Ch.2: Anatomical References Comprehensive Review (Lessons 1-3)
1/121
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Body planes, directions, cavities, quadrants and regions
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|

122 Terms
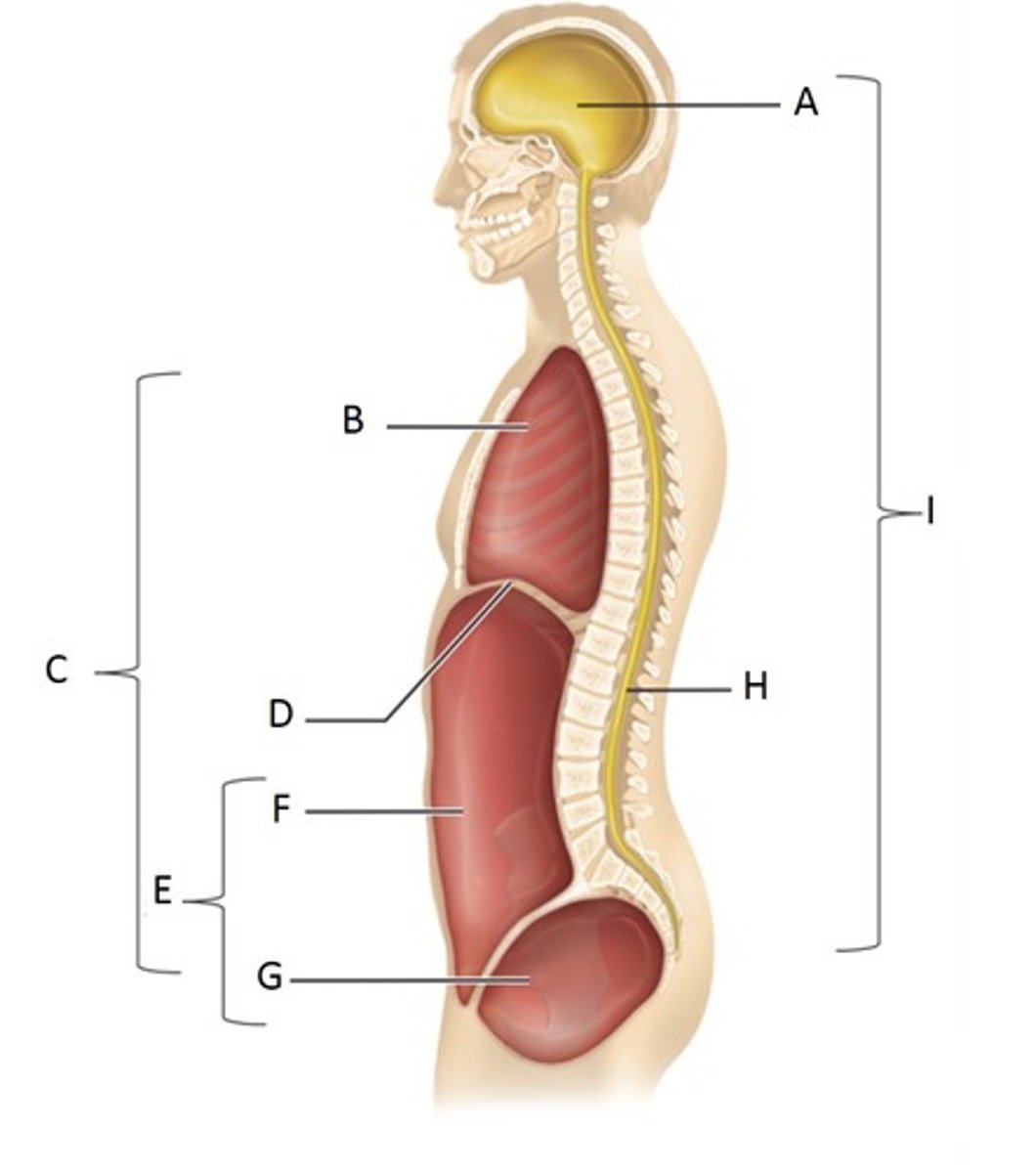
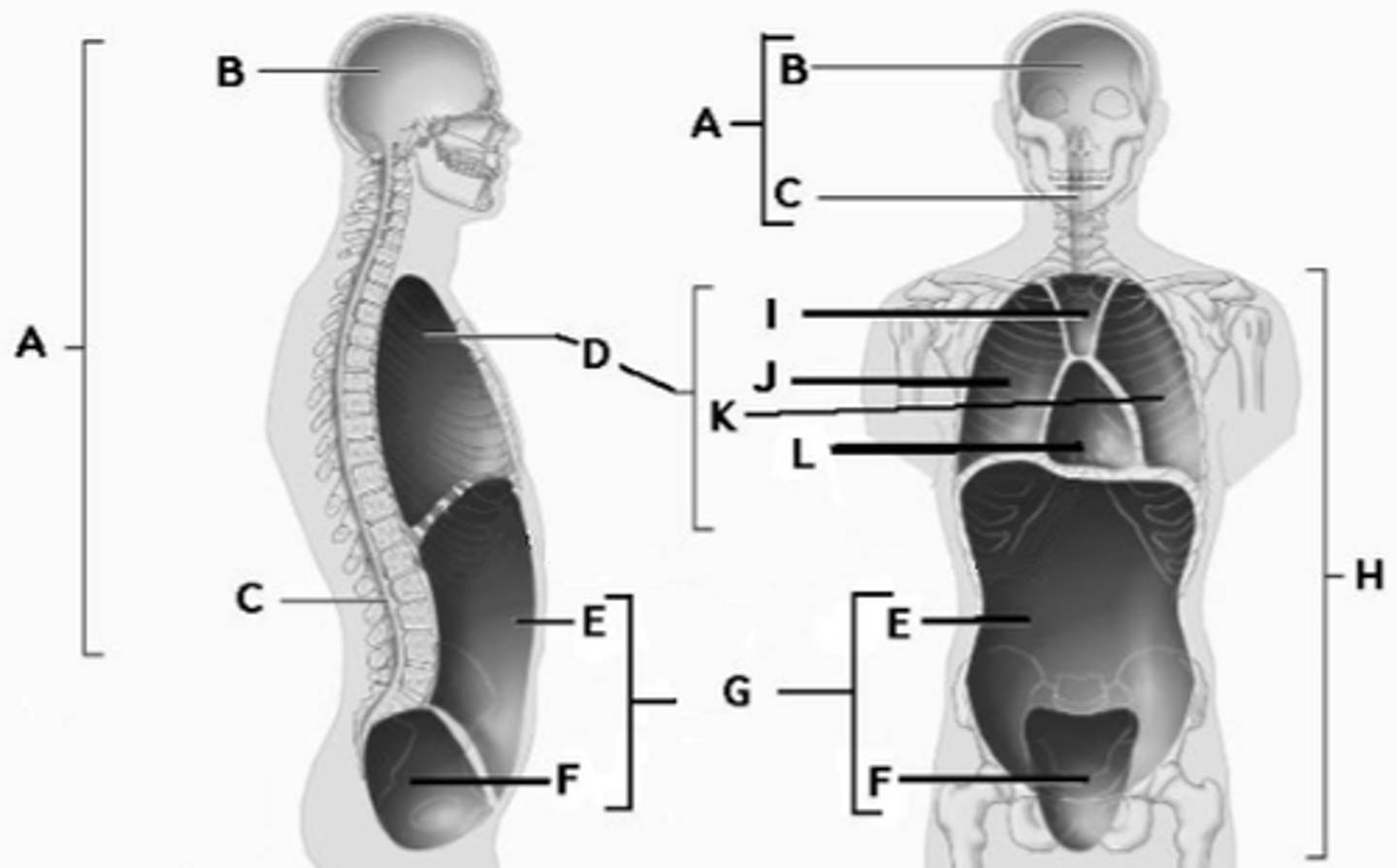
Cranial Cavity
A
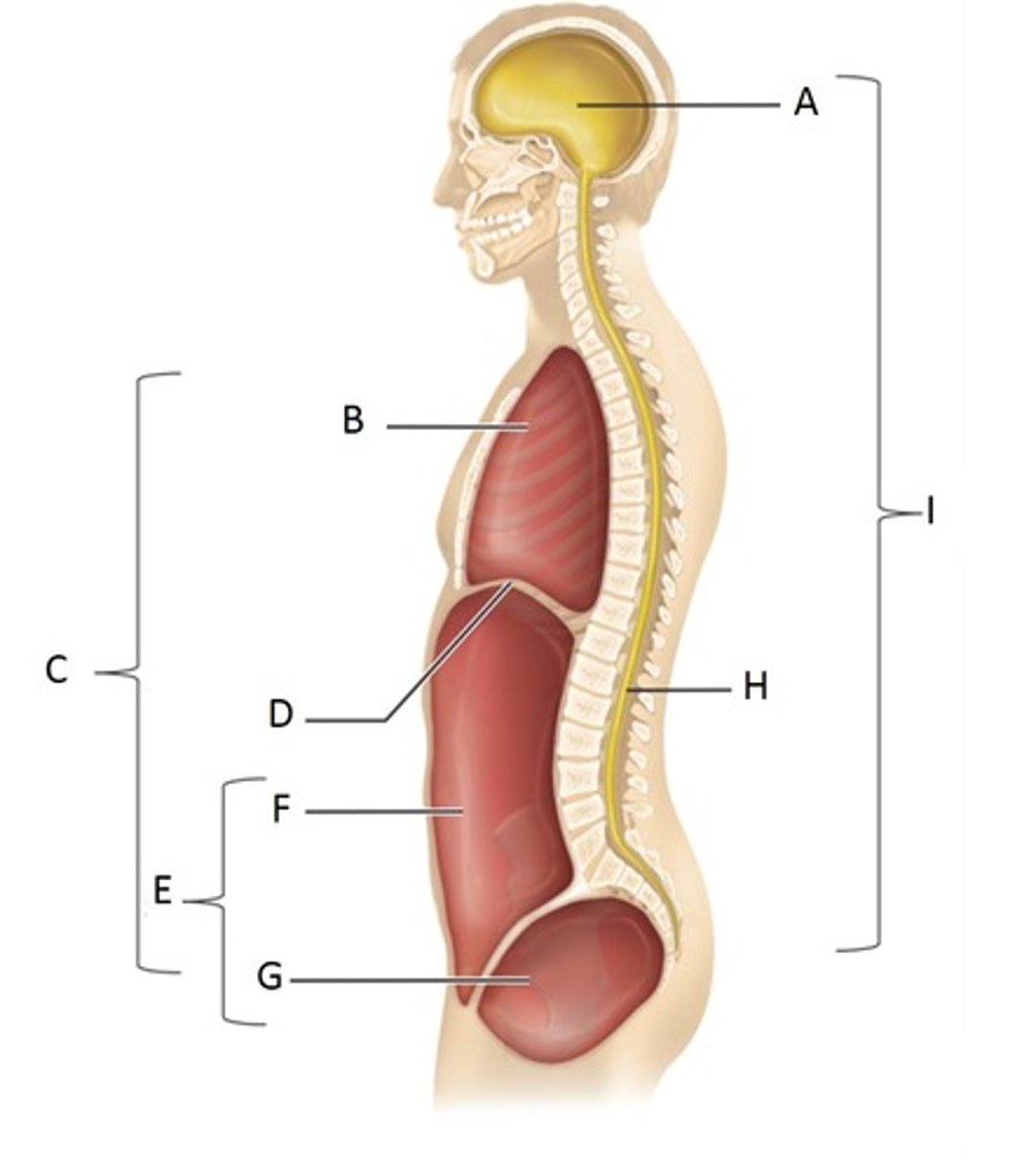
