FINAL FOR E MARKETING
1/74
Earn XP
Description and Tags
CH 5, 6, 7
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
Define search engine optimization (SEO)
Helps websites rank higher on search engine results pages (SERPs)
What are search engine results pages? (SERPs)
Web pages where search results are displayed
What are the first results displayed on SERPs after a customer initiates a search?
Paid advertising (sponsored ads)
A part of an organization’s search engine marketing (SEM)
Each click triggers a cost to an advertiser
Natural/ organic results
Unpaid search results influenced by SEO
Clicks do not directly cost the website operator
What is one long-term benefit of SEO for organizations compared to paid search engine advertising?
It allows organizations to appear high in search engine results without ongoing direct expenses to the search engine.
What are the benefits of properly maintained SEO?
Consumer exposure to brands
Increased visits to digital assets
Increased conversions & revenue
How many types of search are there? List them.
2
Text search
Voice search
Explain text search.
The act of entering words, phrases, or keywords into a search engine bar.
How could results for a search term be influenced?
By a number of factors like:
device
location
interests
Regarding text search, what would natural results display?
Services, articles, social media pages, and other web pages.
Explain voice search.
The consumer speaks the search through a microphone on their device. (This is becoming more popular)
According to PricewaterhouseCoopers (PwC) survey the following groups are adopting voice search at the highest levels:
Young consumers
Households with children
Households with income greater than $100k
What are the 3 basic types of SEO?
On-site SEO
Off-site SEO
Technical SEO
Explain on-site SEO.
Done on an organization’s website, involves:
using appropriate keywords on websites
dedicating pages to specific keywords/ topics
having a good website structure & layout
Explain off-site SEO.
Done off the organization’s website via backlinks from:
blog posts
influencer- generated content
positive reviews
Explain technical SEO.
Done though technical means to the website backend
What are the key objectives of SEO?
Drive traffic to an organization
Create leads
Convert consumers from leads to purchases
Build the organization’s brand image
Enhance the organization’s reputation
Explain leads.
Prospective customers who may be converted to actual customers
Explain qualified leads.
Consumers who are more likely than other leads to convert to customers because of their demonstrated buying potential and interest.
How can digital marketing identify qualified leads based upon interactions that may indicate they are most likely to buy?
Visiting a website
Watching videos
Responding to calls to action (CTAs)
How can appearing in organic search results on the first page of a SERP benefit an organization’s image?
Consumers may view the organization as more reputable, which enhances its image.
What are keyword strategies for SEO considerations?
Use very relevant keywords
Conduct keyword research
Avoid keyword stuffing
What are some marketer strategies and tactics considered for a website SEO?
Select an appropriate domain name
Help search engine crawl website
Add an effective sitemap
Improve page speed
Implement good website security
Have quality links, references, and mentions
What are some marketing strategies and tactics considerations for SEO content?
Provide relevant
Engaging content
New content
Explain key word research.
Determines which keywords and key phrases to target in an organization’s website.
What are the domain name requirements for SEO purposes?
Should not be lengthy
Should reflect the content of the website
Should be easy to remember
EXAMPLE: brandname.com not iwanttogetbrandname.com
Larger websites use sitemaps. Explain what a sitemap is.
A document that links to key web pages on an organization’s site; it is meant for use by a search engine.
It is a web page that links to important web pages on an organization’s website; meant for use by consumers.
For technical SEOs what will attract the customers?
Privacy and security considerations.
Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS)
What does HTTPS involve?
Data encryption to protect from malicious attackers obtaining confidential information.
What are backlinks?
Links from referral domains to an organization’s website
What do digital marketers do while evaluating the quality and value of the backlinks?
The popularity of the website linking to the organization’s website
How trustworthy the linking site is
The authority of the linking site, as measured by search engine and ranking authorities
What should marketers avoid that may hurt SEO?
Trying to trick search engines using:
Keyword stuffing
Scraped content taken from sources owned by others
Duplicate content
Using techniques disfavored by search engines such as:
Automatically generated content
Link buying (aka link spamming)
Cloaking by providing different content to search engine bots than to consumers
What are the differences between black-hat, white-hat, and gray-hat SEO techniques in digital marketing?
Black-hat SEO: deceptive methods like link spamming and keyword stuffing.
