SCI112 Quest 2 Review
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
What determines the carrying capacity of an environment?
The limiting factors with an ecosystem such as food, shelter, water, space
How do humans differ from other organisms in terms of carrying capacity?
Scientists believe that humans will exceed Earth's carrying capacity
Immigration
Moving in to a country
Emigration
Moving out of a country
Crude Birth Rate
The number of births per 1000 individuals per year.
What is meant by the doubling time of a population?
The number of years it takes a population to double.
What is Toral Fertility Rate?
TFR is an estimate of the average number of children that each woman in a population will bear.

Replacement-Level Fertility
The number of children each woman needs to replace the previous generation and keep the population size stable

What is infant mortality?
The number of deaths of children under 1 year of age per 1000 live births.
Developing Country
Countries with relatively low levels of industrialization and income of less that $3 per person per day. TFR is usually greater than 2.1 to attain replacement level fertility.
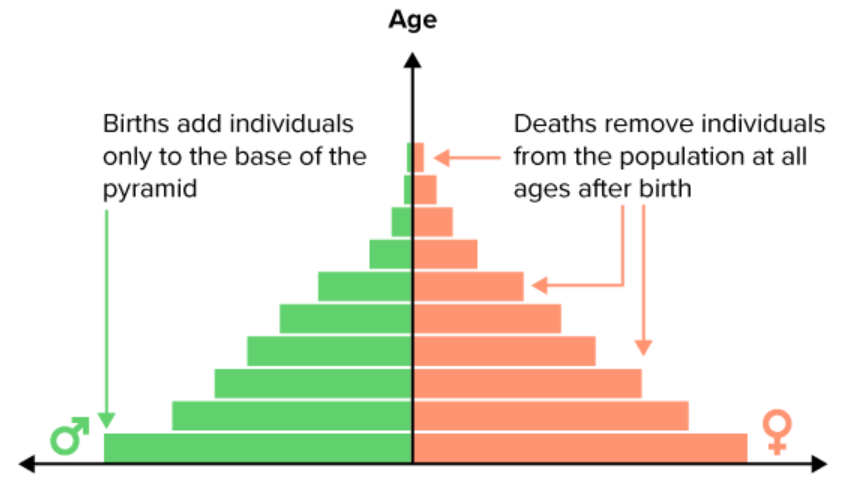
An age structure diagram that is wider at the bottom than the top is called a _________ ________ (two words).
Negative growth
How many stages are there in the Demographic Transition Model? What are they?
5 stages
High stationary
Early expanding
Late expanding
Low stationary
Declining
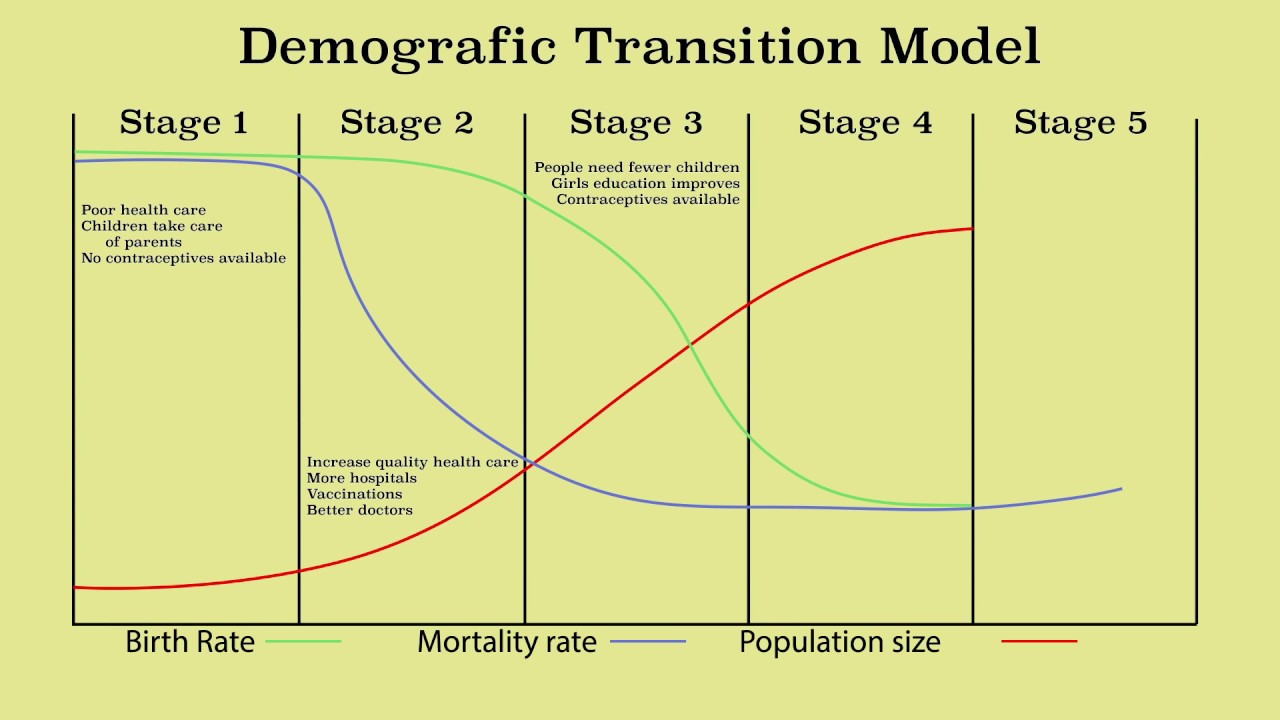
In which phase does population decline?
Stage 5
When the death rate becomes higher than the birth rate
What are the main factors influencing human population growth?
Changes in population size
Fertility
Life expectancy
Age structure
Migration
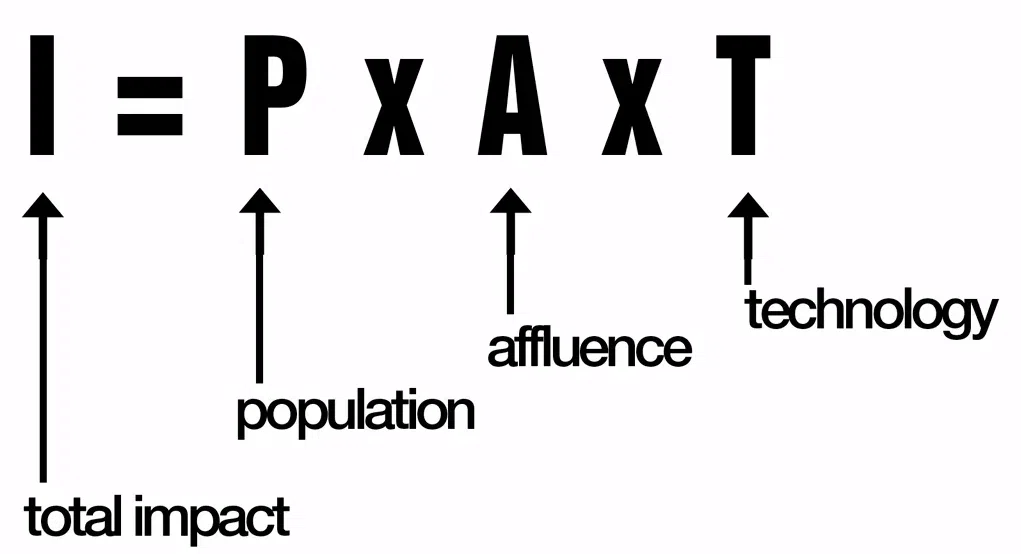
Describe the IPAT equation, and explain what it means.
To estimate the impact of human lifestyles on Earth we can use the IPAT equation:
Impact = Population × Affluence × Technology
What are point sources of contamination?
When harmful substances are emitted directly into a body of water

What are nonpoint sources of contamination?
Pollution which cannot be traced back to a single origin or source

