7.1 Parts of Microscope, Prokaryote/Eukaryote and Cell Theory
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
magnification
how large microscope can make image
resolution
how sharp/clear microscope can make image
cell theory
all living things are made of cells, cells are the basic unit of life, and cells arise from other cells
eukaryotes
DNA is enclosed by nucleus, lager than prokaryotes
ocular lens magnification
10x
low power objective magnification (WITHOUT OCULAR LENS)
4x
medium power objective magnification (WITHOUT OCULAR LENS)
10x
high power objective magnification (WITHOUT OCULAR LENS)
40x
total magnification of lenses on microscope (ocular is 10x)
40x, 100x, and 400x
all of this cell type have a cell wall
prokaryote
this cell type has no membrane-bound organelles
prokaryote
all of this cell type lack a nucleus (free-floating DNA)
prokaryote
this cell type is larger than the other (eukaryote/prokaryote)
eukaryote
animals, plants, fungi, protists, and some fungi have this cell type
eukaryote
bacteria and archaea have this cell type
prokaryote
image
the thing you see when you look into a microscope
object
the thing that the image is based off when you look into a microscope
what is the orientation of image on microscope
inverted version of object
eyepiece
contains ocular lens

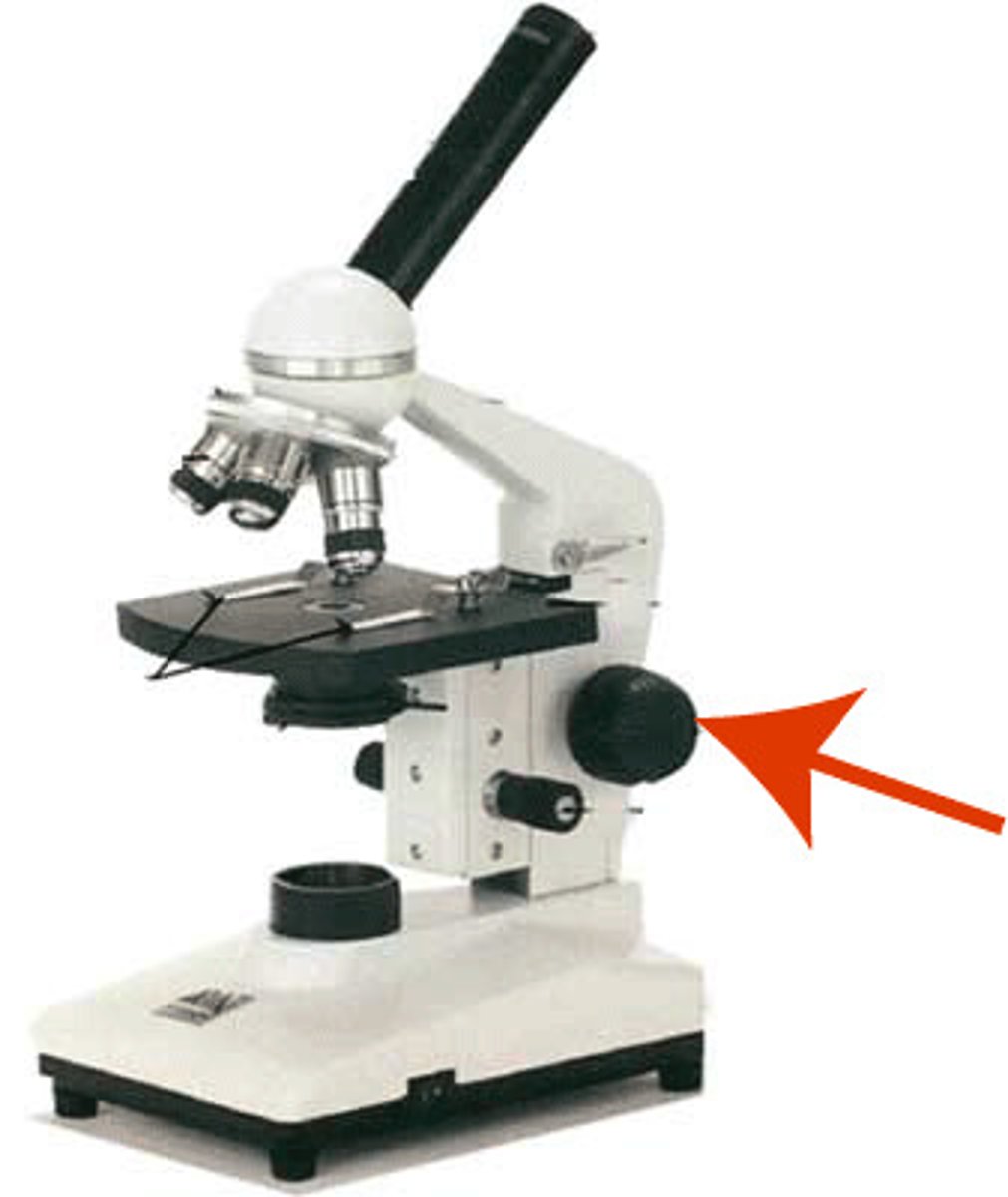
coarse adjustment knob
