Child and Adolescent Psych - Psy 112-030
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Created from notes taken in person at COM
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Fetal origins
Malnutrition or stress during pregnancy impacts a child's development and health later in life.
Ways to reduce stress during pregnancy
Practice relaxation techniques, maintain a healthy lifestyle, and seek support. Consider therapy, avoid harmful substances, and engage in regular exercise.
A method for assessing the health of a newborn between 1 and 5 minutes after birth, scoring 0-2 points in five criteria, where <4 is bad, >7 is good.
A = Appearance (skin color)
P = Pulse (heart rate)
G = Grimace response (reflexes)
A = Activity (muscle tone)
R = Respiration (breathing effort)
Brazelton’s Neonatal Assessment
Newborns have 9 months experience when born
Newborns communicate through reflexes and behaviors
Newborns are capable of controlling their environments
Low birthweight
less than 5.5 pounds, associated with various developmental delays and health risks:
increased vulnerability to infections, respiratory issues, and long-term cognitive impairments.
Fetal Alcohol Syndrome Disorder (FASD) and Opiates
Symptoms of FASD: underdeveloped brain, lungs, small eyes and other facial differences.
Later in life: behavioral issues due to brains function differently and have low impulse control, learning disabilities, physical ailments. High rate of FASD in prison system.
Opiate exposure can result in stillbirth, death, newborn withdrawal, foster care or adoption, development delays, facial differences. Lack of attachment with mother leads to learning and behavioral issues.
Contact comfort
Nurturing through touch that fosters emotional development and attachment in infants.
Research of Harry and Margaret Harlow
Experiments with rhesus monkeys showed that comfort and security in maternal bonding are more important than nourishment for emotional development and attachment.
The ability to understand and share the feelings of another person.
“I understand you’re hurt”
Object Relations Theory
Ainsworth, Bowlby
The bond you form with your mother is the basis for all future bonds in life.
Mom should be a secure base and haven of safety
Mom should be sensitive and responsive
Long term impact of lack of attachment
How do love, self esteem develop?
Bids for attention
affects relationships, self esteem, overall well being
Enhanced bonding
