midterm 4 bio99
1/116
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
117 Terms
proteins are
chains of amino acids joined together
how many different amino acids
20
amino group has
N
carboxyl group has
C
R group has
side chain, each AA has diferent R
each amino acid has ___ and ______ letter nickname
3, 1
bond that joins 2 AA togteher
peptide
prootein also known as
peptide
front of polypeptide, similar to 5’ on DNA/RNA
N terminus
back of polyoeptide, similar to 3’ on DNA/RNA
C terminus
adapter molecule
reads DNA or mRNA and translates to AA sequence
degenerate
multiple codopns encoden same AA
codon family
4 codons specify same AA in same box of chart
for wobble hypothesis
Anticodon Base (1st position, 5' end) | Can Pair With (Codon 3rd base) |
|---|---|
G | U or C |
C | G |
A | U (standard only) |
U | A or G |
I (Inosine) | U, C, or A |
inosine is
adenosine in wobble anticodon position of trna deaminated
genetic code read in
non overlapping triplets
if overlapping model was true
single base mutation would result in multiple amino acid changes in the polypeptide.
open reading frame steps
determned by stop codon
scnan ntil first AUG start codon
follow sequence 3 ases a a time until stop codon
each trna has this many “arms
4 to 5
anticodon arm
contains anticodon, interacts with mrna sequence
amino acid arm
attatches to amino acid
other arms
strucutral, interact with ribosome, trna synthetase
trnatyr
trna that recognizes codon for tyrosie but doent necessarily have tyrosine aa attatched to it
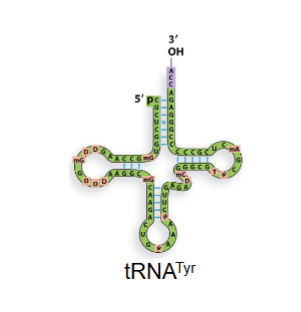
tyr-trnatyr
trna that recignuzes codon for tyrosuine and charged with tyrosine aa
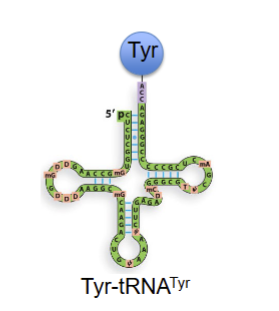
aminoacyl-trna
trna with aa attatched to it
types of trna processing
base modification
cleavage
cca addition
introms removed
base modification
specific nucleotides modified
cleavage
ends of transcripts removed
cca addition
cca attatched to 3’ end of transcript, what aa attaches to
introns removed
only in eukaryotes
trna activation steps
adenylation
trna charging
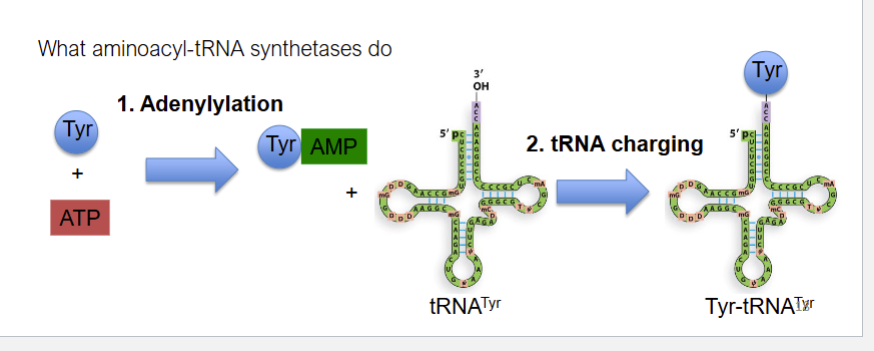
trna activation steps catalyzed by
aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases (AATS),
trna activation step 1- adenylation
AA+ ATP to aminoacyl-AMP + PPi
AMP attatcheds to carboxyl group of AA
pyrophostape PPi generatedin rna, laterb hydrolyzed to 2 phosphates giving eenergy to make rxn irreversible
TRNA activation step 2- trna charging
aminoacyl amp+ trna= aminoacyl trna+amp
aminoacyl transferred off amp to trnas caa arm
2 classes of amino acyl trna synthesizes o trna charging different
class 1- attatch aa on 2’-oh of cca
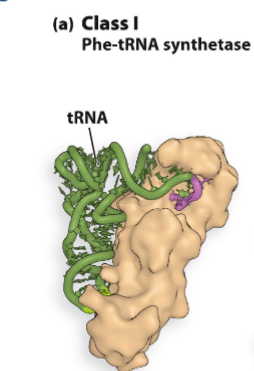
class 2
attatch aa onto 3-oh of cca
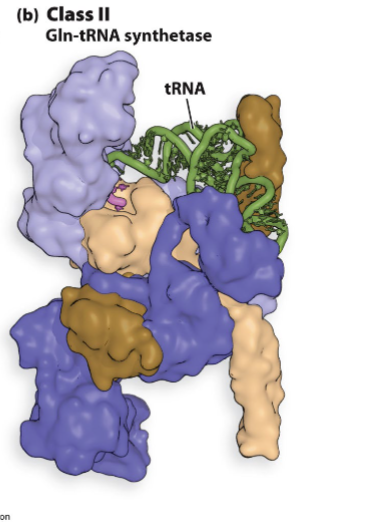
what can aminoacyl trna synthetases do
aminoacyl trna synthetases distinguish between trnas
idenitty nucleotides
nucloetides of trna recongized by specific syntheases
scattered through trna
each synthase recongzes unique set of identity nucleotides
different trnas for same aa have same idenitty ucleotides and recog ized by same synthase
