Organic Chemistry R&C, Type of Reactions and Mechanisms
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
From Alkenes to Alkanes
R&C: H2 (g) , Ni catalyst, heat
Rxn: Reduction
Describe FRS mechanism
Free-radical Substitution
R&C: Limited X₂ and UV light
3 Steps: IPT
1) Initiation step
Breaking of X₂ to form X radicals
2) Propagation step
Reacting alkane with X radical
Reacting alkane radical with X₂
3) Termination step
Reacting radicals together (3 possible steps)
From Alcohols to Alkenes
R&C: Excess conc H2SO4, heat
(OR Al2O3 high temperature)
Rxn: Elimination
From Halogenoalkanes (R-X) to Alkenes
R&C: KOH, ethanol, heat
(OR ethanolic KOH, heat)
Rxn: Elimination
From Alkenes to Halogenoalkanes (R-X)
R&C: dry gaseous HX
Rxn: Electrophilic Addition
Describe Electrophilic Addition Mechanism
Electrophilic Addition
2 Steps:
Step 1: slow step
Identify δ+ and δ- , Full arrow from π electrons from C=C attacking δ+
Draw carbocation + and anion
Step 2: fast step
Electron rich anion attacks carbocation
Forming new bond
From Alkene to Dihalogenoalkane
R&C: X₂ in inert organic solvent (e.g CCl4)
Rxn: Electrophilic Addition
Observation: pale-yellow Cl₂ / orange-red Br₂ decolorises
From Alkene to Halohydrin
R&C: Aqueous X₂
Rxn: Electrophilic Addition
Observation: pale-yellow Cl₂ / orange Br₂ decolorises
From Alkene to Alcohol
R&C:
Industrial: H₂O(g) , H3PO4 catalyst (phosphoric acid) ,high temperature , high pressure
Laboratory: conc H2SO4 , room temperature, followed by heating with liquid water
Rxn: Electrophilic Addition
From Alkene to Diol
R&C: cold, alkaline KMNO4
Rxn: Mild oxidation
Observation: Purple KMNO4 solution turns green (MnO42- )
followed by formation of brown ppt of MnO2
Strong Oxidation of Alkene
R&C: Hot KMNO4
Rxn: Strong Oxidation
Observation: Purple KMNO4 decolourises.
If CO2 gas formed, gas evolves forms white ppt with limewater.
Don’t change anything, the structure.
Splitting the C=C, and H just add O,
be aware of whether there is CO2 formed
ID Test for C=C bond
1) Add a few drops of Br2 (aq) | orange Br2 decolourises
2) Add a few drops of acidified KMnO4 | Purple KMnO4 decolourises
3) Add a few drops of cold alkaline KMnO4 | Purple KMnO4 solution turns green (MnO42- ) and brown ppt is formed (MnO2)
ID Test for Terminal Alkene ( =CH2 group)
Test: Add few drops of acidified KMnO4 , pass any gas evolved through lime water
Observations:
Purple KMnO4 decolourises
For Terminal Alkene ( =CH2 group), gas evolved forms white ppt with limewater
Benzene to Cyclohexane
R&C: H2 , Ni catalyst, heat
Rxn: Reduction
Benzene to Halogenoarenes
R&C: X2 , anhydrous AlX3 / FeX3 catalyst, heat
Rxn: Electrophilic Substitution
Describe Electrophilic Substitution
Electrophilic Substitution
3 Steps:
Step 1: Generation of Electrophile
Step 2: Electrophilic Substitution (Slow step)
Benzene ring attacks E+ forming arenium ion
Step 3: Restoration of aromaticity and regeneration of catalyst (Fast step)
C-H bond full arrow to “+” arenium ion
+ anion
Benzene to Nitrobenzene
R&C: conc HNO3 , conc H2SO4 catalyst, 50 °C
Rxn: Electrophilic Substitution
Benzene to Alkylbenzene
Friedal-Crafts Alkylation
R&C: RX, anhydrous AlX3 catalyst, heat
Rxn: Electrophilic Substitution
Benzene to Aromatic carbonyl compounds
Friedal-Crafts Acylation
R&C: RCOCl, anhydrous AlX3 catalyst, heat
Alcohol to Halogenoalkanes (R-X)
With PCl5
ROH + PCl5 = RCl + POCl3 + HCl
R&C: PCl5 (s), room temperature
Rxn: Nucleophilic Substitution
With PX3
3ROH + PX3 = 3 RX + H3PO3
R&C: PX3, heat
Rxn: Nucleophilic Substitution
With SOCl2
ROH + SOCl2 = RCl + SO2 (g) + HCL (g)
R&C: SOCl2, heat
Rxn: Nucleophilic Substitution
Describe SN1 Mechanism
Nucleophilic Substitution
Usually for Tertiary 3° H-X (Have to draw 3D structure)
2 Steps
Step 1: (Slow step)
Identify δ+ and δ- from C-X polar bond.