The act of a caregiver verbally and nonverbally reflecting the emotions and actions of a child, facilitating emotional nurturing and attachment.
Risks for opiate-addicted babies
include low birth weight, developmental delays, and higher rates of stillbirth.
5 characteristics of Attachment
cry-response ratio = the balance between crying and the caregiver's response to it.
secure base / close bodily contact = the ability to explore the environment while knowing a caregiver is nearby.
safe haven = the ability to return to a caregiver for comfort and safety.
separation distress = the ability to seek comfort and support from caregivers during distress.
relationships = child cooperation w/ mom, building trust
4 types of attachment
Secure, anxious-ambivalent, anxious-avoidant, disorganized.
These styles reflect how children relate to their caregivers and can influence their emotional and social development.
stages of emotional deprivation
John Bowlby identified:
protest
despair
detachment
These stages describe the emotional responses of children when separated from their primary caregivers.
long term effects of lack of attachment (5)
emotional isolation
mistrust of others
no spiritual connections
try to get needs met in other ways
poor self esteem
poor emotional regulation skills
lack of meaning, purpose, direction in life
solutions to lack of attachment
connect with self
connect with others
be more open
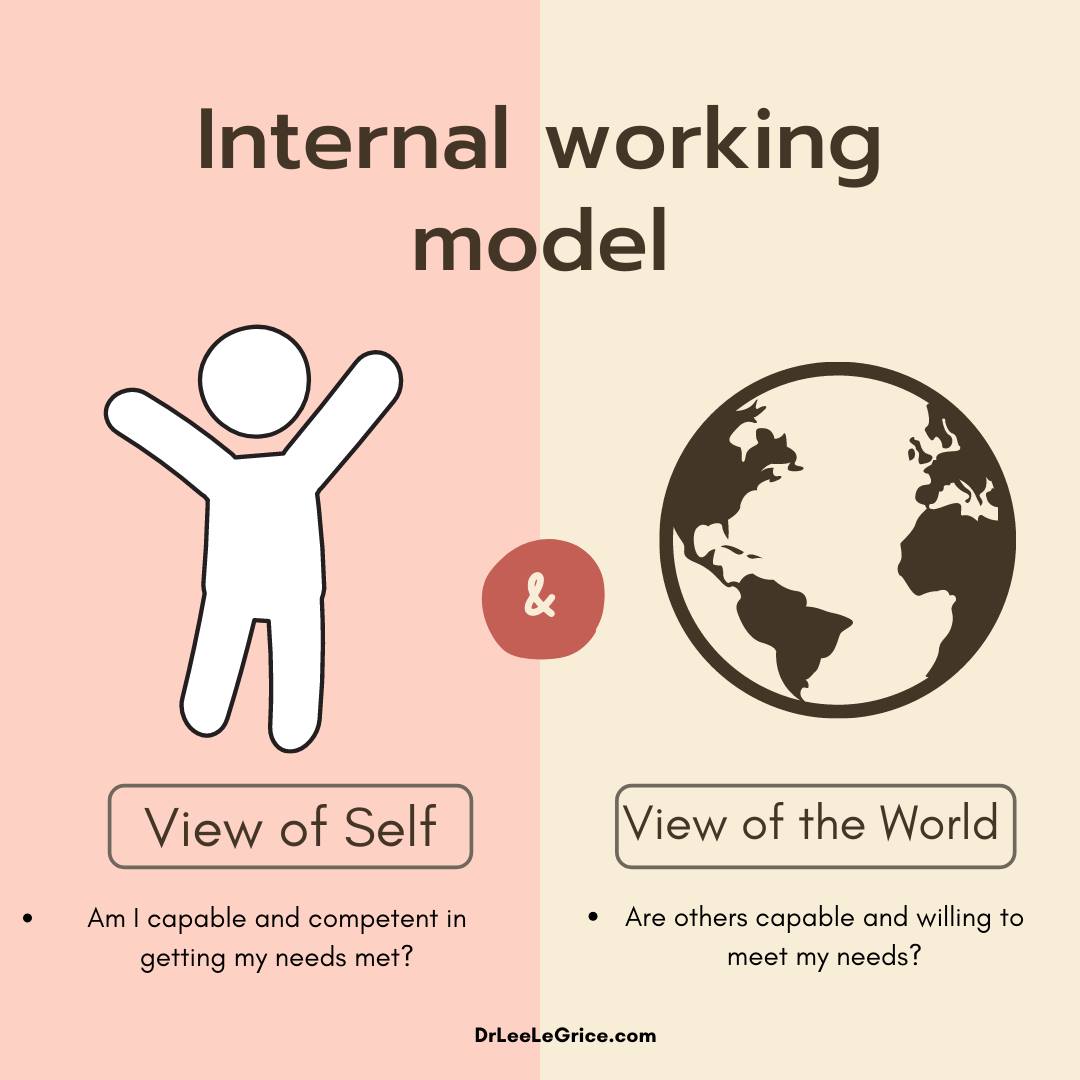
internal working model (Bowlby)
internal representation of our thoughts, feelings, goals, & expectations, based on early attachments for navigating emotional and social world
Adverse Childhood Experiences - ACEs impact on kids
ACEs are:
Abuse
Neglect
Household Dysfunction
brain development
mental health
physical health
social and behavioral issues
long-term effects can be cumulative, >4 suicide & addiction 12 x more likely , >6 20 yrs shorter life span
sensorimotor stage of cognitive development (Piaget)
ages 0-2
sensorimotor: where infants learn about the world through their senses and actions. Key milestones include object permanence and separation anxiety.
simple reflexes - grasping, sucking, turning head
primary circular reactions - noticing own body, and repeating pleasurable actions
secondary circular reactions - noticing the effects of their actions on the environment: shaking a rattle to make a sound.
object permanence & importance
The understanding that objects and people continue to exist even when they cannot be seen.