Wastewater treatment is very effective in doing what?
Breaking down the organic matter into carbon dioxide and inorganic nutrients
What percentage of the Earth's water is available for consumption?
1%
What percentage of the Earth's water is freshwater?
3%
Pathgen
A micro-organism that causes disease
List Examples of Pathogens
Typhoid fever
Infectious hepatitis
Cholera
Salmonellosis
E.coli
What are the two most common symptoms of waterborne illnesses?
Diarrhea & fever
What are examples of biodegradable organic matter?
Human & animal waste
Leaves & grass clippings
Trash
Groundwater contamination
When harmful substances gets into the water stored underground in soil and rock layers
What are the principal sources of groundwater contamination?
Pesticides
Gasoline stations
Landfill & sewer systems
Leakage from fault hazardous waste containers
Deicing road salt
What is the primary wastewater treatment?
Solid materials settles out of wastewater
What is the secondary wastewater treatment?
air is pumped in to help bacteria digest 85-95% of the remaining organic material
Air pollution
Chemicals, particulate matter, or microorganisms found in the atmosphere at concentrations high enough to harm plants, animals, and materials such as buildings or to alter ecosystems
What are several types of major air pollutants?
Nitrogen oxides
Carbon oxides
Particulate matter and methane
Volatile organic compounds
Ozone
Lead
Mercury
What is carbon monoxide, and why is it so dangerous?
Fuel combustion (especially vehicles), industrial processes, fires, waste combustion, and residential wood burning.
Reduces the amount of oxygen reaching the body's organs and tissues; aggravates heart disease, resulting in chest pain and other symptoms leading to hospital admissions and ED visits.

