GNP IV Final Practice Questions
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
The RN is orienting a new graduate nurse who is preparing to administer a unit of packed red blood cells (PRBCs) to a post-operative patient. Which action by the new graduate nurse requires the RN to immediately intervene?
A. The graduate nurse waits 10 minutes after obtaining the PRBCs before starting transfusion.
B. The graduate nurse starts an IV with a 20-gauge catheter in the patient's left arm.
C. The graduate primes the transfusion tubing with 5% Dextrose in water.
D. The graduate nurse tells the patient that he may have a transfusion reaction
C. The graduate primes the transfusion tubing with 5% Dextrose in water.This is inappropriate because packed red blood cells should only be infused with normal saline to prevent hemolysis.
A patient who uses injectable drugs asks the nurse about preventing HIV. Which response by the nurse is best?
A. "It is important to participate in a needle-exchange program."
B. "Avoid sexual intercourse when using injectable drugs."
C. "You should ask those who share equipment to be tested for HIV."
D. "Cleaning drug injection equipment is recommended after each use."
A. "It is important to participate in a needle-exchange program
to reduce the risk of HIV transmission.
Mr. A. presents to the emergency department complaining of SOB and fever.
ABG results are as follow: pH: 7.32; PCO2: 58; PaO2: 68; HCO3 24; O2 Sat: 93%.
Analysis of these findings leads the nurse to conclude the patient is experiencing:
A. Metabolic acidosis
B. Respiratory acidosis
C. Respiratory alkalosis
D. Metabolic acidosis
Mr. A. is experiencing respiratory acidosis due to elevated PCO2 levels and low pH, indicating an accumulation of carbon dioxide in the blood.
The nurse is triaging patients in the ED. Which patient can wait to be seen by the ED staff?
A. 57-year-old patient complaining of chest pain and diaphoresis
B. 34-year-old patient with a possible right tibia fracture
C. 78-year-old patient with a headache and a purple spotted rash
D. 24-year-old patient found unresponsive with a syringe in his arm
B. 34-year-old patient with a possible right tibia fracture is likely stable and can wait for treatment compared to the other patients with more urgent conditions.
An unconscious patient with a severe head injury has coarse breath sounds, a temperature of 102.2F, HR 70 bpm, BP 130/60, ICP 36. Which of the following actions should the nurse perform first?
A. Administer IV Mannitol
B. Suction the patient
C. Encourage the visitors to leave the room
D. Administer rectal acetaminophen
The nurse should perform the action that addresses the patient's immediate airway management and potential airway obstruction. Therefore, the first action is to suction the patient.
The nurse is discussing funeral arrangements with a family of a deceased patient whose organs and tissues are being donated. Which information should the nurse discuss with the family?
A. It is advised to dress the deceased in a long sleeve garment
B. There is no need to change plans for an open casket viewing.
C. Funeral services will be delayed pending harvesting the organs and tissues.
D. A private viewing is recommended.
When taking care of a patient with a chest tube for a pneumothorax, the nurse would assess for an air leak in which chamber?
A. Collection chamber
B. Suction chamber
C. Water seal chamber
D. Air chamber
C. Water seal chamber
The nurse suspects the possible onset of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) in a patient who develops:
A. Dyspnea, restlessness, and refractory hypoxemia
B. Tachypnea and hypertension with elevated PaO2
C. Diffuse crackles on chest auscultation
D. Cough with blood tinged sputum and respiratory acidosis
a. dyspnea, restlessness, refractory hypoxemia
When caring for a patient with cardiogenic shock, what would most concern the nurse?
A. Weak peripheral pulses
B. Auscultation of S3 heart sounds
C. Cold, clammy skin
D. Restlessness and agitationwould most concern the nurse?
A. Weak peripheral pulses
B. Auscultation of S3 heart sounds
C. Cold, clammy skin
D. Restlessness and agitation
D. Restlessness and agitation
After the nurse has finished teaching a patient about the use of sublingual nitroglycerin, which patient statement indicates that the teaching has been effective?
A. "I can expect some nausea as a side effect of nitroglycerin."
B. "I should only take the nitroglycerin if I start to have shortness of breathe."
C. "I will call an ambulance if I still have chest pain after taking three (3) nitroglycerin 5 minutes apart."
D. "Nitroglycerin helps prevent a clot from forming and blocking blood flow to my heart."
C. "I will call an ambulance if I still have chest pain after taking three (3) nitroglycerin 5 minutes apart." This indicates understanding of the critical response to chest pain.
What population is most at risk for contracting HIV?
A. IV drug users
B. Black men who have sex with men
C. Hispanic women
D. White men who have sex with men
B. black men who have sex with men
The nurse is caring for a patient receiving mechanical ventilation. During the assessment, the high-pressure alarm rings. The nurse should:
A. Check for cuff pressure leaks
B. Suction the airway
C. Provide oral care
D. Adjust the pressure alarm
B. suction the airway
The incidence of ischemic stroke in patients with TIAs and other risk factors is reduced with the administration of which medication?
A. Warfarin
B. Aspirin
C. Nitroglycerin
D. Metoprolol
B. aspirin
What are the clinical manifestations of DKA?
1. Thirst
2. Ketonuria
3. Dehydration
4. Metabolic acidosis
5 Kussmaul respirations
6. Sweet, fruity breath odor
7. Respiratory acidosis
A. 1, 2, 3, 4
B. 1, 5, 6, 7
C. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6
D. 1, 2, 4, 5, 6
C. 1,2,3,4,5,6
The nurse obtains a rhythm strip on a patient who has had a myocardial infarction and makes the following analysis: no visible P waves, P-R interval not measurable, ventricular rate 162, R-R interval regular, and QRS complex wide and distorted, QRS duration 0.18 second. The nurse interprets the patient's cardiac rhythm as
A. Atrial flutter
B. Sinus tachycardia
C. Ventricular fibrillation
D. Ventricular tachycardia
D. Ventricular tachycardia
Following a T2 spinal cord injury, the patient develops paralytic ileus. While this condition is present, what should the nurse anticipate that the patient will need?