Thoracic Cavity
B
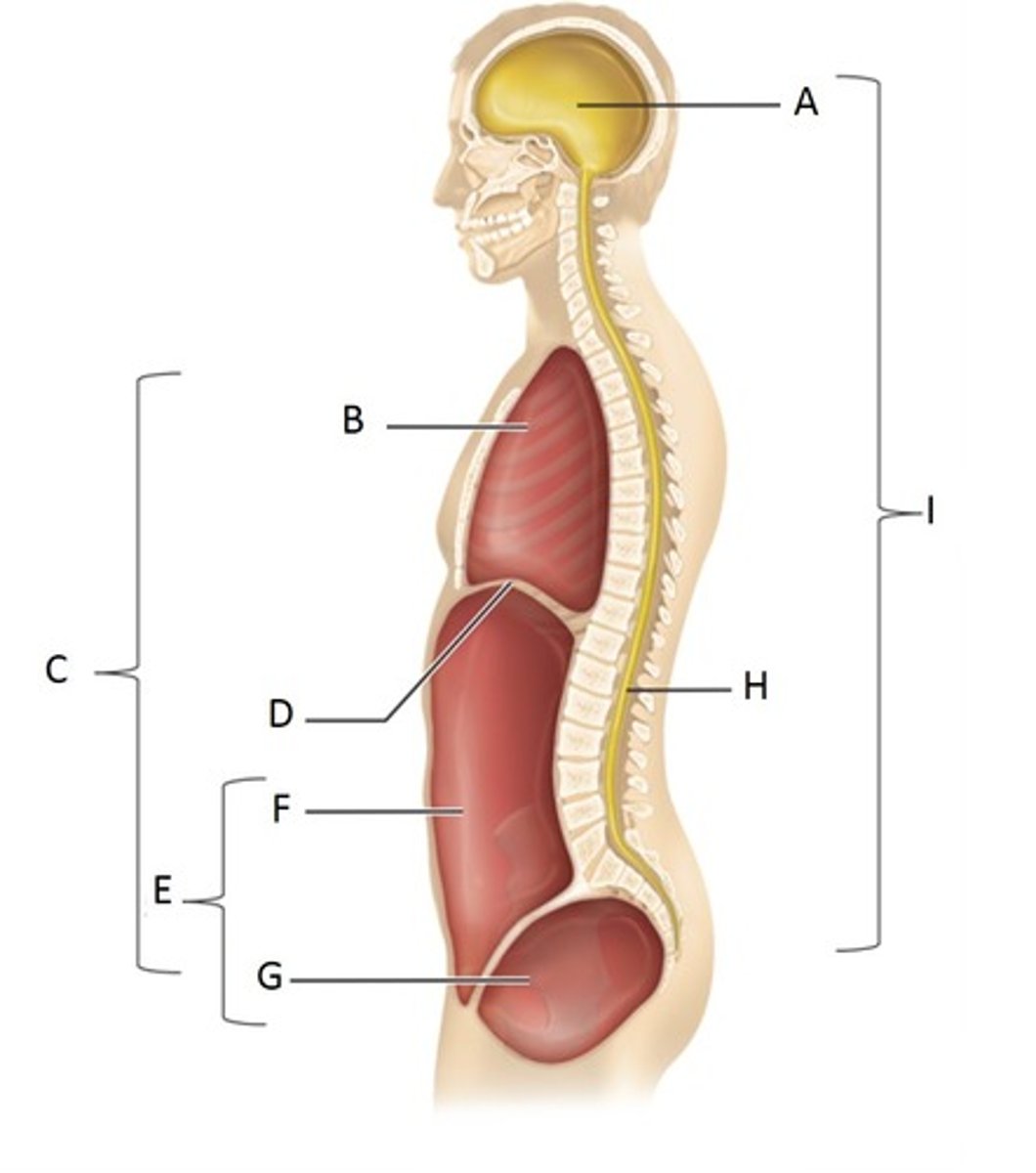
Ventral Cavity
C
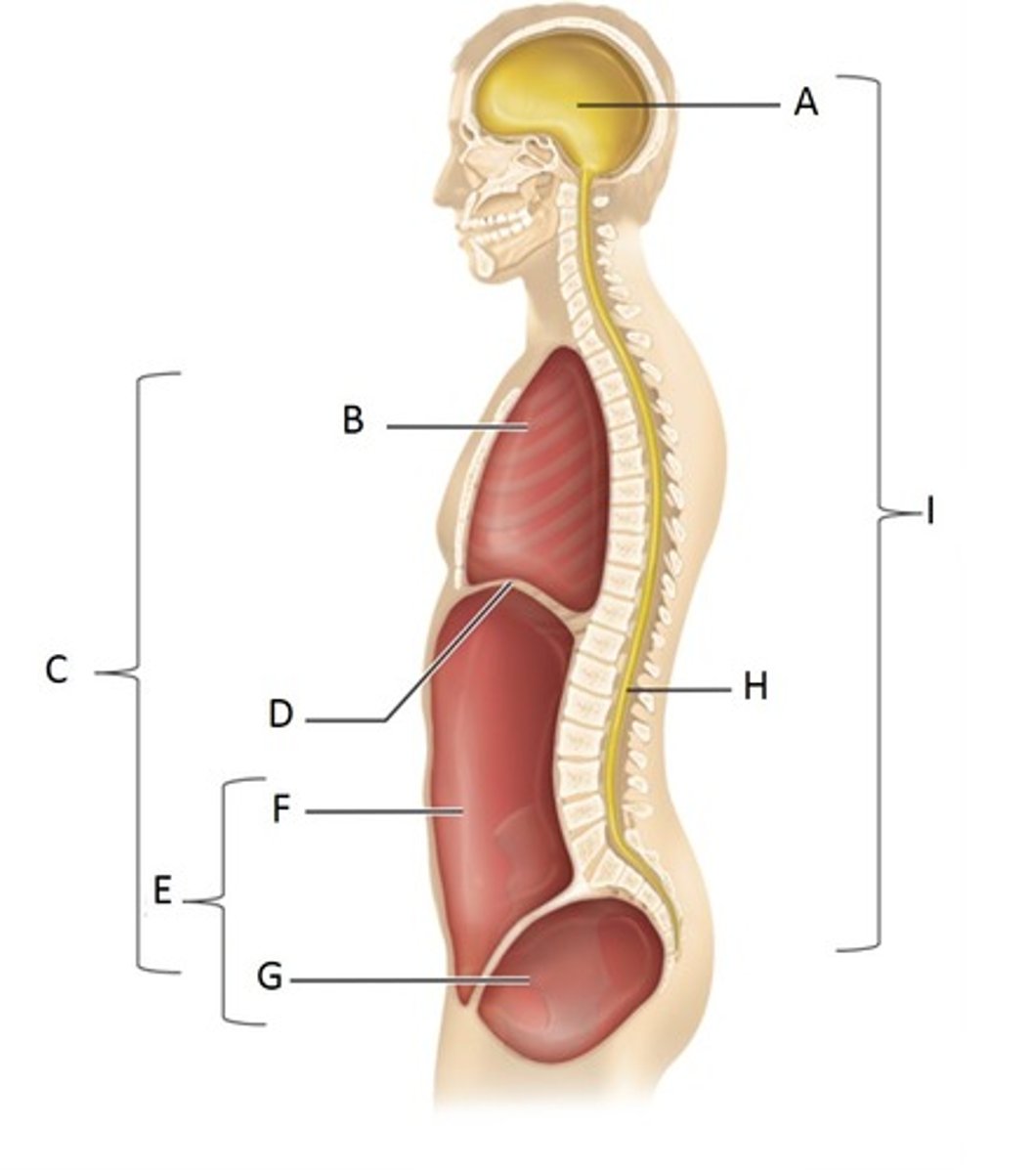
Diaphragm
D
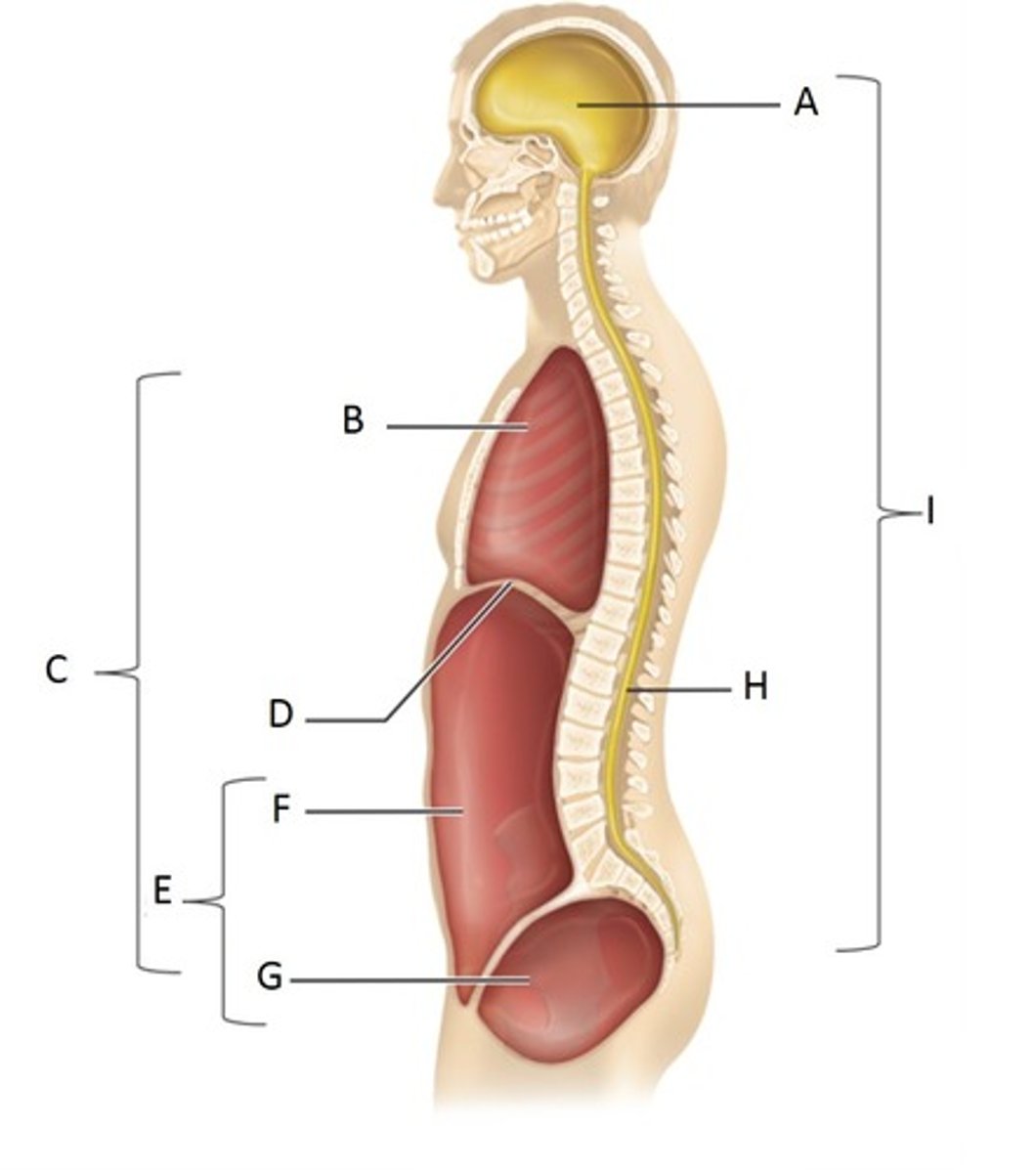
Abdominopelvic Cavity
E
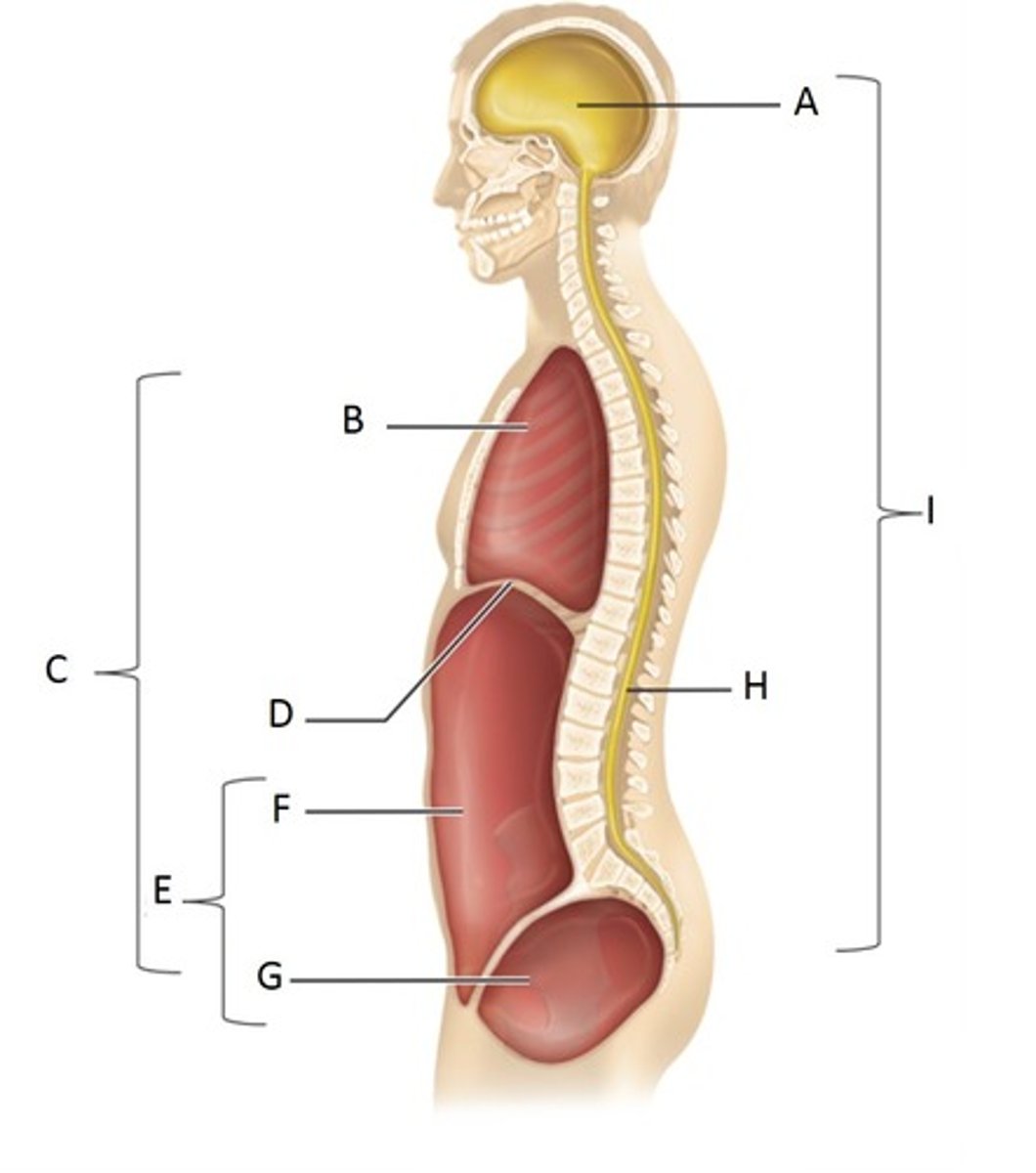
Abdominal Cavity
F
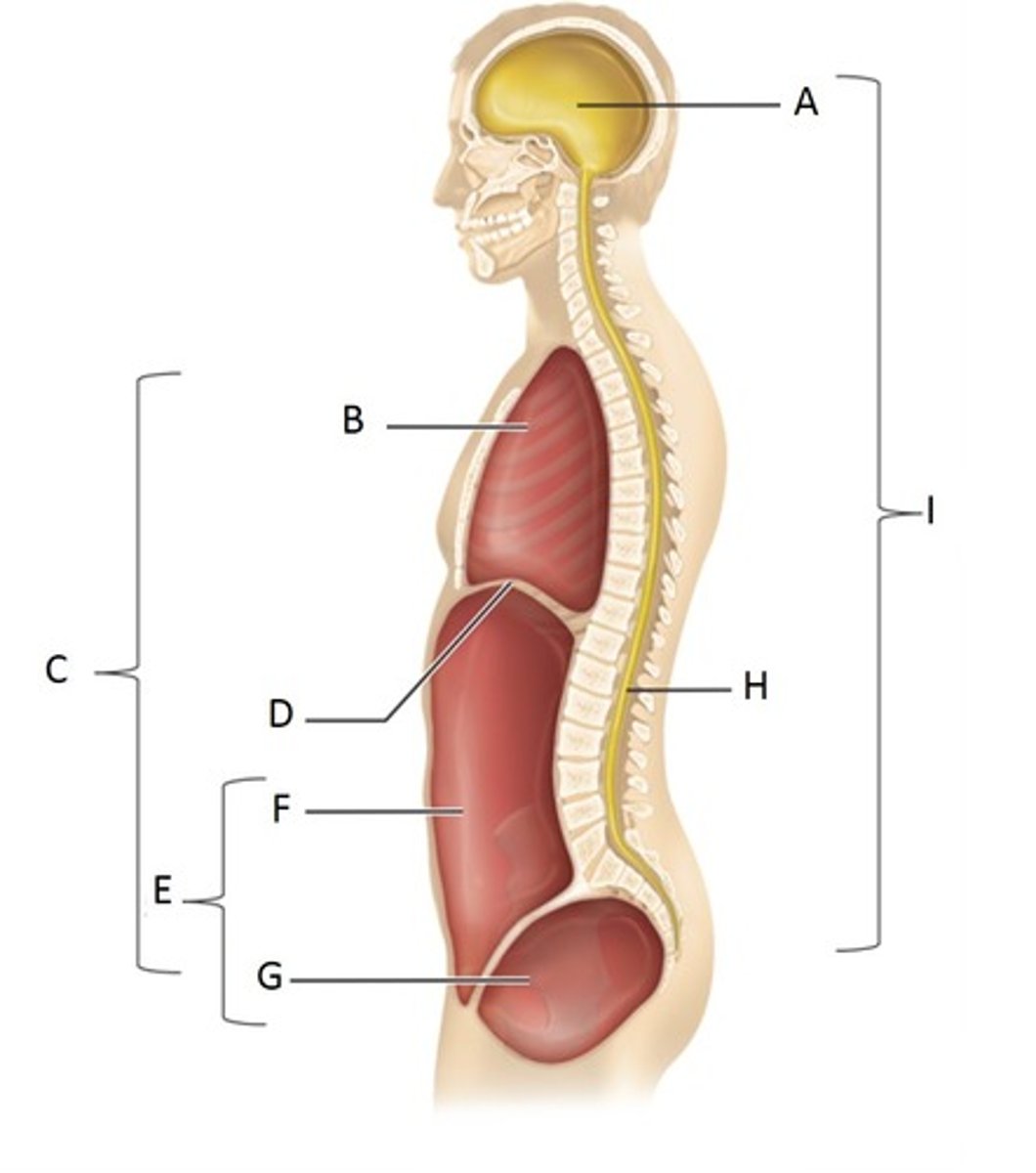
Pelvic Cavity
G
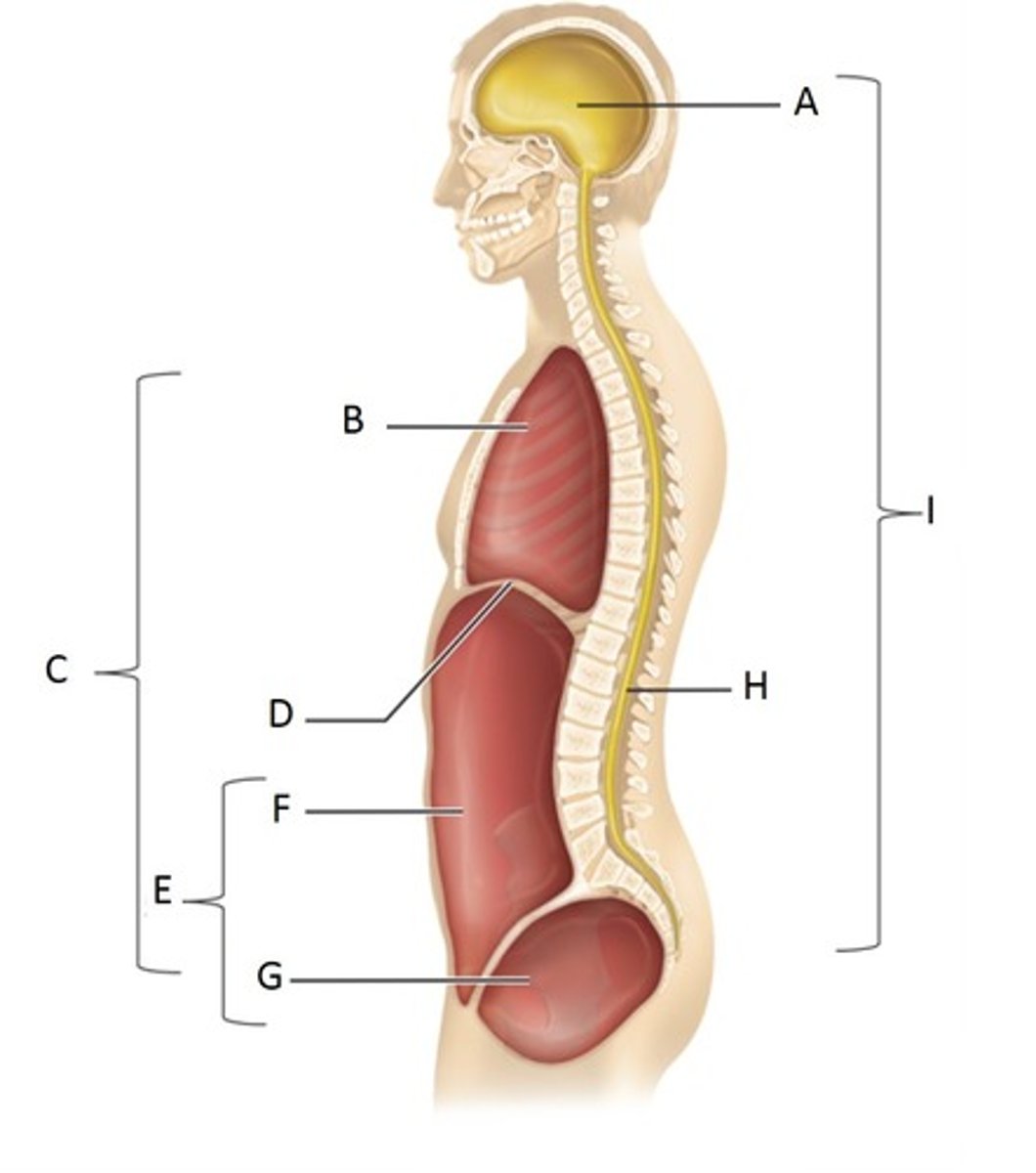
Vertebral (spinal) cavity
H
