Osmoregulation - Part 2 (11/14)
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
What does the kidney do in osmoregulation?
Performs filtration and absorption in mammals
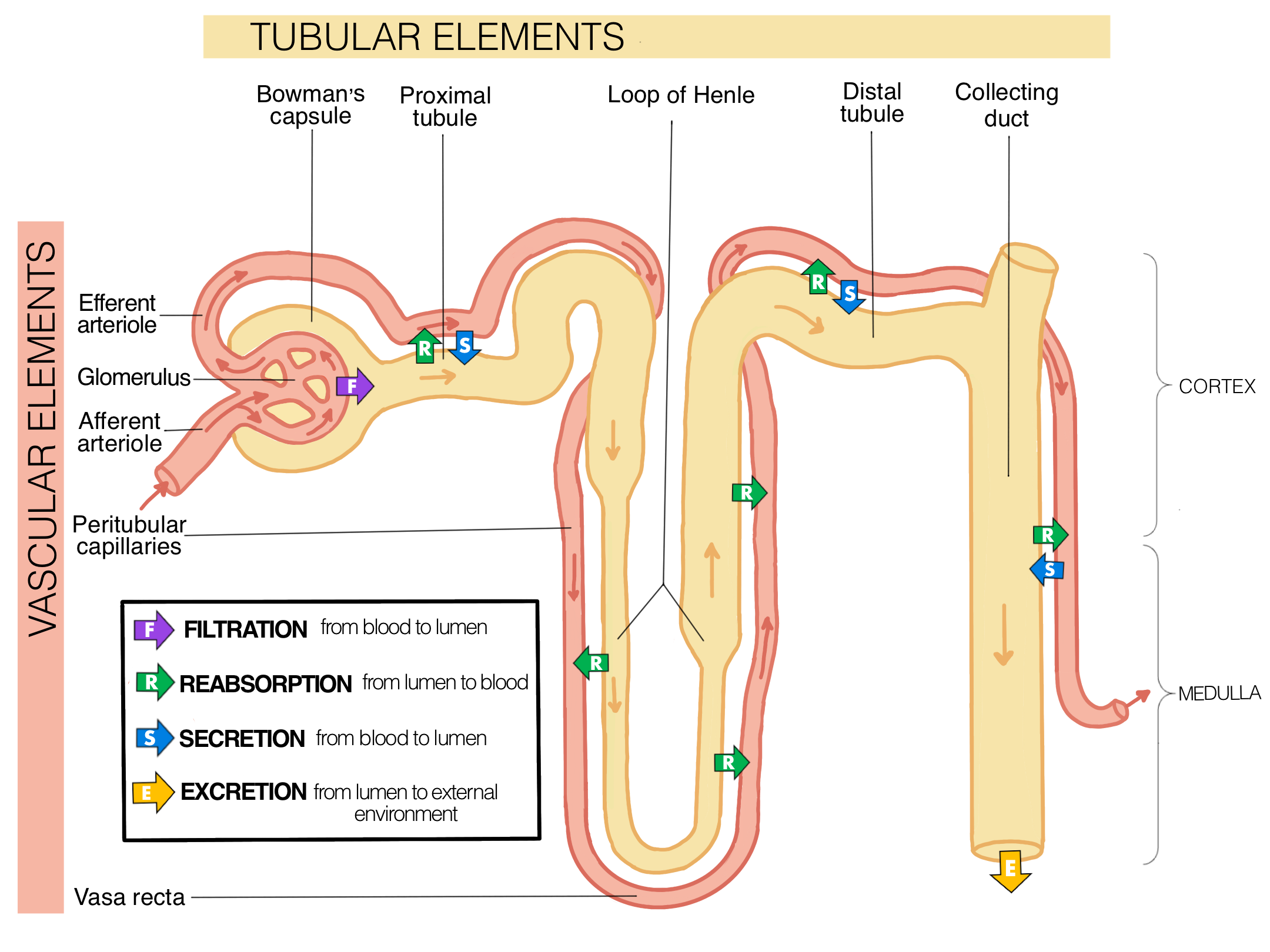
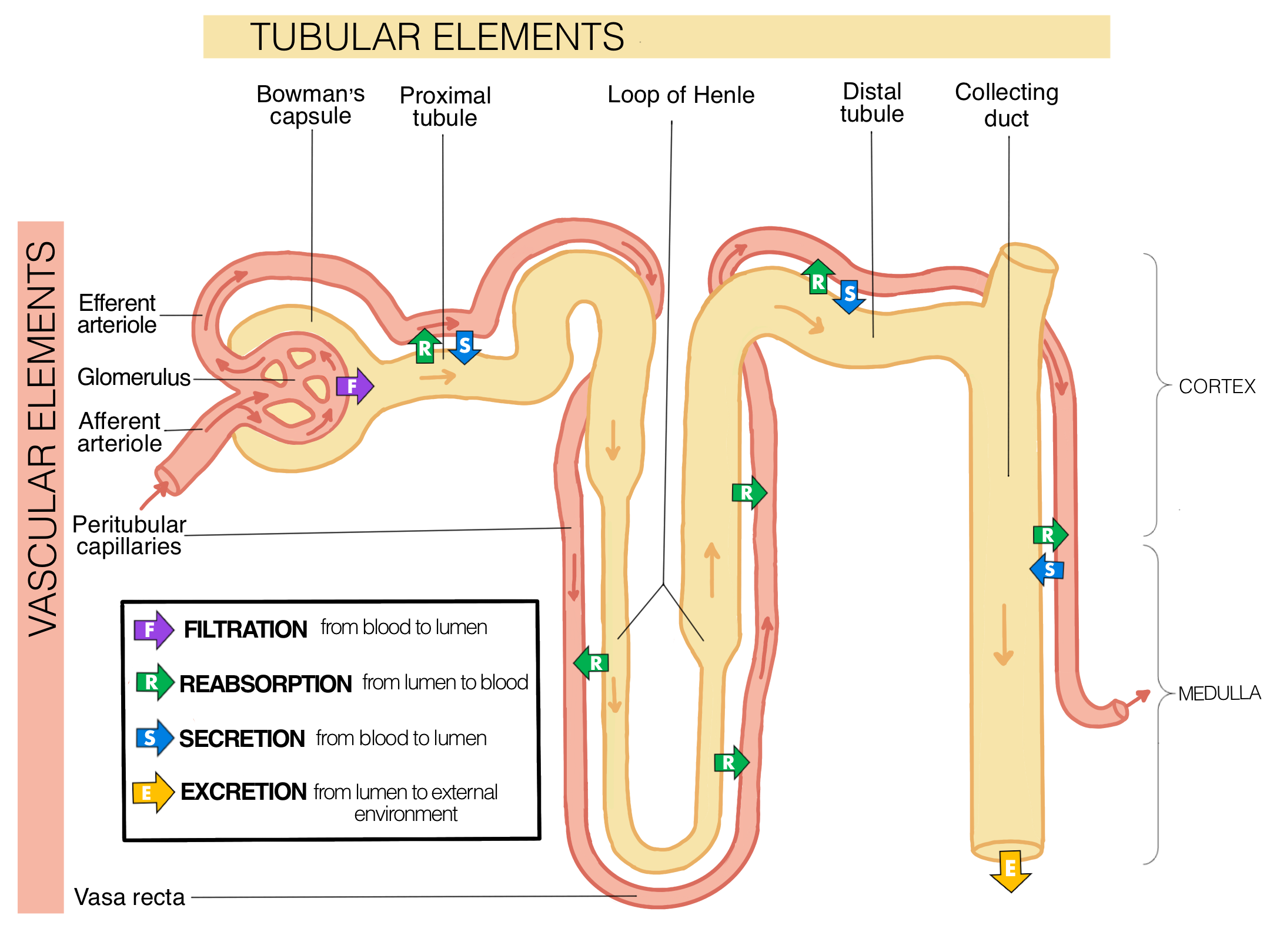
How does the kidney use filtration and reabsorption in osmoregulation?
