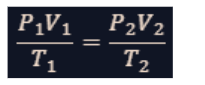Chemistry: Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
kinetic molecular theory of gases
It is a model that explains the behavior and properties of gases in terms of the motion and interactions of their molecules.
kinetic molecular theory of gases
This theory is based on several key postulates that help us understand gas behavior at the microscopic level.
gas composition
no intermolecular forces
elastic collisions
continuous random motion
average kinetic energy and temperature
What are the five key postulates of the kinetic molecular theory?
gases
These consist of a large number of tiny particles (molecules or atoms) that are in constant, random motion.
gases
These particles are far apart relative to their size, meaning the volume of the gas molecules themselves is negligible compared to the volume of the container.
no intermolecular forces
There are no attractive or repulsive forces between gas molecules.
no intermolecular forces
This means that molecules move independently of each other, except when they collide.
elastic collisions
It is when gas molecules collide with each other or with the walls of the container, the collisions are perfectly elastic.
elastic collisions
This means there is no loss of kinetic energy in the collisions; the total kinetic energy of the molecules remains constant.
continuous random motion
It is when move in straight lines until they collide with other molecules or the container walls.
kinetic energy and temperature
The average kinetic energy of gas molecules is directly proportional to the absolute temperature of the gas.
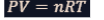
ideal gas law
It is a fundamental equation in chemistry and physics that describes the behavior of an ideal gas.
ideal gas law
This law combines several empirical laws into a single equation and provides a good approximation for the behavior of real gases under many conditions.
boyle’s law
This law states that the pressure (𝑃) of a gas is inversely proportional to its volume (𝑉) when the temperature and the number of gas molecules are held constant.
boyle’s law
It is the relationship between pressure and volume at a constant temperature.
boyle’s law
If the volume of a gas decreases, its pressure increases, provided the temperature remains constant.
gay-lussac’s law
It is the relationship between pressure and temperature at constant volume.
gay-lussac’s law
It states that the pressure (𝑃) of a gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature (𝑇) when the volume and the number of gas molecules are held constant.
gay-lussac’s law
If the temperature of a gas increases, its pressure increases, provided the volume remains constant.
charles’ law
It is the relationship between volume and temperature at constant pressure.
charles’ law
It states that the volume (𝑉) of a gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature (𝑇) when the pressure and the number of gas molecules are held constant.
charles’ law
If the temperature of a gas increases, its volume increases, provided the pressure remains constant.
combined gas law
This lawmerges Boyle's, Charles's, and Gay-Lussac's laws into a single equation
ideal gas law
.
boyle’s law
.
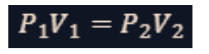
charles’ law
.
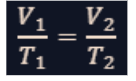
gay-lussac’s law
.
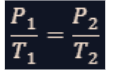
combined gas law
.