A. IV fluids
B. Tube feedings
C. Endotracheal Suctioning
D. Nasogastric suctioning
A. IV fluids
When titrating nitroglycerin IV for a patient with a myocardial infarction (MI), which action will the nurse take to evaluate the effectiveness of the medication?
A. Monitor heart rate
B. Ask about chest pain
C. Check blood pressure
D. Observe for dysrhythmias
B. ask about chest pain
A nurse is caring for a patient with third degree full thickness burns. While assessing the area, the nurse would anticipate which of the following in the traumatized area?
A. Absence of pain, loss of hair, and thrombosed blood vessels
B. Pain, hair growth, and blister formation
C. Paresthesias, pallor and capillary refill to be normal
D. Loss of bone and muscle, charred appearance, and pain
a. absence of pain, loss of hair, and thrombosed blood vessels
A patient arrives in the ED unconscious with a suspected head and neck injury. Before x-rays are obtained, the best way to stabilize the head and neck while performing CPR is:
A. Head tilt chin lift
B. Modified jaw thrust
C. Hyperextension of the neck for placement of the ETT
D. No special precautions are needed in the above instance
B. Modified jaw thrust
The patient's 6 a.m. blood glucose was 352 mg/dL. The sliding scale for subcutaneous coverage is as follows:
Blood sugar <60 hypoglycemic protocol
Blood sugar 80-200 regular insulin 0 units
Blood sugar 201-250 regular insulin 2 units
Blood sugar 251-300 regular insulin 4 units
Blood sugar 301-350 regular insulin 6 units
Blood sugar 351-400 regular insulin 8 units
Blood sugar > 400 notify health care provider
How much insulin should the patient receive for coverage at 6 a.m.?
A. 2 units
B. 4 units
C. 6 units
D. 8 units
D. 8 units
The CDC guidelines recommend human immunodeficiency virus screening for:
1. Individuals who describes risky behaviors (unprotected sex and drug use)
2. Only those that ask for the test
3. Everyone should have a HIV test
4. Minorities starting at age 16
5. Only those involved in rape cases
A. 2, 5
B. 1, 4, 5
C. 2, 4
D. 1, 3
After receiving 2 liters of NSS, the CVP for a patient who has septic shock is 10 mm Hg. The BP remains 82/40. The nurse anticipates an order for:
A. Nitroglycerin
B. Norepinephrine
C. Nicardipine
D. Sodium nitroprusside
The nurse is caring for a ventilator dependent patient with non-survivable neurological illness or injury. To increase the number of transplantable organs, the nurse should do all of the following except:
A. Maintain the patient's hemodynamic status by following the "Rule of 100's"
B. Mention organ donation to family prior to declaration of brain death
C. Provide families with information and updates regarding their loved one's condition
D. Optimize end-organ function
B. mention organ donation
A nurse is palpating around a chest tube site and feels slight crackling around the site. This condition would be known as: A. Tactile fremitus B. Stridor C. Subcutaneous emphysema D. Elastic turgor
c. subcutaneous emphysema
The finding of normal breath sounds on the right side of the chest and absent breath sounds on the left side of the chest in a newly intubated patient is probably caused by a
A. Right pneumothorax
B. Left pneumothorax
C. Gastric intubation
D. Right mainstem bronchus intubation
D. right mainstem bronchus intubation
A patient's pulse oximeter alarm goes off. The monitor reads 82%. What is the first action the nurse should perform?
A. Prepare to intubate
B. Assess the patient's condition
C. Turn off the alarm and reapply the sensor
D. Increase O2 level to 4L/ NC
B. Assess the patient's condition
A patient who is recovering from an acute myocardial infarction (AMI) asks the nurse about when sexual intercourse can be resumed. Which response by the nurse is best?
A. "Most patients are able to enjoy intercourse without any complications."
B. "Sexual activity uses about as much energy as climbing two flights of stairs."
C. "The doctor will provide sexual guidelines when your heart is strong enough."
D. "Holding and cuddling are good ways to maintain intimacy after a heart attack."
B
Tina Jones, a type II diabetic, comes to the ED with a fever and complaints of a painful foot and open toe wound. Family states she has not been herself lately and slightly confused. VS: HR: 122, BP 80/60, RR 28. The nurse suspects:
A. Tina has dementia
B. Tina is in early stages of septic shock
C. The family is over reacting
D. Tina is in the hypovolemic shock
B. septic shock
A patient with suspected meningitis is scheduled for a lumbar puncture. Before the procedure, the nurse will plan to
A. Enforce NPO status for 4 hours.
B. Transfer the patient to radiology.
C. Administer a sedative medication.
D. Help the patient to a lateral position.
D. lateral position
The patient's wife asks how her husband could have developed DKA, since they have been so careful to manage his diabetes properly these past 10 years. Which of the following statements could the nurse provide to this question?
A. "Your husband must have been cheating on his diet or skipping insulin doses"
B. "In times of stress, the body produces more cortisol than normal, and blood sugar increases."
C. "Diabetes ketoacidosis is the result of a genetic abnormality affecting every other generation."
D. "Your husband recently started a daily exercise routine without consulting his primary care provider."
B. "In times of stress, the body produces more cortisol than normal, and blood sugar increases."
An unrestrained driver is admitted following a MVA with a diagnosis of severe pulmonary contusion. The patient's respiratory rate is 23. ABGs on room air are: pH 7:46, paCO2 30, PaO2 65, HCO3 24. Which of the following interventions is the most appropriate for this patient?