Filters the blood by separating the water-based part of the blood (blood plasma) from the blood
Reabsorbs most of the water, electrolytes, and non-waste molecules into the blood
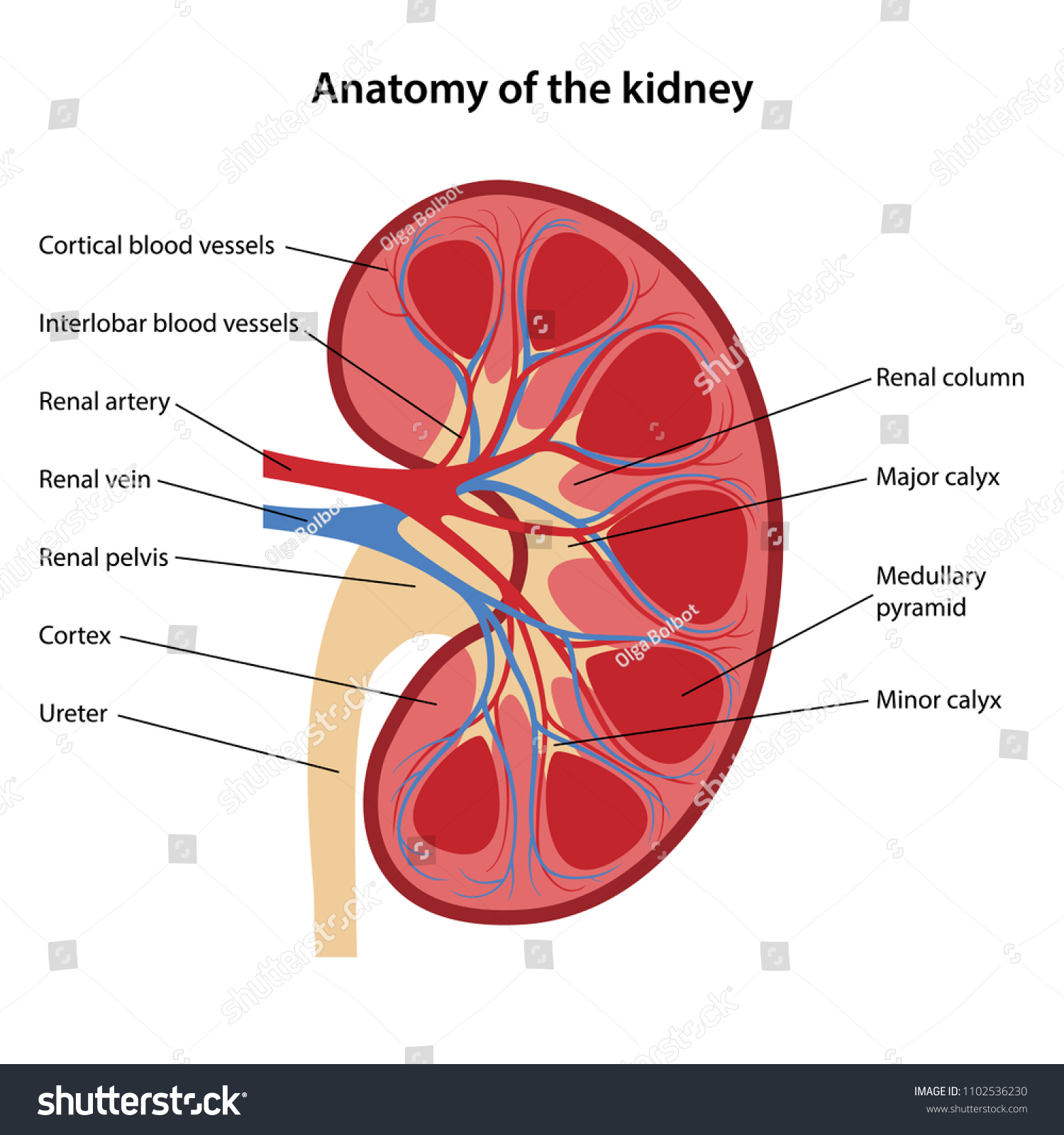
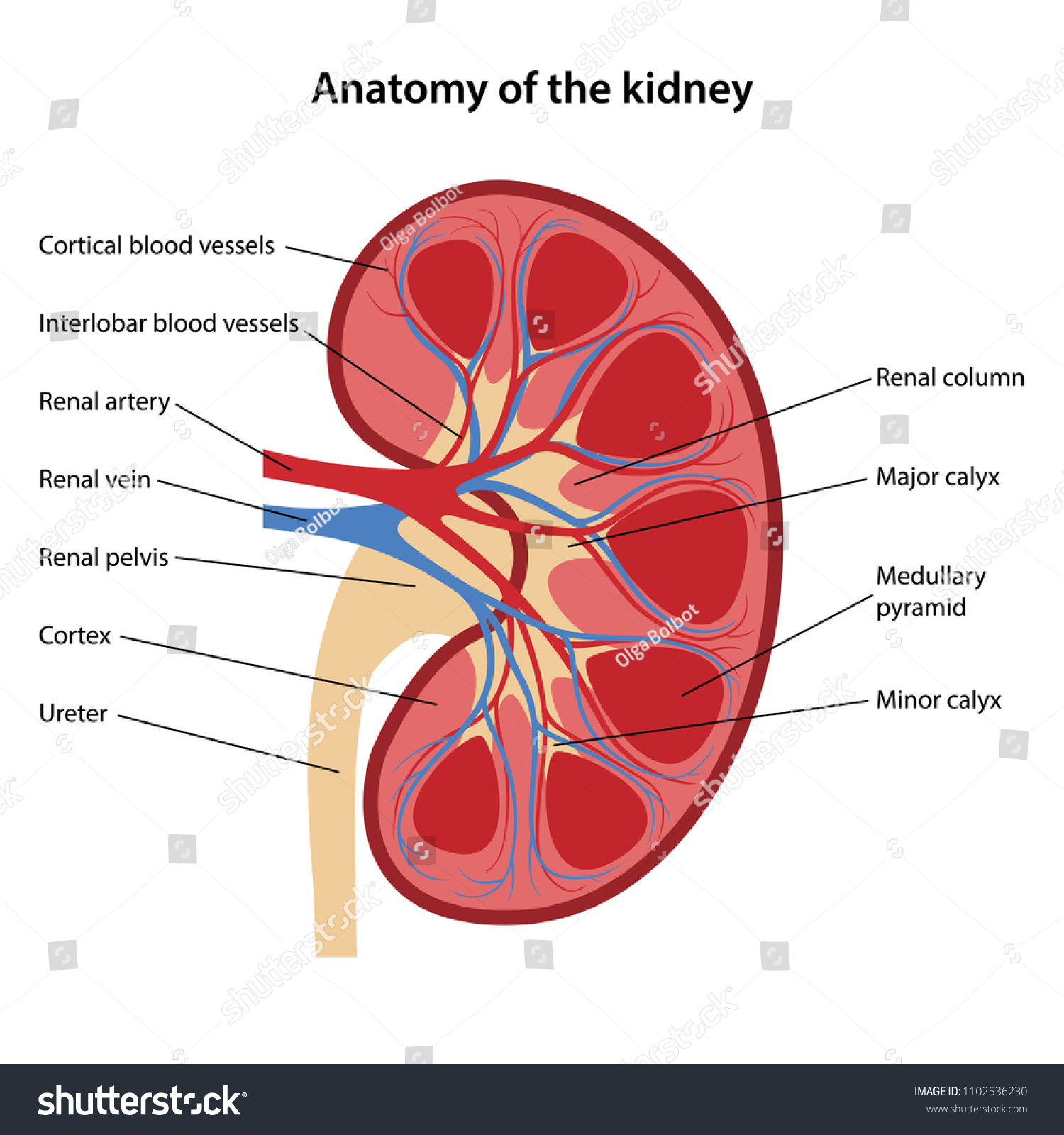
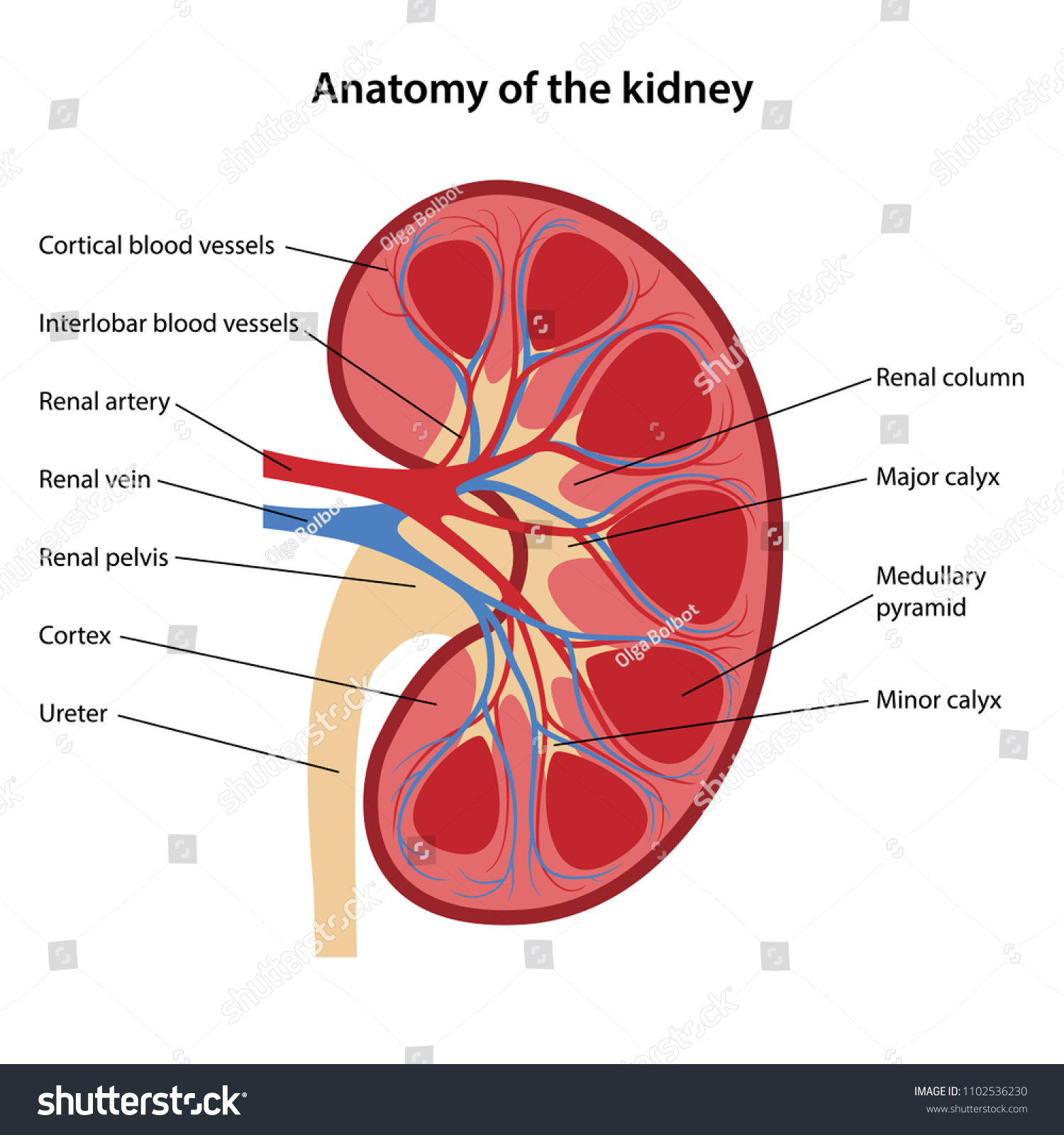
What is the renal artery?
