Pre Lab 7
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/66
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
1
New cards
The end products of digestion of carbohydrates are ________.
monosaccharides
2
New cards
Fat digestion results in ________.
monoglycerides and fatty acids
3
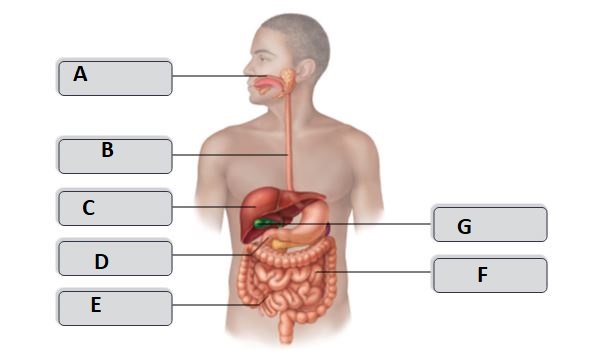
New cards
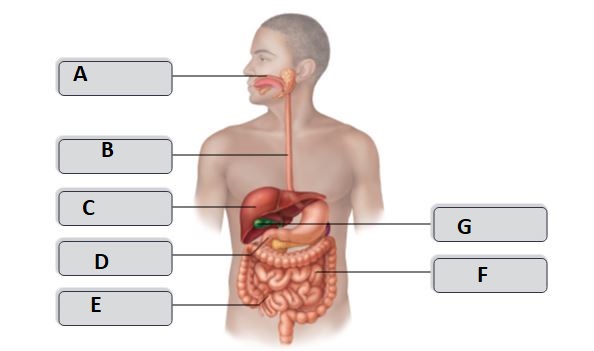
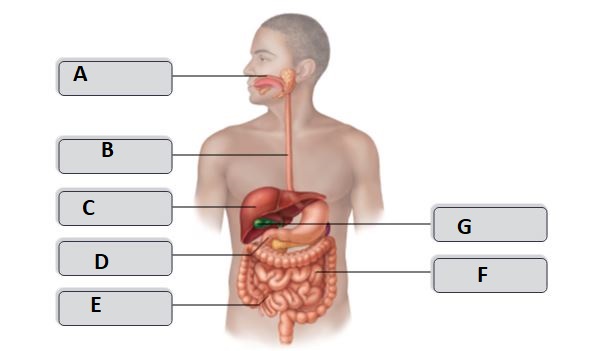
B
esophagus
4
New cards
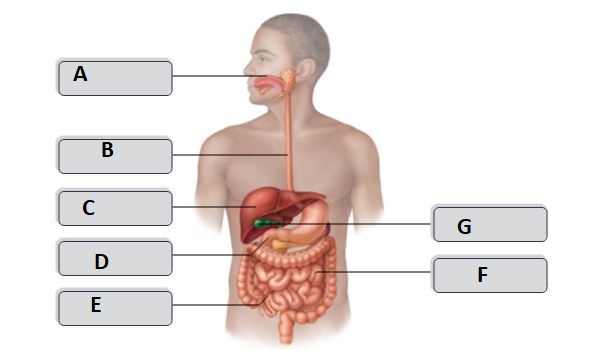
D
duodenum
5
New cards
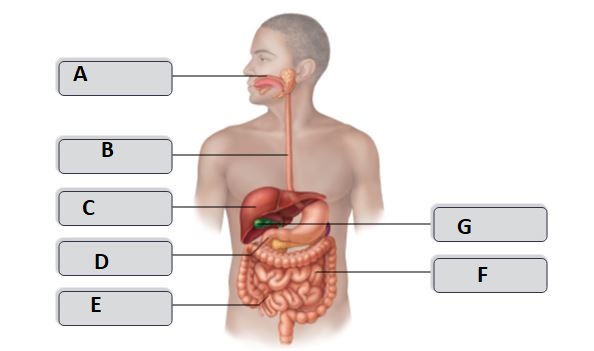
G
gallbladder
6
New cards
A
Tongue
7
New cards
B
Esophagus
8
New cards
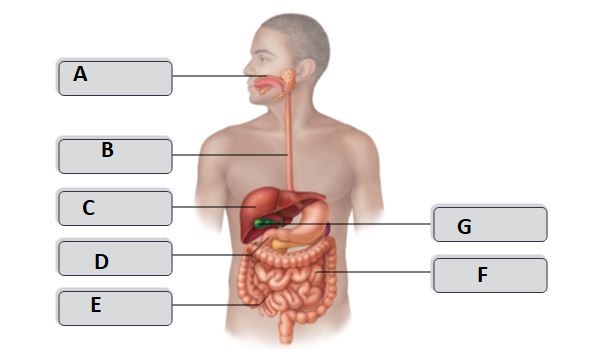
C
liver
9
New cards
F
small intestine
10
New cards
The digestive function of the liver is to ________.
produce bile
11
New cards
A tooth consists of two major regions, the crown and the __________.
root
12
New cards
The crown of the tooth is covered by ________, the hardest substance in the body.
enamel
13
New cards
The alimentary canal is also called the ________.
