biopsych exam 1
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
110 Terms
Behavioral neuroscience
The study of the biological bases of psychological processes and behavior
Dualism
The notion that the mind has an immaterial aspect and is distinct from the material body and brain
Localization of function
The concept that different brain regions specialize in specific behaviors
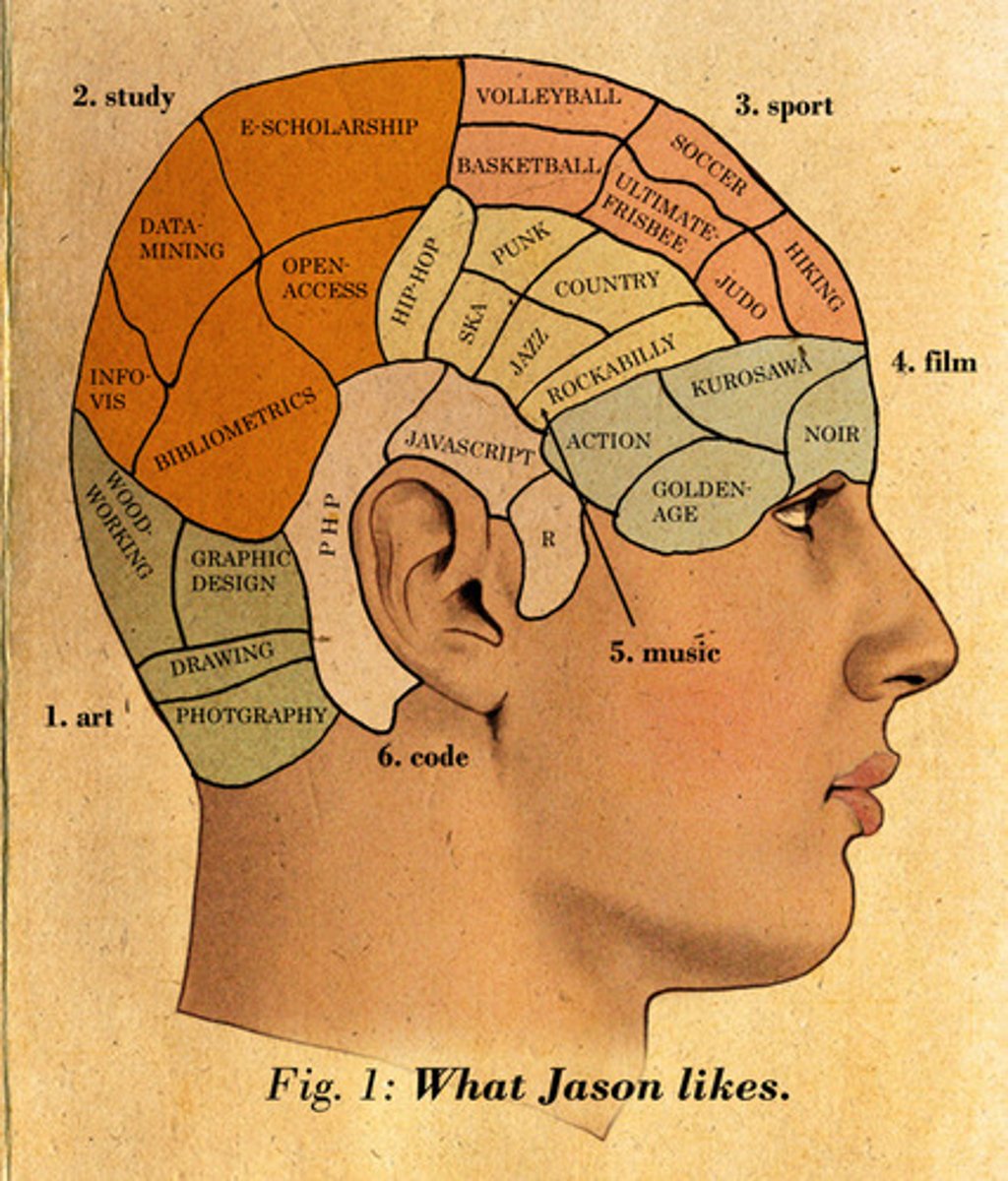
Phrenology
The belief that bumps on the skill reflect enlargements of brain regions responsible for certain behavioral faculties
Neuroplasticity
The ability of the nervous system to change in response to experience or the environment
Neurons
The cell and basic unit of the nervous system
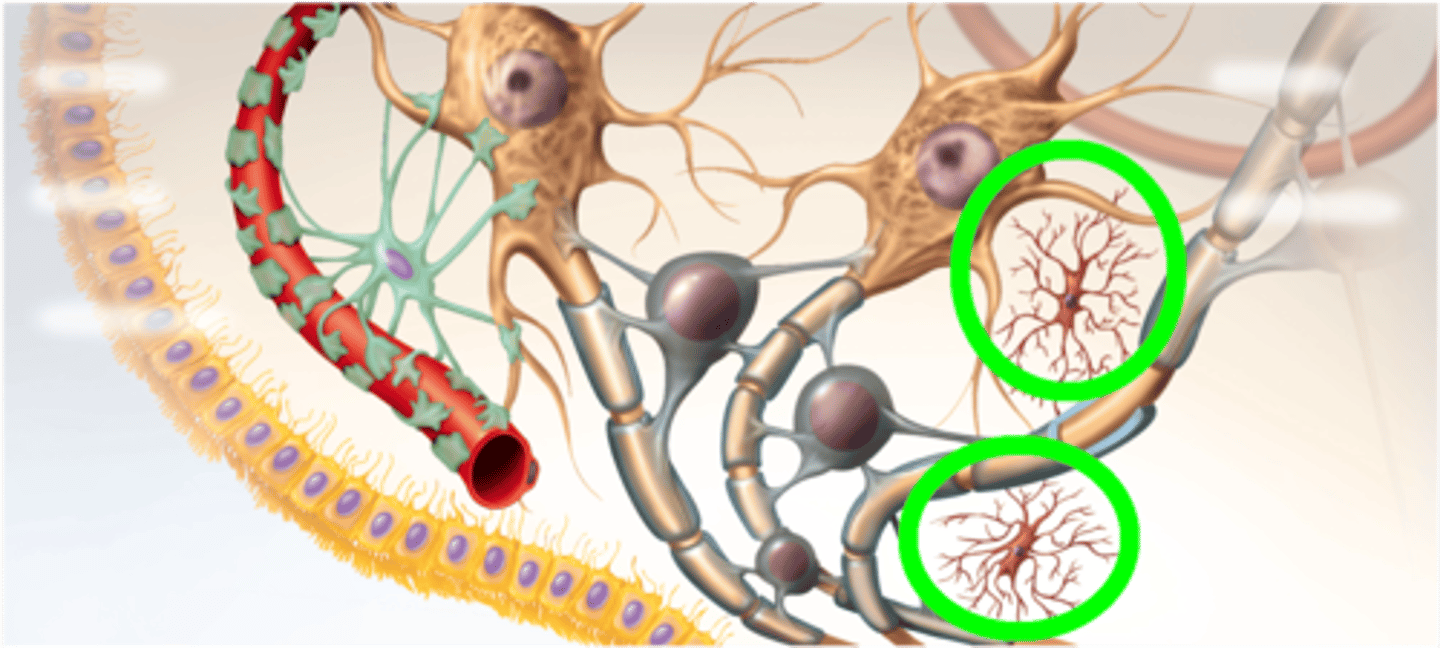
Glial cells
nonneuronal brain cells that provide structural, nutritional, and other types of support to the brain
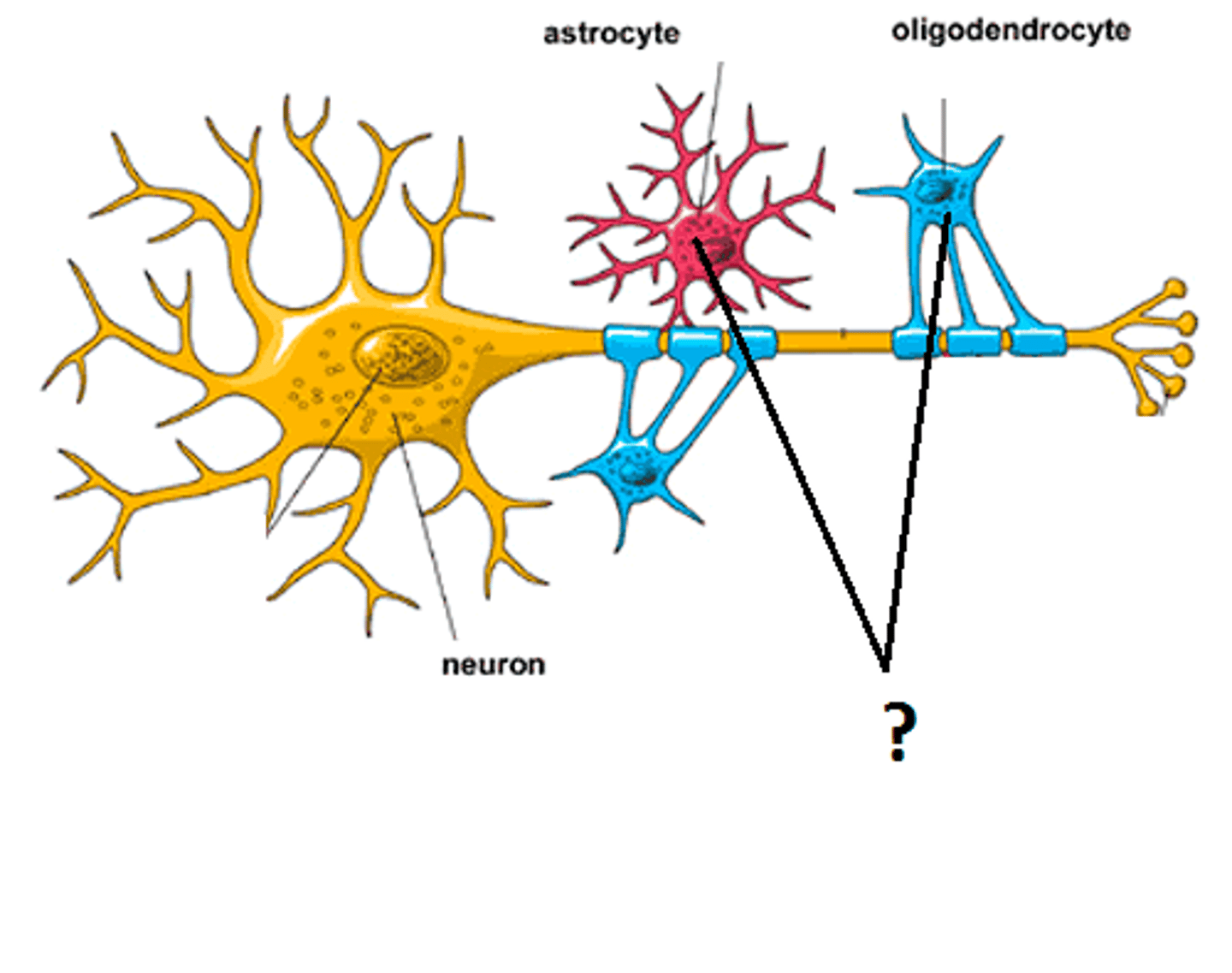
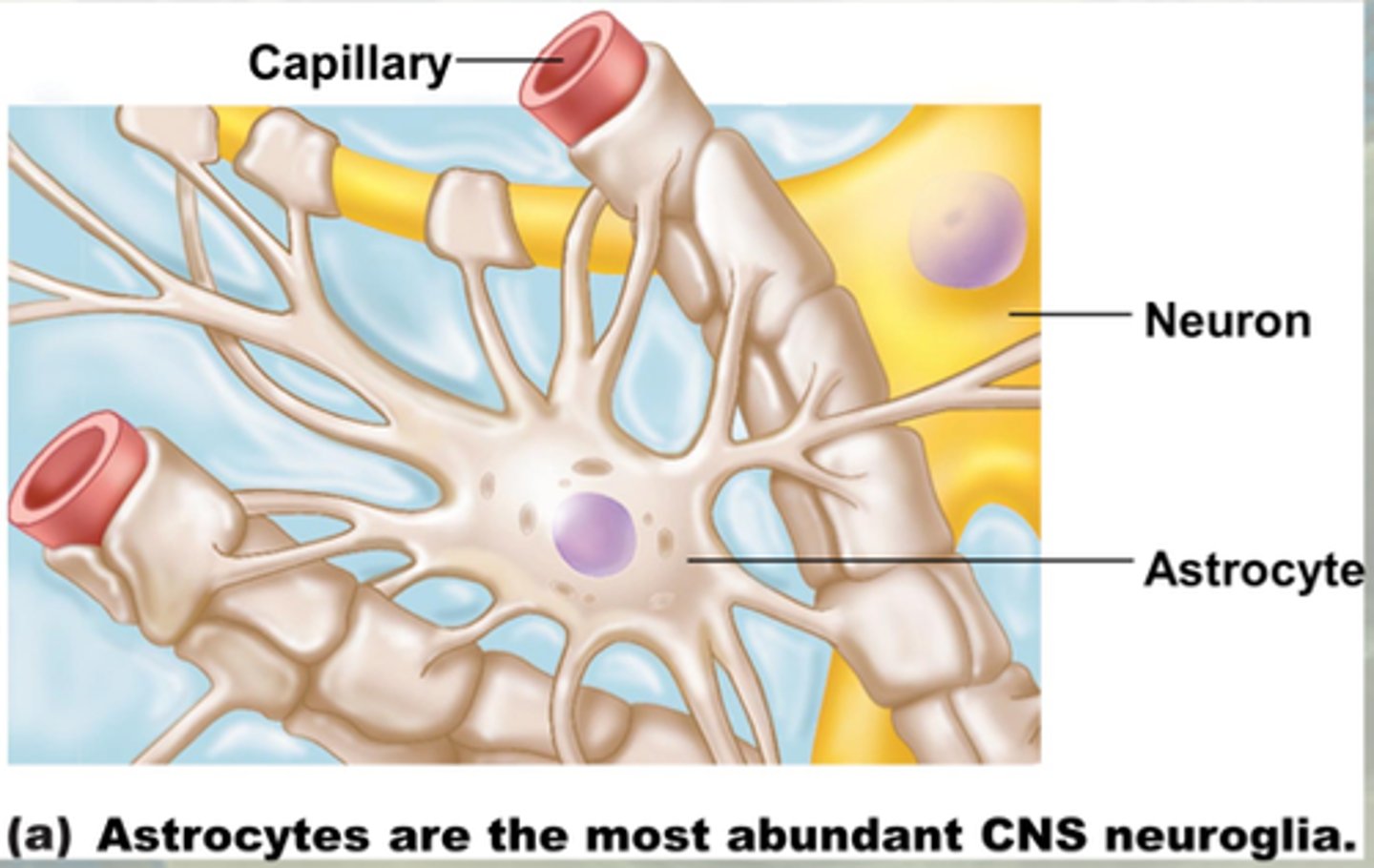
Astrocytes
Type of glial cell that provides structural and metabolic (bloodflow) support for neurons in the CNS.
Oligodendrocytes
Type of glial cell in the CNS that wrap axons in a myelin sheath.