moves stage for focusing

fine adjustment knob
moves stage more slightly to sharpen image (less than coarse adjustment knob)
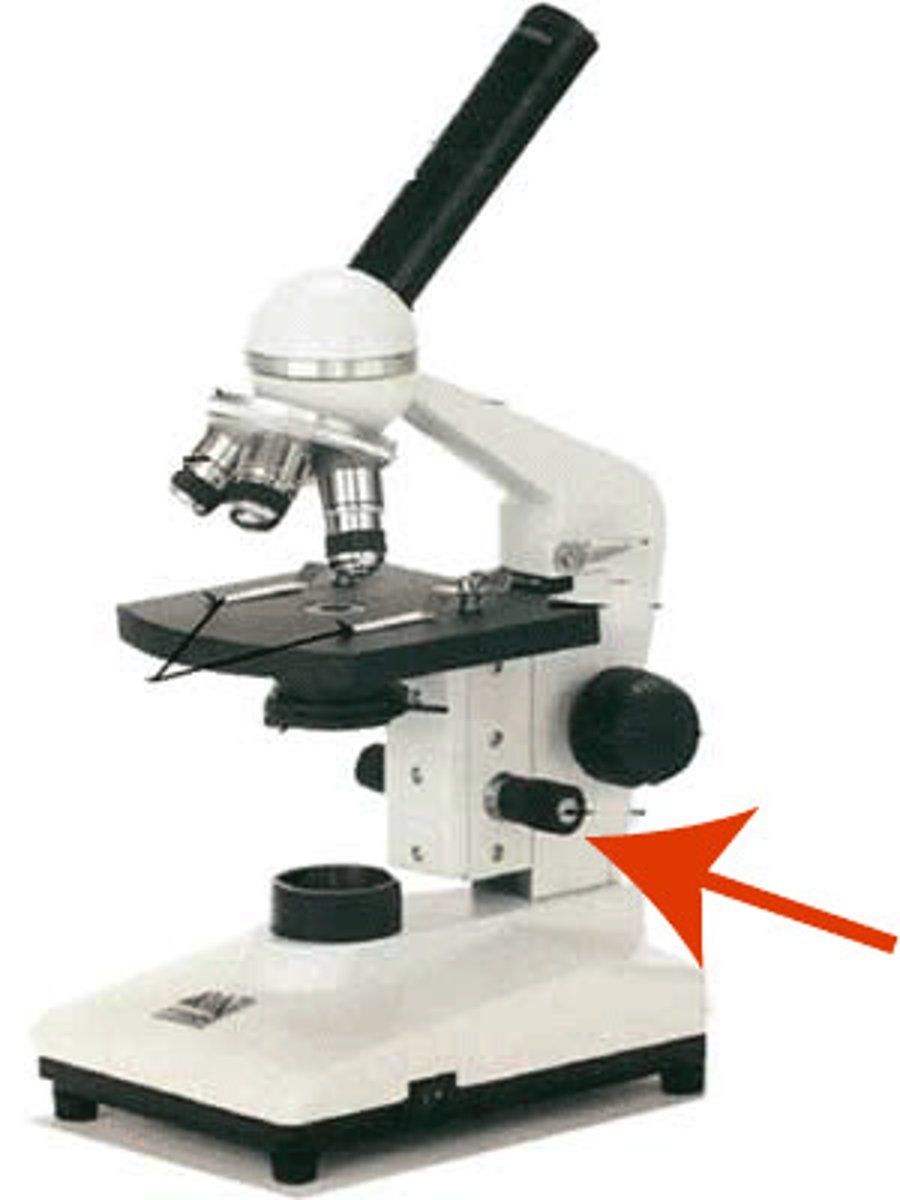
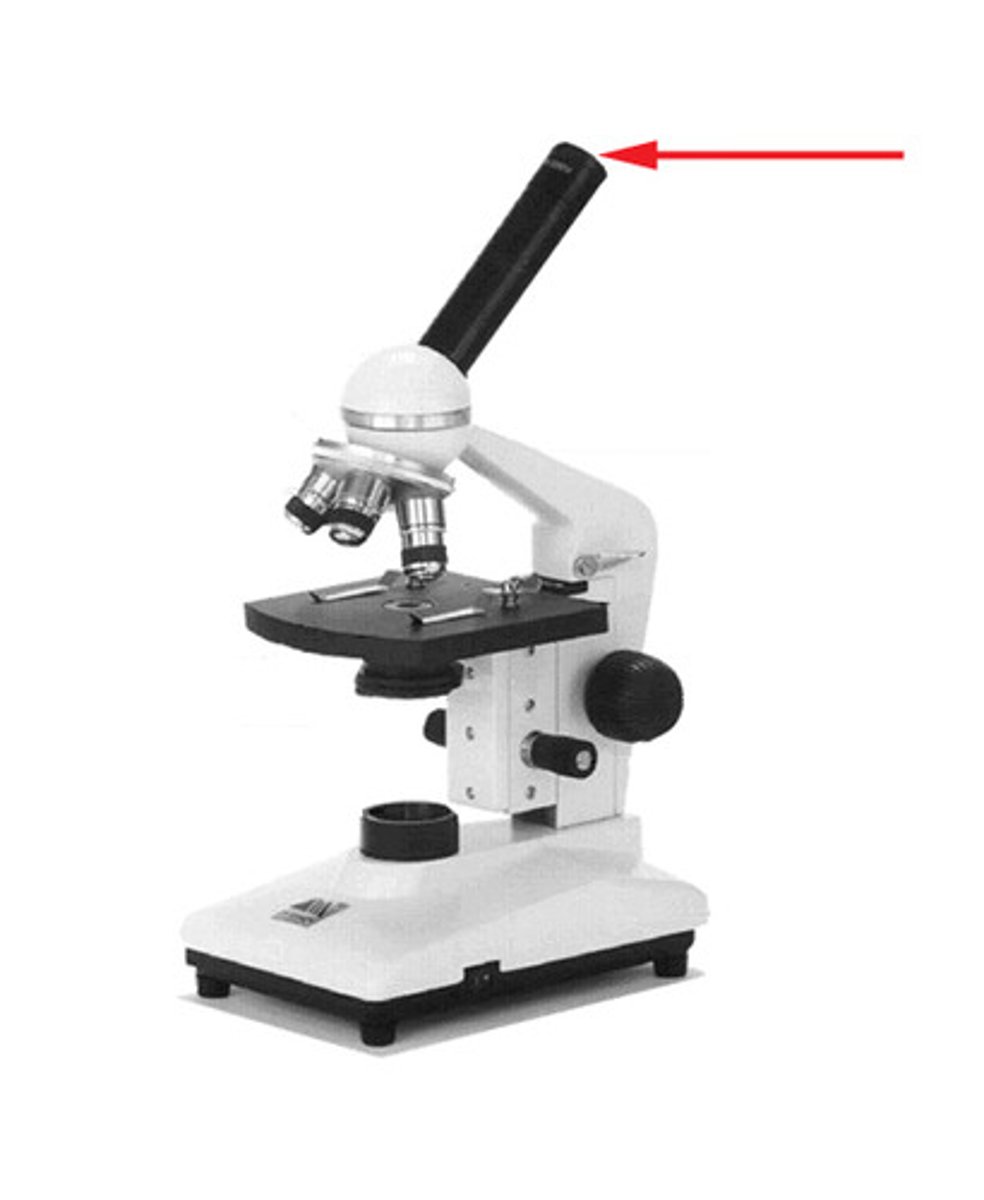
body tube
connects eyepiece to nose piece
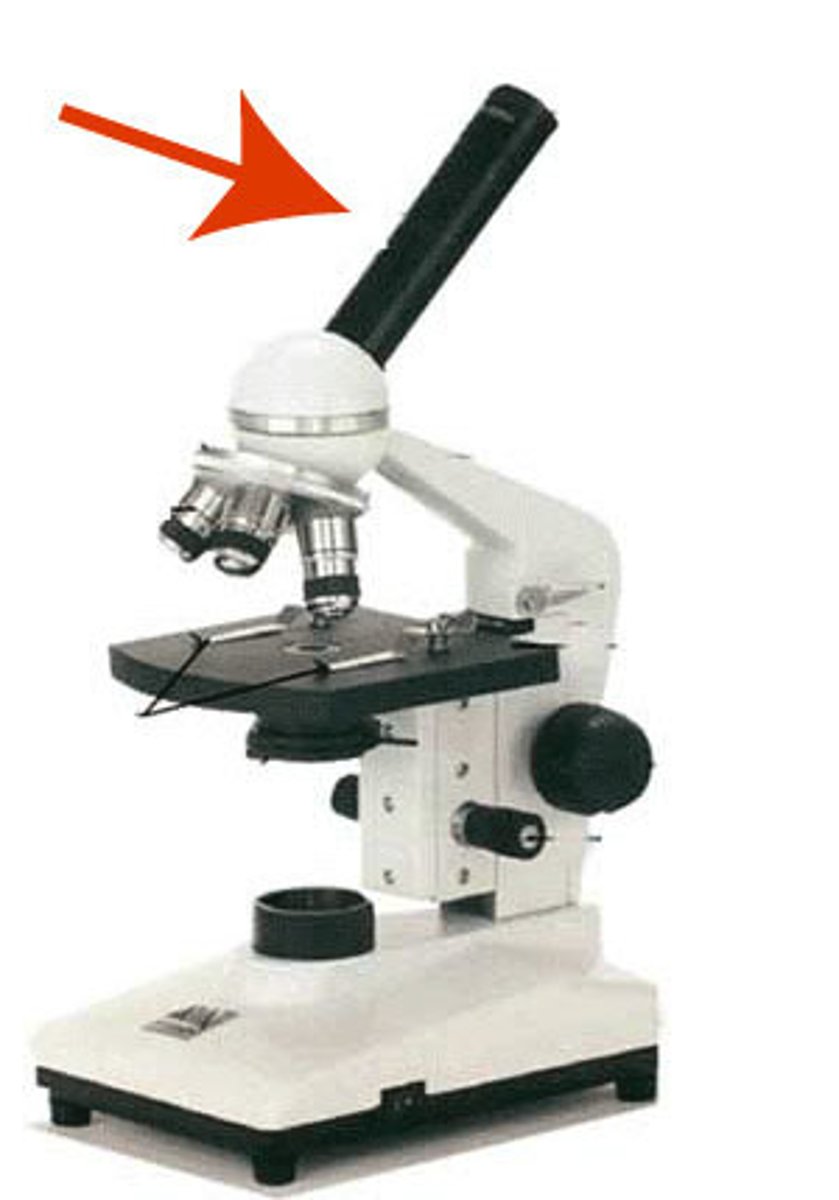
Nosepiece
holds the low power, medium power, and high power objectives