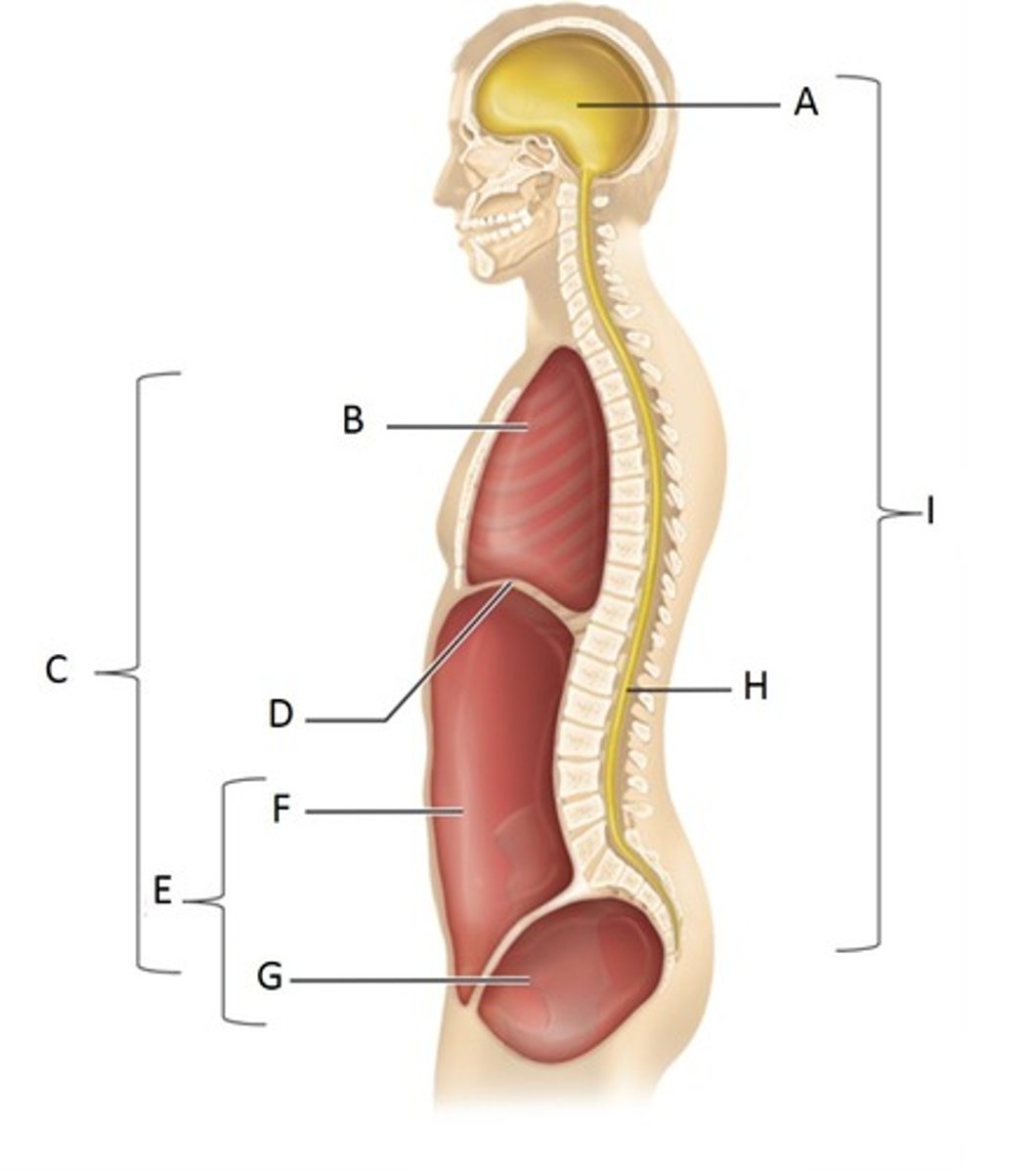
Dorsal cavity
I
Pleural Cavity
B
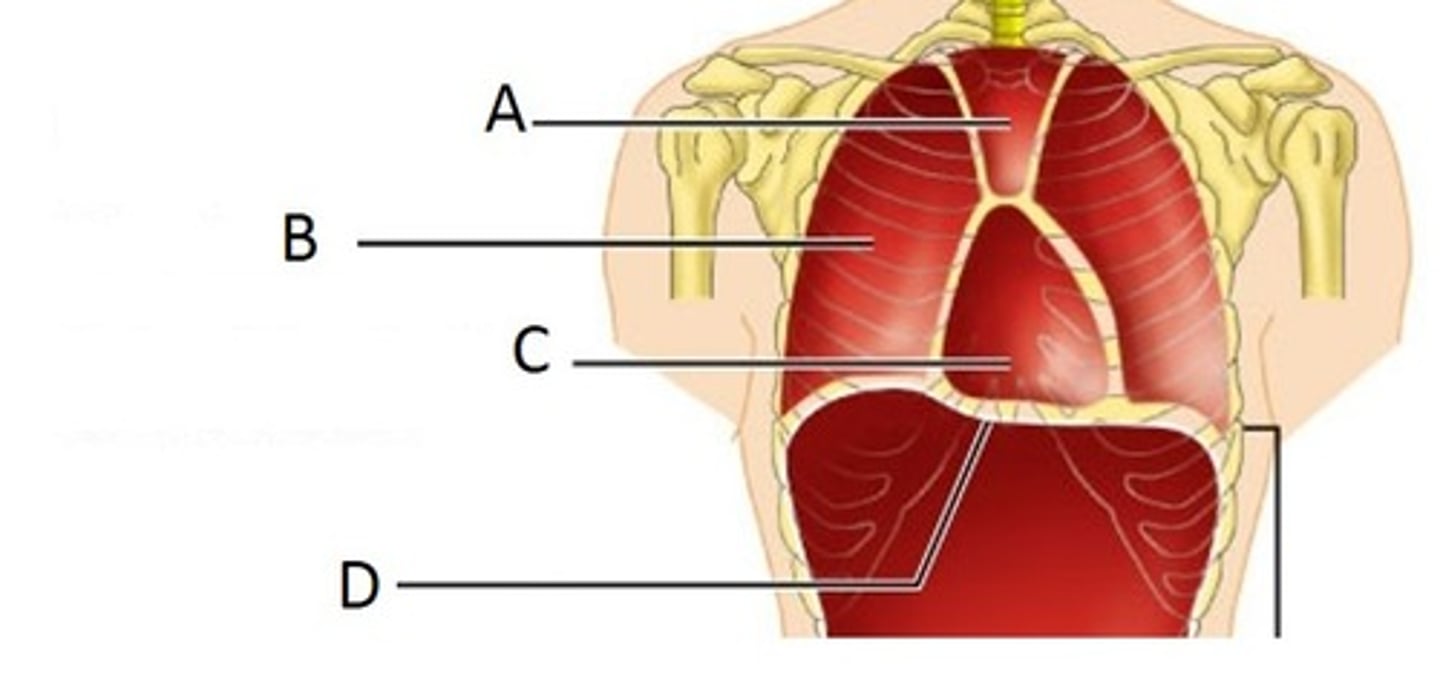
Pericardial Cavity
C
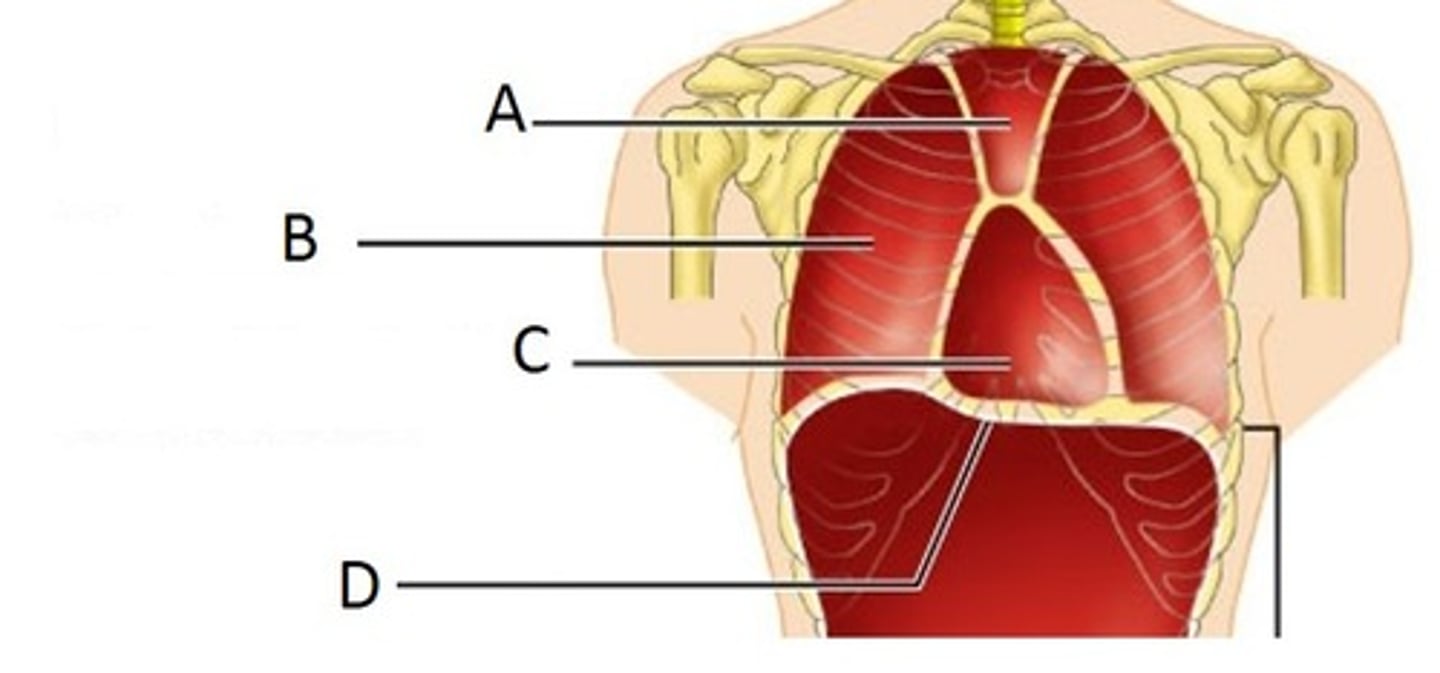
Diaphragm
D
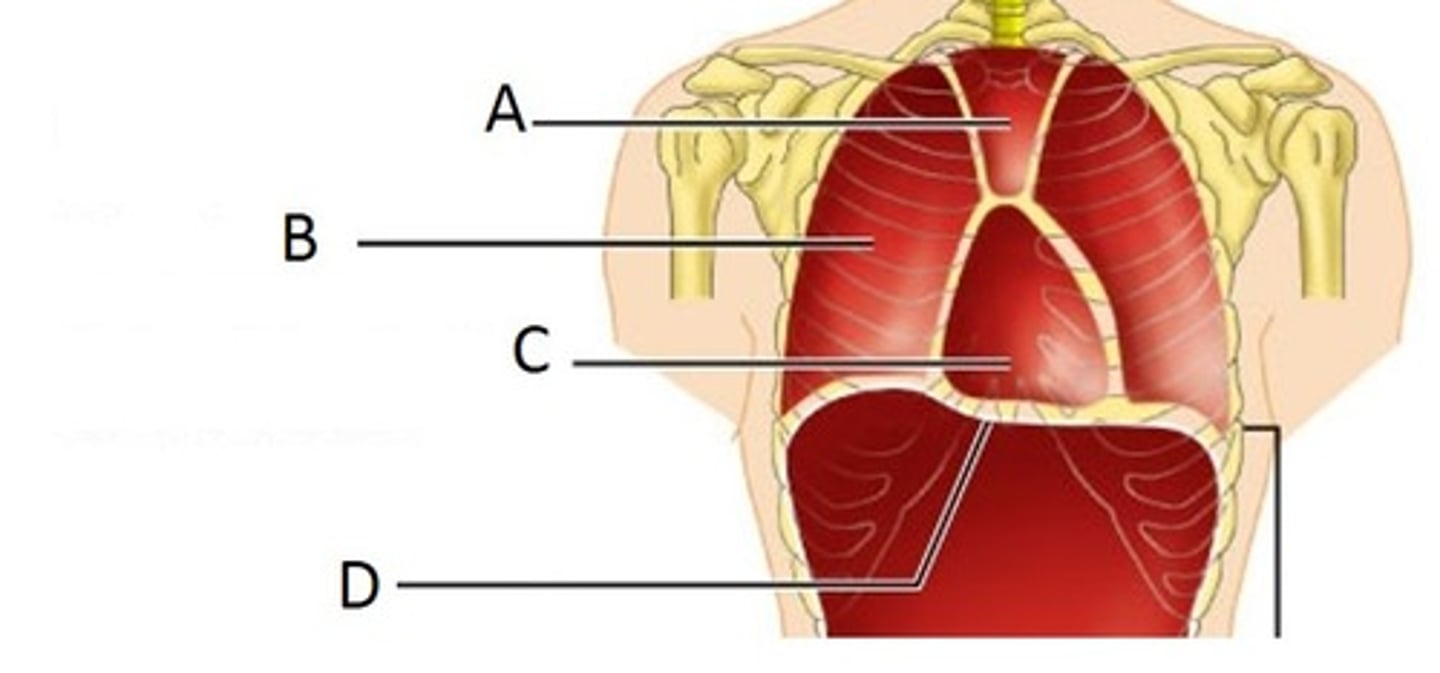
Brain
Name an organ in cranial cavity
Urinary Bladder
Name an organ in the pelvic cavity
Stomach
Name an organ in the abdominal cavity
The diaphragm separates which cavities?
The thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities
Name an organ in the pleural cavities
Lung
Heart
Name the organ in the pericardial cavity
Mediastinum and pleural
Name the two cavities within the thoracic cavity
Abdominal and Pelvic
Name the two cavities in the abdominopelvic cavity
More
The ventral cavity contains _____ (more or fewer) organs than the dorsal cavity.
Fewer
The dorsal cavity contains ____ (more or fewer) organs than the ventral cavity.
breathing
The diaphragm is known as the __________ muscle.
Cranial & Spinal
The dorsal cavity contains the ___ & ___ cavities.
Mediastinum
I
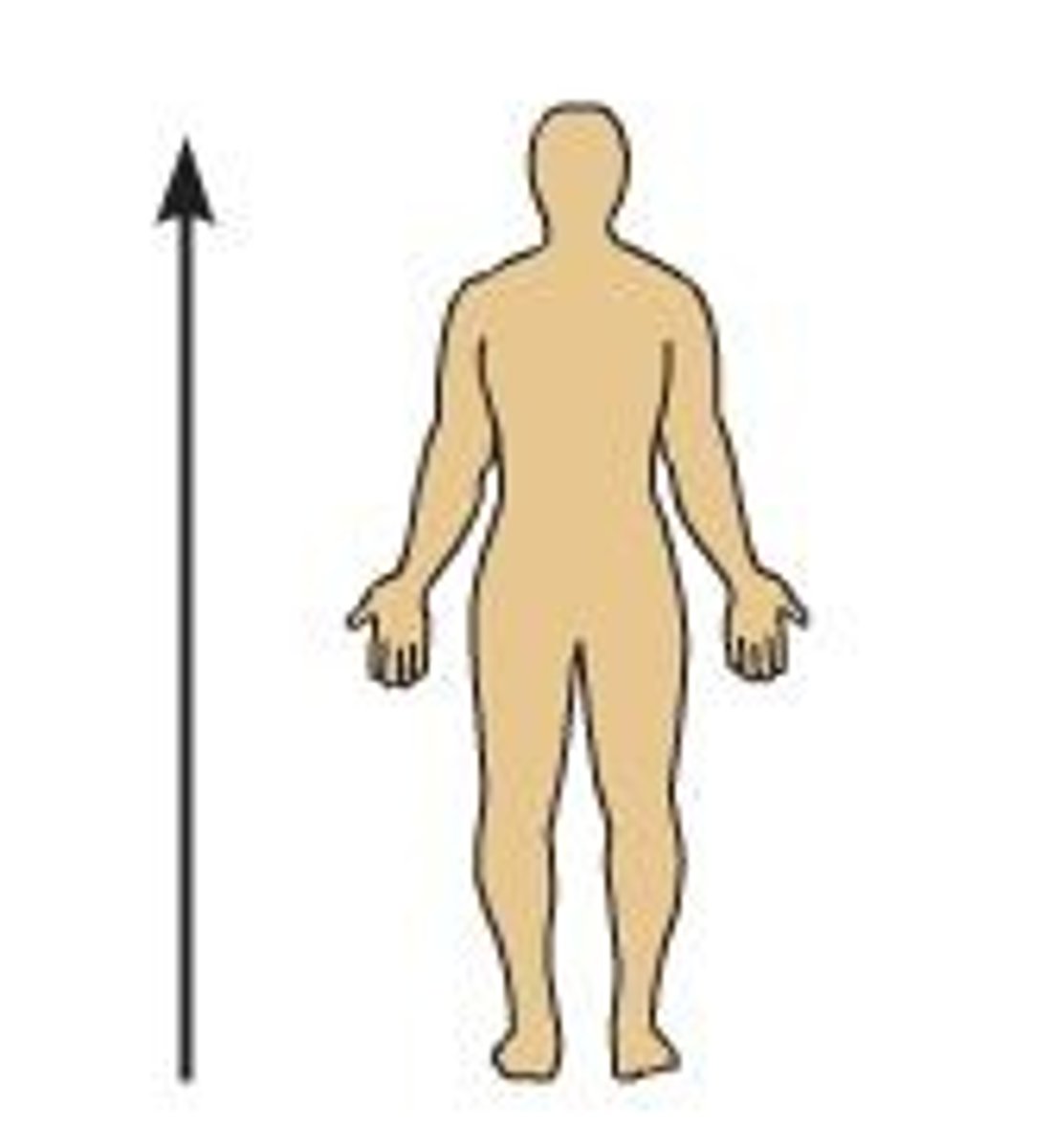
Superior or cephalic
toward the head, away from the feet
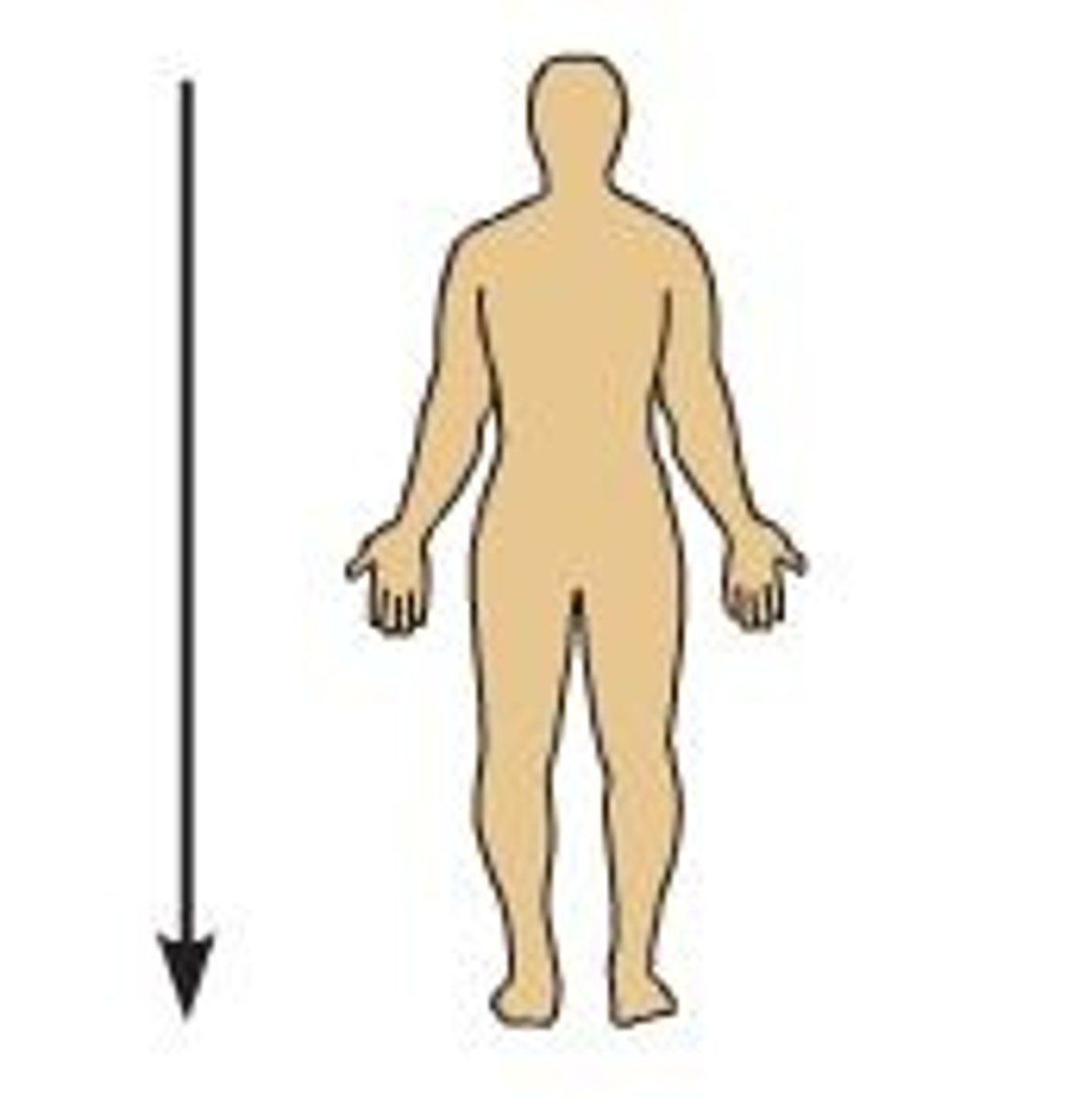
Inferior
away from the head, toward the feet
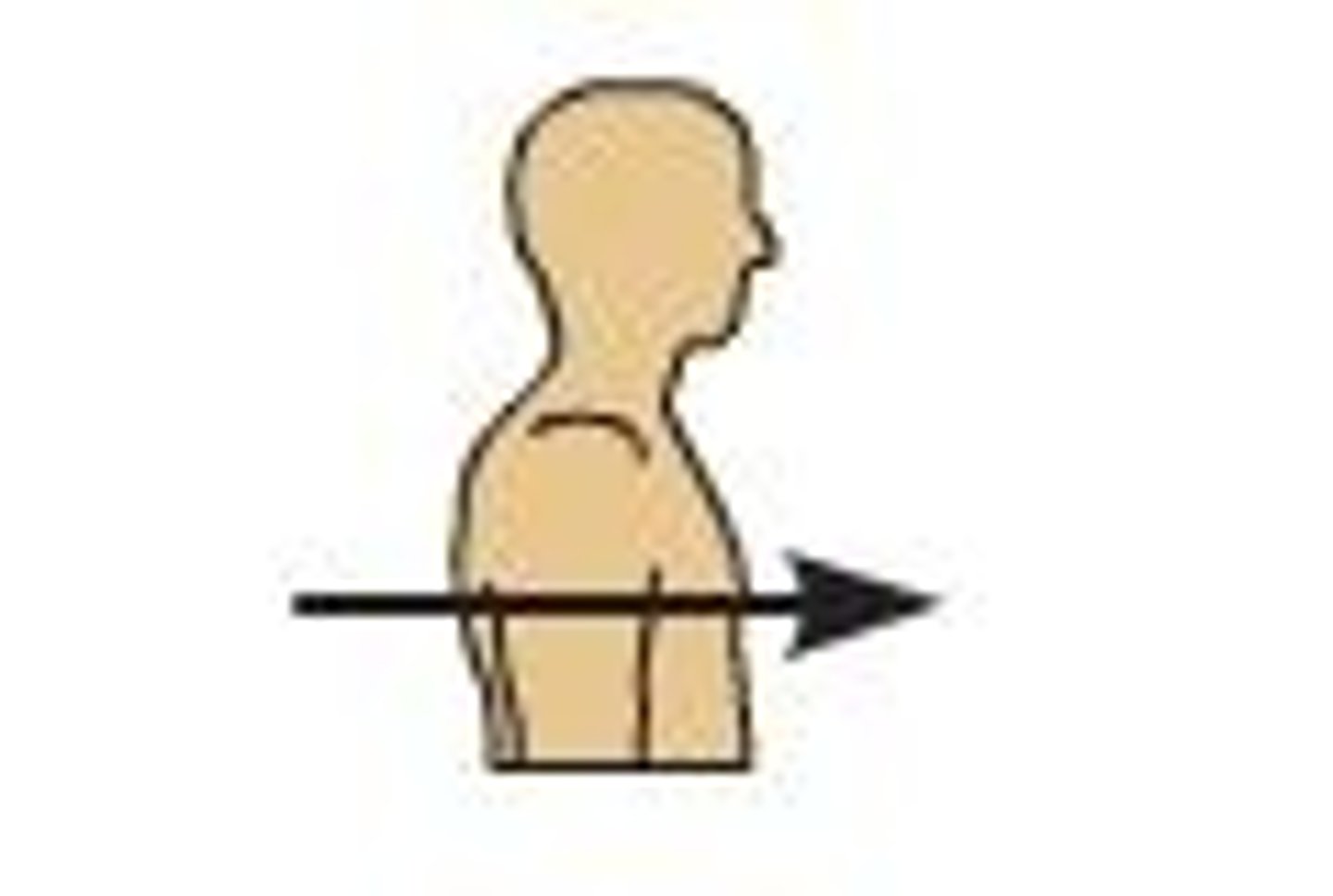
Anterior
toward the front surface of the body, ie. ventral
Proximal
on limbs, toward the shoulders or hips
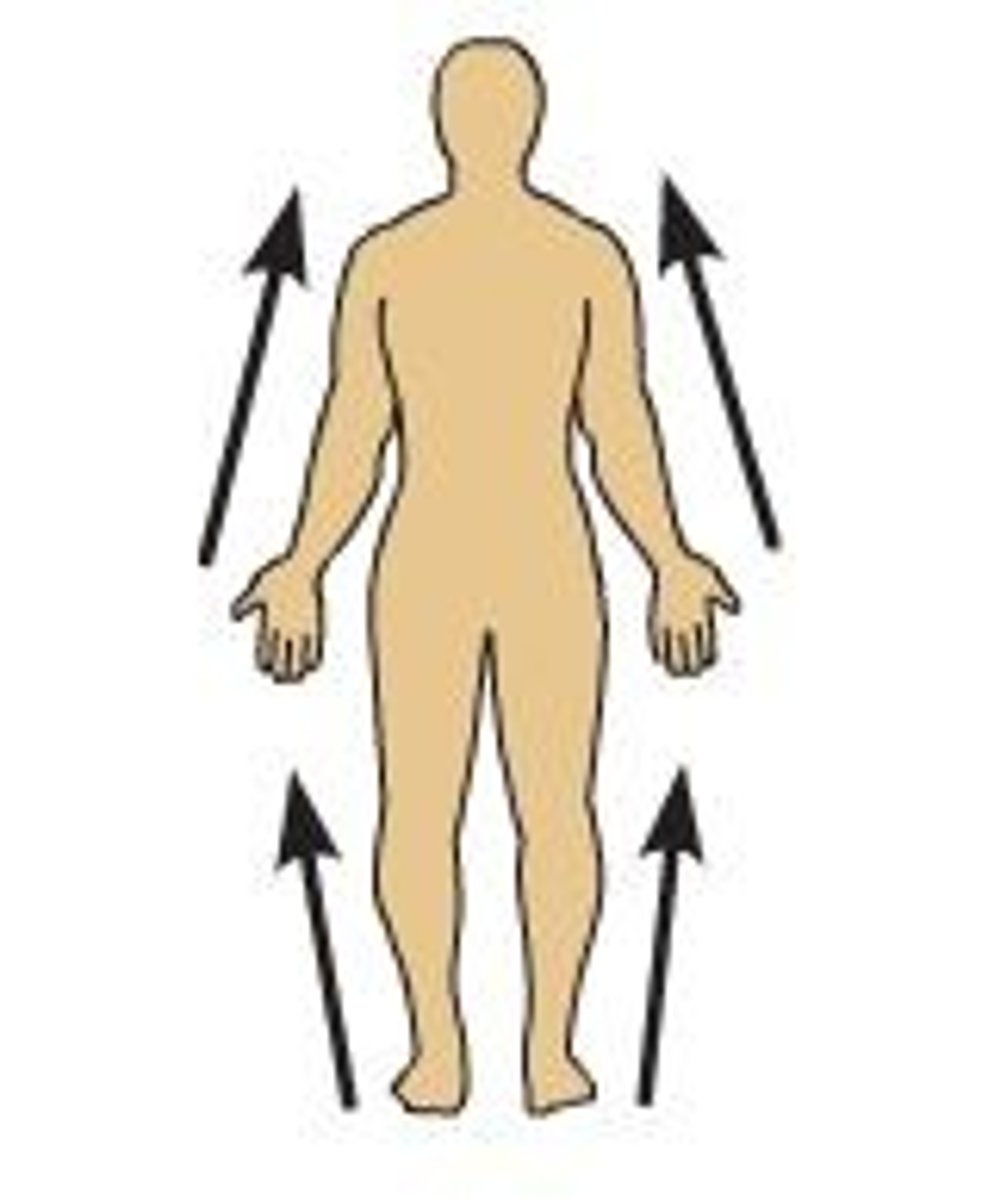
Distal
on limbs, away from shoulders or hips
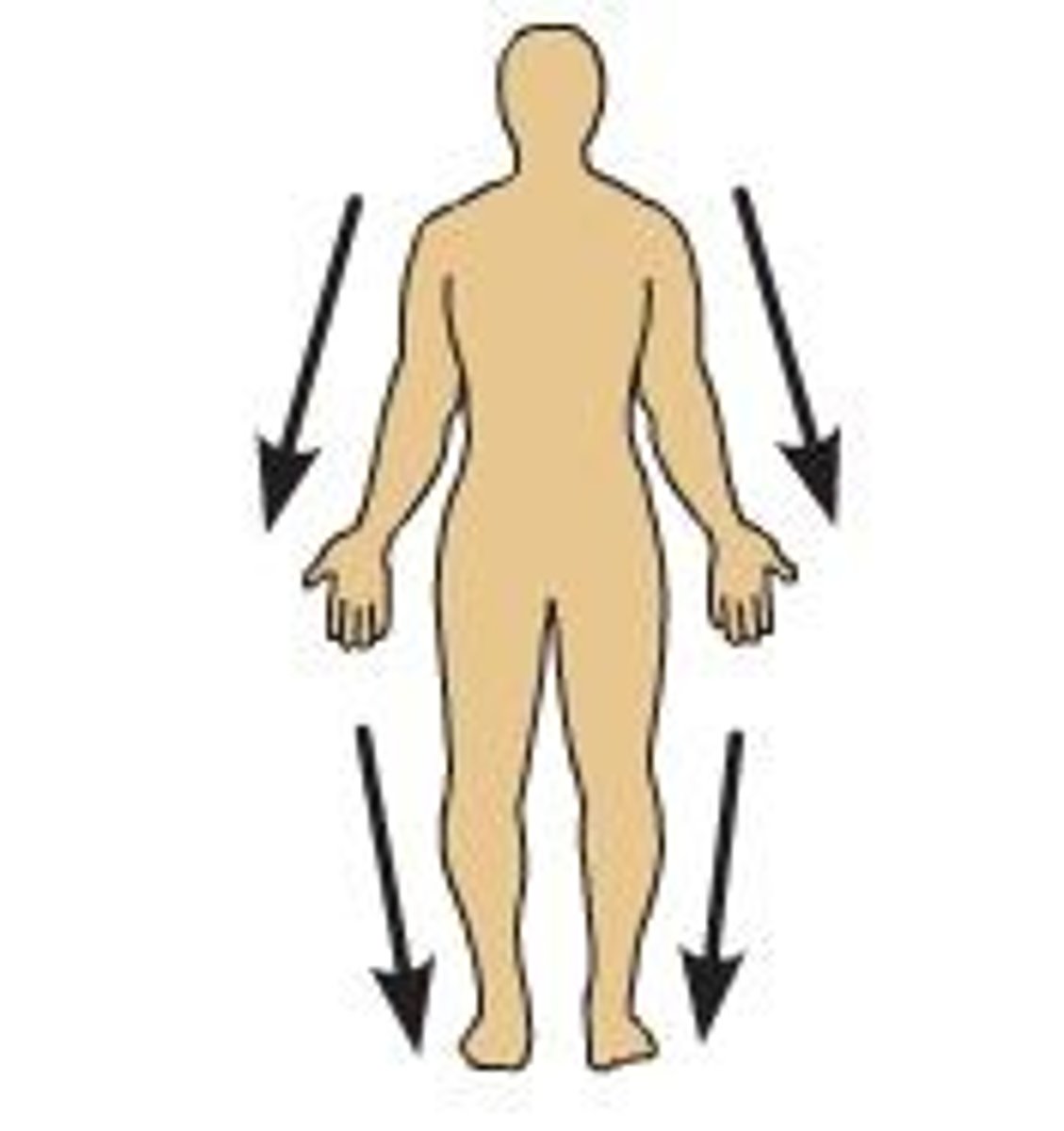
Deep
away from the surface of the body, more internal
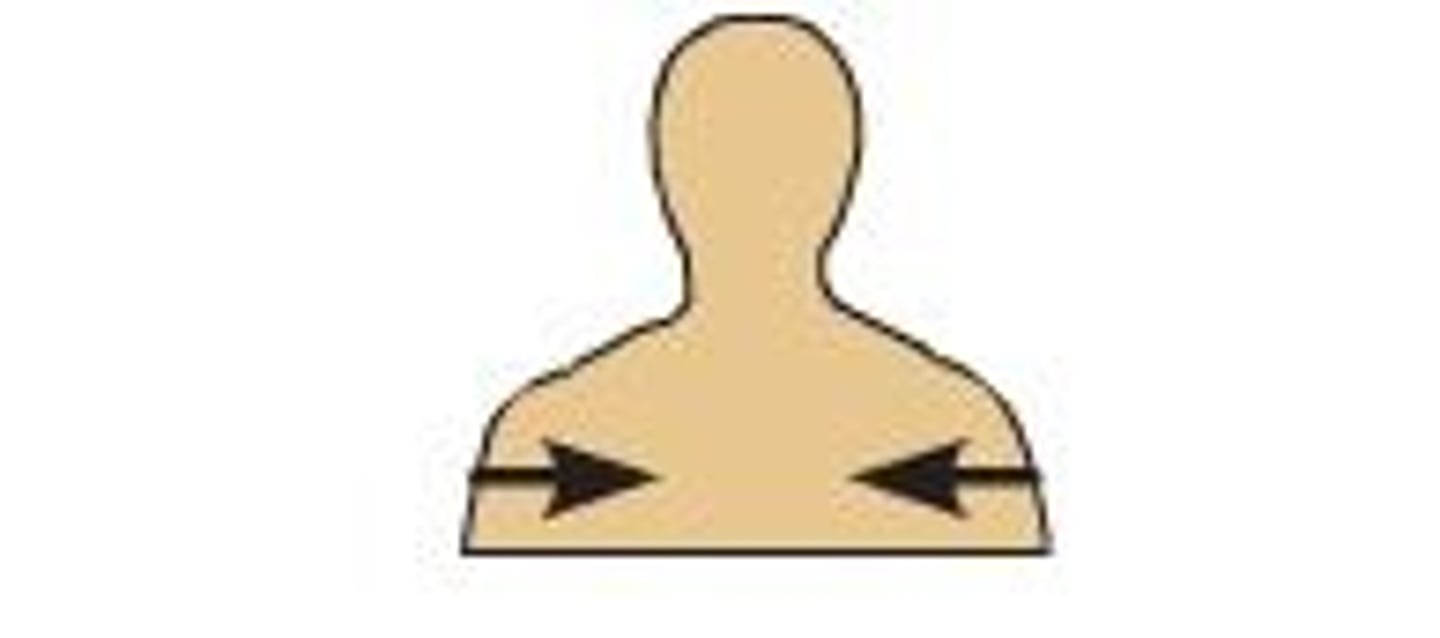
Superficial
toward the surface of the body, ie toward the skin
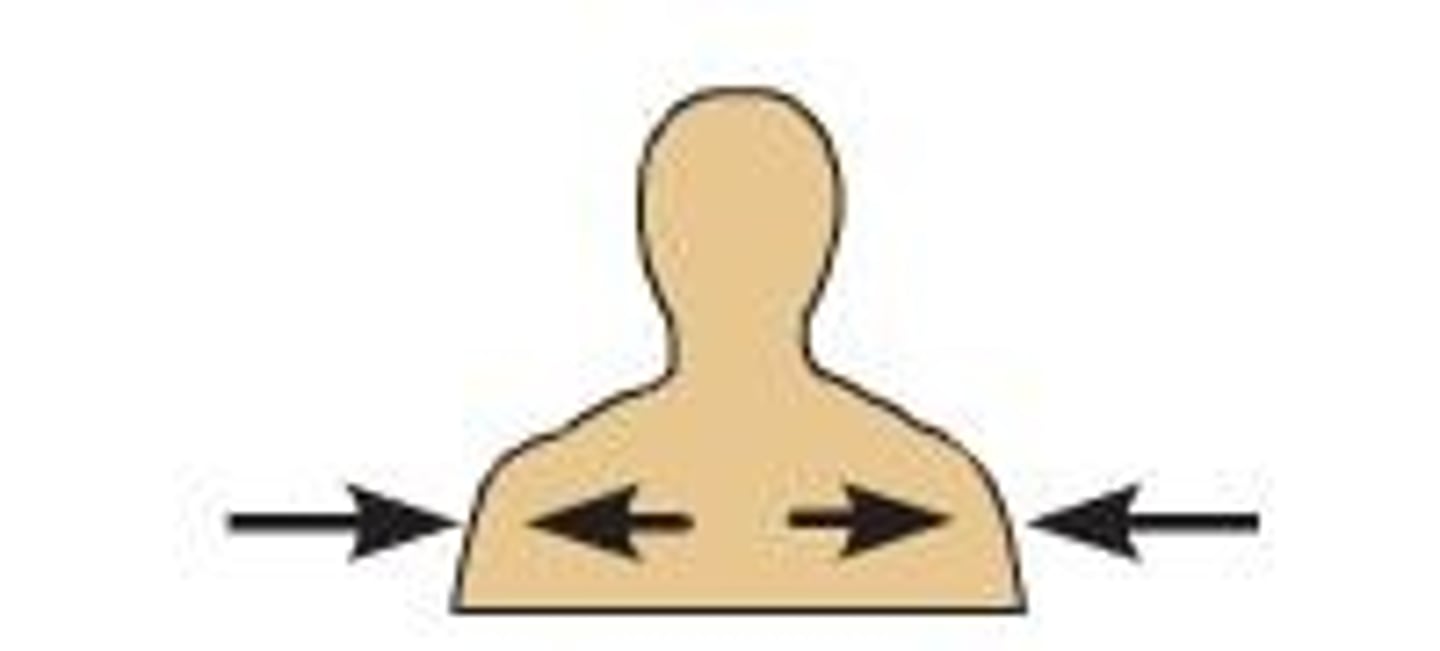
Lateral
away from the midline of the body