Full arrow from C-X bond attacking δ-
Forms from tetrahedral to carbocation (trigonal planar), halide ion
Step 2: (Fast step)
Nucleophile attack C+ equal probability
Just have to draw one product
Describe SN2 Mechanism
Nucleophilic Substitution
Usually for Primary 1° H-X (Have to draw 3D structure)
1 Step
Nucleophile OH- “backside attack” the halogenoalkane
(H-X)
Pentavalent transition state forms
new C-O bond forms, C-X begins to break (Dotted lines)
Structure is now inverted + Halide ion
From Halogenoalkane (R-X) to Alcohol
R&C: NaOH (aq) (or KOH (aq) ) , heat
Rxn: Nucleophilic Substitution
From Halogenoalkane (R-X) to Nitriles (CN group)
R&C: KCN (or NaCN), ethanol, heat
Rxn: Nucleophilic Substitution
From R-CN to R-CO2H
R&C: H2SO4 (aq) , heat
Rxn: Acid Hydrolysis
From R-CN to R-CO2-
R&C: NaOH (aq) , heat
Rxn: Alkaline Hydrolysis
From R-CN to R-CH2NH2
R&C: LiAlH4 , dry ether
Rxn: Reduction
From R-X to R-NH2 (1° Amine)
R&C: excess NH3 , ethanol, heat in sealed tube
Rxn: Nucleophilic Substitution
ID Test for Halogenoalkanes
4 Step Package:
1) Heat R-X with NaOH
2) Cool the mixture
3) Acidify with dilute HNO3
4) Add AgNO3 (aq)
I, Br, Cl (fastest to slowest)
I: yellow ppt
Br: pale cream ppt
Cl: white ppt
From Aldehydes to 1° Alcohol
R&C:
1) LiAlH4 , dry ether
(OR NaBH4 , methanol)
OR
2) H2 , Ni catalyst, heat
Rxn: Reduction
From Ketones to 2° Alcohol
R&C:
1) LiAlH4 , dry ether
(OR NaBH4 , methanol)
OR
2) H2 , Ni catalyst, heat