White-hat SEO: accepted and recommended practices.
Gray-hat SEO: ethically questionable techniques that aren't explicitly illegal.
Explain local search engine optimization (LSO)
Search engines may favor websites optimized for local searches. For organizations with a physical presence or local service options. They should make sure they have a business profile.
Explain people also ask (PAA) SEO.
Gathers and displays questions consumers often use in their searches.
Which phrase puts the importance of content into perspective?
Content is king.
What should an effective searchable website generally contain?
Unique: not reproduced from other websites/ duplicated
Engaging: designed for the consumer rather that for solely SEO purposes
Creative: original conetent that may be imaginative & engages readers
Specific: appropriate to the intended audience (local/ international)
Why might specific content elements require special treatment in SEO?
To help search engines find and potentially rank the content more effectively.
Why is it important for search marketers to consider local and international practices in global digital marketing?
Because events like Cyber Monday or Christmas may not be relevant in all countries, and SEO strategies should reflect local customs and behaviors.
Explain content planning.
Identifying when and what content will be developed for the website.
What content-planning could be included for an editorial calendar?
Purpose of content
Due & publish dates
Authors
Channels
Consistency across channels
Topics to be published
Details of content
Targeted keywords
Retailed digital buyer personas
Specific calls to action (CTAs)
Audience
Skills
Resources
What are some technical considerations relating to content that may affect SEO?
HTML tag: a piece of digital code adopted for a web page & used to define how a web browser must format & display the content
Meta description: a summary of the content on a web page, may be used by search engines as a snippet on SERPs
Types of content: some content, like content containing Flash/ JavaScript, may not be considered by search engines
What is a popular tool for analyzing SEO? Explain what it does.
Provides analytics on how an organization’s website is executing on Google search.
Explain Semrush SEO tool & Bing SEO Reports.
Semrush SEO tool:
Enables digital marketers to track their position on SERPs for keywords such as “Top 3”, etc.
Bing SEO Reports:
Provides a scan of an organization’s website and can highlight some technical SEO errors.
What does PageSpeed Insights provide?
Advanced software analytics on website performance and load speed.
Explain the differences between first contentful paint (FCP) and first input delay (FID).
FCP
The time it takes for the user to see anything happen on screen.
FID
How usable a page is and how long it takes for a website to respond to a user’s input.
What does domain rating measure?
The strength of a backlink profile compared to those of other websites.
Explain search engine marketing. (2001)
An organization bids on keywords within a search account that are relevant to the organization’s products & services, and whose results are displayed on search engine results pages (SERPs).
What is the key difference between SEM and SEO in digital marketing?
SEM focuses on paid search advertising (also called SEA), while
SEO aims to improve rankings in natural (organic) search results on SERPs.
What are some key objectives for SEM?
Drive traffic to an organization
Create leads & qualified leads
Convert consumers from leads to purchases
Gain customer insights
Establish expertise
Build the organization’s brand image
Enhance the organization’s reputation
Increase digital trust
How do Dove and Axe use SEM differently to attract consumers?
Dove highlights customer value with benefits like "Tough on Sweat, Not on Skin," while Axe uses an educational approach ("How to use") along with product value messages like "Odor Protection" and "Stay Fresh."
How can SEM increase conversion rate optimization (CRO)?
Improvement of the percentage of consumers who arrive at a landing page & actually engage in an action that the brand desires, such as a purchase.
How can a search ad guide consumers through the conversion funnel?
A search ad can spark awareness, generate interest, lead consumers to click through to a landing page, and move them forward in the conversion process.
What can the analytics available through paid search advertising tools tell organizations about consumers?
The types of search terms they use
Which search engines they use
Other data
How do these insights help organizations?
Adapt & change their search ad content
Track customer journeys
Identify the stage of the customer journey (at the beginning consumers use broad search terms, towards the end very specific search terms)
Target consumers with relevant advertising (including remarketing/ retargeting)
How can organizations use paid search advertising to establish expertise in a specific area?
By consistently showing ads for targeted keywords, such as niche legal or accounting services, organizations can position themselves as local experts in their field.
Explain reminder/ recall advertising. What can reminder advertising and SEM do?
Prompts consumers to remember specific brands, products. or services, with a goal of having consumers decide to purchase specific brands again.
