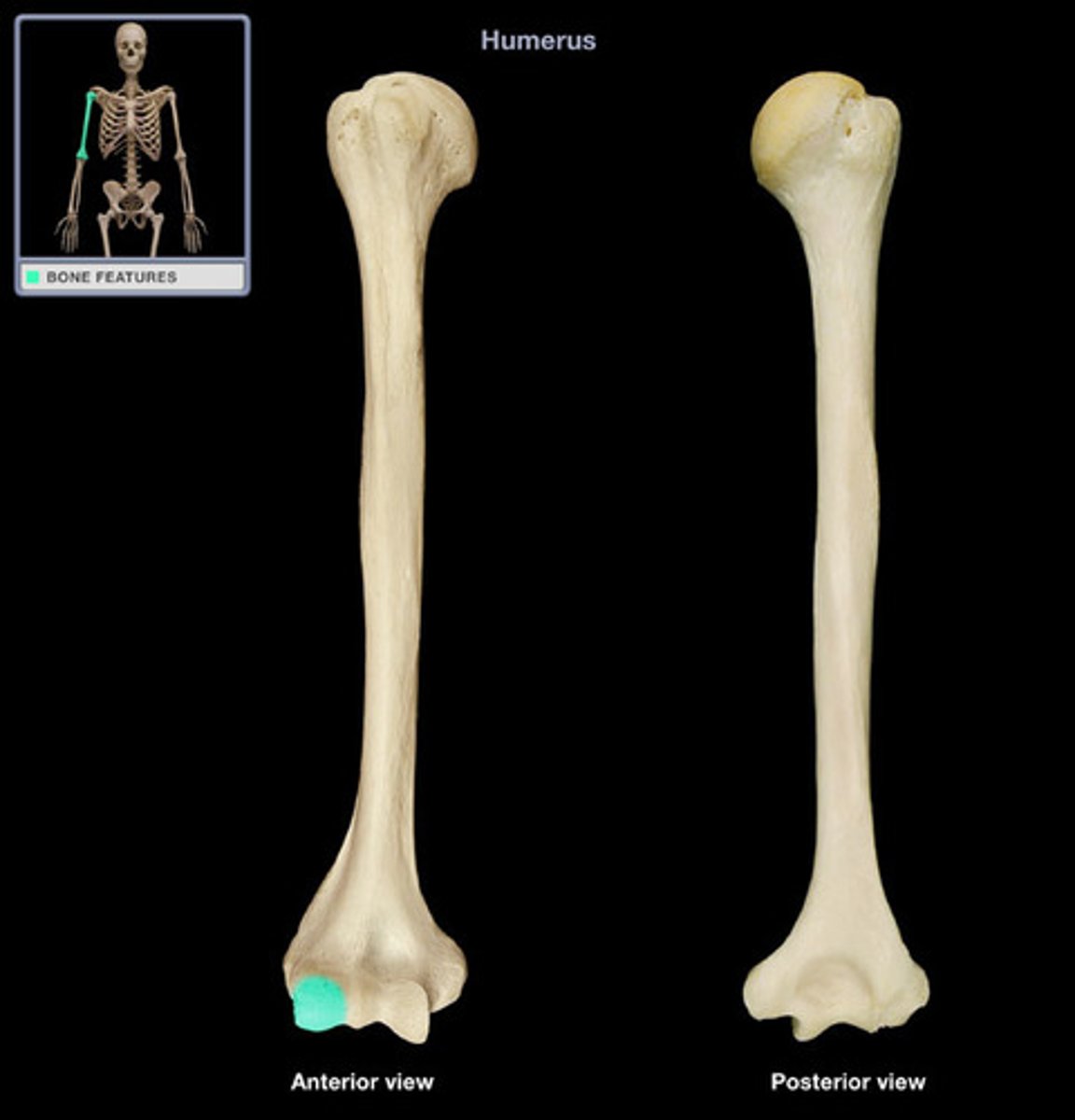
Medial Epicondyles
Ulnar nerve runs in a groove on the posterior aspect (responsible for the funny bone)
Lateral Epicondyles
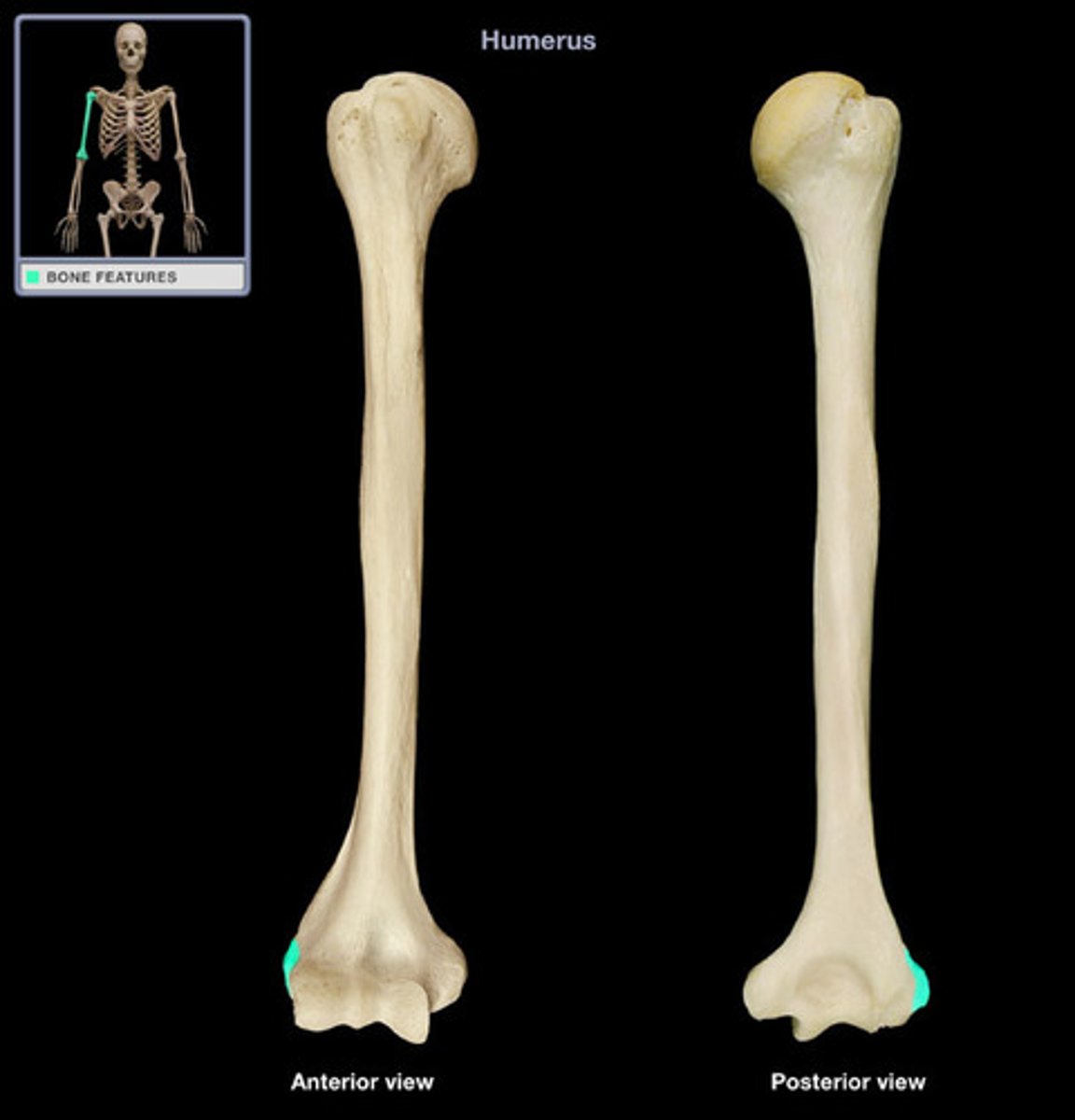
Coronoid Fossa
Superior to the trochlea on the anterior surface
Allows coronoid process on the ulnar to move freely
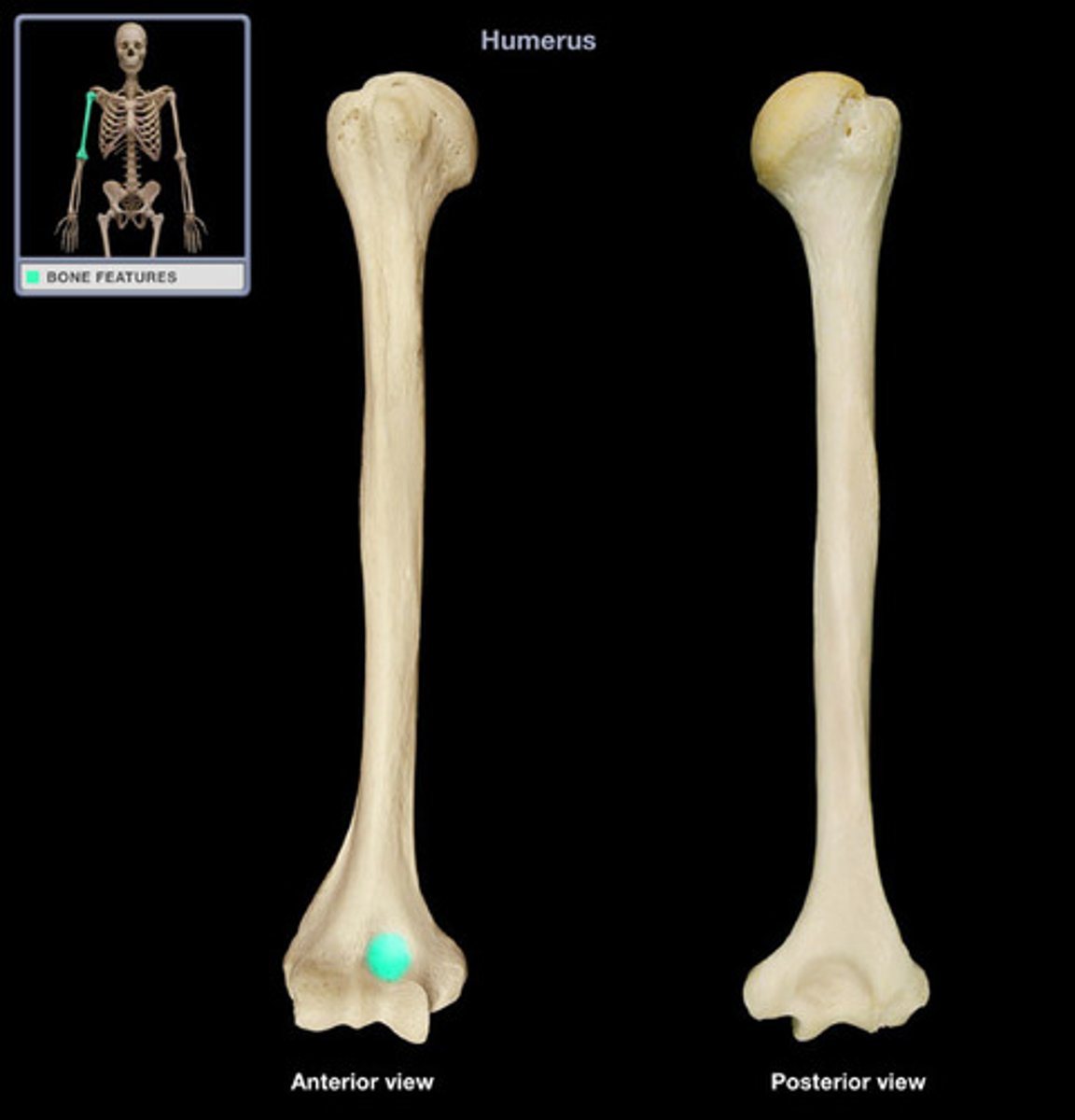
Olecranon Fossa
Superior to the trochlea on the posterior surface
Allows olecranon process on the ulnar to move freely