Schwann cells
Type of glial cell in the PNS that wrap axons in a myelin sheath
Microglia
Type of glial cell that is tiny and mobile and clean sites of injury
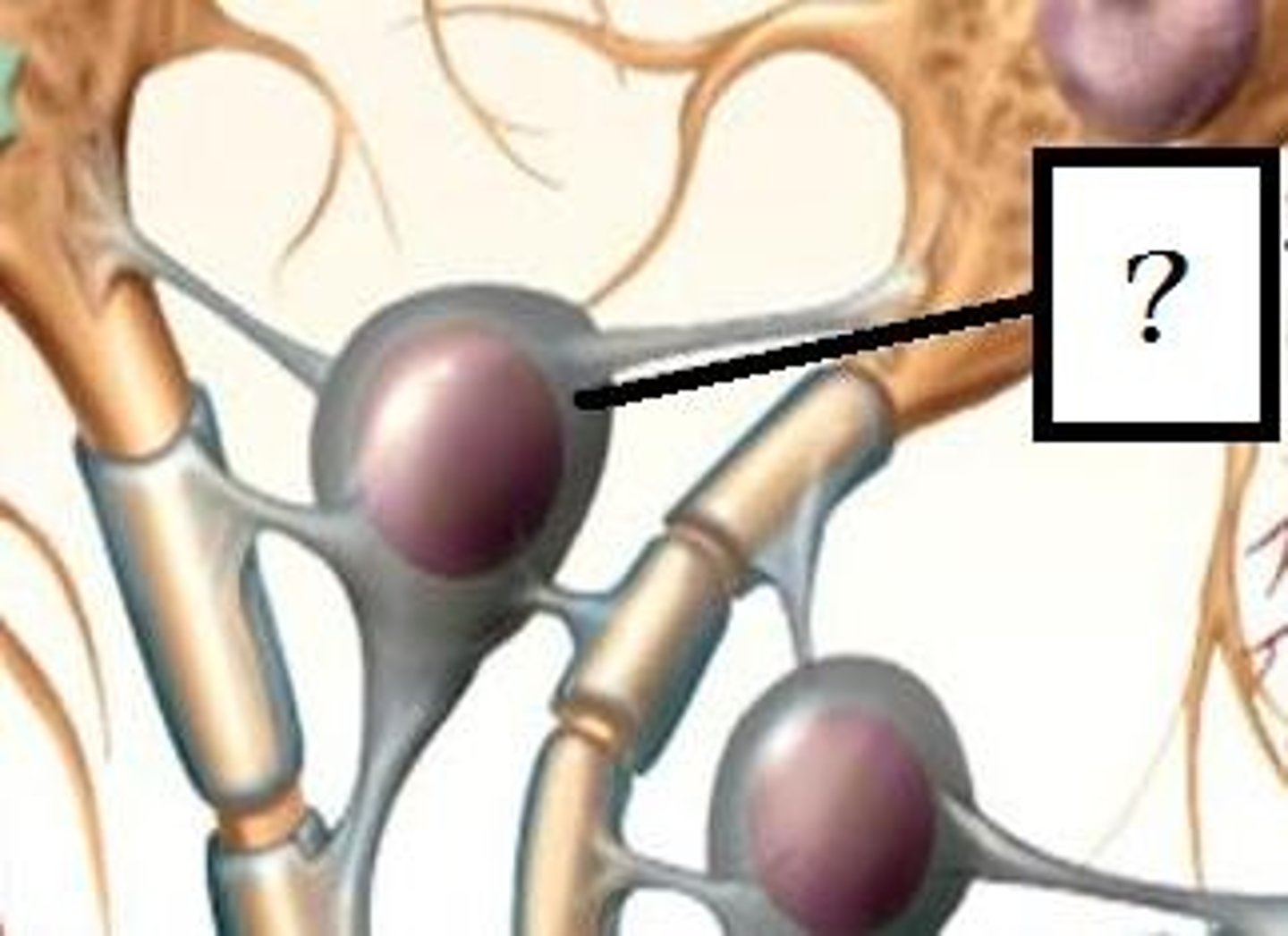
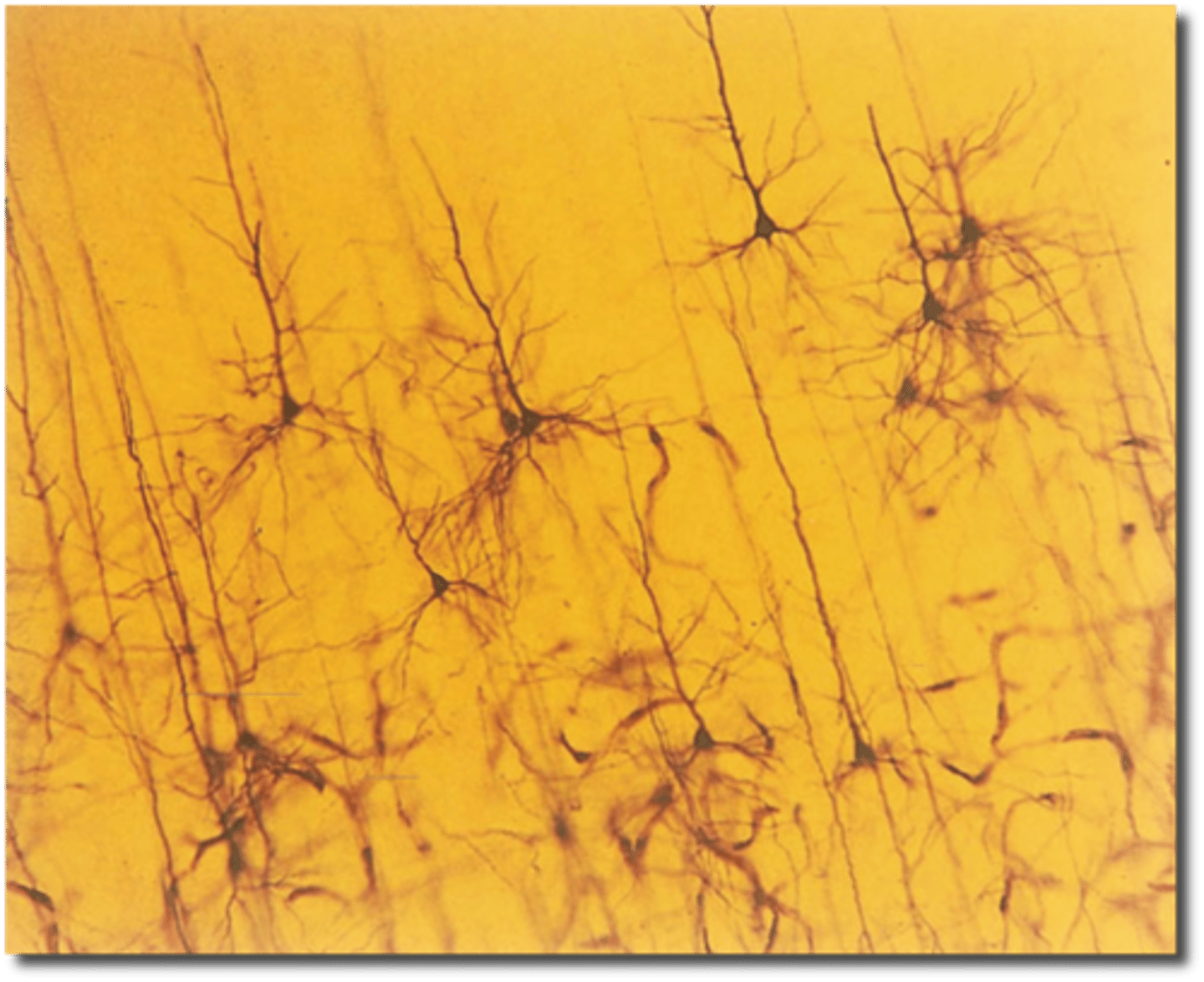
Golgi stains
Histological technique that labels a small amount of neurons in a sample but stained cells are stained completely, revealing fine details
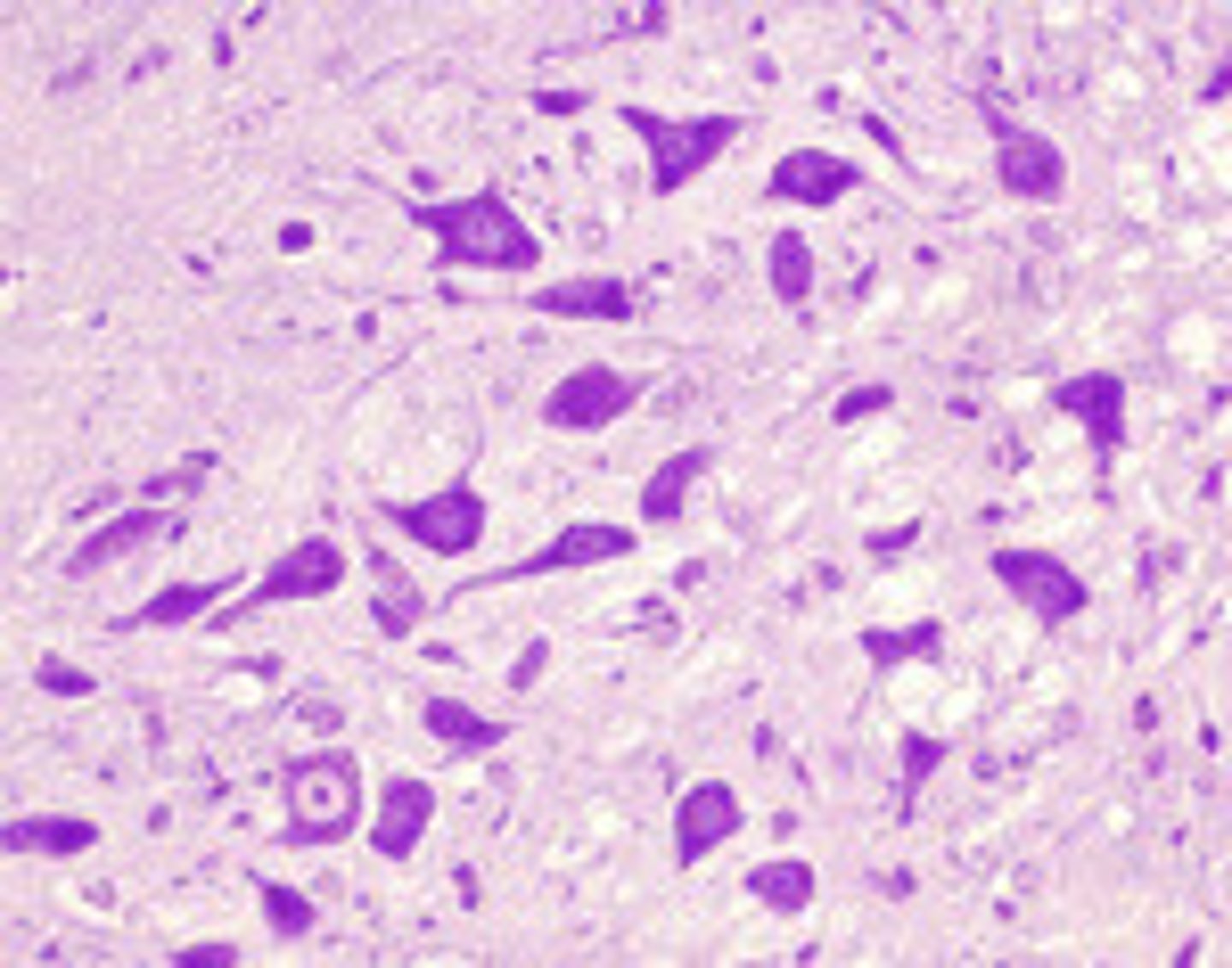
Nissl stains
Histological technique that identifies all cell bodies in a piece of tissue, allowing us to measure the size and number of cell bodies in a region
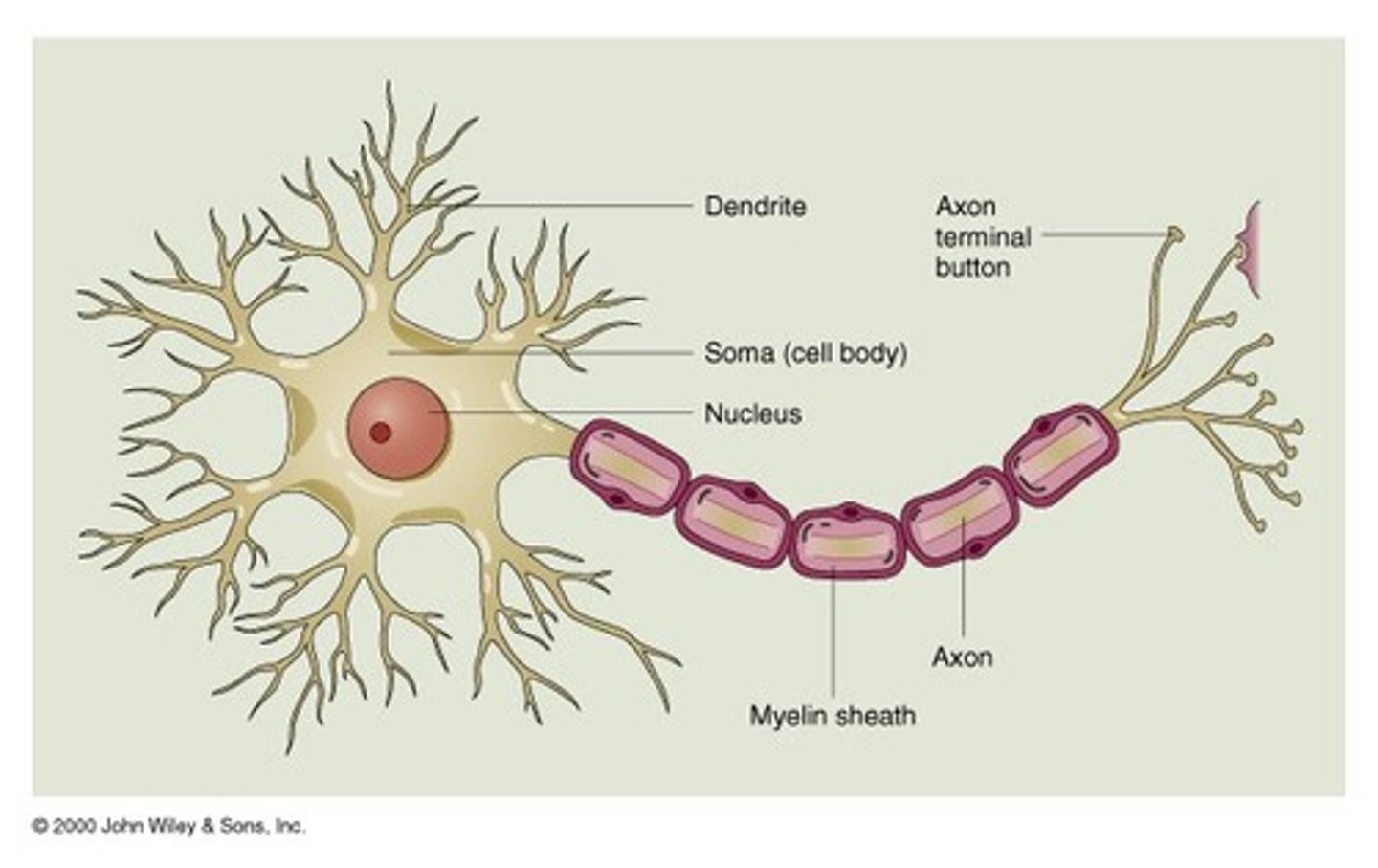
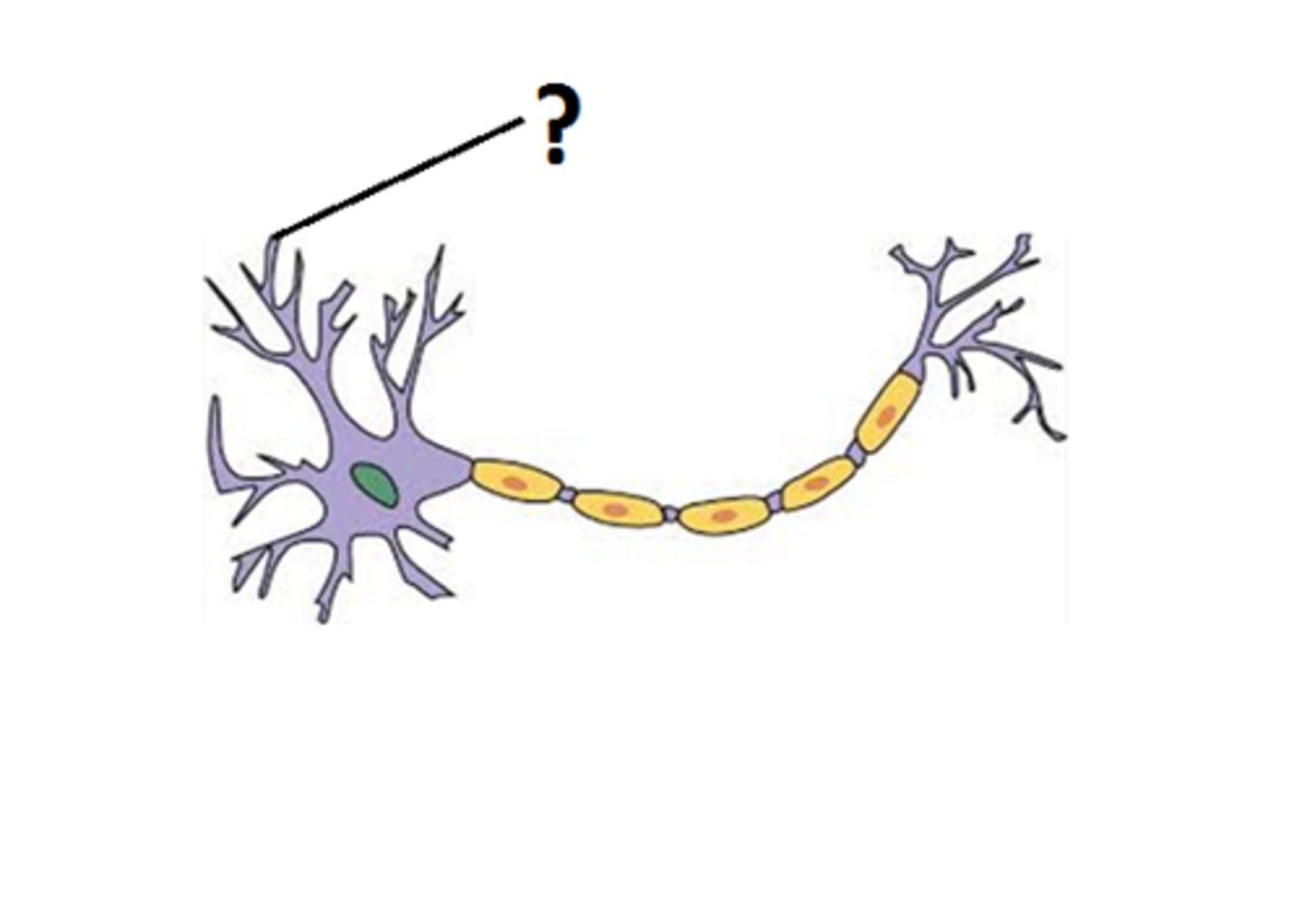
Dendrites
the part of a neuron that receives information from other neurons and relays it to the cell body. The input zone.