Helps child develop emotional security
Helps avoid separation anxiety/abandonment
The Four Horsemen of the Apocalypse in relationships, identified by John Gottman
negative communication patterns that can predict relationship breakdown:
criticism
contempt
defensiveness
stonewalling

John Gottman parenting styles
Parenting styles to help children develop emotionally
Dismissing
disengage
ignore child’s feelings
wants neg emo to go away quickly
Disapproving
judge & criticize neg emo
focus on conformity & good bhvr
neg emo make people weak
Laissez-Faire (Lazy)
accept all emo
little guidance
no limits
Emotional Coach
Aware of Child's Emo
Emo as an Opportunity for Connection and Teaching
Listen w/Empathy; Validate Feelings
Help Label Their Emotions
Set Limits & Explore how to Solve Problem

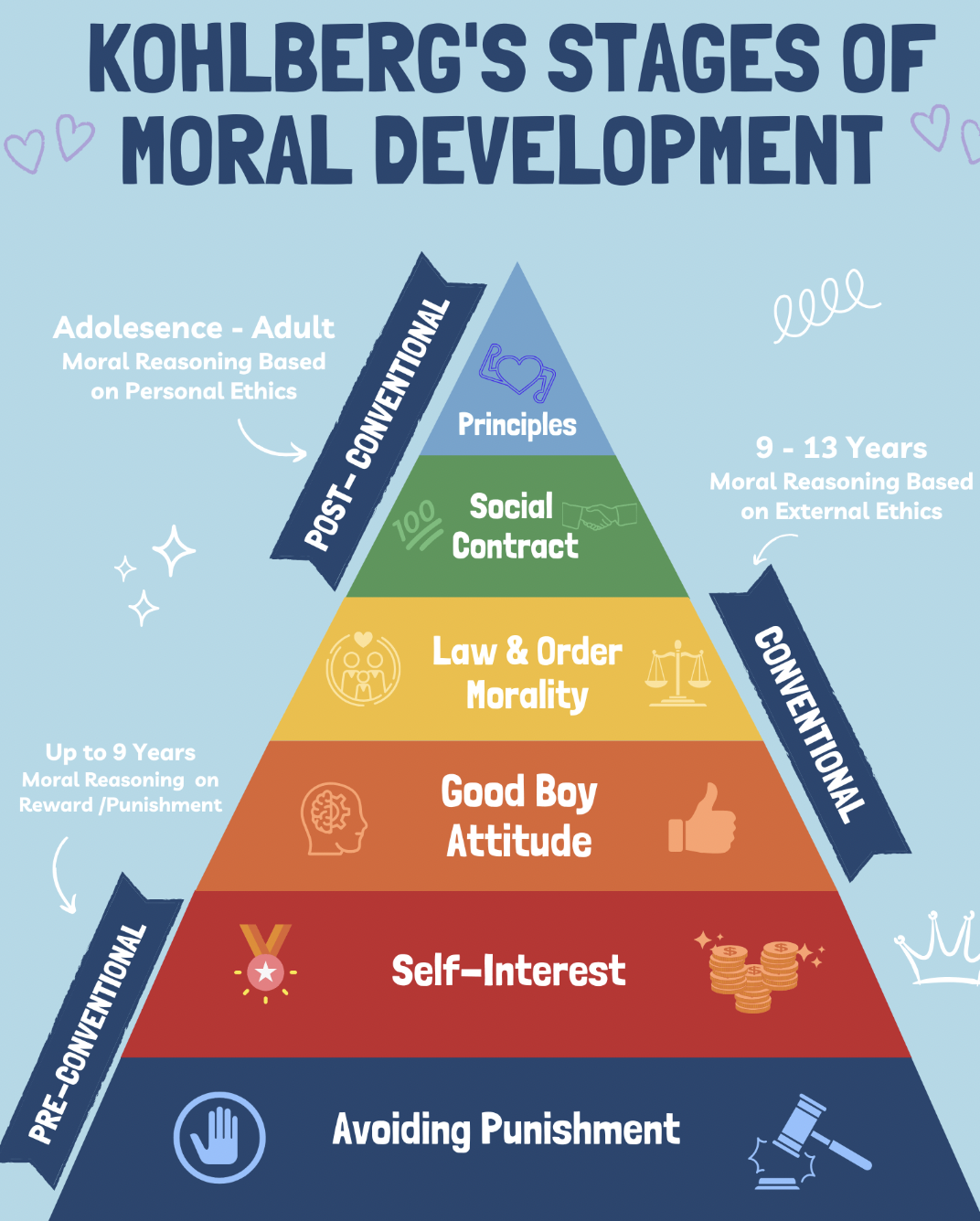
Stages of Moral Development - Kohlberg
kid’s understanding of right and wrong grows with the them
punishment
- obedience, avoiding punishment
pleasure-seeking
- right is what helps me. “what’s in it for me?”
good boy/girl
- want to be seen as nice, please parents/family
authority
- everyone should follow laws/rules, like red lights
Explain dimensions of child-rearing.