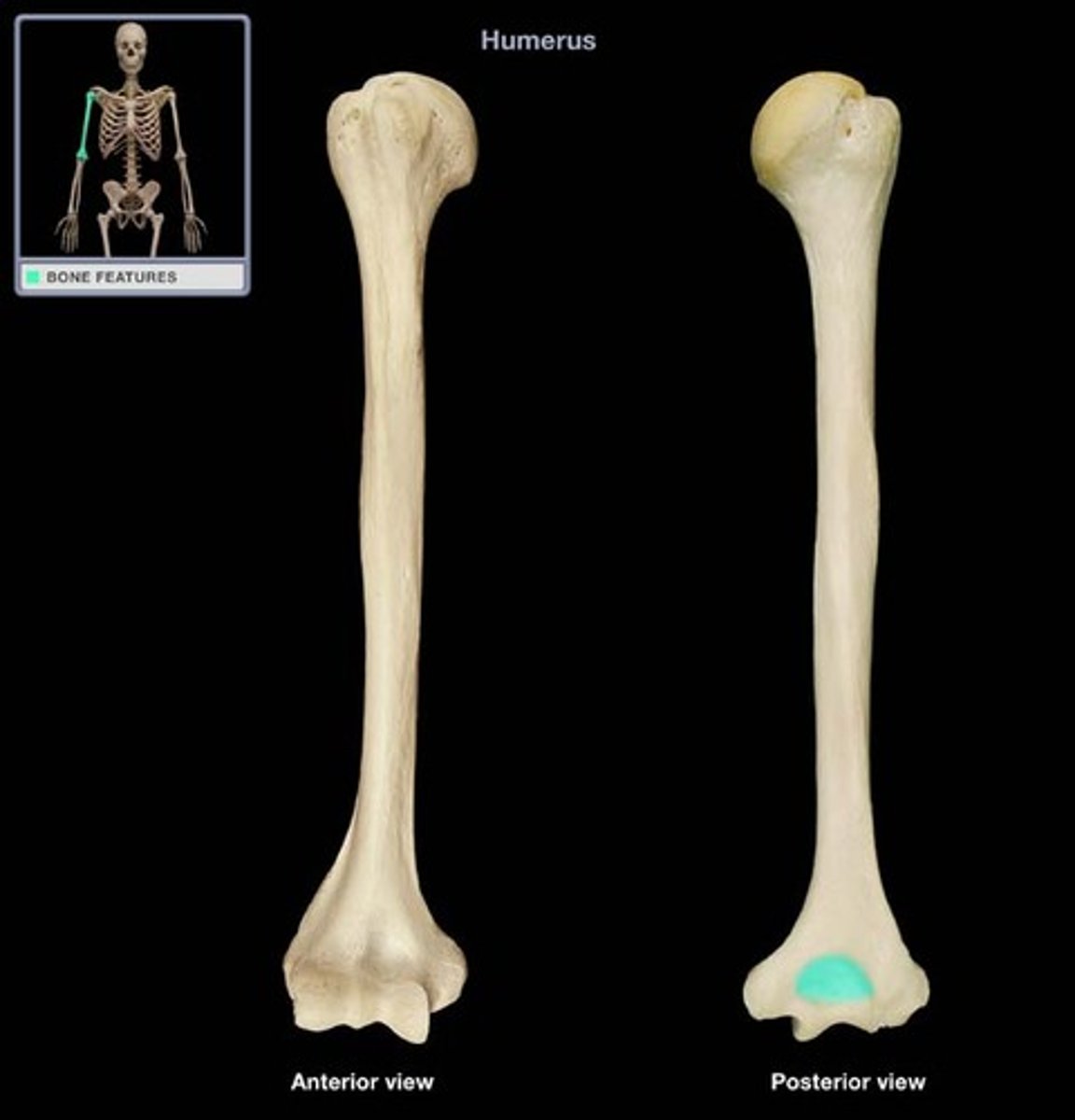
Radial Fossa
Lateral to the coronoid fossa
Allows movement of the head of the radius
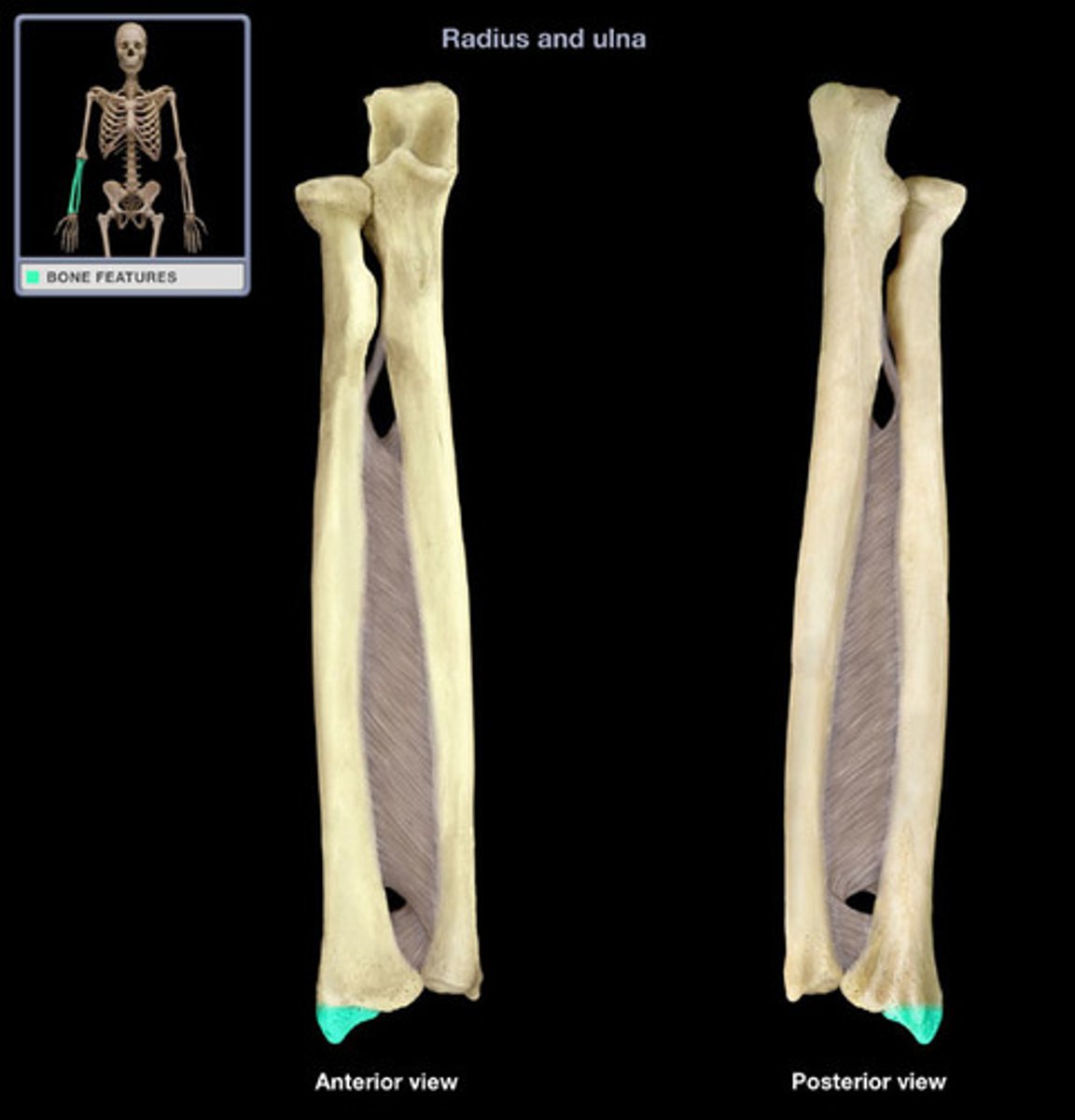
Ulna
Medial bone of the forearm. Articulates with the radius at small radioulnar joints. Connected to the radius via interosseous membrane
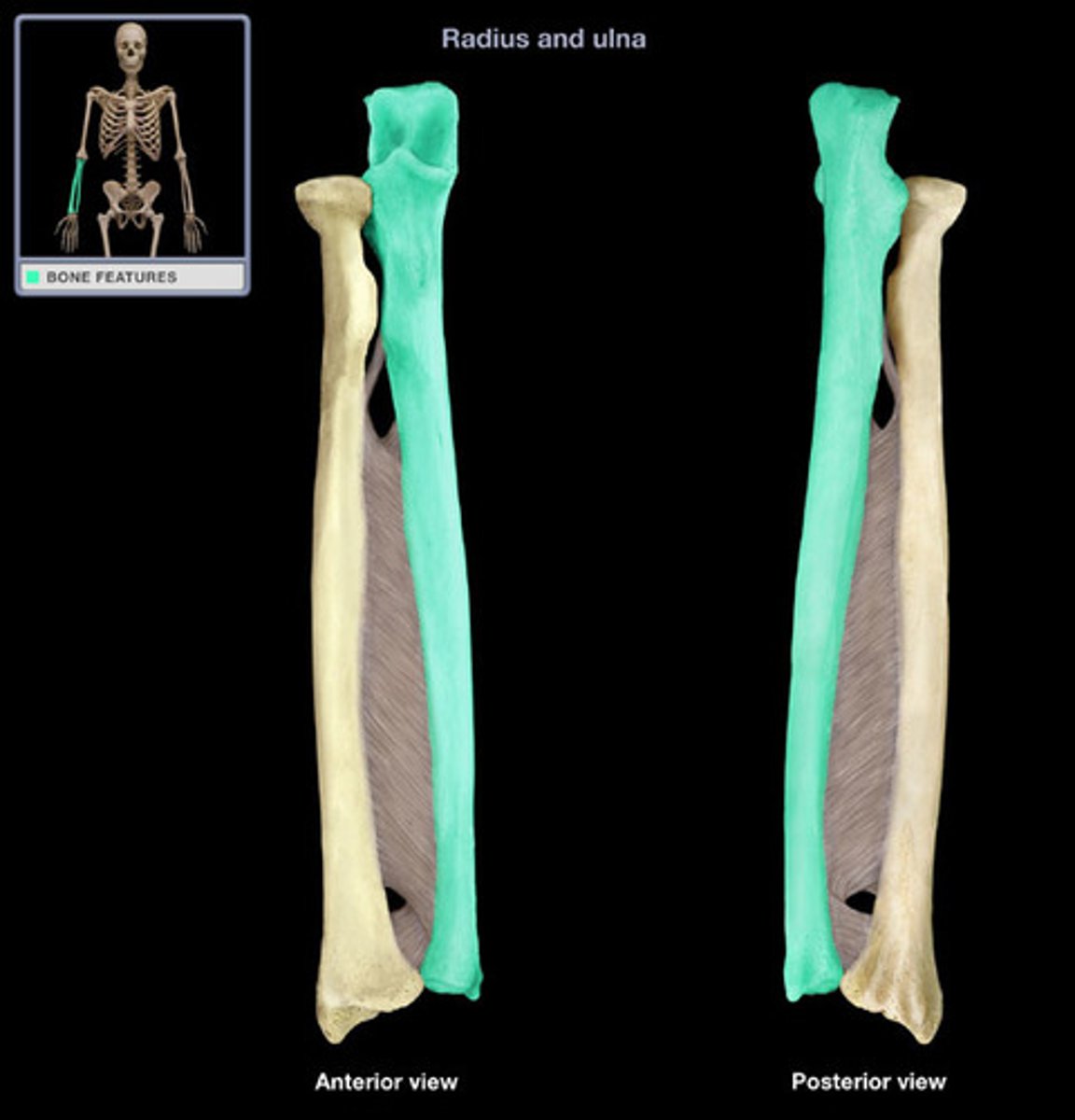
Olecranon Process
Grips the trochlea of the humerus with the coronoid process to form a hinge joint