A. Administer an analgesic
B. Auscultate lung sounds, prepare to insert a chest tube
C. Prepare for immediate intubation, and mechanical ventilation
D. Prepare for immediate thoracentesis and administer oxygen
c. prepare for immediate intubation and mechnical ventilation
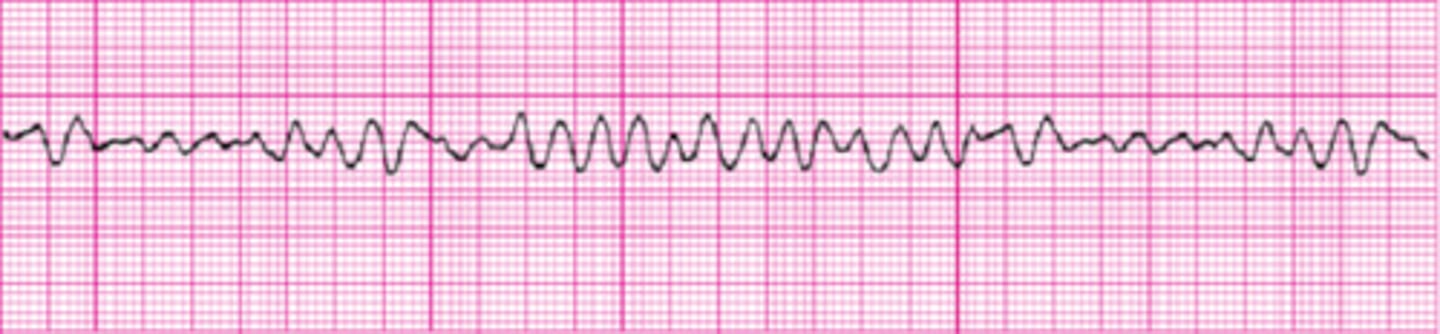
***A critically ill patient's cardiac monitor suddenly changes to the following rhythm. The patient becomes unconscious and pulseless. Which action should the nurse take first?
A. Perform immediate defibrillation
B. Give epinephrine (Adrenalin) IV.
C. Prepare for endotracheal intubation.
D. Give ventilation with a bag-valve-mask device
A
The nurse identifies the nursing diagnosis of decreased cardiac output related to valvular insufficiency for the patient with infective endocarditis (IE) based on which assessment finding(s)?
A. Fever, chills, and diaphoresis
B. Urine output less than 30 mL/hour
C. Petichiae on the inside of the mouth and conjunctiva
D. Increase in heart rate of 15 beats/minute with walking
B. urine output
After the nurse receives report, which patient should the nurse assess first?
A. Patient who has a respiratory rate of 14 after overdosing on oxycodone
B. Patient admitted with cocaine use who has an irregular heart rate of 142
C. Patient who is experiencing hallucinations and extreme anxiety after the use of marijuana
D. Patient with a history of daily alcohol use who is complaining of insomnia and diaphoresis
The nurse should assess the patient with an irregular heart rate of 142 after cocaine use, as this indicates a potential cardiovascular emergency.
A patient arrives in the ED several hours after taking 25-30 acetaminophen tablets. Which action will the nurse plan to take?
A. Administer N-acetylcysteine
B. Discuss the use of chelation therapy
C. Start oxygen using a non-rebreather mask
D. Have the patient drink large amounts of water
A. administer
Family members are in the patient's room when the patient has a cardiac arrest and the staff start resuscitations measures. Which action should the nurse take next?
A. Keep the family in the room and assign a staff member to explain the care given and answer questions
B. Ask the family to wait outside the patient's room with a designated staff member to provide emotional support
C. Ask the family members about whether they would prefer to remain in the patient's room or wait outside the room. If they would like to stay, assign a staff member to provide emotional support and answer questions.
D. Tell the family members that patients are comforted by having family members present during resuscitation efforts
c
Transplant recipients should be educated to avoid (select all that apply):
1. Roast beef (well-done)
2. Pork roast (well-done)
3. Raw honey
4. Unwashed fruit
5. Grapefruit juice
A. 1,2
B. 2,3
C. 3,4,5
D. 2,4,5
c. 3,4,5
Transplant recipients should be educated on prevention of this complication associated with immunosuppressive medications:
A. Skin cancer
B. Kidney stones
C. Hypotension
D. Hypoglycemia
Skin cancer due to increased risk from immunosuppressive therapy.
A patient brought to the ED after a MVA is diagnosed with a subdural hematoma, confirmed by CT scan. After the scan, the patient's BP starts to drop and pulse becomes rapid. The nurse should:
A. Assess for other areas of bleeding
B. Place the patient in Trendelenburg position
C. Wake the patient every hour to check level of consciousness
D. Administer metoprolol as prescribed
a. assess
An 80-year-old patient with a history of an abdominal aortic aneurysm arrives at the emergency department (ED) with severe back pain and absent pedal pulses. Which actions should the nurse take first?
A. Obtain the blood pressure
B. Obtain blood for laboratory testing
C. Assess for the presence of an abdominal bruit
D. Determine any family history of kidney disease
A. obtain blood pressure
The nurse educates a post heart transplant patient and spouse prior to discharge. The nurse determines education was effective when the patient states (select all that apply):
1. "prednisone can increase my blood sugar"
2. "I should avoid sick people"
3. "biopsies of the new heart are necessary to check for rejection"
4. "tacrolimus should be taken at 0800 and 2000 with grapefruit juice"
A. 1,2
B. 2,3
C. 1, 2, 3
D. 1,2,3,4
A. 1,2
Sodium polystyrene sulfonate is ordered stat for a patient with acute kidney injury. A BMP is ordered 4-hours after administration. The nurse evaluates effectiveness of the treatment by assessing the:
A. Creatinine
B. Blood glucose
C. Blood urea nitrogen (BUN)
D. Potassium
D. potassium
A 38-year-old female who had a kidney transplant 8 years-ago is receiving cyclosporine and prednisone. Which assessment data will be of most concern to the nurse?
A. The blood glucose is 144 mg/dL
B. There is a nontender axillary lump
C. The patient's skin is thin and fragile.
D. The patient's blood pressure is 150/92
D. blood pressure
A patient with diabetes who has pneumonia is being treated with vancomycin. The nurse will monitor for adverse effects of the medication by evaluating which lab test:
A. Blood glucose
B. Urine osmolality
C. Serum creatinine
D. Serum potassium
C. serum creatinine
A 62-year-old female patient has been hospitalized for acute kidney injury (AKI) caused by dehydration. Which information will be most important for the nurse to report to the health care provider?
