Molecular Bio Exam #1
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
Meischer
Discovered nuclein, now known as DNA.
Morgan
Linked genes to chromosomes using fruit flies.
Beadle & Tatum
Proposed the "one gene, one enzyme" hypothesis.
Griffith
Demonstrated bacterial transformation in mice
Avery, McCarty & MacLeod
Proved DNA as the transforming principle.
Hershey-Chase
Showed that DNA is the genetic material in viruses.
Watson & Crick
Developed the double helix model of DNA.
Characteristics of Living Systems
Require energy, maintain homeostasis, exhibit growth and reproduction, made of cells, and have genetic material (DNA or RNA).
Central Dogma
DNA → RNA → Protein.
Retroviruses
Use reverse transcription (RNA → DNA).
Rosalind Franklin
Used X-ray diffraction to image DNA.
Crick
Coined "central dogma" and proposed the flow of genetic information.
Nirenberg & Matthaei
Cracked the genetic code.
Deciphered how nucleotides encode amino acids.
RNA World Hypothesis
RNA was the original molecule for storing genetic information and catalysis.
Catalysis
The process of speeding up a reaction.
Enzyme
Proteins that act as biological catalysts.
Horizontal Gene Transfer
Transfer of genes between organisms (not parent to offspring).
Last Universal Common Ancestor (LUCA)
Hypothetical early cell from which all life descends.
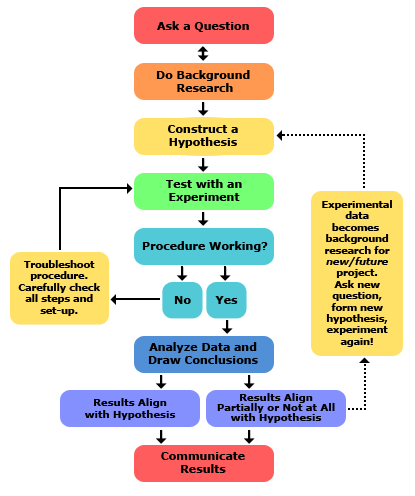
Scientific Method
Systematic process involving hypothesis generation, experimentation, observation, and conclusion.
Model Organisms
Organisms used for studying biological processes due to shared characteristics with humans.
Homozygous
Having two identical alleles.
Heterozygous
Two different alleles.
Genotype
Genetic makeup.
Phenotype
Observable traits.
Alleles
Variations of a gene.
Diploid
Two sets of chromosomes.
Haploid
One set of chromosomes.
autosomal vs. sex-linked trait
Autosomal passed down from parent to offspring
Sex-linked trait: passed down from one parent the offspring of the same sex
Law of Segregation
Alleles segregate during gamete formation.
Law of Independent Assortment
Genes for different traits are inherited independently (for unlinked genes).
Incomplete Dominance
Intermediate phenotype (e.g., red and white flowers produce pink offspring).
Codominance
Both alleles expressed (e.g., AB blood type).
Polygenic Inheritance
Traits controlled by multiple genes (e.g., skin color).
Mitosis
Produces two identical diploid cells.
Meiosis
Produces four genetically unique haploid cells; involves crossing over and independent assortment.
Gene Linkage
Genes close together on the same chromosome are inherited together.
X-linked Traits
Traits associated with genes on the X chromosome.
Crossing Over
Exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes.
Genetic Markers
Help identify locations of genes on a chromosome.
Mutation
A change in DNA sequence that can lead to genetic variability.
Recombination
The rearrangement of genetic material.
Sickle Cell Anemia
Caused by a mutation in hemoglobin gene.
Huntington’s Disease
Caused by expansion of CAG repeats in a gene.
Covalent Bonds
Strong bonds where electrons are shared.
Hydrogen Bonds
Weak interactions, important in DNA and protein structures.
Van der Waals Forces
Weak, non-covalent interactions.
Gibbs Free Energy (ΔG)
Determines if a reaction is spontaneous.
Exergonic Reaction
ΔG < 0, spontaneous.
Endergonic Reaction
ΔG > 0, non-spontaneous.
First Law of Thermodynamics
Energy cannot be created or destroyed.
Second Law of Thermodynamics
Entropy (disorder) increases in an isolated system.
Enzymes
Lower the activation energy of reactions, speeding them up.
ATP Hydrolysis
Releases energy used to drive cellular processes (e.g., protein synthesis, DNA replication).
Negative ΔG
Spontaneous.
Positive ΔG
Non-spontaneous.
Valence
Atom’s capacity to bond.
Free Energy Equation
ΔG = ΔH – TΔS, where ΔH is enthalpy, T is temperature, and ΔS is entropy
Standard Free Energy (ΔG°)
he free energy change under standard conditions (1M, 1 atm, 25°C).
Equilibrium Constant (Keq)
When Keq > 1, products are favored; when Keq < 1, reactants are favored.
Chiral
A molecule that has a non-superimposable mirror image
Polar
refers to molecules with unequal distribution of charges
Chemical Bond
Attraction holding atoms together.
Peptide Bond:
Covalent bond linking amino acids in proteins
Energy in Bonds
Different types of bonds store different amounts of energy, with high-energy phosphate bonds in ATP being crucial for cellular work.
Jacob & Meselson
Showed that ribosomes are the sites of protein synthesis.
Brenner
Identified messenger RNA (mRNA).
Khorana
Synthesized artificial RNA sequences to crack the genetic code
Sutton’s Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance
Chromosomes pass from one generation to another
McClintock’s Non-Crossove
Some genes are inherited together without exchanging genetic material during meiosis
McClintock’s Crossover
Crossover occurs when homologous chromosomes exchange genetic material, leading to genetic diversity
Transcription
5' to 3'
Translation
5' to 3' (mRNA) and N-terminus to C-terminus (polypeptide)
Transcription Phase: Initiation
RNA polymerase binds to the promoter region of DNA, unwinding the DNA strands
Transcription Phase: Elongation
RNA polymerase synthesizes RNA by adding complementary RNA nucleotides in the 5' to 3' direction.
Transcription Phase: Termination
RNA polymerase reaches a termination signal, releasing the newly synthesized RNA strand.
Translation Phases: Initiation
The ribosome assembles around the mRNA, and the first tRNA binds to the start codon.
Translation Phases: Elongation
tRNAs bring amino acids to the ribosome, forming a polypeptide chain in the 5' to 3' direction of mRNA.
Translation Phases: Termination
The ribosome reaches a stop codon, releasing the completed polypeptide
Cystic fibrosis
A genetic disorder caused by a mutation in the CFTR gene
Entropy (ΔS)f
the amount of energy in a physical system that is not available to do work.
Enthalpy (ΔH)
The total heat content of a system.
Ionic Bonds
Occur between oppositely charged groups in molecules, such as between ions in a salt bridge.
Hydrophobic Interactions
Occur when non-polar molecules aggregate to avoid water.
Phosphoanhydride Bonds in ATP
High-energy bonds that release energy when hydrolyzed.
ATP
the primary energy currency of the cell.
Hydrolysis of ATP Formula
TP + H₂O → ADP + Pi + energy.
Protein Synthesis
ATP provides energy for ribosome function during the translation of mRNA
Amino Acid Activation
ATP is used to attach amino acids to tRNA molecules.
DNA Synthesis
ATP powers helicase and other enzymes during replication.
ATP Synthesis
During cellular respiration, ATP is regenerated from ADP in the mitochondria.
Actomyosin Cycle
ATP powers muscle contraction by interacting with actin and myosin.