When fully extended, 'locks' into the fossa preventing hyperextension
Trochlear Notch
Where the trochlea fits into
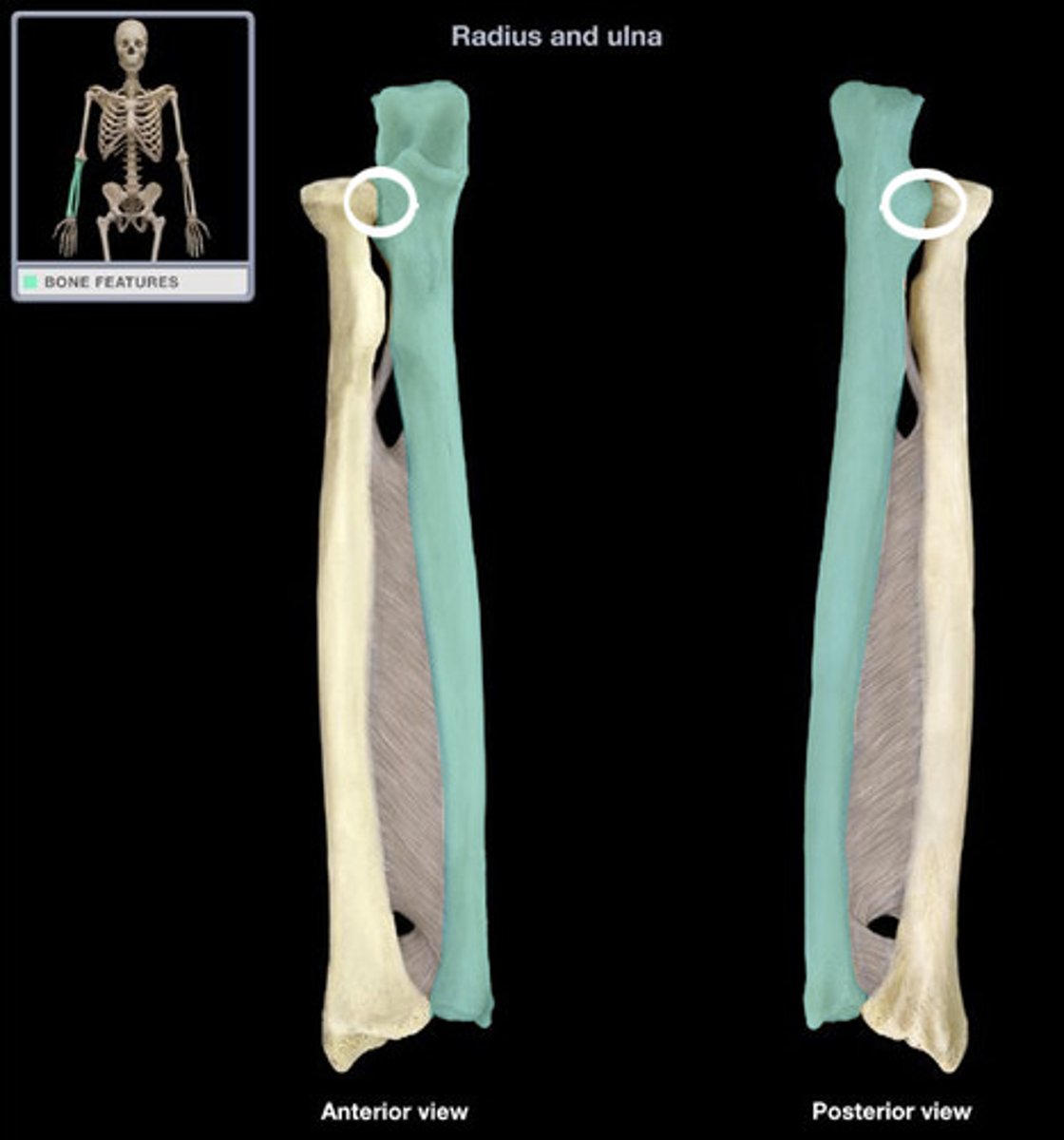
Radial Notch
Lateral to the coronoid process
Articulates with the head of the radius
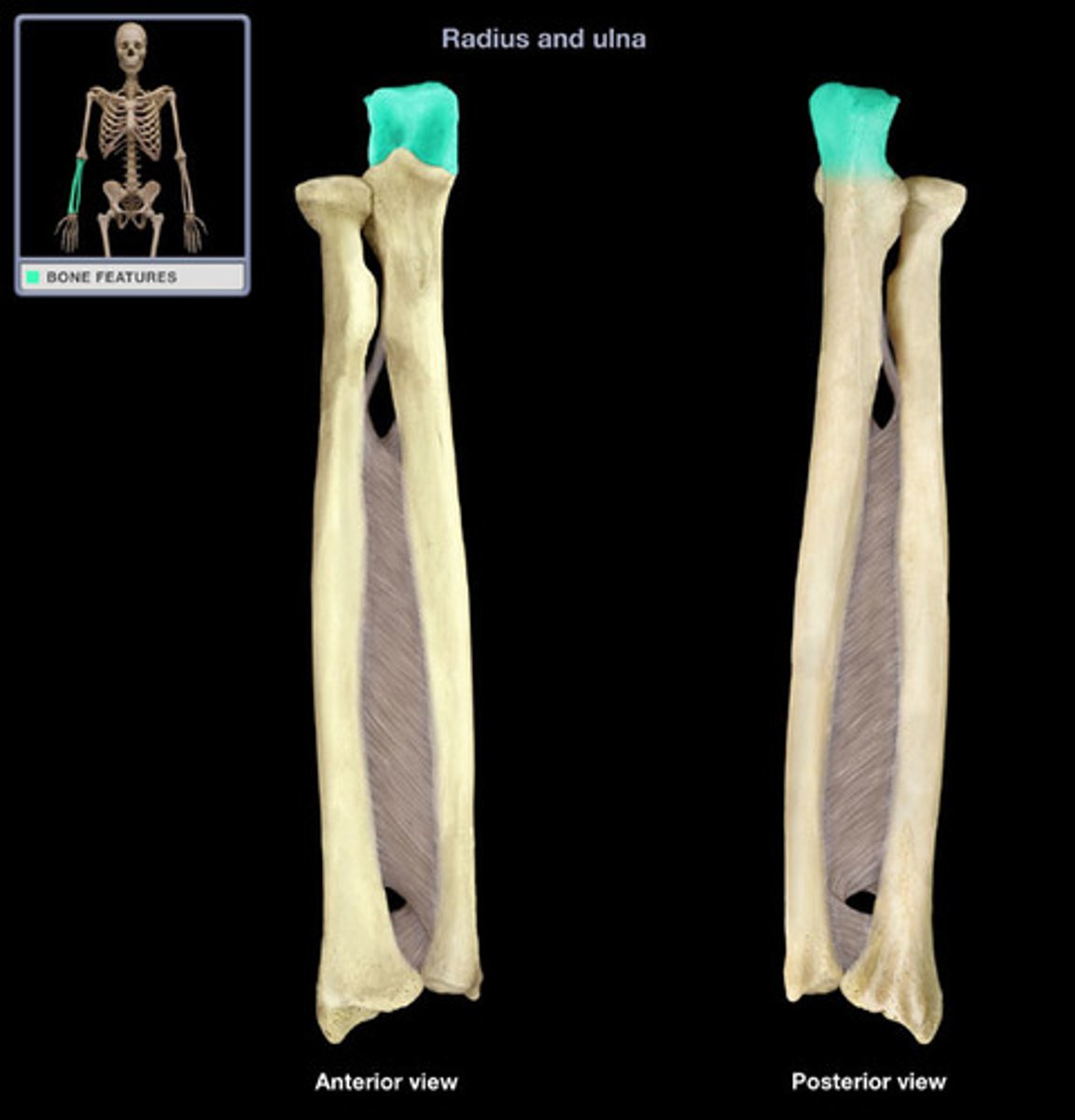
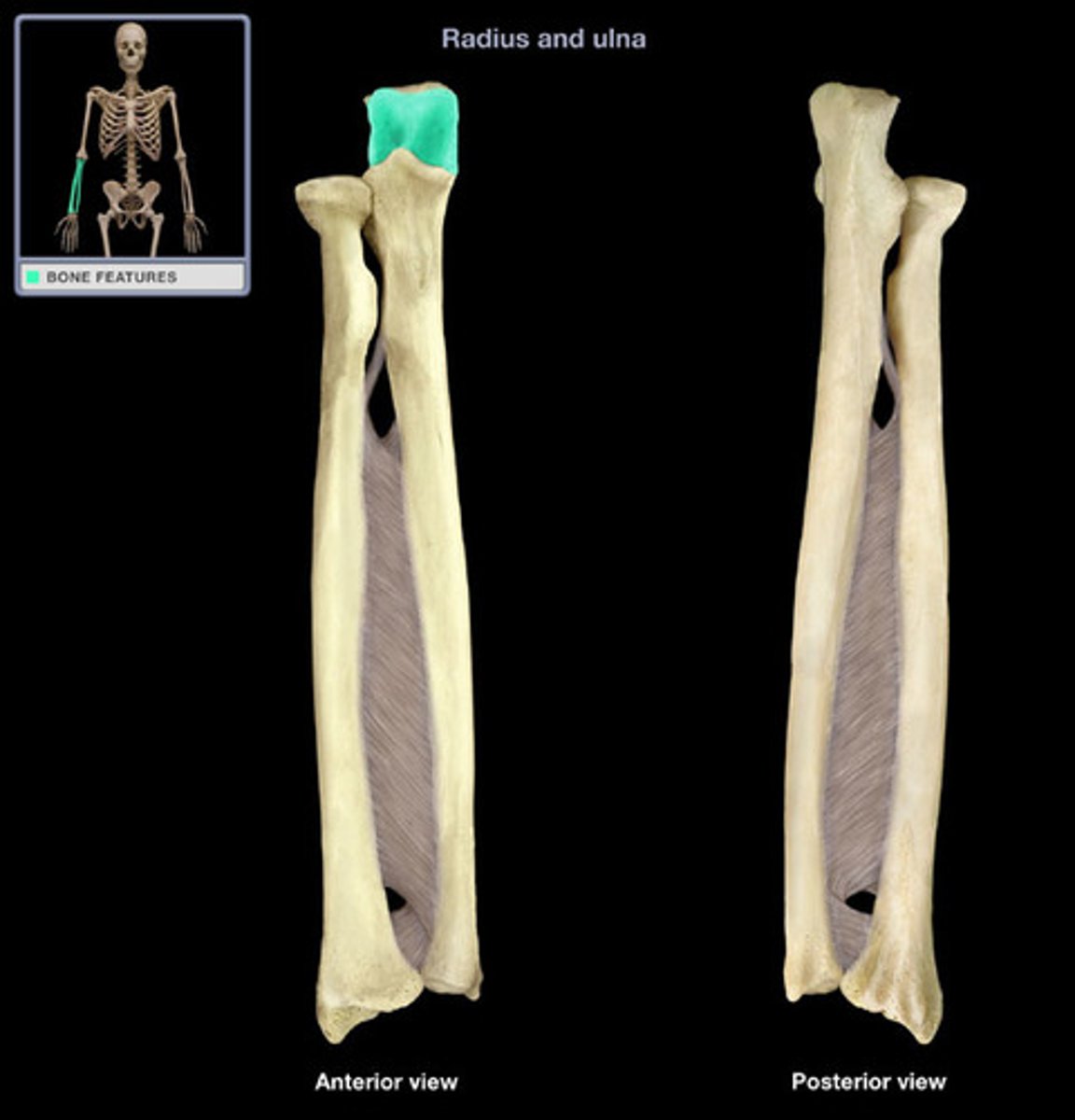
Styloid Process of Ulna
Attachment point for ligaments that extend to the wrist
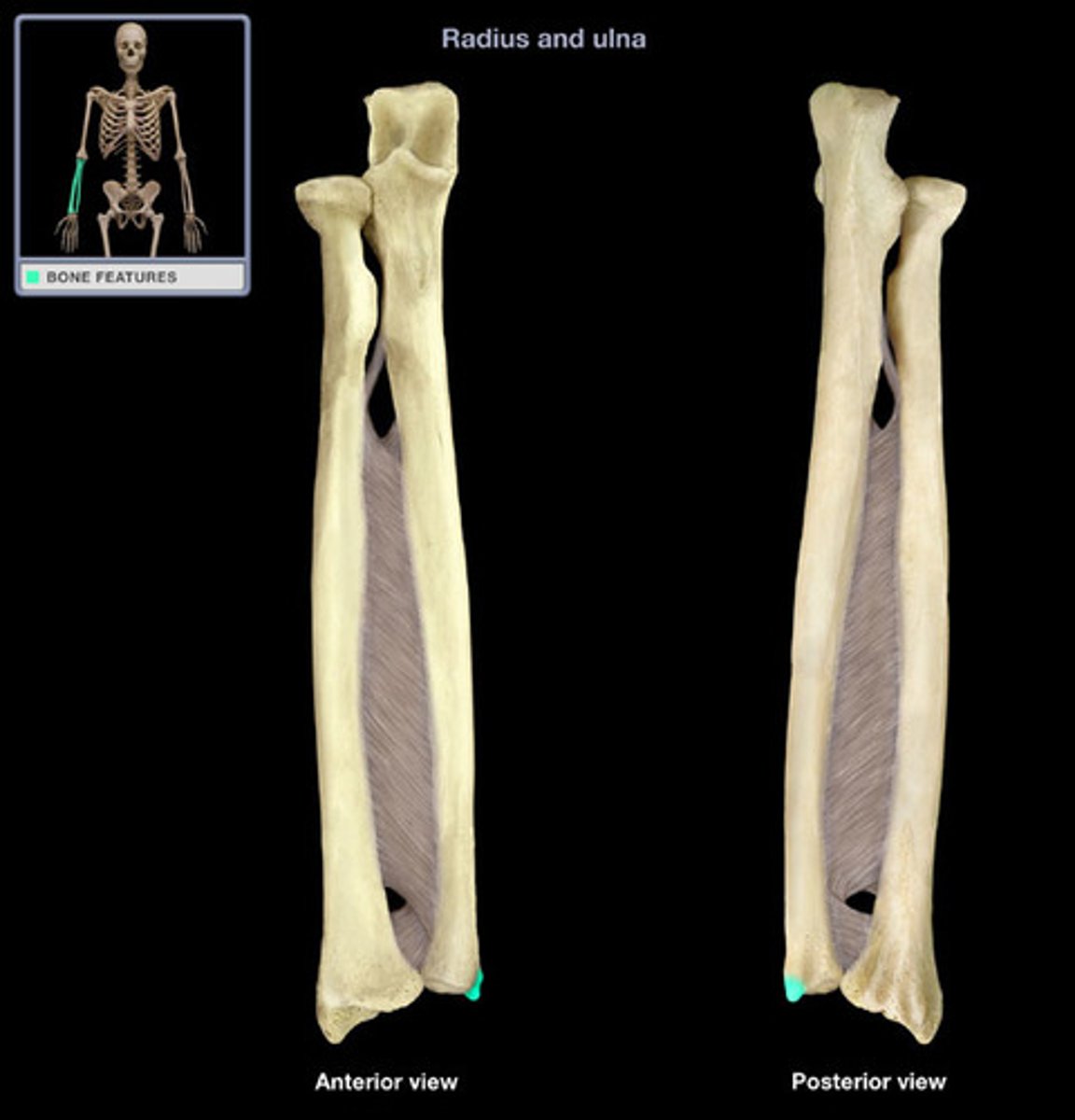
Radius
