International Business
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
Why does international trade occur? (4)
1- can benefit both parties
2- improve competitiveness
3- exports can help the economy of a country
4- imports provide:
- higher quality
-less expensive products
-more quantity
Describe the early country-based theories (3)
1- Focused on the individual country
2- useful to describe trade in commodities (ex: gold, wheat)
3- price is an important factor in the customer’s purchase decision
Describe the modern firm-based theories (3)
1- focus on the firm’s role in promoting international trade
2- useful to describe trade in differentiated goods (ex: cars, smartphones)
3- brand name is an important factor in the customer’s purchase decision)
Explain the difference between interindustry and intraindustry trade
Interindustry trade: different industries
Intraindustry trade: same industry
Explain the four country-based theories
1- Mercantilism: country’s wealth is measured by gold and silver. Promotes exports but not imports
2- Absolute advantage: full specialization (Trade-Off)
3- Comparative advantage: you’re better than everyone, but choose what you’re better at (Opportunity Costs)
4- Relative factor endowments (Hecksher-Ohlin) : a country will have a competitive advantage if it uses resources it has in abundance - Leontief Paradox (research results on the US Trade position were the reverse of what the model predicted)
Explain the two modern firm-based theories
1- Linder’s Country similarity theory: most trade in manufactured goods will be between countries with similar per capita incomes, and intraindustry trade will be common.
2- New trade theory: economies of scale occur if a firm’s average cost of producing a good decreases as its output increases.
Describe the two types of international investments
1- Foreign Portfolio Investment (FPI): passive investments (buy stocks, bonds); No control power in the foreign country
2- Foreign Direct Investments (FDI):
decision making (buy business/assets); Have control power in the foreign country
Describe and explain the two main political factors affecting the FDI decision
1- Avoidance of Trade Barriers: build foreign facilities to avoid tariffs on imported consumer goods
2- Economic Development Incentives: financial tools that governments, utilities, and other organizations use to encourage businesses to relocate, create jobs, or invest in a community. ( make it in my region, get my money)
what are the four main economic rationales to intervene in trade
1- fighting unemployment
2- protecting infant industries
3- developing an industrial base
4- economic relationships with other countries
what are the four noneconomic rationales why governments intervene in trade
1- maintaining essential industries
2- promoting acceptable practices abroad
3- maintaining or extending spheres of influence
4- preserving national culture
what are the two types of trade control
1- direct price influencers
2- direct quantity limiters
two examples of direct price influencers
1- tariffs
2- subsidies
example of direct quantity limiters
quotas (nontariff barier)
what is protectionism
set of government policies that limit international trade to support domestic industries
What is the unemployment argument for government intervention for trade?
Governments may restrict imports or encourage domestic production to protect local jobs and reduce unemployment.
What are 2 consequences of import restrictions
1. Can lead to retaliation by other countries -> Trade wars
2. may decrease export jobs because of price increases and lower incomes abroad
What is the infant-industry argument?
Governments may restrict imports or provide subsidies to protect new or emerging industries from international competition. This allows these industries time to grow, become competitive, and achieve economies of scale.
Pitfalls for infant industries
- Difficult in timing exit as some may become to dependent on protection
- Some may contrinue to seek protection even if they are not 'infants' anymore
- Governments may protect industries that never had potention and waste thier resources
Stakeholders include
- workers
-owners
-suppliers
-local politicians
developing an industrial base
help to improve competitive positioning.