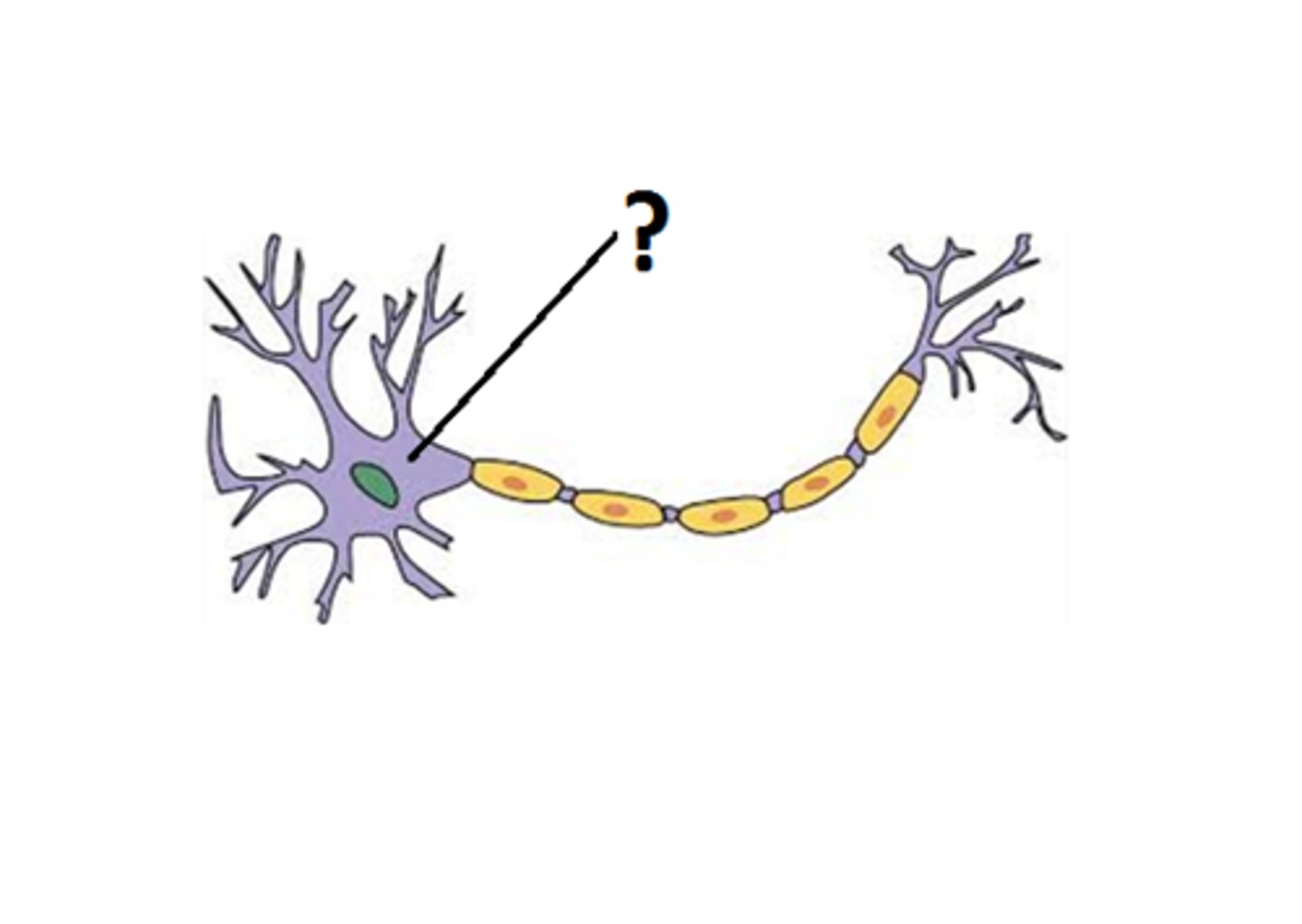
Cell Body/Soma
the part of the neuron that contains the nucleus and other parts of the cell needed to sustain its life. The integration zone
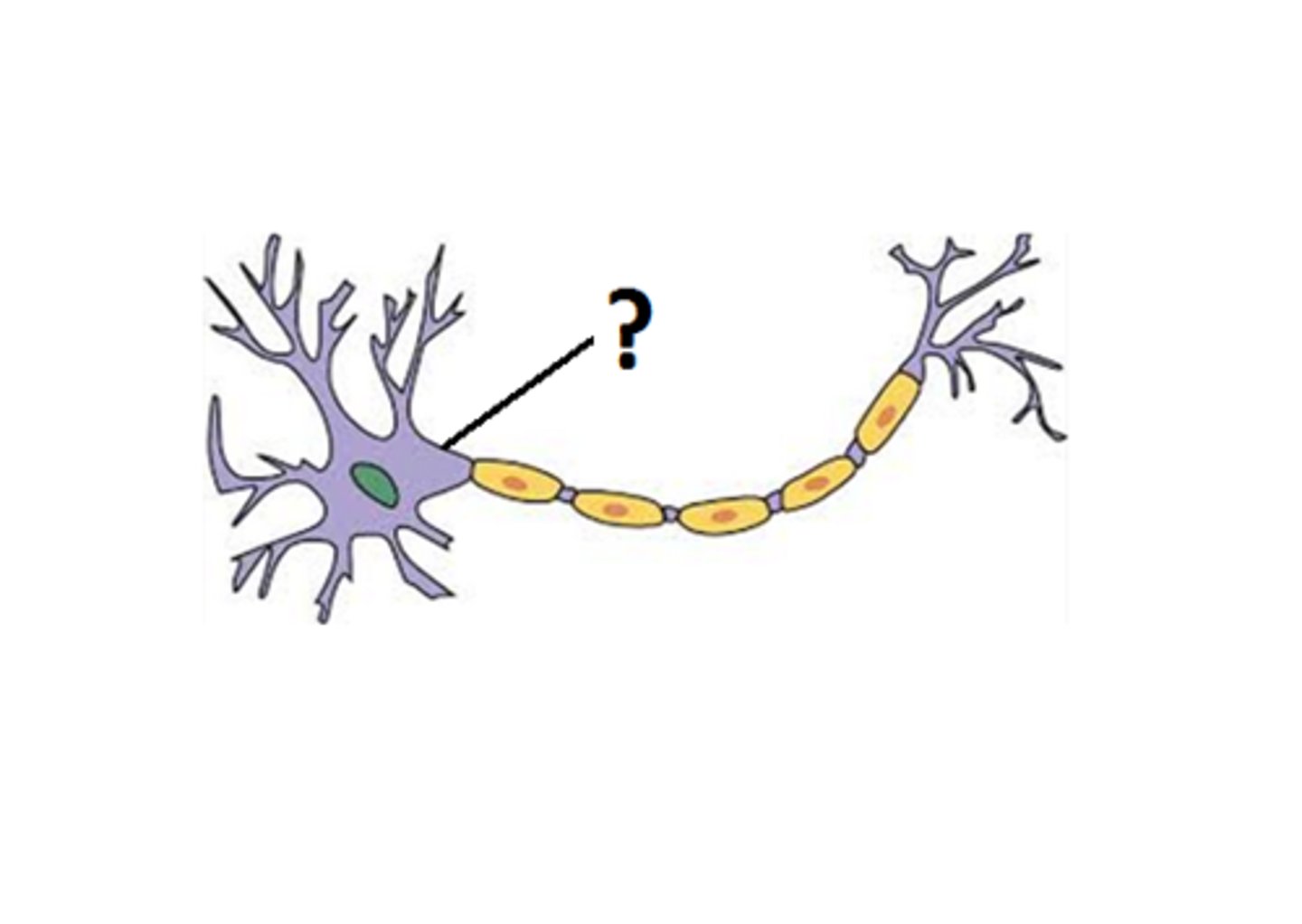
Axon Hillock
the part of the neuron that integrates electrical signals and fires an action potential. The integration zone
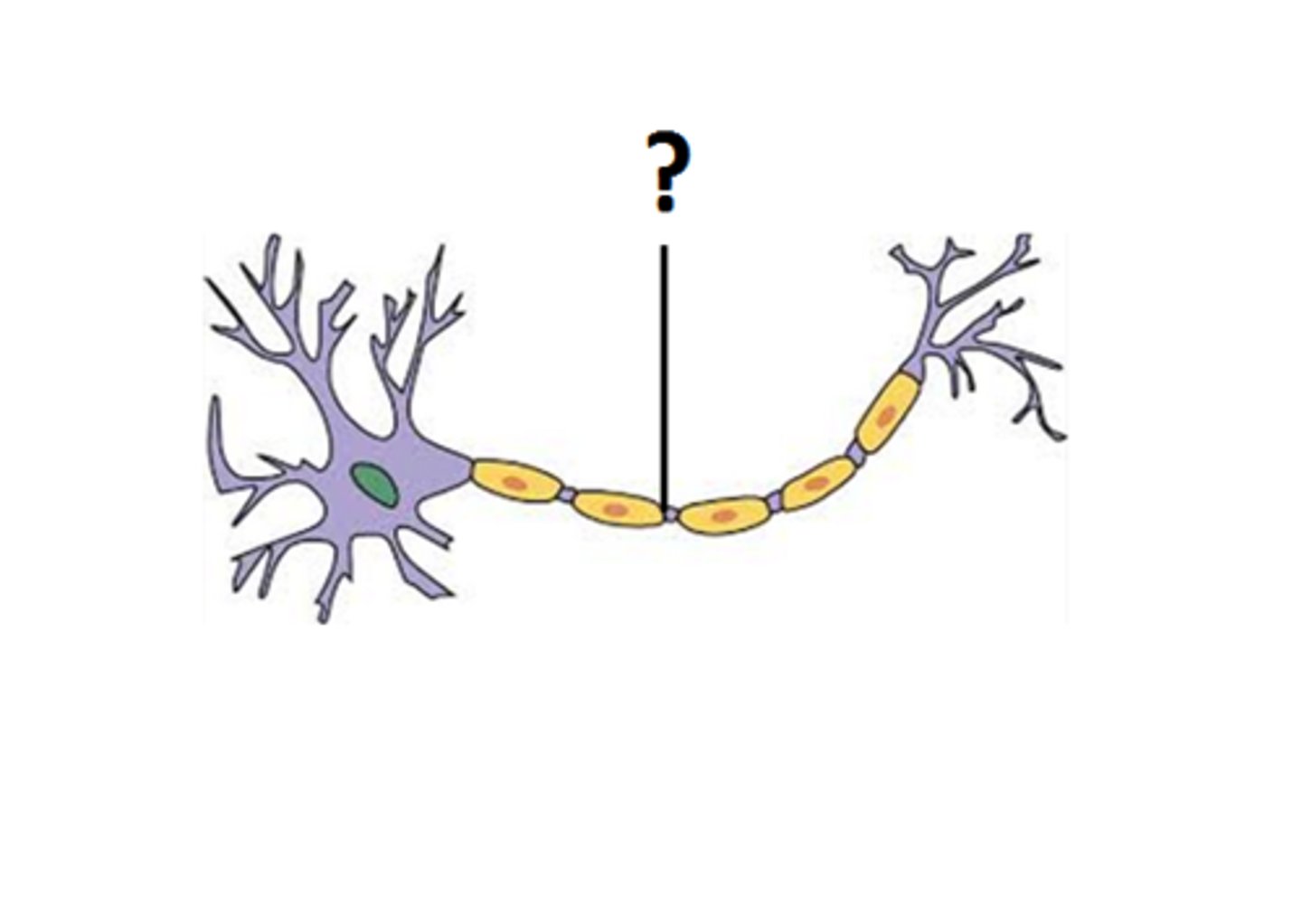
Axon
the part of the neuron that carries action potentials to the axon terminals. The conduction zone
Axon Terminals
the part of the neuron that transmits signals across synapses to other cells: the output zone.
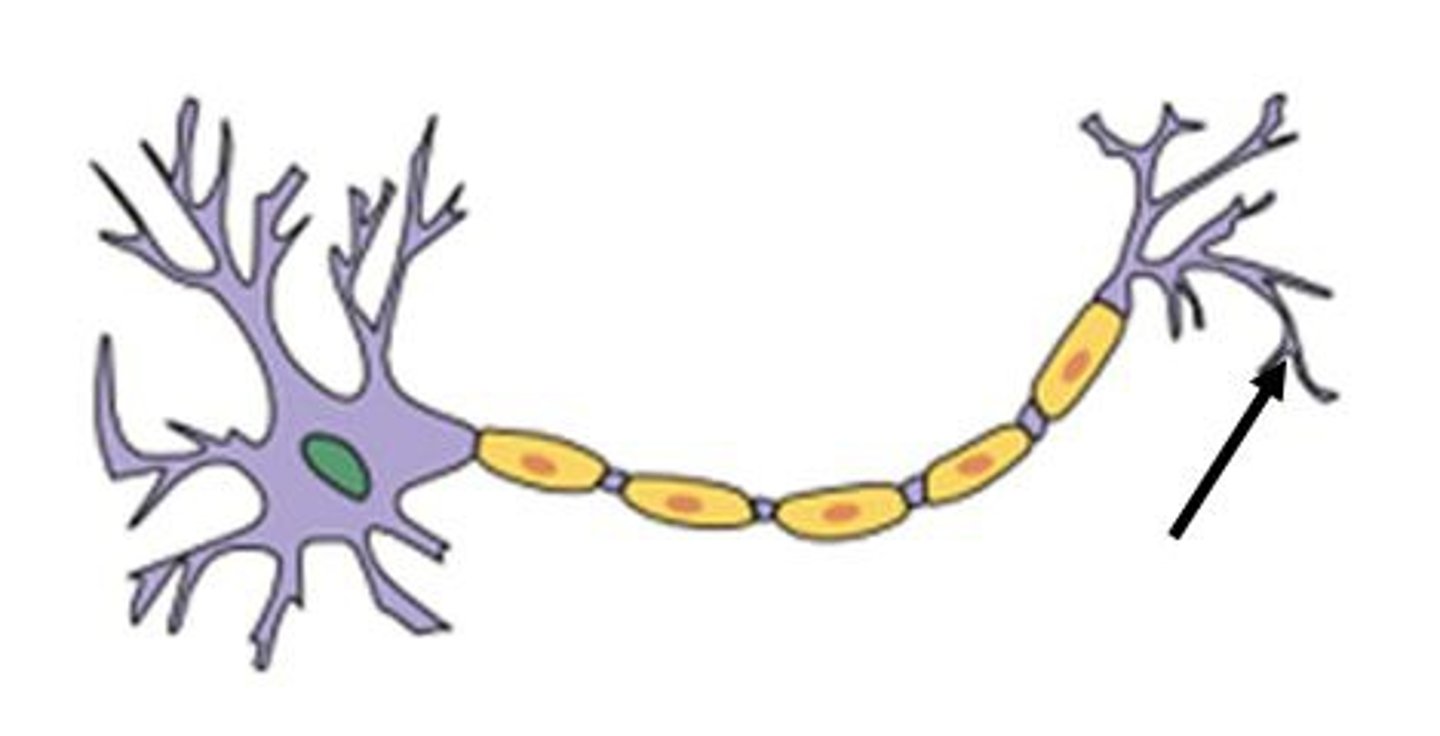
Synapse
Where information is transmitted between neurons across tiny gaps
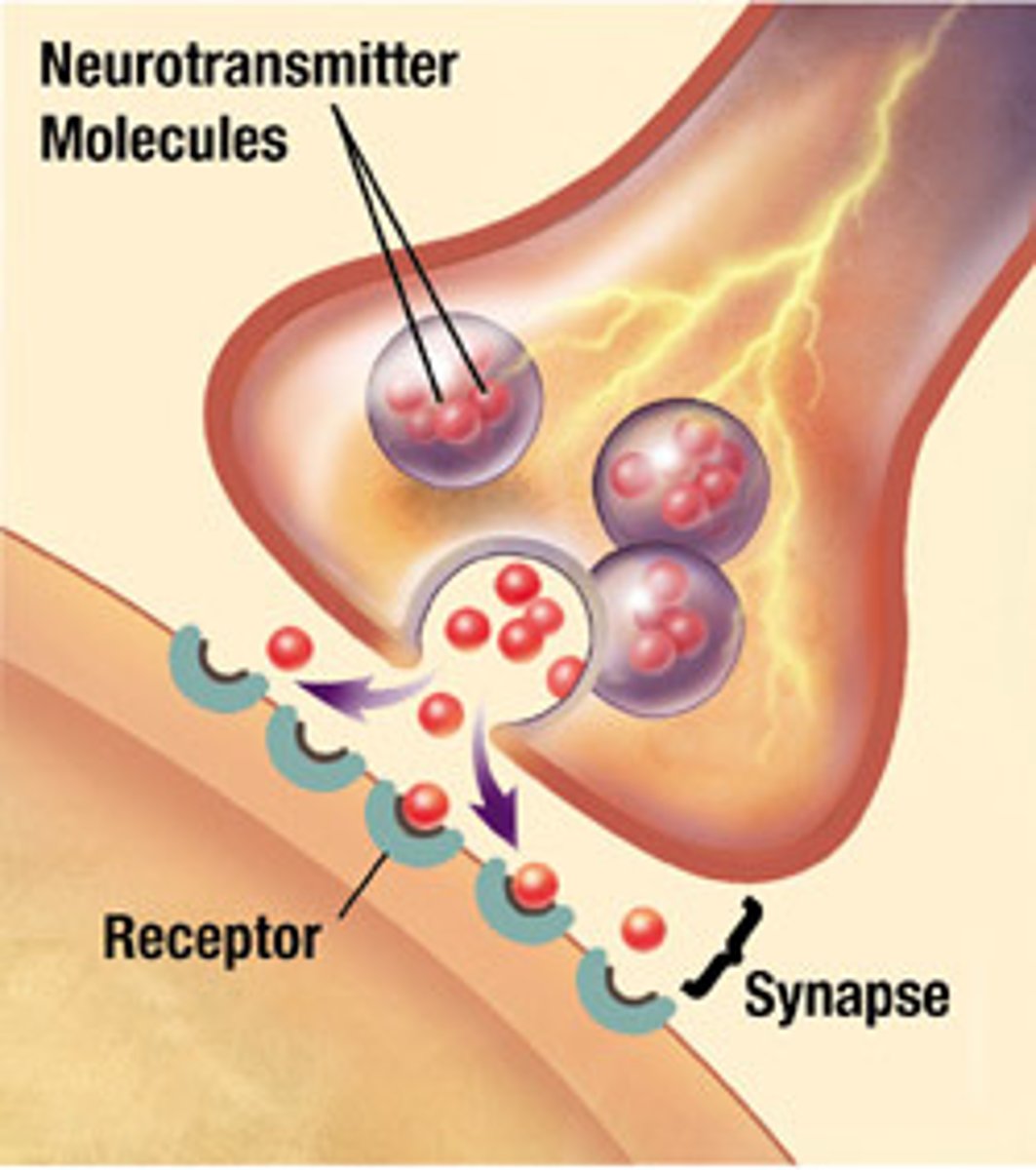
Synaptic vesicles
Sacs in the axon terminal that contain neurotransmitters
Sensory interneurons
A nerve cell that is directly affected by changes in the environment that convey information from sense organs to the brain
Motor interneurons
A neuron that transmits neural messages to muscles
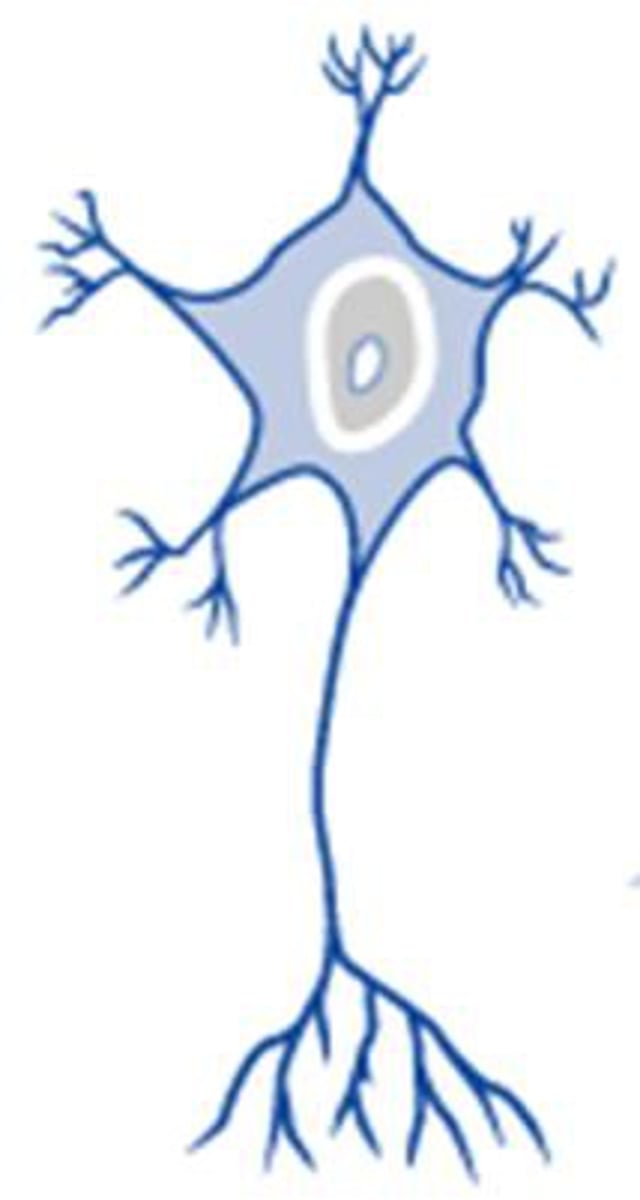
Multipolar neurons
Have many dendrites and one axon; most common type of neuron
Bipolar neurons
Have a single dendrite at the end of one cell and a single axon at the other end; most common in sensory systems
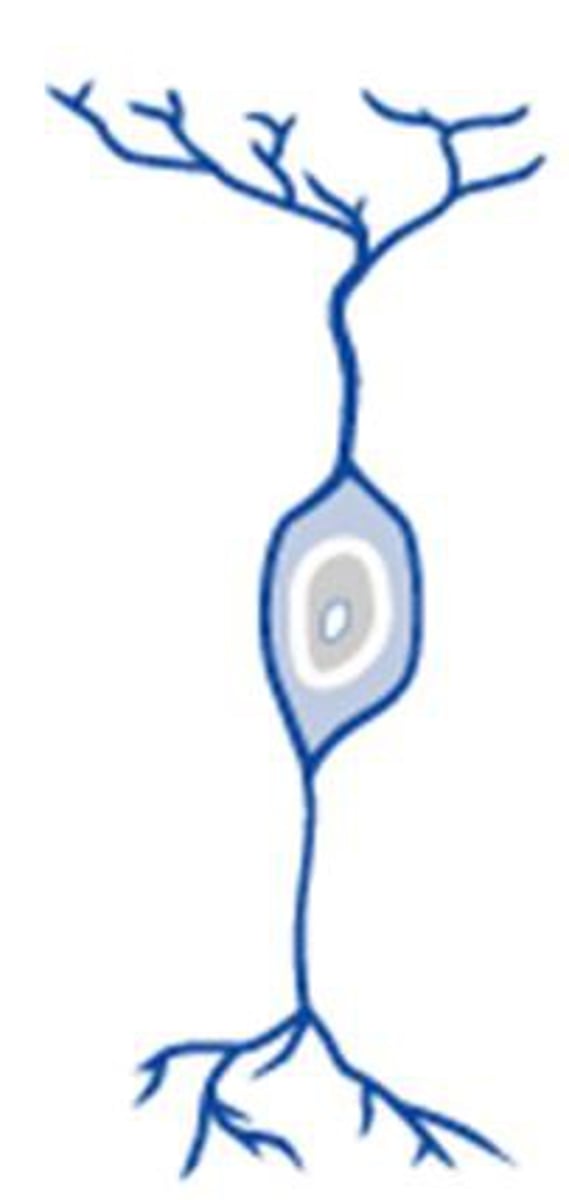
unipolar neurons
