Biology 172 Exam 2 Pt 1
1/419
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
420 Terms
The characteristics of animals are:
Multicellular eukaryotes, heterotrophs, lack cell walls, body is held together by collagen
The most abundant protein in animals is
Collagen
Collagen has three different structures in animals:
Skin, Ligament, Tendon
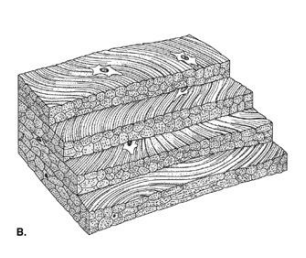
Collagen in skin is shaped…
Irregularly, dense
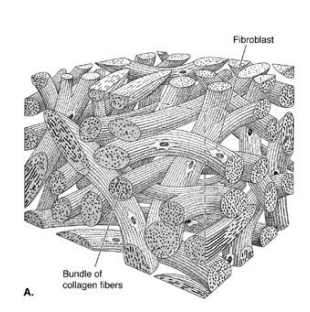
Collagen in your ligaments is shaped as…
Sheets (connects bones)
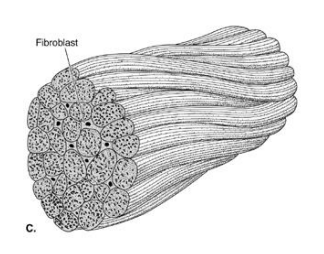
Collagen in your tendon is shaped as…
Cable-like (connects muscle to bone)
Tissues are isolated by…
membraneous layers
Germ layers give rise to…
Tissues & organs
Examples of Diploblastic organisms
Jellyfish, Coral, Combjelly
Examples of Triploblastic organisms
Flatworms, insects, starfish, lobsters
What is the protein in choanoflagellates and animals?
Cadherin
All animals have what protein domain?
CCD
When did the Cambian Explosion occur?
535-525 mya
Protosomes develop which first?
Mouth first, anus later
Deuterosomes develop which first?
Anus first, mouth later
Collagen is _____, has _____, and _____.
Flexible, has high tensile (stretching) strength, and high elastic resilience (returns energy)
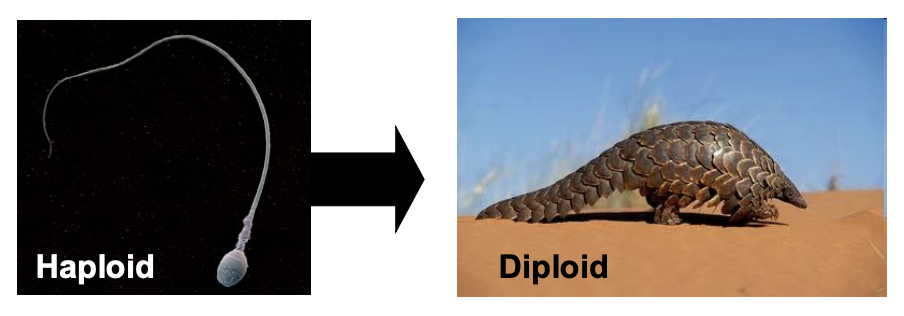
Most animals reproduce ______, with the ____ stage usually dominating the life cycle.
asexually, diploid
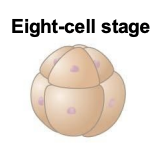
After a sperm fertilizes an egg, the zygote undergoes rapid cell division called…
cleavage
What are tissues?
Collections of specialized cells with a common function, isolated from other tissues by membranous layers
Which types of tissue are unique, in terms of defining characteristics of animals?
Nervous tissue and muscle tissue
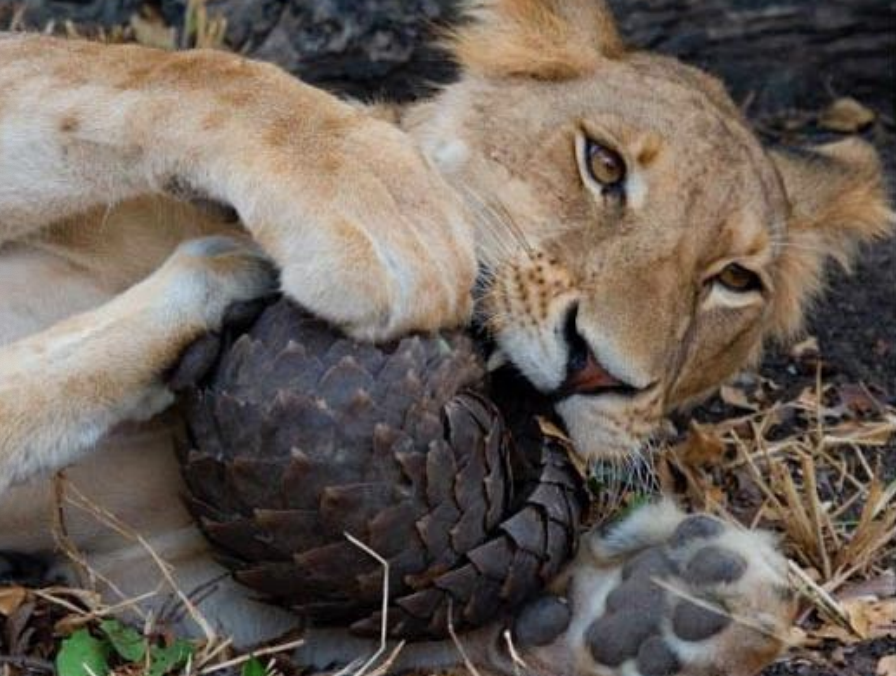
The Manis crassicaudata (Indian Pangolin) is an example of how keratin serves as an…
outer layer protection from predators

During development, ______ give rise to the tissues and organs of the animal embryo.
germ layers
Cell cleavage leads to the creation of a ________.
blastula
The hollow blastula undergoes ______, forming a ____ with layers of embryonic tissues
gastrulation, gastrula
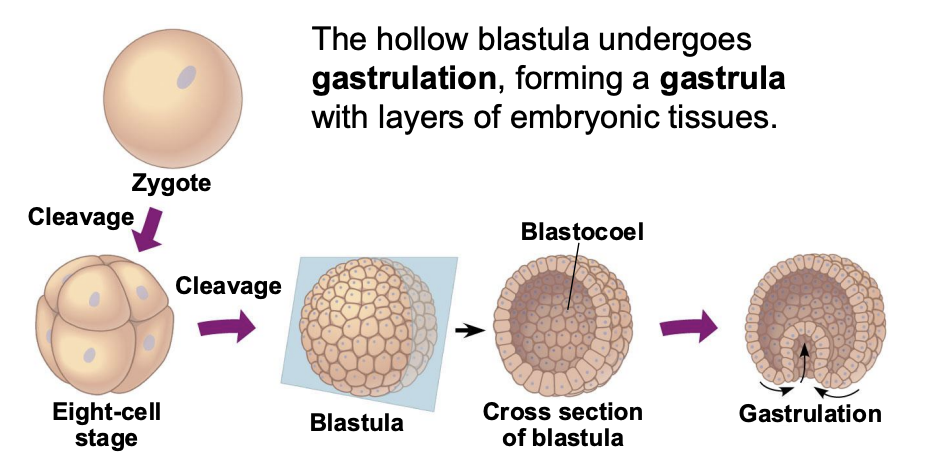
What are the parts of the gastrula?
Ectoderm, Endoderm, Archenteron, Blastopore (archenteron opening)
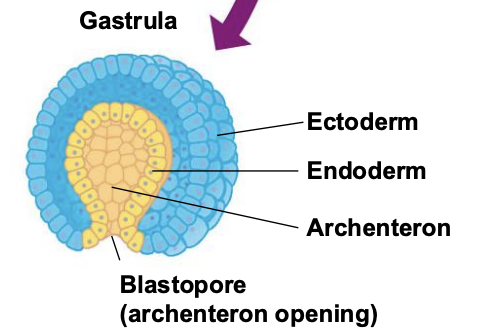
The outermost germ layer covering the embryo’s surface of a Gastrula is called?
Ectoderm
The innermost germ layer that lines the developing digestive tube is called?
archenteron
Diploblastic animals have what type of tissues?
Ectoderm and endoderm tissues
Triploblastic animals have an intervening ________ _____?
mesoderm layer
All bilaterians have a intervening _______ layer
mesoderm
Bilaterians are?
All the multicellular animals other than sponges and cnidarians (jelylfish, sea anemones, corals)
Bilaterians have what type of symmetry?
Bilateral symmetry
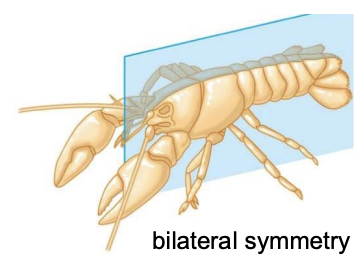
What is cephalization?
Organization of senses and locomotion toward a head region
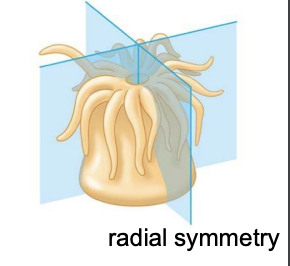
What is radial symmetry?
The body can be split based on a central axis
What is a larva?
Sexually immature and anatomically distinct from the adult. It eventually undergoes metamorphisis
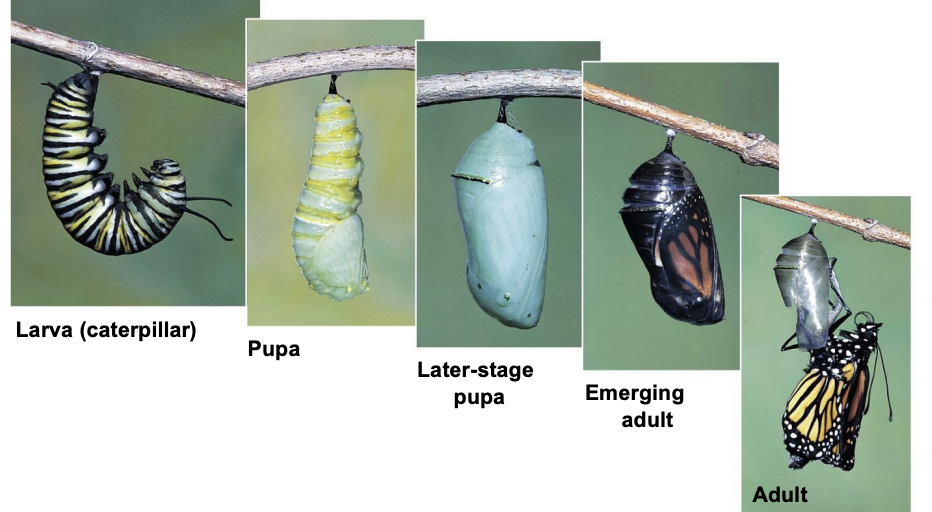
What is a juvenile?