what trade controls can be used for
- improve balance of payments
-gain fair access to foreign markets
-bargaining tool
- control prices (prevent dumping - exporting below cost or below home country prices to get foreign producers to lower their prices)
why do countries promote industrialization
-brings faster growth than agriculture
-brings in investment funds
-diversifies the economy
-creates growth in manufactured goods
-reduces imports and promotes exports
maintaining essential industries
protect essential industries so the country is not dependent on foreign supplies
what do countries must do to maintain essential industries
- determine which industries are essential but any product can be deemed as essential
- consider costs and alternatives
- consider political consequences
promoting acceptable practices abroad: what import trade controls can be used for
promote changes in foreign countries’ political policies or capabilities as a foreign policy weapon to pressure governments to alter their stances on various issues ( human rights. environmental protection)
maintaining or extending spheres of influence
economic agreements while creating political benefits
preserving national culture
certain things we want to protect (ex: rice in Japan)
specific duty
Type of tariff (per unit basis (amount))
type of tariffs (3)
1. Specific duty
2. Ad valorem tariff
3. A compound duty
ad valorem
a percentage of the item
A compound duty
Dollar + percentage
Under the gold standard, all national governments promised to follow the “rules of the game”. What did this mean
Every country agreed to follow the same rules to keep money tied to gold and allow gold to move freely across borders to balance trade and payments.
What did it mean under the gold standard to defend a fixed exchange rate and what did this imply about a country’s money supply
A country promised its currency could always be exchanged for a set amount of gold.
- Gold outflow: Money supply shrinks -> Higher interest rates and lower prices
- Gold inflow: Money supply expands -> Lower interest rates and higher prices
What was the foundation of the Bretton Woods international monetary system, and why did it eventually fail
- $US being the only currency directly peg to gold while other currencier are directly peg to the $US and indirectly peg to gold.
- Each country establish its exchange rate vis-a-vis the US and the calculated the gold par value of their currency
- Failed because countries started to lose confidence in the US$ and wanted gold instead, forcing the US to devalue the dollar (floating rate)
what does a floating rate of exchange mean? what is the role of the government
government does not set the currency’s value or intervene in the marketplace, allowing the supply and demand of the market for its currency to determine the exchange value.
what are the advantages (2) and disadvantages of fixed exchange rates
Pros:
1- Predictable
2- Consistency & Clarity
3- Can help inflation as the rate stays the same
Cons:
1- Necessitate central banks maintain large quantities of international reserves for use
How does a crawling peg fundamentally differ from a pegged exchange rate
Crawling peg: Government will make occasional small adjustments in its fixed rate of exchange
Pegged exchange rate: No changes or adjustments made
explain what is meant by the term impossible trinity and why it is in fact “impossible”
A country cannot simultaneously achieve all 3:
1- Fixed exchange rate
2- Free Capital Mobility
3- Independent monetary policy
Capital flows respond immediately to interest rate differences, hence one of the goal will be dropped
difference between dollarization and currency board
Dollarization: No domestic curency at all, only the foreign currency ($US) is used
Currency board: Keeps domestic currency but 100% backed and pegged to another currency, usually the $US
what are special drawing rights
International reserve asset created by the IMF to supplement the official reserves of its member countries
what are the attributes of the ideal currency
Would possess all 3 attributes:
1. Exchange rate stability (value of currency would be fized in relationship to other major currencies)
2. Full fiancial integration (Complete freedom of monetary flows would be allowed)
3. Monetary independence (Control own monetary policies)
Free-floating vs hard peg (dollarization & currency boards)
Free-floating:
- Pro: Monetary independence
- Con: Exchange rate volatility, hurt trade & investment confidence
Hard peg:
- Pro: Credibility and stability
- Con: No monetary independence & vulnerability to shocks
eras of the evolution of capital mobility
1. classical gold standard
2. inter-war years
3. fixed exchange rates
4. floating exchange rates
5. emerging era
What is the balance of payments?
The measurement of all international economic transactions between the residents of a country and foreign residents
3 specific signals that a country’s BOP data can provide
- Indicator of pressure on a country's foreign exchange rate
- Signal the imposition or removal of controls in various sorts of payments
- Forecast of a country’s market potential
What are the two main types of economic activity measured by a country’s BOP?
- Current transactions having cash flows completed within one year
- Capital and financial transactions, in which investors acquire ownership of a foreign asset
What are the main component accounts of the current account?