Lateral bone of the forearm. Articulates with the ulnar at small radioulnar joints. Connected to the ulnar via interosseous membrane
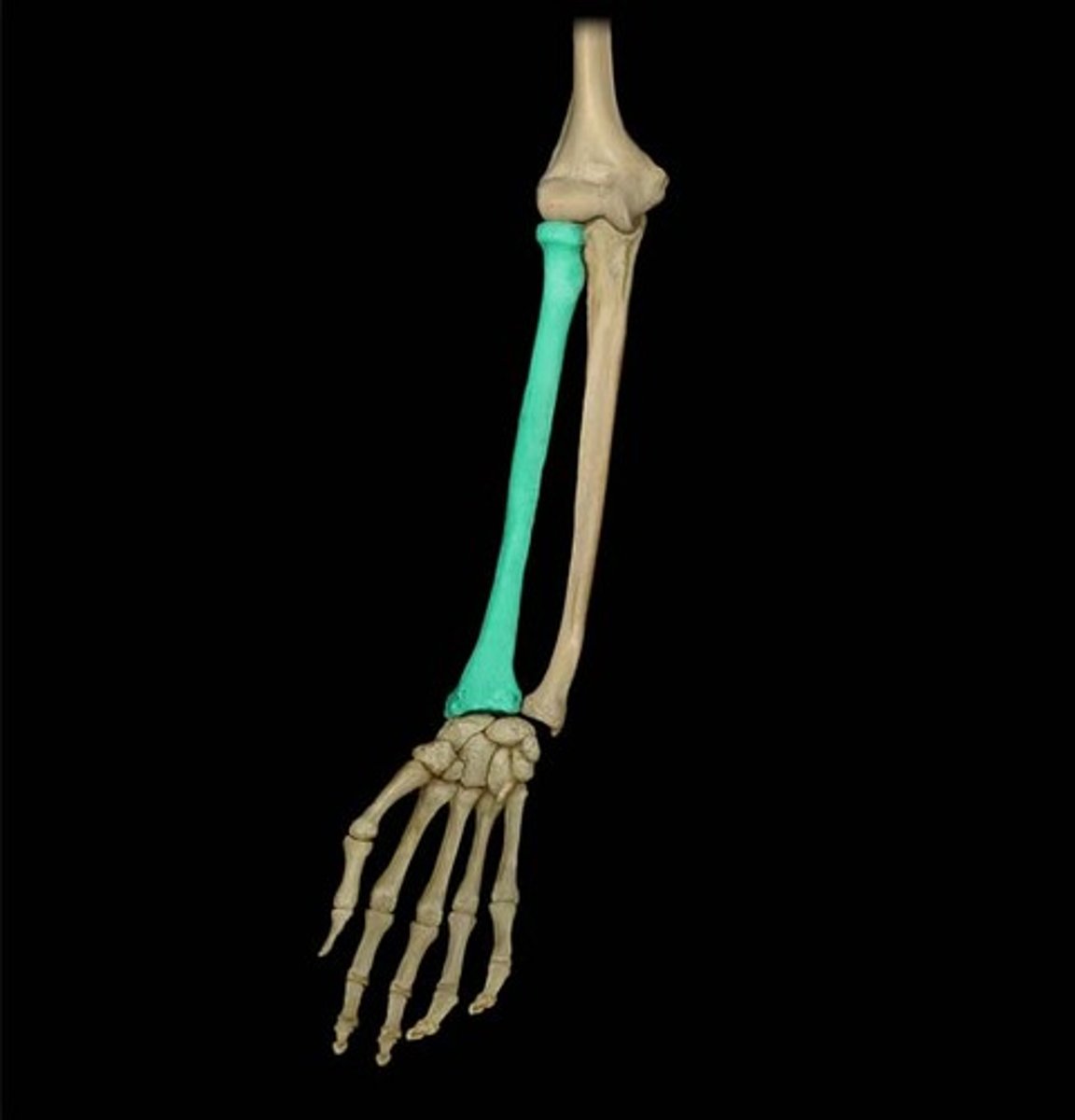
Radial Tuberosity
Serves to anchor the biceps muscle
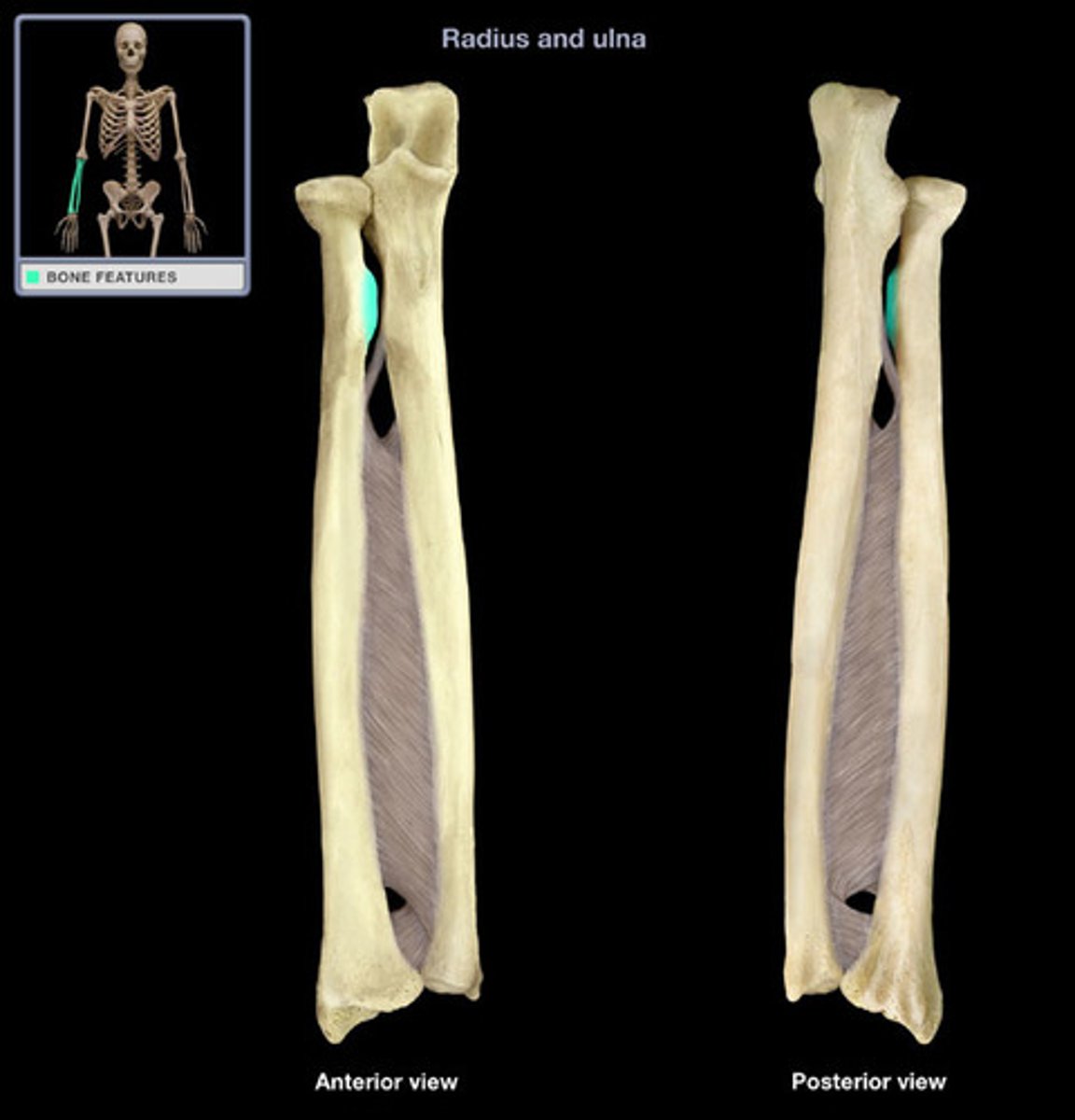
Ulnar Notch
Distal end (towards the hands), articulates with the ulnar
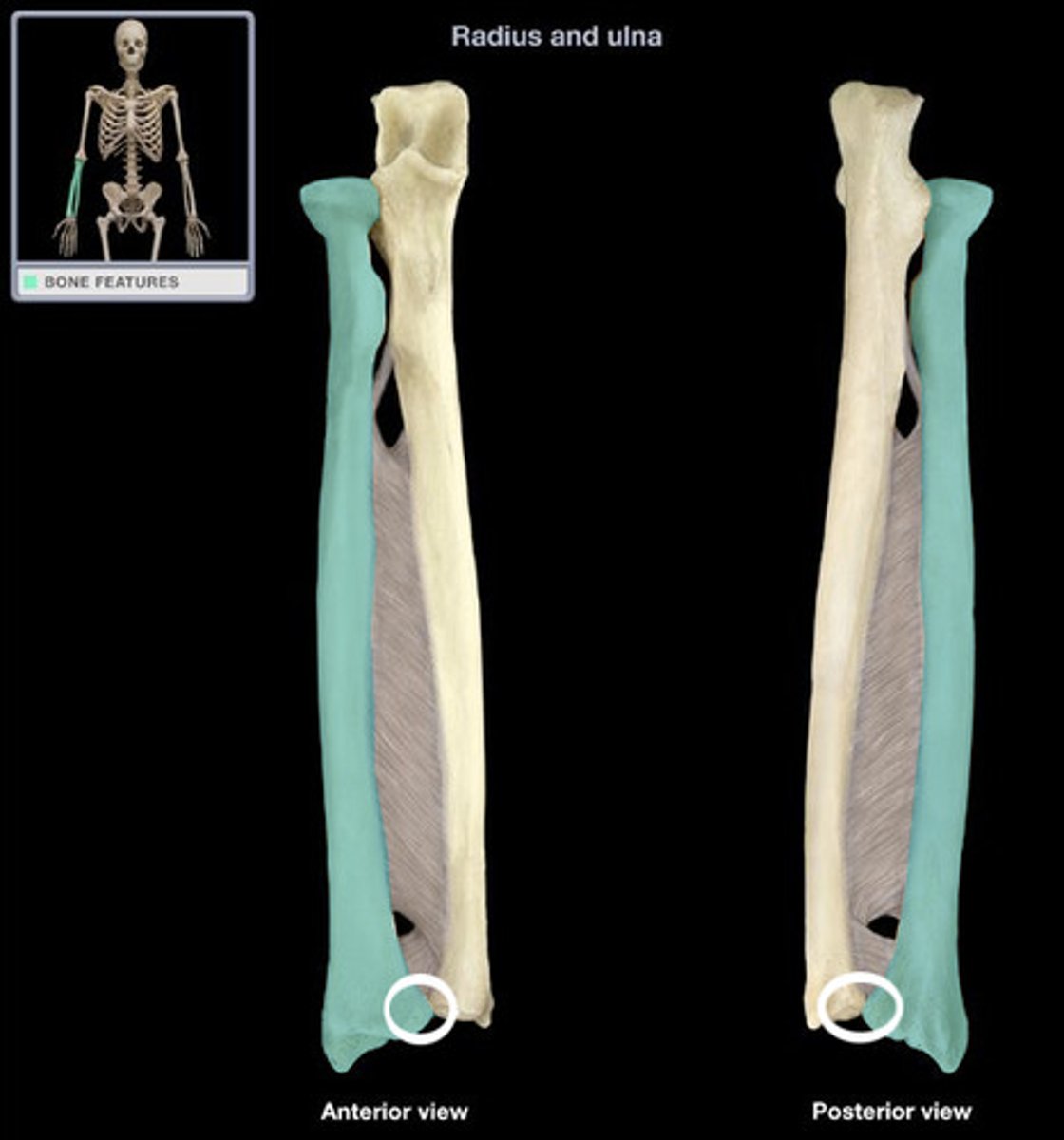
Styloid Process of Radius
Anchoring sites for ligaments that extend to the wrist
Carpus