Supplies oxygen-rich blood to the kidneys
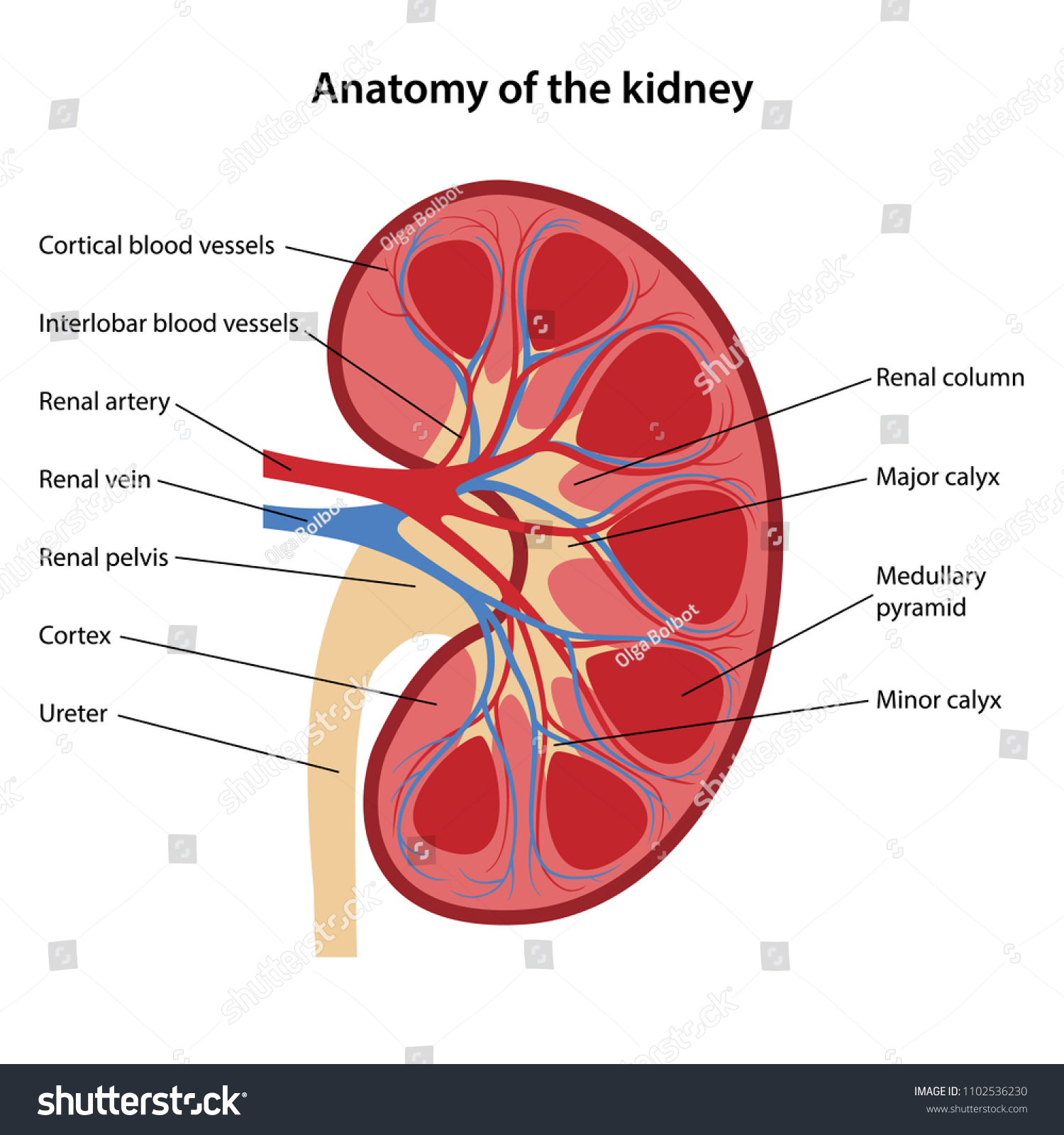
What is the renal vein?
Carries deoxygenated blood back to the heart
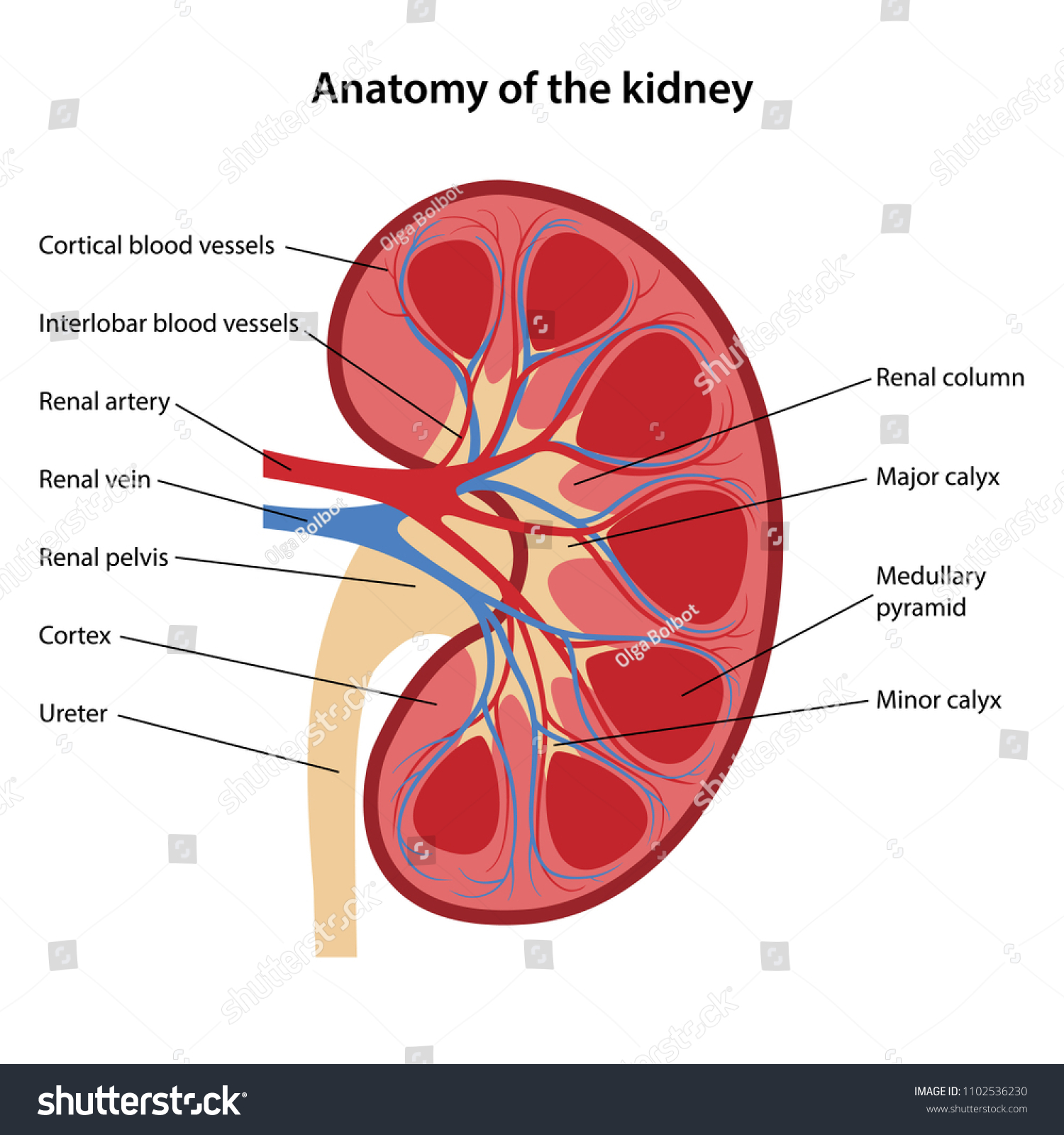
What is the ureter?