gastrointestinal (GI) tract
14
New cards
The myenteric plexus is associated with this tunic of the alimentary canal.
muscularis externa
15
New cards
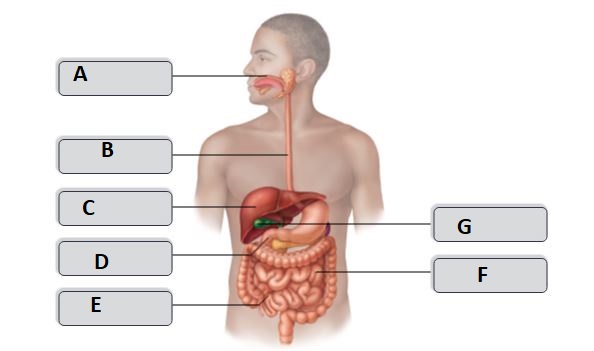
F
uvula
16
New cards
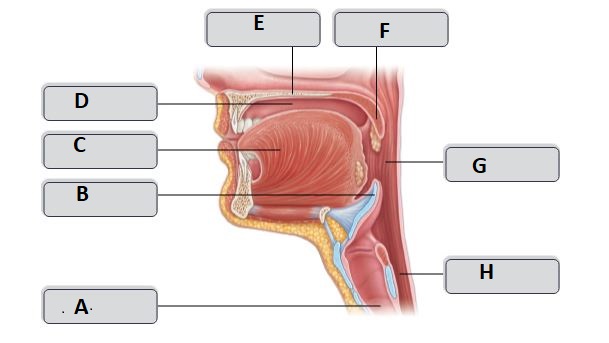
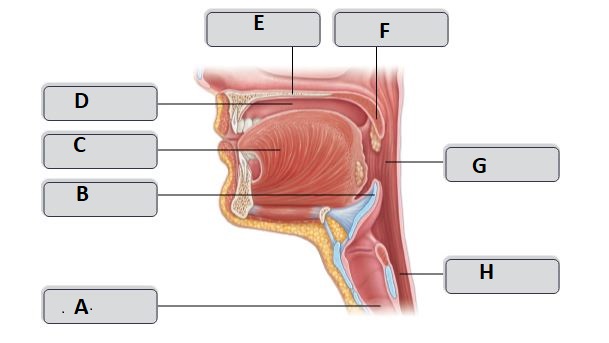
A
trachea
17
New cards
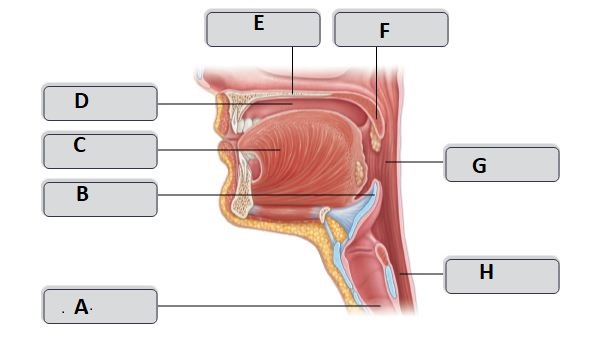
B
Epiglottis
18
New cards
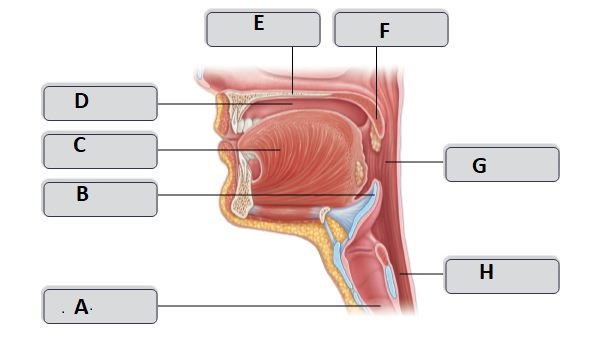
C
Tongue
19
New cards
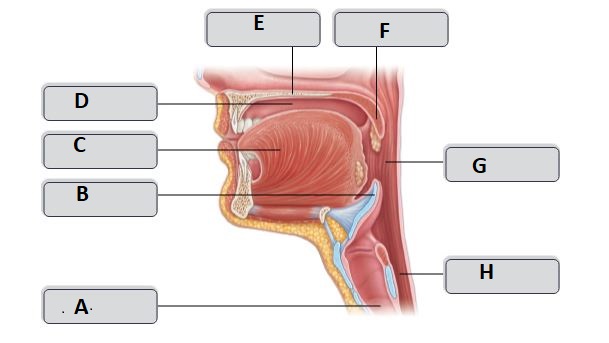
D
Oral cavity
20
New cards