A. The creatinine level is 4.0 mg/dL
B. Urine output over an 8-hour period is 250 mL
C. The potassium level is 6.2 mg/dL
D. The glomerular filtration rate is <30 mL/min/1.73m2
C. potassium level
A patient with acute kidney injury (AKI) has a wider QRS interval on EKG strip than was noted on the previous shift. Which action should the nurse take first?
A. Notify the patient's healthcare provider
B. Document the QRS interval measurement
C. Check the medical record for most recent potassium level
D. Check the chart for the patient's current creatinine level
C. check potassium
The nurse is titrating the IV fluid infusion rate immediately after a patient has had kidney transplantation. Which parameter will be most important for the nurse to consider?
A. Heart rate
B. Urine output
C. Creatinine clearance
D. Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) level
B. urine output
The patient was diagnosed with prerenal acute kidney injury. What is most likely the cause of the patient's diagnosis?
A. IV tobramycin
B. Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)
C. Post streptococcal glomerulonephritis
D. Dissecting abdominal aortic aneurysm
D. dissecting AAA
A type 1 diabetic for the past 25 years reports fatigue, edema, and an irregular heartbeat. On assessment, the nurse finds that the patient has newly developed hypertension. Which diagnostic study will be most indicative of chronic kidney disease (CKD) in this patient?
A. Serum blood urea nitrogen (BUN)
B. Serum potassium
C. Microalbuminuria
D. Calculated glomerular filtration rate (GFR)
C
The nurse is caring for a patient who has an intra-aortic balloon pump (IABP) in place. Which action should be included in the plan of care?
A. Position the patient supine at all times
B. Avoid the use of anticoagulant medications
C. Measure the patient's urinary output every hour
D. Provide passive range of motion for all extremities
Measure urine output
Which assessment finding obtained by the nurse when caring for a patient with a right femoral arterial line indicates a need for the nurse to take immediate action?
A. The left radial pulse is weak
B. The mean arterial pressure (MAP) is 77 mm Hg.
C. The right pedal pulse is absent
D. The flush bag and tubing were last changed 2 days ago
C. The right pedal pulse is absent
Which hemodynamic profile is consistent with cardiogenic shock?
A. CO 5.0 L/min CI 2.8 L/min/m2 PCWP 10 mmHg BP 110/74
B. CO 3.4 L/min CI 1.6 L/min/m2 PCWP 24 mm Hg BP 76/50
C. CO 9.8 L/min CI 4.8 L/min/m2 PCWP 12 mm Hg BP 84/60
D. CO 3.8 L/min CI 2.5 L/min/m2 PCWP 4 mm Hg BP 82/64
B. CO 3.4 L/min CI 1.6 L/min/m2 PCWP 24 mm Hg BP 76/50
Intra-aortic balloon pump (IABP) therapy is initiated for cardiogenic shock. The nurse knows:
A. Coronary artery blood flow increases during IABP inflation
B. Afterload is reduced by IABP deflation through a vacuum effect
C. IABP therapy improves oxygen delivery to the myocardium
D. All of the above
D. all of the above
To assure accurate arterial blood pressure readings, the pressure monitoring transducer is leveled and zero balanced to the:
A. Level of the ventricle
B. Level of the aorta
C. Phlebostatic axis
D. Foramen magnum
C.
Which hemodynamic profile is consistent with hypovolemic shock?
A. CO 5.0 L/min CI 2.8 L/min/m2 PCWP 10 mmHg BP 110/74
B. CO 3.4 L/min CI 1.6 L/min/m2 PCWP 24 mm Hg BP 76/50
C. CO 9.8 L/min CI 4.8 L/min/m2 PCWP 12 mm Hg BP 84/60
D. CO 3.8 L/min CI 2.5 L/min/m2 PCWP 4 mm Hg BP 82/64
D. CO 3.8 L/min CI 2.5 L/min/m2 PCWP 4 mm Hg BP 82/64
A patient in the post anesthesia care unit (PACU) following left knee replacement complains of chest discomfort and nausea. The anesthesiologist orders a 12-lead EKG which reveals ST elevation in leads II, III, aVF. BP 103/78, HR 52, RR 22, O2 sat 96% on 2 l/min. Cardiology is consulted stat.
The nurse suspects the patient is experiencing:
A. Acute pericarditis
B. Acute inferior wall myocardial infarction
C. Massive pulmonary embolism (PE)
D. Acute anterior wall myocardial infarction
B. Acute inferior wall myocardial infarction
A patient in the post anesthesia care unit (PACU) following left knee replacement complains of chest discomfort and nausea. The anesthesiologist orders a 12-lead EKG which reveals ST elevation in leads II, III, aVF. BP 103/78, HR 52, RR 22, O2 sat 96% on 2 l/min. Cardiology is consulted stat.
The cardiologist exams the patient and 12-lead EKG. The nurse anticipates preparing the patient for:
A. Emergency pulmonary embolectomy
B. Thrombolytic therapy
C. Emergency cardiac catheterization
D. Transport to the Surgical Intensive Care Unit (SICU)
C. Emergency cardiac catheterization
A patient in the post anesthesia care unit (PACU) following left knee replacement complains of chest discomfort and nausea. The anesthesiologist orders a 12-lead EKG which reveals ST elevation in leads II, III, aVF. BP 103/78, HR 52, RR 22, O2 sat 96% on 2 l/min. Cardiology is consulted stat.
Post emergency procedure the critical care nurse closely monitors the patient for what common serious complication related to this patient's underlying disease?
A. Bradycardia
B. Pneumothorax
C. Paralytic ileus
D. Pneumonia
A. Bradycardia
A 74-year-old patient with a PMH of rheumatic fever was admitted with heart failure. Cardiac catheterization reveals double vessel coronary artery disease and severe aortic stenosis.
