Histology - Connective Tissue, Glandular Epithelium, etc. etc.
1/316
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
317 Terms
Areolar (INFO)
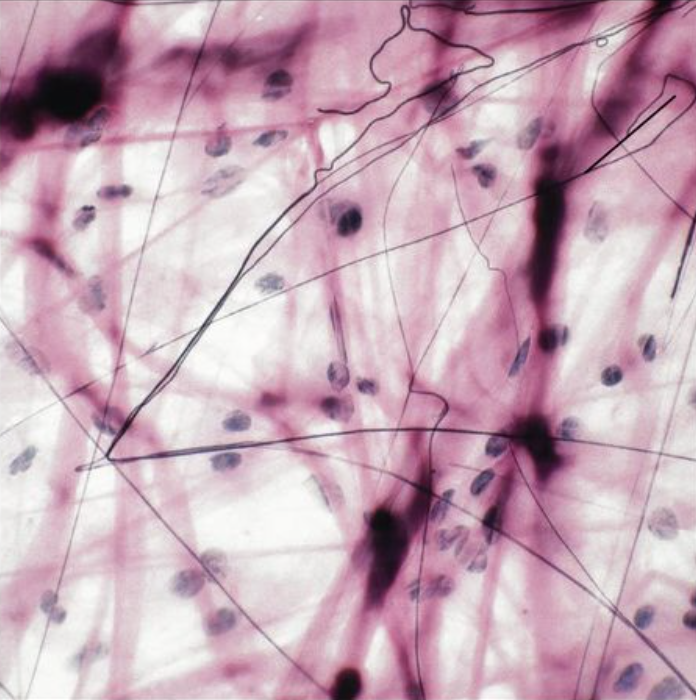
Description: Gel-like matrix Function: binds skin to underlying tissue, holds structures together Location: beneath skin, surrounds organs (under epithelium)
Areolar (IMAGE)
Adipose (INFO)
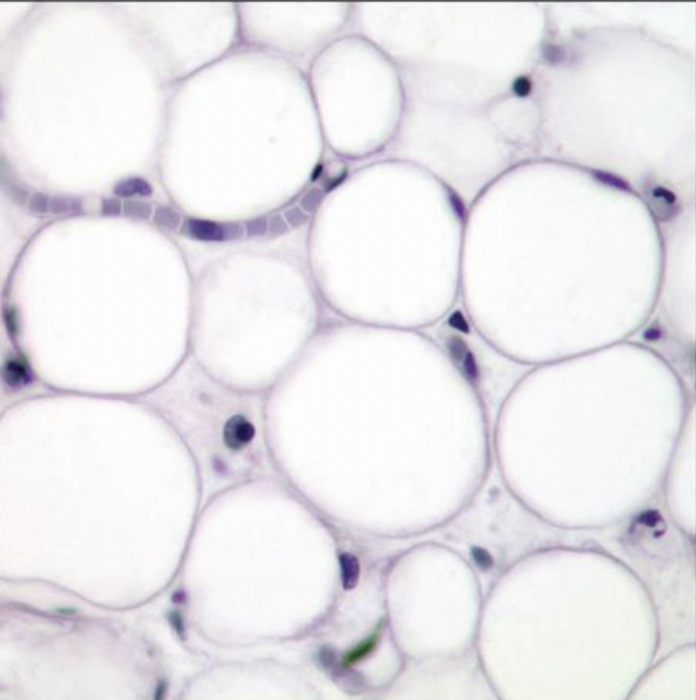
Description: Minimal Matrix Function: protection, stores energy, and insulation Location: beneath skin, around kidneys and heart, behind the eyeballs
Adipose (IMAGE)
Reticular (INFO)
Description: Networks of reticular fibers in a typical loose substance Function: provides support for other cells such as white blood cells, mast cells, and macrophages Location: lymphoid organs
Reticular (IMAGE)
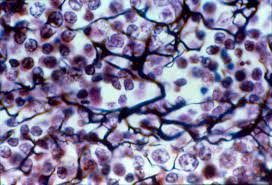
Dense Regular (INFO)
Description: Primarily parallel collagen fibers Function: bind body parts, connect muscle to bone and bone to bone. Location: tendons, ligaments and aponeurosis
Dense Regular (IMAGE)

Dense Irregular (INFO)
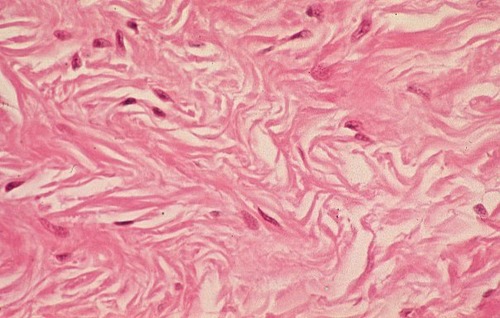
Description: Primarily irregularly arranged collagen fibers Function: Withstands tension Location: dermis of the skin
Dense Irregular (IMAGE)
Hyaline Cartilage (INFO)
Description: firm matrix Function: support, protects, forms, the framework for future bones Location: ends of bones, soft part of the nose, costal cartilage, rings of trachea, embryonic skeleton
Hyaline Cartilage (IMAGE)
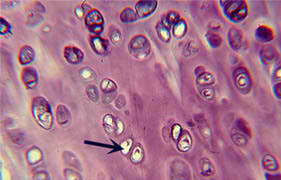
Elastic Cartilage (INFO)
Description: Many Chondrocytes, few fibers in the Matrix Function: supports provides a flexible framework Location: external ear (auricle), vocal cords
Elastic Cartilage (IMAGE)
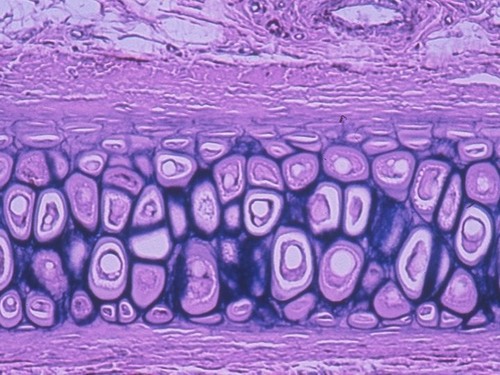
Fibrocartilage (INFO)
Description: thick collagen fibers predominate. Function: supports, protects and acts as a shock absorber Location: between the vertebrae in the back (disks), menisci (pads) of the knees, symphysis pubis (pelvis)
Fibrocartilage (IMAGE)
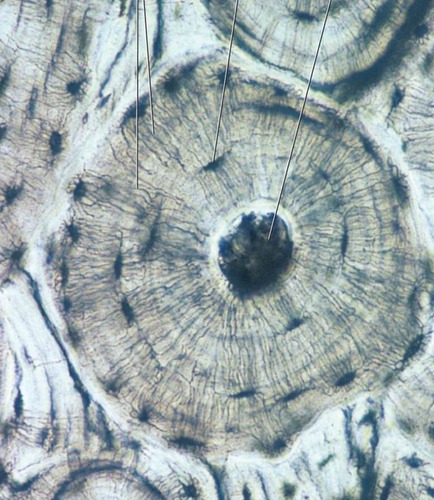
Compact (Osseous) Bone (INFO)