Rxn: Reduction
From Carboxylic Acid to Primary Alcohol
R&C: LiAlH4 , dry ether
Rxn: Reduction
From 1° Alcohol to Aldehydes
R&C: Acidified K2Cr2O7 (aq), immediate distillation
Rxn: Oxidation
Observation: Orange K2Cr2O7 (aq) turns green
From 1° Alcohol to Carboxylic Acid
R&C:
Acidified K2Cr2O7 (aq), heat under reflux
OR
Acidified KMnO4 (aq), heat under reflux
Rxn: Oxidation
Observation:
Orange K2Cr2O7 (aq) turns green
OR
Purple KMnO4 (aq) decolourises
From 2° Alcohol to Ketones
R&C:
Acidified K2Cr2O7 (aq), heat under reflux
OR
Acidified KMnO4 (aq), heat under reflux
Rxn: Oxidation
Observation:
Orange K2Cr2O7 (aq) turns green
OR
Purple KMnO4 (aq) decolourises
Alcohols to Esters
1) R-OH + RCOOH
R&C: RCOOH, conc H2SO4, heat under reflux
Rxn: Condensation
OR
2) R-OH + RCOCl
R&C: RCOCl, room temperature
Rxn: Condensation
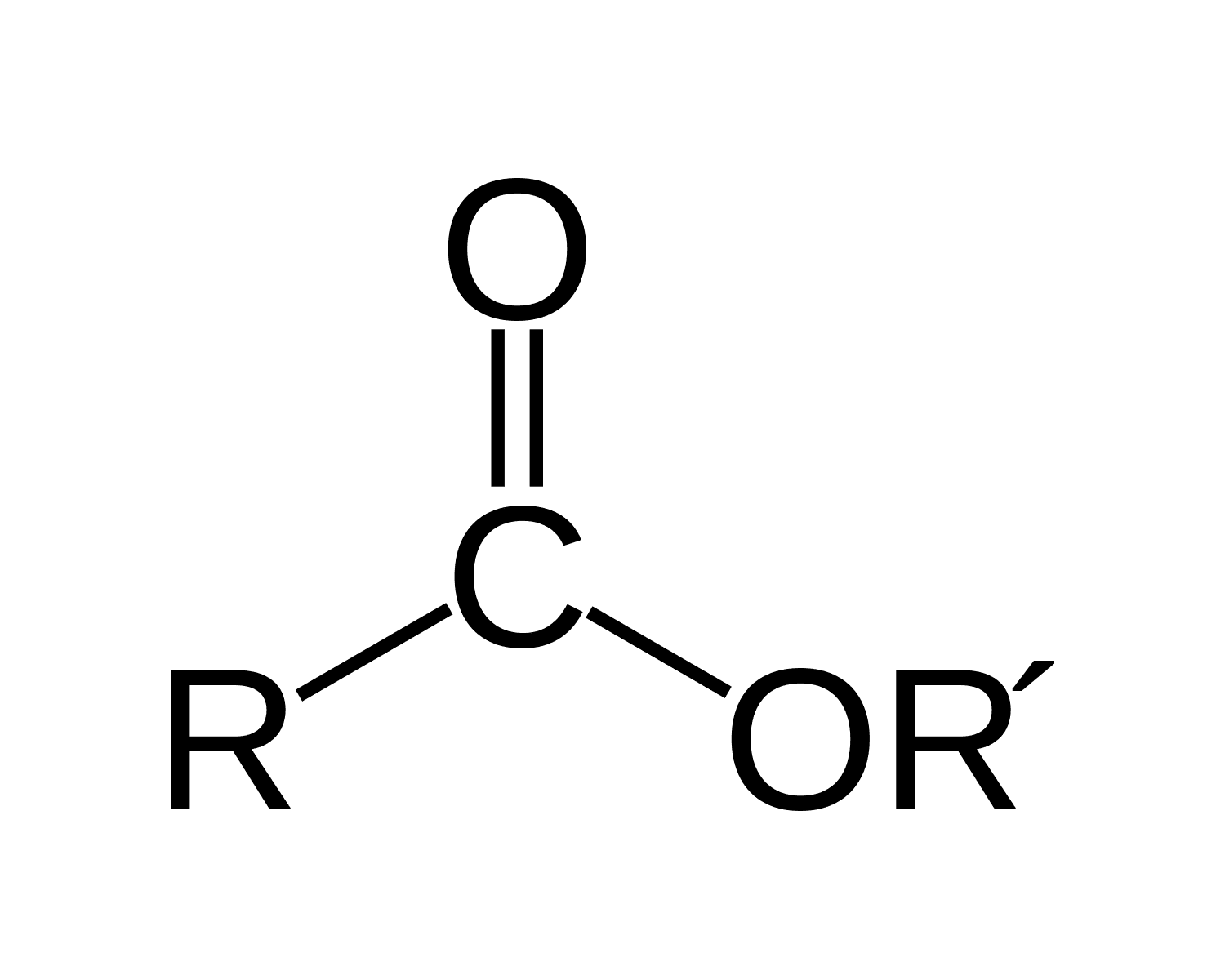
Phenols to Esters
Ring-OH + COCl
R&C:
Phenol in NaOH(aq)
RCOCl, room temperature
Rxn: Condensation
ID Test for Alipathic Alcohols
Test:
1) Add PCl5
Observations: For 1°/2°/3°, white fumes of HCl (g) will be evolved
2) Oxidation: Add Acidified K2Cr2O7 (aq) / KMnO4 (aq)
Observations: Orange K2Cr2O7 (aq) turns green / Purple KMnO4 (aq)
For 3°,
Orange K2Cr2O7 (aq) remains orange / Purple KMnO4 (aq) remains purple
3) Iodoform Test: Add iodine, NaOH (aq) and heat using a hot water bath
Observations:
With -CH(CH3)OH or -COCH3 group, pale yellow ppt of CHI3 will be formed.