The patient is scheduled for CABG and mechanical aortic valve replacement in the morning. The nurse determines pre-operative teaching was effective when the patient states:
A. "I will need to take warfarin for only the first three months following surgery."
B. "My heart failure will be cured after I get the new heart valve."
C. "I will need to take warfarin for the rest of my life."
D. "I will need to take antibiotics for the rest of my life."
C. "I will need to take warfarin for the rest of my life."
A 74-year-old patient with a PMH of rheumatic fever was admitted with heart failure. Cardiac catheterization reveals double vessel coronary artery disease and severe aortic stenosis.
The patient is receiving an epinephrine infusion at 2 mcg/min on post-operative day one. The 0800 hemodynamic profile reveals: CO 6.2 L/min, CI 3.1, PAP 30/14, CVP 6, HR 88 NSR, BP 124/84. The plan of care is discussed during interprofessional rounds. The nurse anticipates which order?
A. Increase epinephrine infusion
B. Start norepinephrine infusion
C. Discontinue epinephrine infusion
D. Furosemide 40 mg IV push now
C. Discontinue epinephrine infusion
A 74-year-old patient with a PMH of rheumatic fever was admitted with heart failure. Cardiac catheterization reveals double vessel coronary artery disease and severe aortic stenosis.
On post-operative day two, while ambulating in the hallway the cardiac surgery patient complains of feeling dizzy. The cardiac monitor alarms revealing a change in rhythm to:
A. Sinus tachycardia
B. Ventricular fibrillation
C. 3rd degree heart block
D. Atrial fibrillation
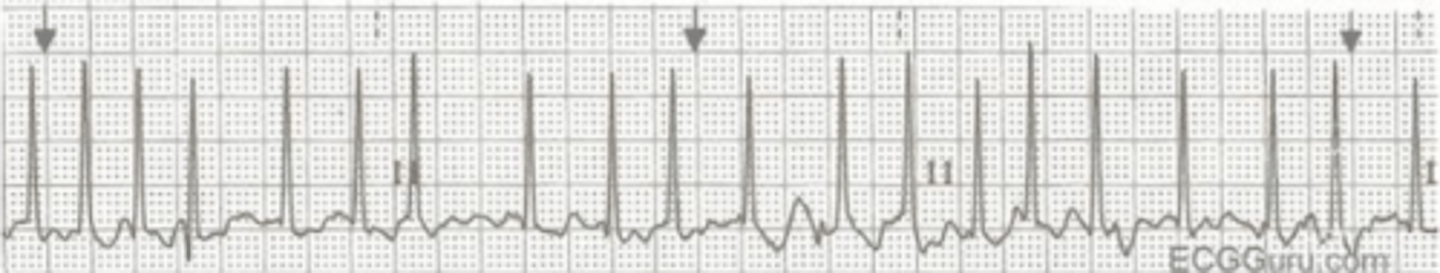
A 74-year-old patient with a PMH of rheumatic fever was admitted with heart failure. Cardiac catheterization reveals double vessel coronary artery disease and severe aortic stenosis.
The nurse assists the patient back to bed and summons the cardiac surgery team. BP 98/60, RR 22, O2 sat 96% on 2 L/min. The nurse anticipates the following order:
A. Start norepinephrine infusion
B. Start IV Amiodarone per dysrhythmia protocol
C. Start nitroglycerin infusion
D. Start PO Diltiazem
A. Start norepinephrine infusion
The nurse will anticipate teaching a patient with a possible seizure disorder about which test?
A. Cerebral angiography
B. Evoked potential studies
C. Electromyography (EMG)
D. Electroencephalography (EEG)
D. Electroencephalography (EEG)
Admission vital signs for a brain-injured patient are blood pressure 112/60, pulse 108, and respirations 22. Which set of vital signs, if taken 1 hour after admission, will be of most concern to the nurse?
A. Blood pressure 124/68, pulse 86, respirations 18
B. Blood pressure 90/64, pulse 90, respirations 22
C. Blood pressure 188/60, pulse 60, respirations 10
D. Blood pressure 96/72, pulse 130, respirations 30
A patient has increased intracranial pressure and a ventriculostomy after a craniotomy. Which action can the nurse delegate to unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP) who regularly work in the intensive care unit?
A. Document intracranial pressure every hour.
B. Turn and reposition the patient every 2 hours.
C. Check capillary blood glucose level every 6 hours.
D. Monitor cerebrospinal fluid color and volume hourly.
A 68-year-old patient is being admitted with a possible stroke. Which information from the assessment indicates that the nurse should consult with the health care provider before giving the prescribed aspirin?
A. The patient has dysphasia.
B. The patient has atrial fibrillation.
C. The patient reports that symptoms began with a severe headache.
D. The patient has a history of brief episodes of right-sided hemiplegia.
C. The patient reports that symptoms began with a severe headache.
A 73-year-old patient with a stroke experiences facial drooping on the right side and right-sided arm and leg paralysis. When admitting the patient, which clinical manifestation will the nurse expect to find?
A. Impulsive behavior
B. Left-sided neglect
C. Hyperactive left-sided tendon reflexes
D. Difficulty comprehending instructions
C. Hyperactive left-sided tendon reflexes
A 56-year-old patient arrives in the emergency department with hemiparesis and dysarthria that started 2 hours previously, and health records show a history of several transient ischemic attacks (TIAs). The nurse anticipates preparing the patient for:
A. Surgical endarterectomy.
B. Transluminal angioplasty.
C. Intravenous heparin administration.
D. Tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) infusion.
D. Tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) infusion.
Which stroke risk factor for a 48-year-old male patient in the clinic is most important for the nurse to address?
A. The patient is 25 pounds above the ideal weight.
B. The patient drinks a glass of red wine with dinner daily.
C. The patient's usual blood pressure (BP) is 170/94 mm Hg.
D. The patient works at a desk and relaxes by watching television.
C. The patient's usual blood pressure (BP) is 170/94 mm Hg.
A patient with right-sided weakness that started 2 hours earlier is admitted to the emergency department and diagnostic tests are ordered. Which test should be done first?
A. Swallowing study
B. Echocardiogram
C. 12-Lead electrocardiogram (ECG)
D. CT scan of the head without contrast
D. CT scan of the head without contrast
After receiving change-of-shift report on the following four patients, which patient should the nurse see first?