aa-trna proofreading cases
larger aa trying to attatch to smaller aa’s trna
small aa attahcing to larger aas trna
larger aa trying to attatch to smaller aa’s trna
amino acid binding site
if aa big wont fit
if aa small fits
small aa trying to attach to larger aas trna
Ile-tRNA synthetase has an acylation site,
as well as a separate proofreading site
Normal scenario: Isoleucine in Ile-tRNA synthetase
bacteria
initiator met trna
trnafmet
bacteria
internal met trna
trnamet
transformylase converts ____ to __________
methionine to N formylmethionine (fmet)
fmet
formyl group attatches to nterminus of fmet, prevents fmet from attatching to aa in front of it, fmet can pnly be first aa
cant be added 9nternally
trnafmet only one recongized by ribosome initiation complex
eukaryotes
initiator trna
trnai met
eukaryotes internal trna
trna met
aminopeptidases
remove n terminal met in bacteria and eukaryotes
codon bias
some AA prefer specific codons and offer additional ways to regulate translation
DNA sequence can contain
5’UTR
coding exons
introns
3’UTR
types of mutations
single base substitutions
silent
missense
nonsense
frameshift
deletion
silent mutation
change in codon doesn’t AA
missense mutation
change in codon results in aa
nonsens mutation
change in codon creates early spot codon
frameshift
insertion or deltion that alters reading frame, cant be in multiple of 3
deletion mutations
deletes 1+ nucleotides
transition mutation
1 purine subsituted for another purine (A to G or G to A)
most frameshift mutation result in
early stop codon
reversion mutation
acquiring second mutation to restore protein function
reversion mutation for missense
second mutation reverses back to original aa
reversion mutation for nonsense
changes stop back to aa
reversion mutation for frameshift
deletion of single nucleotide
translation process
processed mrna shuttled from nucleus
ribosome assembeld into mrna
trna with bound aa enters ribosome, base pairs with codon sequence on mrna
ribosome catlayzes formation of peptide bond between 2 aa bound to trna
ribosome moves along mrna 3 nucleotides at a time, new trnas enter and have aa attatched to growing polypeptide
are nucleotides or aa bigger
nucleotides
how many subunits do ribisomes have
2
small subunit and large subunit
how is rrna transcribed
as 1 long transceript
svedberg units (S)
roughly non linear relationship to size
based on sedimentation rates of ultracentrifugation
harry noller
looked at what is necessary for peptide bond formation
rrna protein or both
puromycin
mimics trna, binds directly to large subunit, ribisomes attatche it to a growing polypepetide chain
protein denaturing compounds
unravels proteins structure
kethoxal
damages guanine in rna
ribozyme
rna with enzymatic activity (thomas steitZ)
how many trna binding sites does ribosome have
3
what are the trna binding sites of ribosome
a site
p site
e site
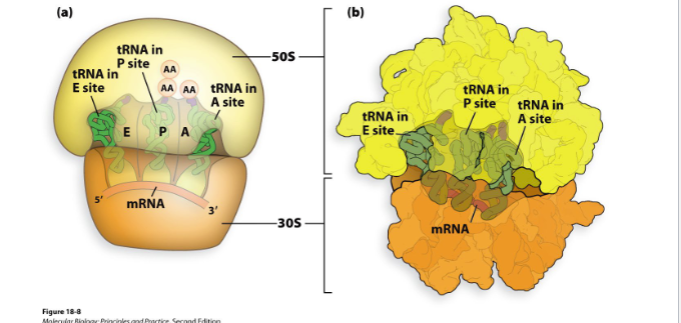
a site
acceptor site, new trnas enter ribosome
p site