Carries urine from the kidney to the urinary bladder
What is the urinary bladder?
Stores urine
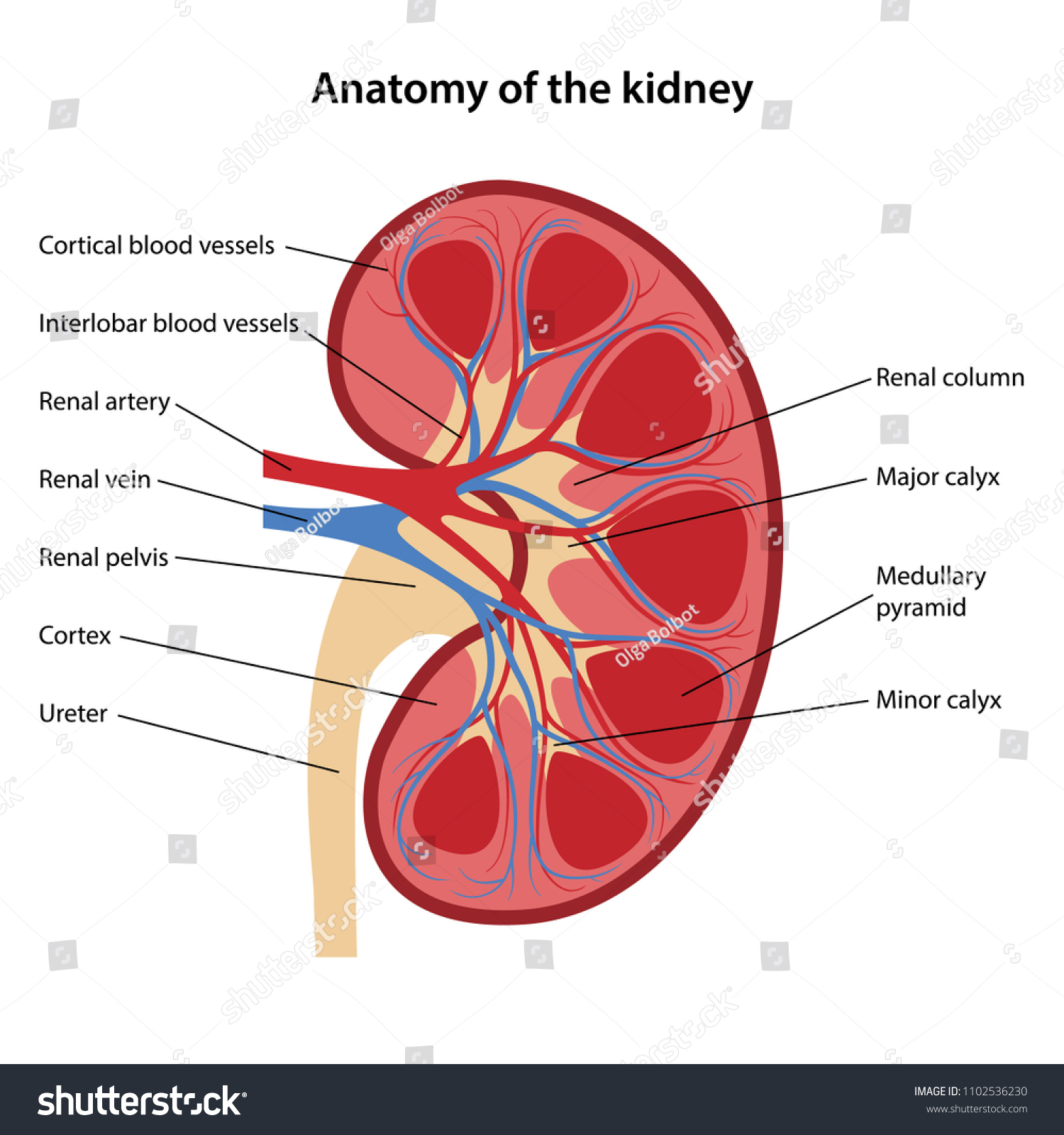
What are the three major regions of the kidney and what happens in each?
Renal Cortex
Area where the majority of the filtering units, called nephrons, can be found
Renal medulla
Area where filtered blood plasma is concentrated into its final form (urine)
Renal Pelvis
Catches urine as it is produced in the renal medulla and funnels it into the ureter
What is a nephron and how does it function?
Windy, tube-shaped filtering units called nephrons