Description: Hard, Densely Packed Function: support, forms a framework for body, stores ions (calcium and phosphorus) and produces blood cells
Location: skeletal bones and middle ear
Compact (Osseous) Bone (IMAGE)
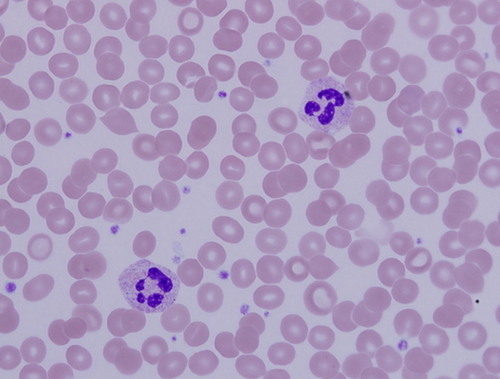
Blood (INFO)
Description: Red and white blood cells in a fluid matrix. Function: transports gases (O2, CO2), fights infection and blood clotting Location: blood vessels and heart chambers
Blood (IMAGE)
Simple Squamous Epithelium
Function: Diffusion, filtration, and lining
Simple Squamous Epithelium
Location: Mesothelium, endothelium, loop of henle, bowman's capsule
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
Function: Absorption, secretion, and lining/covering
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
Location: Ducts, kidney tubules, thyroid gland, and ovary covering
Simple Columnar Epithelium
Function: Secrete mucin, absorption, and lining
Simple Columnar Epithelium
Location: Stomach, gallbladder, intestine, cervix
Pseudostratified Epithelium
Function: Move mucus, lining and secretion
Pseudostratified Epithelium
Location: Upper respiratory tract and urethra
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
Structure:
-Cuboidal basement with squamous top layer
-Cell division in basal layer
-Keratinized or not
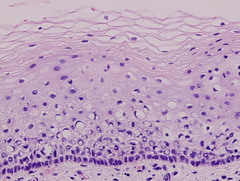
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
Function: Protection from wear and tear
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
Location: Vagina, anus, lining of mouth and throat
Transitional Epithelium
Structure: Dome shaped cells on top, polyhedral cells in the middle, and cuboidal/columnar near basement
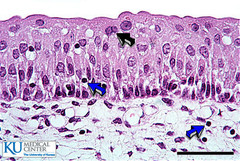
Transitional Epithelium
Function: Stretchable and toxic resistant leak-proof barrier
Exocrine Gland Epithelium
Function: Secretion empty through ducts to the epithelial surface, include sweat and oil glands, liver, and pancreas
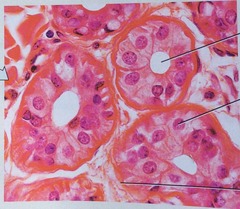
Endocrine Gland Epithelium
Description:
Often cuboidal cells inside gland secrete to interstitial fluid
Functions:
Secreted hormones regulate metabolism and maintain homeostasis