ID Test for Phenols
1) Add neutral FeCl3 (aq)
Observation: Violet colouration will be observed
2) Add Br2 (aq)
Observation: Orange Br2 (aq) decolourises,
White ppt of 2,4,6-tribromophenol formed
Carbonyl compounds (Aldehydes/ Ketones) to cyanohydrins
R&C:HCN, trace amount of NaCN
Rxn: Nucleophilic Addition
Describe Nucleophilic Addition
Nucleophilic Addition
Generation of Nucleophile
2 Steps:
Step 1: (Slow step)
Identify δ+ and δ- , Full arrow from π electrons from C=C attacking δ- , O
Lone pair from Nucleophile attacks δ+, C
Step 2: (Fast step)
Lone pair from O- attacks δ+ H
Cyanohydrins to COOH
R&C: H2SO4 (aq), heat
Rxn: Acid Hydrolysis
Cyanohydrins to CH2NH2
R&C: LiAlH4 , dry ether
OR H2 (g), Ni catalyst, heat
Rxn: Reduction
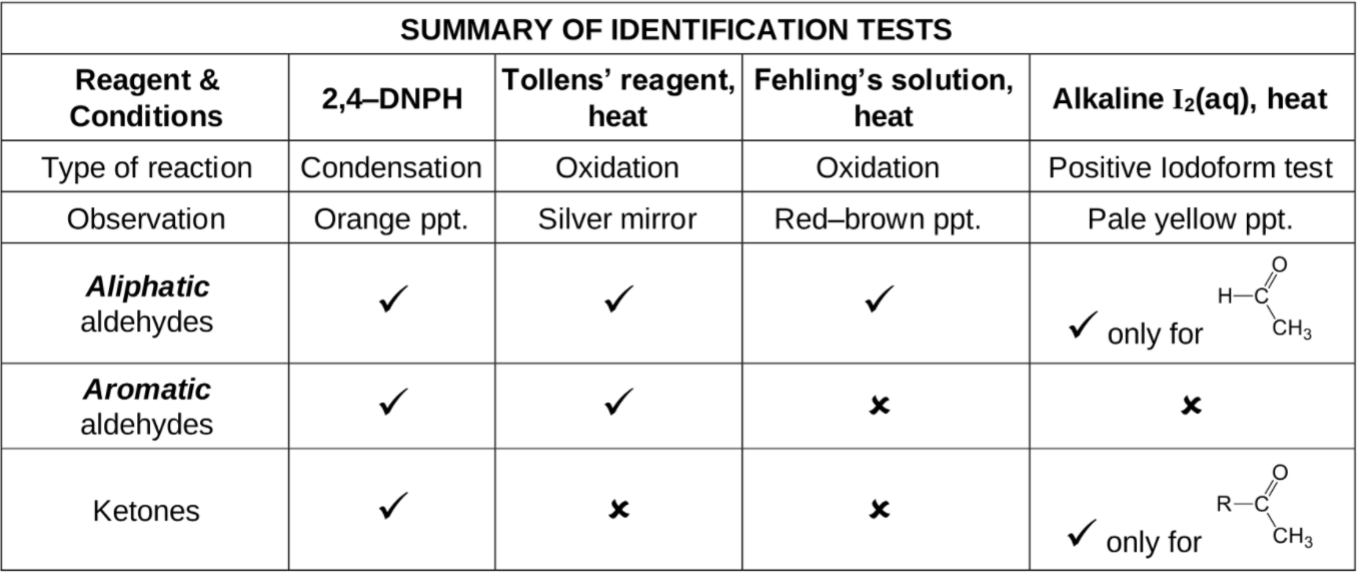
ID Test for Hydroxy compounds
Remember table form
1) 2,4 - DNPH , condensation, orange ppt
2) Tollens’ reagent, oxidation, silver mirror
3) Fehling’s solution, oxidation, red-brown ppt
4) Alkaline I2 (aq), heat, iodoform test, pale yellow ppt
From Alkylbenzene to Benzoic acid
R&C: Acidified KMnO4 (aq), heat
Observations: Purple KMnO4 (aq) decolourises
RCN to RCOOH
1) Acid Hydrolysis
R&C: H2SO4 (aq), heat
2) Alkaline Hydrolysis followed by acid-base reaction
R&C:
1) NaOH (aq), heat
2) acidify with H2SO4 (aq)
RCOOH to RCOO-
1) Redox
R&C: Na/ K/ Mg
Observation: Effervescence H2 (g), gives ‘pop' sound with lighted splint
2) Acid-Base reaction
R&C: NaOH (aq) / KOH (aq) / NH3 (aq)
3) Acid-carbonate reaction
R&C: NaCO3 (aq) / NaHCO3 (aq)
Observation: Effervescence of CO2 (g), forms white ppt with limewater
RCOOH to Ester
R&C: Alcohol, conc H2SO4 (l) catalyst, heat
Rxn: Condensation
RCOOH to Acyl Chloride (RCOCl)
Rxn: Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution
1) PCl5
2) PCl3 , heat