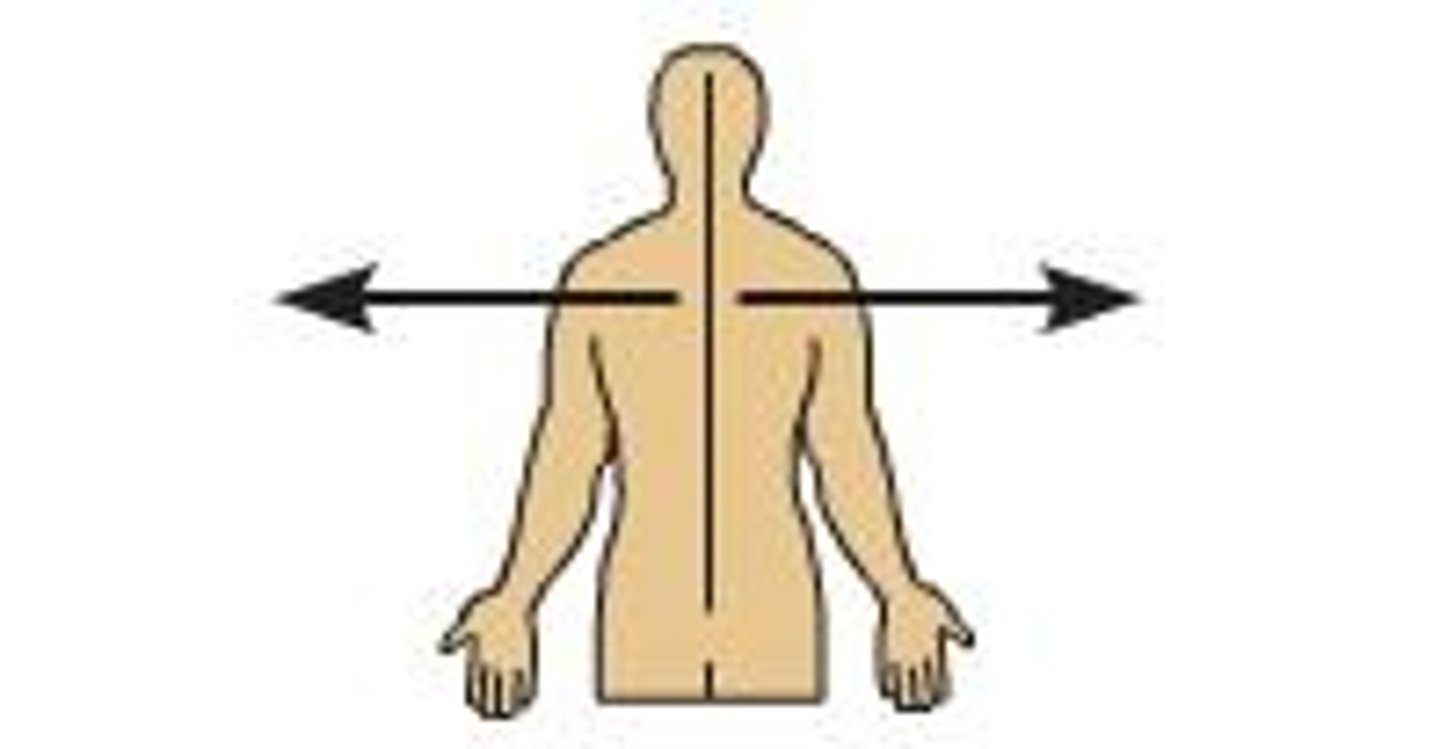
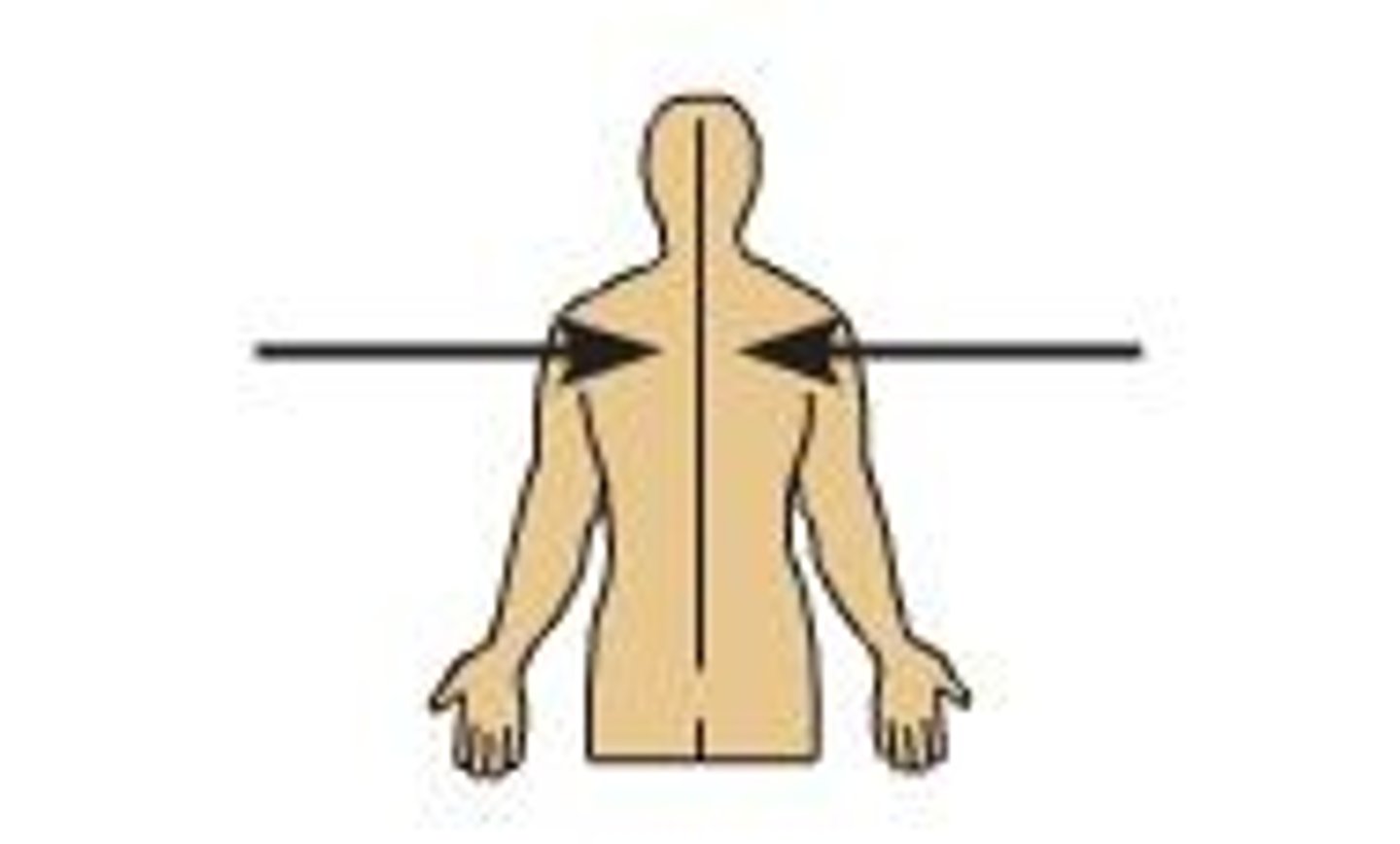
Medial
toward the midline of the body
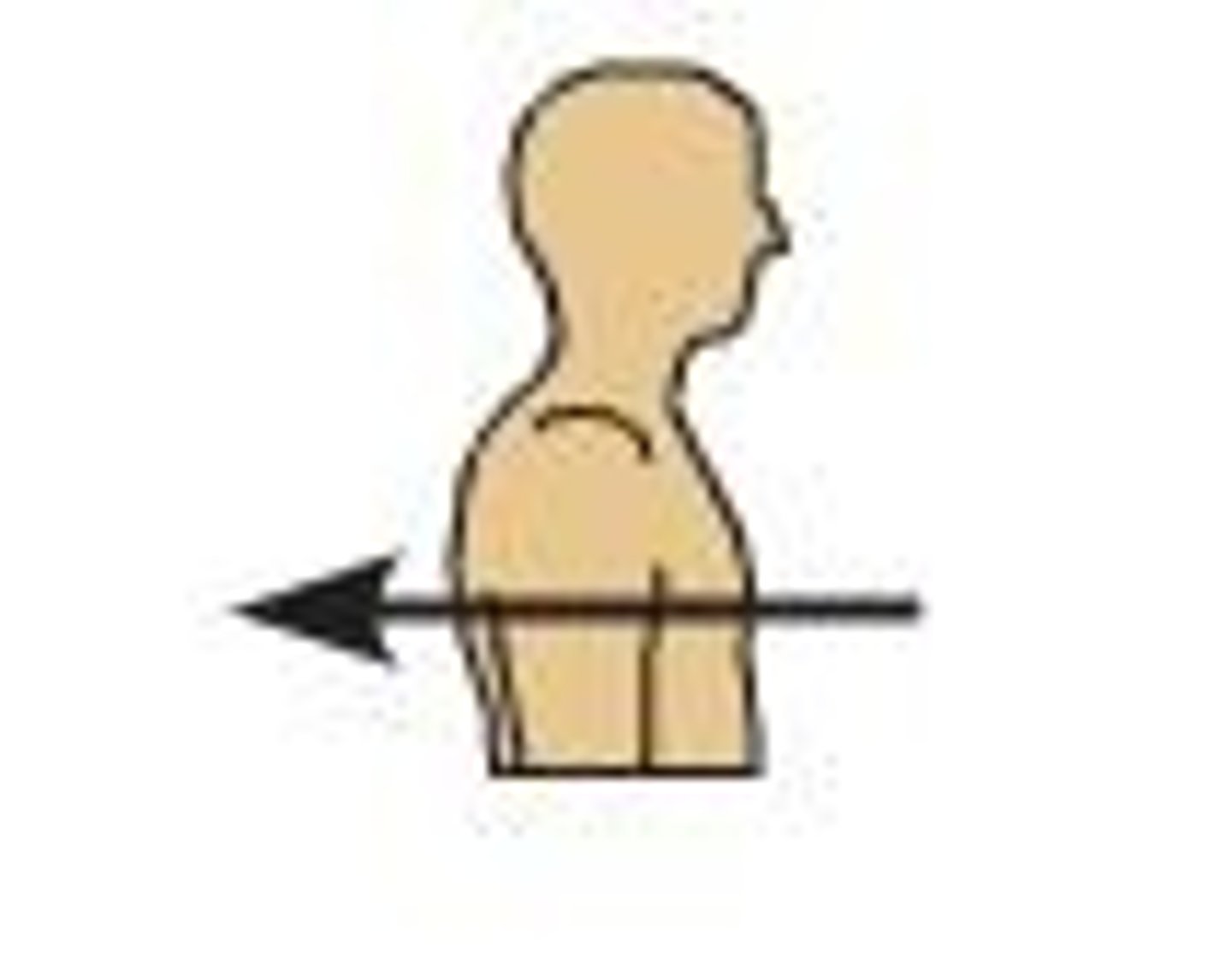
Posterior
toward the back surface of the body, ie. dorsal
Prone
lying on the stomach, face down
Supine
lying on the back, face up
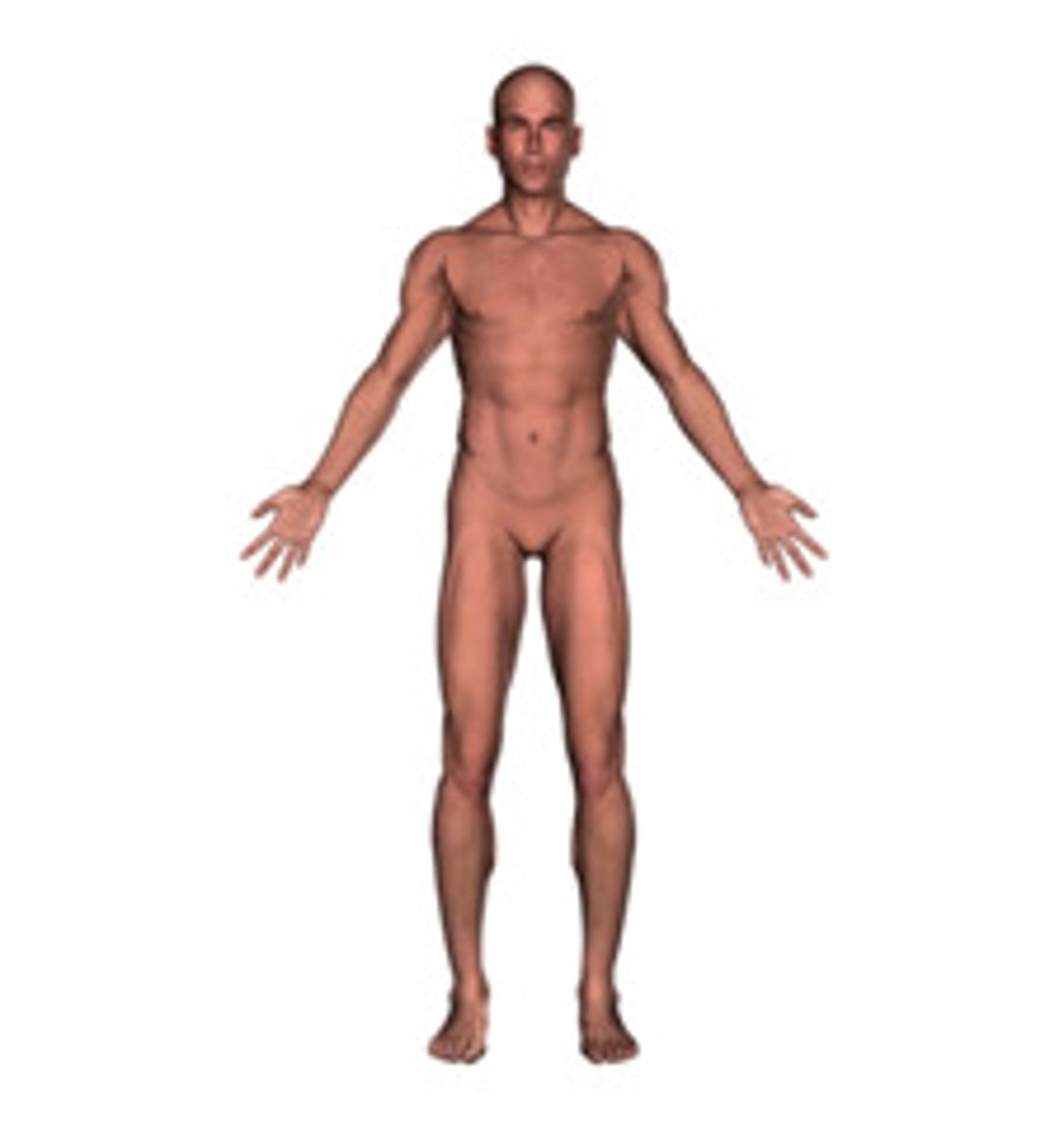
anatomical position
To stand erect with arms at the sides and palms of the hands turned forward
Anter/o
front or forward aspect of the body or an anatomical structure.
Ventr/o
belly, belly side or abdominal area of the body.
Poster/o
back or rear aspect of the body or an anatomical structure.
Dors/o
back or posterior aspect of the body or an anatomical structure.
Medi/o
middle or medial aspect of the body or an anatomical structure.
Later/o
side or lateral aspect of the body or an anatomical structure.
Super/o
upper or above aspect of the body or an anatomical structure.
Infer/o
lower or below an anatomical structure.
Proxim/o
nearer to the trunk of the body or point of attachment.**
Dist/o
farther from the trunk of the body or **point of attachment. **
Caud/o
**Tail end**or lower part of the body.
Cephal/o
Head or head-end of the body.
Coron/o
crown or circle of the head
Para-
beside, near, alongside
Mid-
middle
Trans-
across
-ior
suffix that means **pertaining to**
-al