A. 60-year-old patient with right-sided weakness who has an infusion of tPA prescribed
B. 50-year-old patient who has atrial fibrillation and a new order for warfarin (Coumadin)
C. 40-year-old patient who experienced a transient ischemic attack yesterday who has a dose of aspirin due
D. 30-year-old patient with a subarachnoid hemorrhage 2 days ago who has nimodipine scheduled
A. 60-year-old patient with right-sided weakness who has an infusion of tPA prescribed
D. normal sinus rhythm
Identify the following cardiac rhythm:
A. Junctional
B. Sinus bradycardia
C. Atrial fibrillation
D. Normal sinus rhythm
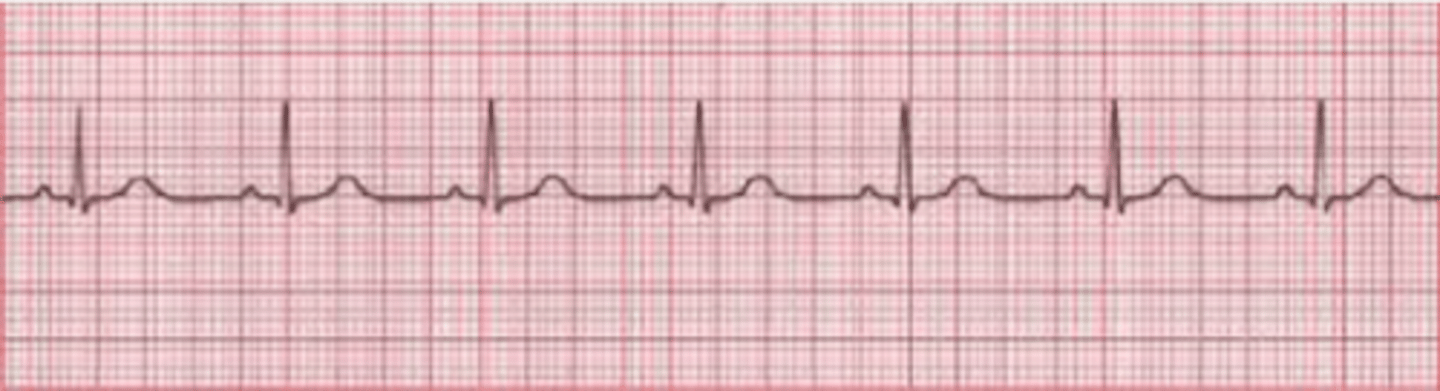
C. sinus tachycardia
Identify the following cardiac rhythm:
A. Normal sinus rhythm
B. Atrial fibrillation
C. Sinus tachycardia
D. Ventricular tachycardia
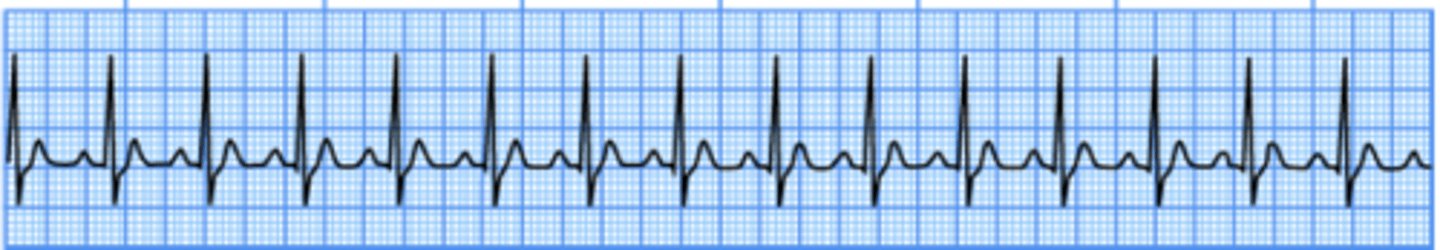
C. atrpoine bc symptomatic sinus bradycardai
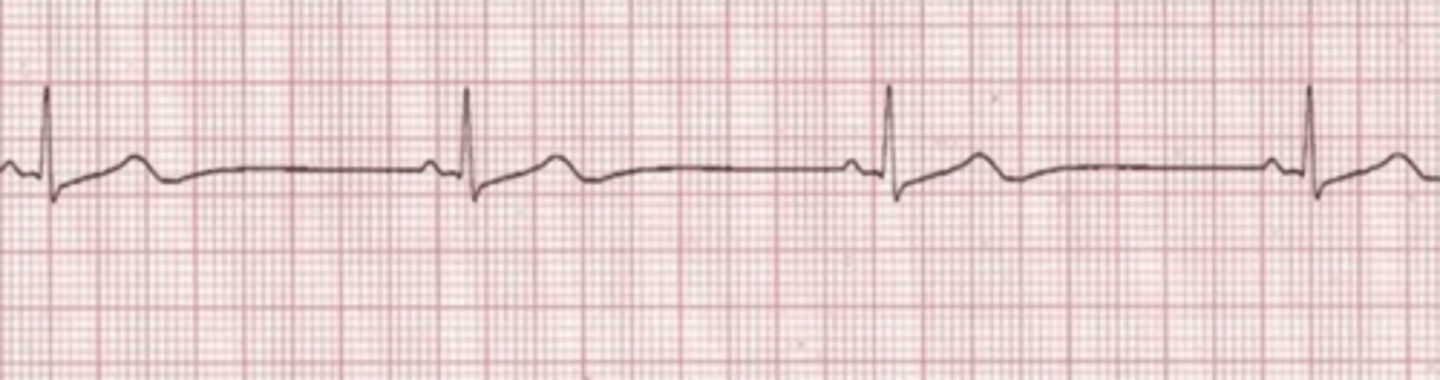
A patient on the telemetry floor complains of SOB and feels weak. Skin cool, diaphoretic, BP 78/50, RR 24. The following rhythm is on the cardiac monitor. The nurse activates the rapid response team and anticipates an order for:
A. Amiodarone IV push
B. Cardioversion
C. Atropine IV push
D. Norepinephrine infusion
A patient presents to the ED complaining of fatigue, weakness, and black tarry stools. BP 104/54, HR 102 sinus tachycardia, RR 20, O2 sat 96% on room air. Results of a stat CBC: WBC 9.0, Hg 7.8, Hct 28.4, platelets 154. The nurse anticipates the following priority order:
A. Transfuse RBC 1 unit
B. Repeat CBC in 6 hours
C. Transfuse platelets 5 units
D. Vancomycin 1 Gm in 250 cc NSS IVPB stat
A hemodialysis patient that missed two (2) treatments presents to the ED with SOB. BP 160/90, HR 100 and irregular, RR 28, O2 sat 91% on room air. Stat BMP results: Na 138, K+ 7.2, Cl 99, CO2 22, BUN 98, creat 6.2, BS 188. Which collaborative intervention should the nurse do first?