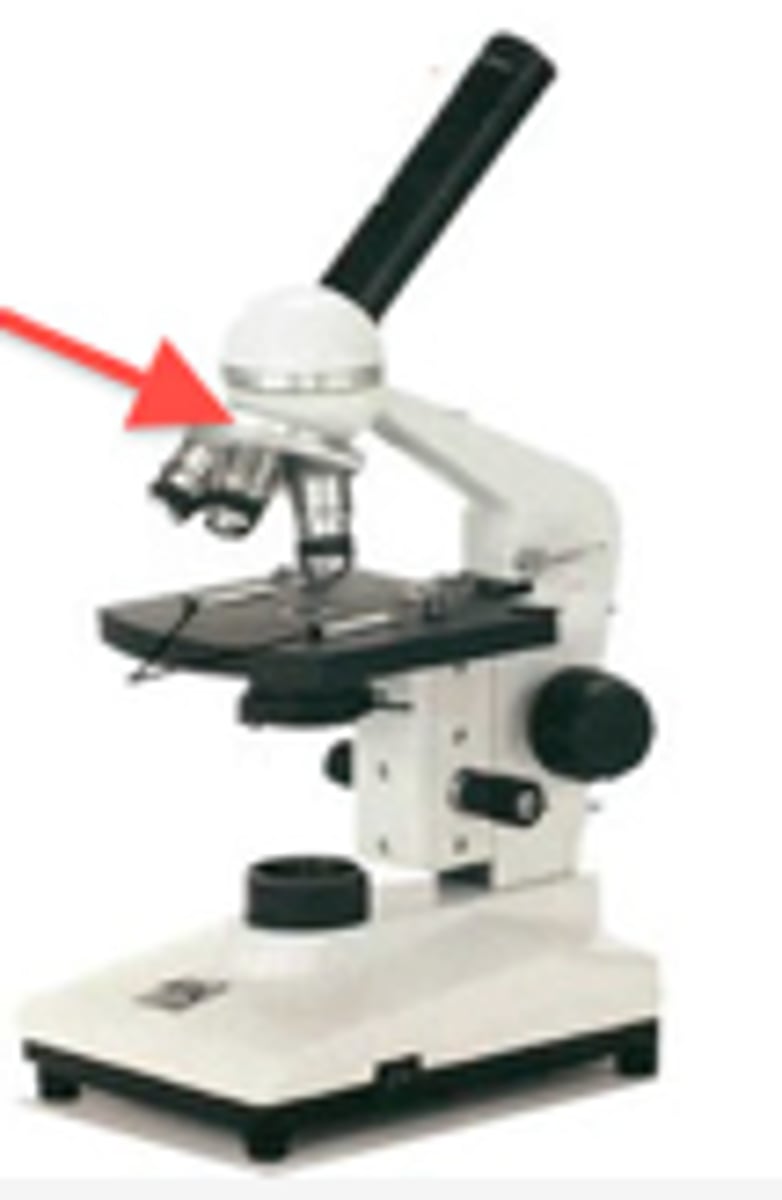
low power objective
shortest stub on nosepiece, magnification power is 4x
medium power objective
medium length stub on nosepiece, magnification power is 10x
high power objective
longest stub on nosepiece, magnification power is 40x
stage
where you put the specimen on