- Goods Trade
- Services Trade
- Income
- Current Transfers
What are the primary sub-components of the financial account?
- Direct Investment
- Portfolio Investment
- Other Investment Assets/Liabilities
What are the main summary statements of the balance of payments accounts and what do they measure?
- Balance on current account: Measures the country’s overall trade in goods, services, and income flows
- Basic Balance: Measures all of the international transactions (current, capital, and financial) that come about because of market forces.
- Overall Balance: Total change in a country’s foreign exchange reserves caused by the basic balance plus any governmental action to influence foreign exchange reserves
What is the relationship between the balance of payments and a fixed or floating exchange rate regime?
- Under a fixed exchange rate system: The government bears the responsibility to ensure that the BOP is near zero.
- Under a floating exchange rate system: The government has no responsibility to peg its foreign exchange rate.
What factors seem to play a role in a government’s choice to restrict capital mobility?
- Protect monetary control
- Financial stability
- Exchange rate stability
Law of one price
If identical products or services can be sold in two different markets, and no restrictions exist on the sale or transportation of product between markets, the product's price should be the same in both markets.
What is capital flight?
Rapid outflow of capital in fear of domestic political and economic conditions and policies
Define the two forms of purchasing power parity
- Absolute PPP: If the law of one price were true for all goods and services, the PPP exchange rate could be found from any individual set of prices.
- Relative PPP: If the spot exchange rate between two countries starts in equilibrium, any change in the differential rate of inflation between them tends to be offset over the long run by an equal but opposite change in the spot exchange rate
Define the Fisher effect
The nominal interest rate is equal to the required real rate of return plus compensation for expected inflation.
Define the international Fisher effect
A country with a higher nominal interest rate will see its currency depreciate relative to a country with a lower nominal interest rate.