Resembles an adult, but it is not sexually mature
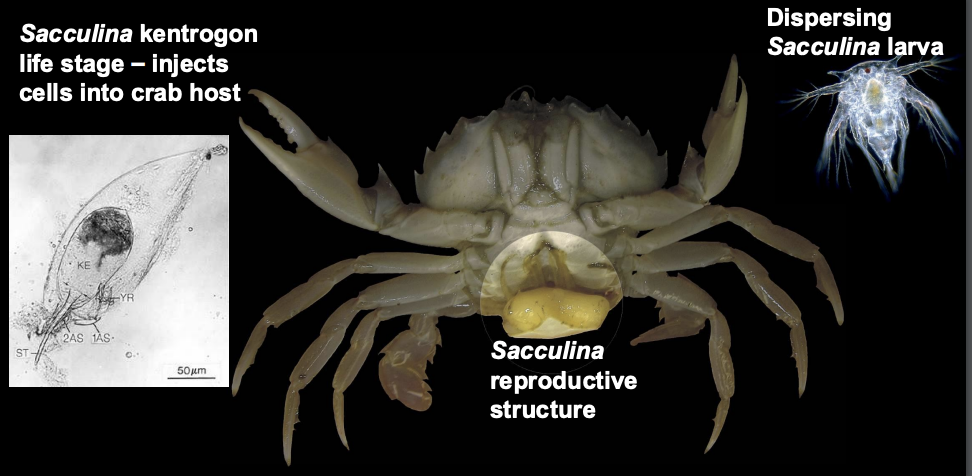
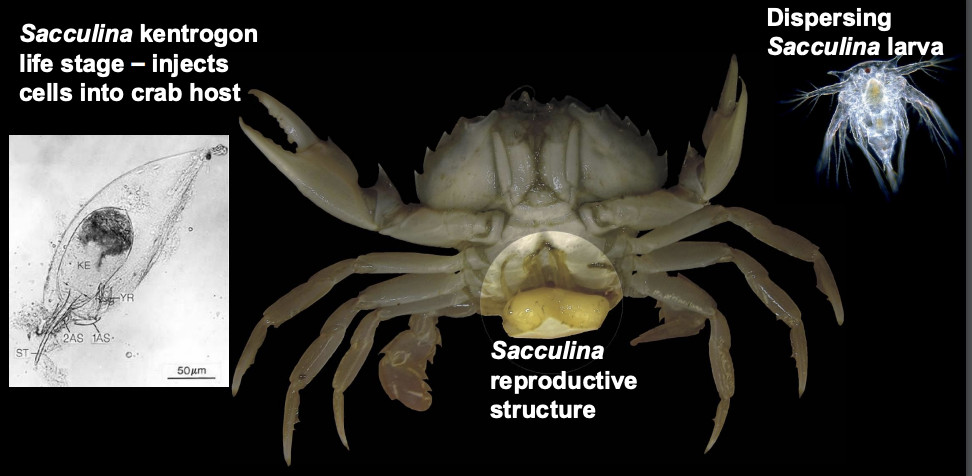
What does the barnacle Sacculina do to crabs?
Parasitic, injects cells into body, has a superficial appearance of a crab egg mass, causing the crab to take care of it.
Animal diversity arose from a hypothesized ancestor living between…
675 and 800 mya
What protists are the closest living relatives of animals?
Choanoflagellates
Cadherin proteins can be found in both
Choanoglagellates and animals
The Cambrian explosion marks what?
The earliest fossil appearance of many major groups (phyla) of living animals.
There are several hypotheses regarding the cause of the Cambrian explosion. What are they?
1) New predator-prey relationships
2) A rise in atmospheric oxygen
3) The evolution of the Hox gene complex
Only animals have what type of genes?
Hox genes, that regulate many other genes and control the development of body form
The Hox family of genes is able to
produce a wide diversity of animal morphologies
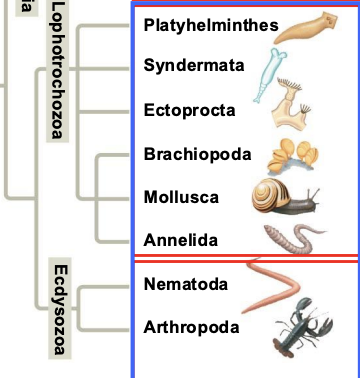
Most species are _____ (animals with joined exoskeletons)
arthropods
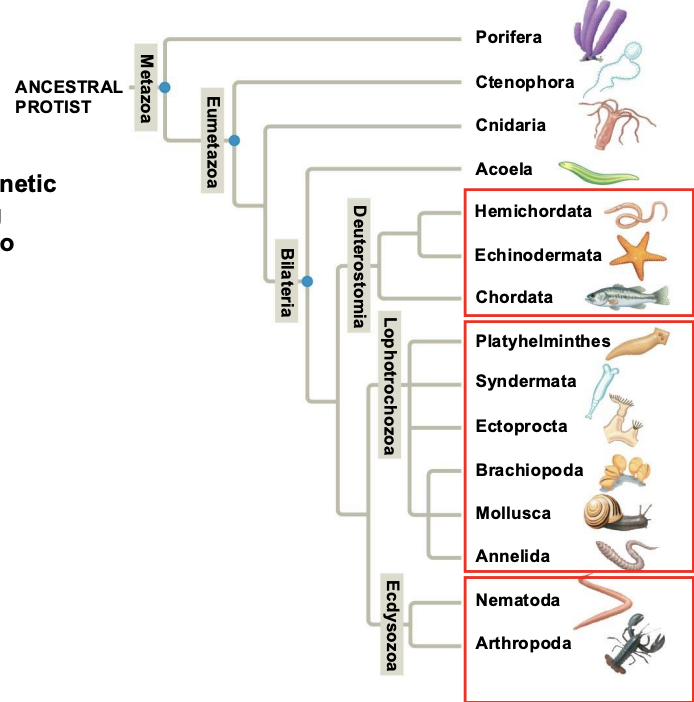
Genetic evidence suggests a phylogenetic hypothesis splitting bilateral animals into three major groups.
1. Deuterostomes
2. Lophotrochozoa
3. Ecdysozoa
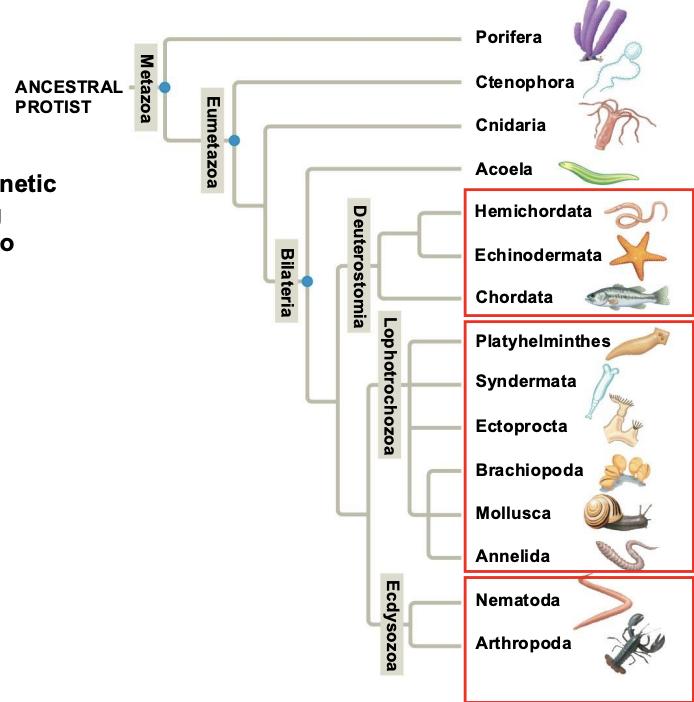
Traditional examination of body form groups the bilateral animals other than deuterostomes as…
Protostomes
In protosomes, cell proliferation following fertilization is by?
spiral cleavage
In deuterostomes, celll proliferation following fertilization is by?
radial cleavage
In protosomes, where does the coelom form?
The coelom (body cavity) forms within the middle tissue germ layer
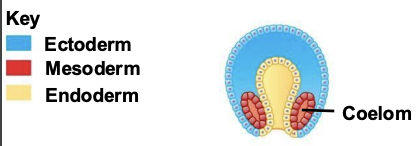
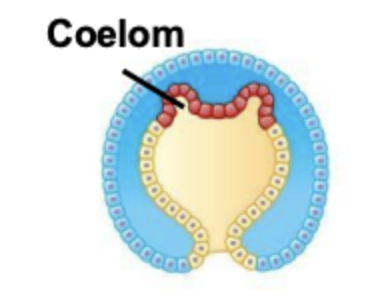
In deuterostomes, where does the coleom form?
The coelom forms from outpocketing of the middle tissue germ layer
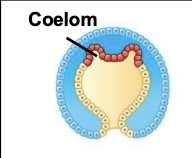
In protosomes, the initial opening into the gut is…
the mouth
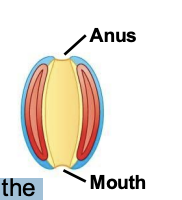
In deuterostomes, what forms first?
Initial opening into the gut becomes the anus

What is the coelom?
The body cavity surrounding the gut
The coelom was previously the basis for?
major classification within the protostomes.
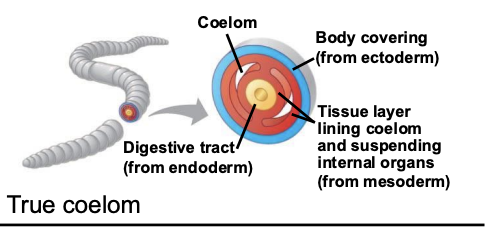
What is a true coelom?
