FOREBRAIN
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
CEREBRUM
Make up the most mass of the brain
CEREBRUM
Divided into left and right cerebral hemispheres by a deep cleft called longitudinal sulcus
longitudinal sulcus
CEREBRUM
Divided into left and right cerebral hemispheres by a deep cleft called____
FRONTAL LOBE, PARIETAL LOBE, OCCIPITAL LOBE, TEMPORAL LOBE, CENTRAL LOBE (AKA INSULA)
5 lobes of each cerebral hemisphere include
Central Lobe
called INSULA)
FRONTAL LOBE
1
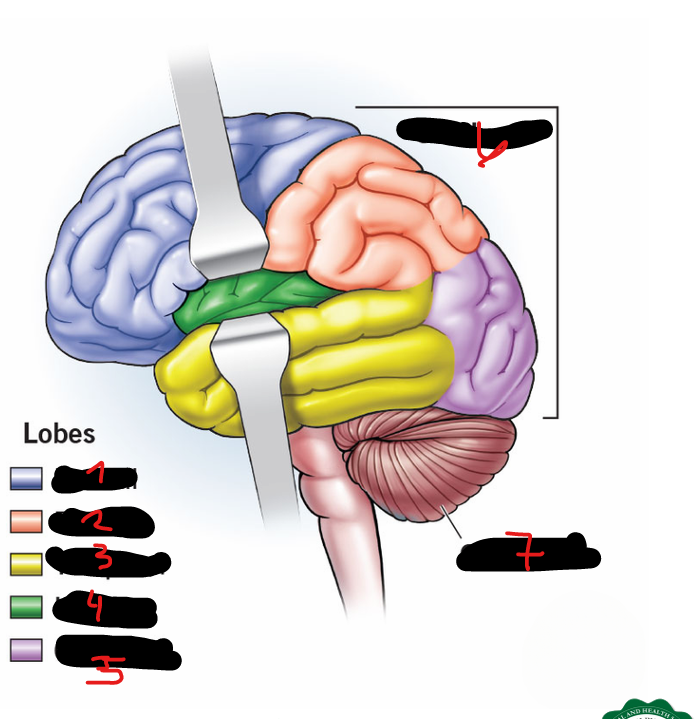
PARIETAL LOBE
2
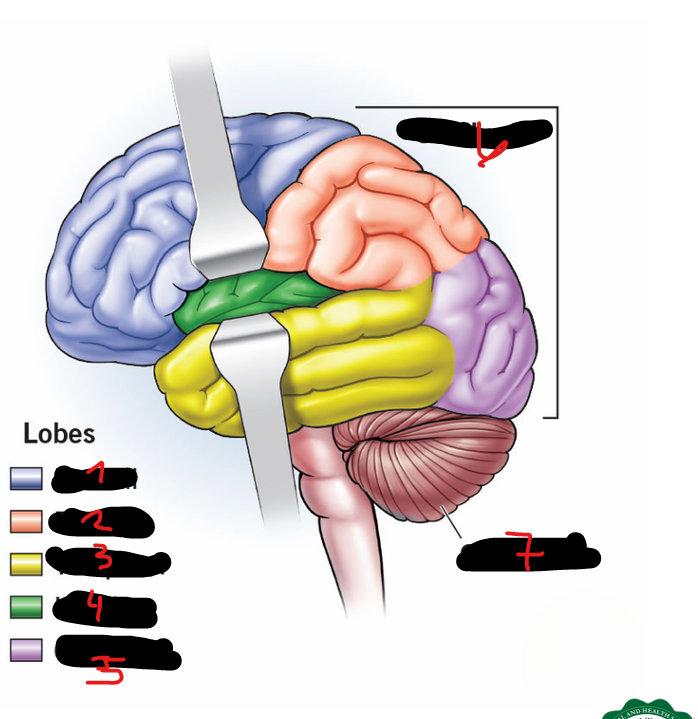
TEMPORAL LOBE
