Two non-paired continuous variables
1/4
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
5 Terms
TWO NON-PAIRED CONTINUOUS VARIABLES
What does an independent samples t-test evaluate? (t.test() or independentSamplesTTest())
Formal name: Student’s independent samples t-test
It compares the means of two independent groups to see if they are significantly different
H₀: population means of both groups (samples) are equal
H₁: population means of both groups (samples) are not equal
What is the test statistic for an independent samples t-test and how are degrees of freedom calculated?
Values further away from zero (i.e., higher absolute values) correspond to a lower probability of H0 being true
Degrees of freedom: df = N−2
N is the total number of observations across both groups (in the data set)
*exact rejection regions depend on degrees of freedom
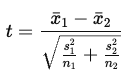
What is Cohen’s d and how is it interpreted for independent samples t-tests? (cohensD()) - Effect size
Cohen’s d measures the magnitude of difference between group means:
0.20 = small effect
0.50 = medium effect
0.80 = large effect
What are the 3 assumptions of the independent samples t-test?
The continuous variable is normally distributed in both groups
Check with Shapiro-Wilk test, histogram, Q-Q plot
If violated: use Wilcoxon rank sum test (wilcox.test())
Homoskedasticity: variances are equal between groups (the variance is the same in both groups)
Check with Levene’s test (leveneTest())
If violated: use Welch’s t-test
Observations are independent