Microbe Genetic Variability
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Describe things that can lead to vertically transferred mutations in bacteria
DNA mutations: spontaneous, replication errors, mutagens
How can DNA be transferred horizontally?
conjugation
transduction
transformation
What is conjugation in bacteria and what does it require?
horizontal transfer of DNA
requires cell to cell contact, sex pulus, relaxomosome, T4SS
plasmid/episome
What is a plasmid?
independently replicating non-chromosomal DNA; contains non-vital DNA; own origin and replicatino
What is an episome
independently replicating plasmids with own origin integrated into chromosome
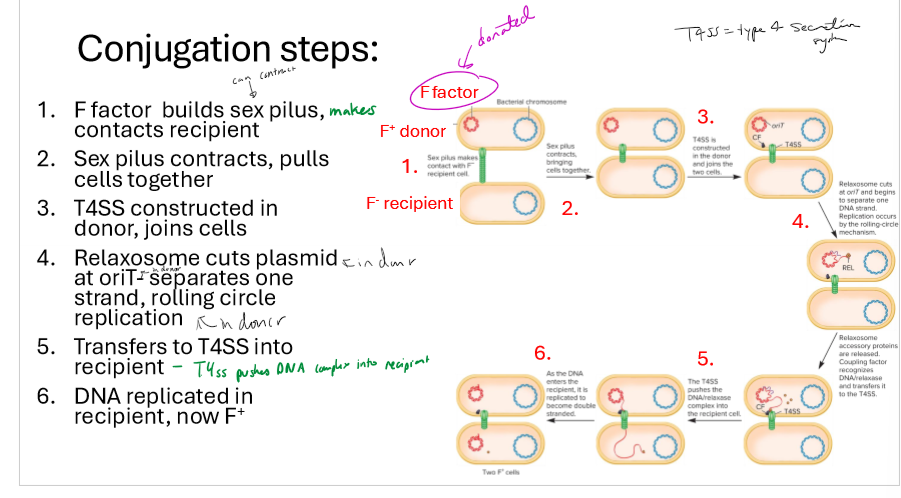
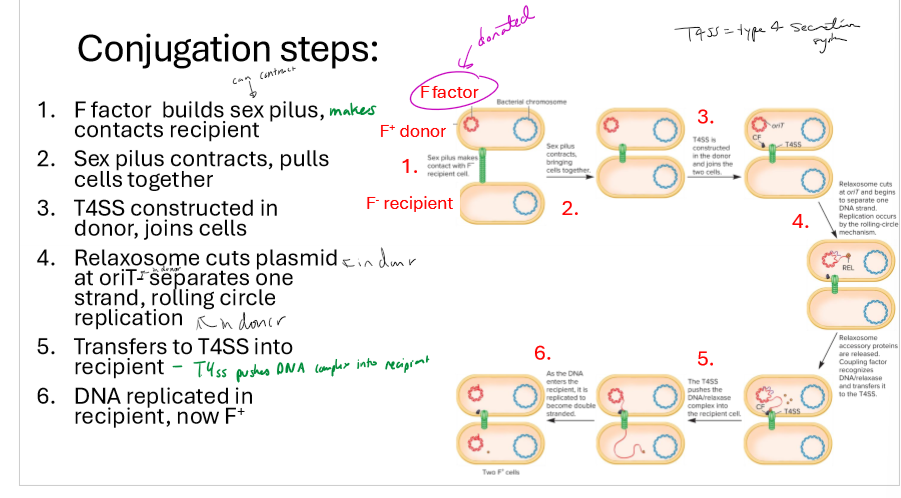
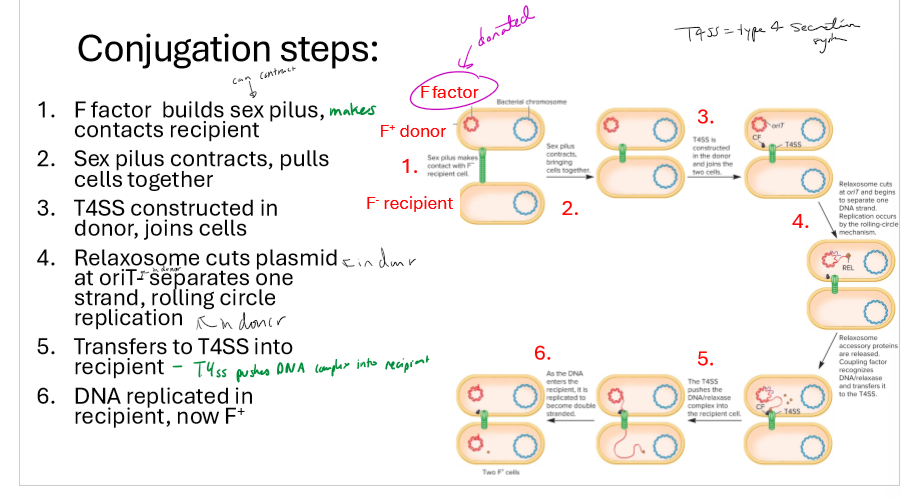
Describe the steps of conjugation
F factors in F+ donor builds sex pilus, makes contact with F- recipient
Sex pilus contracts, pulling cells together
T4SS constructed in donor, joins cells
relaxosome cuts plasmid in donor at OriT, separating one strand via rolling circle replication
T4SS puts DNA into recipient cell
DNA replicated in recipient, now F+
What is transformation?
bacterial uptake of DNA lying around
requires cells with DNA uptake machinery (pilus, nuclease, etc.)
What is transduction and how does it work?
virus mediated transfer of DNA
1. phage infects bacteria
2. phage picks up pieces of bacterial chromosome during replication and assembly
3. phage can transfer DNA to new recipient after infection
What is a plasmid carrying antibiotic resistance genes called?
R plasmid
what is a transposon?
a segment of DNA that can move from one location in a genome to another
How can R-plasmids move?
horizontal gene transfer (transduction, transformation, conjugation)
carried in transposon (moving gene) like ICE and MGI