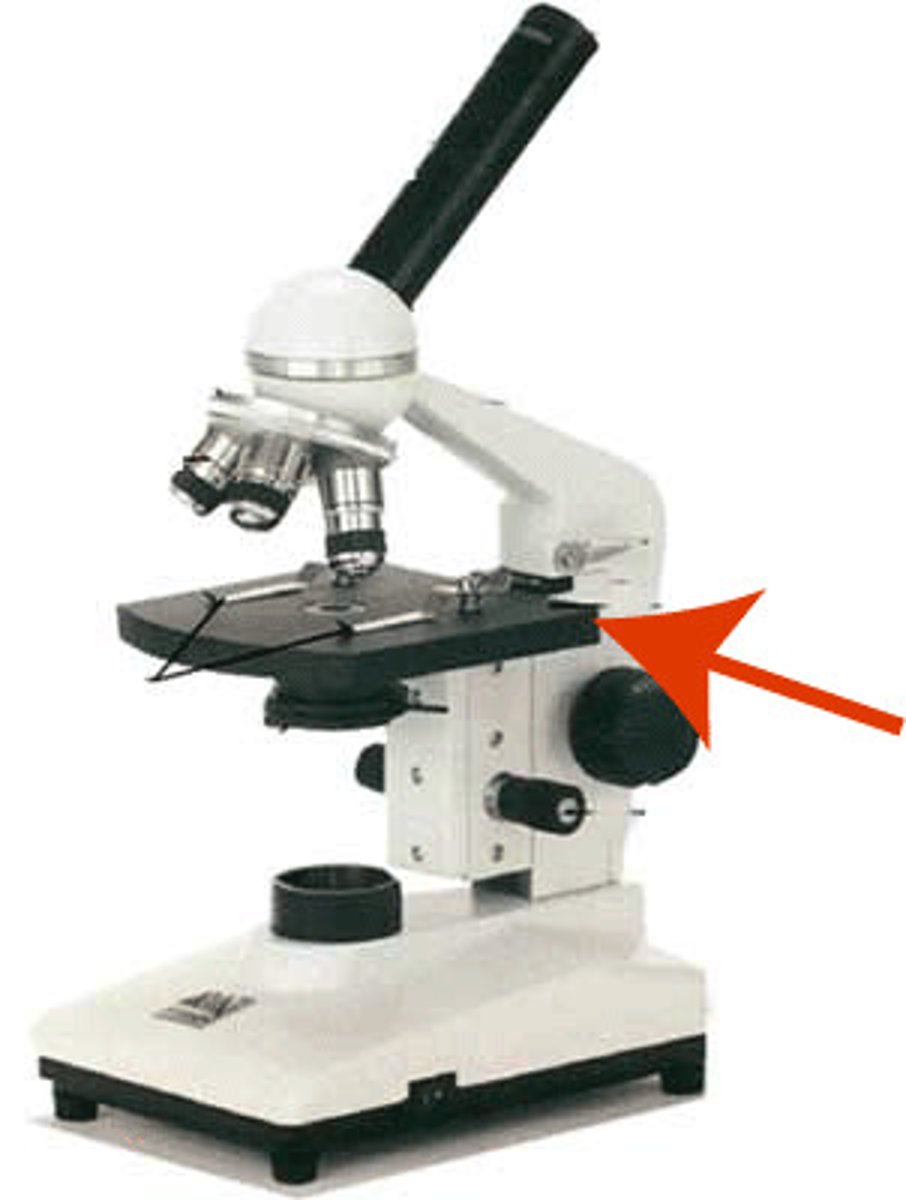
stage clips
holds specimen in place on stage
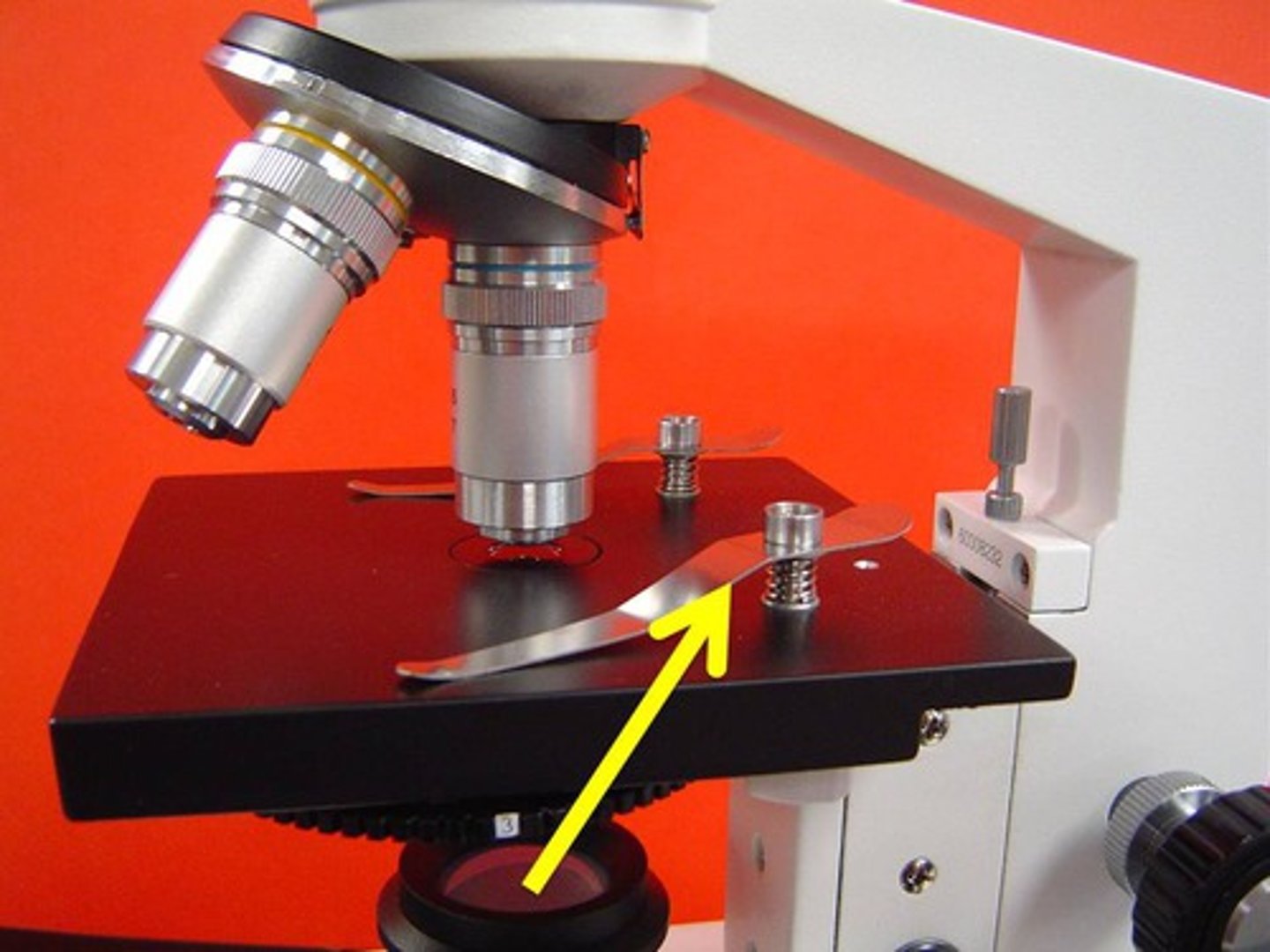

Diaphragm
controls amount of light going through specimen and stage and into the objectives
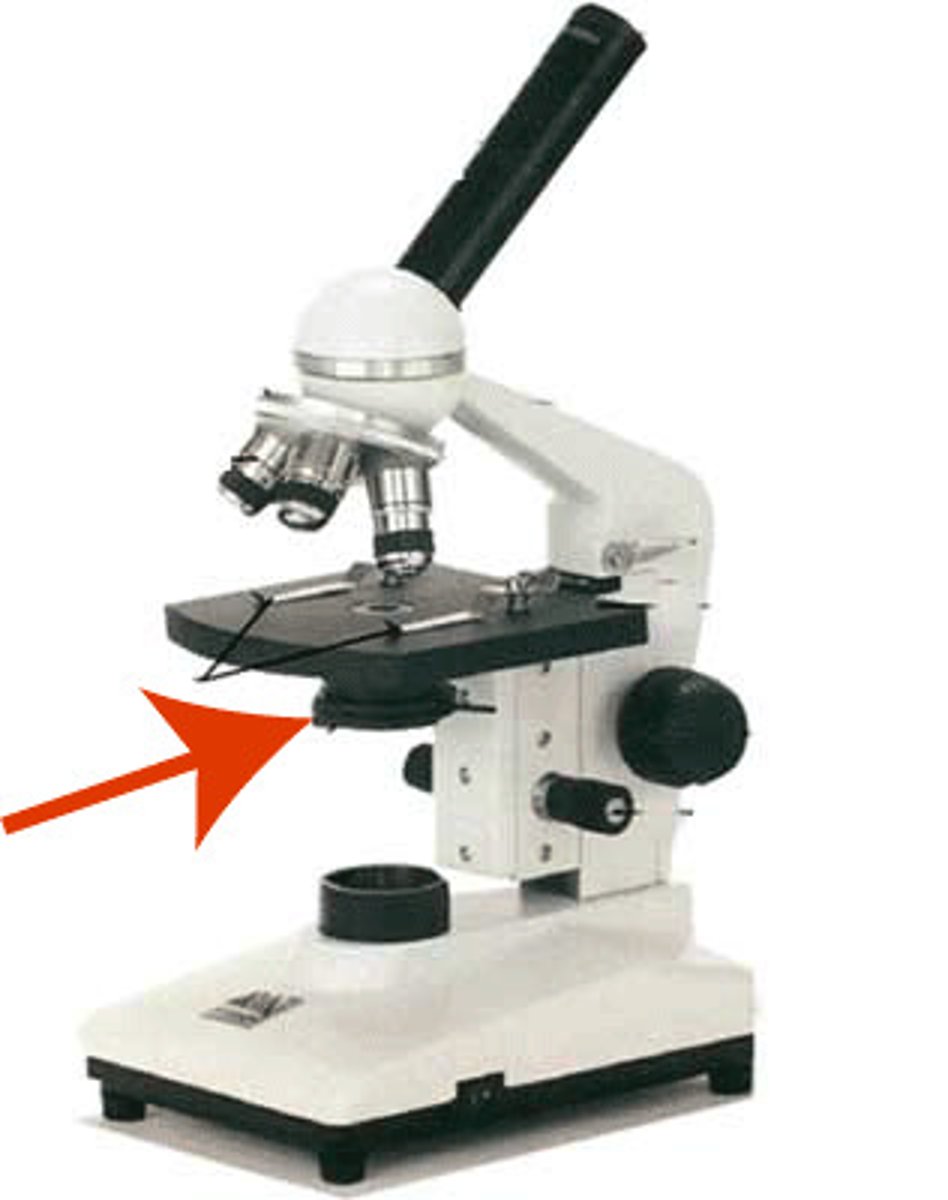
base
the bottom of the microscope that supports everything on top