3
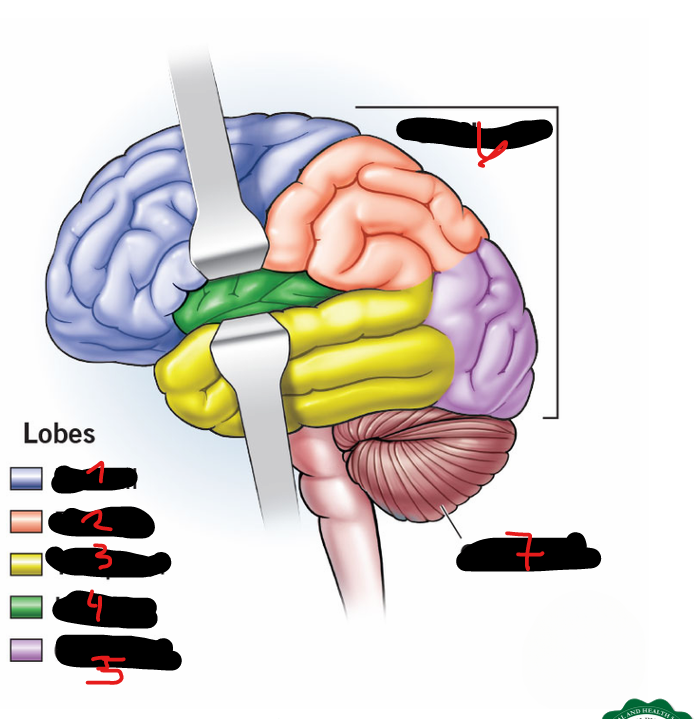
INSULA
4
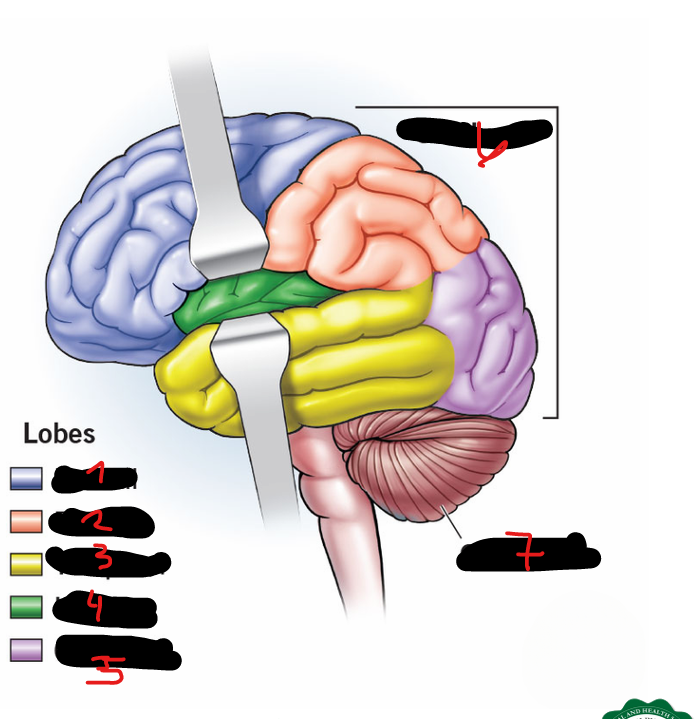
OCCIPITAL LOBE
5
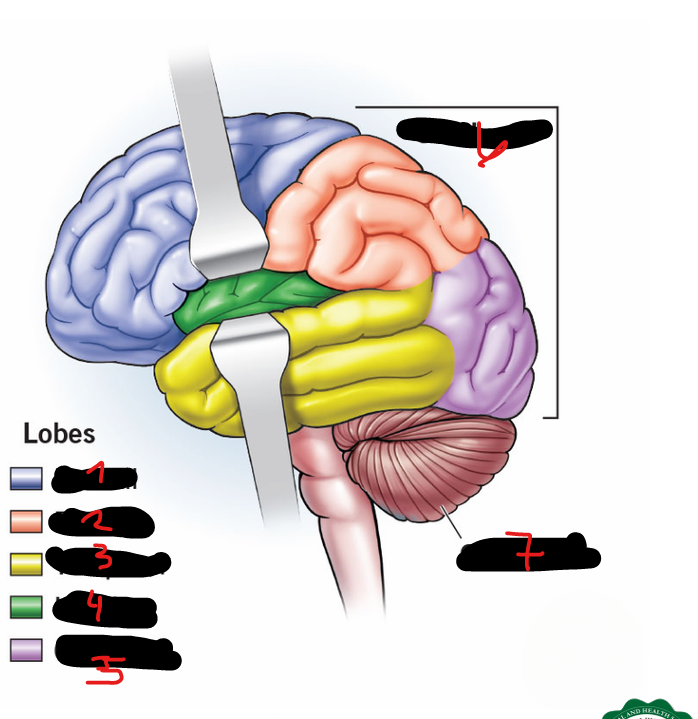
CEREBRUM
6
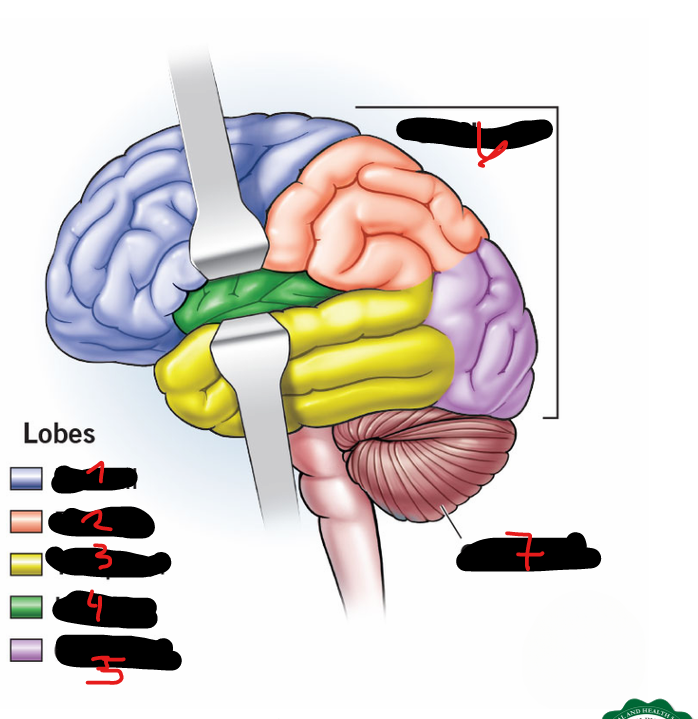
CEREBELLUM
7
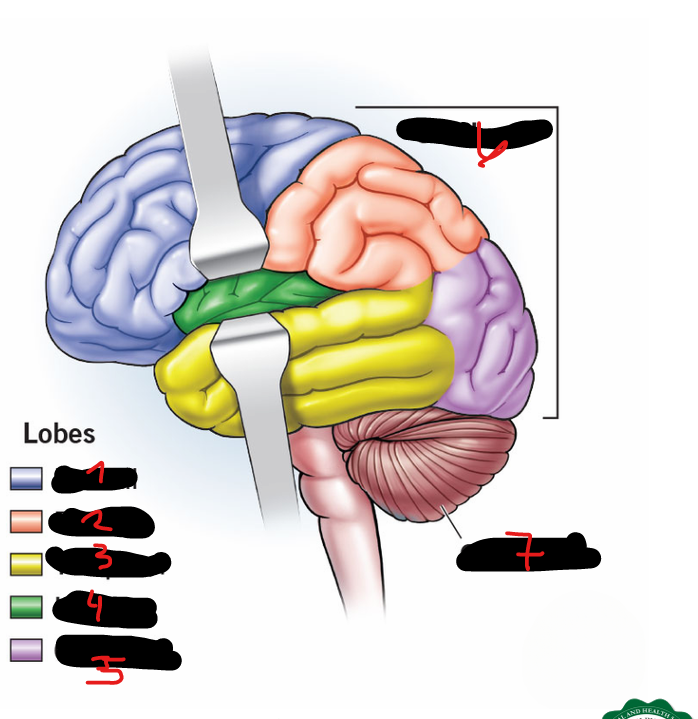
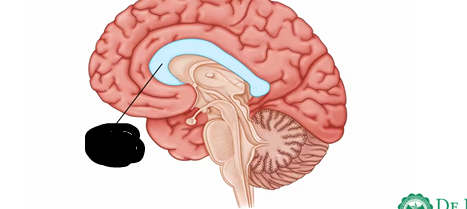
CORPUS CALLOSUM
Located deep within the longitudinal sulcus that consist of an arched mass of transverse fibers that connect the 2 cerebral hemispheres
CORPUS CALLOSUM
CEREBRAL VENTRICLES
Consists of 4 irregular, fluid-containing cavities that communicate with one another