polypeptide sit, where growing polypeptide chain is held
e site
exit site, where trnas expelled after aa removal
which ribosomal subunit holds mrna
30s small subunit
which ribosomal subunit catalyzes peptide bond formation
50s large subunit
translation steps
aa-trna
initiation
elongation
termination
what makes puromycine a strong antibiotic
new aa can;t be added to puromycin so terminates translation
initiation basic steps
small subunit binds mrns
smal subunit binds initiator trna
large subunit binds to rest
initiation final product has
small subunit
large subunit
mrna (start codon at p site)
initiator trna (paired with start codon)
shine dalgarno sequence
consensus sequence in front of start codon
recruits small subunit to mrna
directs mrna start sire to correct positon on ribosom
kozak sequence
similar but slightly different function as shine dalgarno sequence in eukaryotes
if-1
fills a site to prevent trna from binding
if-2
escorts initiator trna
if-3
prevents large subunit from binding
translation initiation in bacteria
1a. blocking sites on small subunit
1b. leading mrna
loading initiator trna
loading large subunit
initiation in eukaryotes step 1
blocking sites on small subunit
similar to if1 bacteria, elf1a binds to and blocks a sire
similar to if3 in bacteria, elf3 and elf1 block large subunit from assembling
major difference from bacteria - mrna doesnt attatch at this step
initation eukaryotes
loading initiator trna
similar to if2 in bacteria, elf2 binds to initiator trna and escorts into p site of small subunit
elf2 bound to gtp
major differences from bacteria steo 2
elf5b- alos like if2 bound to gtp, joins initiator trna at p site
ststill no mrna
initiation eukaryotes step 3
loading mrna
elf4f- binds to 5’ cap of mrna and escorts to small subunit, no bacterial equicalent
3 factors
elf4e- binds to 5’ cap
elf4a-atpase and rna helicase
elf4g- adapter, binds to elf3 and elf4e, links mrna to small subunit
requires hydrolysisof atp
mrna binds at 5’ cap not start codon
initiation eukaryotes step 4
scanning for start codon
scanning- complex travels along mrna until first start codon is found then stops
kozak sequence- helps identify start codon
initiation eukaryotes step 5
loading large subunit
both gtps hydrolyzed
drives release of all initiation factors
2 gtps requires
1 atp required to load mrna
large subunit can bind to pre initiation complex
elf4g
elf4g
part of elf4f complex, can bind to poly a binding (PABP)
most of eukaryotic translation called
cap dependent translation
internal ribosonak entry site (IRES)
sequence that can bind ELF4F and direct ribosome assembly and translation away from 5’cap
first identified in viruses that block cap dependent translation but allow their own genes to translate
some eukaryotic geens also use ires
makes eukaryotic polycistronic transcripts
bacterial polysomes
multiple ribosomes can translate same mrna simultaneously
translation elongation steps
aminoacyl trna enters ribosome
peptide bond forms
ribosome shifts to next codon
very similar between bacteria and eukaryotes