L2: Membrane Structure and Function
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
What are membranes?
Phospholipid polymers of fatty acids, glycerol, phosphate and a terminal amine or alcohol group
What is phosphatidyl choline?
It comprises choline - a phosphate linkage to glycerol which is esterified with two fatty acids.
Are membrane heads and tails hydrophobic or hydrophilic?
Head = hydrophilic
Tail - hydrophobic
Membrane phospholipids are amphipathic molecules, what does that mean?
In water, they spontaneously form monolayers and bilayers
Monolayer
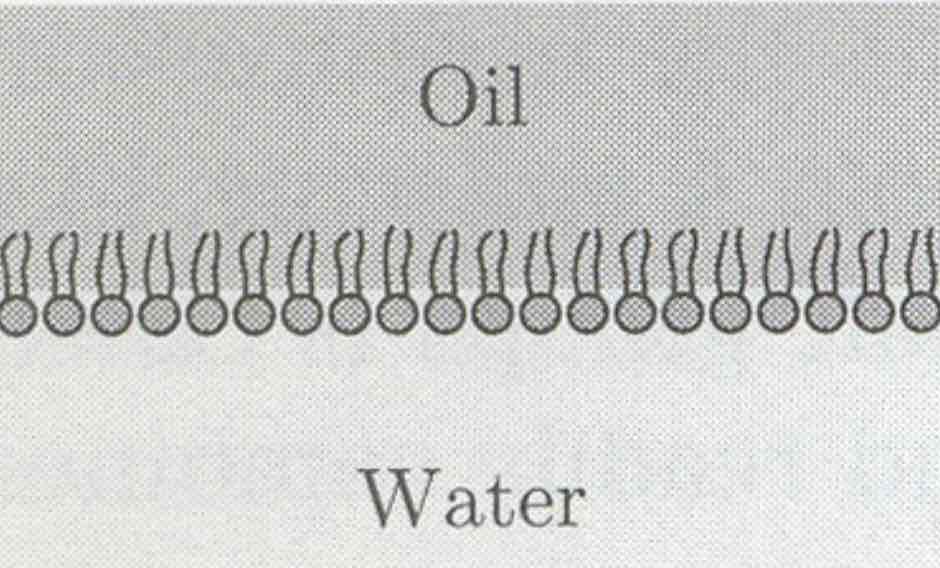
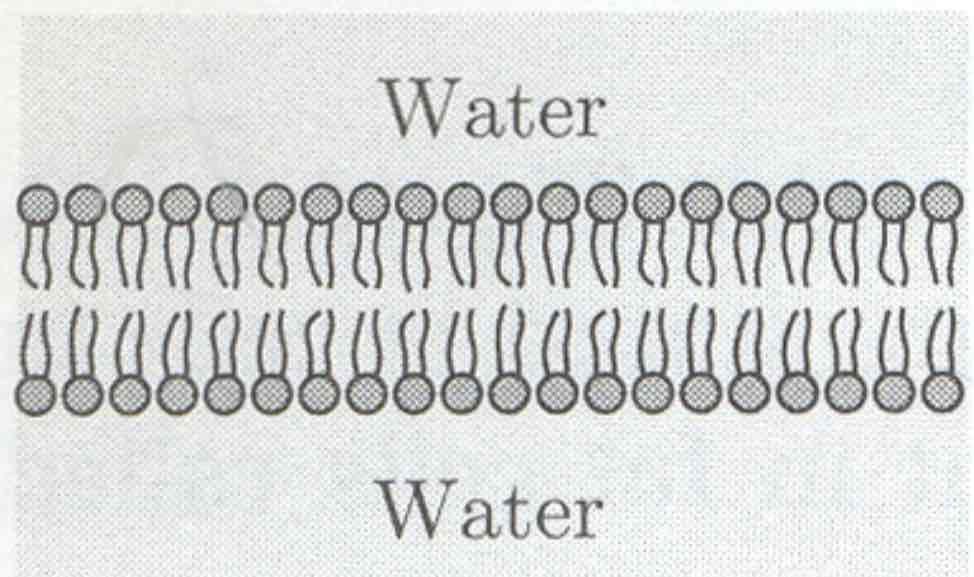
bilayer
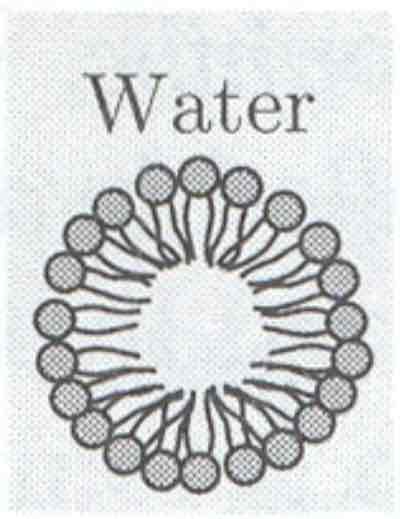
Micelle
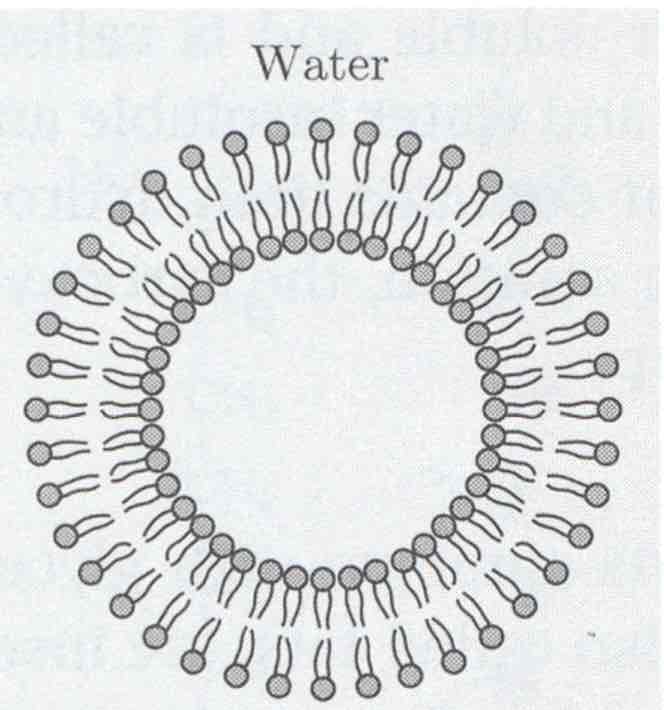
Liposome
What are simple detergents?
Salts of fatty acids which retain the amphipathicity and are able to interact and dissolve other organic compounds
The function of cellular membranes
To compartmentalize metabolic activities
To separate/protect cellular components
To provide a scaffold for signalling
Medium for cellular energy generation
What does the compartmentalization, protection and energy generation of membranes come from?
The immiscibility of water and membranes.
How much slower is sucrose diffusion across membrane bilayers?
1000000 fold slower
What is a diffusion rate?
How long it takes a compound to diffuse a distance X
What limits membrane dimensions and cell size?
Physical properties (diffusion) of compounds in water
What is the diffusion of ions across membranes driven by?
Chemical and electrical gradients
What does selective diffusion generate across semi- permeable membranes?
A small ion imbalance
What does the Nernst equation describe?
The equilibrium between chemical and electrical forces on an ion
What is bioenergetics
The use of ion gradients across membranes to generate biological energy.
How is the voltage across cell membranes measured?
Using microelectrodes implanted in cells
How is the voltage across endomembranes measured?
Eg. Mitochondria or lysosomes
Can be measured with voltage - sensitive dyes.
Where are membranes found?
Delimiting all organelles (determining their boundaries) in eukaryotic cells.
What does electron microscopy do?
Gives a static picture of the cell
What suggests chloroplasts and mitochondria are endosymbiont progenitors?
Double membranes
Division of chloroplasts & mitochondria
They undergo independent division