Fluid-filled body cavity COMPLETELY surrounded by mesoderm surrounding the digestive tract.
What is pseudocoelom?
Fluid-filled body cavity PARTIALLY lined by mesoderm surrounding the digestive tract.
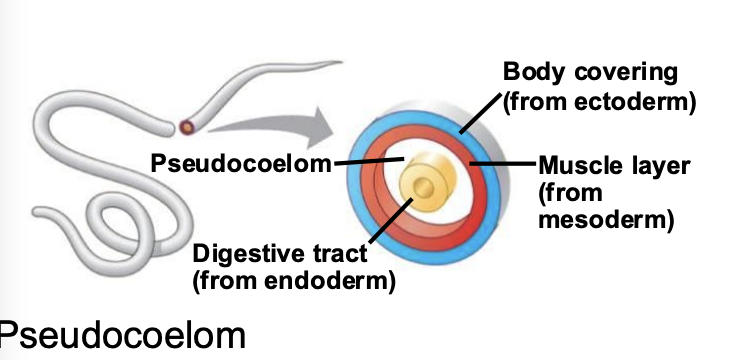
What does it mean to have no coelom?
NO fluid-filled body cavity. Only mesoderm surrounding the digestive tract.
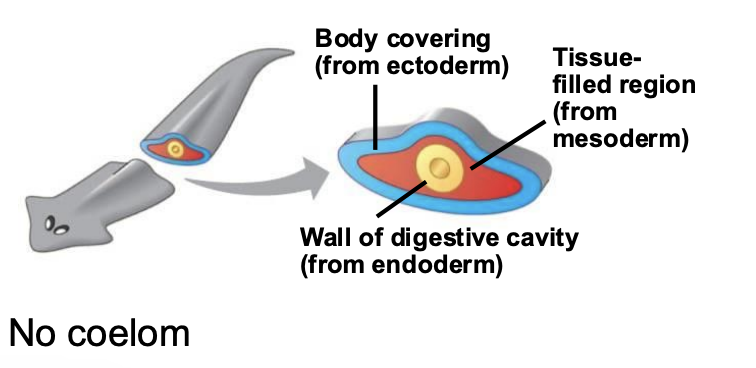
Groups based on coelom form have since been shown to be?
polyphyletic (not directly related to each other).
What is the simplest animal?
Phylum Placozoa —> Trichoplax adherens
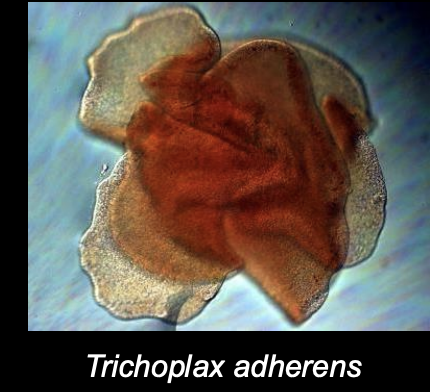
Why is Trichoplax adherens the simplest animal?
Smallest genome (Only 11,500 genes)
Only four cell types
No symmetry
No organs
No muscles
No nervous system
Classifying invertebrate species into groups based on _____ helps us to understand their great diversity.
evolutionary relationships
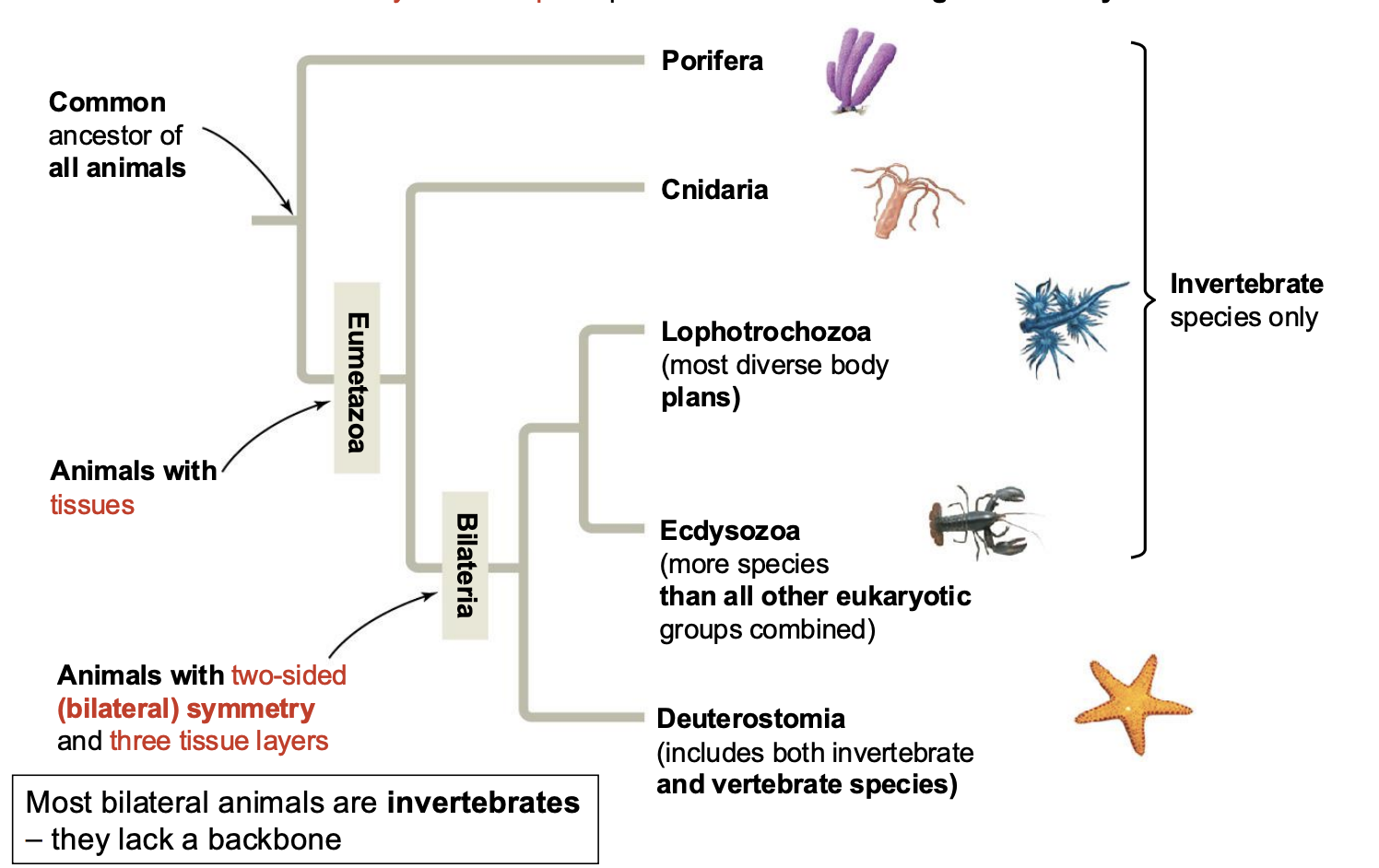
What are invertebrates?
Animals that lack a backbone
What are the Phylums of Invertebrates? (think sponges, jellyfish, molluscs, arthropoda)
Porifera, Cnidari, Lophotrochozoa, Ecdysozoa
What phyla are a part of Eumetazoa (Animals with tissues)?
Cnidaria, Bilateria (Lophotrochozoa, Ecdysozoa, Deuterostomia)
Which Phyla are a part of Bilateria (animals with two-sided bilateral symmetry and three tissue layers)?
Lophotrochozoa, Ecdysozoa, and Deuterostomia
Bilateria consists of animals with what type of symmetry AND how many tissue layers?
Two-sided (bilateral) symmetry and three tissue layers
Eumetazoa consists of animals with _______.
Tissues
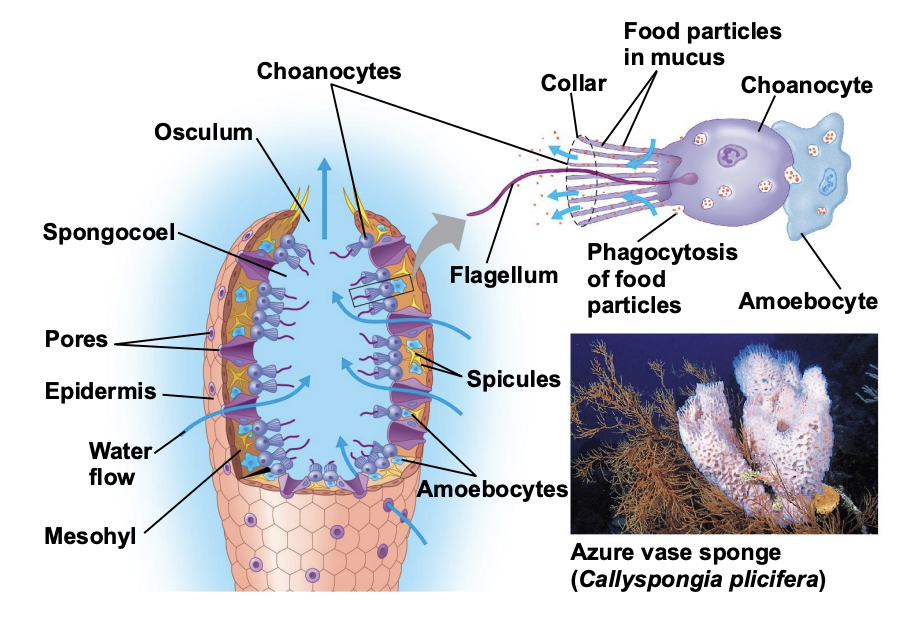
What are the characteristics of Phylum Porifera?
Sponges have specialized cell types but no true tissues.
Sponges are sessile, they do not exhibit locomotion.
Movement occurs in flagella-bearing collar cells (choanocytes), create water currents that move through the body of the sponge.