A neuron with a single projection serving as an axon that extends from the input to output zone
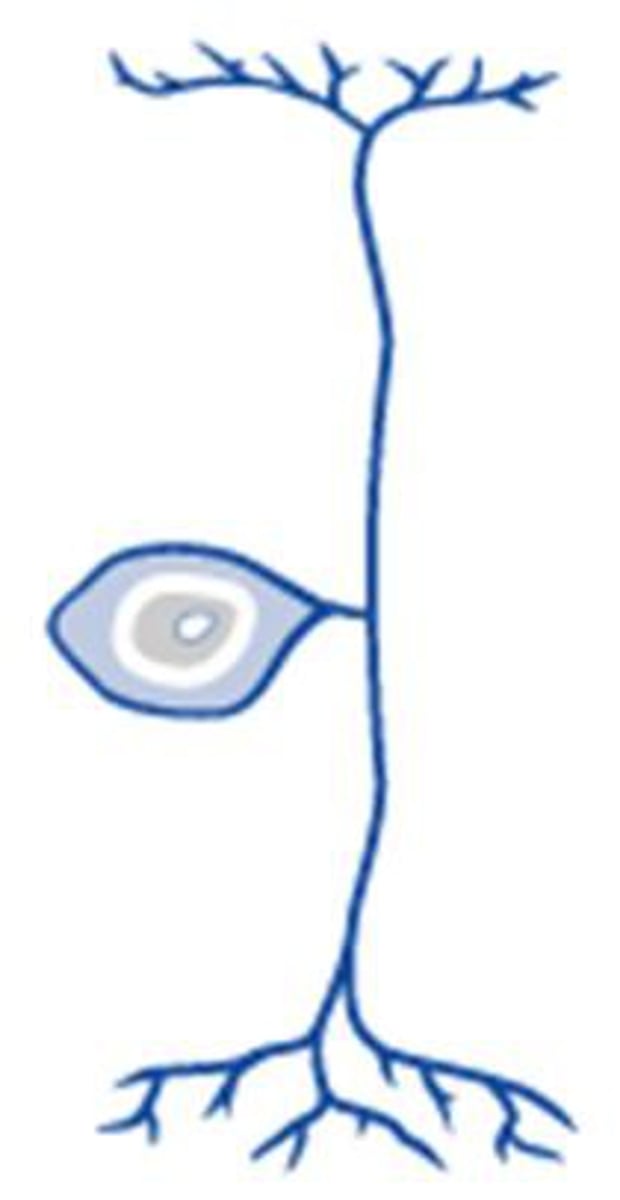
presynaptic neuron
The neuron that transmits a signal through the synapse
postsynaptic neuron
The neuron that receives a signal through the synapse
neurotransmitter
The signaling chemical released from the presynaptic neuron that diffuses across the synaptic cleft to alter the functioning of the postsynaptic neuron
receptors
parts of the cell membrane that receive the neurotransmitter and initiate or prevent a new electric signal
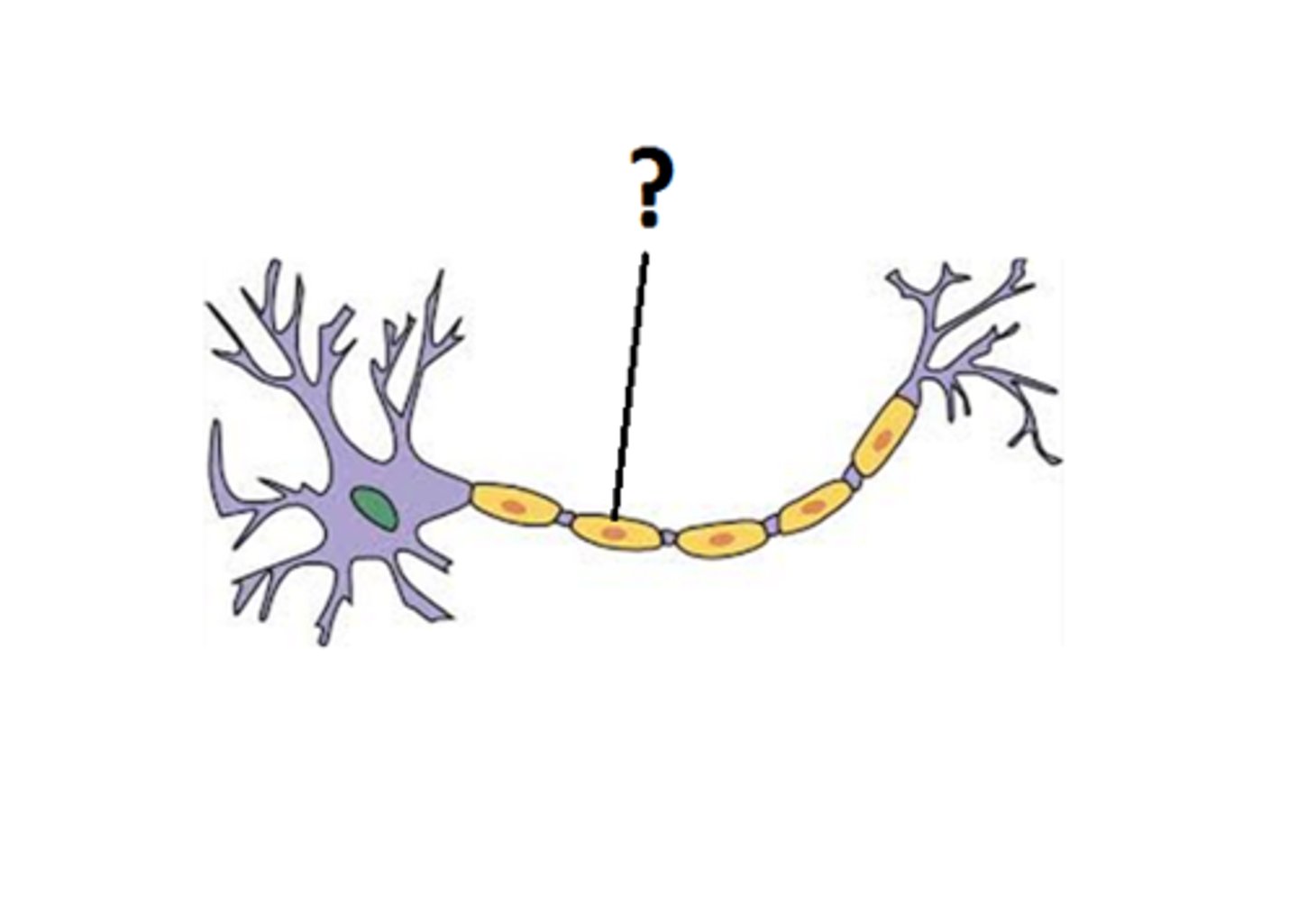
myelin
a fatty substance that helps insulate neurons and speeds the transmission of nerve impulses
central nervous system
consists of the brain and spinal cord
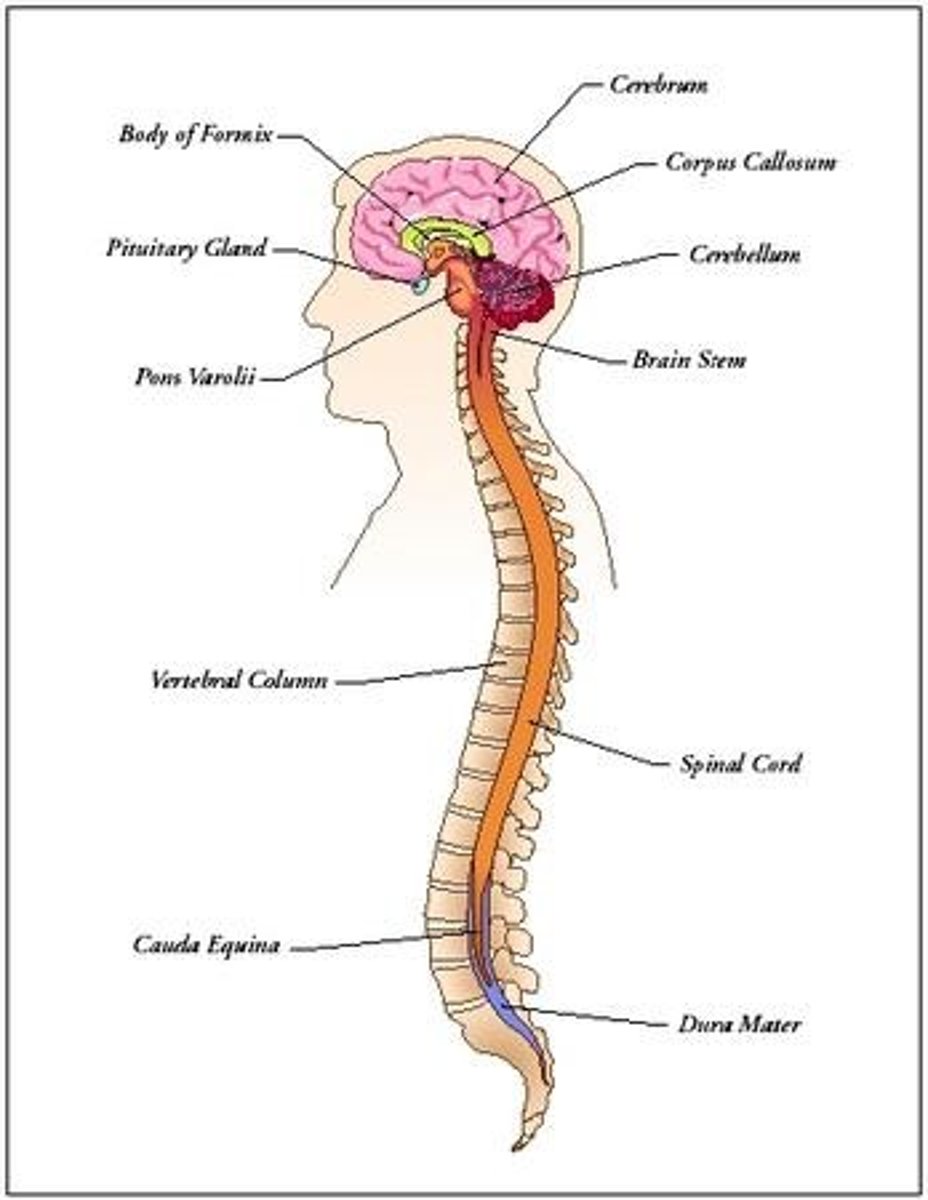
peripheral nervous system
The portion of the nervous system that includes all the nerves and neurons outside the spinal cord and brain.
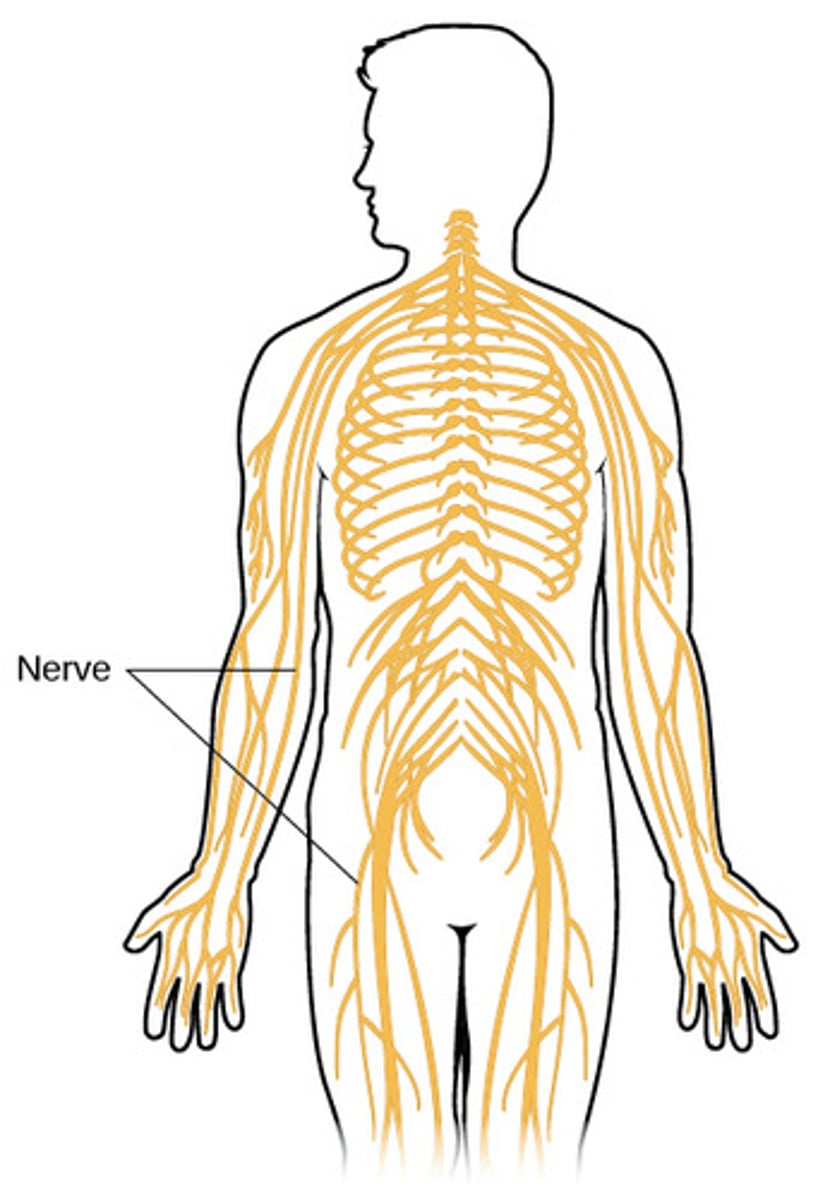
somatic nervous system
The main pathway through which the brain controls movement and receives sensory information from the body and sensory organs of the head.
autonomic nervous system
the part of the peripheral nervous system that controls the glands and the muscles of the internal organs (such as the heart). Its sympathetic division arouses; its parasympathetic division calms.