The proximal end of our 'hand'. This is the true wrist
8 sets of bone in 2 rows by 4 columns
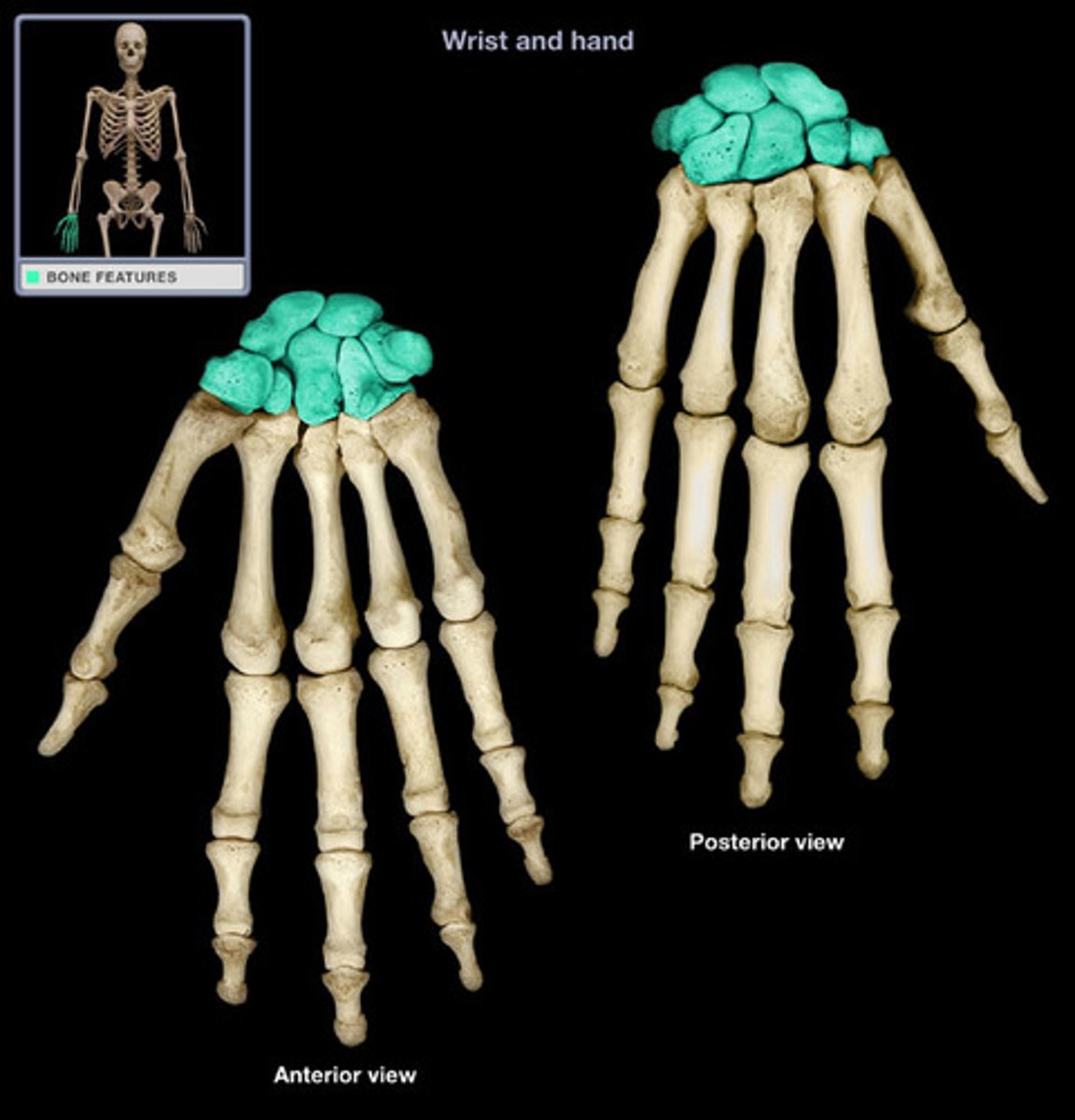
Carpals
The 8 short bones which are located in the carpus
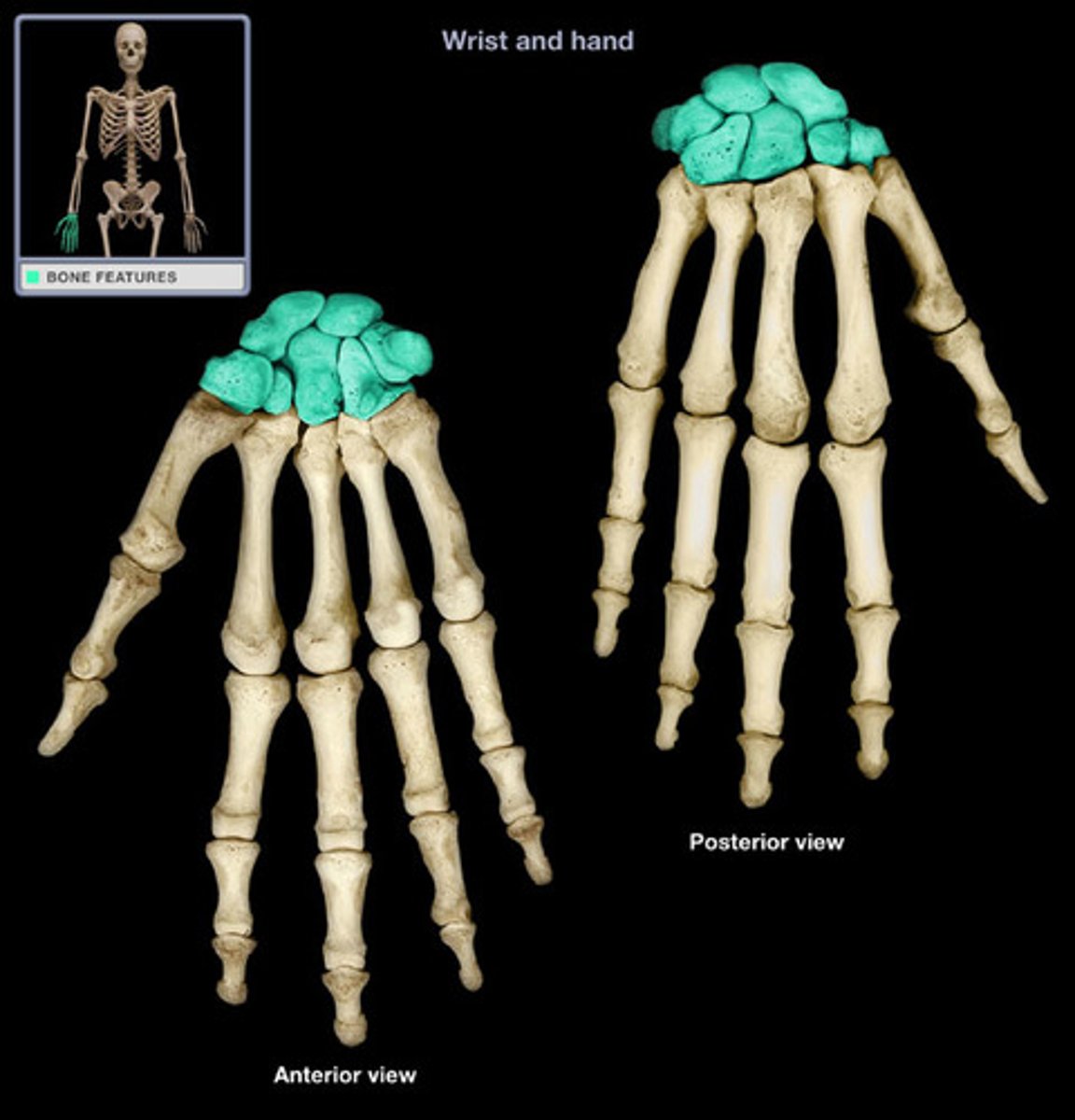
Scaphoid
A large carpal bone articulating with the radius below the thumb
Etymology:
Skaphos: meaning boat
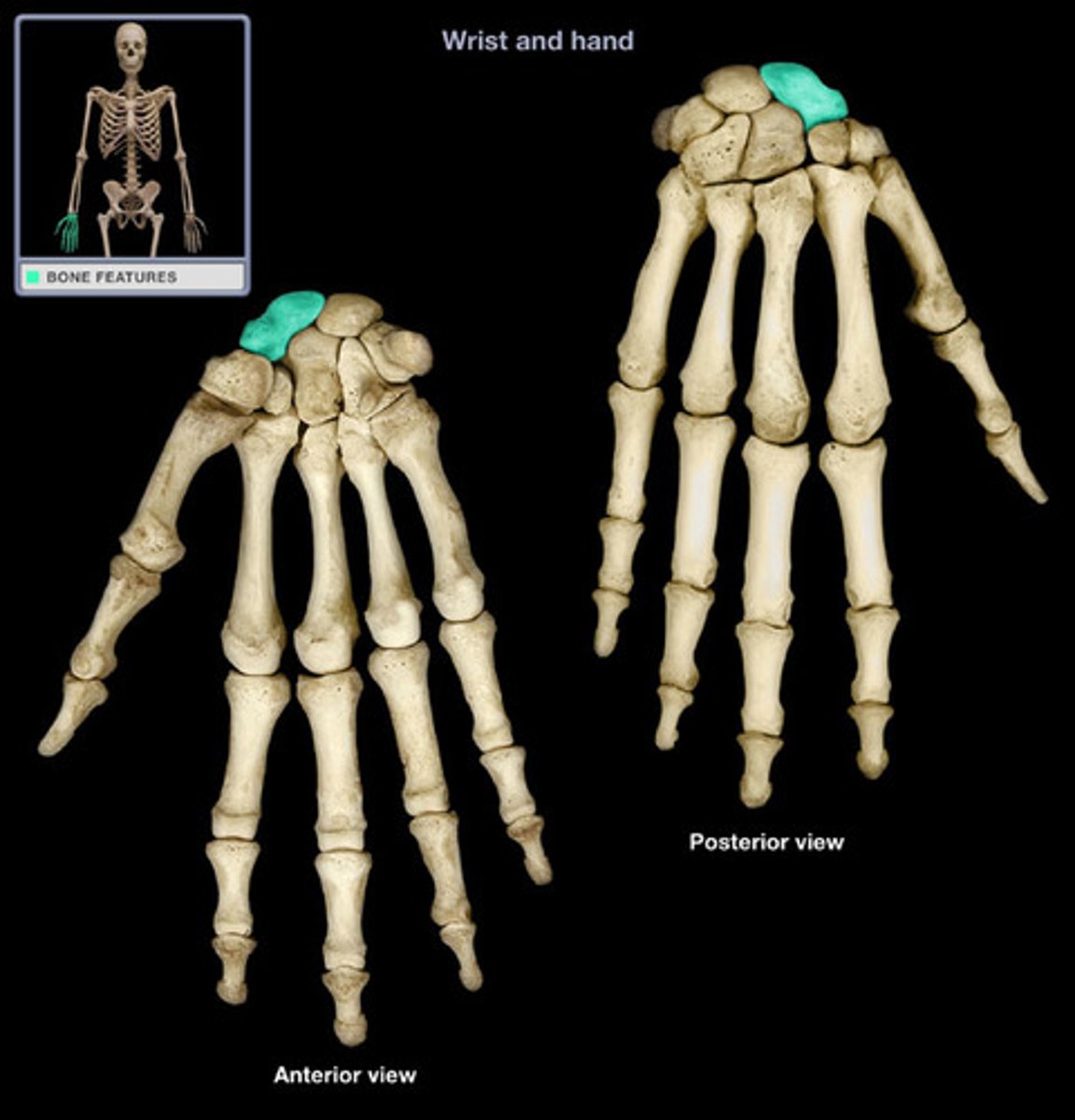
Lunate
The bone immediately medial to the scaphoid. Connects to the radius