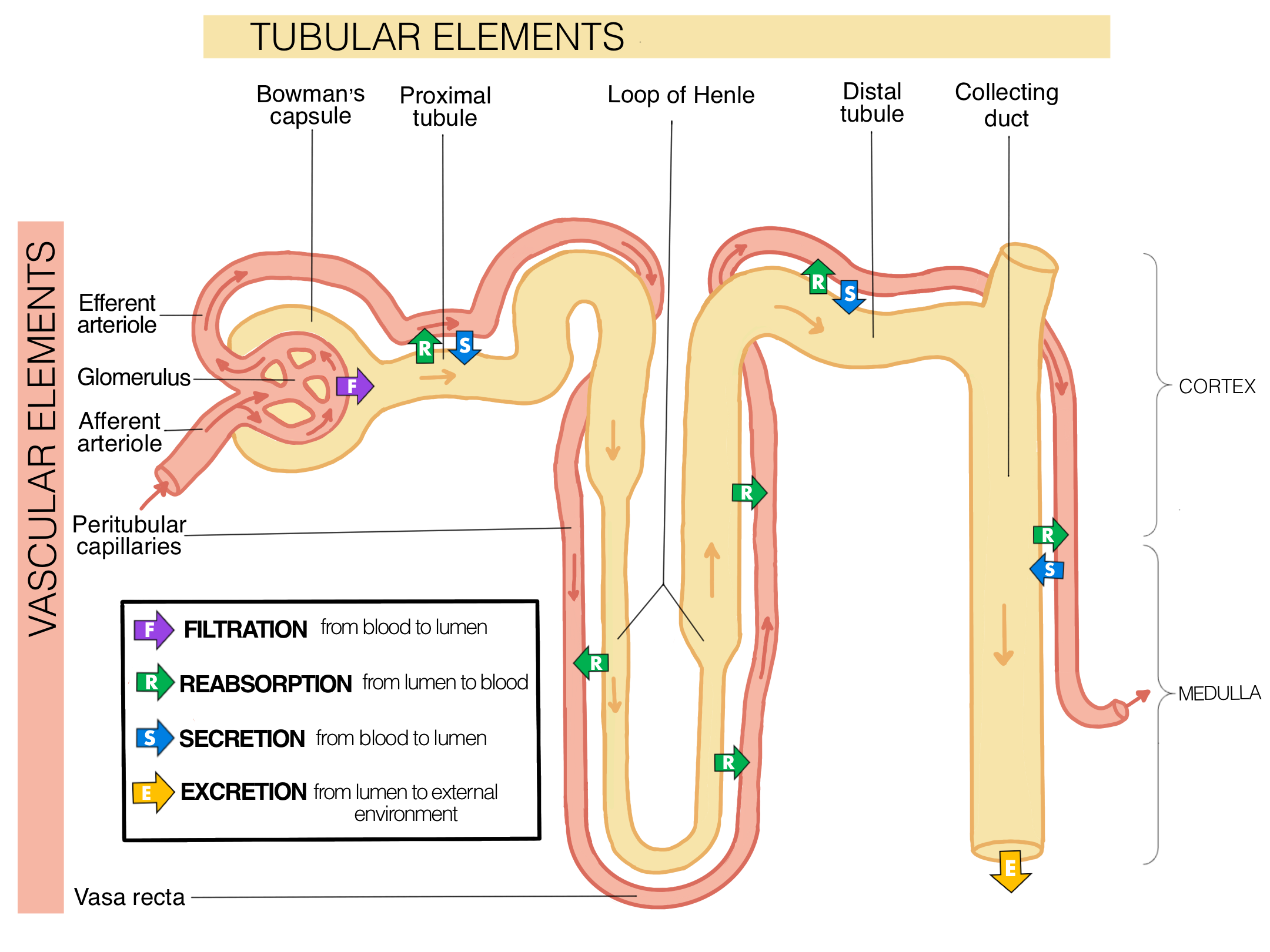
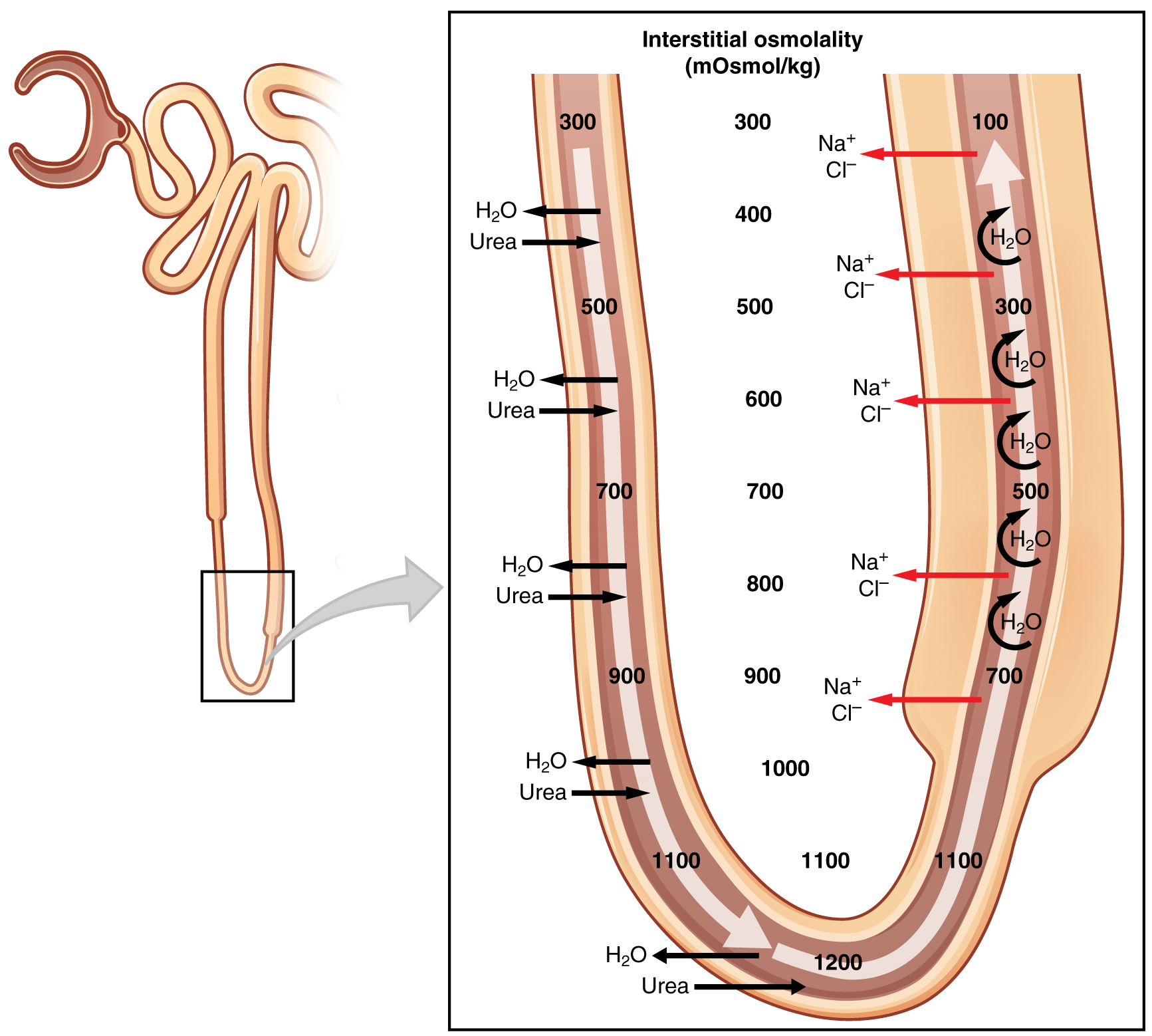
What is the medullary gradient and how does it function?
An osmotic gradient of electrolytes that allows the nephron to use active transport, diffusion, and osmosis to reabsorb filtered plasma back into the blood.
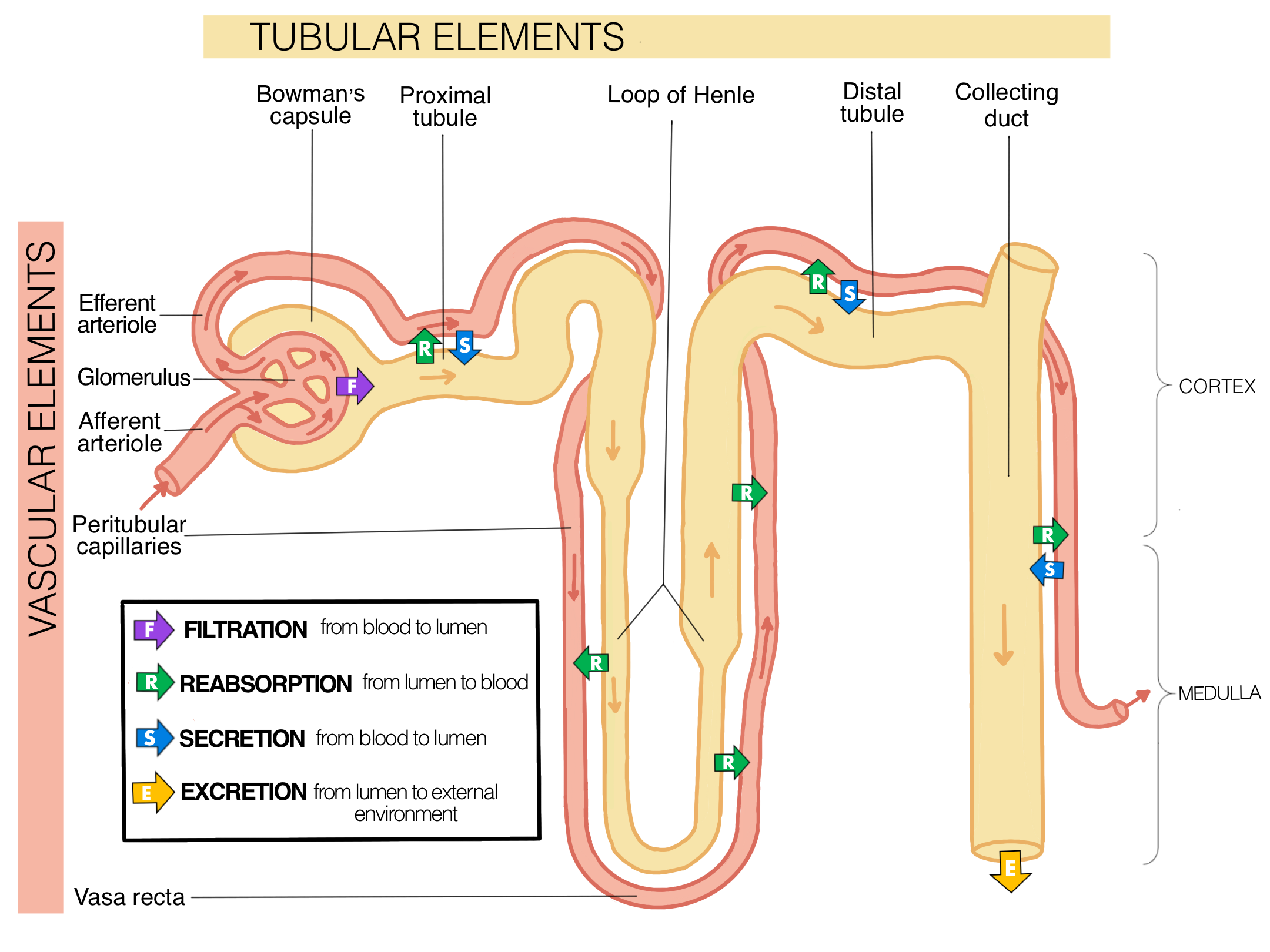
What are the five major sections of the nephron in order that pre-urine flows through them?
Renal corpuscle
Proximal tubule
Loop of Henle
Distal tubule
Collecting duct
What does the renal corpuscle do and how does it do it?