Smog
Air pollution that reduces visibility in the surrounding air
What is the difference between a primary and a secondary pollutant?
Primary pollutants: polluting compounds coming directly out of smoke-stacks, exhaust pipes, or natural emission source
--> E.g., CO, CO2, SO2, NOx, and most suspended particulate matter and methane
Secondary pollutants: pollutants transformed in the presence of sunlight, water, oxygen or other compounds
--> E.g., ozone, sulfate, and nitrate
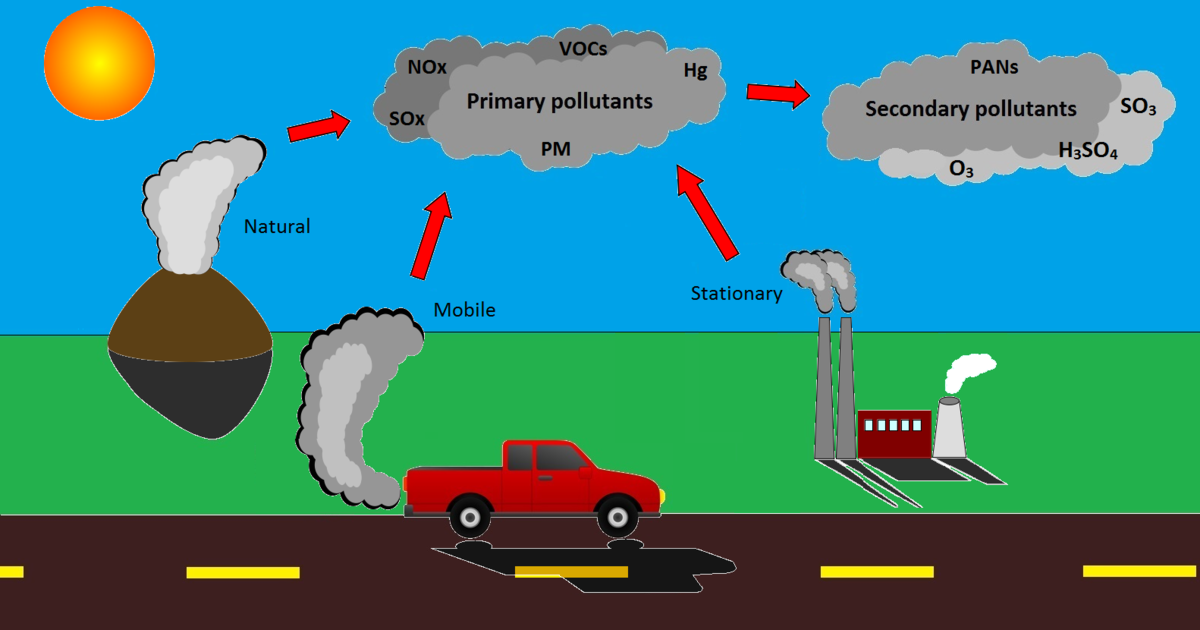
Natural air pollution
Air pollution occurs naturally in the wild
volcanoes
forest fire
Anthropogenic air pollution
Air pollution caused by humans
cars
fossil fuels
Thermal Inversion
A relatively warm layer of air at mid-altitude covers a layer of cold, dense air below.
How are thermal inversions important to air pollution?
The warm layer traps the pollutants under it with the cold air, thus accumulating high concentrations of smog
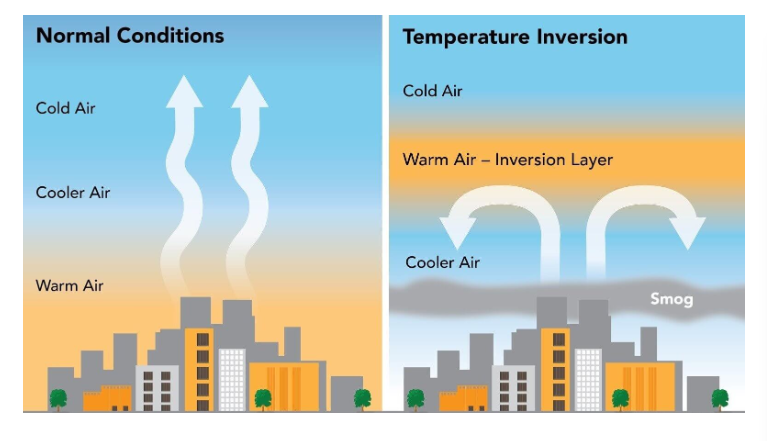
How does smog form?
Smog forms when sunlight, nitrogen oxides (NOx), and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are present.
Acid Deposition
The transfer of atmospheric acids to Earth's surface and impacts water and soil.
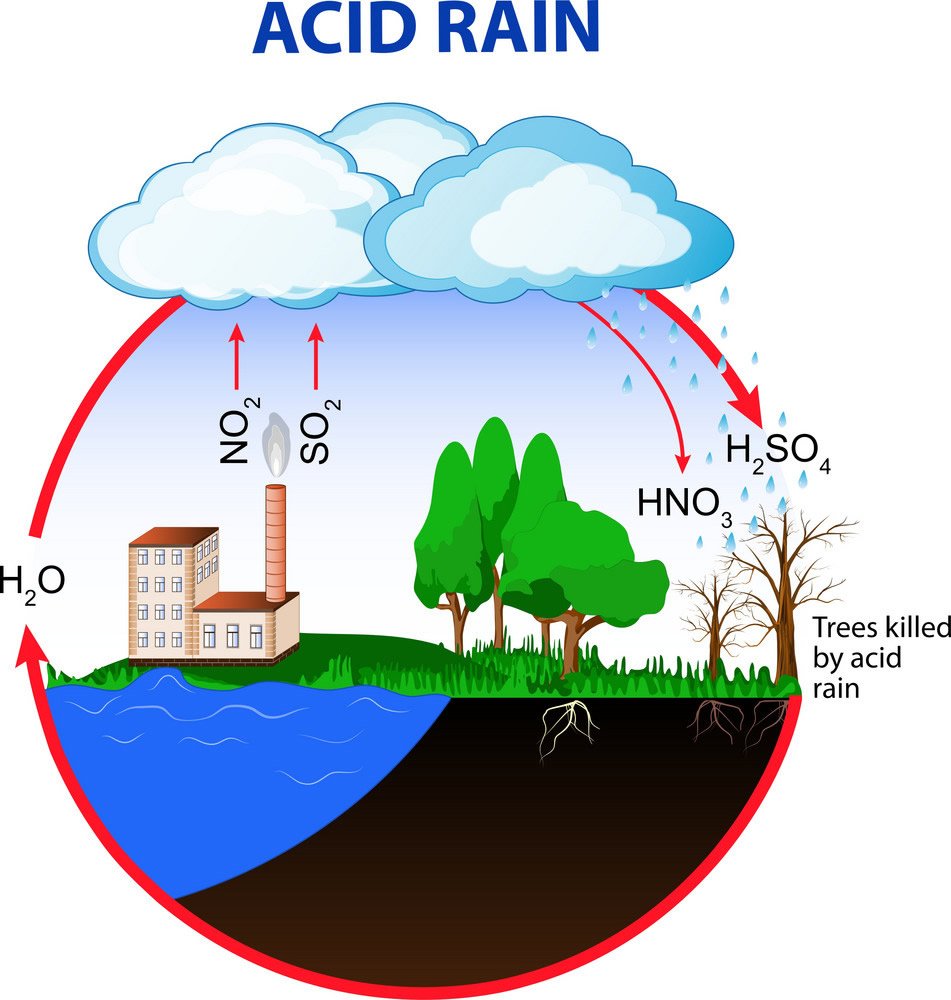
Describe some effects of acid deposition
Lowers the pH of lake water
Decreases species diversity in aquatic ecosystems
Mobilizes metals found in soils and releases these into surface waters