LATERAL VENTRICLES (right and left), THIRD VENTRICLE, FOURTH VENTRICLE
CEREBRAL VENTRICLES
Consists of 4 irregular, fluid-containing cavities that communicate with one another
LATERAL VENTRICLES (right and left)
located on each side of the midsagittal plane, in the inferior medial part of the corresponding hemisphere
THIRD VENTRICLE
each of the lateral ventricle connects to the ____ that is located in the midline
FOURTH VENTRICLE
the third ventricle connects here posteroinferiorly through a process known as the cerebral aqueduct
CHOROID PLEXUS
filters the blood to form cerebrospinal fluid
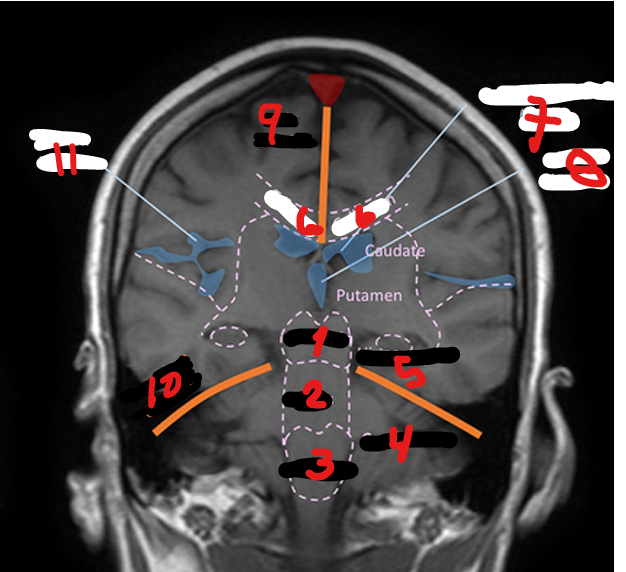
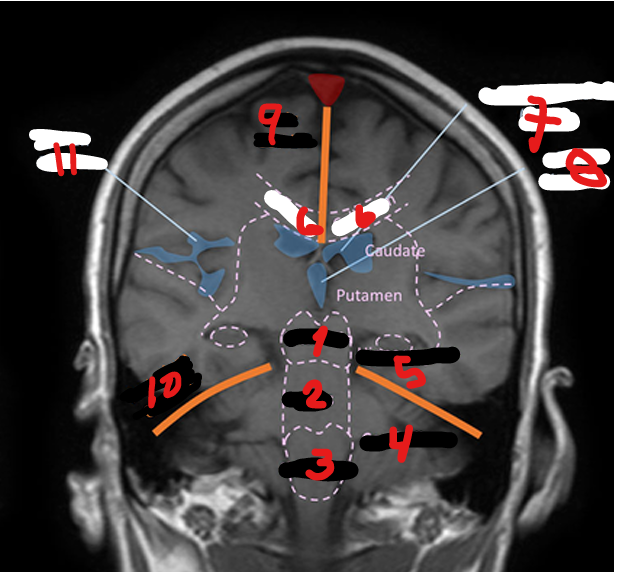
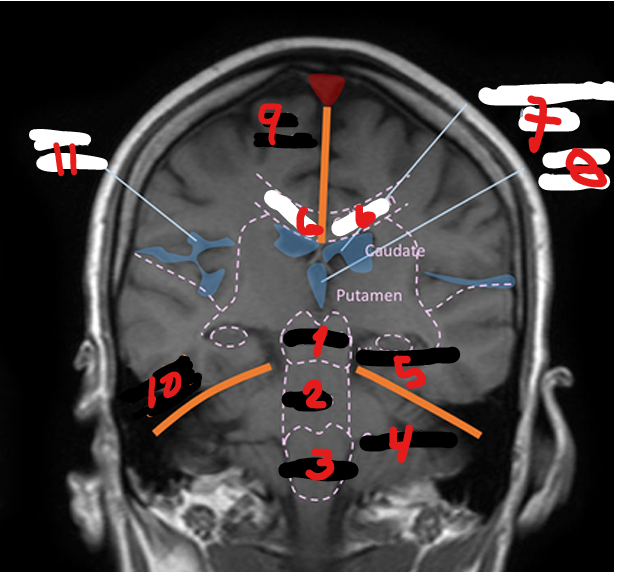
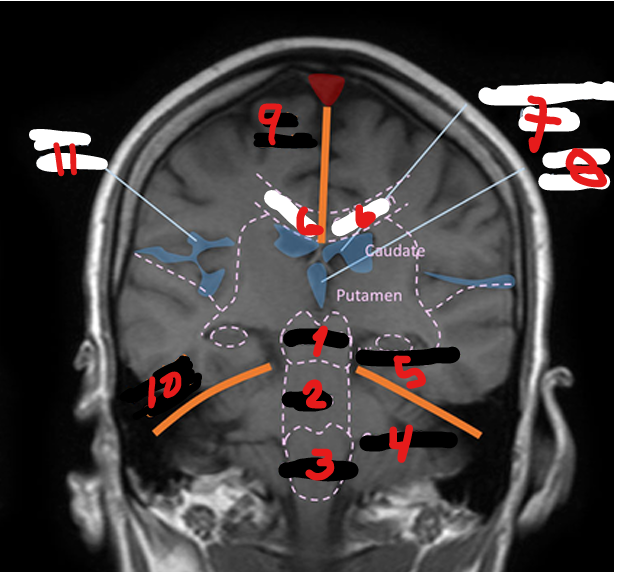
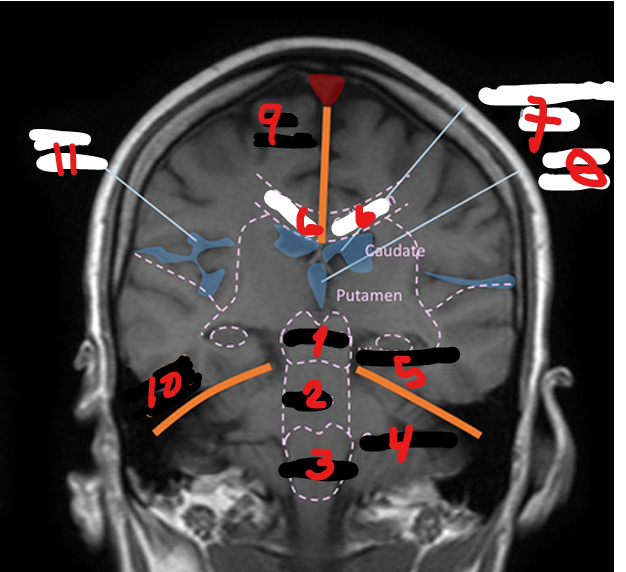
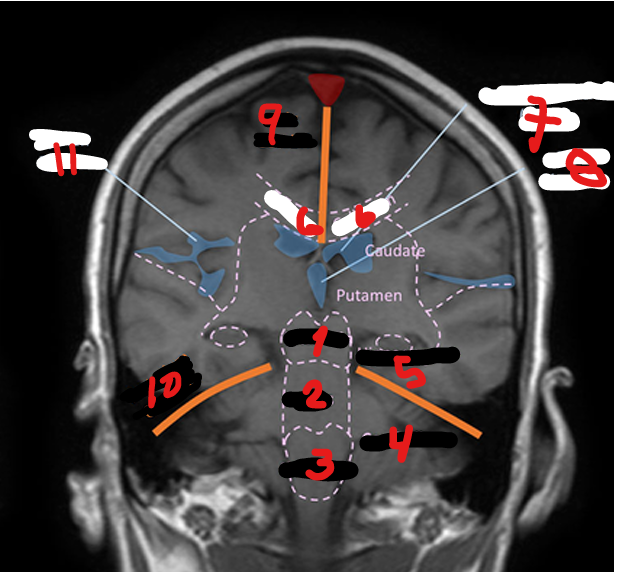
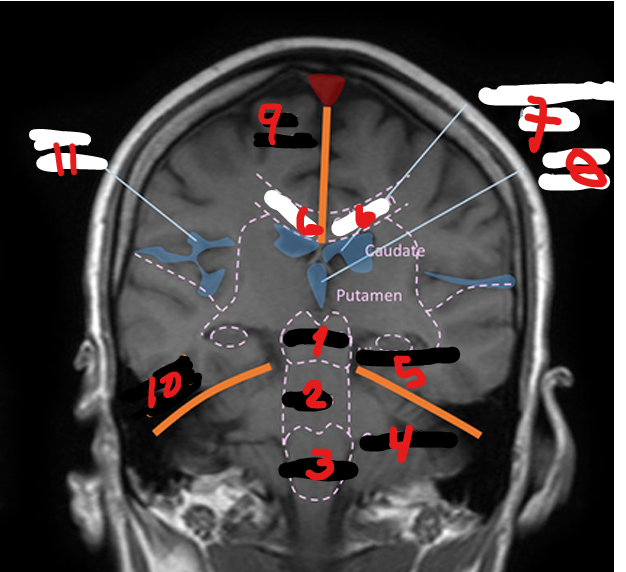
LATERAL VENTRICLES (R&L)
1
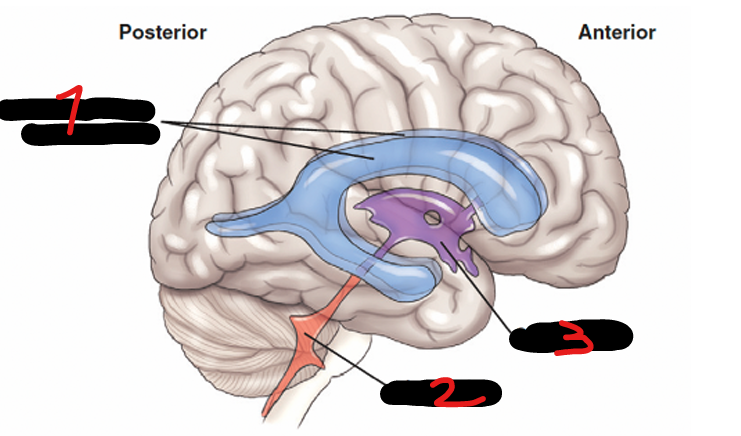
4TH VENTRICLE
2
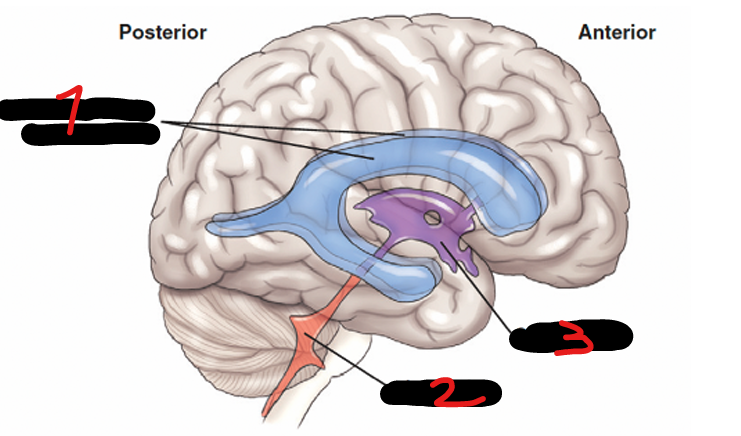
3RD VENTRICLE
3
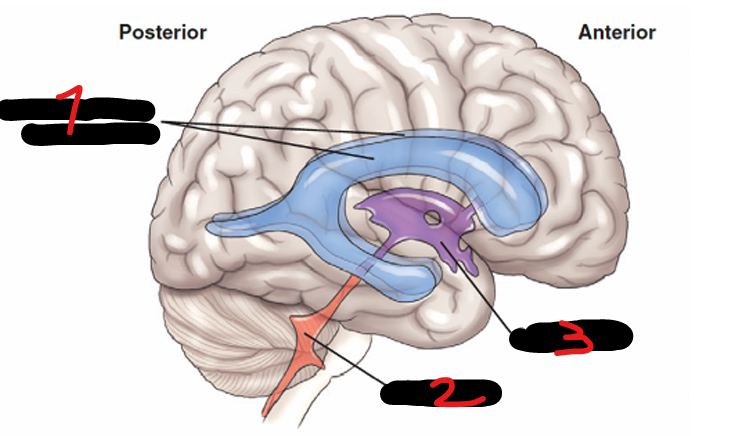
THALAMUS
Small, oval structure that is located just above the midbrain under the corpus callosum
THALAMUS
