Topic 4 - Types of Macromolecules
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
What is the general chemical make-up of carbohydrates
Carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen
What are carbohydrates monomers and what types of polymers do they form?
monosaccharides, simple sugars like glucose, fructose, galactose
Why do different carbohydrates such as starch and cellulose have unique structures and functions?
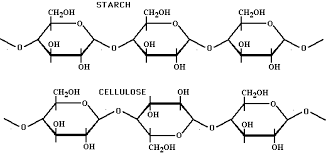
starch - energy storage
cellulose - plant cell wall structure - acts as dietary fiber
what is the general structure of lipids?
a glycerol backbone and one or more fatty acid tails
What is the difference between saturated vs. unsaturated fatty acids? How does this affect their functions?
Saturated fats have straight chains, pack tightly, unsaturated fats have kinks from double bonds, remain liquid. Alters shape, composition, or environment
What is the function of fats
energy storage, regulate hormones, cell structure
What is the function of steroids
signaling molecules and structural components
What is the function of cholesterol
building block for cell membranes, structure, support, controlling what goes in and out of the cell
What is the function of phospholipids
form a lipid bilayer, aid signaling molecules and cellular transport
What are the structural sub-components of nucleotides?
nitrogenous base (adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine/uracil), five-carbon sugar (deoxyribose in DNA, ribose in RNA), and phosphate group (mono-, tri-, di-, phosphate)
How are nucleotides linked together to form nucleic acids?
phosphate group of one nucleotide attaches to the sugar of the next at the 3' carbon, creating a sugar-phosphate backbone with bases sticking out, building the strand in a 5' to 3' direction
What determines the directionality of a nucleic acid chain (what are the 3’ and 5’ ends)?
numbering of carbons in the sugar. 5’ end has a free phosphate group, 3’ end has a free hydroxyl group
How does the directionality of a nucleic acid affect how it’s made and how it functions?
dictates that new nucleotides are only added to the free hydroxyl group on the 3' carbon, making synthesis unidirectional and ensuring accuracy by allowing easy proofreading
What chemical interactions occur to create a DNA double-helix?
strong covalent bonds linking nucleotides within each strand and weaker, specific hydrogen bonds between complementary base pairs (A-T, G-C)
What are the structural similarities and differences of DNA and RNA?
both nucleic acids made of nucleotides (sugar, phosphate, base) but differ in sugar (deoxyribose vs. ribose), bases (Thymine in DNA vs. Uracil in RNA), structure (double helix vs. single strand)
What parts of amino acid monomers are linked together to form a polypeptide chain?
peptide bonds formed between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group (-NH2)
What determines the directionality of a peptide chain?
the chemical structure of amino acids
How do the amino acids different from one another?
R-group (side chain), which determines their size, shape, charge (acidic, basic, neutral), and polarity (hydrophilic/polar or hydrophobic/nonpolar)
The 3 categories of chemical properties of the R groups
Nonpolar (Hydrophobic), Polar (Uncharged/Hydrophilic), and Charged (Acidic or Basic)
What are the four levels of protein structure and what are the characteristics of each?
Primary, Secondary, Tertiary, and Quaternary. amino acid sequence (Primary) to localized folding like alpha-helices and beta-sheets (Secondary), the overall 3D shape of a single polypeptide (Tertiary), and the arrangement of multiple subunits (Quaternary)
How do each of the levels of protein structure contribute to the overall structure and function of a protein?
A change in the primary sequence (e.g., one amino acid substitution) can disrupt all subsequent folding, leading to a misfolded protein that can't perform its job, highlighting the absolute link between structure and function.