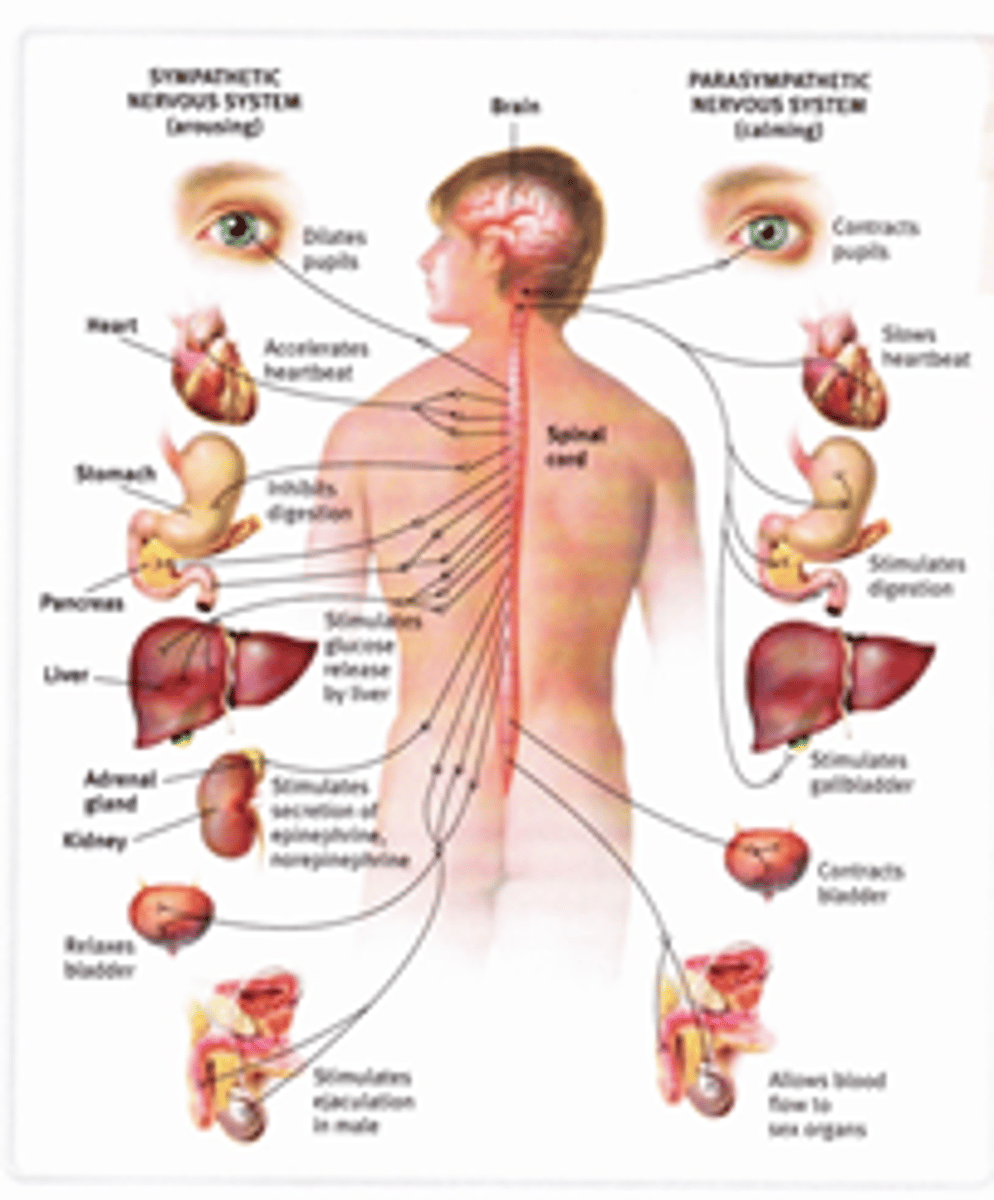
sympathetic nervous system
The part of the autonomic nervous system that acts as the fight-or-flight system, preparing the body for action
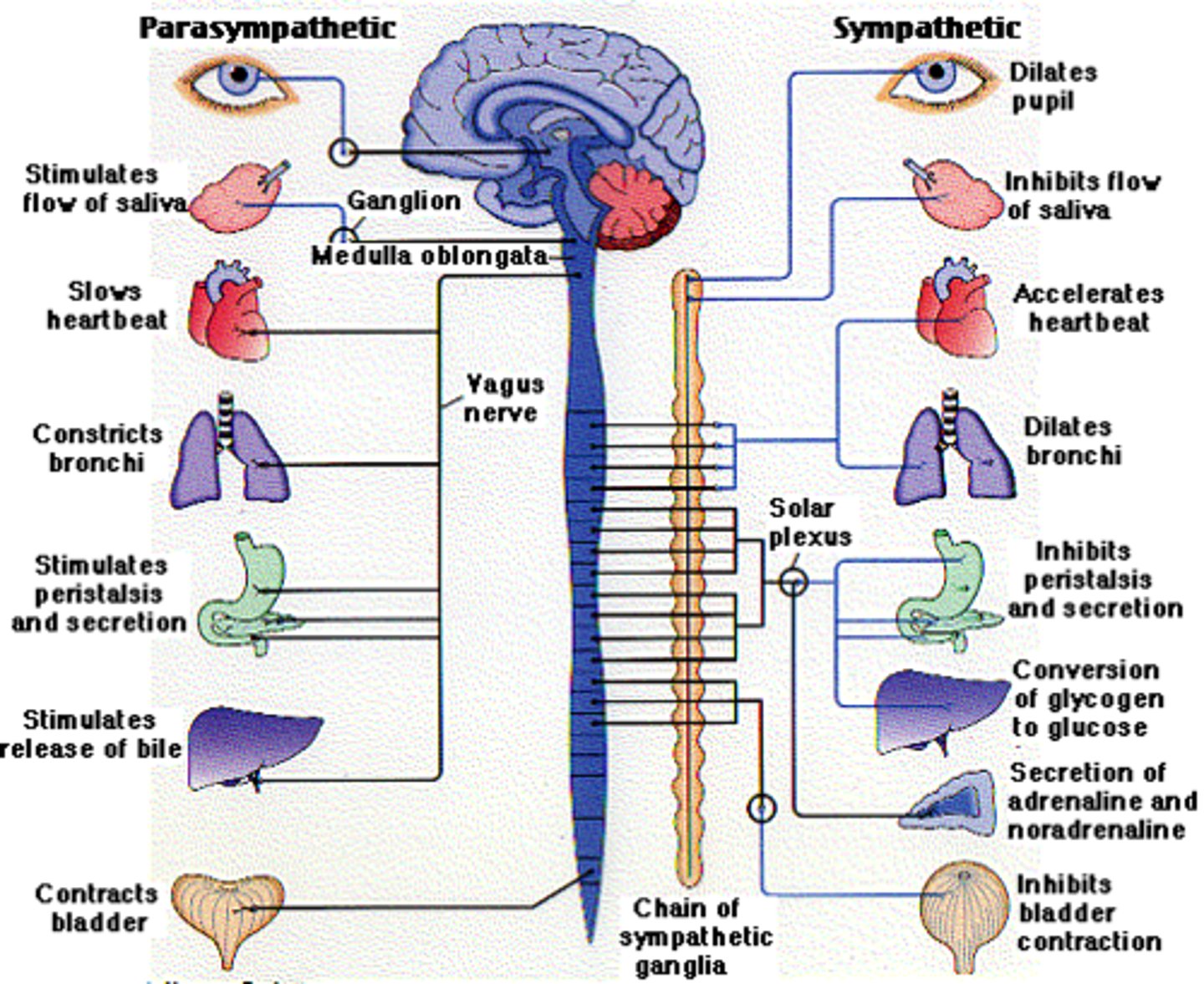
parasympathetic nervous system
The part of the autonomic nervous system that acts as the rest-and-digest system, preparing the body to relax and recuperate
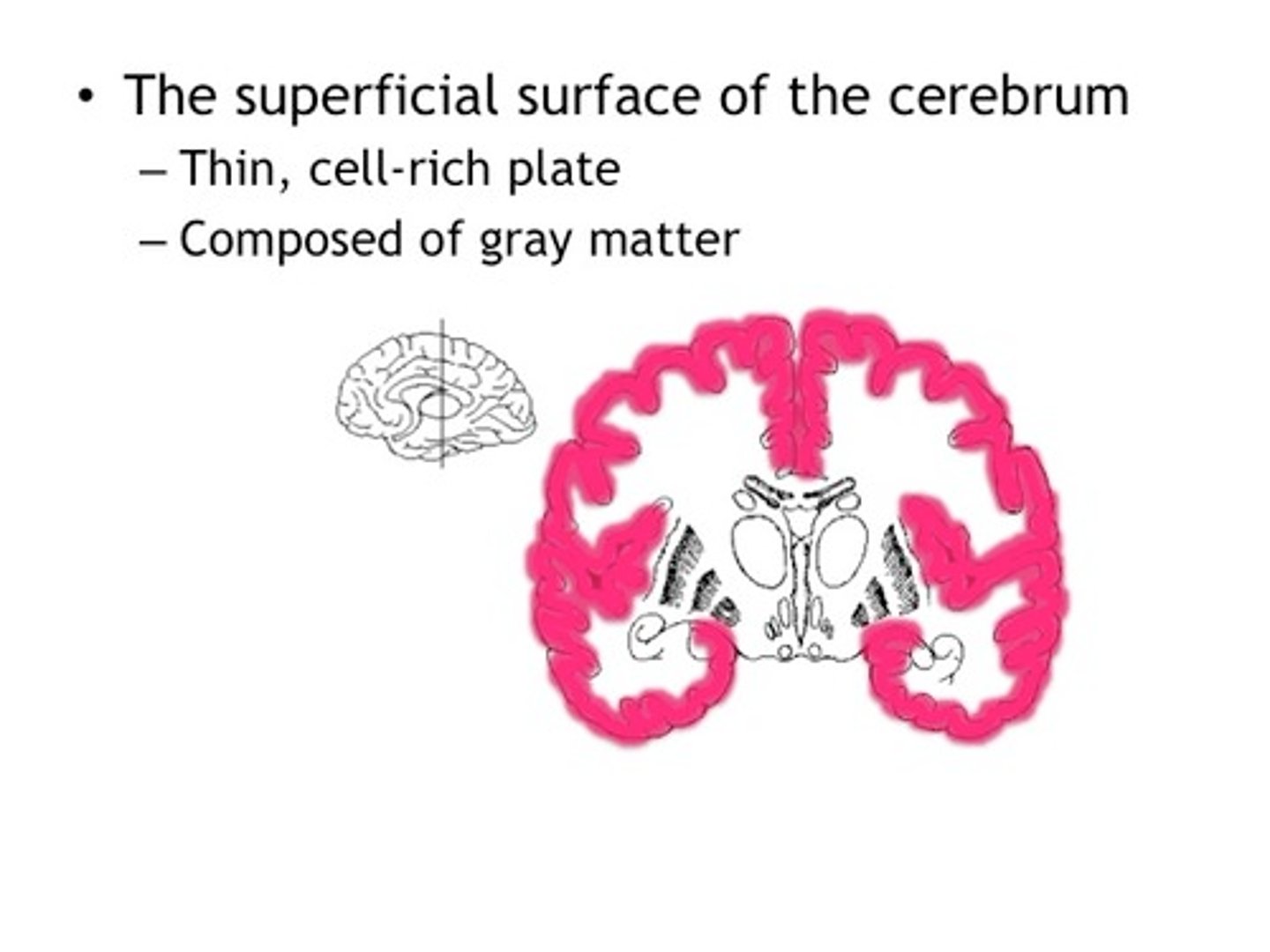
cerebral cortex
The outer covering of the cerebral hemispheres
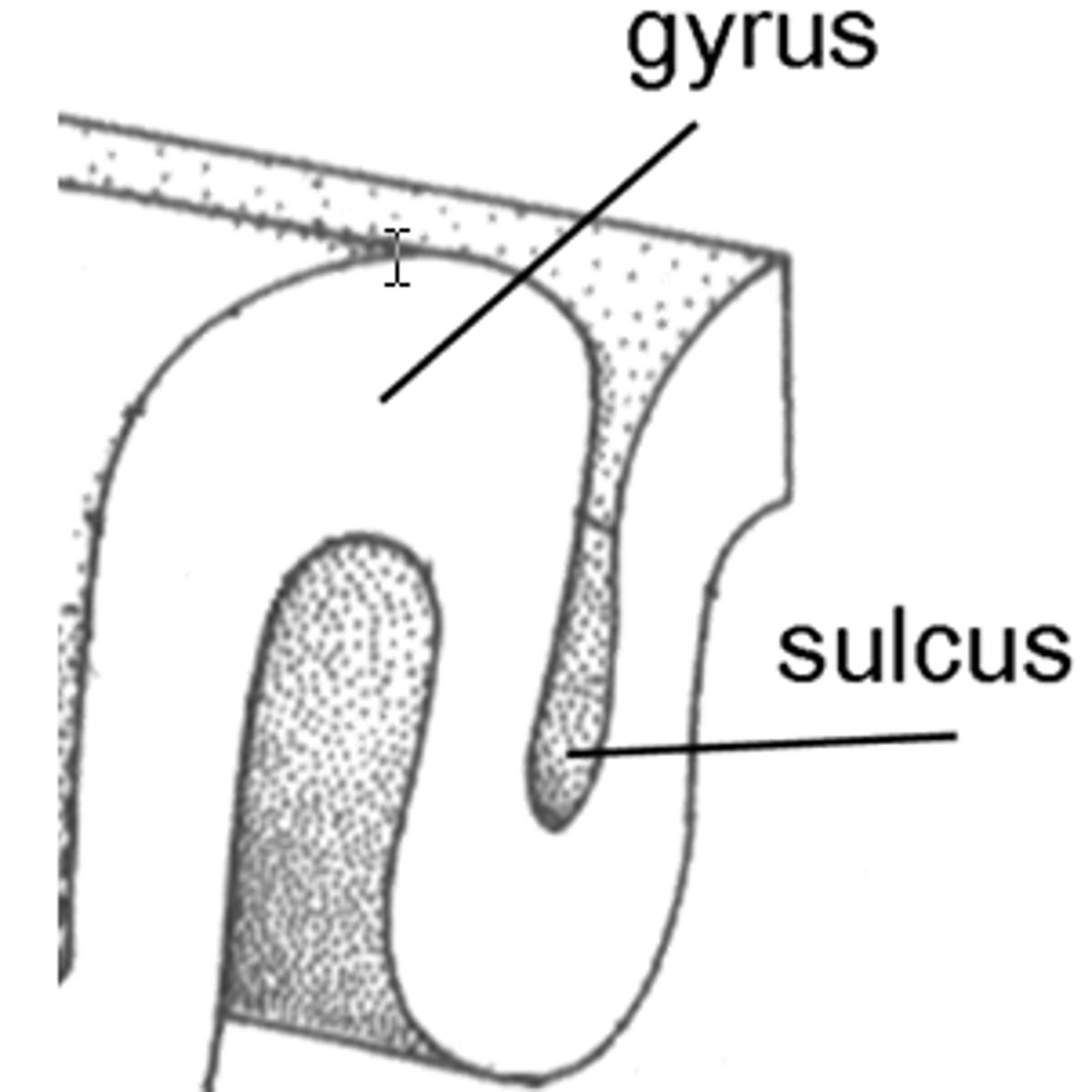
gyri/gyrus
Ridges or the cortex
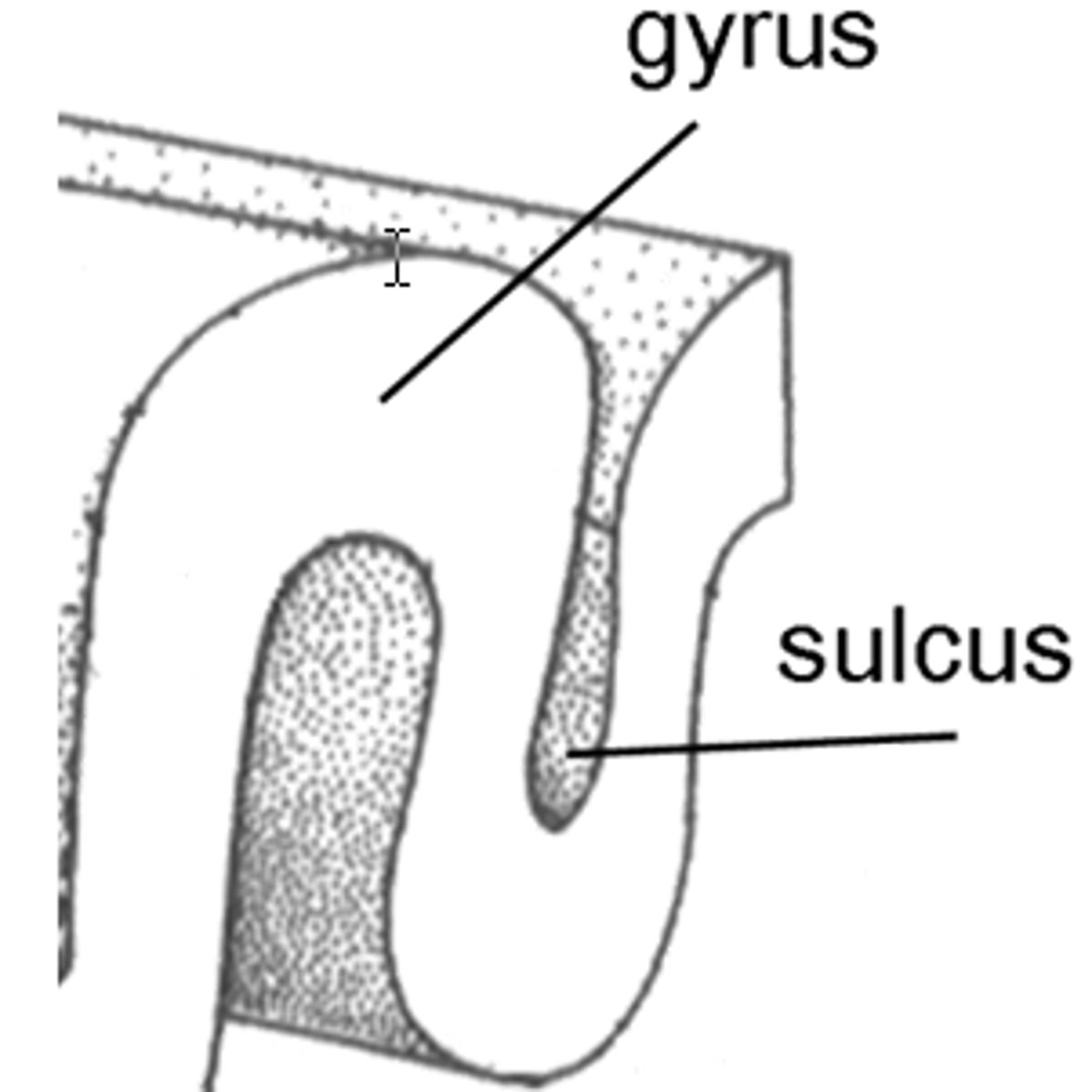
sulci/sulcus
grooves of the cortex
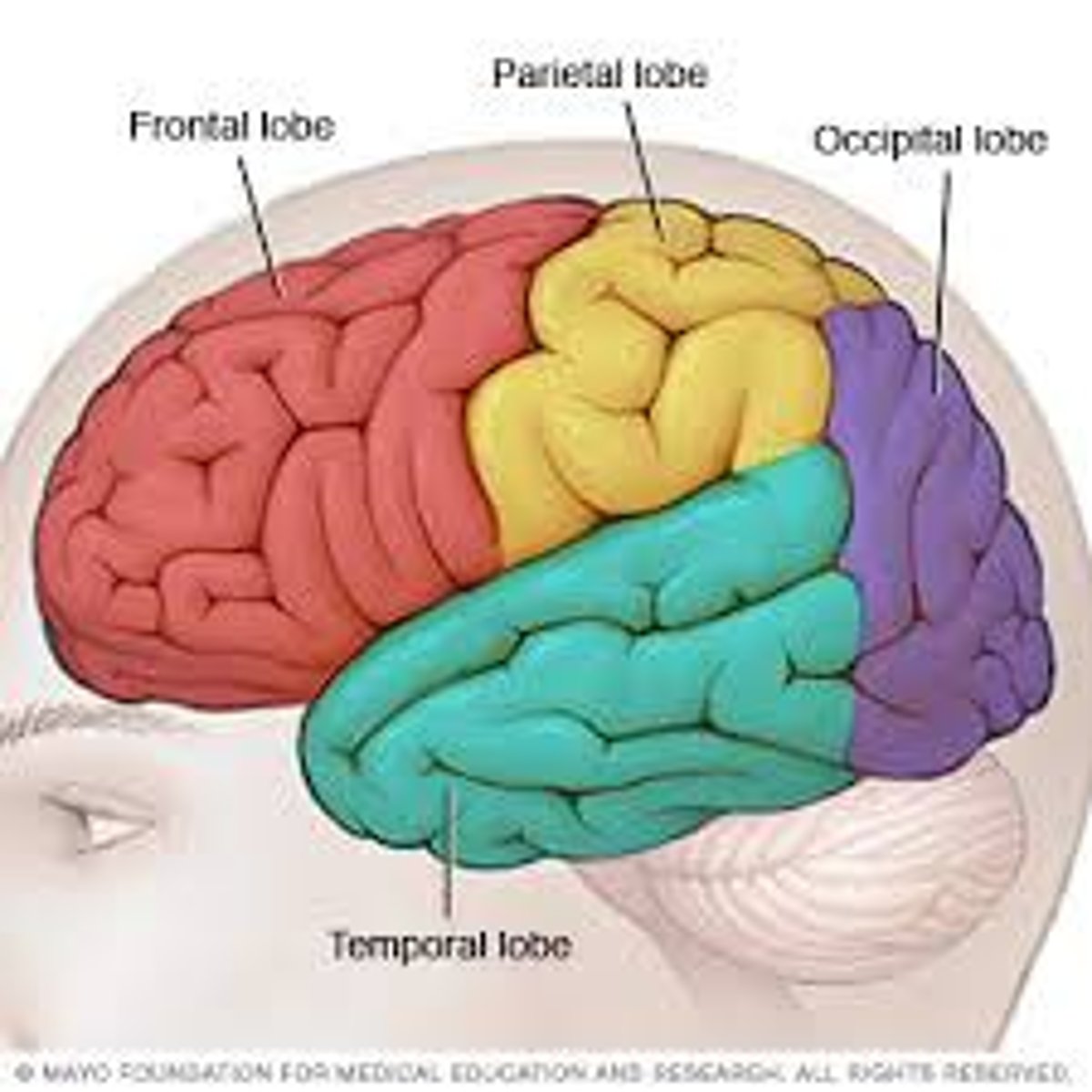
Four lobes of the cortex
frontal (motor), parietal (somatosensory(touch)) , occipital (vision), temporal (Audio)
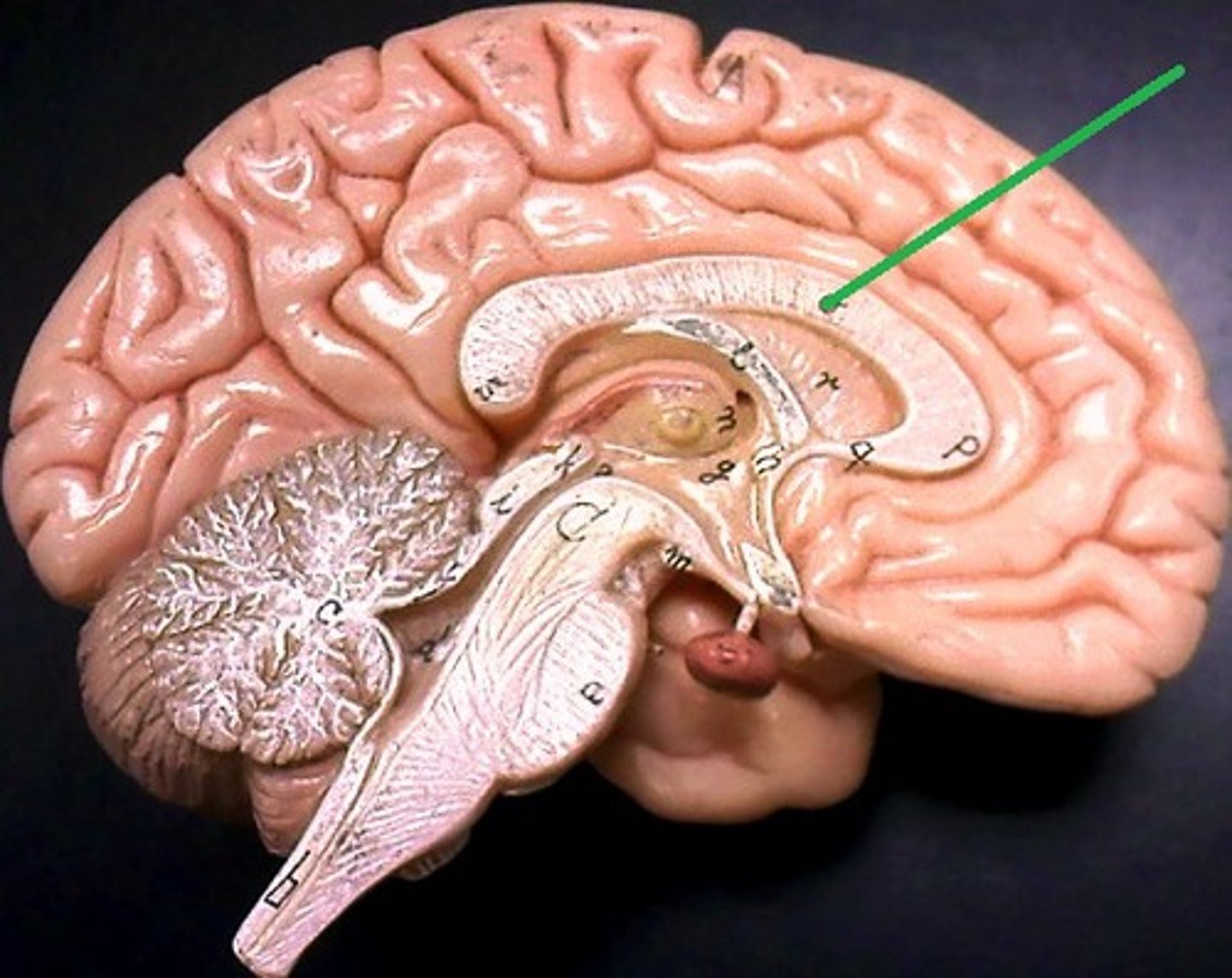