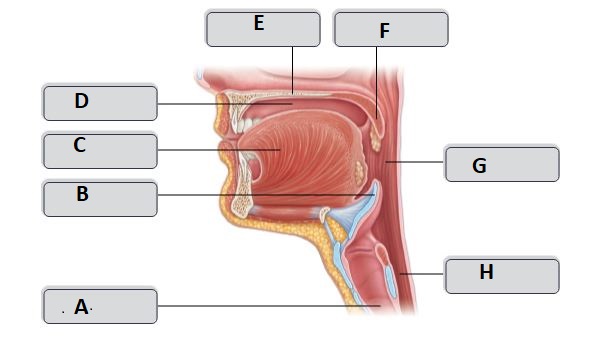
E
Hard palate
21
New cards
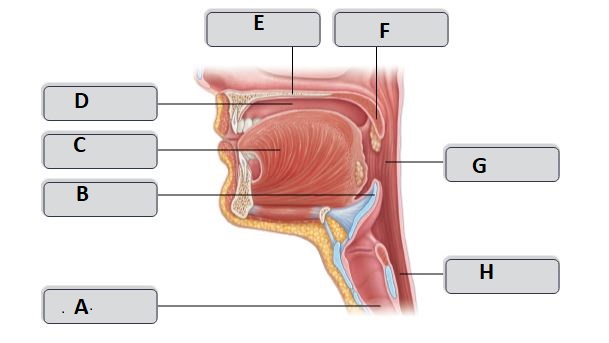
G
Oropharynx
22
New cards
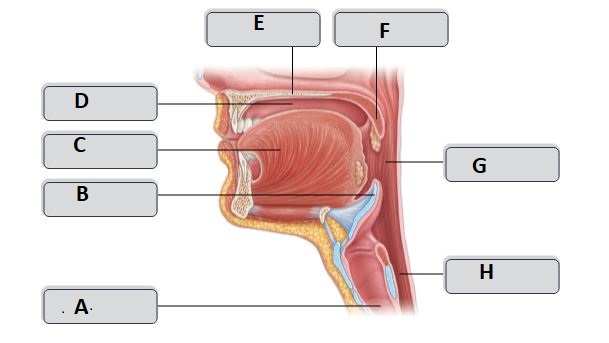
H
esophagus
23
New cards
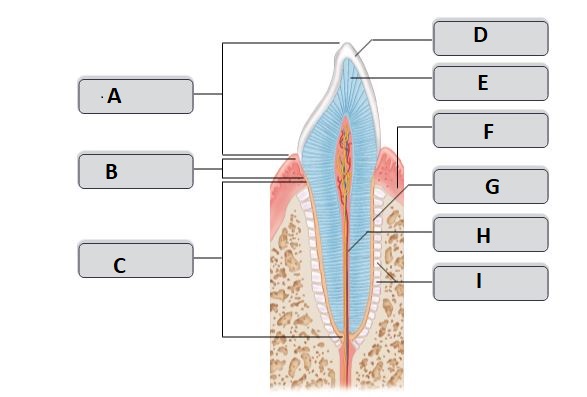
C
Root
24
New cards
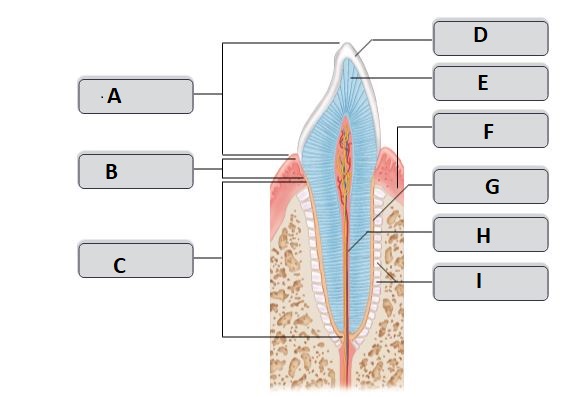
G
cementum (cement)
25
New cards
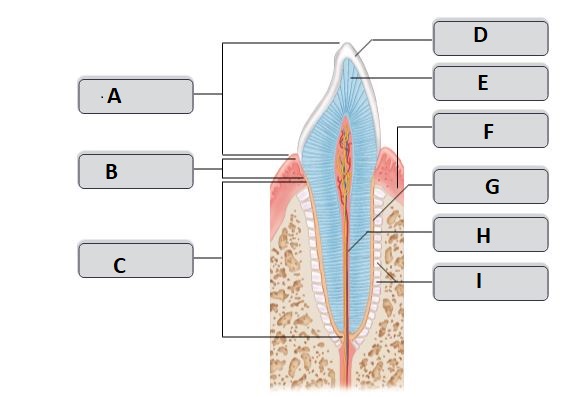
I
periodontal ligament
26
New cards
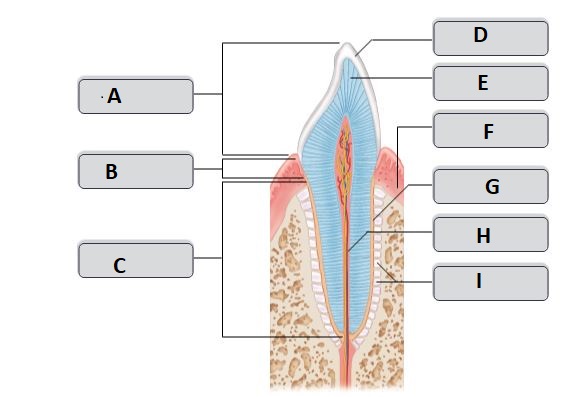
H
root canal
27
New cards
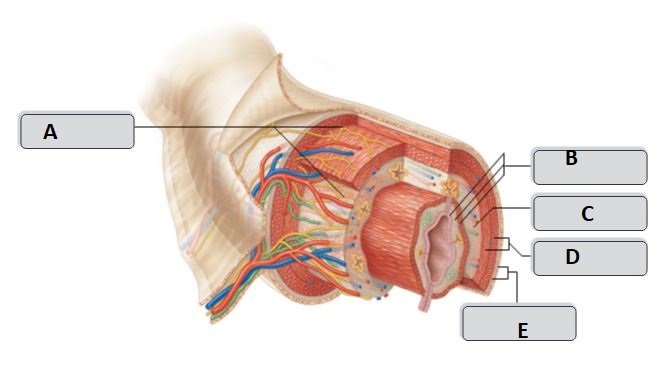
E
serosa
28
New cards