Interpretation center for sensory impulses such as pain, temperature, and touch, and for certain emotions and memory
HYPOTHALAMUS
Forms the floor and lower walls of the third ventricle
HYPOTHALAMUS
Controls important body activities through a link with endocrine system
MIDBRAIN
Seen as a short, constricted portion of the upper brainstem that connects the forebrain to the hindbrain
HINDBRAIN
Consists of cerebellum, pons, and medulla
CEREBELLUM
Shaped like a butterfly and consists of right and left hemispheres united by a median strip called vermis
CEREBELLUM
Coordinates the important motor function of the body such as coordination, posture, and balance
PONS
Forms the upper portion of the hindbrain
PONS
Is the bridge between the cerebrum, cerebellum, and medulla oblongata
MEDULLA OBLONGATA
Forms the lower portion of the hindbrain
MEDULLA OBLONGATA
Extends between the pons and spinal cord, in which all the nerve fiber tracts (sensory and motor) between the brain and spinal cord pass through
CEREBELLUM, PONS, MEDULLA OBLONGATA
HINDBRAIN PARTS 3
MIDBRAIN, HINDBRAIN
BRAINSTEM 2
FRONTAL SINUS
1
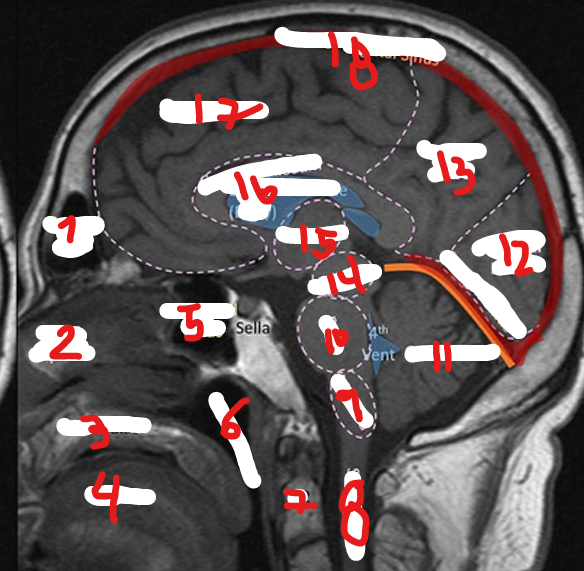
NASAL SEPTUM
2
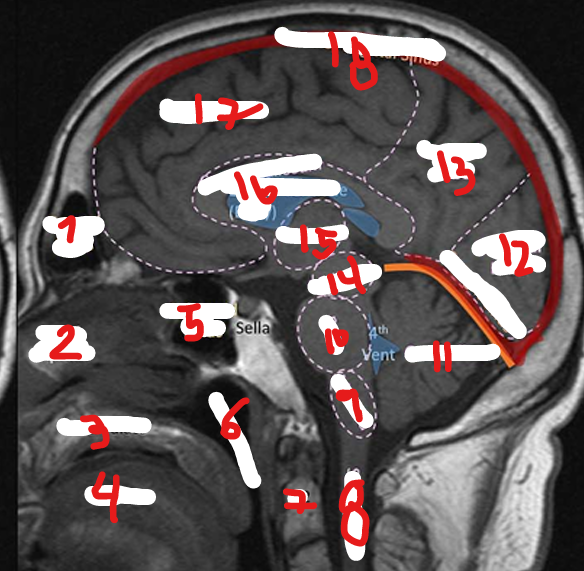
HARD PALATE
3