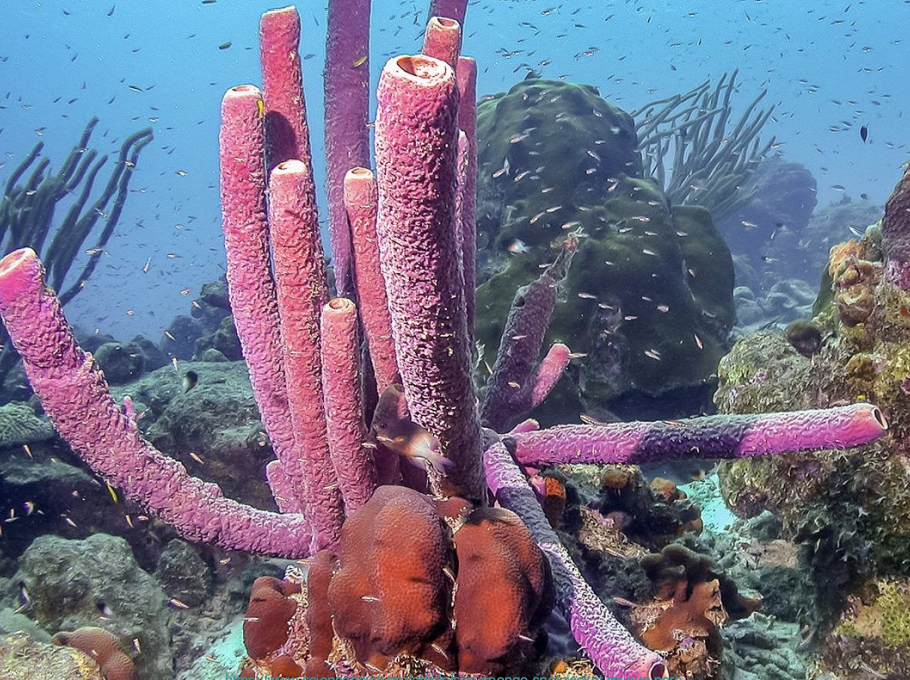

What are spicules?
Tiny calcium/silica structures that provide support for the sponge body.
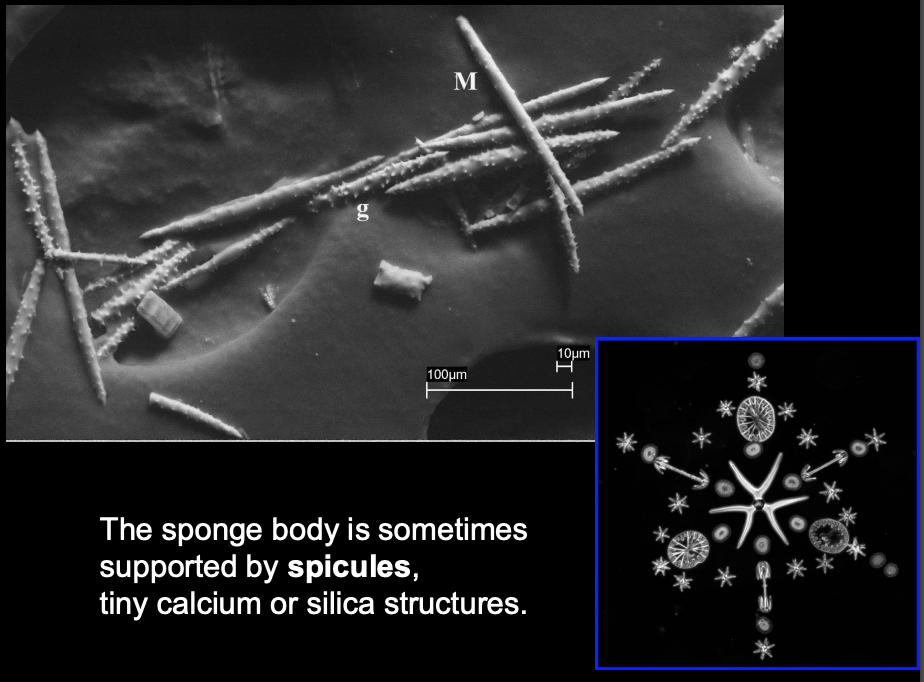
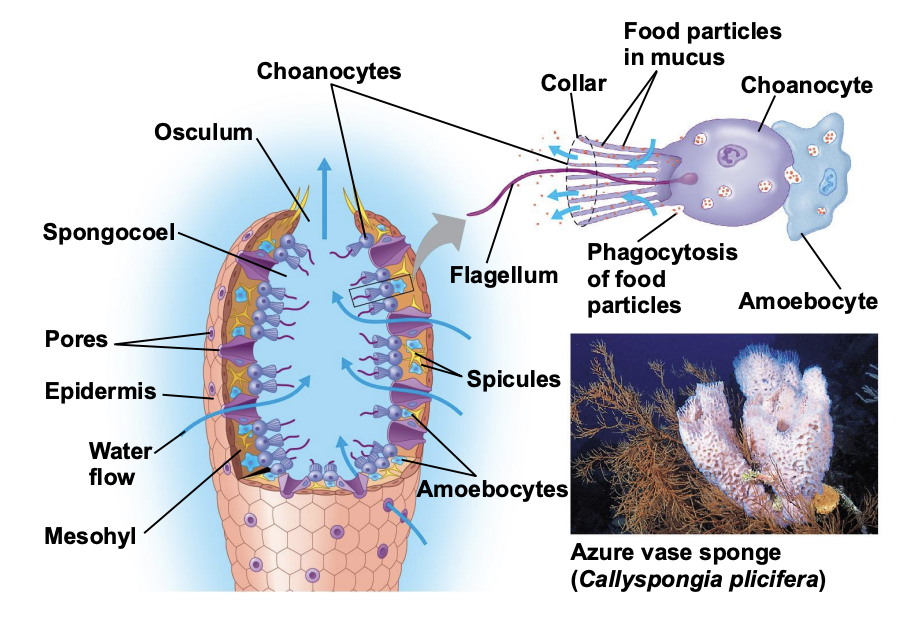
What are amoebocytes?
Amoebocytes function in digestion of food particles pulled from the water current by the collar cells.
Sponges have both male and female reproductive structures, meaning that they are?
hermaphrodites (both female and male reproductive structures)
What is released into the environment by all sponges?
Sperm are released into the environment by all sponges.
What are the characteristics of Phylum Cnidaria?
Cnidarians include jellyfish, anemones, and corals and possess a wide range of body forms having radial symmetry.
Cnidarians have two specialized cell layers (tissues) and nerve cells.

Which phylum of invertebrates has radial symmetry?
Phylum Cnidaria

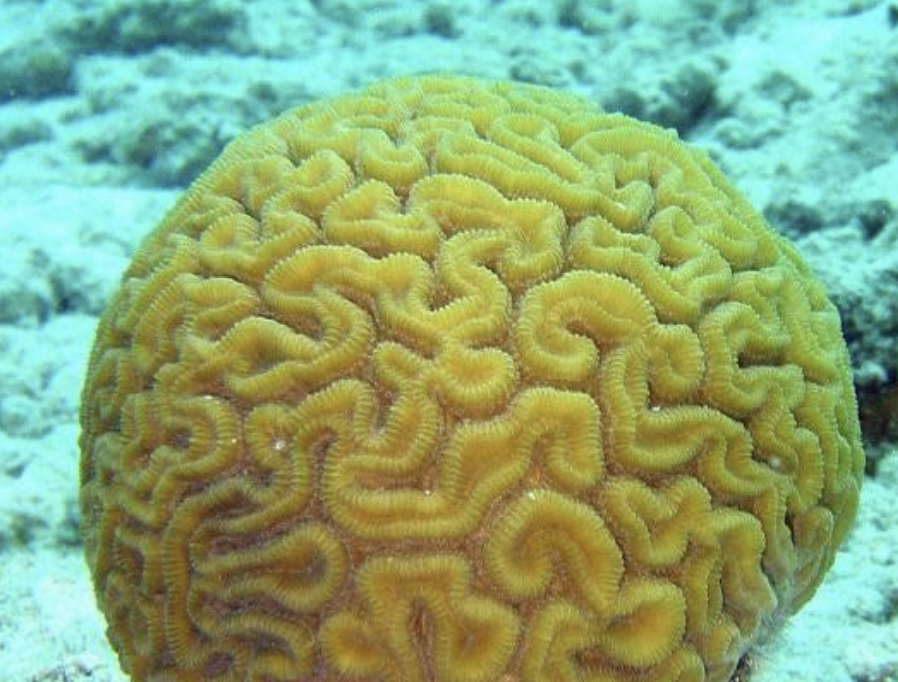
The brain coral is a part of which phylum of invertebrates?
Phylum Cnidaria, which includes corals

What phylum of invertebrates do anemones belong to?
Phylum Cnidaria, which includes anemones
Cnidarians occur in two body forms, what are they?
a sessile polyp and a freeswimming medusa.
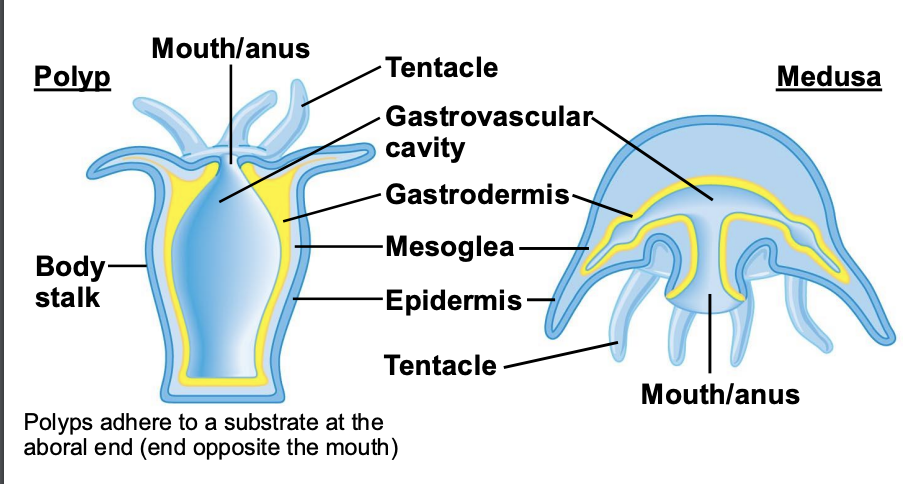
What cavity is the central digestive compartment in Cnidarians?