corpus callosum
The amin bands of axons that connects the two cerebral hemispheres
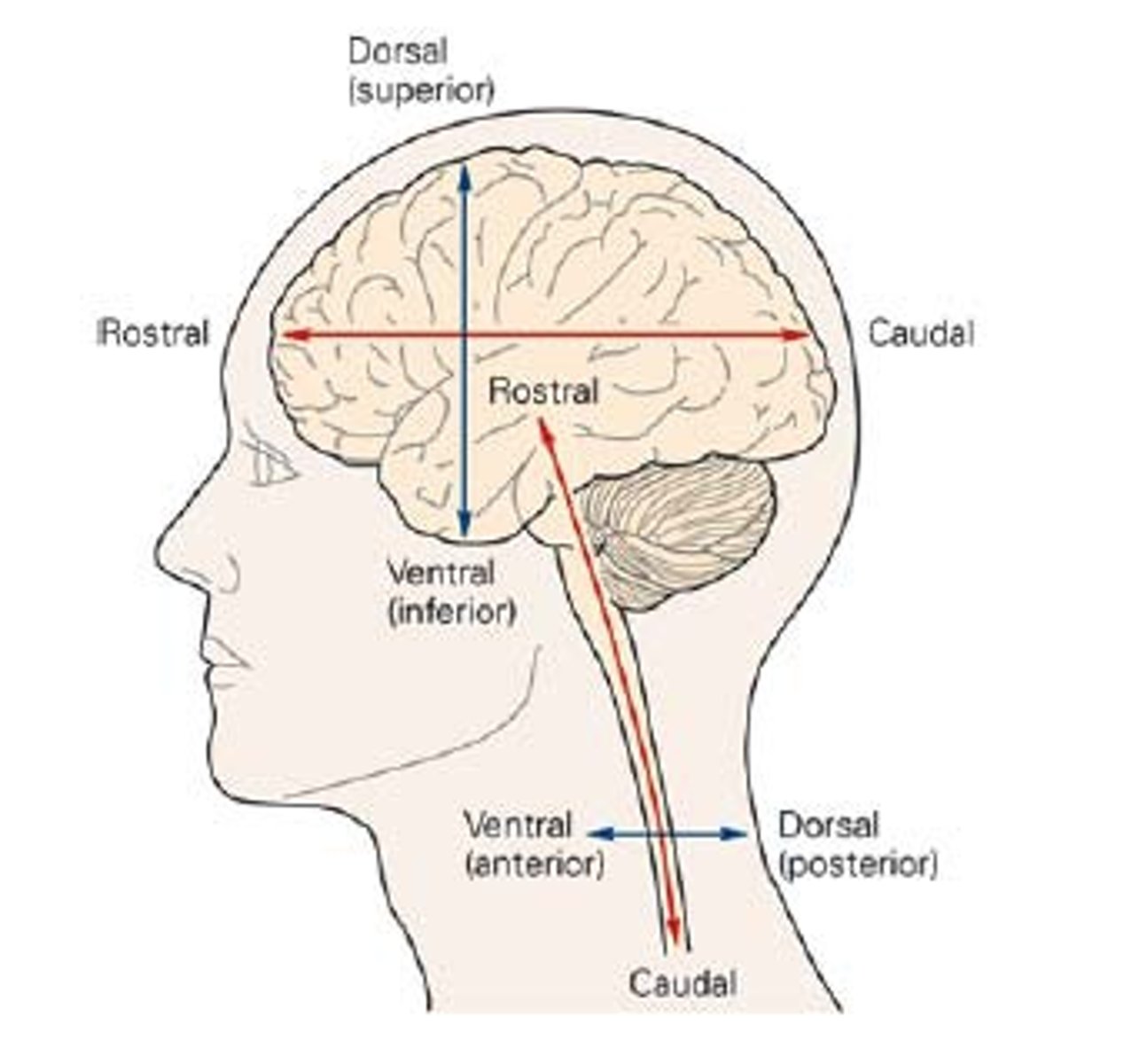
dorsal/ventral
towards the top and towards the bottom
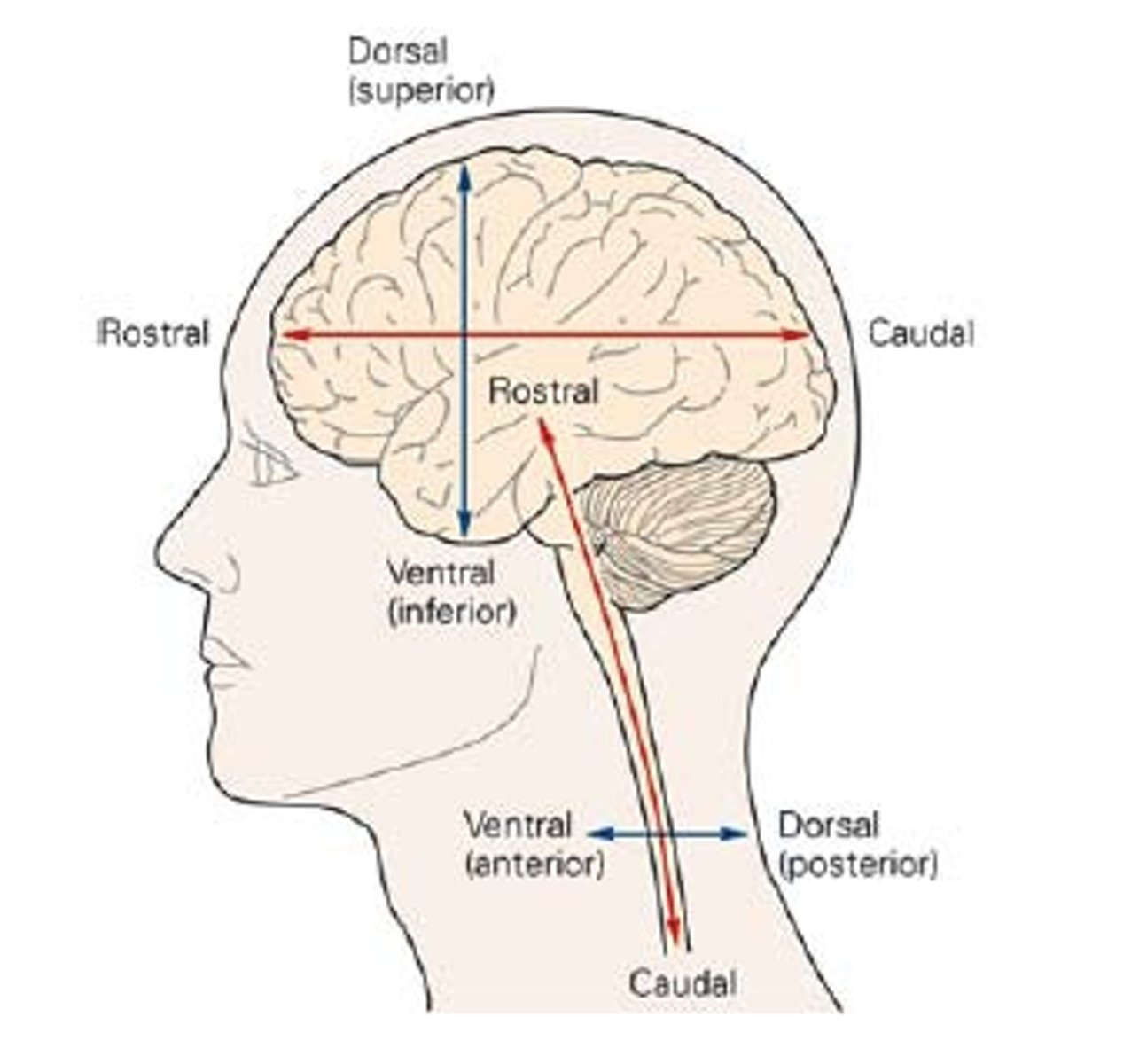
rostral/caudal
Towards the head, and towards the tail (front and back)
white matter
contains myelinated axons and lies underneath the gray matter of the cortex. Mostly transmits information.
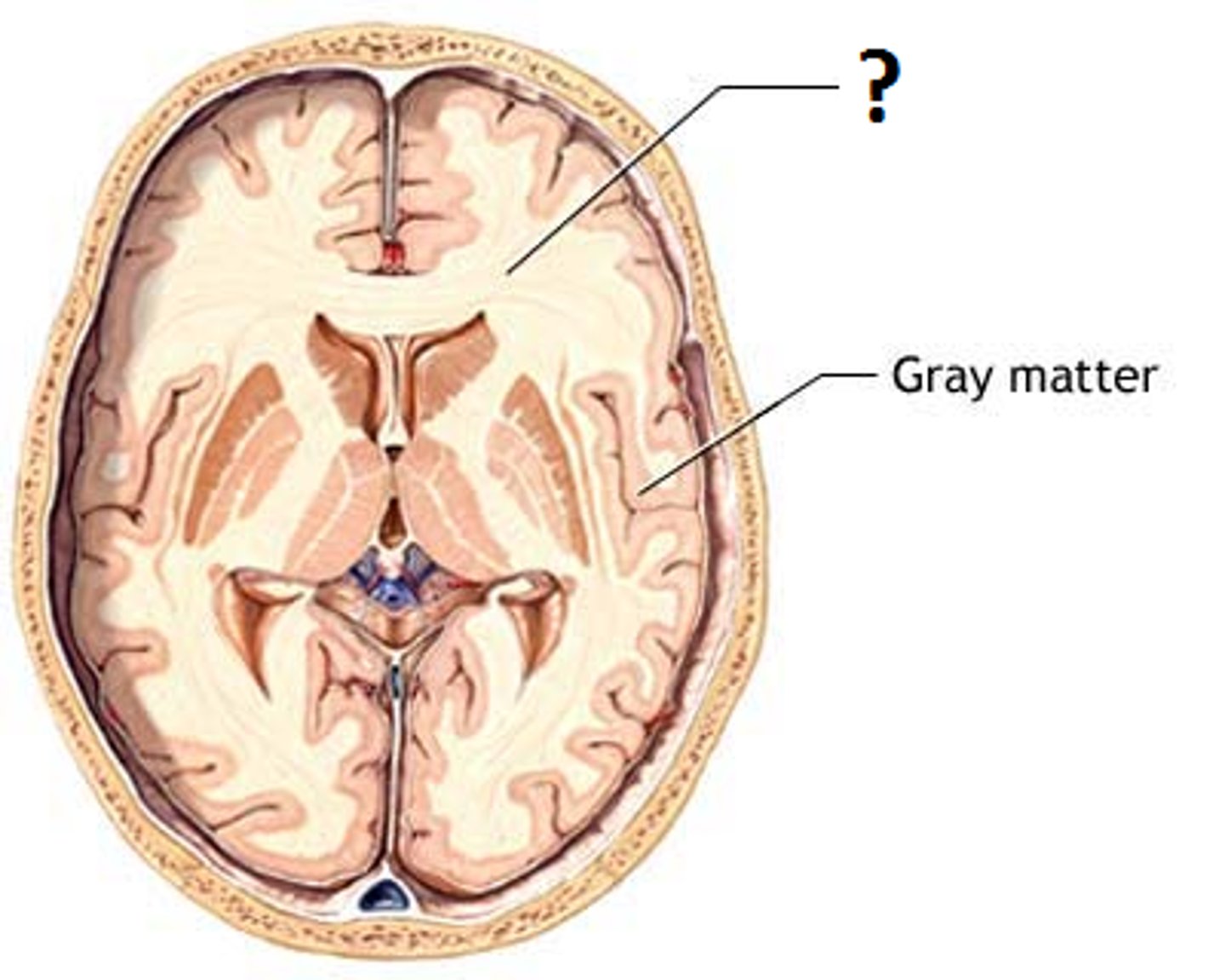
gray matter
areas of the brain that are dominated by cell bodies and are devoid of myelin. Mostly receives and processes information
Forebrain
The top section of the brain; Includes the telencephalon and diencephalon, which contain the cerebral cortex, basal ganglia, limbic system, amygdala, hippocampus, thalamus, and hypothalamus.