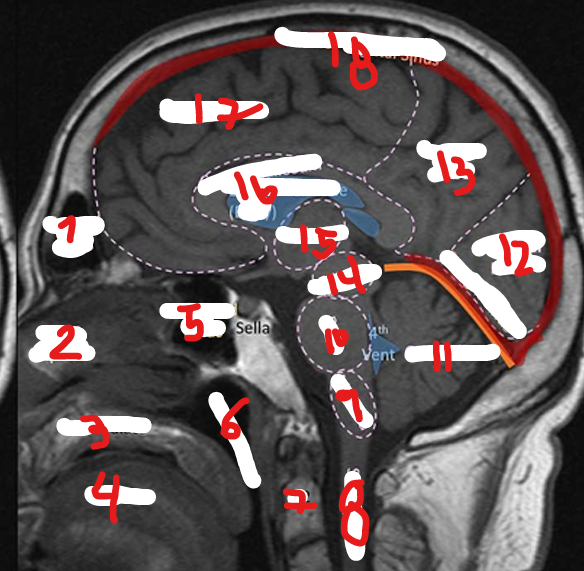
TONGUE
4
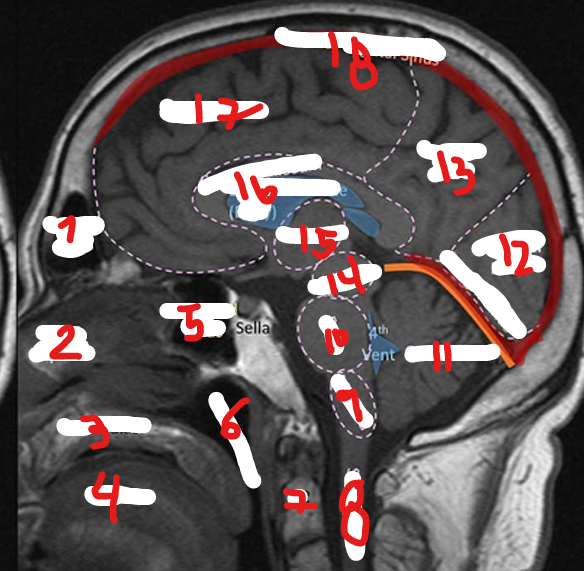
SPHENOID SINUS
5
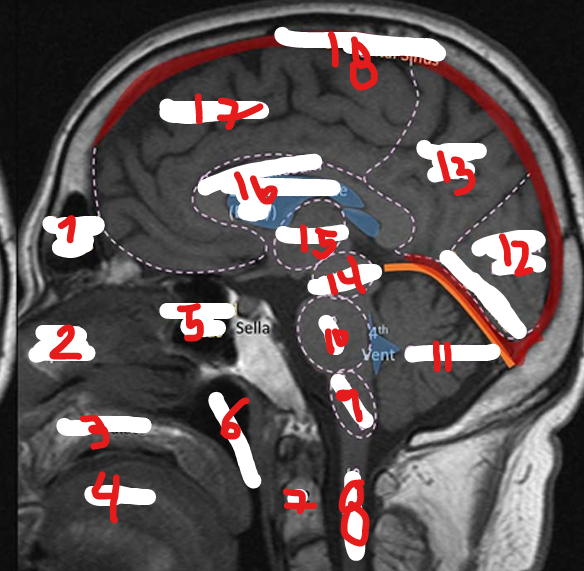
NASOPHARNYX
6
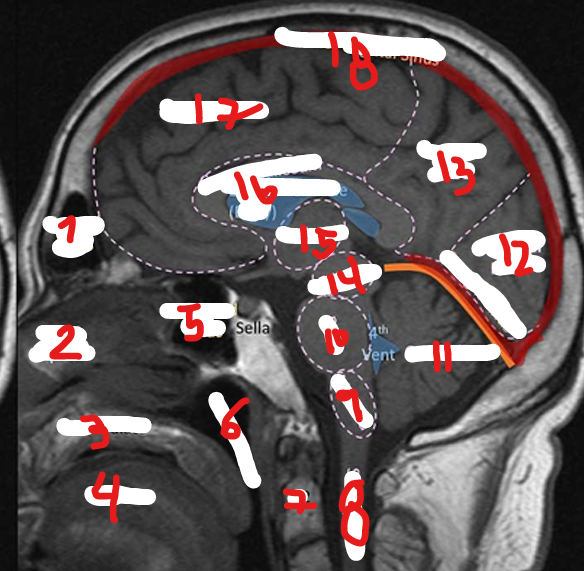
FRONTAL LOBE
17
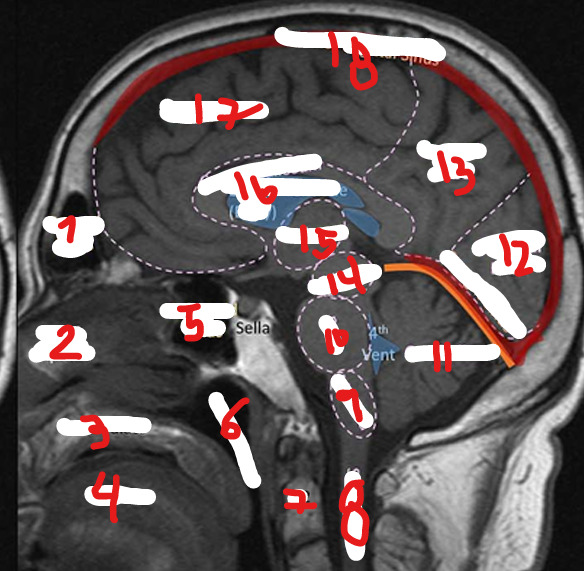
C2
7
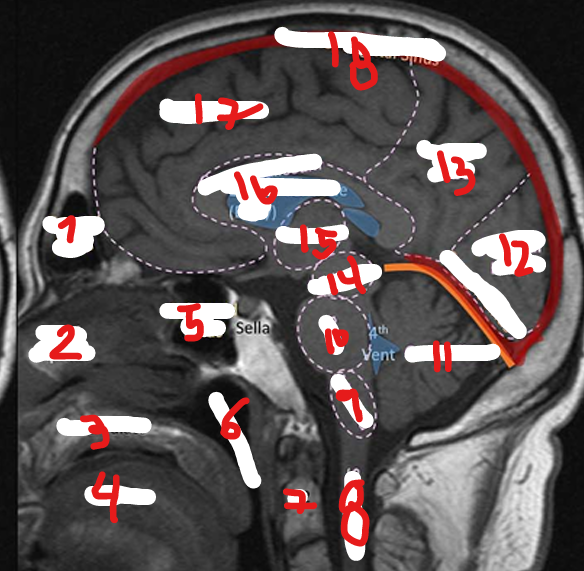
SPINAL CHORD
8
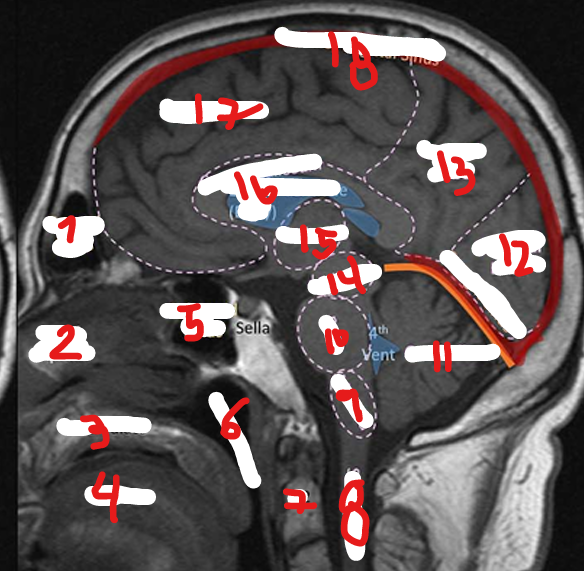
MEDULLA
9
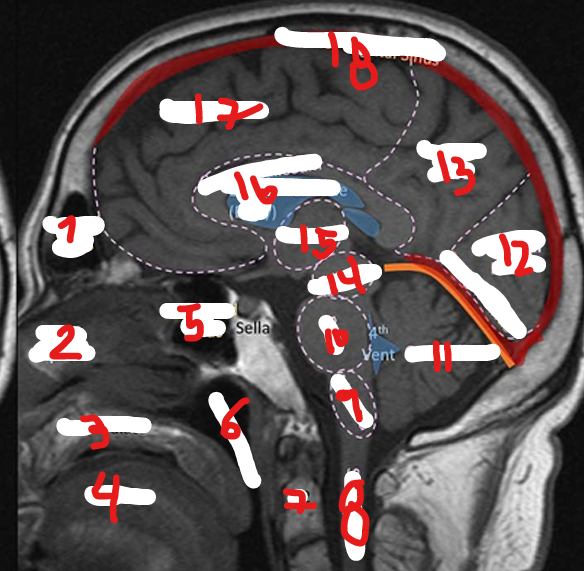
PONS
10
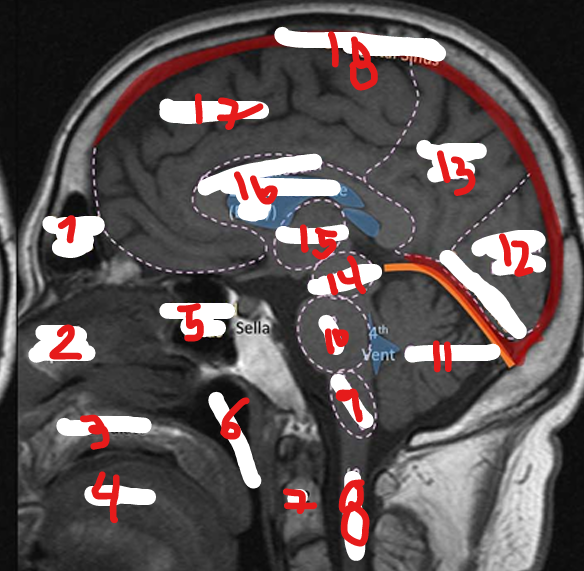
CEREBELLUM
11
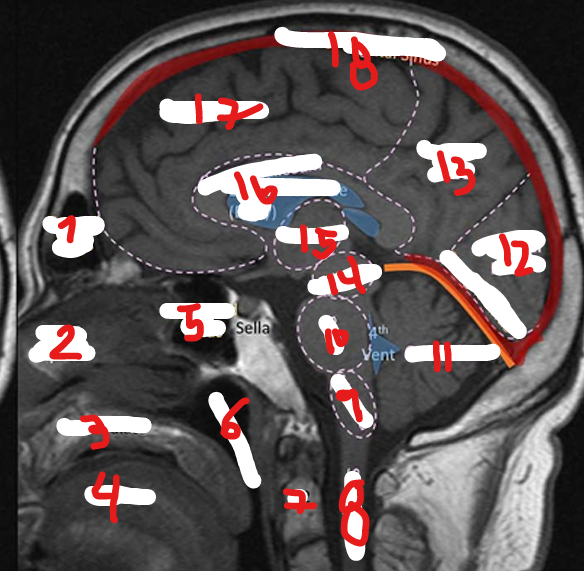
OCCIPITAL LOBE
12
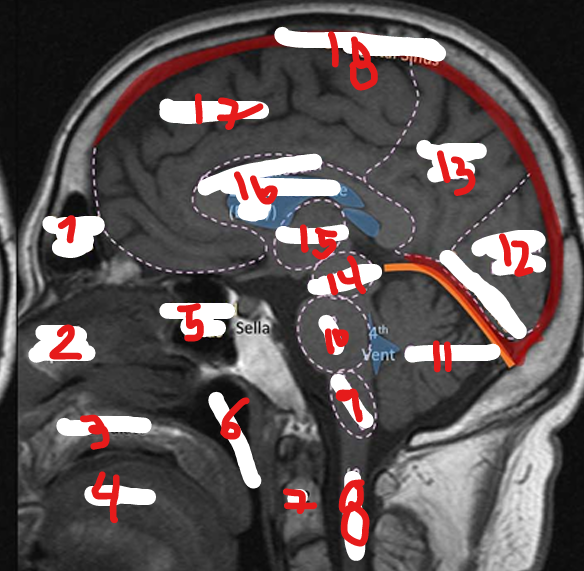
PARIETAL LOBE
13