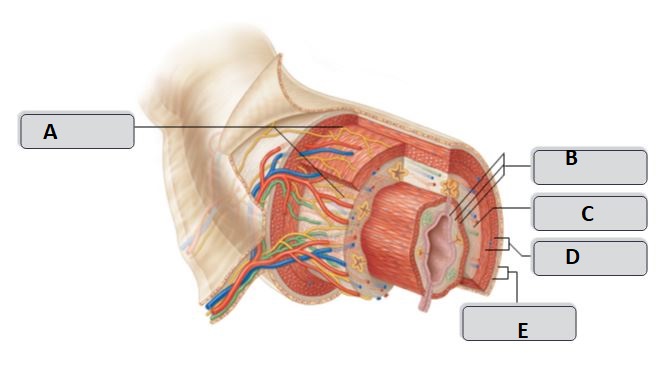
D
Muscularis externa
29
New cards
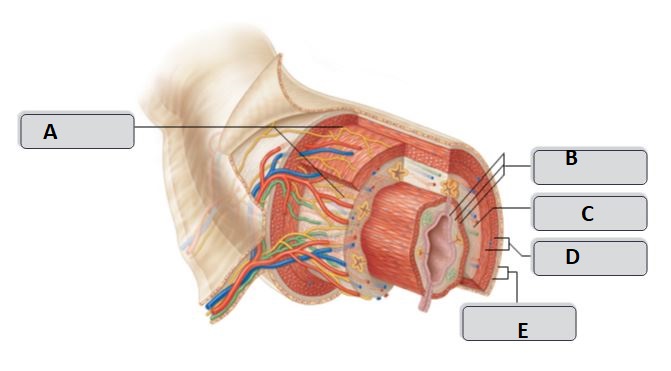
C
Submucosa
30
New cards
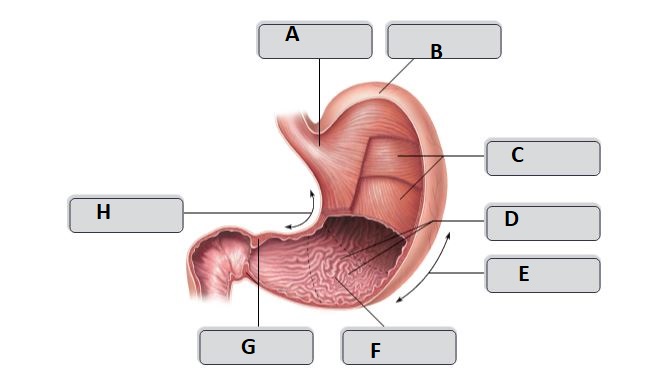
B
fundus
31
New cards
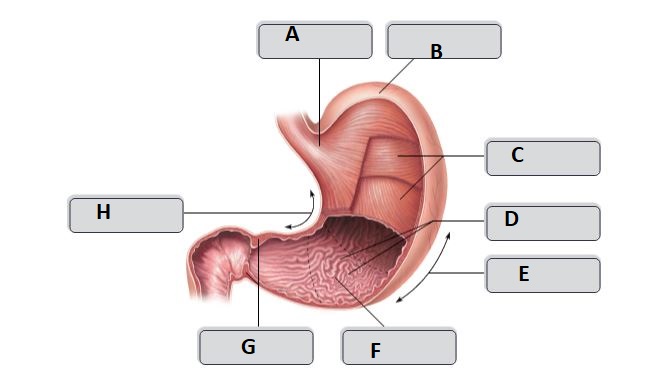
C
Body
32
New cards
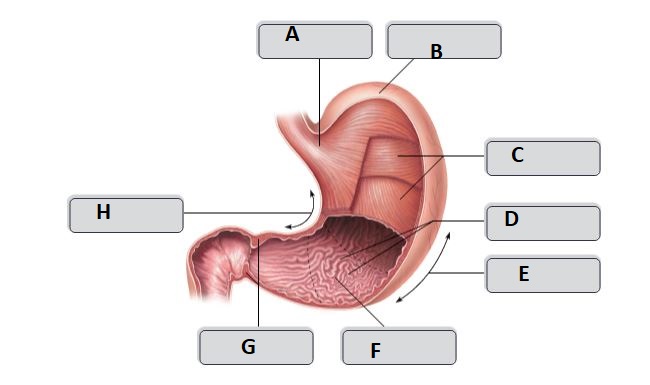
A
Cardia
33
New cards
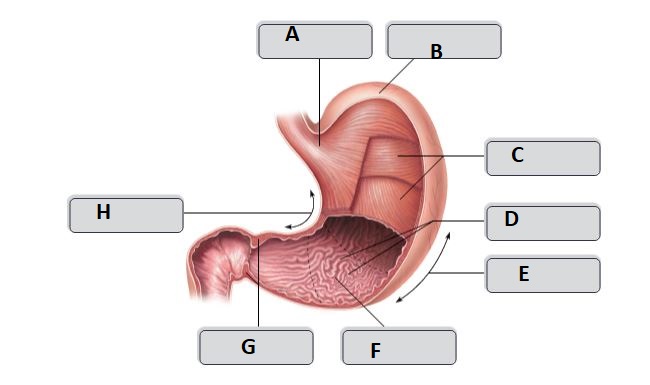
D
Rugae (gastric folds)
34
New cards
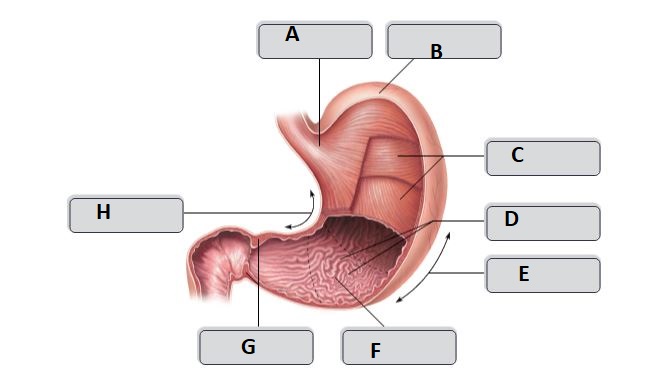
E
greater curvature
35
New cards
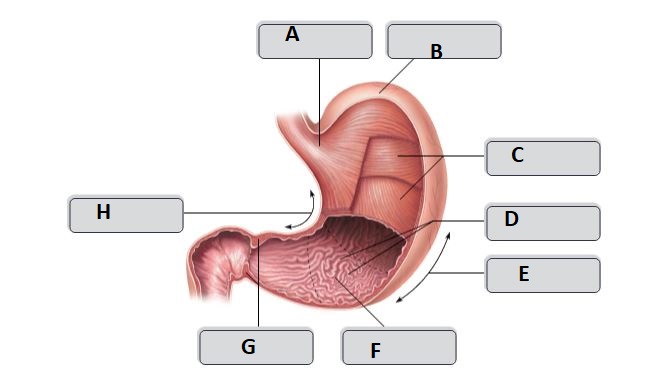
F