Define interest rate parity. What is the relationship between interest rate parity and forward rates?
The difference in the national interest rates for securities of similar risk and maturity should be equal to, but opposite in sign to, the forward rate discount or premium for the foreign currency, except for transaction costs.
Define the terms covered interest arbitrage and uncovered interest arbitrage.
- CIA: The spot and forward exchange markets are not constantly in the state of equilibrium described by interest rate parity. When the market is not in equilibrium, the potential for “riskless” or arbitrage profit exists.
- UIA: The transaction is “uncovered” because the investor does not sell the higher yielding currency proceeds forward, choosing to remain uncovered and accept the currency risk of exchanging the higher yield currency into the lower yielding currency at the end of the period.
What are the formulas for international parity conditions in equilibrium?
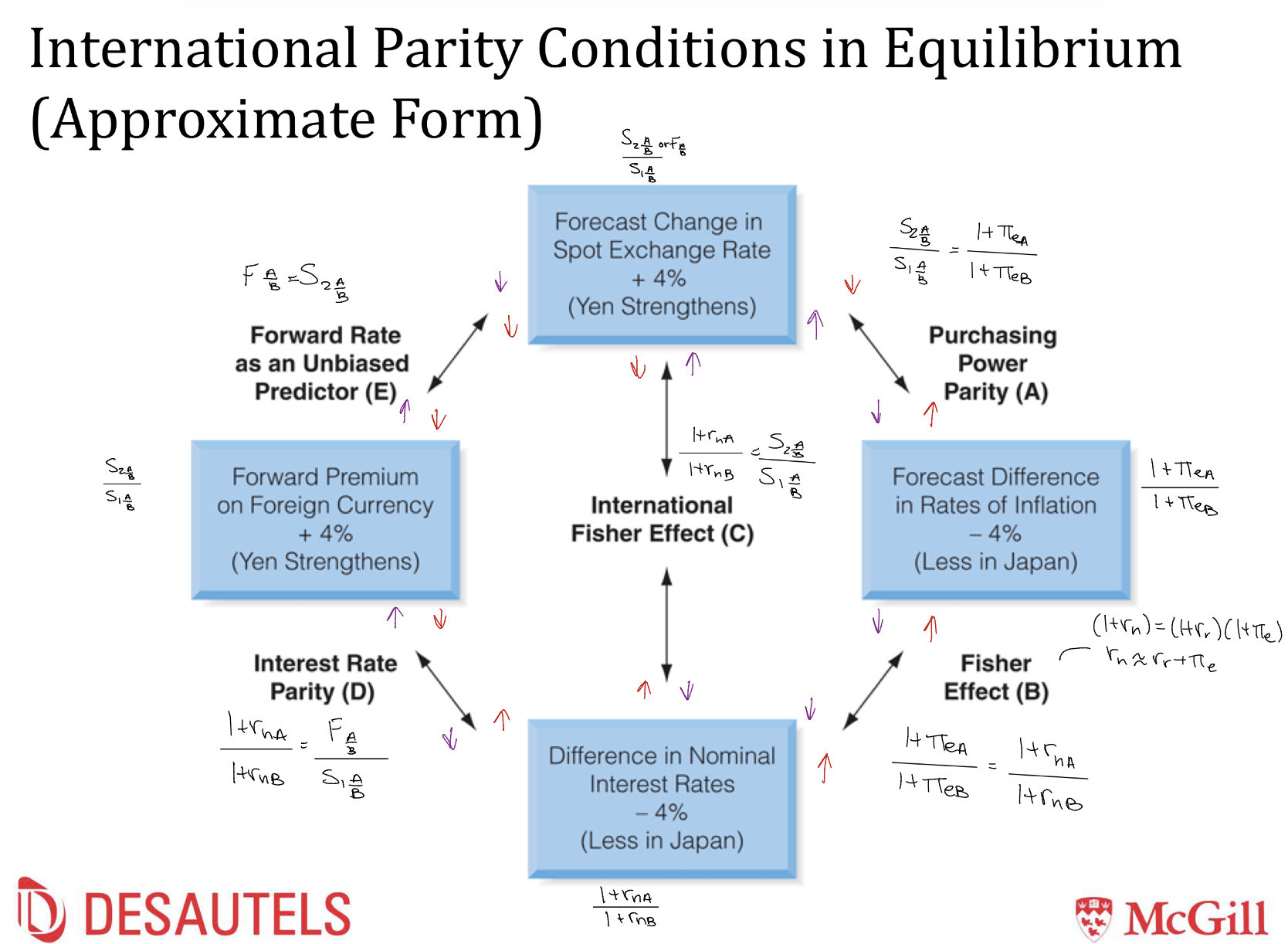
What is the formula to know which way CIR goes?
(Spot/Forward)*(1+foreign interest rate) > or < than (1 + home interest rate)
If >: Home → Foreign;
If <: Foreign → Home
Always borrow lowest amount and invest highest amount
What is the formula to know which side to solve for spot rates?
If we want to solve for the currency on top: (Implied Spot rate - Actual Spot rate) / Actual Spot rate
If we want to solve for the currency on the bottom: (Actual Spot rate - Implied Spot rate) / Implied Spot rate-
If Negative → Undervalued
If Positive → Overvalued
If I have a S = 1.2971 pounds/USD & 6-month F = 1.3018 pounds/USD. What is the premium/discount?
USD forward rate is selling at a 0.7% premium compared to the spot rate
What does this mean: 1.2971 pounds/USD
1 USD can be exchanged for 1.2971 British pounds
Bottom currency will be your base currency
US view: USD/JPY = 150
1 yen costs 150 USD
(US view): JPY/USD = 0.0067
1 USD gets you 0.0067 yen
What are 3 things that are key to fully take advantage of these types of opportunities?
Go as fast as possible
Guarantee (lock-in) all the rates
Invest as much as possible
Classification of Currency Regimes
Hard peg (Use of Currency board or Dollarization)
Soft peg (Bretton Woods)
Floating Arrangements: Mostly market driven (free floating or managed float)
Residual: Don’t well fit the previous categorizations