Reminder advertising and SEM:
help consumers gravitate toward familiar brands like google
may be regulated in some industries
may increase digital trust if it enhances a consumer’s conviction about the brand
Explain rapid positioning.
Success showing up on search engine in top advertising spots to establish a brand's authority and increase visibility for target keywords.
What are the few SEM strategies and tactics employed?
Search engine selection strategy
Account, campaign, & group strategies & tactics
Search ad auction & bidding strategy
Keyword strategy
Display ad strategies & tactics
Remarking & audience- targeting strategies
Landing page & website- related strategies
Budgeting strategies & tactics
What should the considerations include while choosing the search engine on which to conduct SEM?
Placement of search ads on SERPs
Search ad options
Competition
Search ad pricing
Expected results
Why should search marketers compare different search engines when planning search advertising?
Because ad costs and ranking difficulty vary by platform. Analyzing ROI helps determine if a search engine like Bing offers a more cost-effective option for advertising.
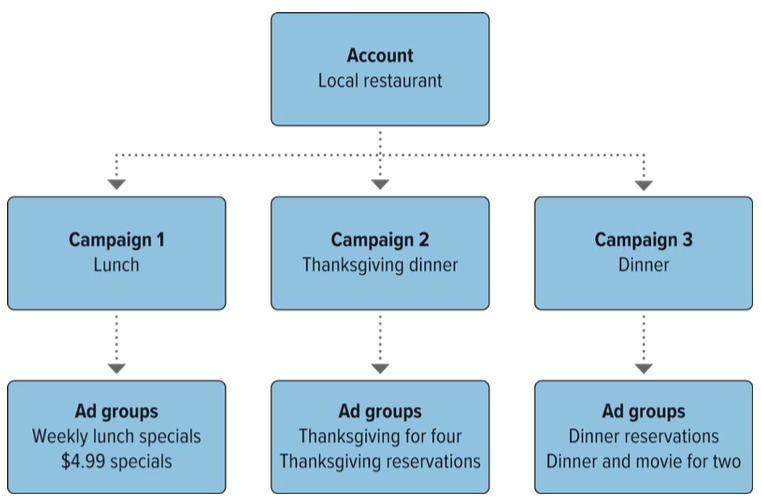
Digital marketers should employ SEM strategies and tactics at various levels:
Account level:
umbrella-like level, may include a number of campaigns
Campaign level:
individual subsets of strategic SEM activities intended to promote a goal/ objective; each campaign has its own budget, goals, target consumers, & search ads
Group level:
groups of search ads that are related; ad groups contain one/ more search ads that “share similar targets”
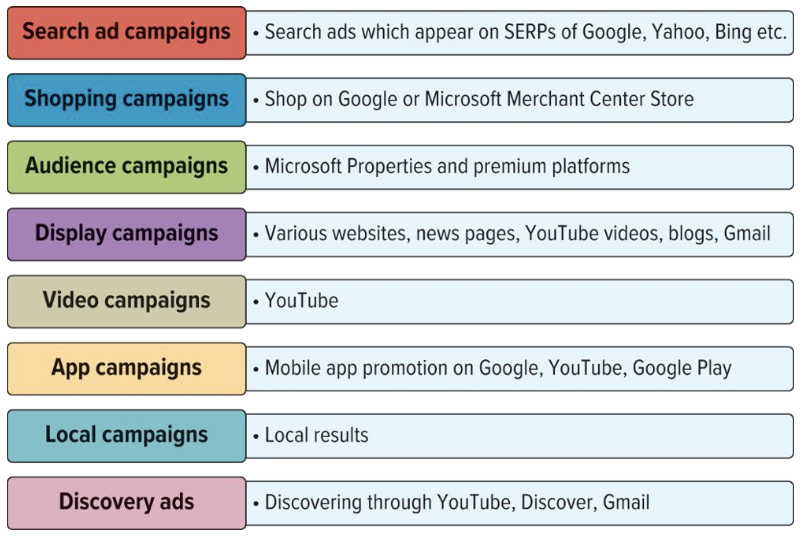
What are the different types of digital ad campaigns and their main focus?