pyloric antrum
36
New cards
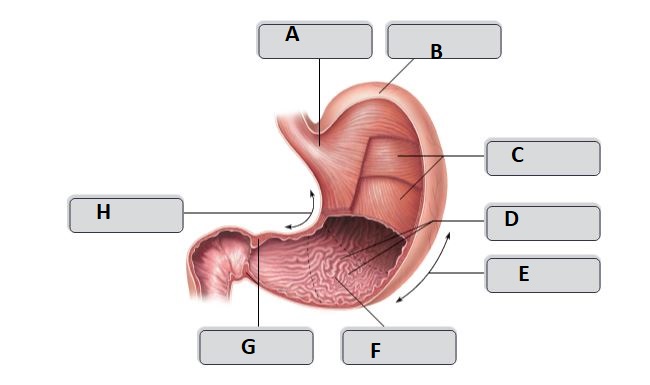
G
pyloric sphincter
37
New cards
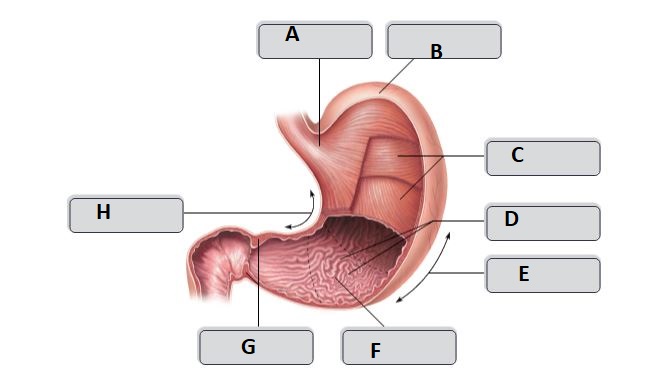
H
lesser curvature
38
New cards
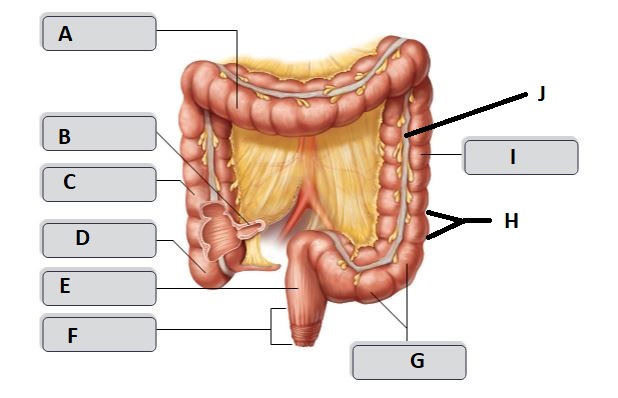
J
tenia coli
39
New cards
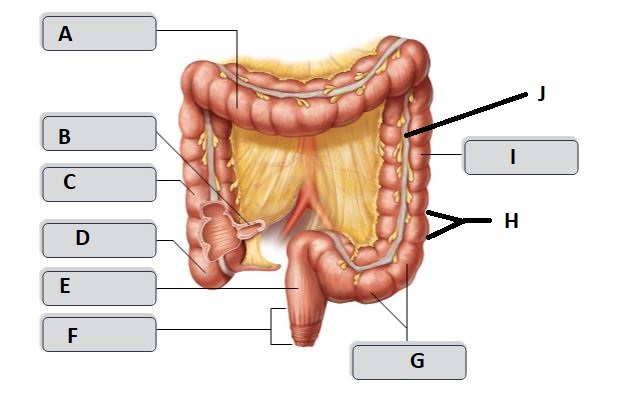
A
transverse colon
40
New cards
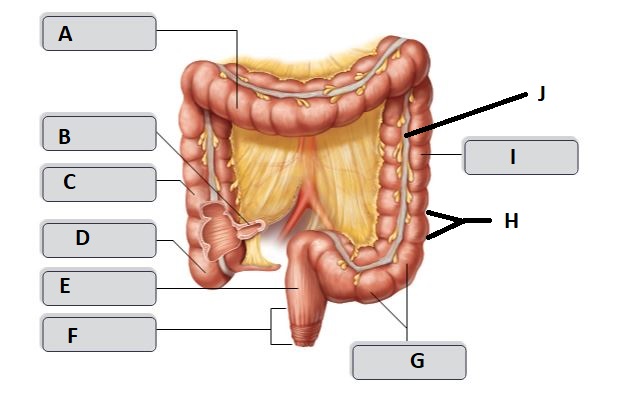
B
Ileum
41
New cards
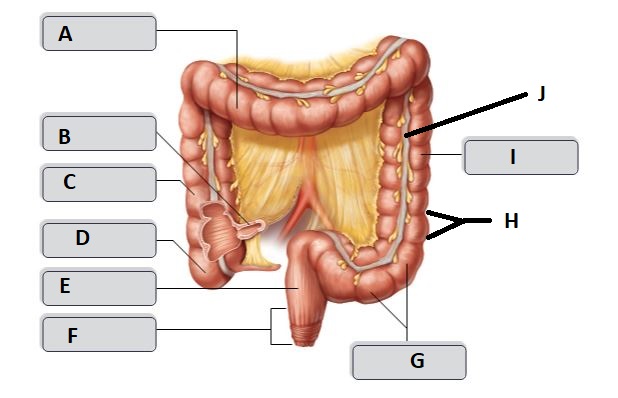
C
Ascending colon
42
New cards
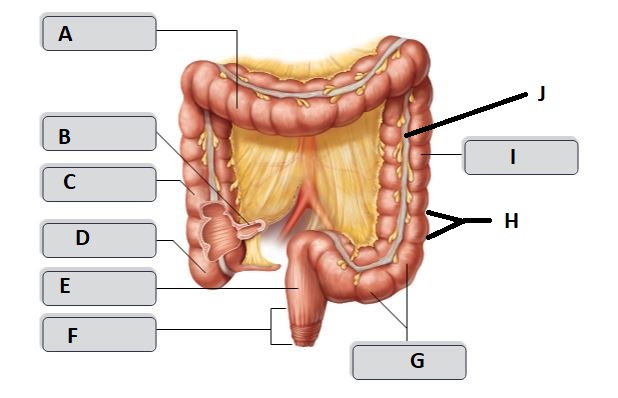
D
Cecum
43
New cards