Gastrovascular cavity
Polyps in Cnidarians adhere to what?
a substrate at the aboral end (end opposite the mouth)
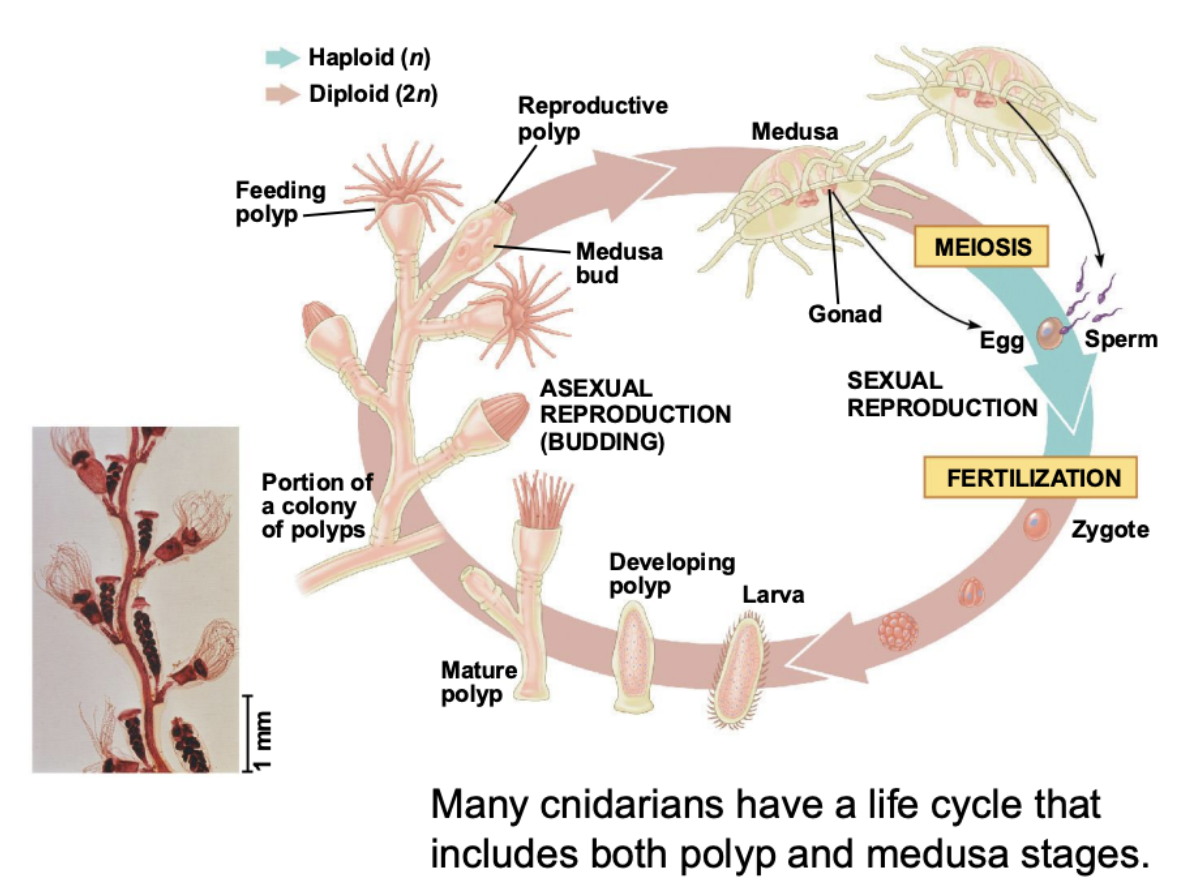
Many Cnidarians have a life cycle that includes both
polyp and medusa stages
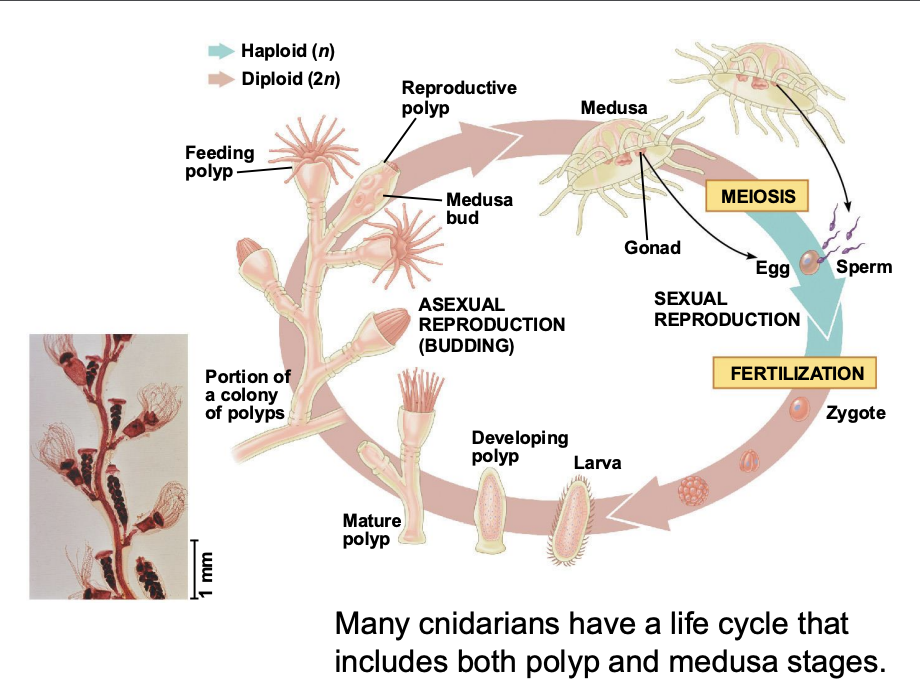
Cnidarians possess sense organs for?
balance and light detection (think jellyfish)
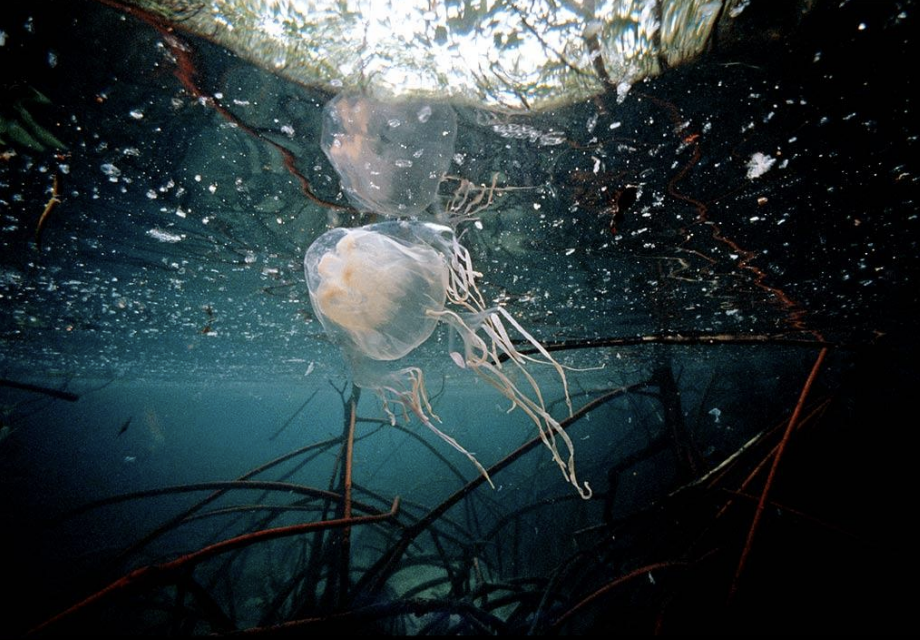

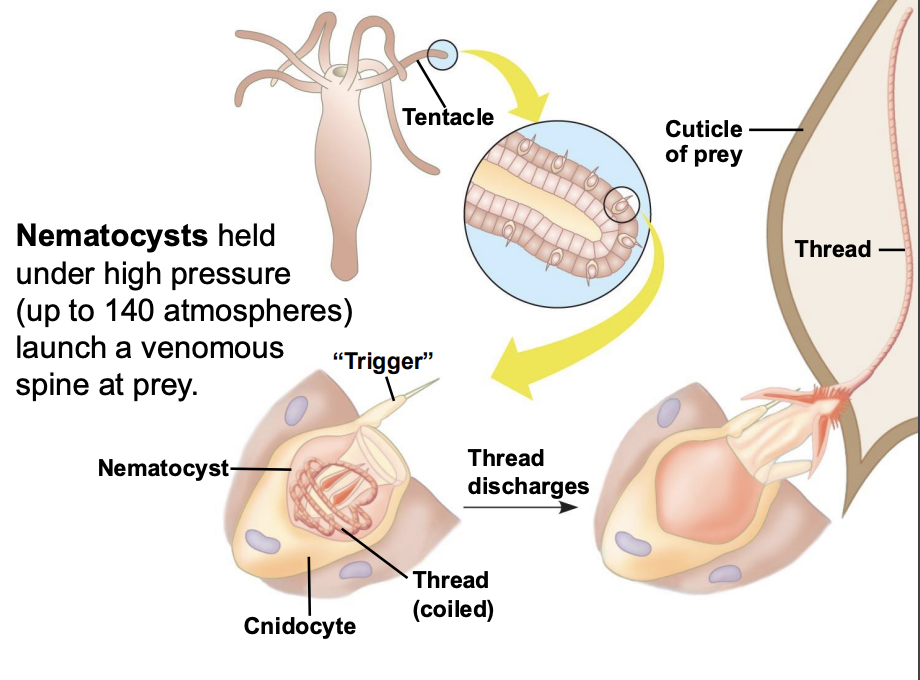
What are nematocysts?