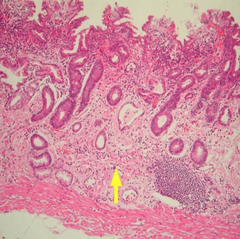
Collagen (Type I)
Structure: Collagen, fibroblasts, and ground substance
Collagen (Type I)
Function: Tensile strength, secretions, responsible for tissue repair and maintenance of cells
Collagen (Type I)
Location: Tendons, dermis, sheaths, capsule
Collagen (Type I)
Stain: Masson's Trichrome
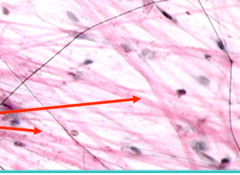
Reticulin (Type III)
Structure: Branching small fibers
Reticulin (Type III)
Function: Support and stroma of highly cellular organs
Reticulin (Type III)
Location: Bone marrow, kidney, liver, spleen etc
Reticulin (Type III)
Stain: Silver impregnation technique
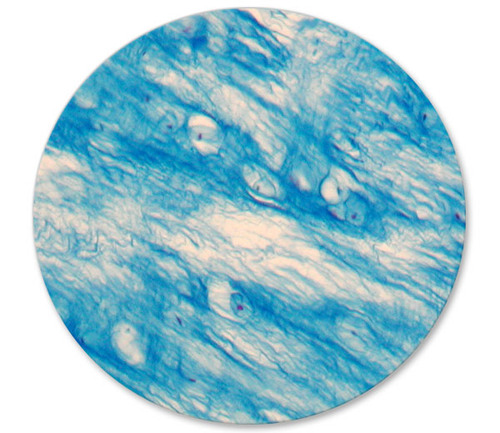
Elastic Tissue
Structure: Single fibers, branched network of fibers, and fenestrated sheets
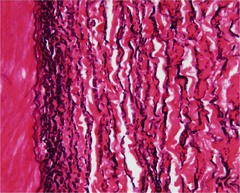
Elastic Tissue
Location: Dermis, respiratory, blood vessels, connective tissue proper
Elastic Tissue
Stain: Van Gieson (acid and base dyes)
Basement Membrane
Structure: Collagen type IV and some reticulin. A thin sheet like membrane
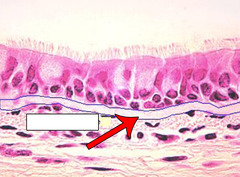
Basement Membrane
Function: Anchors epithelium and permits flow of nutrients and waste
Basement Membrane
Stain: Silver Impregnation Technique, Periodic Acid
Loose Irregular Connective Tissue
Structure: Lots of ground substance, type I collagen fibers, elastic fibers, fibroblasts, vascular, contains macrophages, mast cells, and lymphocytes
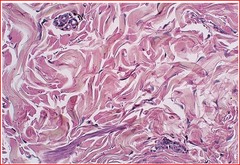
Loose Irregular Connective Tissue
Function: Interconnection, nourishment, allows movement
Loose Irregular Connective Tissue
Location: Submucosa and adventitia in digestive system. Papillary dermis and hypodermis in skin
Dense Irregular Connective Tissue
Structure: Less ground substance, lots of collagen, fibroblasts and fibrocytes, vascular
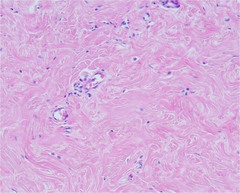
Dense Irregular Connective Tissue
Function: Support and strength, fibers run in different directions
Dense Irregular Connective Tissue
Location: Dermis of skin, organ capsules, nerve and blood vessel sheaths
Dense Regular Connective Tissue