What is glycerol
A 3 carbon alcohol
Dehydration reaction
Extracting water from 2 molecules to join them together
Amphipathic
Molecules having both hydrophobic and hydrophilic sides
What are micelles or liposomes?
Micelles and liposomes are both nanostructures used in various applications, including drug delivery and cosmetics, but they differ in their structure and function.
Micelles are spherical, single-layered structures formed by amphiphilic molecules in an aqueous environment, the hydrophobic tails cluster together to form a core, while the hydrophilic heads are on the outer surface, creating a spherical structure. Micelles can encapsulate hydrophobic molecules within their core, preventing them from dissolving or dispersing in the aqueous environment. They are used in various applications, including cleaning agents, drug delivery, and emulsification
liposomes are spherical, double-layered vesicles formed by phospholipids. Liposomes are formed by phospholipids, which also have hydrophobic tails and hydrophilic heads. In an aqueous environment, phospholipids self-assemble to form a double-layered (bilayer) membrane enclosing an aqueous compartment. Liposomes can encapsulate both water-soluble and hydrophobic molecules within their inner aqueous core and lipid bilayer, respectively. They are used as drug delivery systems, particularly for delivering drugs to specific locations in the body
Gas diffusion in air
Relatively quick: around 10 × 10 -I cm '2 /s
What happens to diffusion of material in water?
Drastically slowed
How does fluorescence work?
The electron is excited by a photon of light and moves to a higher energy state
The excited molecule loses some energy as heat
The electron returns to a lower energy state and the rest of the energy is emitted as light
What is green fluorescent protein?
A naturally occurring protein found in the aequorea Victoria jellyfish which exhibits fluorescence when exposed to UV or blue light.
The fluorescence does not require a co-factor and can be fused with proteins.
What is SYP121?
A vesicle trafficking protein that normally is secreted in secgfp and leaves the cell or it is activated and accumulates in the Golgi or ER
Is the Golgi interconnected?
No, it is discrete structures which form an accumulation around the nucleus.
What else do chloroplasts & mitochondria do?
Communicate with eachother by exchanging material via tubule like structures.