A. Administer Regular Insulin 10 units IVP, Sodium bicarbonate 1 amp IVP, D50 1 amp IVP
B. Initiate CVVHD
C. Prepare for hemodialysis
D. Administer sodium polystyrene sulfonate via NGT
C. Prepare for hemodialysis
A patient with mild COPD and type 1 diabetes presents to the Emergency Department with vomiting and a change in level of consciousness. Interpret the following arterial blood gas: PH 7.10, pCO2 35, pO2 72, HCO3 12, O2 sat 91%
A. Respiratory alkalosis
B. Respiratory acidosis
C. Metabolic alkalosis
D. Metabolic acidosis
D. Metabolic acidosis
The HCP orders the following ventilator settings: tidal volume (TV) 600 ml, FIO2 50%, IMV, rate 14. The nurse knows:
A. The ventilator delivers a set number of mandatory breaths while allowing the ventilated patient to breathe spontaneously (and unassisted) between mandatory breaths.
B. The tidal volume (VT) of each delivered breath is the same, regardless of whether it was triggered by the patient or the ventilator.
C. The patient initiates every breath and the ventilator delivers support with the preset pressure value
D. PEEP is automatically set at 12
B. The tidal volume (VT) of each delivered breath is the same, regardless of whether it was triggered by the patient or the ventilator.
Following an earthquake, a patient with survivable, but life-threatening injuries would be tagged with which color?
A. Black
B. Green
C. Yellow
D. Red
D. Red
The nurse is administering an insulin infusion to a patient in DKA. Which insulin is the only one that can be given intravenously?
A. NPH
B. Aspart
C. Regular
D. Glargine
C. Regular
A nurse is caring for a 9-year-old child who has a grave prognosis after receiving a closed injury from being struck by a car. Which health team member should approach the family about organ donation?
A. Nurse-manager
B. Transplant coordinator
C. Emergency department nurse
D. Pastoral care staff member
A nurse assesses a patient shortly after living donor kidney transplant surgery. Which postoperative finding must the nurse report to the physician immediately?
A. Serum potassium level of 4.9 mEq/L
B. Serum sodium level of 135 mEq/L
C. Temperature of 99.2° F (37.3° C)
D. Urine output of 20 ml/hour
The nurse is caring for a patient being discharged following kidney transplantation. The patient is ordered mycophenolate mofetil to prevent organ rejection. Which nursing instruction is essential regarding medication use?
A. Administer medication following breakfast daily.
B. Contact the health care provider at first signs of an infection.
C. Sprinkle the contents of the capsule on food.
D. Administer the medication with an antacid to prevent stomach upset.
B. Contact the health care provider at first signs of an infection.
A nurse is caring for a 9-year-old child who has a grave prognosis after sustaining a closed-head injury after being struck by a car while riding a bike. The child is on mechanical ventilation without spontaneous respirations. Which of the following is the nurse's priority concerning a referral to a transplant coordinator?
A. The nurse should discuss the decision about donation of organs with the parents.
B. The nurse should make the referral to a transplant coordinator as soon as possible.
C. The nurse should ask the family if they would like to talk with someone in transplant service regarding organ donation.
D. The nurse should talk with the parent's religious representative about donation
B. The nurse should make the referral to a transplant coordinator as soon as possible.
Twenty minutes after a transfusion of packed red blood cells is initiated, a patient reports shivering, headache, and lower back pain. The vital signs show a normal temperature and increased pulse and respiratory rate. What should be the first nursing actions?
A. Stop the transfusion, continue with saline infusion, and notify the physician regarding a suspected hemolytic reaction.
B. Slow the transfusion, notify the physician regarding a possible febrile reaction, and follow the physician's orders.
C. Slow the transfusion, give an antihistamine as ordered, and notify the physician regarding a possible allergic reaction.
D. Stop the transfusion, check the oxygen saturation levels, and check the urine volume.
A. Stop the transfusion, continue with saline infusion, and notify the physician regarding a suspected hemolytic
The following statement(s) regarding PRE exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) are true: (select all that apply)
1. given prior to HIV diagnosis to prevent disease acquisition
2. given within 72-hours of exposure to prevent HIV
3. efficacy is dependent on adherence
4. Truvada (emtricitabine + tenofovir) is taken PO daily
A. 1,2,3
B. 2,3,4
C. 1,3,4
D. 1,2,3,4
C. 1,3,4
A patient with a history of IV drug use presents to the ED with possible opioid overdose. A nurse suffers a needle stick when starting an IV on this patient. POST exposure (PEP) is recommended. The nurse understands: (select all that apply)
1. PEP means taking a combination anti-retroviral treatment (ART) regimen
2. ART should be given within 72-hours of potential exposure to HIV
3. PEP is indicated for sexual assault
4. PEP means taking Truvada once a day
A. 1,2
B. 2,4
C. 1,2,3
D. 2,3,4
A. 1,2
The nurse is reviewing the provider's order to give a postoperative heart transplant patient tacrolimus 1 mg PO every 12 hours. What nursing care interventions should be completed prior to administering tacrolimus at 0800? (Select all that apply.)