Damages statues, monuments, and buildings and other structures
What are some methods used to reduce air pollution?
Removing sulfur dioxide from coal by fluidized bed combustion
Catalytic converters on cars
Scrubbers on smoke stacks
Baghouse filters - large filters that collect dust particles
Electrostatic precipitators - positively charged particles are attracted to negatively charged plates
Stratospheric Ozone Layer
The layer in the atmosphere that exists roughly 45-60 kilometers above the Earth.
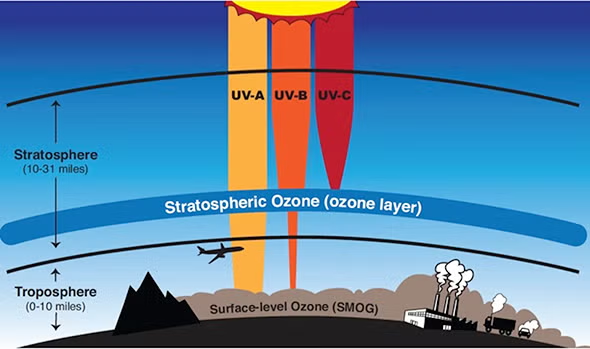
Why is the Stratosphere important to humans and other organisms?
Ozone has the ability to absorb ultraviolet radiation and protect life on Earth.
What are some indoor air pollution problems in developing countries?
Wood, animal manure or coal, used for cooking and heating in developing countries; VOCs indoors: volatile cleaning products.
Lack of indoor ventilation can lead to carbon monoxide (CO) poisoning and increase in particulates in the air.
This increases the risk for respiratory diseases such as infections and even cancer.
What are some indoor air pollution problems in developed countries?
In developed countries, people are spending more time inside.
Houses are sealed more tightly for better insulation.
This results in increased exposure to a number of indoor air pollutants.
Acute Disease
Rapidly impair the normal functioning of a person's body