Etymology:
Luna: moon
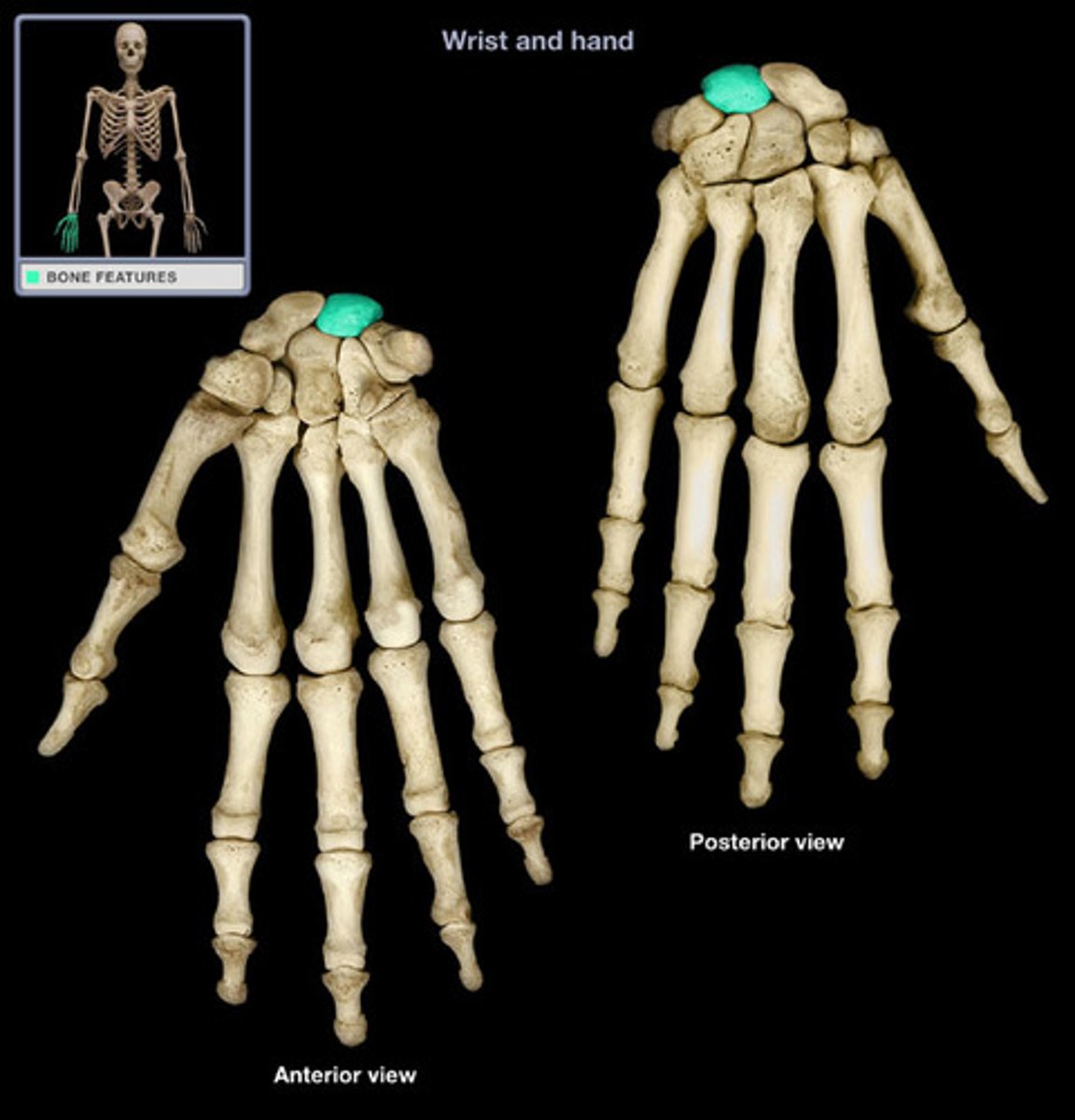
Triquetral
The third bone in the proximal row counting from the lateral side. Articulates with the lunate, hamate and pisiform
Etymology:
Triquetrus: three cornered
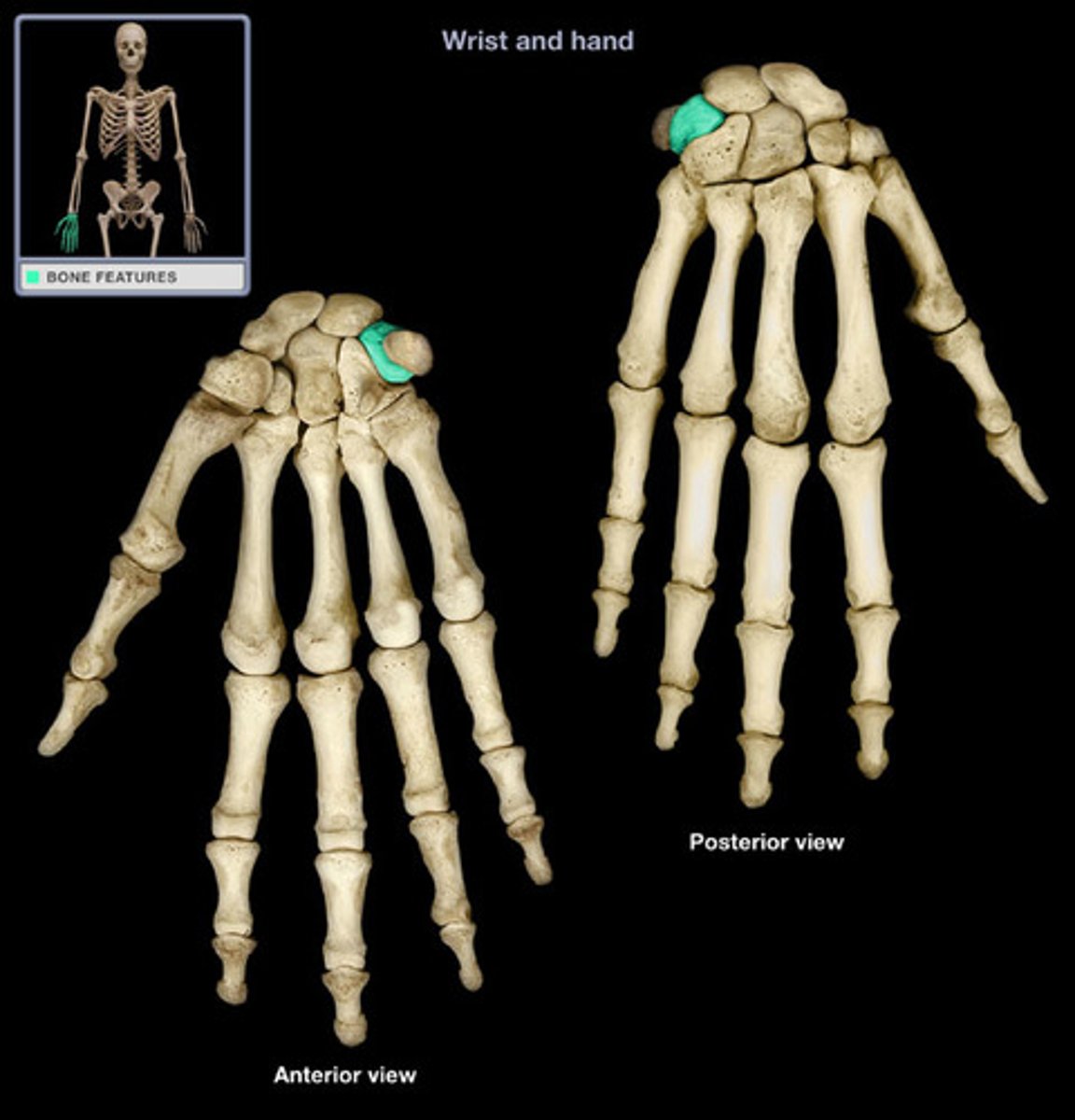
Pisiform
The bone in the proximal row that is the most medial
Etymology:
- Pisum: pea
- Forma: shaped
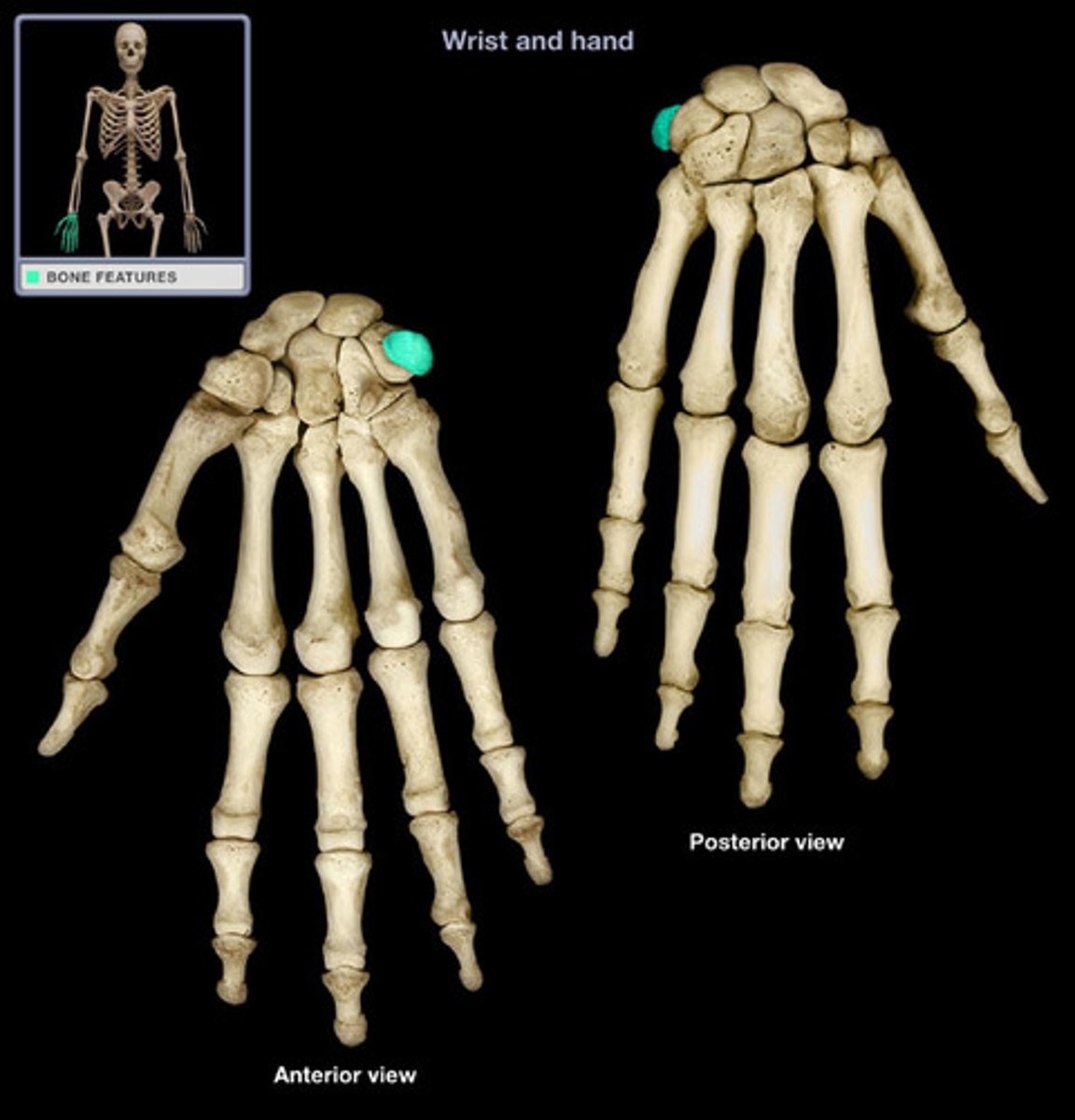
Trapezium
The distal bone immediately below the thumb.