3) SOCl2 , heat
RCOOH to CO2 (g) and H2O (l)
R&C: Acidified KMnO4 (aq), heat under reflux
Observations: Purple KMnO4 (aq) decolourises, Eff CO2 (g), forms white ppt with limewater
RCOOH to CO (g) and H2O (l)
R&C: excess conc H2SO4 (l), heat
Rxn: Elimination
ID Test for RCOOH
1) Add Na2CO3 (aq) / NaHCO3 (aq)
Observation: Eff CO2 (g), forms white ppt with limewater
2) Add a few crystals of PCl5 at room temperature
Observation: white fumes of HCl is liberated
RCOCl to RCOOH
R&C: water, room temp
Rxn: Hydrolysis
RCOCl to Esters
1) RCOCl + ROH
R&C: Alcohol , room temperature
Rxn: Condensation
OR
2) RCOCl + Phenol
R&C: Phenol in NaOH(aq) , room temperature
Rxn: Condensation
RCOCl to Amides
Rxn: Condensation
1) Primary Amides 1°
R&C: NH3 , room temperature
2) Secondary Amides 2°
R&C: R’NH2 (primary amine), room temperature
3) Tertiary Amides 3°
R&C: (R’)2NH (secondary amine) , room temperature
ID Test for RCOCl
Test: Add AgNO3 (aq)
Observations: white ppt of AgCl formed immediately
ID Test for Esters
Test:
1) Hydrolysis of esters (acidic/ alkaline)
2) Analyse alcohol and ID test for alcohols
From RCN to Amines
R&C:
LiAlH4 , dry ether
OR
H2 (g), Ni catalyst, heat
Rxn: Reduction
*LiAlH4 , dry ether recommended if got benzene ring; don’t want to reduce benzene ring
From Amides to Amines
R&C: LiAlH4 , dry ether
Rxn: Reduction
From Nitrobenzene to Phenylamine
R&C:
1) Sn, conc HCl, hear
2) followed by NaOH (aq)
Rxn: Reduction
From RNH2 to RNH3+
R&C: HCl (aq) or H2SO4 (aq), room temperature
Rxn: acid-base reaction
From Phenylamine to 2,4,6 tribromophenyl
R&C: Br2 (aq)
Rxn: Electrophilic Substitution
Observation: orange Br2 (aq) decolourises, white ppt formed
ID Test for Primary Amides
Test: Insert damp red litmus paper
Observations: NH3 (g) turns damp red litmus paper blue