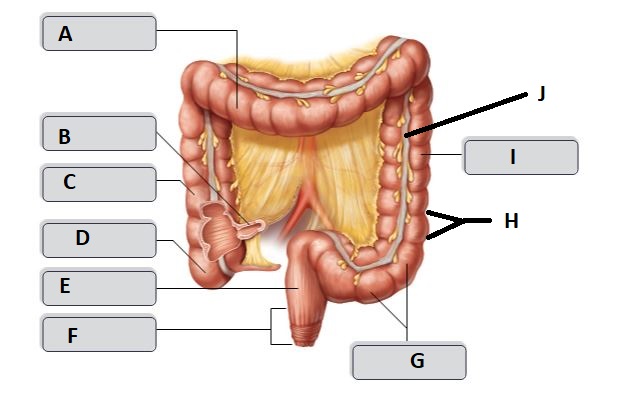
E
Rectum
44
New cards
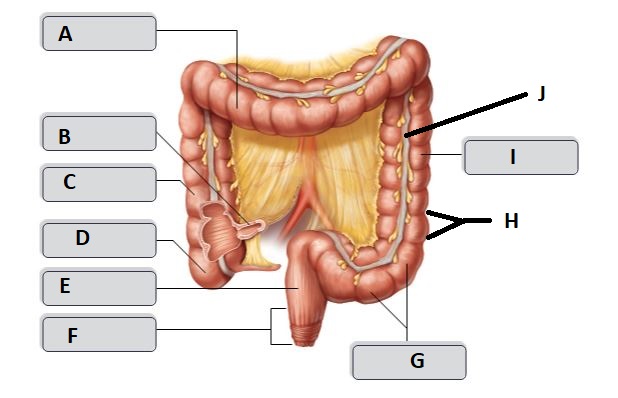
F
Anal canal
45
New cards
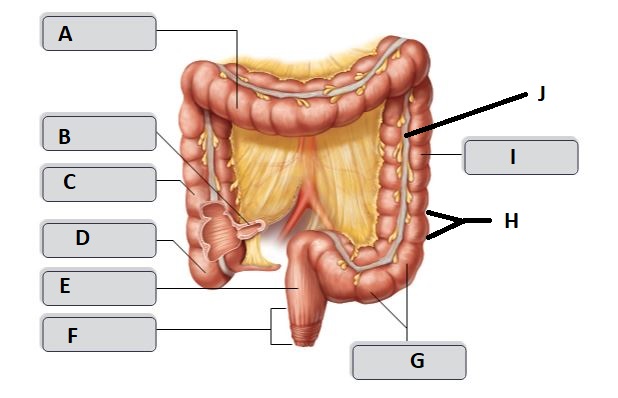
G
sigmoid colon
46
New cards
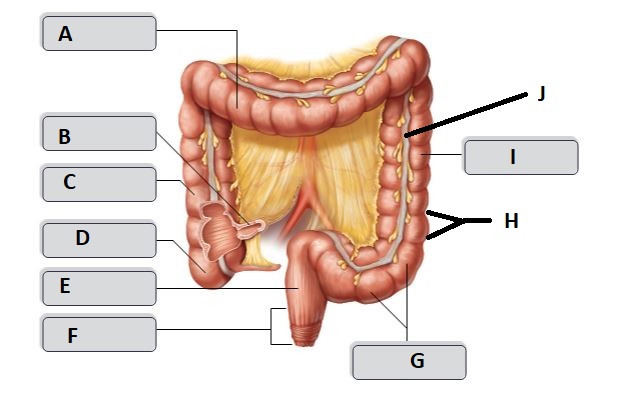
I
descending colon
47
New cards
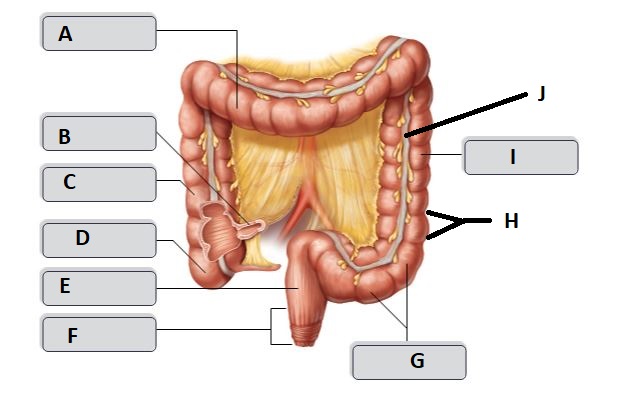
H
haustrum
48
New cards
Bile ________.
emulsifies fat, keeping tiny fat droplets suspended in the aqueous contents of the gut
49
New cards
Which type of movement in the GI system propels food along the entire alimentary canal?
peristalsis
50
New cards
The walls of the alimentary canal share a common pattern from esophagus to anus. How many tunics (layers) make up the wall?
4
51
New cards
The tube that connects the oral cavity to the stomach is called the ________.
esophagus
52
New cards
The __________ is located on the left side of the abdominal cavity and is hidden by the liver and diaphragm.
stomach
53
New cards
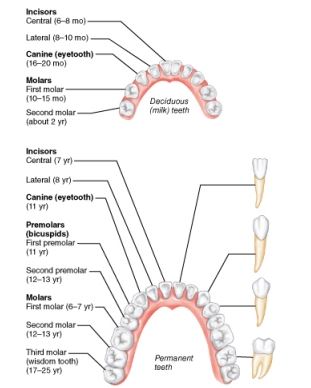
How many total permanent teeth should an adult have, assuming none have been lost or removed?