Etymology:
- Trapeza: table
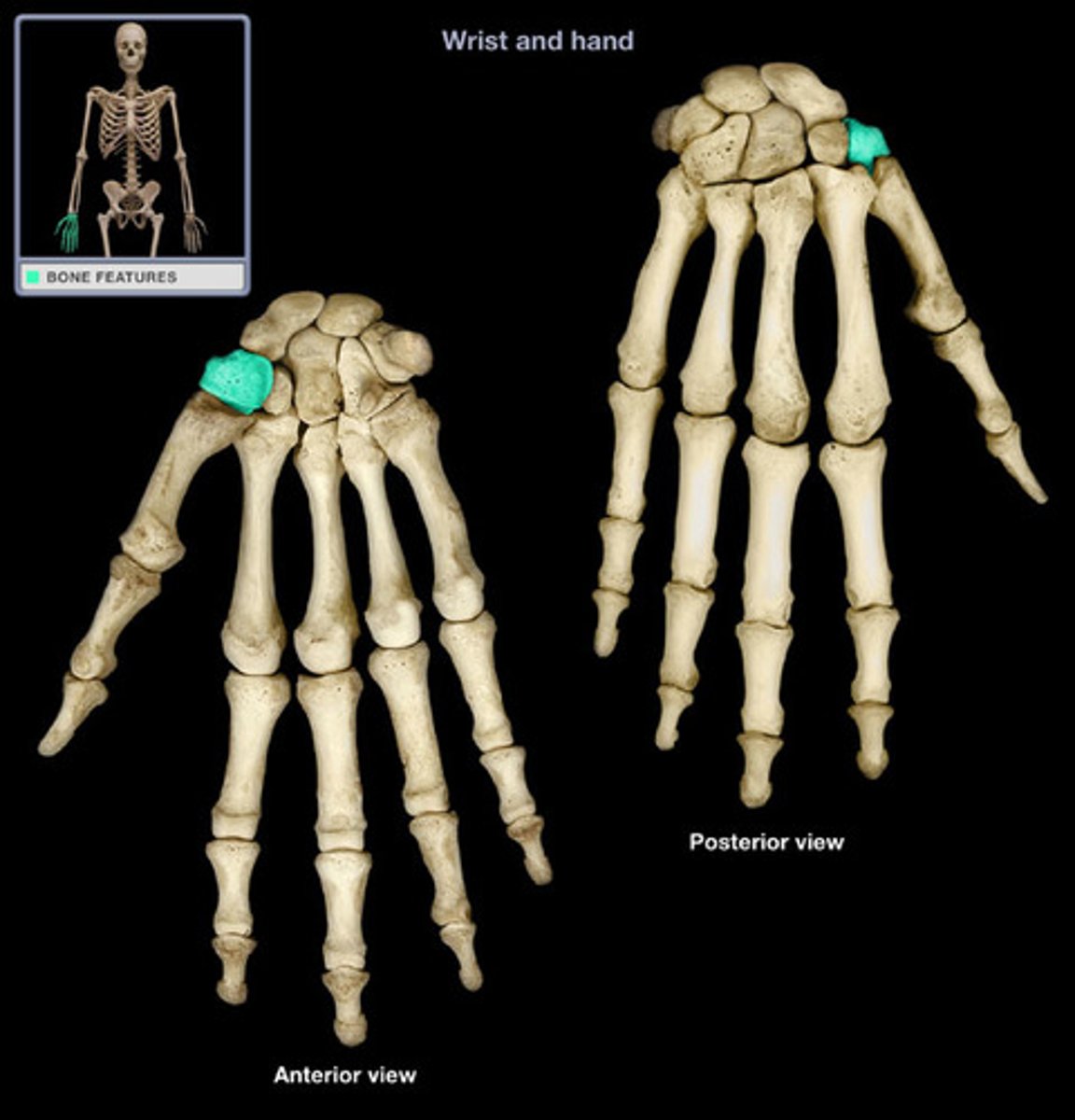
Trapezoid
The bone immediately medial to trapezium. Articulates with the index finger metacarpal.
Etymology:
- Trapeza: table
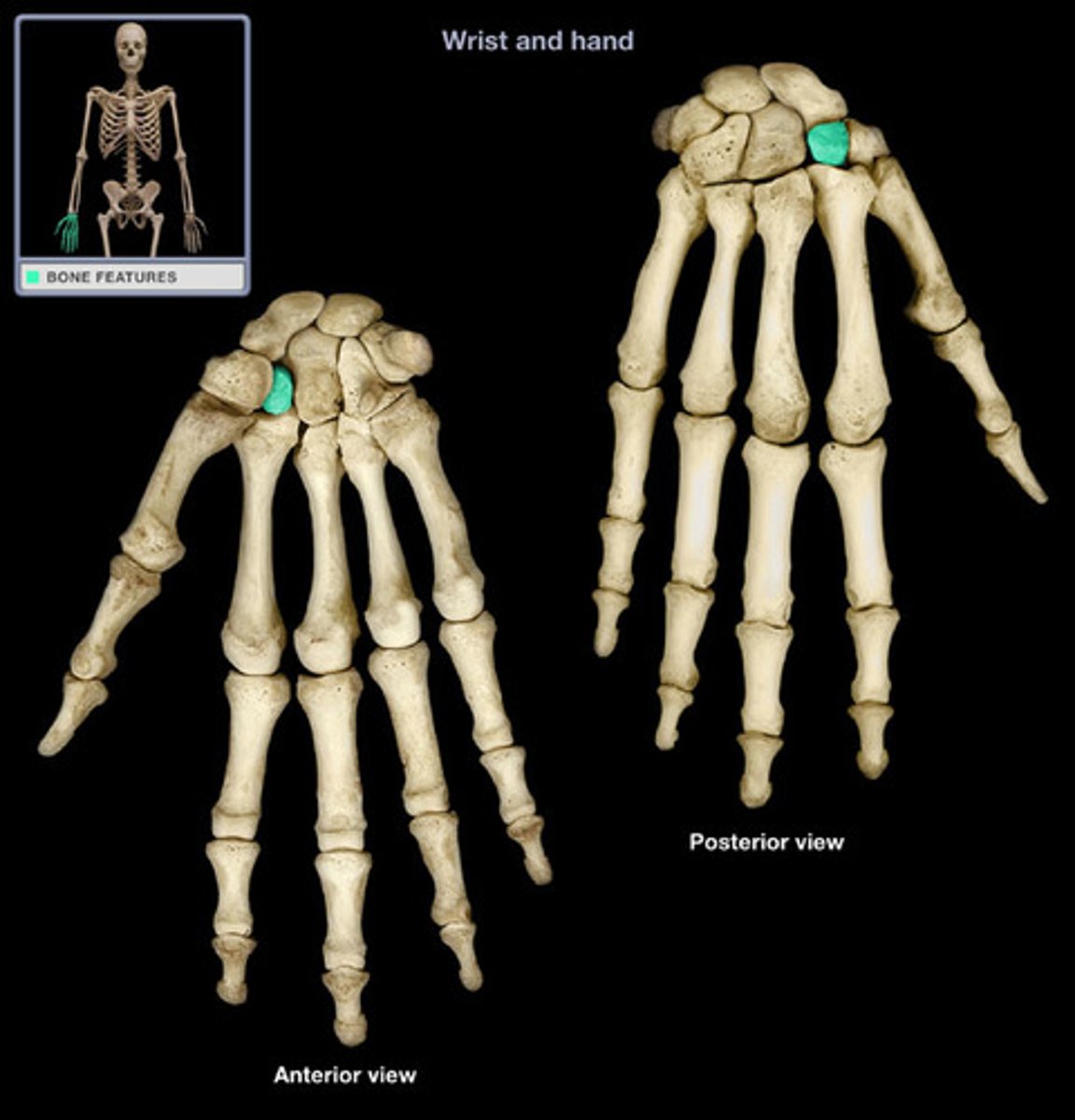
Capitate
The largest carpal bone that articulates with the third metacarpal
Etymology:
- Capit: head
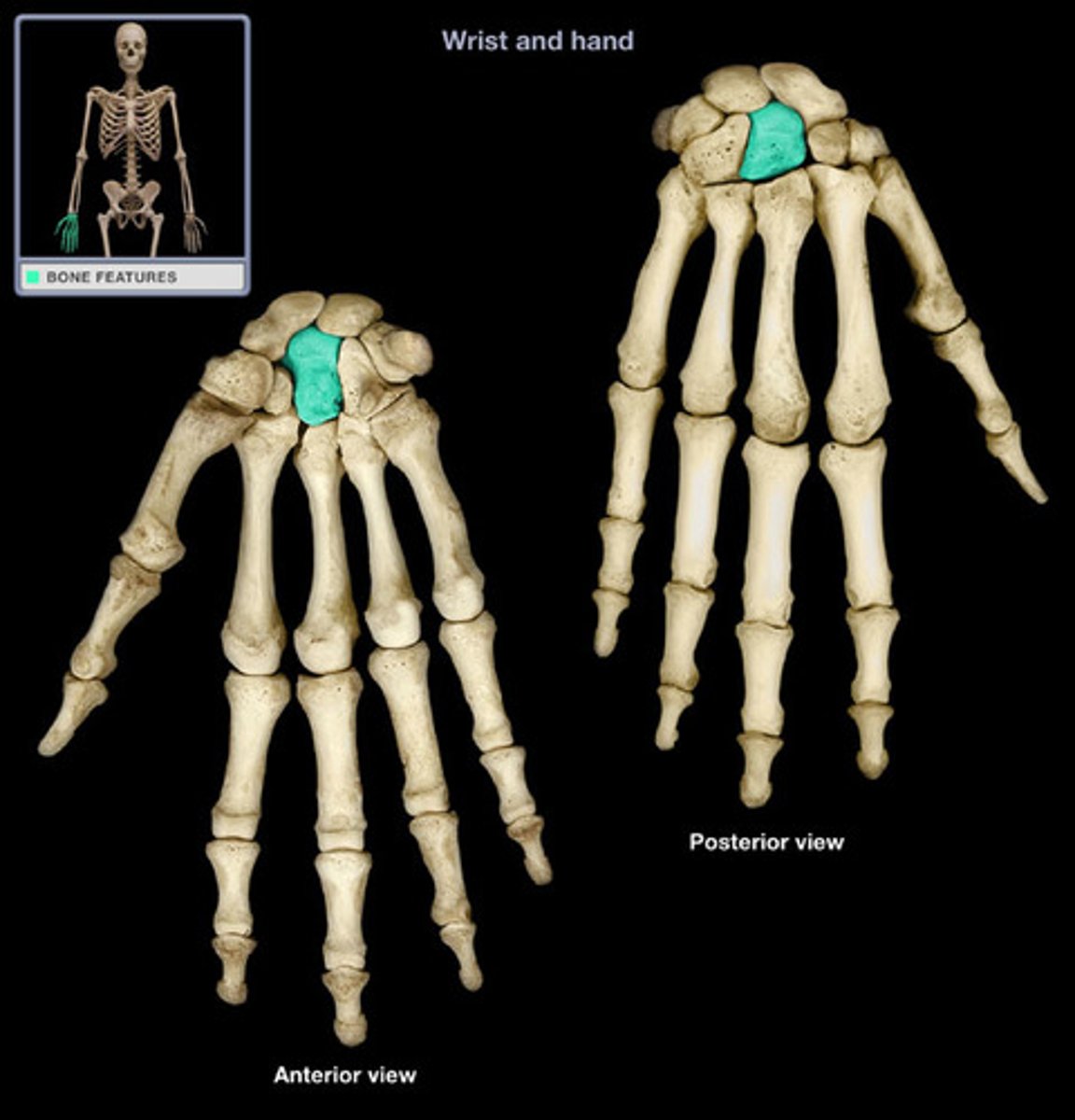
Hamate
Situated on the lower outside edge of the hand. It has a hook-shaped projection on the palmar side to which muscles of the little finger are attached.