suffix that means **pertaining to**
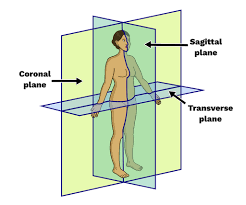
Transverse (Horizontal) Plane
A horizontal plane that divides a body structure into top (superior) and bottom (inferior) portions.
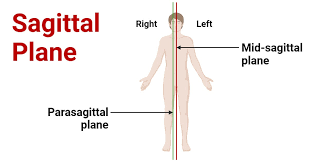
Sagittal Plane
A vertical plane that divides the body into right and left sections.
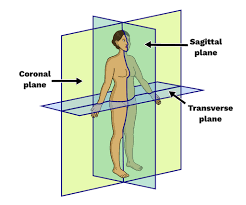
Coronal (Frontal) Plane
A vertical plane that divides the body into front (anterior) and back (posterior) portions.
superficial
Structures closer to the surface of the body.
Deep
Structures that are more internal or further from the surface of the body.
cav/o, cavit/o
cavity or hollow space in the body
crani/o
skull
Vertebr/o
vertebrae or backbone
spin/o
spine or spinal column
encephal/o
brain
myel/o
bone marrow or spinal cord
ventr/o
belly side
thorac/o
chest, thorax
abdomin/o
abdomen
peritone/o
peritoneum
pelv/i, pelv/o
pelvis, hip, pelvic bone
pleur/o
pleura
diaphragm/o, phren/o
diaphragm
pericard/o, pericardi/o
pericardium (also known as the pericardial sac)
retro-
prefix meaning behind
peri-
prefix meaning surrounding, around
intra-
prefix meaning within or inside
sub-
prefix meaning under, below
-al, -ic
suffixes that mean pertaining to
The two planes that create the 4 abdominopelvic quadrants intersect at what structure?