The renal corpuscle is where plasmids are filtered out by the blood (called filtrate or pre-urine)
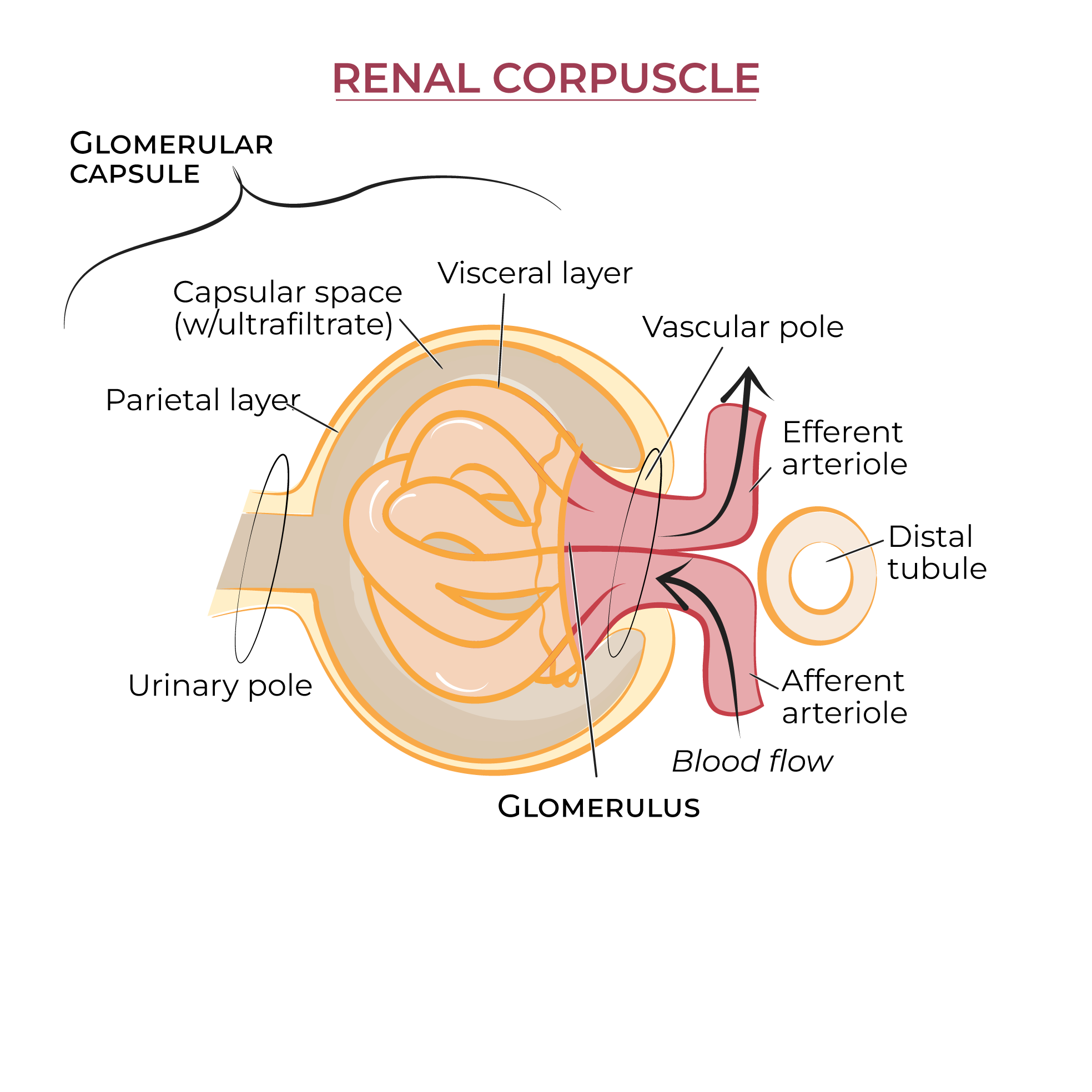
What is the glomerulus and what force “pushes” filtration in the glomerulus?
A network of tiny blood vessels inside the corpuscle
Allows the blood plasmid + small molecules in it to leave

How can the imbalances of blood pressure cause kidney problems?
Long term high blood pressure (hypertension) damages the corpuscle and causes kidney failure
Short term low blood pressure (hypotension) stops the filtration process and allows toxic waste products to build up in the body
What is obligatory reabsorption and where in the nephron does it happen?
Obligatory reabsorption is the process that automatically reabsorbs 90% of pre-urine
Happens in:
Proximal tubule
Loop of Henle
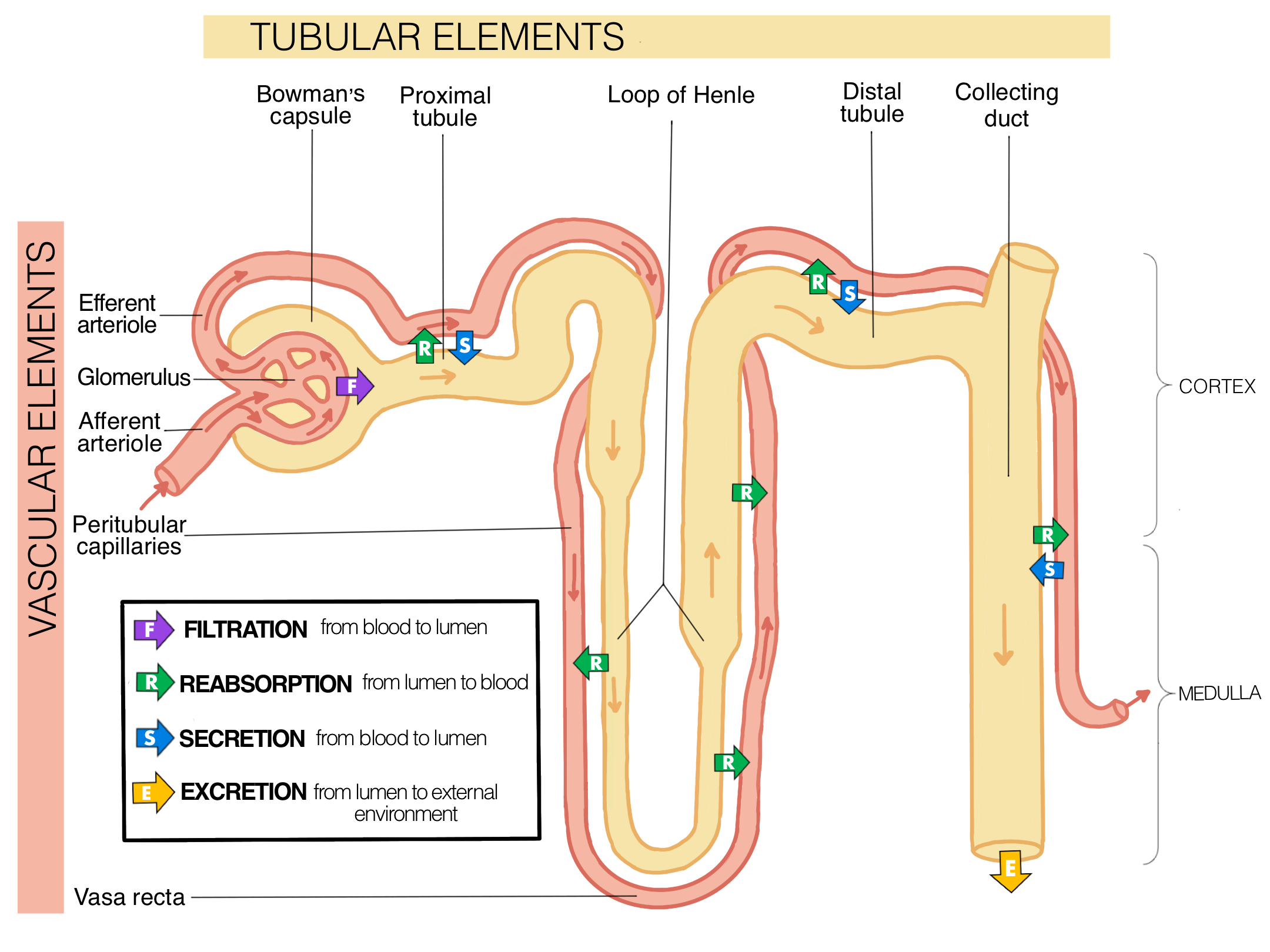
What does the proximal tubule do during obligatory reabsorption? How does it happen?
Proximal tubule
Uses active transport, diffusion, and osmosis to selectively reabsorb 2/3 of all materials in the pre-urine
Reabsorbs some of the water and electrolytes
Reabsorbs all of the nutrients and vitamins
Pre-urine that exits the Proximal tubule contains water, electrolytes, and waste products
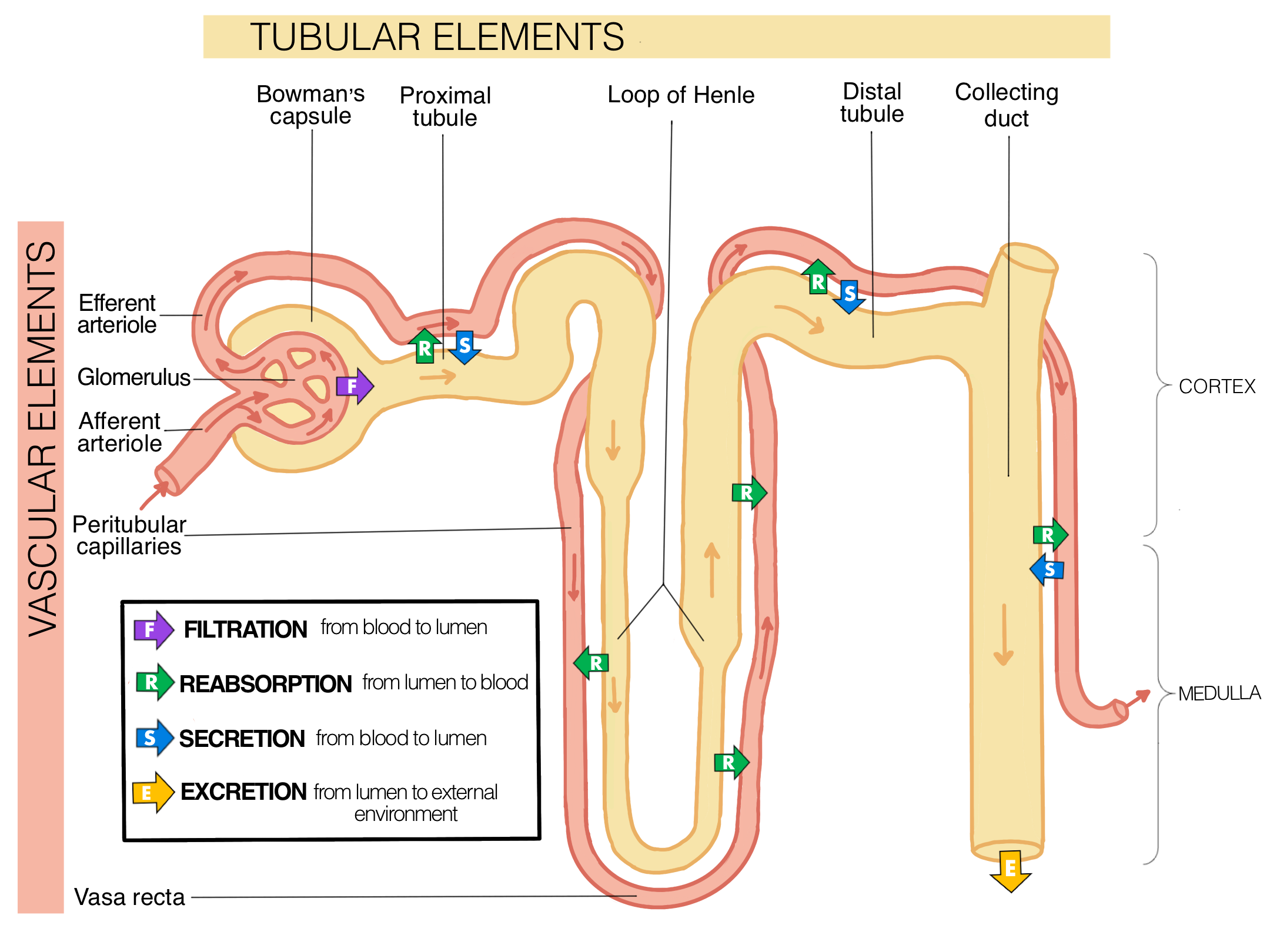
What does the Loop of Henle do during obligatory reabsorption? How does it happen?