Nematocysts are held under high pressure (up to 140 atmospheres) and launch a venomous spine at prey
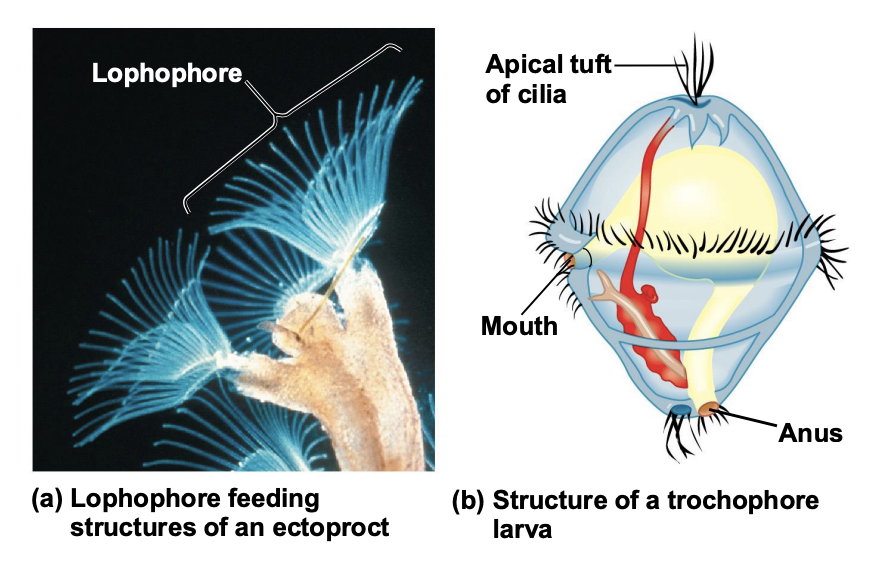
What are the traits of Lophotrochozoa clade?
A horse-shoe shaped feeding structure called a lophophore, or a ciliated larva called a trocophore
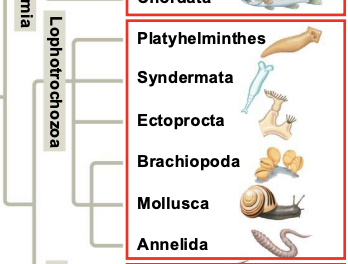
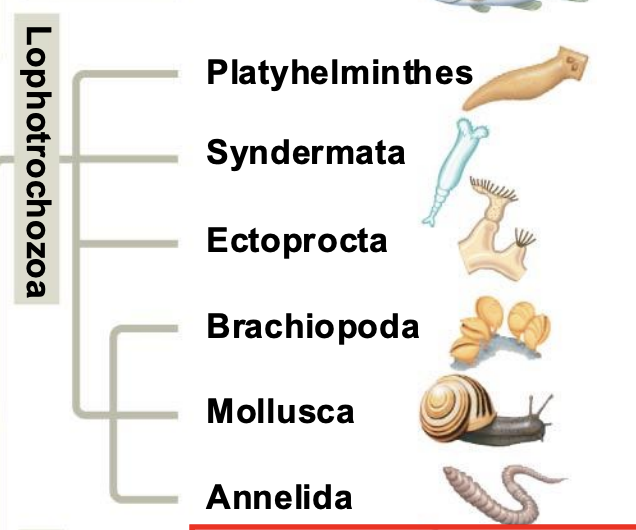
Whare are the 6 Phylum of the Lophotrochozoa clade?
Platyhelminthes, Syndermata, Ectoprocta, Brachiopoda, Mollusca, and Annelida
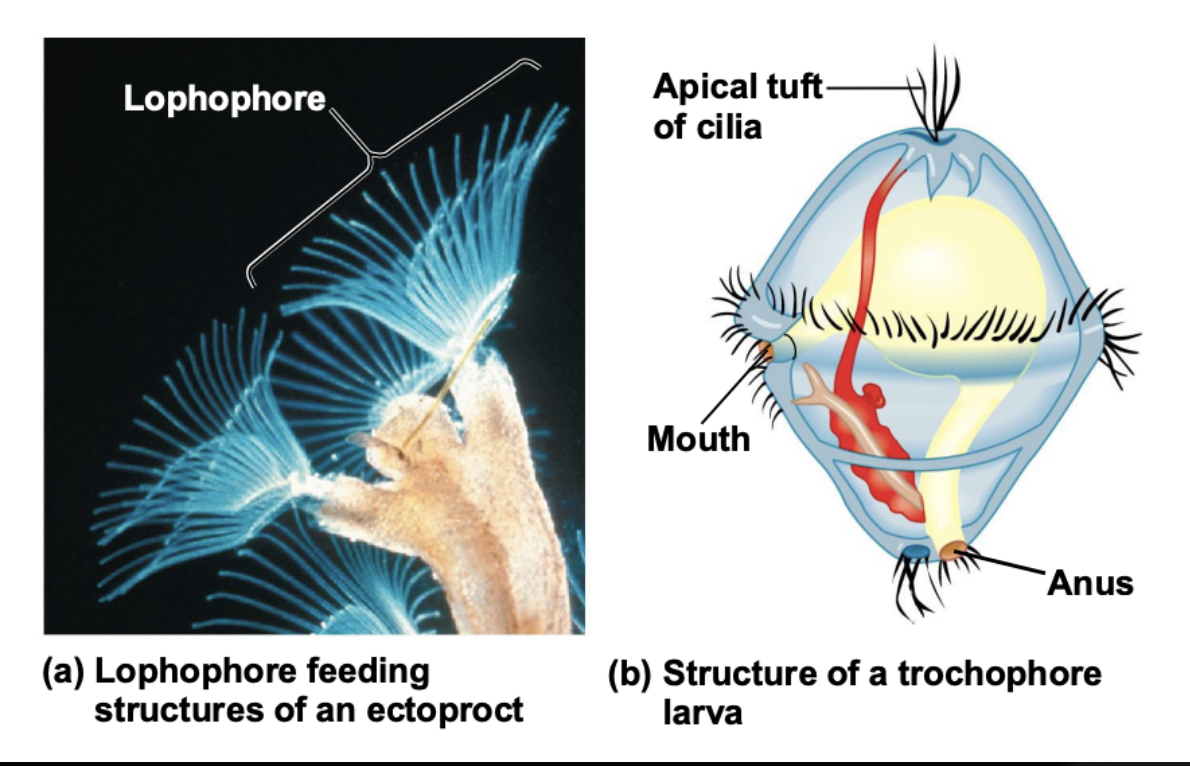
What is a trocophore?
ciliated larva
What are flatworms in Phylum Platyhelminthes?
Flatworms lack circulatory, respiratory, and skeletal systems.
Coelom is absent and gut incomplete.
Size range is from less than one mm to several meters.
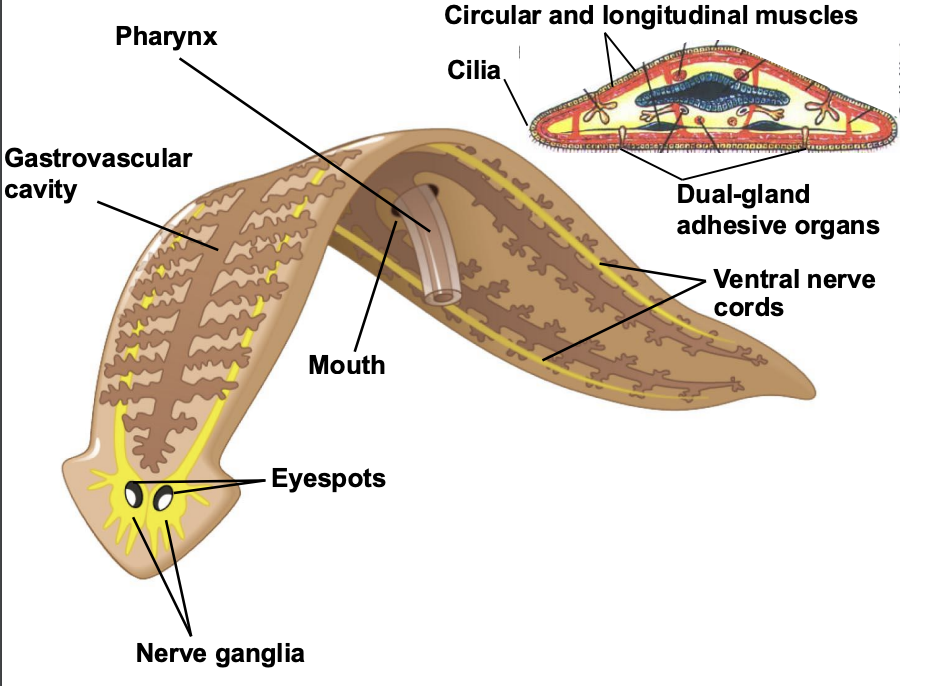
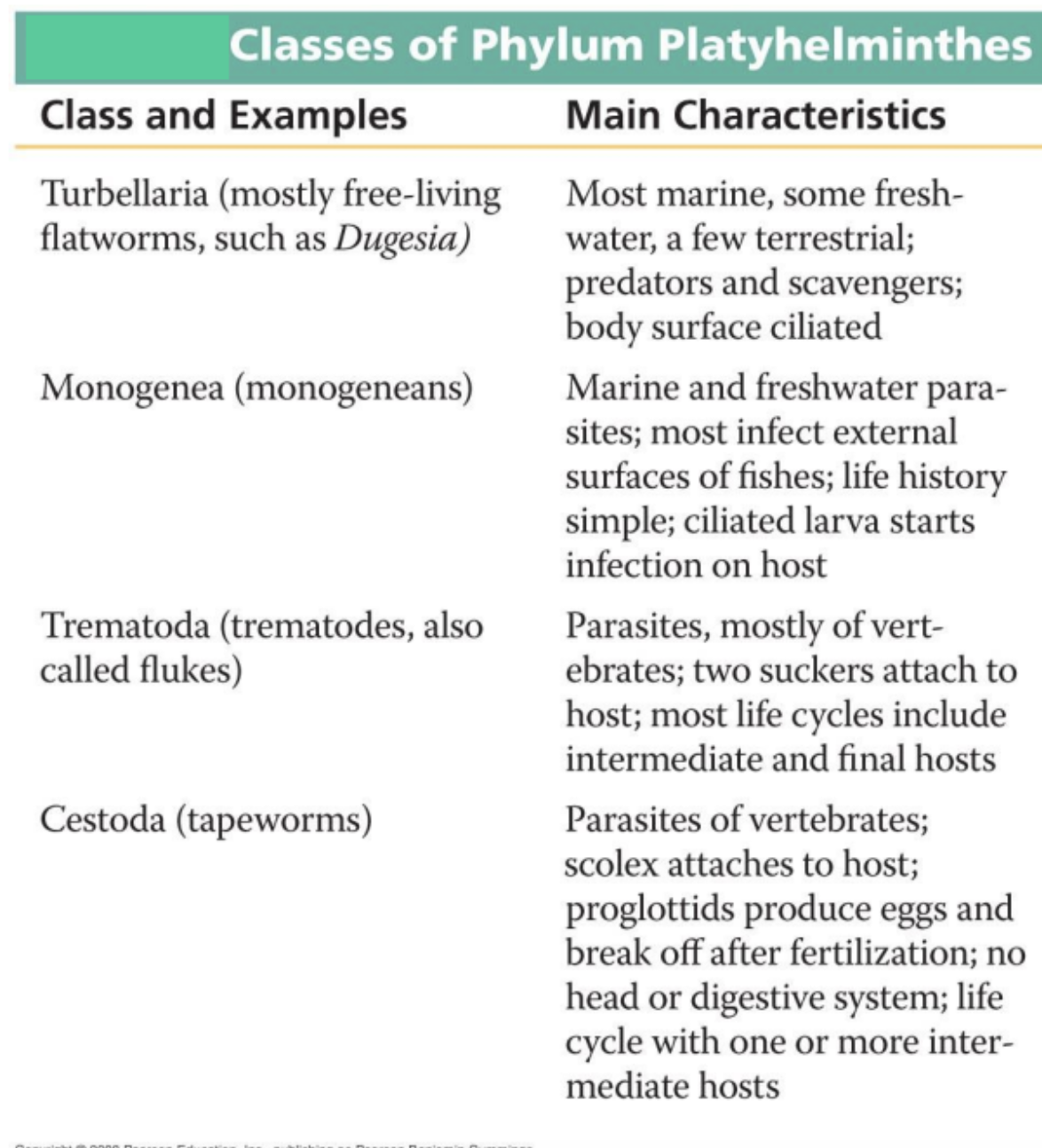
What are the FOUR (4) classes of Phylum Platyhelminthes?