Etymology:
- Hamus: hook
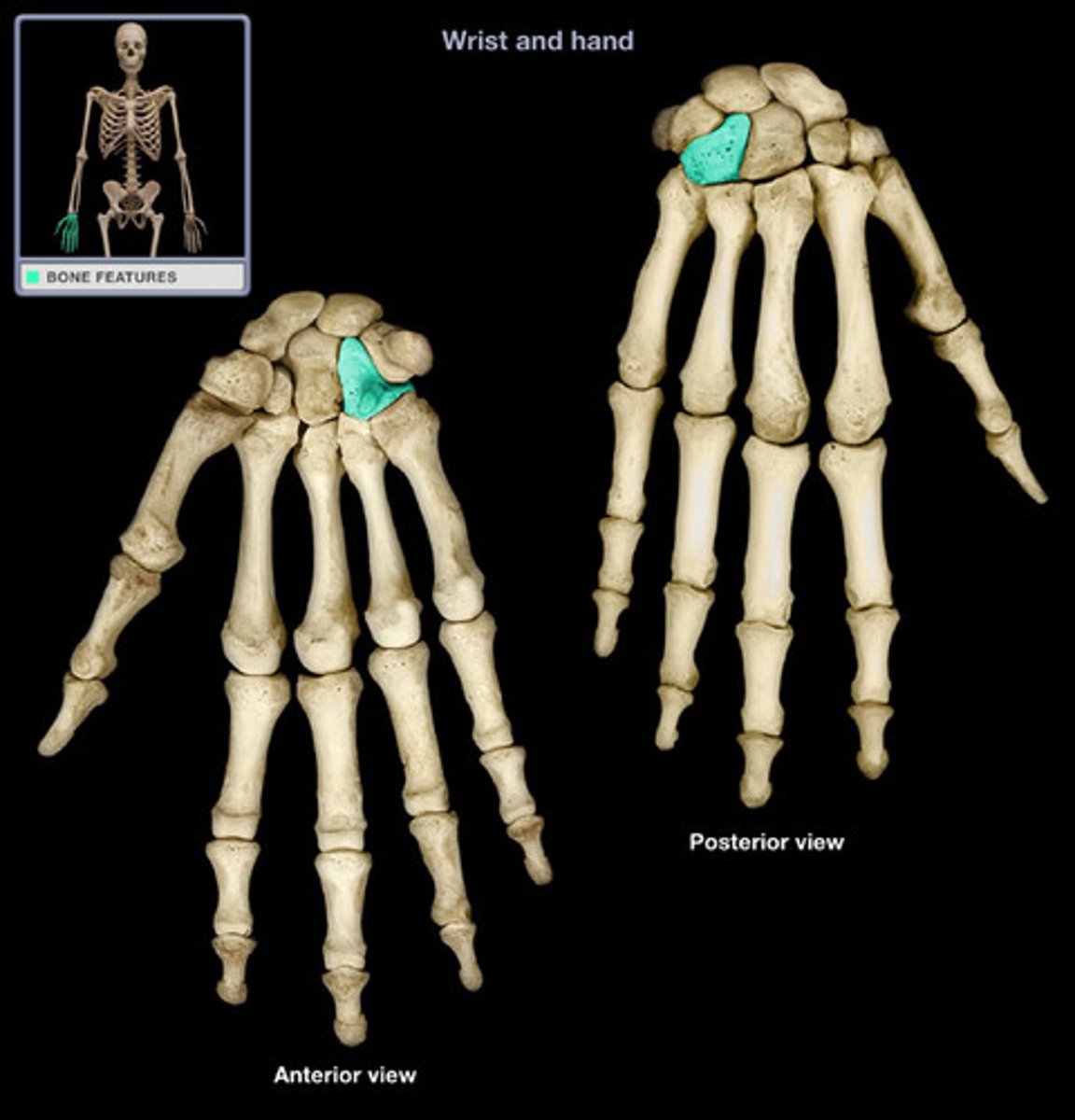
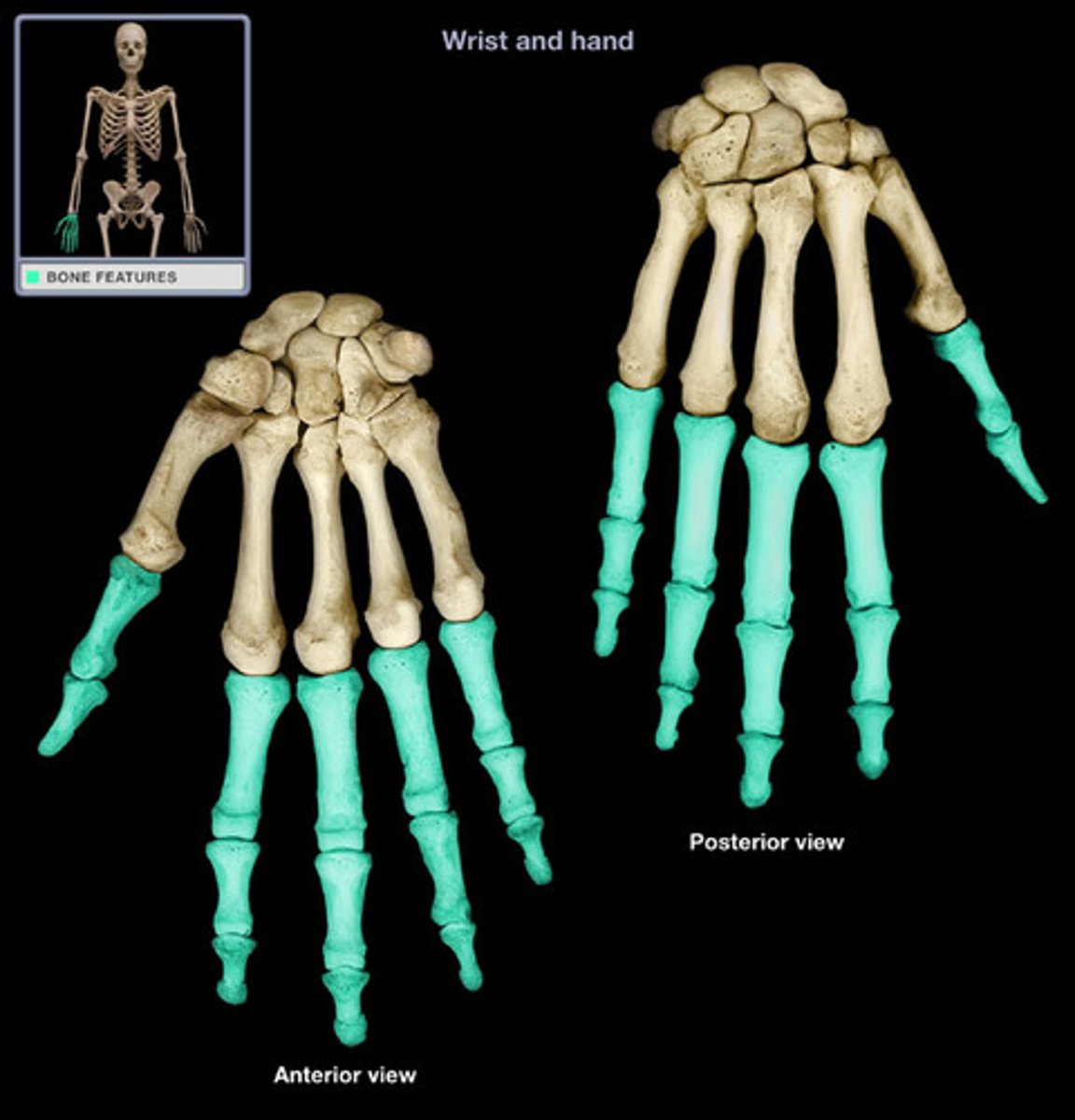
Metacarpus
The palm of the hand. The bones are numbered 1-5 from medial to lateral. The bases articulate with the carpals and each other laterally.
The head are the knuckles when you clench your fists.
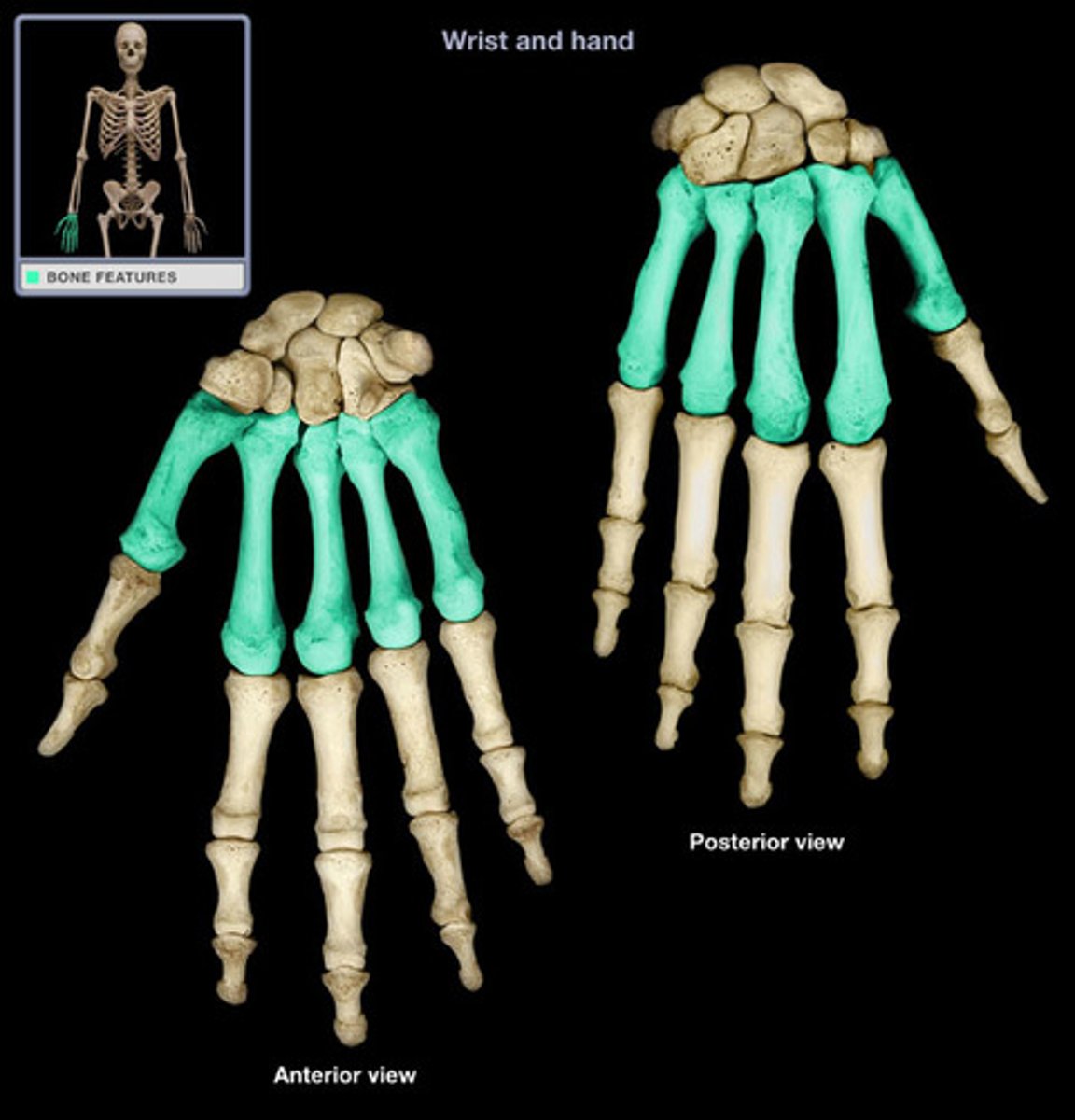
Phalanges
The fingers of the hand. Numbered 1-5 from medial to lateral.
Sans the thumb, each finger has 3 phalanges: distal, middle and proximal.
The thumb has no middle phalanx.