Chronic Disease
Slowly impair the normal functioning of a person's body
constant
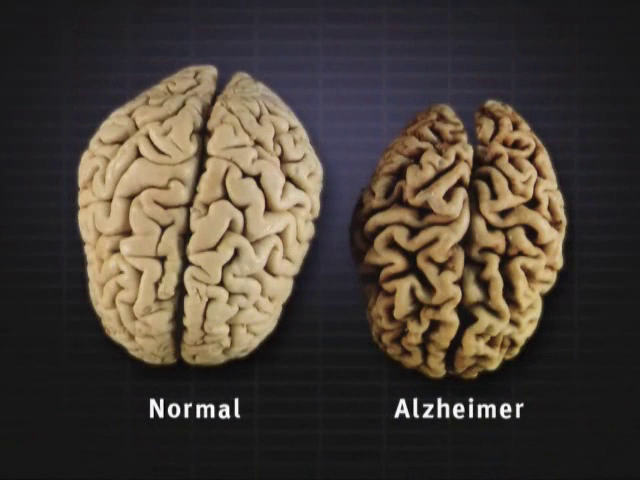
Is poverty a risk factor for disease?
Yes in lower income countries, the risks for diseases are higher
Name three historically important infectious diseases.
Plague
Malaria
Tuberculosis
How is plague transmitted? What is another name for plague?
"Bubonic Plague" or "Black Death"
Spread by fleas associated with rodents, particularly rats
How is malaria transmitted?
Caused by one of several species of
Plasmodium, a protist.
Life cycle includes incubation and transmission inside a mosquito.
Is malaria a serious disease today?
Yes
Still infects hundreds of millions of people today
An estimated one million people (mainly children) die from it each year.
What is an emergent infectious disease? List examples.
Outbreaks of a new disease that was unknown before the outbreak:
HIV/AIDS
Ebola
Mad Cow Disease
Bird Flu
West Nile Virus
CoronaVirus - Covid- 19
What is HIV/AIDS? On which continent is it of special concern?
Viral disease can be communicated by blood and other body fluids.
Less-developed nations in Africa have significant numbers of HIV-positive people.
What is "mad cow disease"? How is it transmitted and how can this transmission be prevented?
Caused by poorly understood proteins (prions) and can be transmitted by eating parts of the central nervous system of infected cattle.
Controlled by strict regulation of meat supply.
Is West Nile Virus a potential threat in the United States?
Spread to the United States and has infected and killed people, but is declining.
Toxicology
The study of chemical risks
Neurotoxins
Chemicals that disrupt the nervous system (insecticides, lead, mercury)