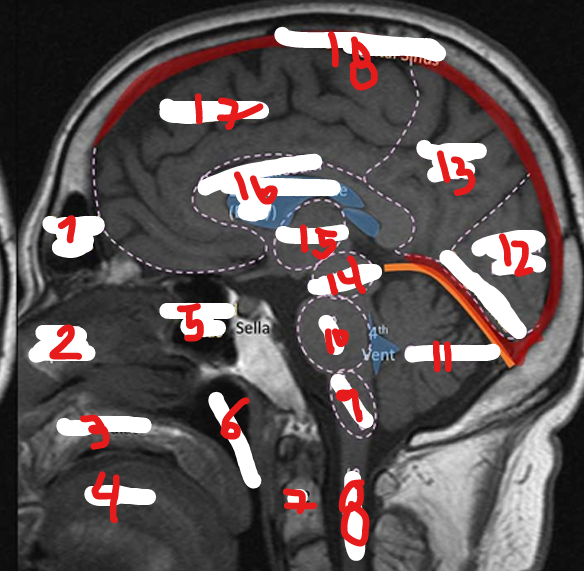
MIDBRAIN
14
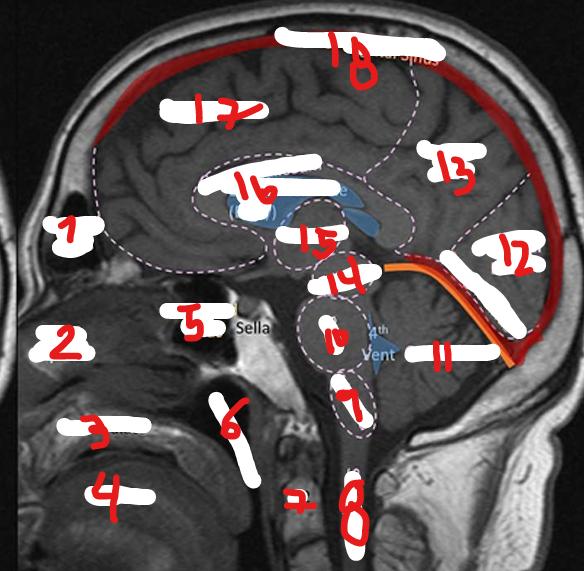
THALAMUS
15
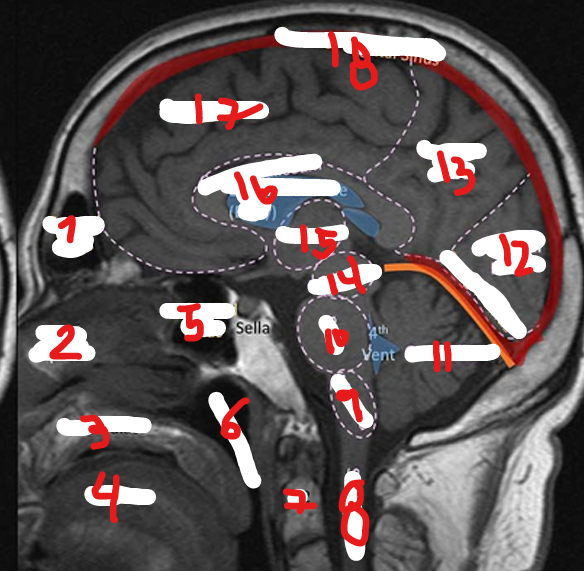
CORPUS CALLOSUM
16
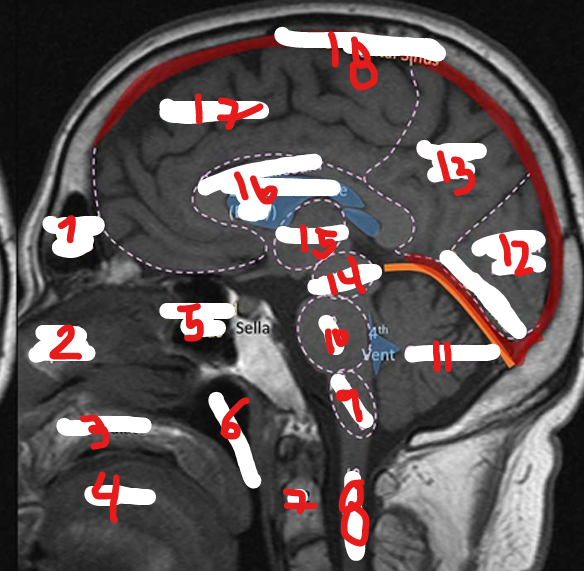
SUPERIOR SAGITAL SINUS
18
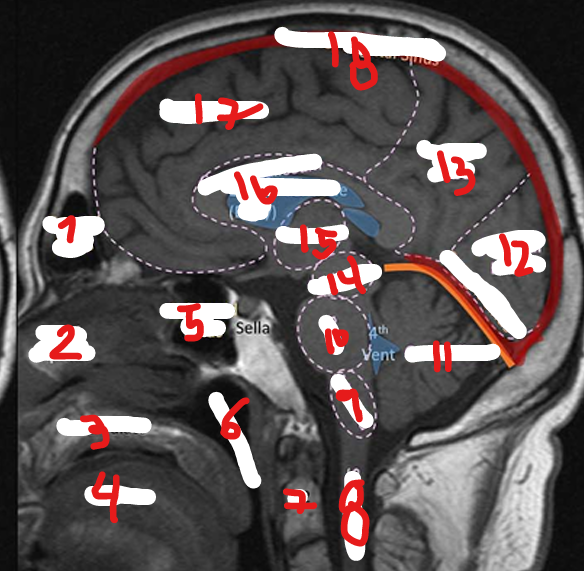
MIDBRAIN
1
PONS
2
MEDULLA
3
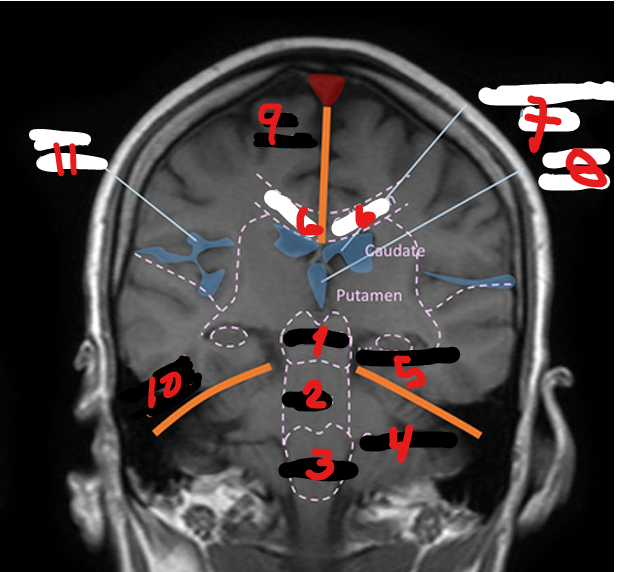
CEREBELLUM
4
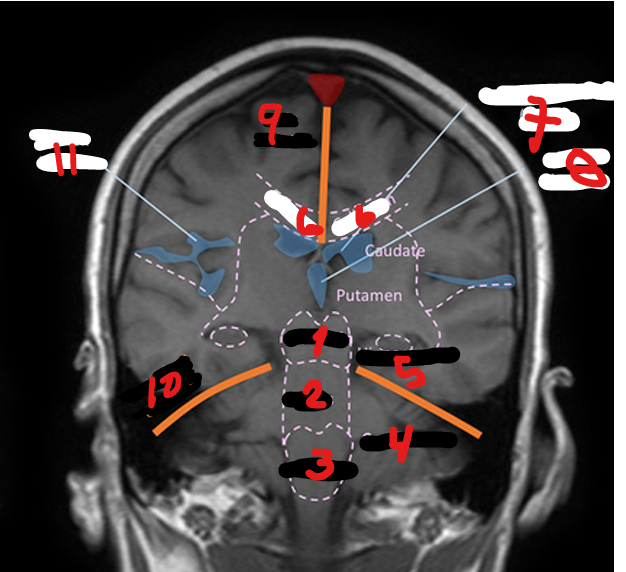
HIPPOCAMPUS
5
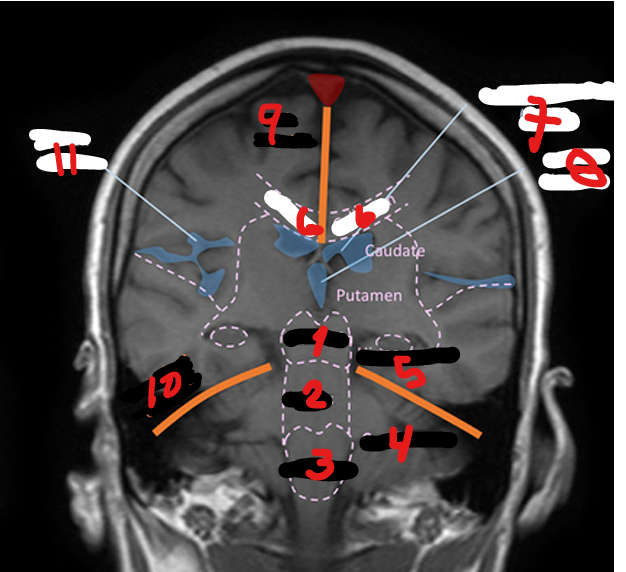
CORPUS CALLOSUM
6
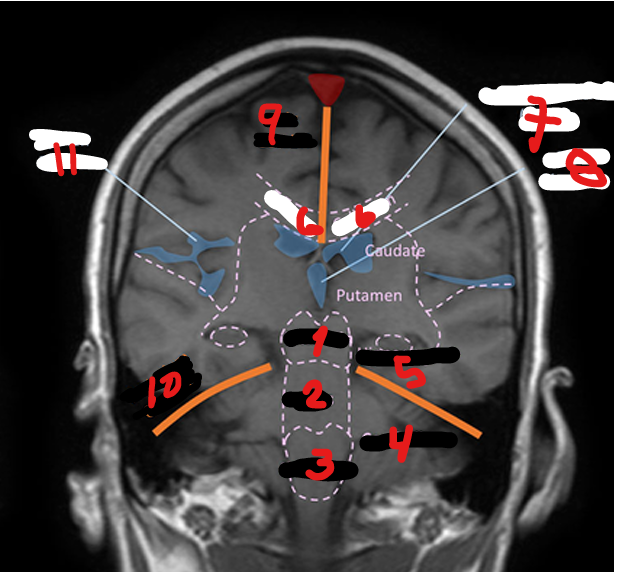
LATERAL VENTRICLE
7
THIRD VENTRICLE
8
FALX CEREBRI
9
TENTORIUM CEREBELLI
10
SYLVIAN FISSURE
11