power assertion
- control, yell, hit, bully, “because I said so”
withdrawal of love
- leaves or threatens to leave, passive aggressive, “silent treatment”
induction
- teaches empathy, “explainer”
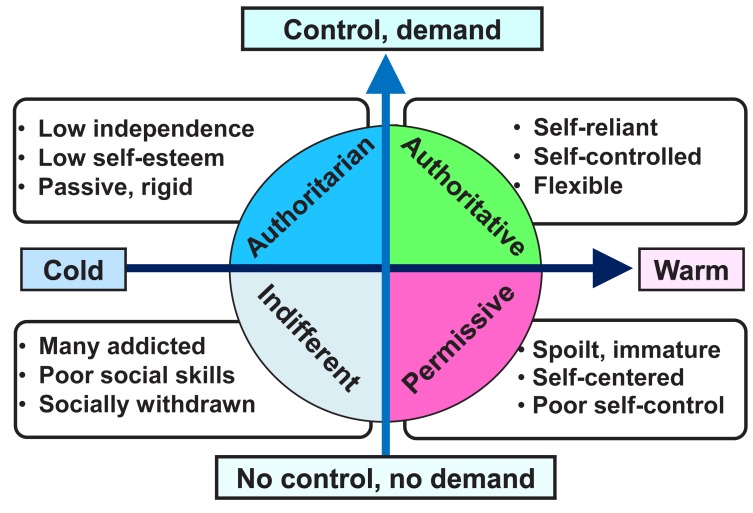
Parenting Styles in Moral Development - Baurind
balance rules and love
amount of involvement and explaining
AUPA
Authoritarian:
Rules with no explanation.
"my way or the highway"
- low independence, low self esteem, passive, rigidUninvolved: checked out, very few rules.
"hands-off"
- many addicted, low social skills, withdrawnPermissive: want to be liked, too easygoing.
"friend"
- spoilt, immature, self-centered, poor self controlAuthoritative: clear rules and expectations, explains reasons, open to discussion
"best of both worlds”
- self control, self reliant, flexible
Explain Pre-operational stage (Piaget)
ages 2-7
symbolic thought
- language has meaning
- imaginary play, gives dolls life
egocentrism
- unable to take another perspective
conservation begins
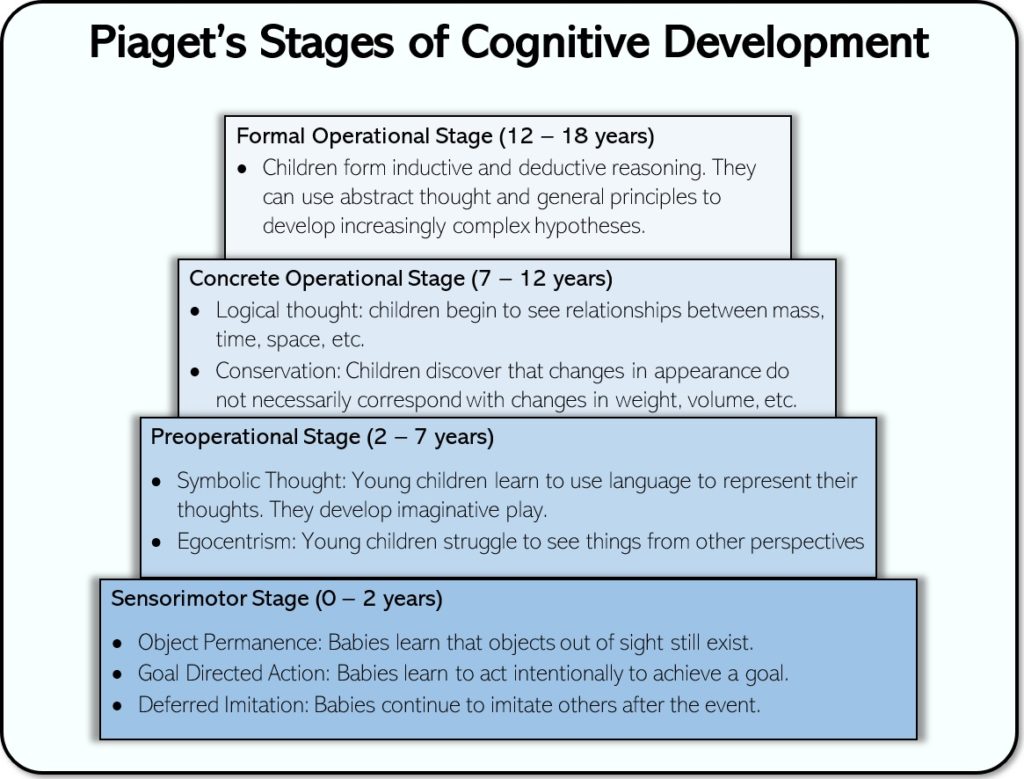
Explain Concrete Operational Stage (Piaget)
ages 7-11
basic skills acquired
logical thought: see relationships in mass, time, space, etc
conservation: change in appearance does not always affect weight, volume, etc
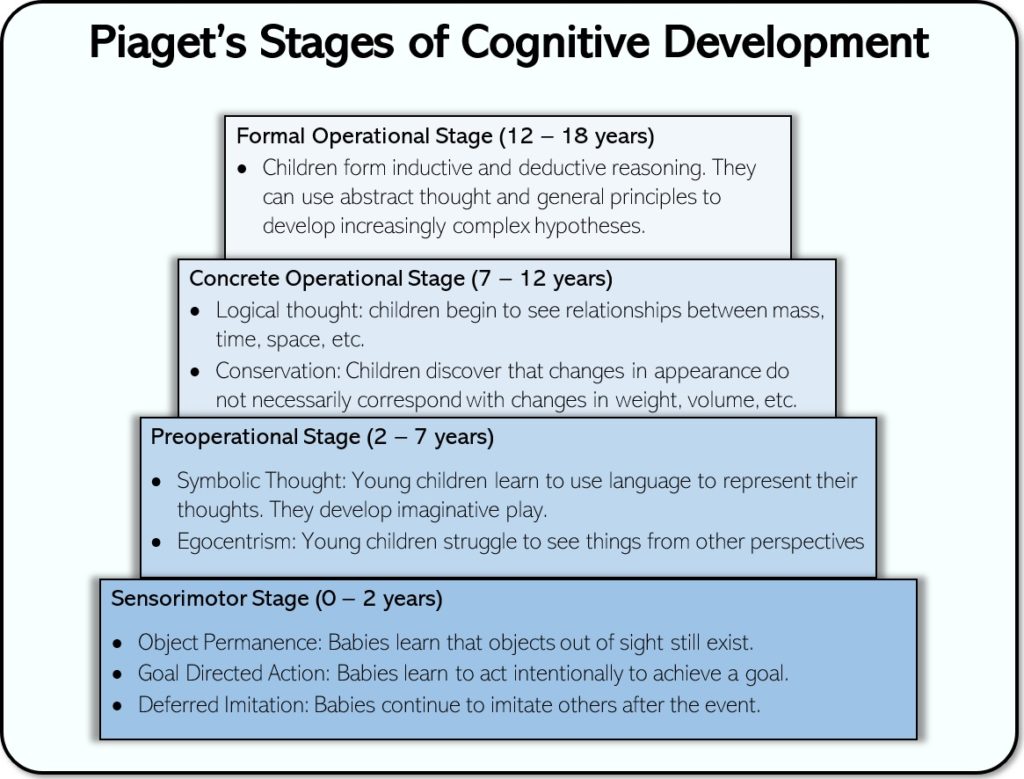
Explain Formal Operations Stage (Piaget)
ages 12+
can use abstract thought to form general principles, hypotheticals
Explain Vygotsky’s Work (4 points)
PLAY-LANGUAGE-SPEECH-CONTEXT
Play helps emotional regulation
Language is key to development
Outer speech becomes inner speech
Development tied to social context
Explain ZPD and scaffolding