The umbilicus, navel or belly button
Right Upper quadrant
liver, gallbladder (A)
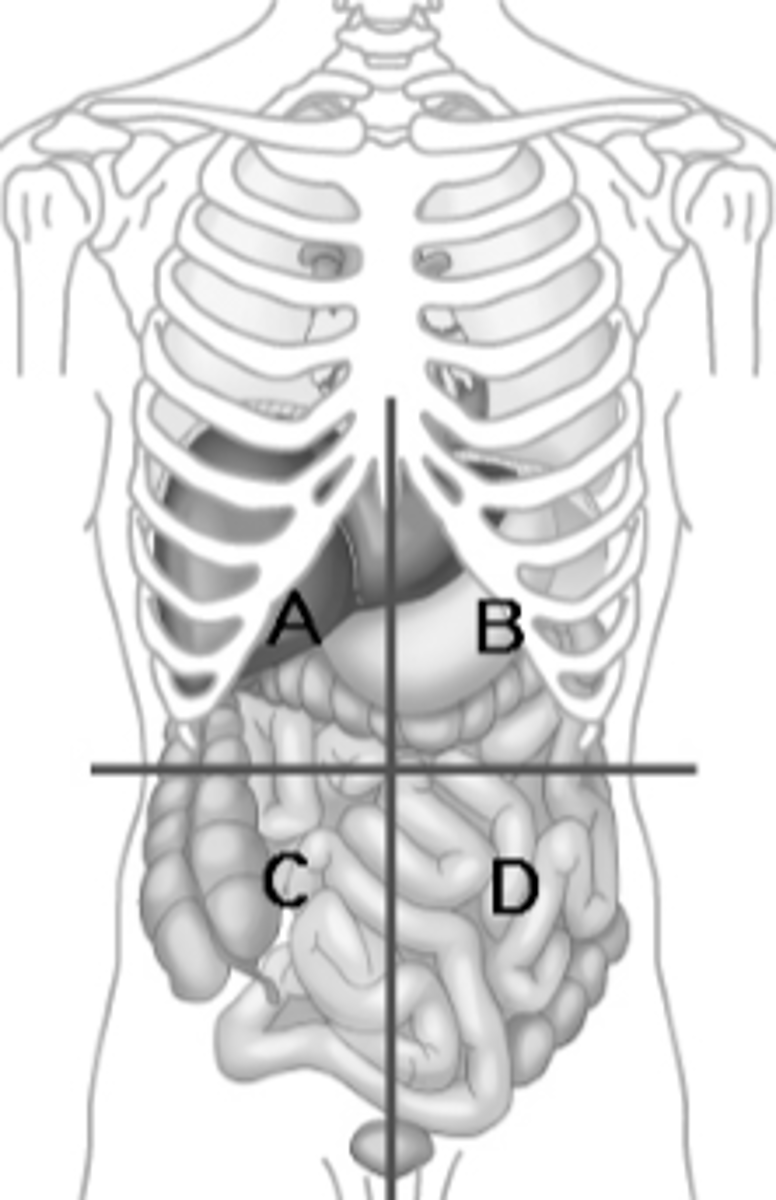
Right Lower quadrant
Cecum, small intestines, and appendix (C)
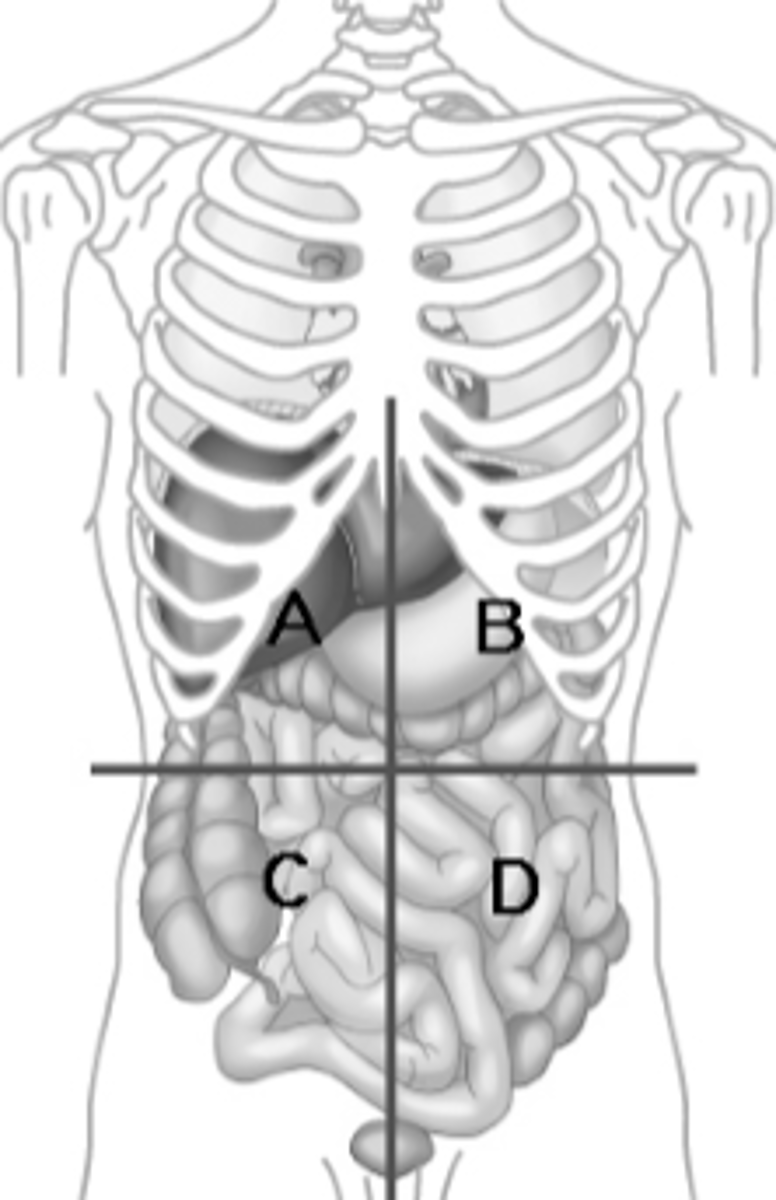
Left Upper quadrant
diaphragm, stomach, and spleen (B)
Left Lower quadrant
Descending colon, small intestines (D)
Right hypochondriac region
liver, gallbladder (A)
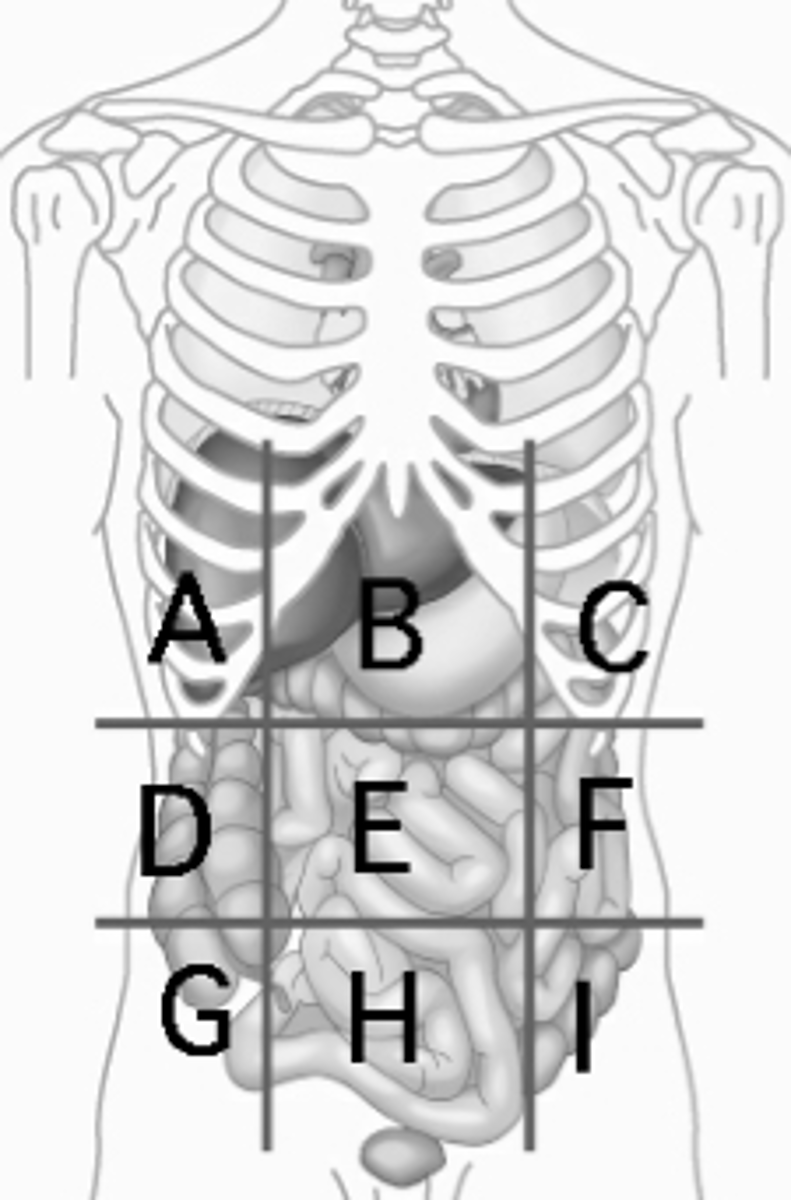
Epigastric region
stomach (B)
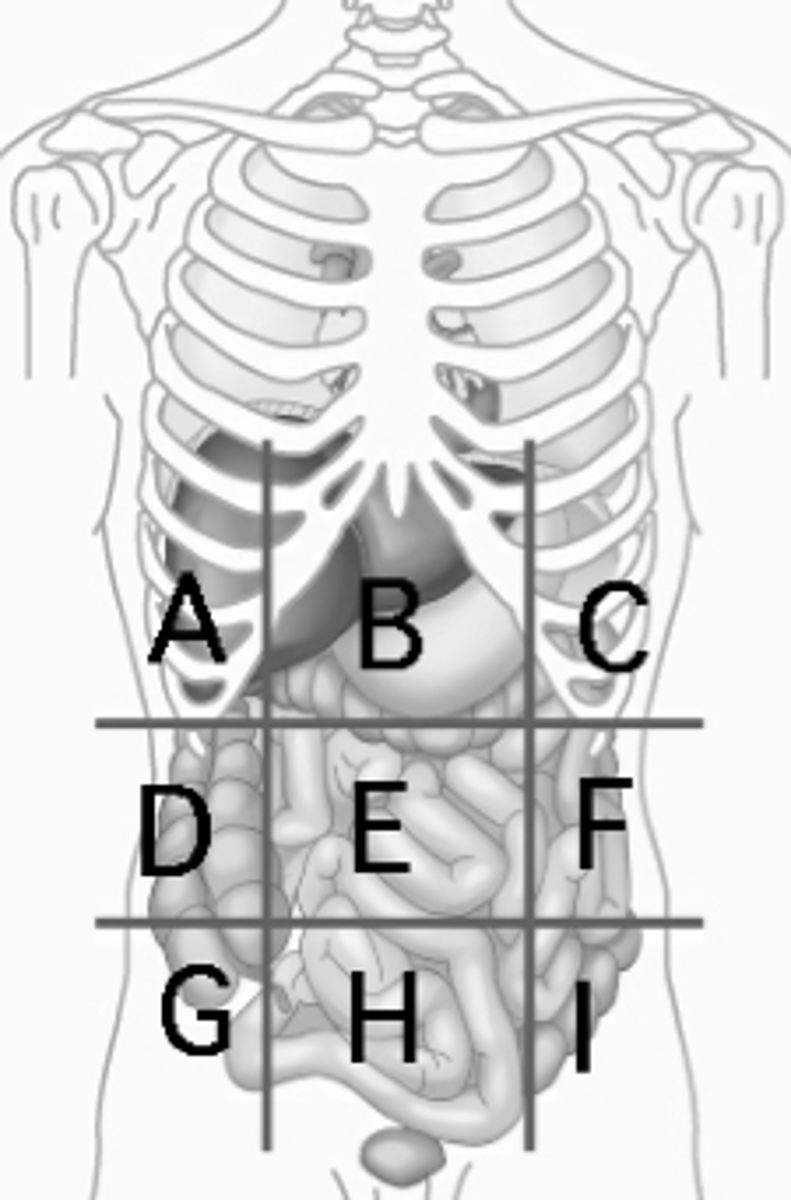
Left hypochondriac region
Diaphragm, spleen (C)
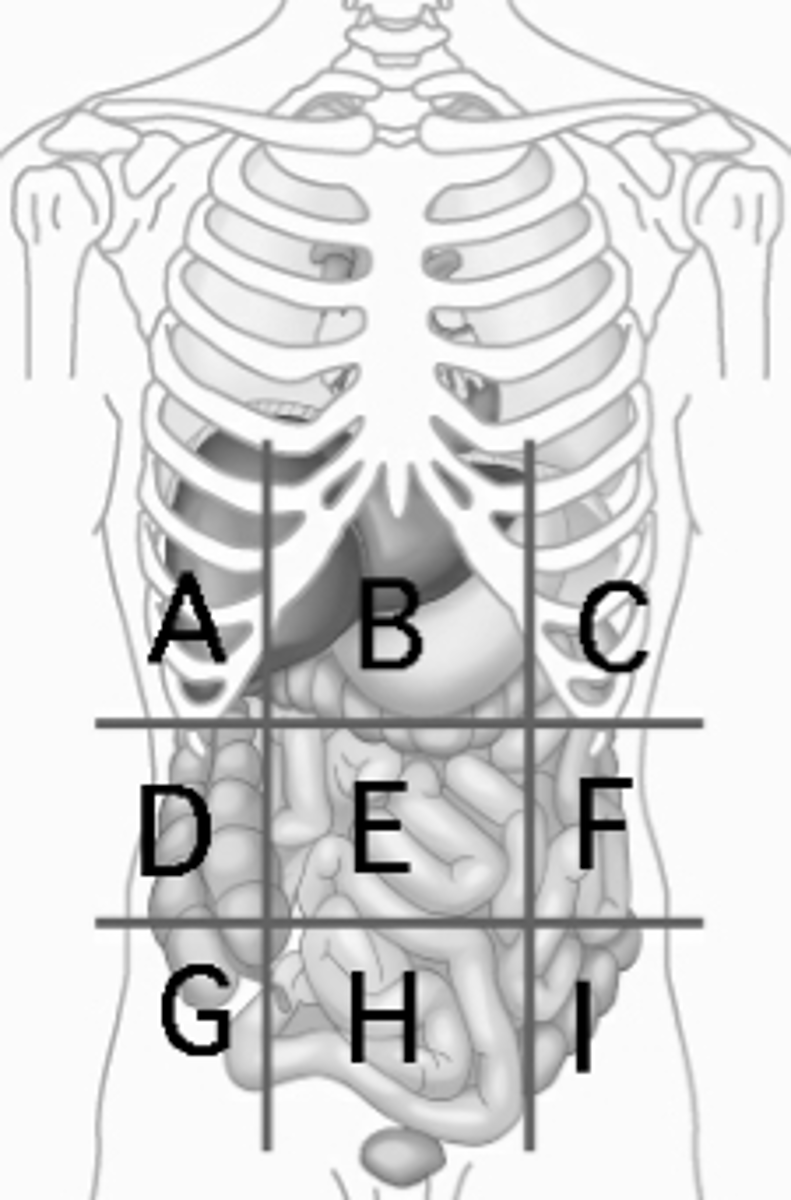
Right Lumbar region
ascending colon of the large intestines (D)
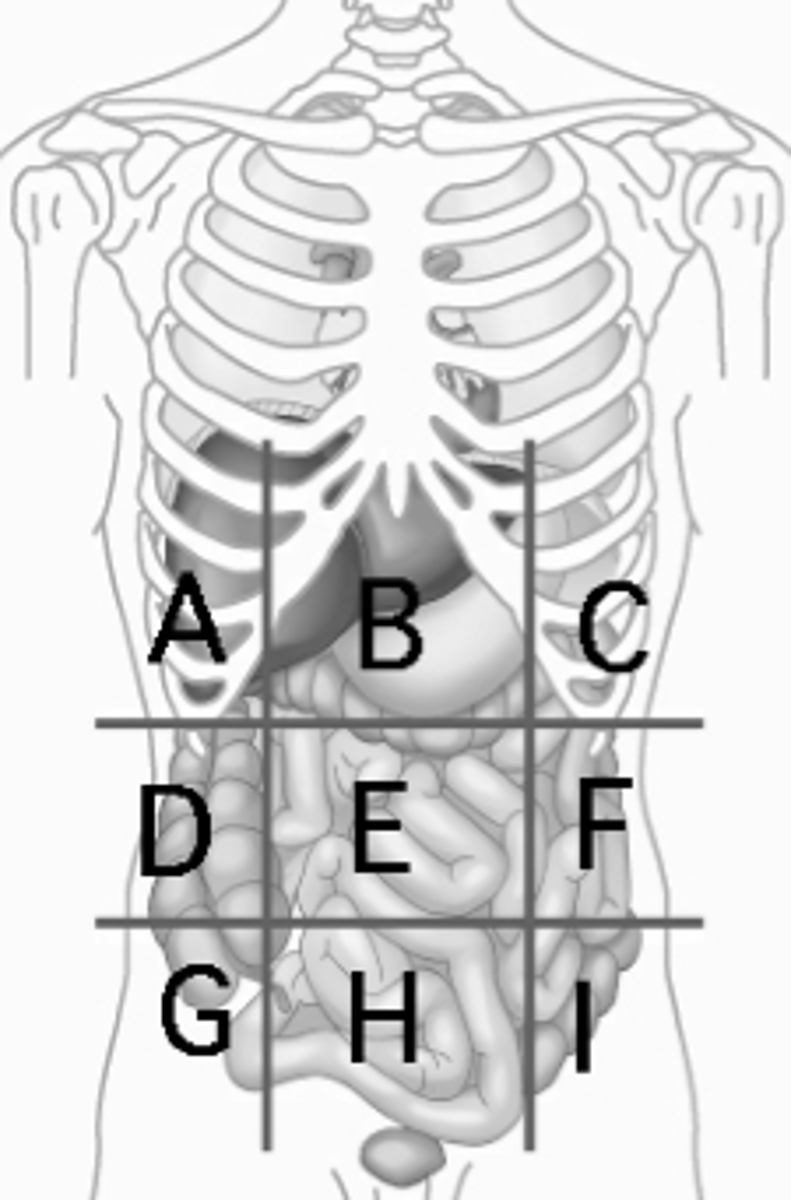
Umbilical region