Shopping campaigns:
retail-focused, attract qualified leads using product data
Audience campaigns:
build awareness through ads in content
Display campaigns:
reach broad audiences on various sites
App campaigns:
promote mobile apps
Local campaigns:
target consumers in specific locations
What factors influence the outcome of Google ad auctions?
Bid amount
Ad quality (CTR, relevance, landing page experience)
Ad rank (which affects visibility)
Ad position relative to other ads. (smart bidding, using machine learning to increase ad conversion rates)
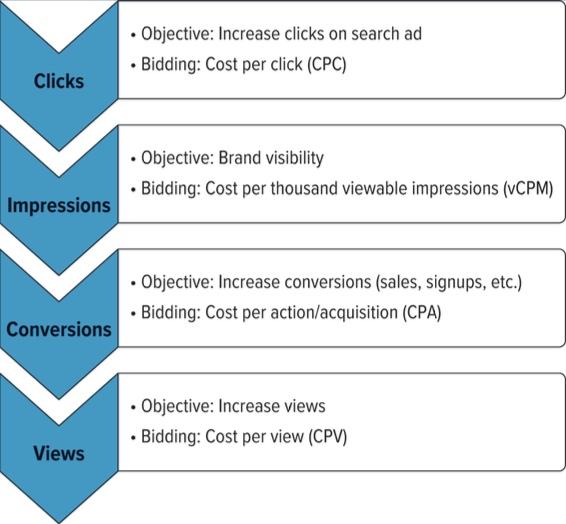
What are the main digital advertising bidding models and what do they charge for?
CPC: pay per ad click
CPM/vCPM: pay per impression or view
CPA: pay per conversion
CPV: pay per video view or interaction
What are the different types of keywords used in digital marketing?
General: broad terms (e.g., bike)
Branded: include brand names (e.g., Nike)
Competitive: used by competitors
Affinity: related but not direct
Long-tail: longer, specific phrases
Negative: excluded to avoid unwanted ad appearances
Can you give examples of different keyword types using Burger King?
General: "fast food" – broad, low conversion
Branded: "Burger King coupons" – targets brand-seeking users
Competitive: "McDonald’s Happy Meals Coupons" – attract rival’s audience
Affinity: "charbroiled burgers" – related to offerings
Long-tail: "Burger King near me open now" – very specific intent
Negative: "vegan" – avoids mismatched traffic
When creating a keyword list:
it is important to keep in mind various factors like:
target consumer
how they search
targeted stage in the conversation funnel
Explain negative keywords.
Terms excluded from ad targeting to prevent ads from appearing for irrelevant searches, thus optimizing budget and increasing the relevance of the audience reached.
What are some tools used to select effective keywords in digital marketing?
Google Keyword Planner: suggests relevant keywords
Microsoft Keyword Planner: offers keyword and bid insights
Semrush: finds optimal keywords, analyzes competitors, manages spending
Moz Keyword Explorer: provides suggestions, SERP and competitive analysis
What are display campaigns?
Marketing campaigns that advertise by placing visuals on display networks, a group of websites, apps, or social media that show banner ads to targeted audiences.
Display ads:
Stand out from the rest of the website in a box/ banner
Market specific brands, products, or services
Can be clicked on to lead to landing pages
Include banner ads
What is an example of remarking/ retargeting?
A consumer performs a search, clicks on a search ad, & ends up on an organization’s website.
The consumer borrows especially on pages that display specific types of dresses.
The consumer then leaves the website without making a purchase.
The website employs a tracking code that captures data about the consumer.
Consumer is presented the organization’s ads when they go to popular websites.
What are key components of a digital marketer’s search ad content strategy?
Search Ad Copy: visible content in search results
Responsive Ad Content: adapts to user queries using AI
Relevant & Brand-Appropriate: aligns with keywords and brand
Personalized Content: tailored to the user’s search
Culturally Sensitive: respects regional differences
Testing Content: uses methods like A/B testing to improve performance
What are the main parts of a search ad?
Display URL: website address (e.g., eco-tribe.com)
Headline: main clickable text
Description: brief ad summary
Ad Extension: extra links or info below the description
What are the different types of ad extensions in search ads?
Call extension: adds phone number or call button
Sitelink extension: links to specific pages
Callout extension: highlights key benefits (e.g., free delivery)
Price extension: shows product/service prices
Location extension: displays business location and hours