1. Check BP
2. Draw therapeutic blood level immediately prior to dose
3. Draw therapeutic blood level 1-hour after administration
4. Assess creatinine prior to administration
A. 1,2,3
B. 2,3,4
C. 1,3,4
D. 1,2,4
D. 1,2,4
A. Hypokalemia and hypoglycemia
The nurse is performing triage in the emergency department. Which patient should be seen first?
A. The patient with flank pain.
B. The patient who has an open fracture of his radius.
C. The patient with burns to his chest and neck with singed nasal hair.
D. A primipara who is 39 weeks pregnant having contractions every 15 minutes.
C. The patient with burns to his chest and neck with singed nasal hair.
The patient is 2 days postoperative AAA repair. Which assessment data would require immediate intervention from the nurse?
A. Patient attains 750 ml when using the incentive spirometer
B. Urine output is 300ml over 8 hours
C. Temp 98.8, HR 90, RR 20 BP 134/84
D. Dorsalis pedis pulse is not palpable
D. Dorsalis pedis pulse is not palpable
Which nursing interventions should be included in the plan of care for a patient with an endotracheal tube ETT and mechanical ventilation?
1. Document position of ETT (at lip line) at least every shift
2. Alternate the ETT from side to side in the mouth daily
3. Deflate the ETT cuff twice a day
4. Provide mouth care with chlorohexidine per hospital protocol
5. Elevate head of bead at least 30 degrees
A. 1, 3, 5
B. 2, 3, 4
C. 1, 2, 4, 5
D. All of the above
A. 1, 3, 5
When should Gift of Life be consulted for organ donation evaluation?
1. At first indication, the patient has suffered a non-recoverable neurological injury/illness.
2. Prior to the first formal brain death examination
3. Prior to family discussion of DNR or withdrawal of support
4. When non-recoverable neurological injury is due to: Head Trauma, Anoxia, CVA
A. 1 and 2
B. 2 and 3
C. None of the above
D. All of the above
D. All of the above
To detect treatment-related barotrauma complication in a mechanically ventilated patient with Adult Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) who is receiving PEEP + 15 cm with a tidal volume set at 10ml/kg of ideal body weight, the nurse assesses the patient for
A. Bradycardia
B. Refractory hypoxemia
C. Subcutaneous emphysema
D. Inspiratory wheezing
C. Subcutaneous emphysema
A patient is admitted to the emergency department with a stab wound to the right chest. He has moderate bleeding from the site, and his vital signs show symptoms of shock. Air can be heard entering his chest with each inspiration. To decrease the possibility of a tension pneumothorax in the patient, the nurse should:
A. Position the patient on his injured side
B. Leave the chest wound open to air
C. Cover the sucking chest wound with a petroleum gauze dressing
D. Apply a dressing to the chest wound, taping three sides and leaving one side untapped
D. Apply a dressing to the chest wound, taping three sides and leaving one side untapped
Which patient statement would make the nurse suspect the patient is experiencing a pulmonary embolism?
A. "I have pain in my foot and it feels numb."
B. "I have chest pain that is radiating down my right arm."
C. "My chest hurts and I feel like something bad is going to happen."
D. "I hear myself wheezing and it is hard to catch my breath."
B. "I have chest pain that is radiating down my right arm."
Two hours after administering IV furosemide, the patient's cardiac monitor shows frequent PVCs and a short run of bigeminy. Which of the following collaborative treatments would the nurse anticipate implementing?
A. Start D51/2 NSS at 100 cc/hour
B. KCL supplement
C. Atropine IV push
D. Prepare for temporary pacemaker insertion
B. KCl replacement
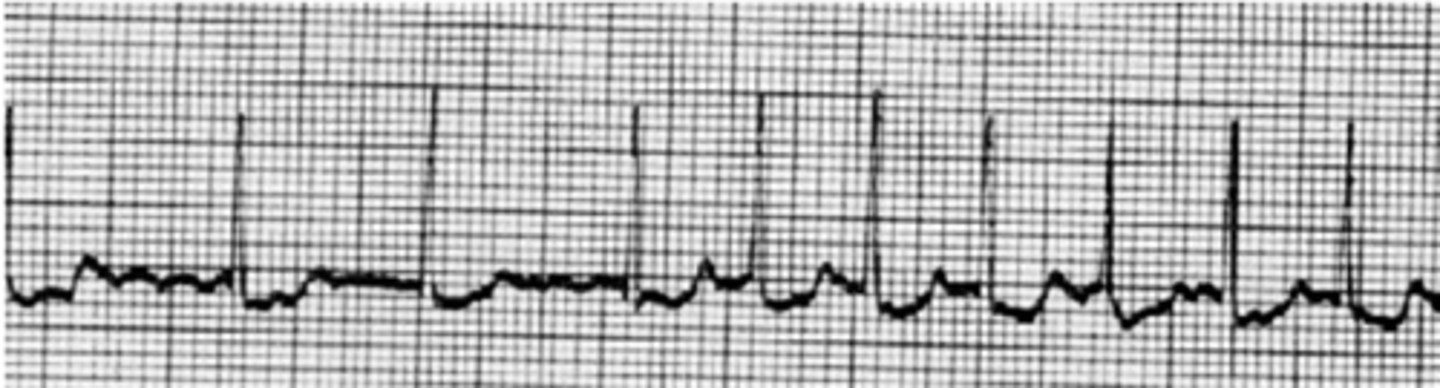
The following rhythm strip is a change from the patient's baseline. Based on the interpretation of the following rhythm strip, what medication would the nurse anticipate administering?
A. Lidocaine
B. Atropine
C. Dobutamine
D. Heparin
D. heparin
What is the nurse's most important intervention for a patient having a tonic-clonic seizure?
A. Protect the patient from further injury
B. Time the duration of the seizure
C. Note the origin of seizure activity
D. Insert a padded tongue blade to prevent the patient from biting his tongue
A. protect from further injury
The nurse is changing the dressings of a patient with partial thickness burns who is being treated with Silvadene cream. Which action should the nurse perform first?
A. Administer pain medication
B. Soak the site with normal saline
C. Check the white blood count
D. Cover the site with a dermal substitute
Administer pain medication