Structure: Thick collagen bundles in one plane, avascular. These tissues provide great tensile strength and are designed to withstand pulling forces in one direction. Sometimes called white fibers
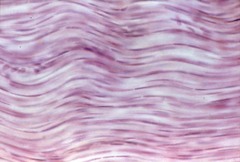
Dense Regular Connective Tissue
Function: attaches muscles to bones or to muscles; attaches bones to bones; withstands great tensile stress when pulling force is applied in one direction
Dense Regular Connective Tissue
Location: Tendons and ligaments
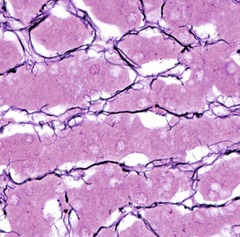
Adipose Tissue
Stain: Oil Red O
Hyaline Cartilage
Structure: Perichondrium, contains: chondroblasts, chondrocytes, and matrix
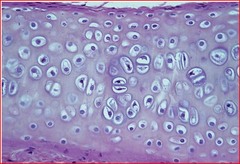
Chondrocytes
Cells that secrete cartilage.
Perichondrium
membrane that covers cartilage
Chondroblasts
cartilage forming cells
Hyaline Cartilage
Function: Semi-rigid support and smooth surface for sliding
Hyaline Cartilage
Location: Fetal skeleton, growth plates in long bones
Fibrocartilage
Structure: Cartilage that contains fibrous bundles of type I and II collagen
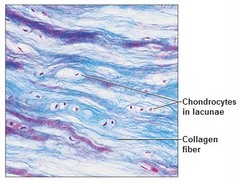
Fibrocartilage
Function: Support and rigidity. Strongest cartilage
Fibrocartilage
Location: Intervertebral discs and junctions in pelvis bone
Elastic Cartilage
Structure: Similar to hyaline but has elastic fibers. Type II collagen
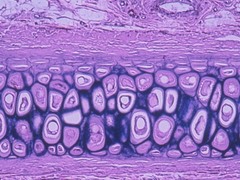
Elastic Cartilage
Function: Elasticity and support to surrounding structures. Flexible semi-rigid support
Elastic Cartilage
Location: External ear, larynx
Elastic Cartilage
Stain: Elastic staining technique
Compact Bone
Structure: Contain osteoblasts, osteocytes, osteoclasts, haversian canal, lamellae, canaliculi, and lacuna
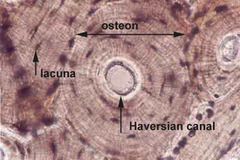
Osteoblasts
Create bone matrix (osteoid)
Osteocytes
Mature bone cells found in lacunae
Osteoclasts
Giant bone-destroying cells in bones
Cancellous Bone/Spongy Bone
Structure: Similar to compact bone with an outer covering, trabeculae, howship's lacunae, and bone marrow
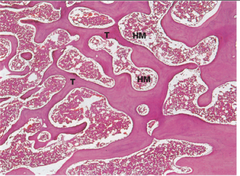
Blood
Stain: Romanowsky stain
Matrix
The material between the cells of connective tissue. It consists of protein fibers and ground substance.