midbrain
The midsection of the brain; functions as a relay system, transmitting information for vision and hearing
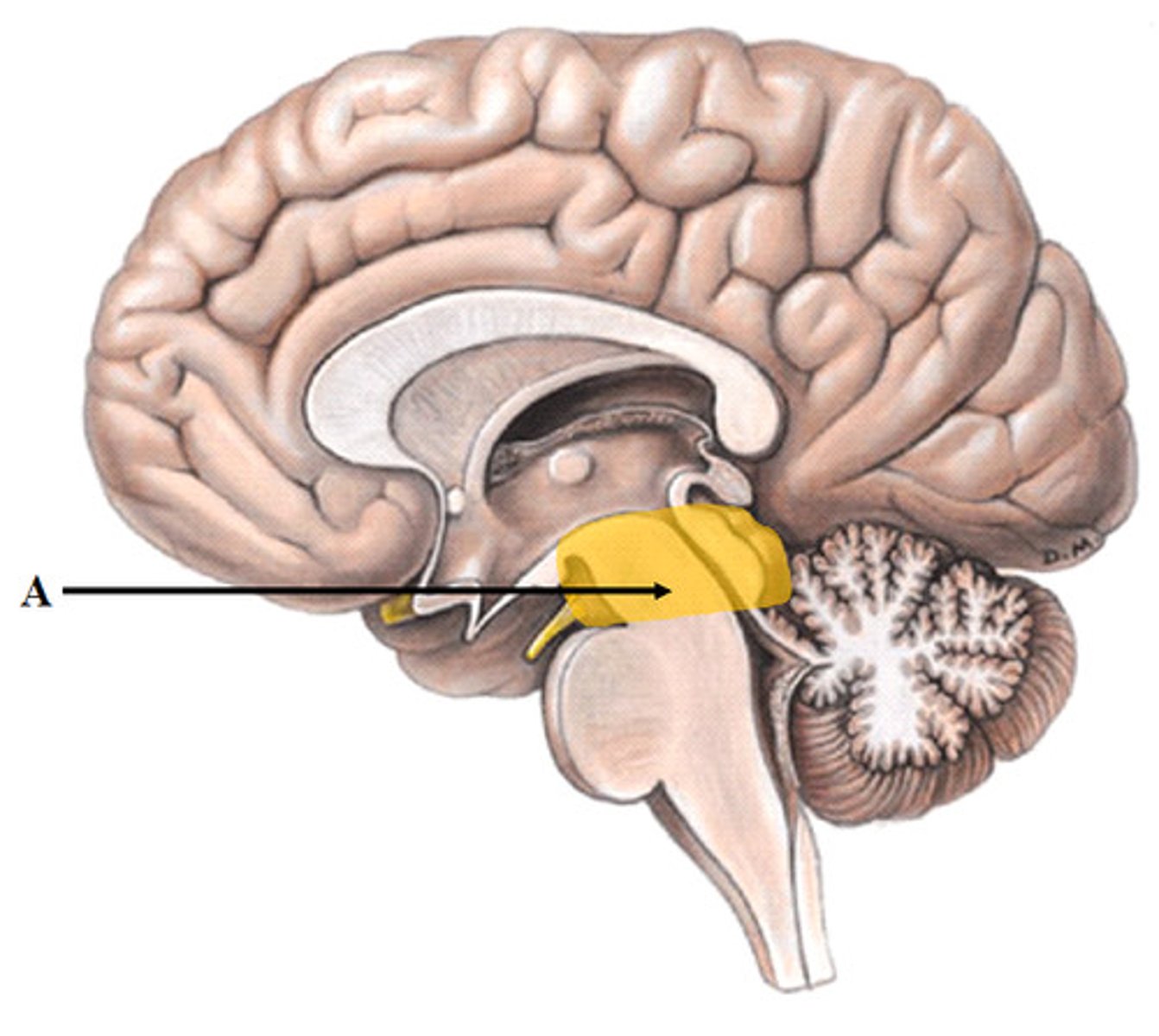
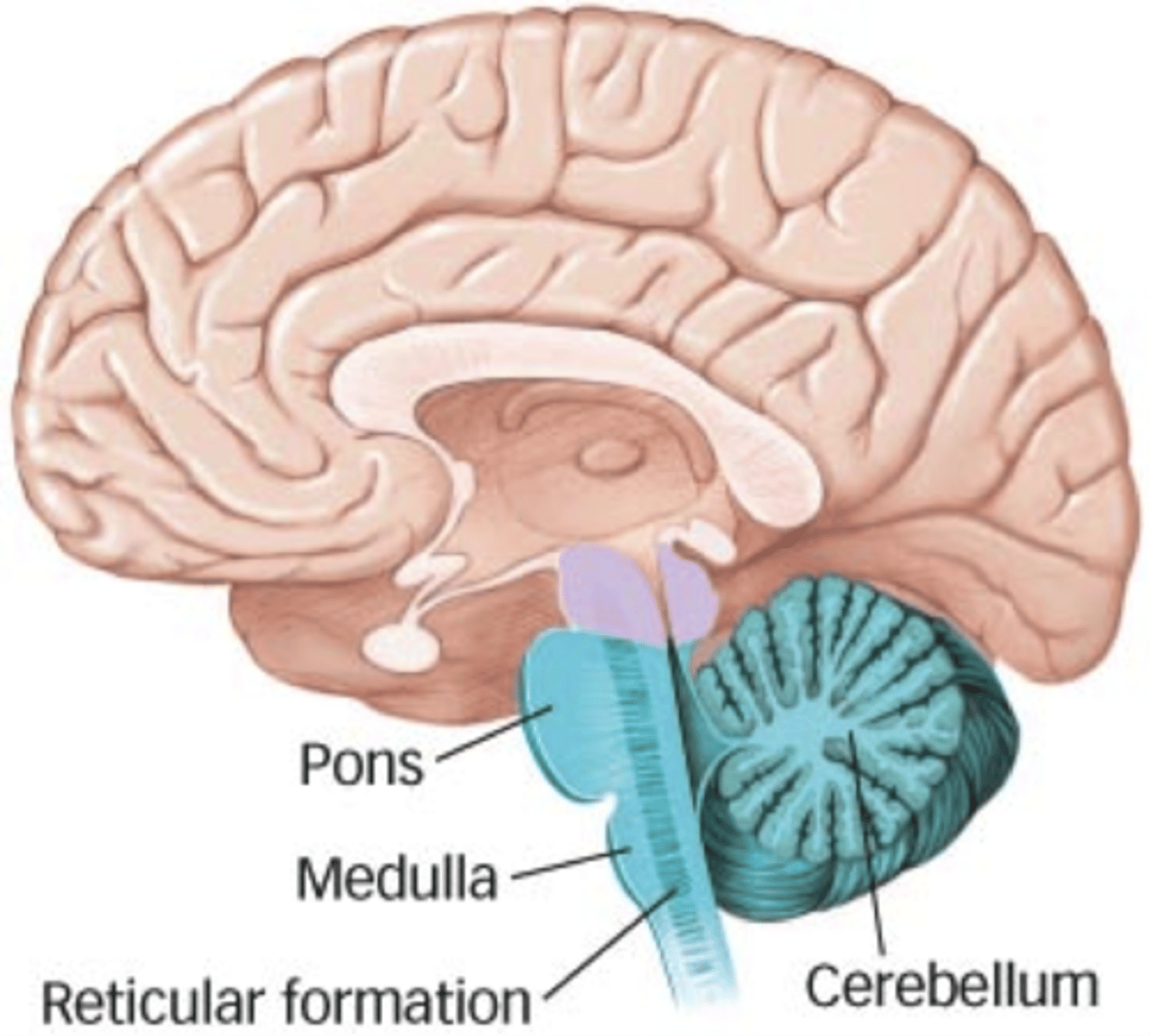
hindbrain
The rear division of the brain, containing the cerebellum, pons, and medulla
basal ganglia
A group of nuclei in the forebrain and plays a critical role in the control of movement/motor functioning
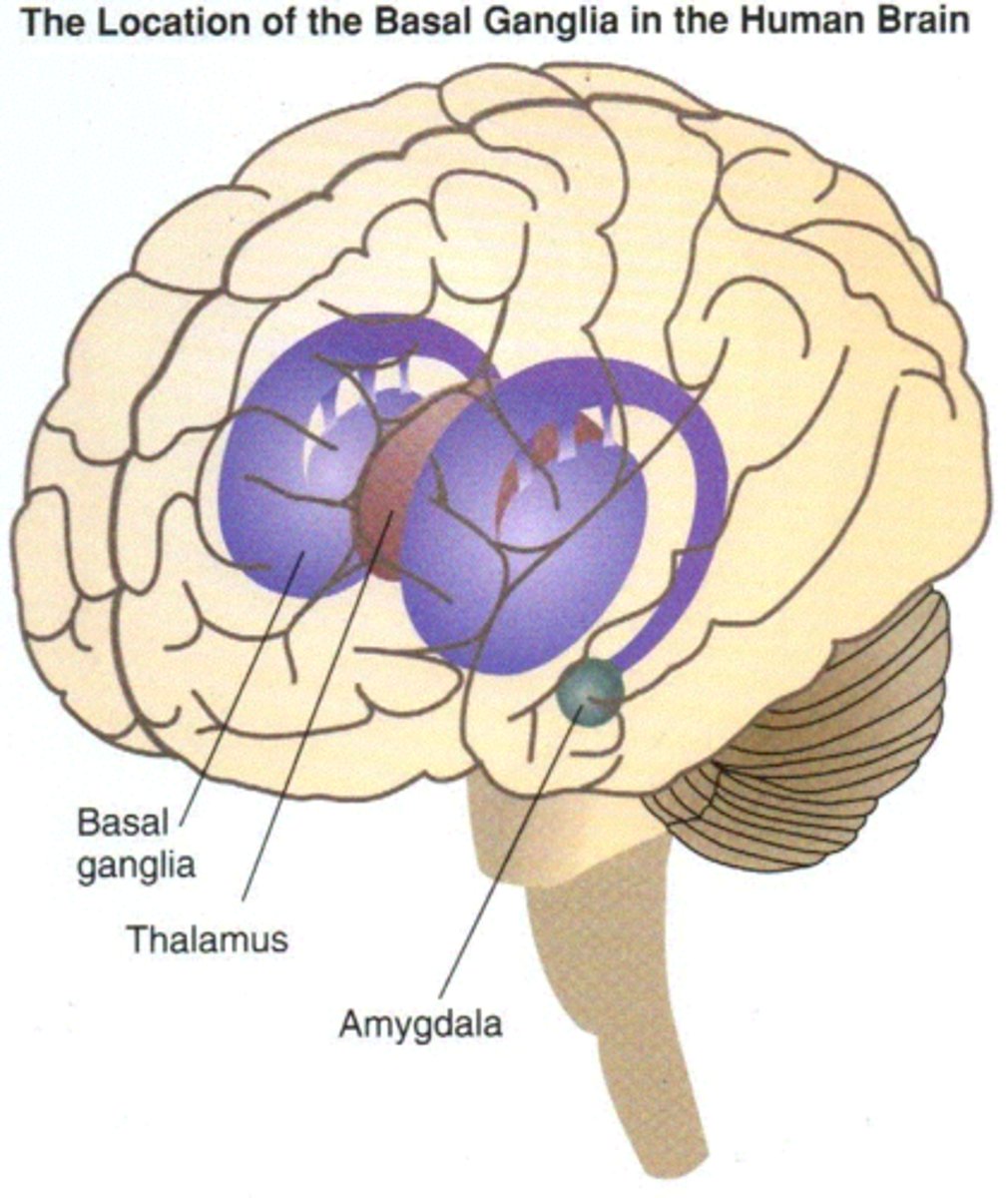
amygdala
A limbic system structure involved in memory and emotion, particularly fear and aggression.
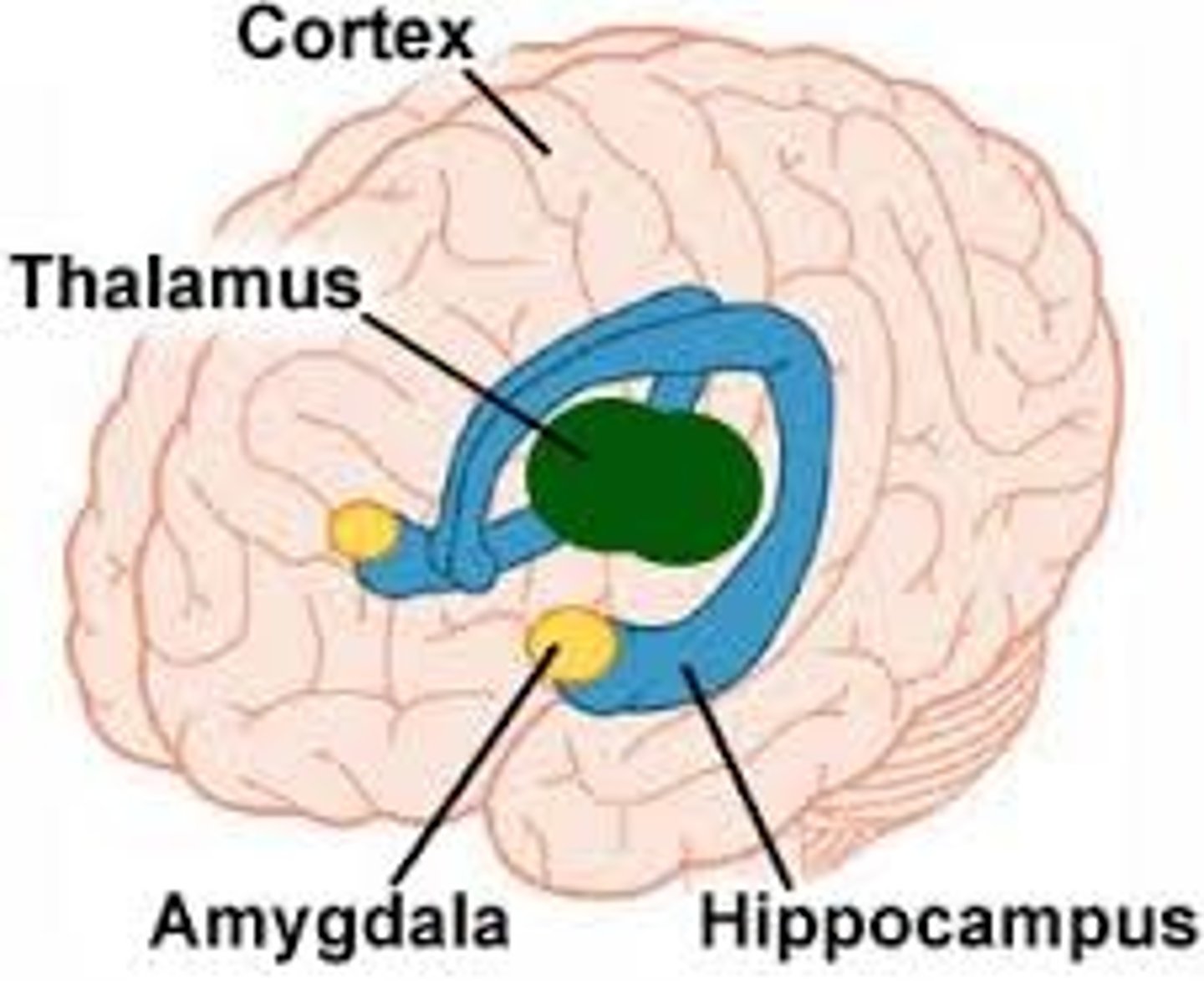
Hippocampus
A medial temporal lobe structure that is important for learning and memory
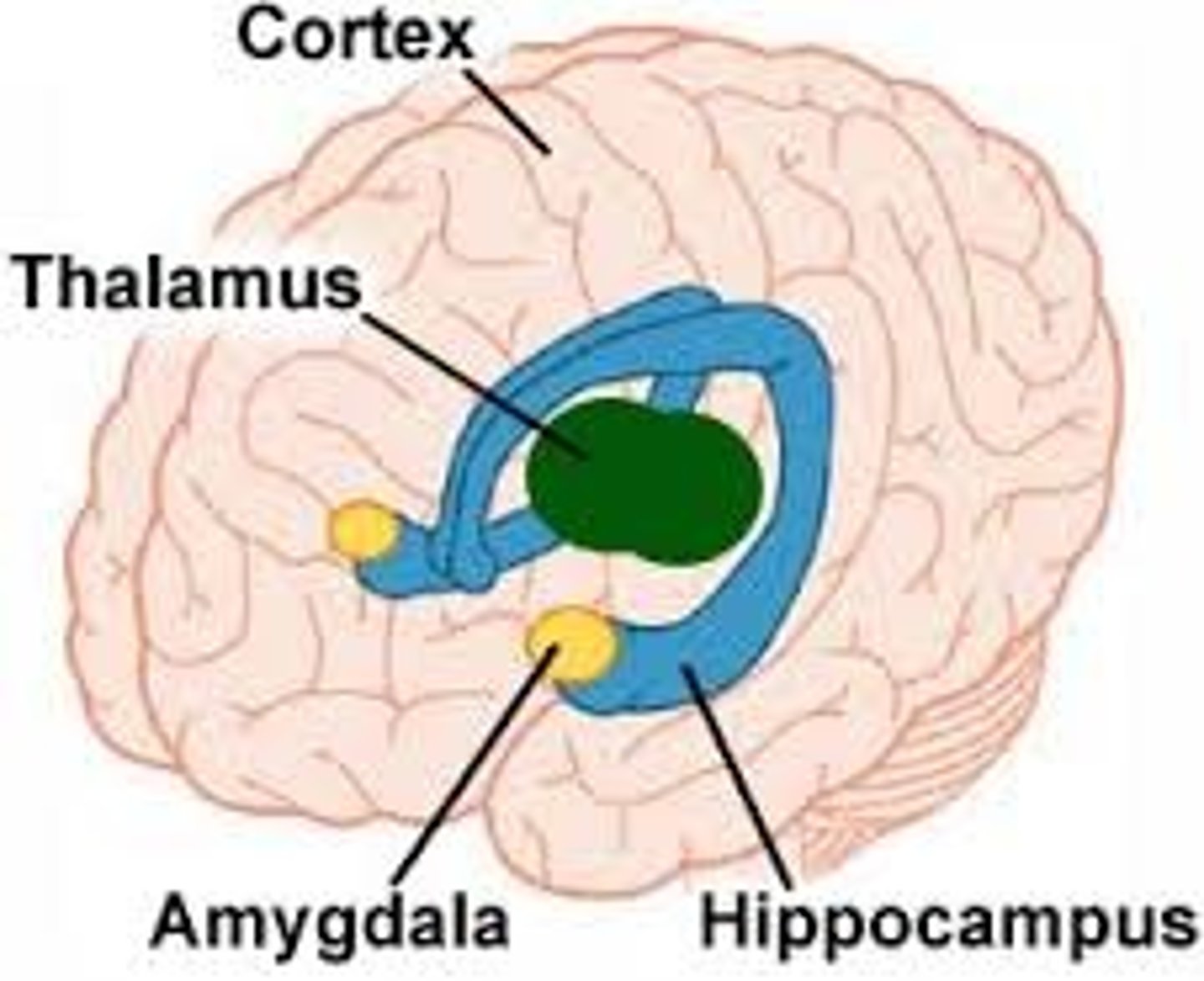
thalamus
The messenger: relays sensory, motor, and other information, and routes information from where sensory information occurs and sends it to the cortex
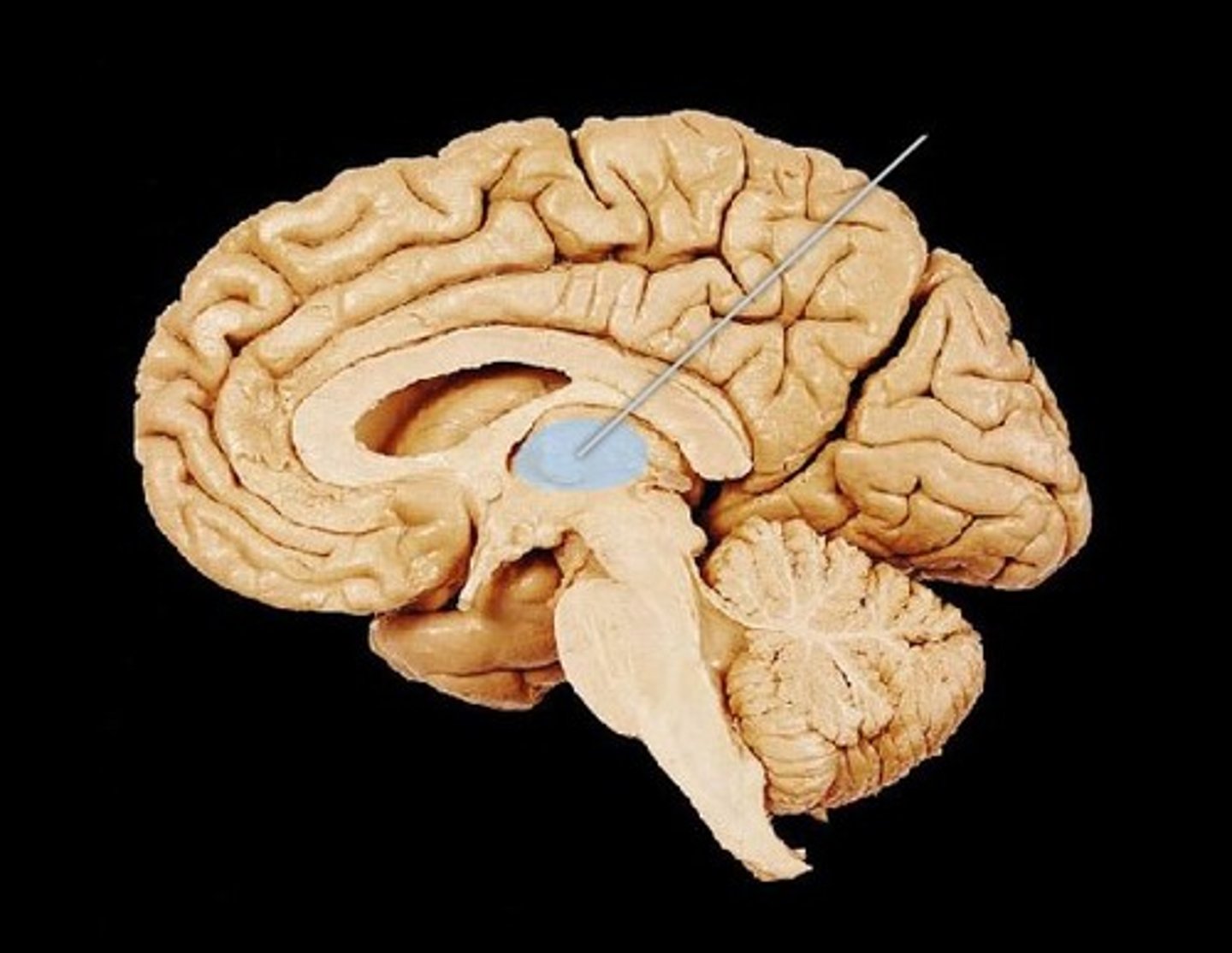
hypothalamus
The motivator: coordinates hormones, Controls pituitary gland, and thus hormones, and controls four "f's" (fighting, fleeing, feeding, and... sex)
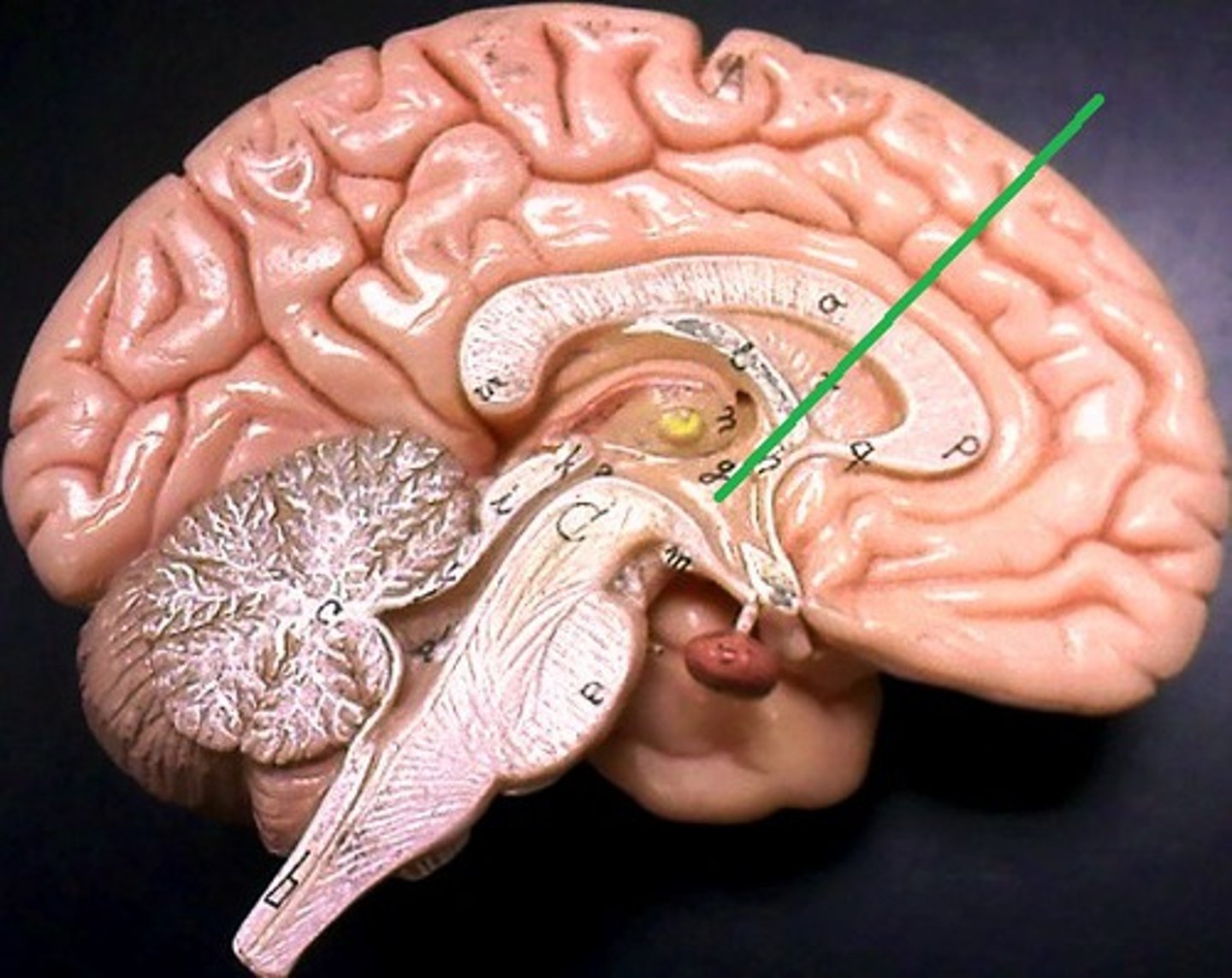
substantia nigra
Brainstem structure that produces dopamine and innervates the basal ganglia. Loss of its neurons leads to Parkinson's disease as there is a deficiency in dopamine
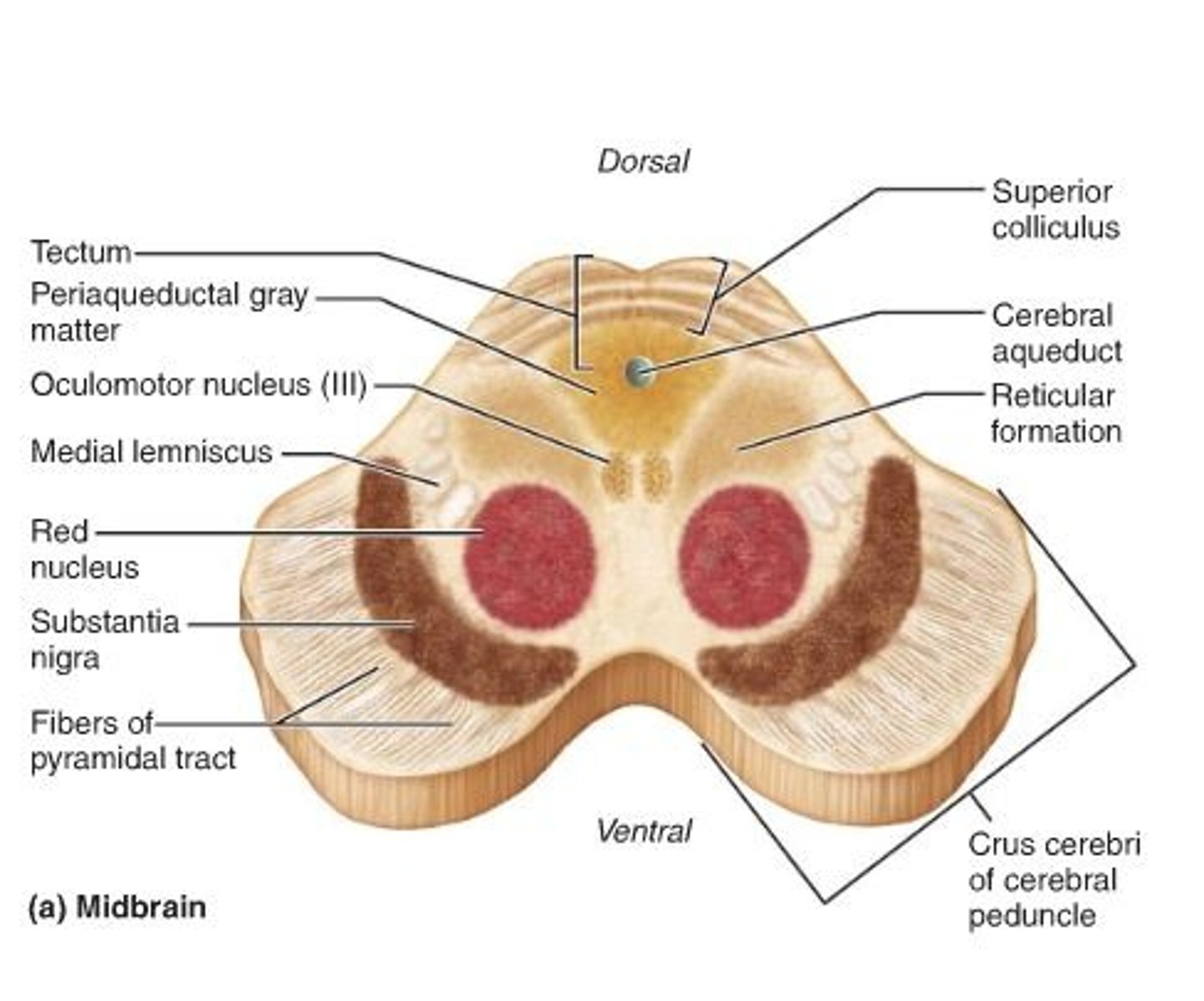
parkinson's disease
A disorder of the central nervous system caused by dopamine deficiency that affects movement, often including stiffness and tremors.
cerebellum
Coordinates movements and balance and associative learning
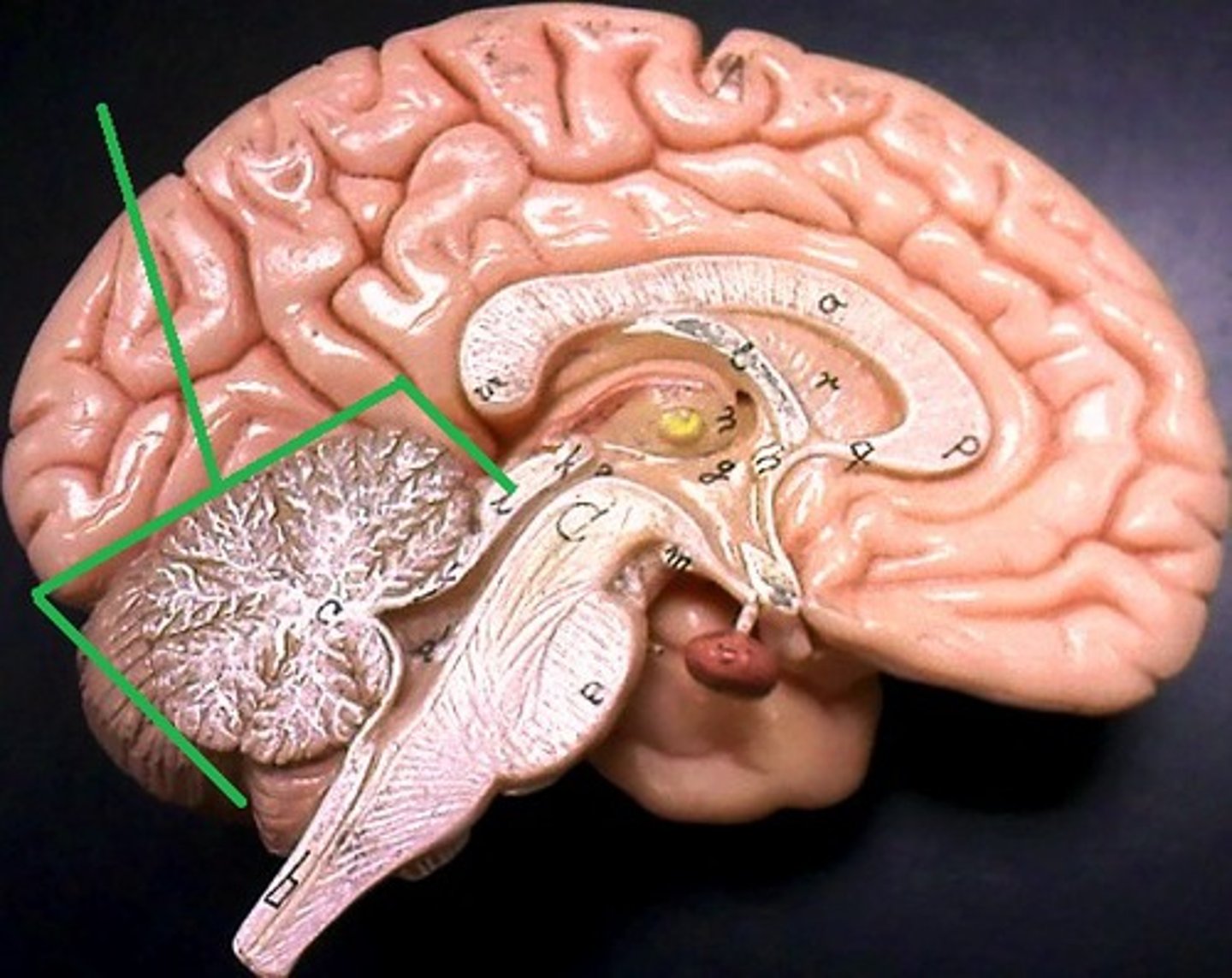
pons
A brain structure that relays information between the cerebellum and cerebrum. Includes sleep/wake cycle
medulla
Connects the brainstem to spinal cord, and involves involuntary functions like breathing and bloodflow. Brainstem injuries are often lethal
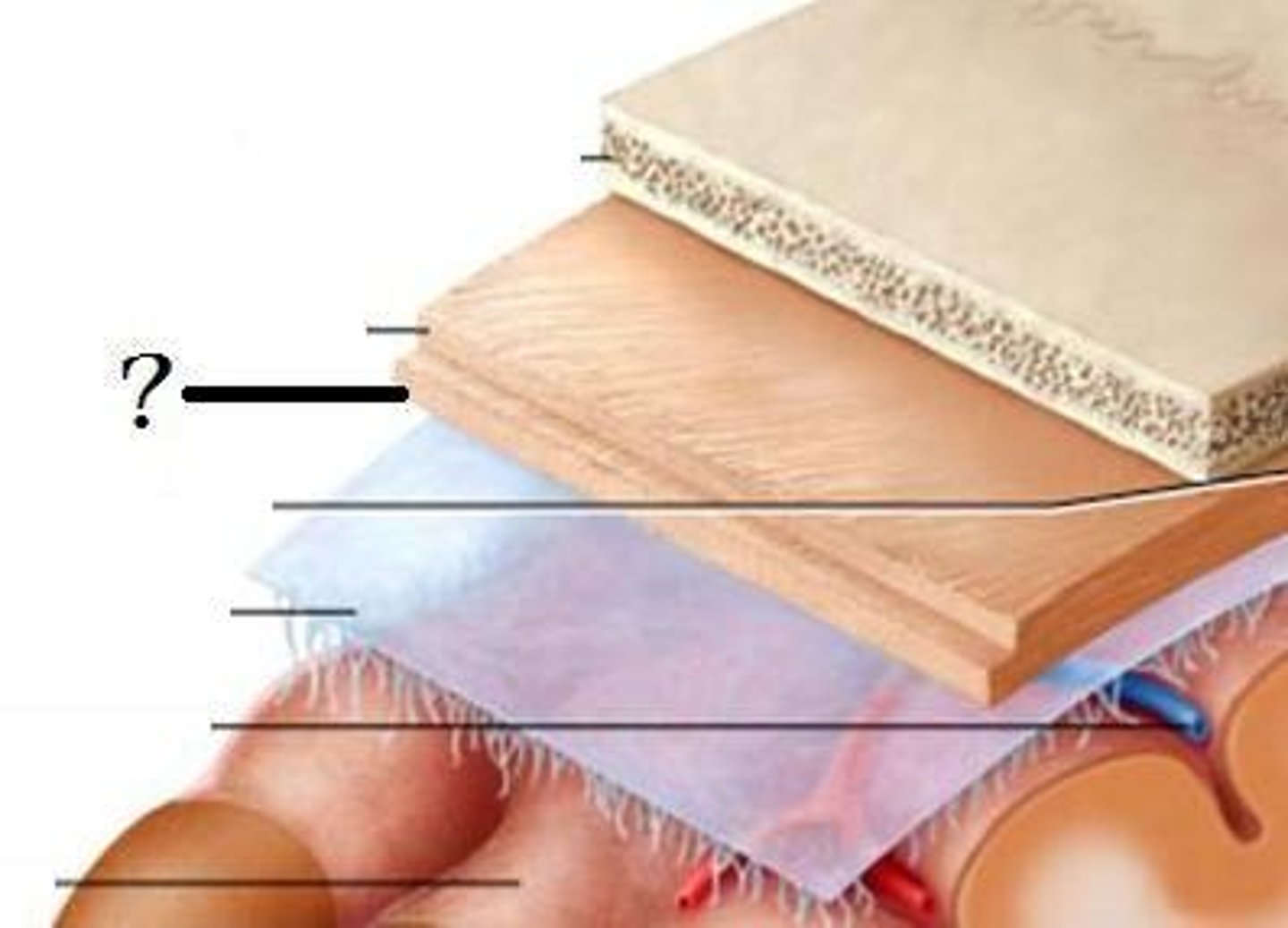
meninges
three protective membranes that surround the brain and spinal cord
cerebrospinal fluid
A liquid that protects the brain and spinal cord while also passing along nutrients and signaling chemicals to the brain
ventricles
Chambers in the brain filled with cerebrospinal fluid
Lateral ventricles
The ventricles that create the cerebral spinal fluid
third ventricle
the ventricle that carries cerebrospinal fluid into the fourth ventricle
fourth ventricle
The ventricle that sends cerebrospinal fluid to surround the brain and spinal cord
blood-brain barrier
A filtration system that makes it more difficult for blood to enter the brain, protecting it from substances found in blood
somatic interventions
Manipulating the body or brain and measuring changes in behavior
behavioral interventions
Manipulating behavior and measuring changes in the body and brain
independent variables
variables that cause changes in dependent variables
dependent variables
a variable changed by other variables
correlation
The tendency of two variables to vary in similar patterns, and change in patterns with each other
causality
The cause and effect relationship between two variables
levels of analysis
the scope of an experimental approach, which ranges from social interaction down to the molecular level
CAT scan (computerized axial tomography)
xrays are used to make images of the brain. Have medium resolution and are useful for visualizing strokes, tumors, and cortical shrinkage.
MRI (magnetic resonance imaging)
a technique that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce computer-generated images of soft tissue. Produce higher resolution images than CAT scans.
fMRI (functional MRI)
functional MRI that detects oxygenated bloodflow, producing a bunch of images over time and displaying changes