32
54
New cards
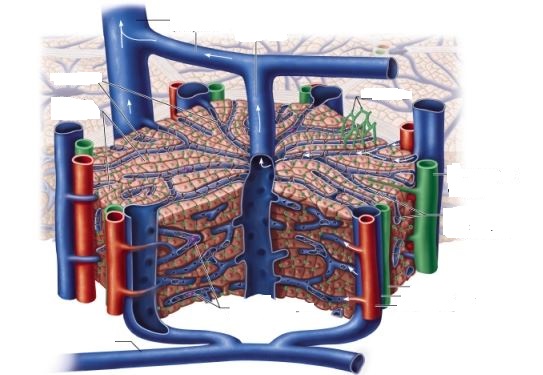
Which of the following best describes the capillary wall structure found in the liver lobules?
The capillary walls have openings that allow large proteins and small cells to pass through.
55
New cards
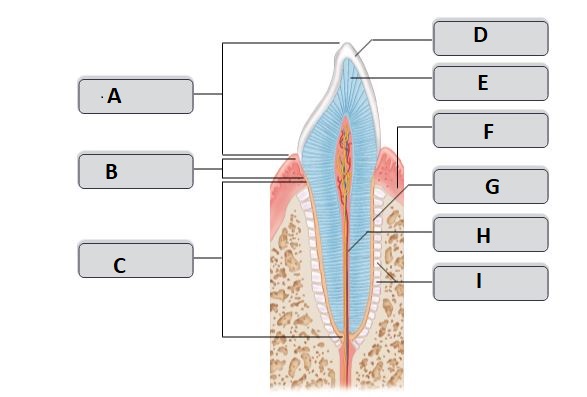
A
crown
56
New cards
The dental formula for the permanent teeth indicates two ________ and two ________ in both upper and lower quarters of the mouth.
incisors; premolars
57
New cards
This fat-digesting enzyme does the major work of digesting fats in the small intestine.
lipase
58
New cards
The pancreas produces this protein-digesting enzyme.
trypsin
59
New cards
This tunic of the GI tract is important for the secretion of enzymes and absorption of nutrients.
mucosa
60
New cards
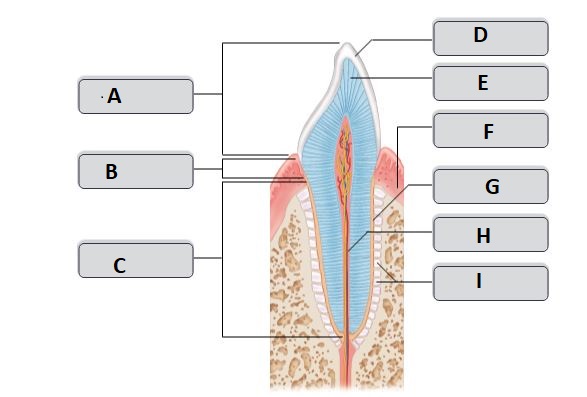
D
enamel
61
New cards
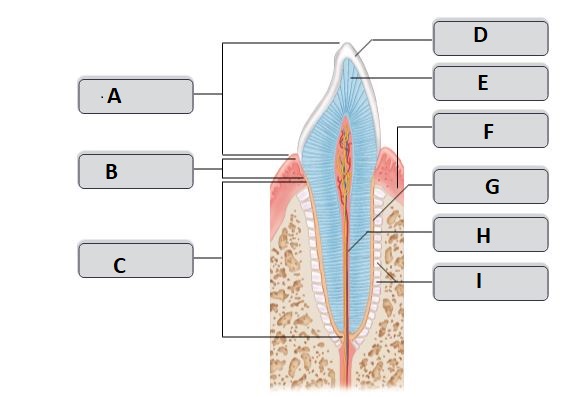
H
root canal
62
New cards
Which type of movement in the GI system is primarily responsible for moving chyme back and forth, mixing it with digestive juices and promoting the absorption of nutrients?
segmentation
63
New cards
__________ occurs when small molecules pass through epithelial cells into the blood for distribution to the body cells.
absorption
64
New cards
This GI tract organ stores food temporarily, and continues the mechanical and chemical breakdown of food.
stomach
65
New cards
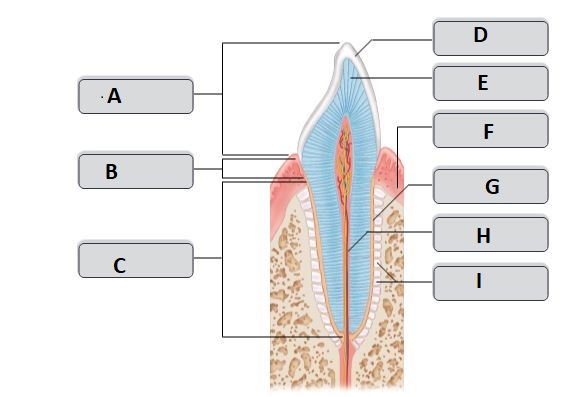
B
neck
66
New cards
The lining of the alimentary canal is a ________.
mucosa (mucous membrane)
67
New cards
The tube that leaves the stomach (and is the first part of the small intestine) is called the ________.
duodenum