mastered tasks = learner can do without help
ZPD = learner can do with help
beyond reach = cannot do
scaffold = concept, object, or support from adult or skilled peer to help child progress to mastery and establish new level of independence
Explain Fixed vs Growth Mindset
fixed = believe abilities are innate and unchangeable
growth = believe abilities can be developed and improved over time
How to increase Emotional Regulation (3 bullets)
name it - tame it. understand emotions
work on impulse control: diet, exercise, sleep
many feelings communicate a need. What is the need?
Peer Pressure (4 Types)
DINP
Direct
- hands a drink
- makes a sexual advance
Indirect
- go along with the crowd
Negative
- asking someone to go against family values/morals
Positive
- group influences someone in a positive way “let’s not drink during the season”

Explain ADHD and Treatment
symptoms for 6 months, in 2 settings
Inattention
- fail to pay attention
- don’t finish things
- lose things often
- avoid difficult tasks
Hyperactivity
- fidget often
- leave seat, on the go
- talk a lot
Impulsivity
- blurt
- can’t wait turn
- interrupt
MYDEBT: meditation, yoga, diet, exercise, build social skills, therapy, then meds
How might social media impact development? Gaming?
depression, anxiety, body dysmorphia, ADHD symptoms
Gaming Disorder
like other types of addiction:
lack of control
compulsion to game, despite negative consequences
deny how much they play
use it to escape
Conduct Disorder and Treatment
BAD-AIR:
Bully (fight, rape, etc)
Aggression
Destruction of property
Arson
In Legal system
Rule or law breaking
TEPET:
token economy, parent education, therapy