Ground Substance
The material between the cells and protein fibers of connective tissues. It makes up part of the matrix.
Fibroblasts
produce fibers and ground substance
Macrophages
engulf bacteria and cellular debris
Mast cells
Widely distributed among connective tissue. Location: Near blood vessels, release heparin, compound that prevents blood clotting. Cells that release histamine, a chemical that promotes inflammation.
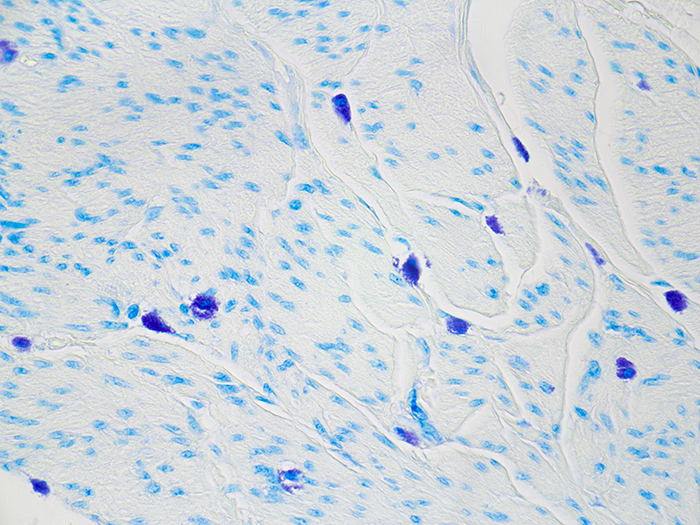
adipocytes
Energy storage cells.
Collagen fibers
Strong, flexible protein fibers that resist stretch.
Elastic fibers
Thinner, branching fibers that have the ability to stretch then return to original shape.
Reticular fibers
Fibers made of collagen that form the stroma/framework for organs like the spleen and lymph nodes.
Basement membrane
Connects epithelial tissue to underlying connective tissue.
Loose connective tissue
areolar, adipose, and reticular connective tissue
areolar connective tissue
A loose connective tissue containing collagen, elastic, reticular fibers; as well as fibroblasts, mast cells, and white blood cells. I t help for the subcutaneous layer, which holds the skin to underlying structures.
adipose tissue
A loose connective tissue composed primarily of fat cells.
reticular connective tissue
Connective tissue that contains reticular fibers and cells; used to make the framework of major organs
Dense connective tissue
dense regular, dense irregular, elastic connective tissue
Dense regular connective tissue
Composed of large quantities of collagen fibers running parallel to each other and fibroblasts; found in tendons and ligaments.
Dense irregular connective tissue
Composed of large quantities of collagen fibers running in multiple directions; found in the periosteum and pericardium.
Elastic connective tissue
Connective tissue made from elastic fibers that allows stretching; found in the lungs and artery walls.
chondrotin sulfate
Chemical found in the ground substance of cartilage that provides rubbery property.
Chondrocytes
cartilage cells
Perichondrium
Dense irregular connective tissue membrane covering cartilage
hyaline cartilage
Most common type of cartilage; it is found on the ends of long bones, ribs, and nose.