Loop of Henle
Uses only diffusion and osmosis to reabsorb water and electrolytes
Uses the medullary gradient instead of using any energy
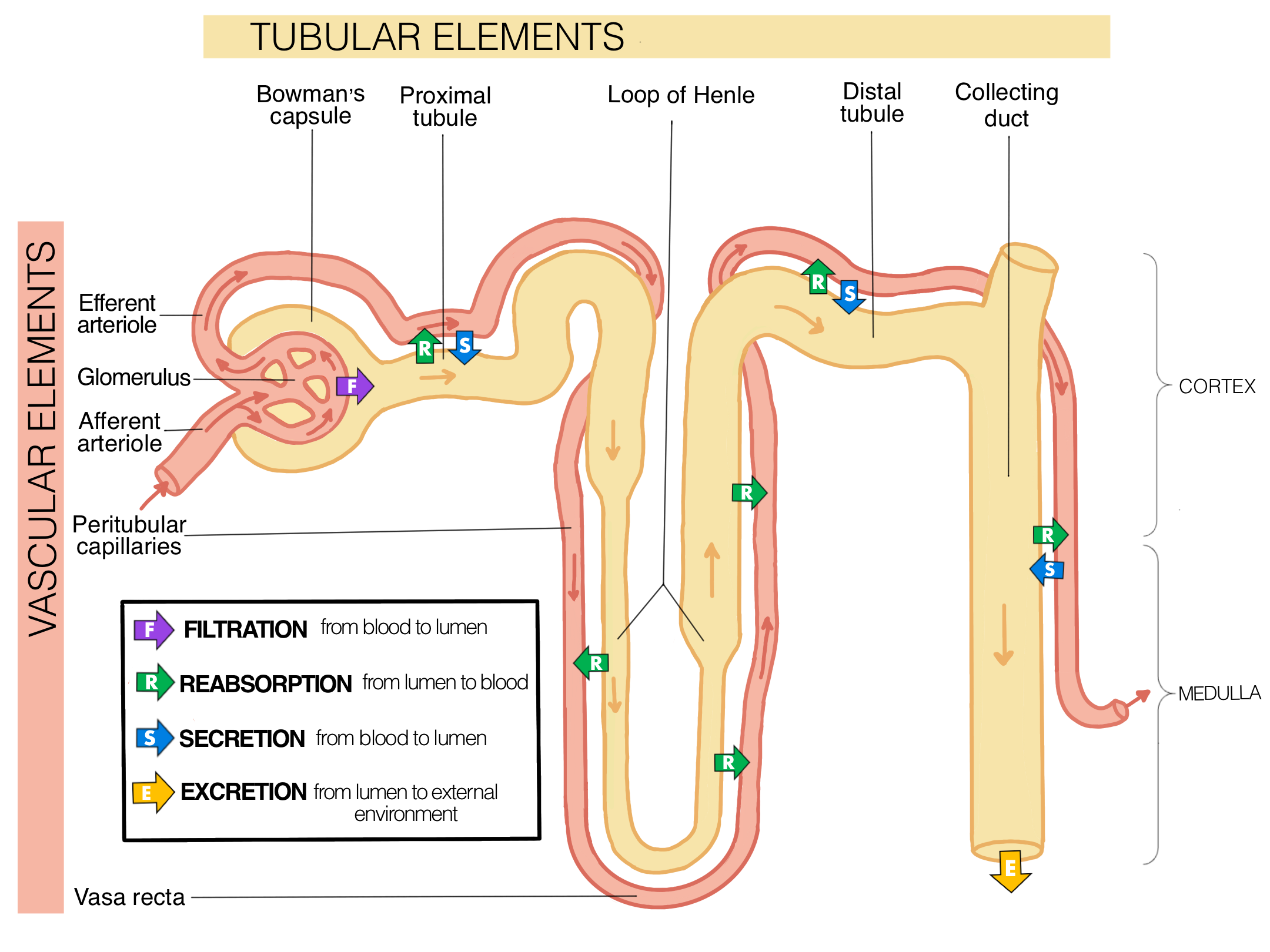
What are the descending limb and ascending limb and how is reabsorption different in each limb?
Descending limb is only permeable to water
Ascending limb is only permeable to electrolytes
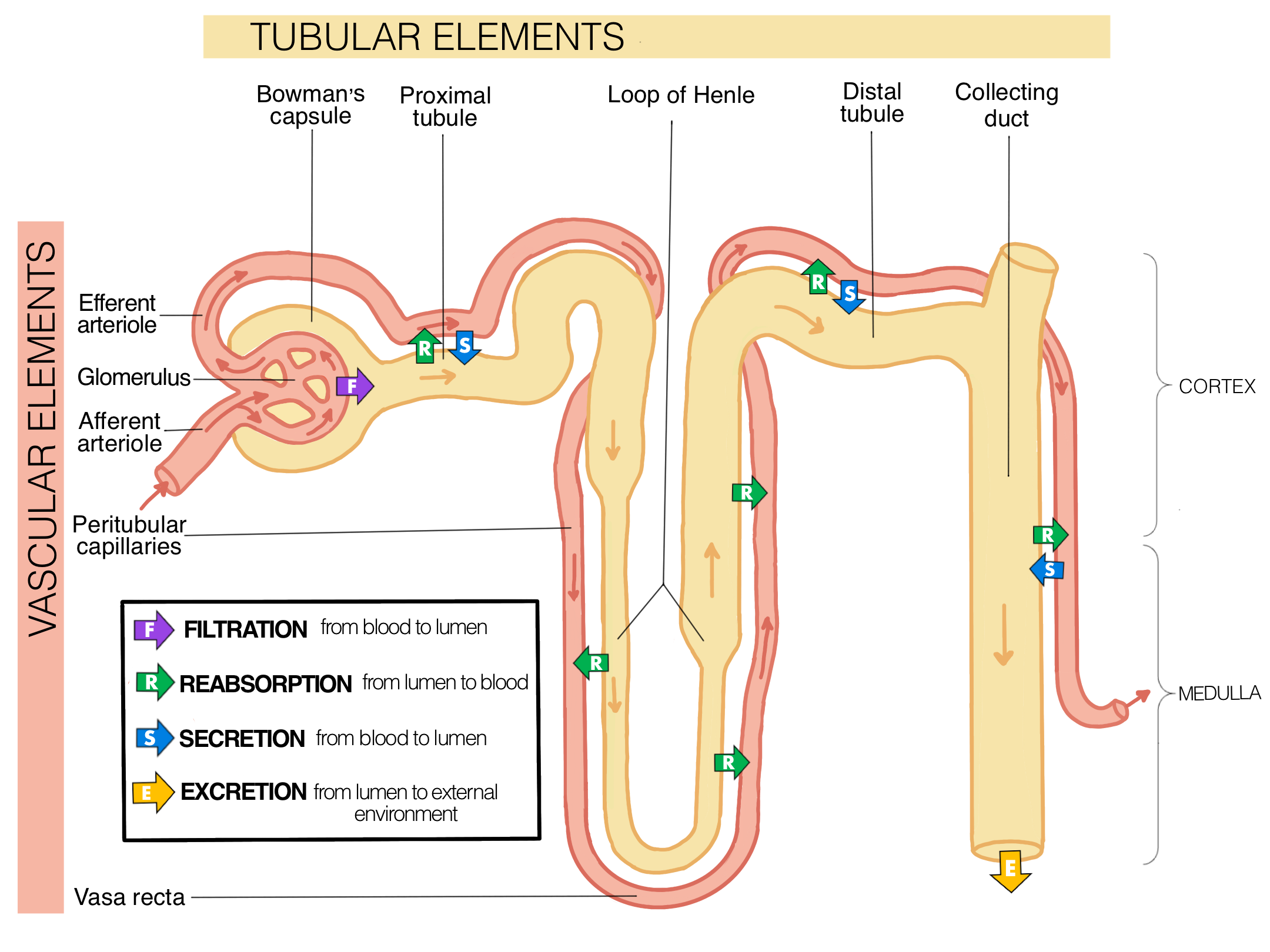
What is regulated reabsorption and where in the nephron does it happen?