small intestines (E)
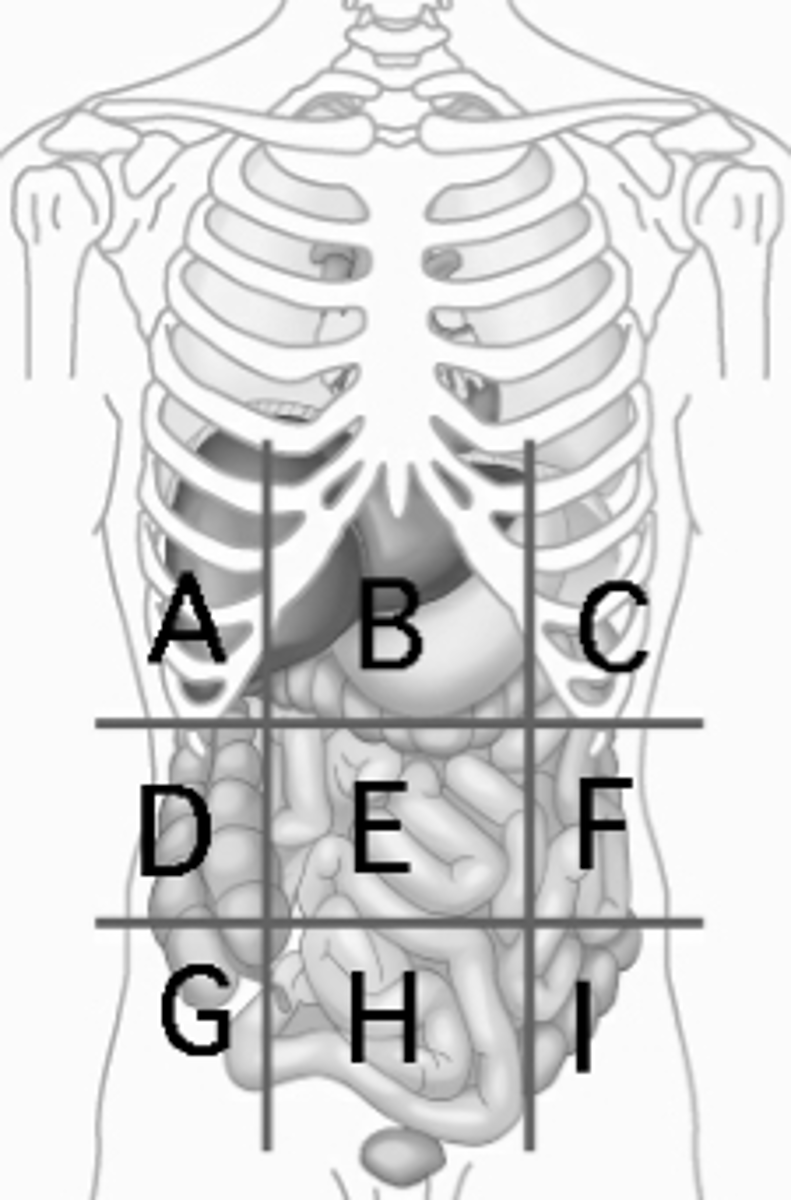
Left Lumbar region
descending colon of the large intestines (F)
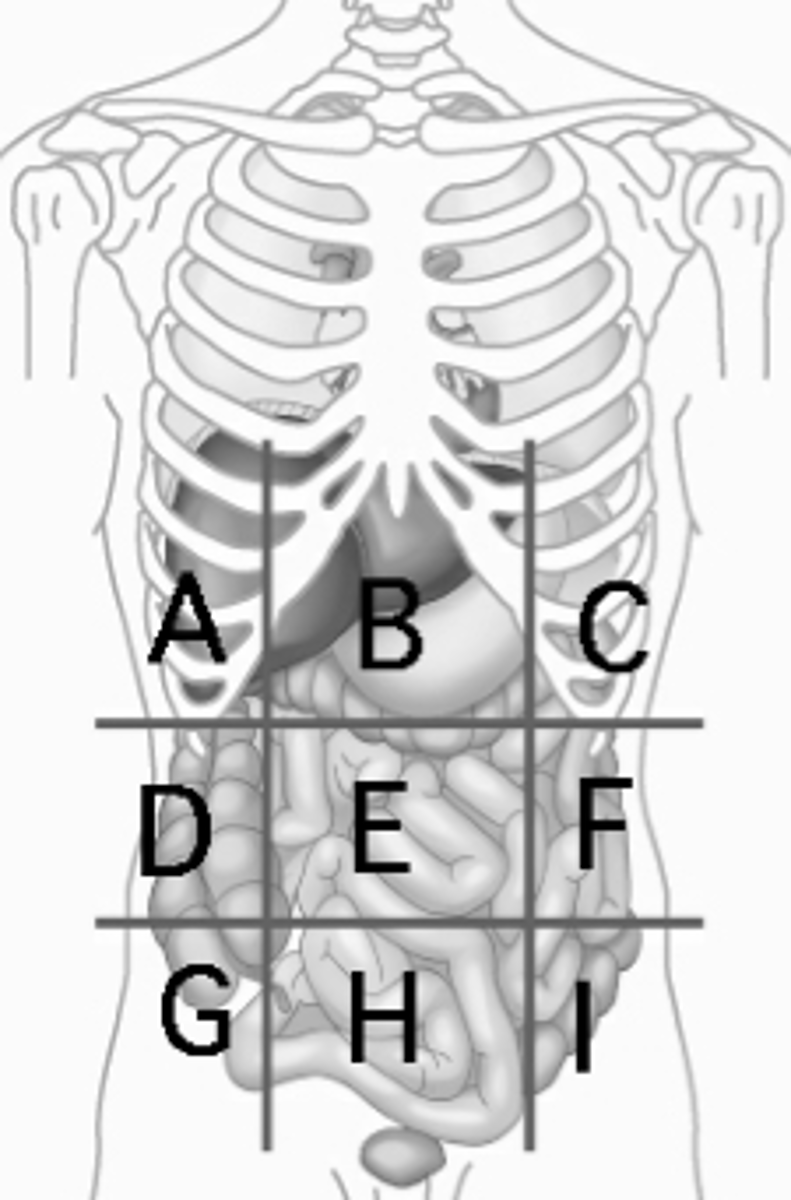
Right Iliac Region
Cecum, Appendix (G)
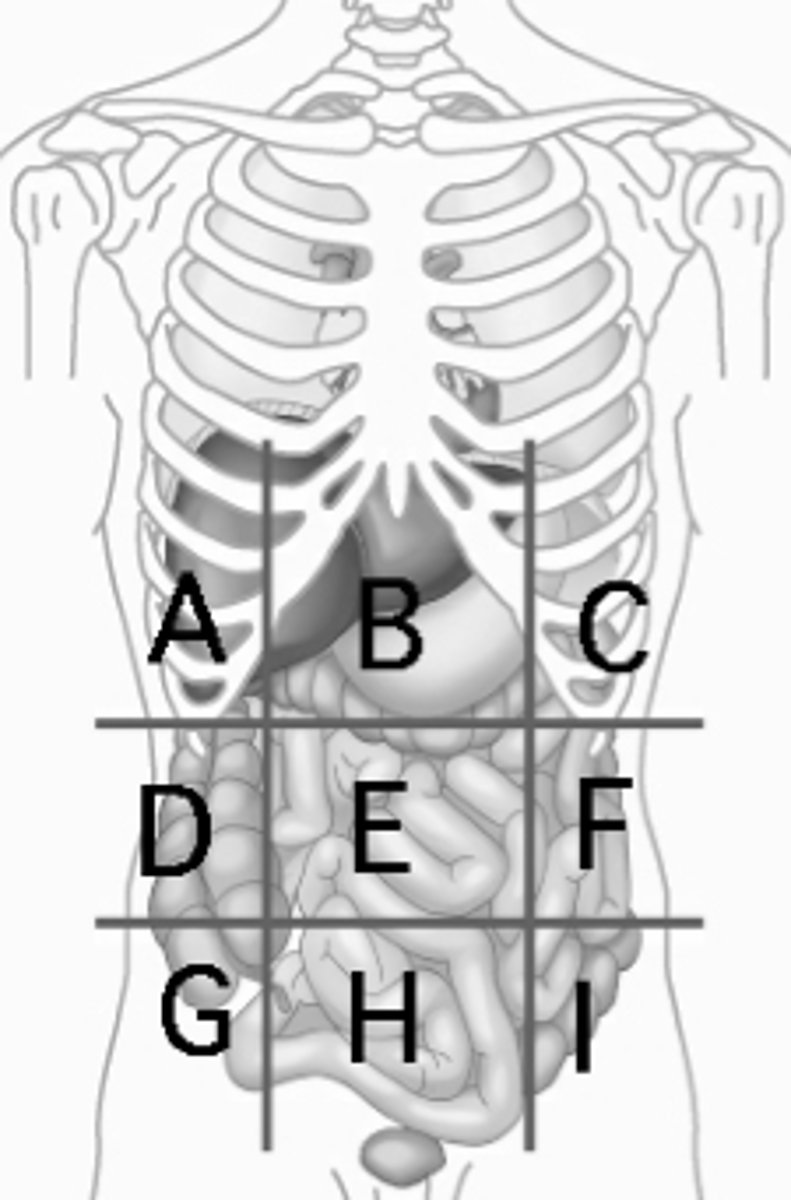
Hypogastric region
urinary bladder (H)
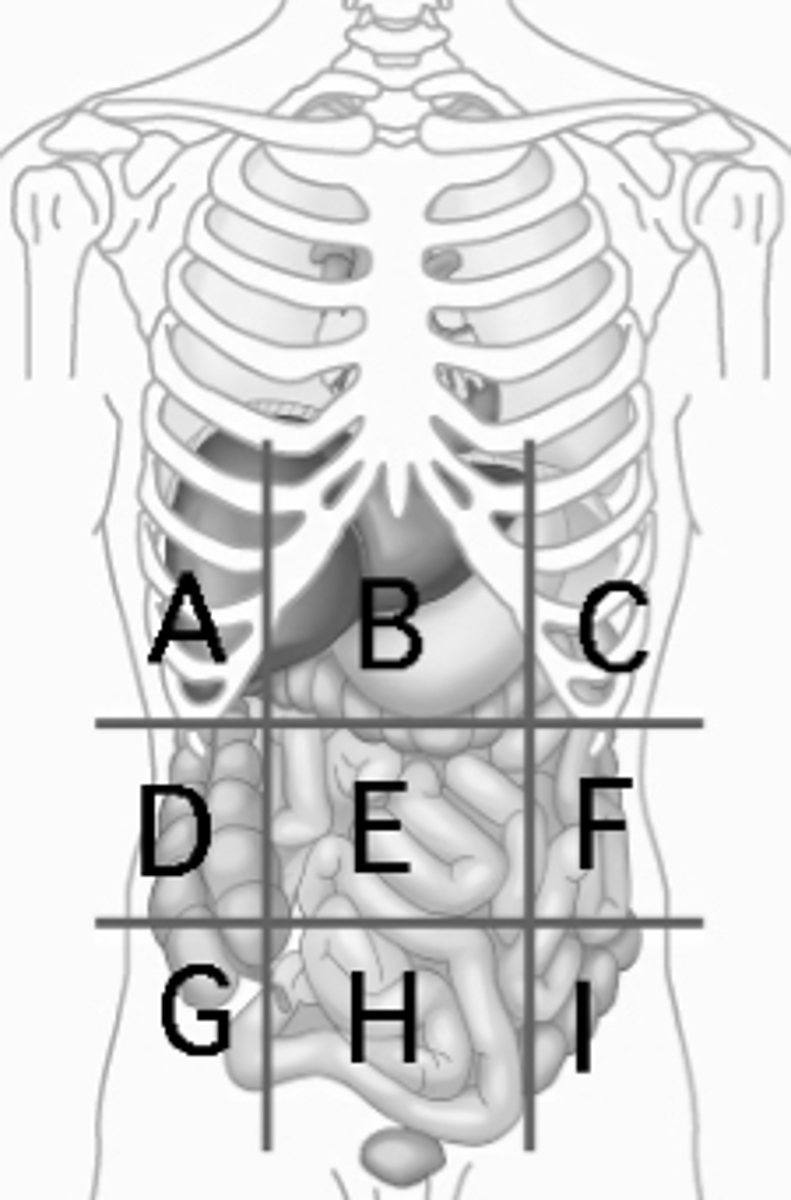
Left Iliac region
sigmoid colon (I)
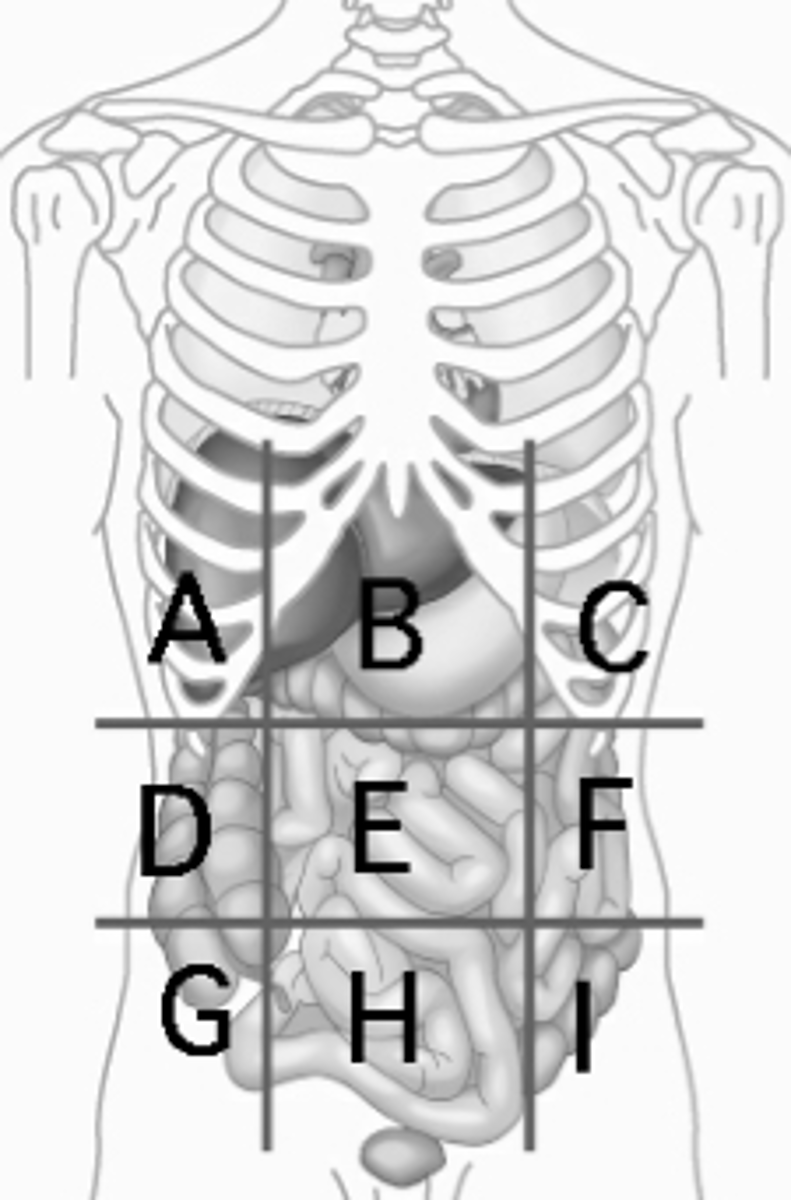
Proximal
Closer to the point of attachment
Distal
away from the point of attachment
frontal plane
Divides the body into front and back portions.
midsagittal plane
divides the body into equal right and left sides
transverse plane
horizontal division of the body into upper and lower portions
Anterior
front of the body