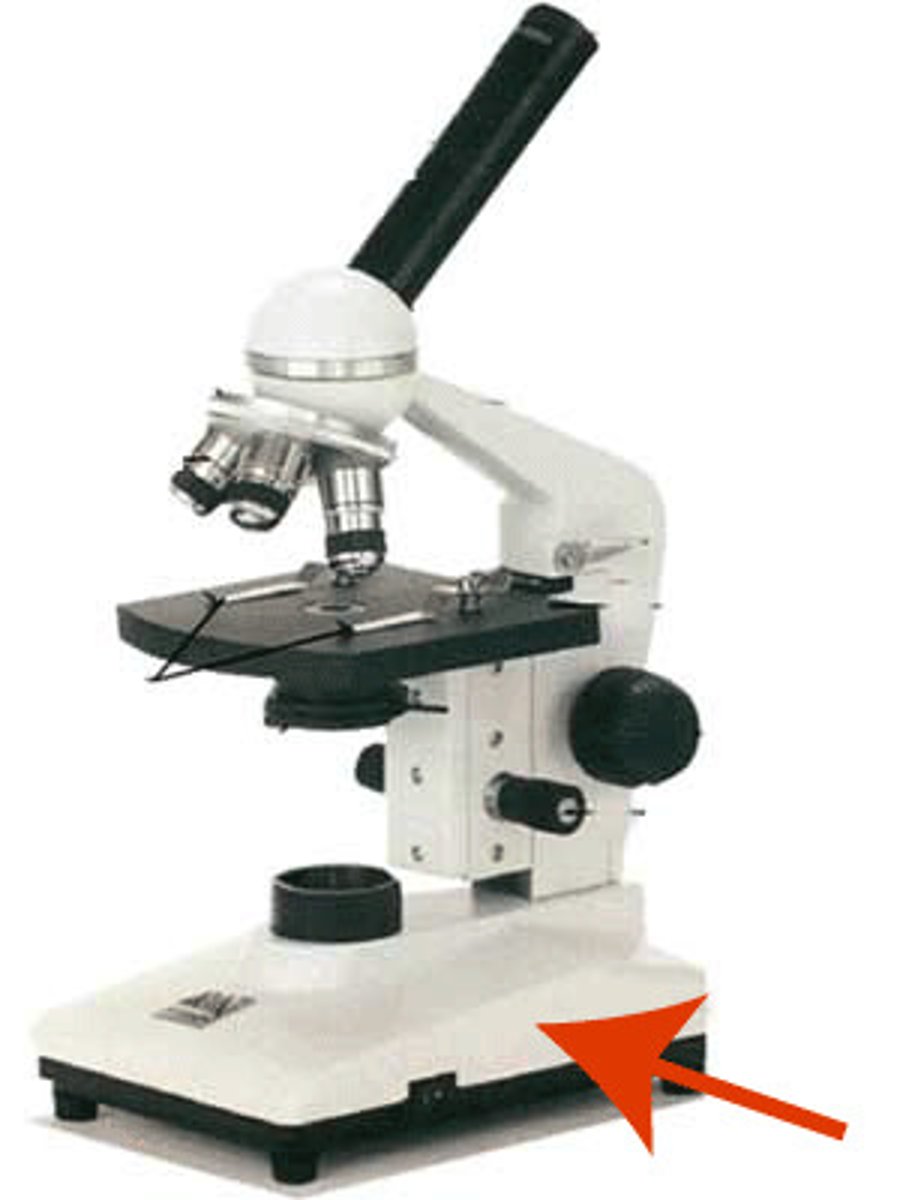

illuminator
makes light from the bottom to observe the specimen

how to calculate magnification
ocular lens magnification power (usually 10x) * objective magnification power (4x, 10x, or 40x depending on the type)
Field of View (FOV)
how much distance you can see in the microscope, usually 4.5 mm when on low power