The remaining 15-18 liters of pre-urine is regulated by homeostasis
Happens in the:
Distal tubule
Collecting duct
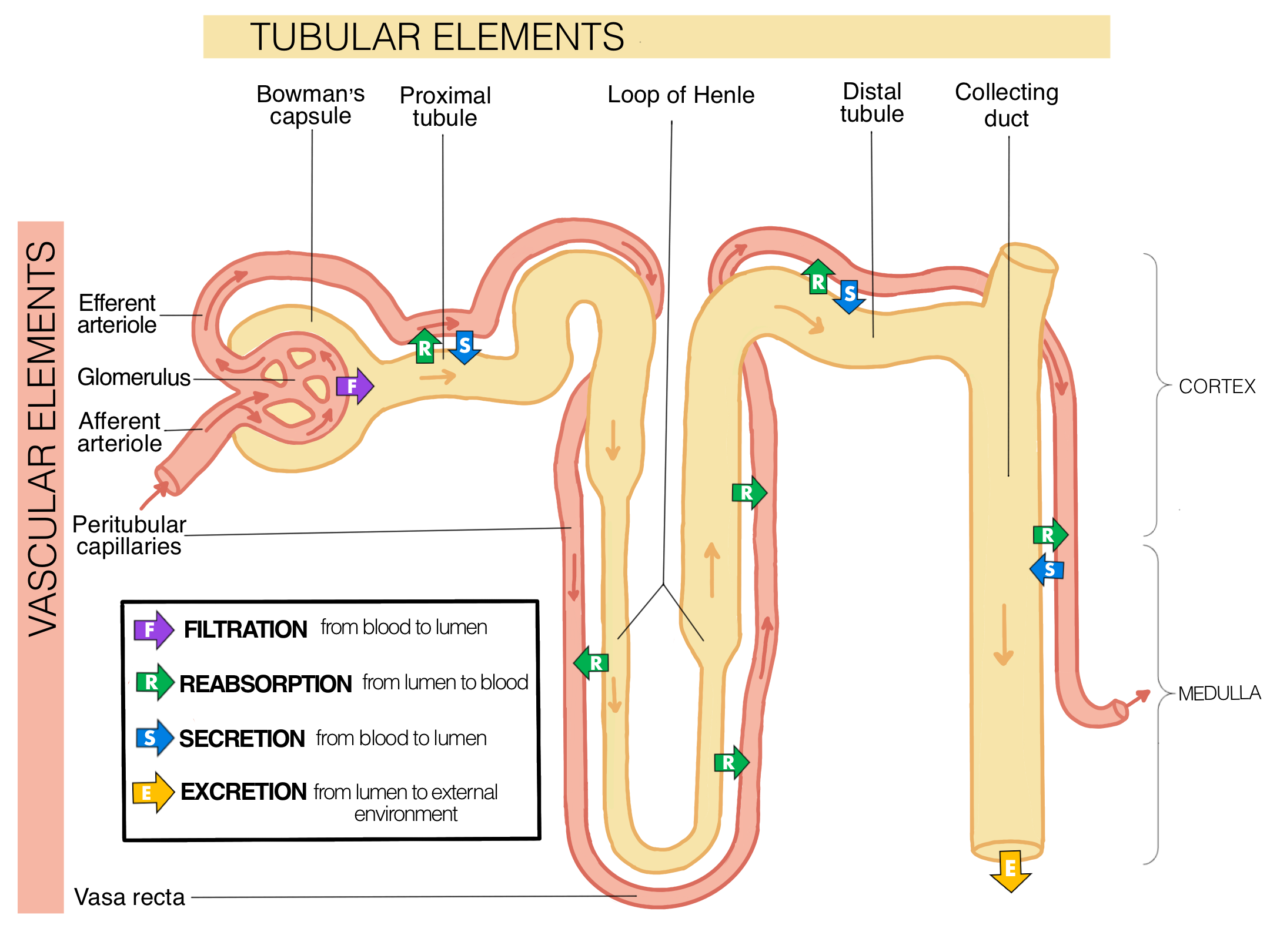
What does the distal tubule do in regulated reabsorption and how is it regulated by aldosterone levels?
The distal tubule reabsorbs sodium and chloride by active transport, how much is reabsorbed is regulated by aldosterone
If sodium levels in the body are low:
A large amount of aldosterone is released
Distal tubule reabsorbs more sodium and chloride
If sodium levels in the body are high:
A small amount of aldosterone is released
Distal tubule reabsorbs less sodium and chloride
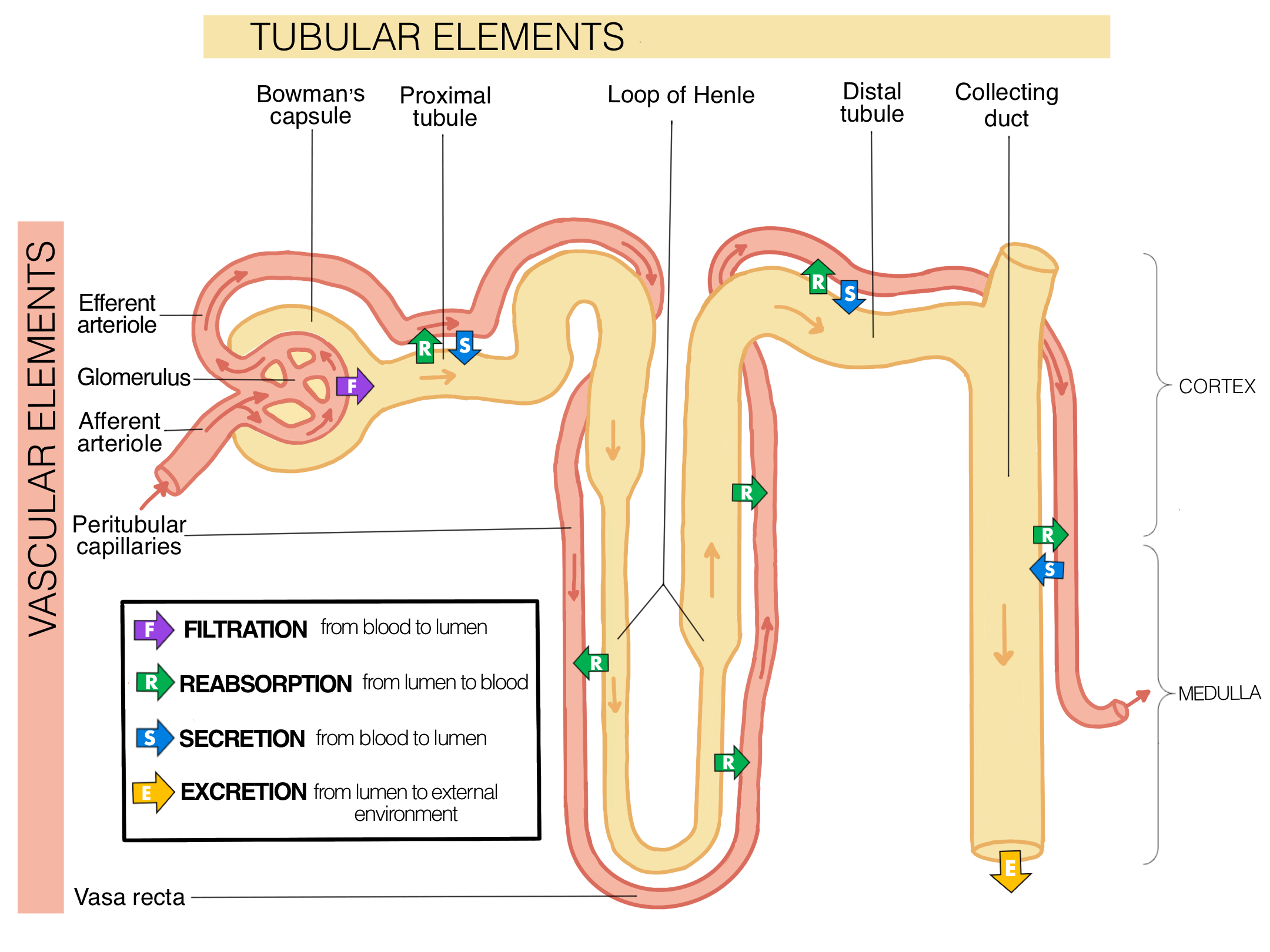
What does the collecting duct do in regulated reabsorption and how is it regulated by ADH levels?
The collecting dust only reabsorbs water, how much is absorbed is regulated by the hormone anti-diuretic hormone (ADH)
If there is a low level of water in the body:
Large amount of ADH is released
Collecting duct reabsorbs more water
If there is a high level of water in the body:
Low amount of ADH is released
Collecting duct reabsorbs less water