Carcinogens
Chemicals that cause cancer through inflicting damage to cells (tobacco smoke, asbestos, radon)

Teratogens
Chemicals that interfere with the normal development of embryos or fetuses (alcohol, some medications); Thalidomide

LD50
Effective dose that kills 50%
ED50
Effective dose that harms 50%
Biomagnification
The increase in a chemical concentration in animal tissues as the chemical moves up the food chain.
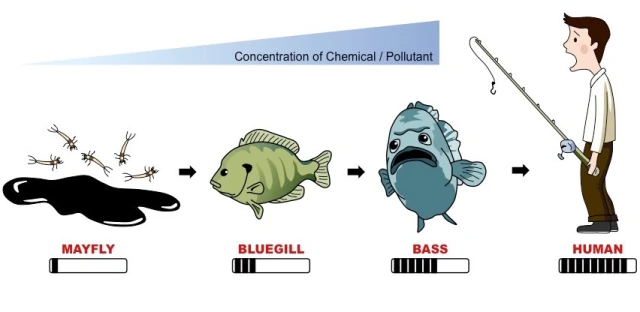
Perceived Risk
Subjective judgment of decisions and behaviors that may lead to negative outcomes.
Actual Risk
The quantifiable aspects of risk, the statistical likelihood of an adverse event occurring based on empirical data.
Precautionary principle
If a hazard is plausible but not proven, steps must be taken to reduce or remove the hazard.
What was the outcome of the Stockholm Convention?
In 2001, a group of 127 nations met in Stockholm to reach an agreement to restrict global use of some chemicals.
Twelve chemicals ("the dirty dozen") were to be banned, phased out, or reduced.
These include DDT, PCBs, and certain chemicals that are by-products of manufacturing processes.
Waste
Anything that is produced but is not useful or is not consumed
How are wastes usually handled in natural systems?
In the natural world, detritivores and decomposers recycle wastes from other organisms
What is unique about the wastes humans generate?
Only humans generate wastes that cannot be used by other organisms
Municipal Solid Waste
MSW is also known as trash or garbage
E-waste
Electronic waste
TVs, computers, and cell phones that contain toxic metals
What are some sources of waste?
31% - paper
33% - organic materials (yard waste, food scraps, wood)
12% - plastic
18% - durable goods (appliances, tires)
Three Rs
Reduced, Reuse, Recycle
Compost
Organic material that has decomposed under controlled conditions and creates natural fertilizer
What happens currently to most solid waste?
Most solid waste is buried in landfills or incinerated.
Landfill
Engineered ground facilities that hold MSW with minimal contamination of the environment
How are dumps different from landfills?
Open dumps do not regulate what goes into the dumps, and chemicals and other hazardous materials are able to run into groundwater
Landfill Leachate
Water that becomes contaminated by traveling through solid waste and picking up various chemical compounds

Incineration
Process of burning waste materials to reduce volume and mass, sometimes also generating electricity and heat
Is incineration a good method for getting rid of solid waste?
NO... it may release air pollutants and create concentrated ash that is toxic and must be landfilled
Hazardous Waste
Liquid, solid, gaseous, or sludge waste harmful to humans or ecosystems

Superfund
Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act (CERCLA) that gives clearance to clean up hazardous waste sites to the EPA
Life-cycle Analysis
A systematic approach to evaluating the environmental impact of a product, process, or activity from the acquisition of raw materials to final disposal
Integrated Waste Management
IWM is an analysis and planning process that starts with source reduction and ends with waste reduction