EEG (electroencephalogram)
Looks at electric potentials from the scalp resulting from neural activity. Has good temporal resolution but poor spatial resolution
MEG (magnetic encephalogram)
Changes in electrical currents affect magnetic fields. Has better spatial resolution than EEG but still worse than fMRI and PET
TMS (transcranial magnetic stimulation)
A way to create reversible, "virtual" lesions. This creates "virtual" patients in labs and allows temporary case studies. These are safe when one properly.
Anions
negatively charged ions
Cations
positively charged ions
Resting potential
The difference in electric charge between the inside and outside of a neuron's cell membrane when the nerve cell is at rest
Ion Channel
holes that allow specific ions to pass through when the channel is open. Some are gated and need a "key" neurotransmitter to open
Potassium Ions (K+)
Ions concentrated inside of the axon. Diffusion wants to move it outside of the cell while electrostatic pressure wants it to stay inside of the cell at resting potential.
Sodium Ions (Na+)
Ions concentrated outside of the axon. Both diffusion and electrostatic pressure want to move it into the cell, but it can only enter through sodium voltage gated channels.
Diffusion
Movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
Electrostatic pressure
The force that causes ions of the same charge to repel and ions of opposite charges to attract.
Sodium-potassium pumps
pump out three sodium ions for every two potassium ions pumped in in order to maintain resting potential
Equilibrium potential
The potential in which the forces of diffusion and electrostatic pressure are balanced and there is no driving force moving ions in and out of the cell.
Depolarization
A decrease in electrical potential in the cell membrane so its voltage comes closer to the threshold. A neuron's Voltage at resting potential is -65 mV while the threshold is -45mV
Hyperpolarization
An increase in electrical potential in the cell membrane so its voltage strays further from zero. Voltage at resting potential is Voltage at resting potential is -65 mV while hyperpolarization is between -70mV and -75mV.
Threshold
The point at which an action potential is triggered in a neuron, which is when the voltage reaches -40mV to -55mV
Action Potential
A rapid reversal of membrane potential so the cell membrane is more positive than the outside for a brief moment before returning to the resting potential
All-or-none property
The property that all action potentials only fire when threshold is reached, and always fire at the same, full amplitude, no matter how strong depolarization is
Voltage-gated channels
Ion channels that open or close in response to changes in membrane potential.
Refractory Phase
a period during and immediately after a nerve impulse when a neuron cannot produce another action potential
absolute refractory period
time during which another action potential is impossible
relative refractory period
A period after firing when a neuron is returning to its normal polarized state and will fire again only if the incoming message is much stronger than usual
saltatory conduction
the propagation of action potentials along myelinated axons from one node of Ranvier to the next node, increasing the velocity of action potentials
Multiple Sclerosis (cause + symptoms)
A disease in which myelin is compromised due to antibodies attacking myelin molecules to the point where saltatory conduction is disrupted. Symptoms may include impaired motor and sensory functionality.
EPSP (excitatory postsynaptic potential)
Occurs when an excitatory presynaptic neuron fires and causes depolarization in the postsynaptic neuron