Turbellia (mostly free-living flatworms, such as Dugesia)
Monogenea (monogeneans)
Trematoda (trematodes, also called flukes)
Cestoda (tapeworms)
The hammerhead worm belongs to what phylum and class?
Phylum Platyhelminthes, class Turbellaria

What is an example of a flatworm that belongs to Phylum Platyhelminthes, class Turbellaria
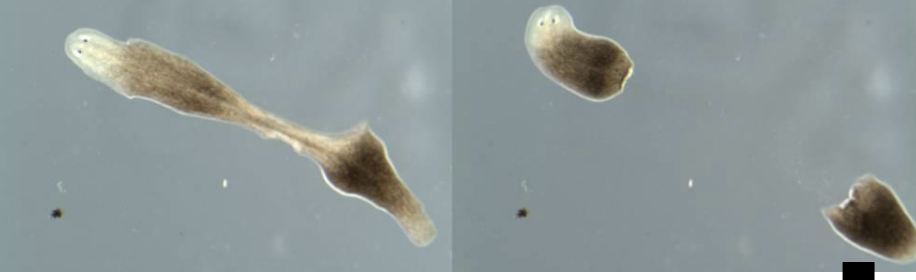
The planarian flatworm
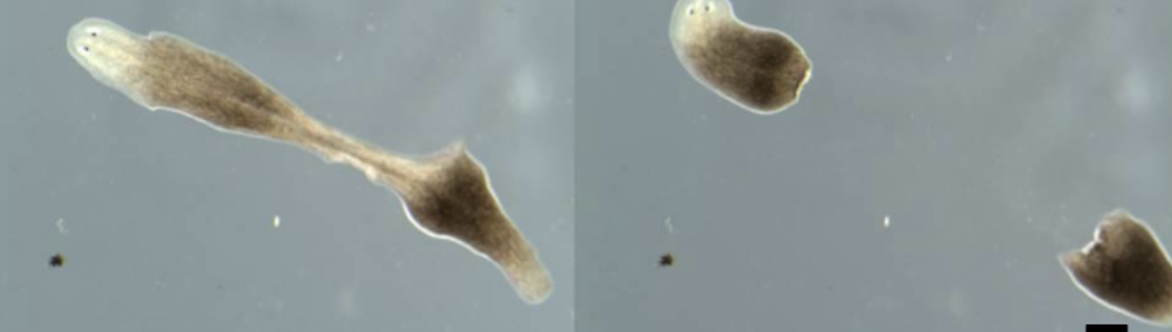
Most flatworms are _____, but asexual reproduction is common in some life cycles
hermaphrodites
What is class Monogenea?
Monogeneans have the unciliated synctial outer layer (cells connected so that cytoplasm is shared) typical of flat worms other than the Turbellaria.
Monogenea are all parasites, mostly on the skin and gills of fish, and have relatively simple life cycles.
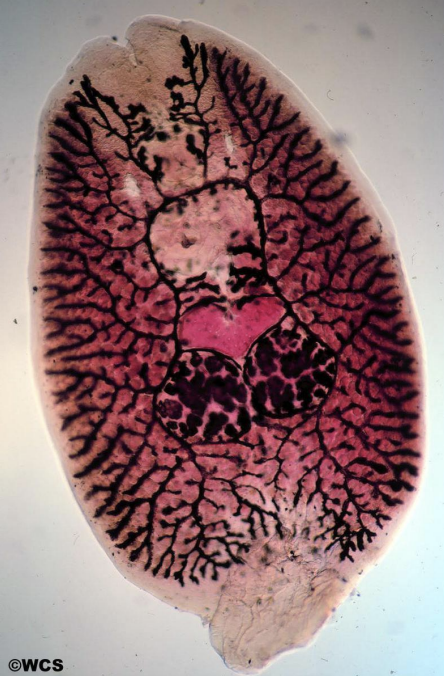
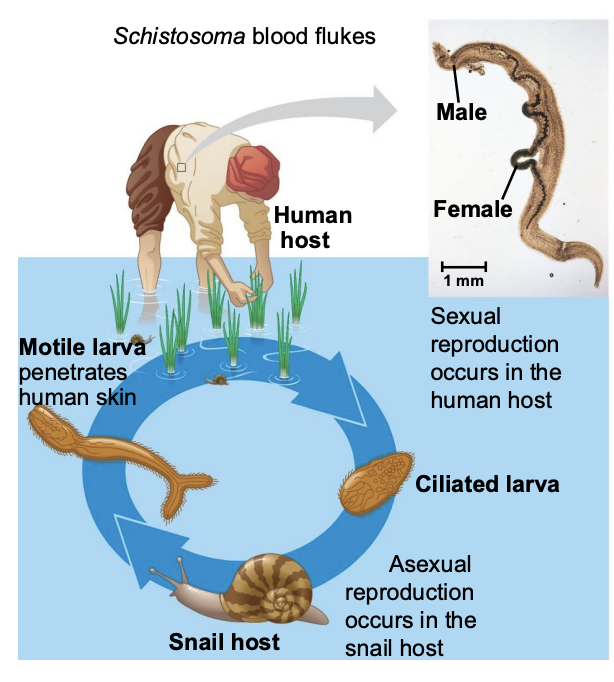
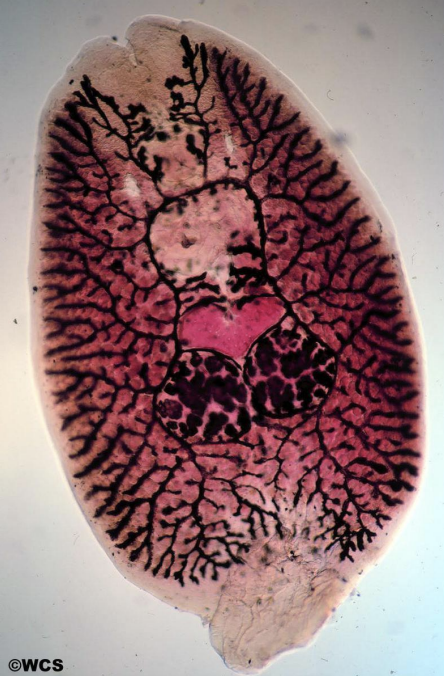
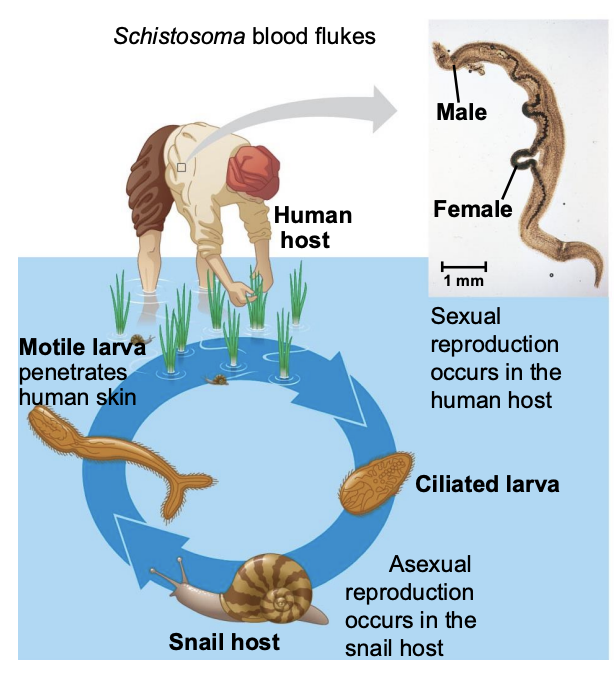
What is class Trematoda (flukes) and what do they do?
Trematodes (flukes) are all parasitic, usually with a mollusc and vertebrate host.
Infection with flukes (schistosomiasis) affects over 200 million people.
Symptoms include pain, anemia, dysentery and liver damage.
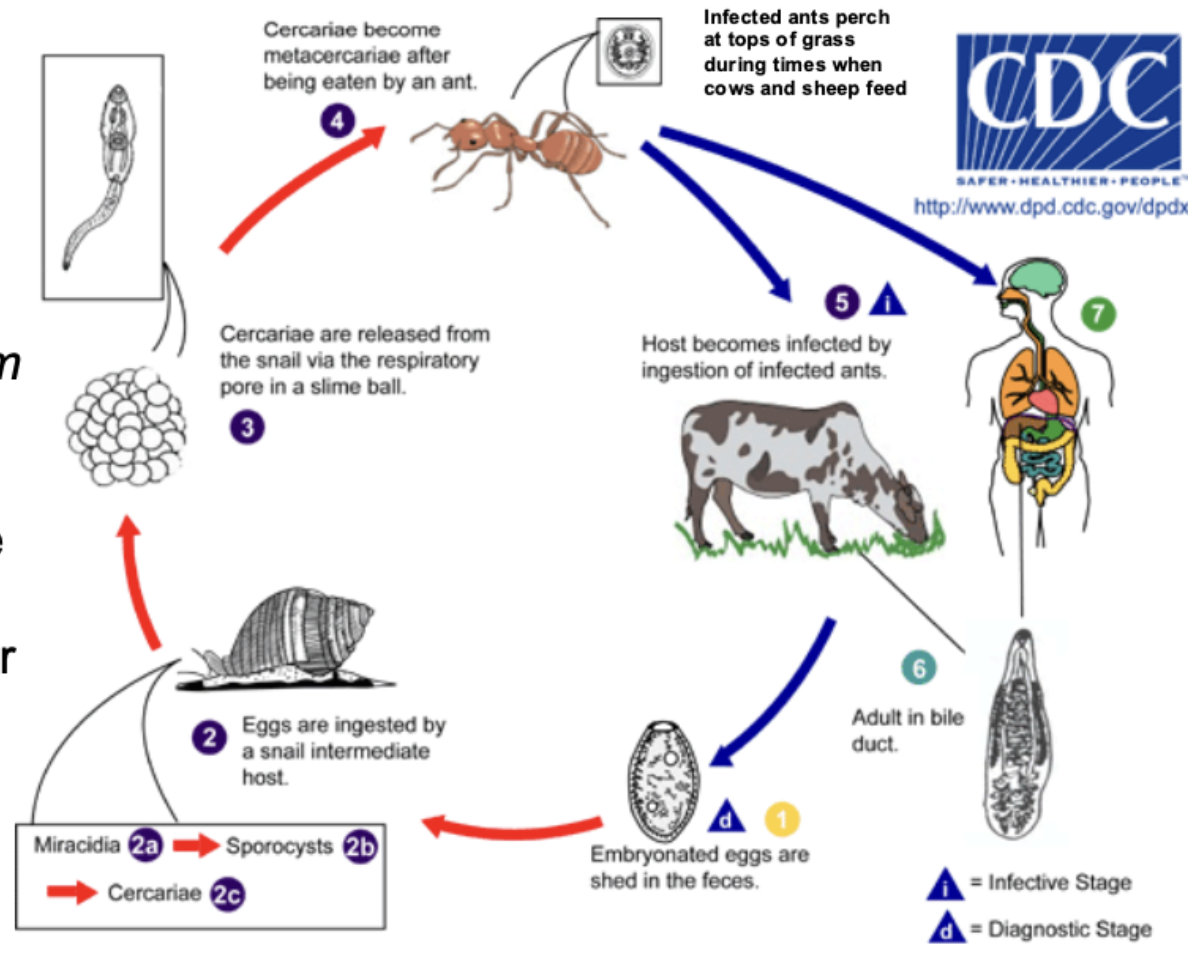
What does the lancet fluke, Dicroelium dendriticum from class Trematoda do?
Alters ant behavior to increase the likelihood of passing their parasite on to the next host.

What are tapeworms?
Tapeworms are all parasites, mostly of the intestine of vertebrates. They lack a head, digestive system and sense organs.
What is a proglottid?
The body of tapeworms. Contains both male and female sex organs.
What is the scolex?
A hooked structure that attaches the tapeworm to the host’s intestine
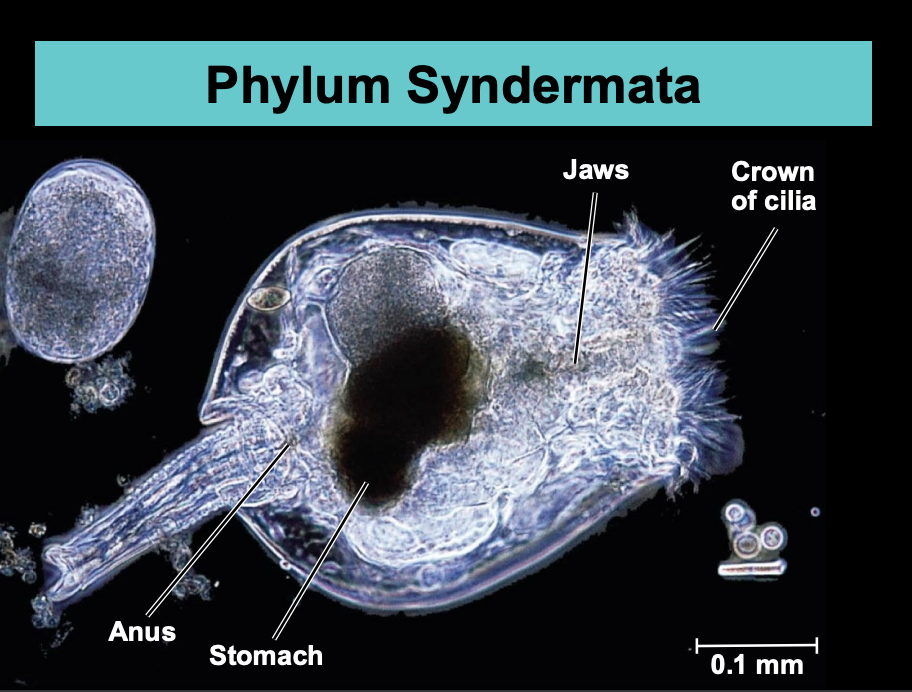
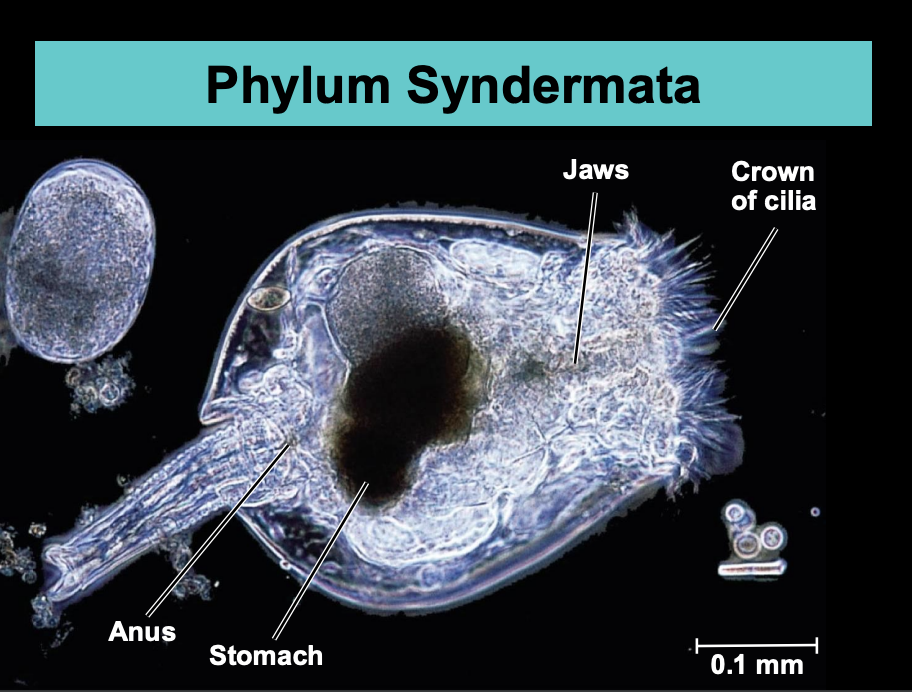
What is Phylum Syndermata?
Syndermata includes rotifers.
Maximum size of rotifers is 3 mm.
Rotifers occupy a wide range of aquatic and marine habitats and some can survive extreme conditions of drying and cold.
Rotifers are predators, parasites and filter feeders (some sessile).
The mouth is equipped with hard, muscular jaws.
Rotifers have separate sexes or are asexual
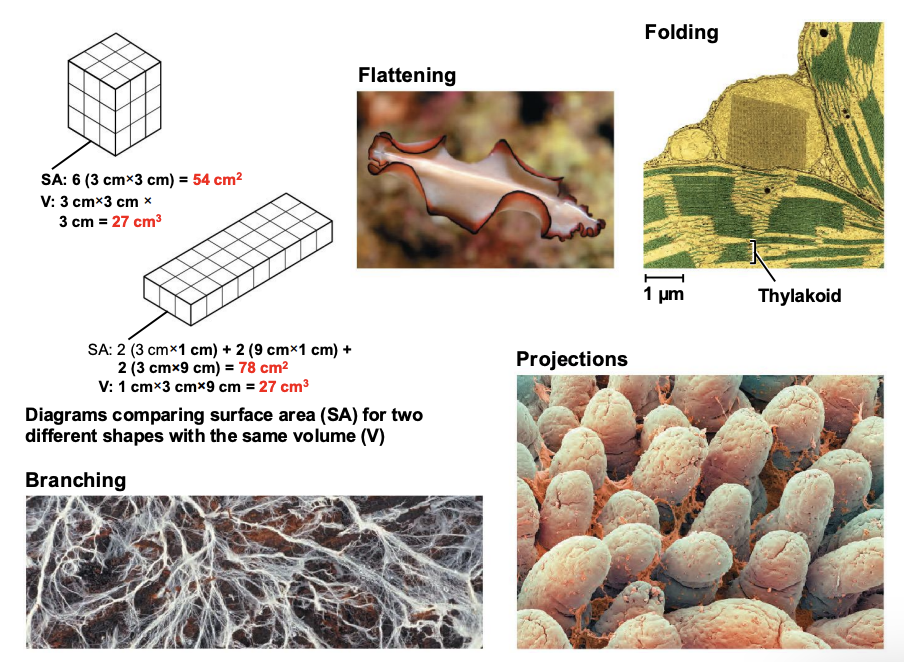
What are some ways that organisms shape themselves based on surface area while keeping the same volume?
Flattening, Folding, Branching, Projections
What is Phylum Mollusca?
Mollusca is one of the largest animal phyla - >90,000 species.
Molluscs occupy a huge range of habitats from polar to tropical regions, but are limited by a need for moisture.
They are important to humans as food, crop pests and intermediate hosts for human parasites.
Size ranges from almost microscopic to almost one ton