Chapter 3: The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life
1/134
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Exam 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
135 Terms
Active Transport involves the movement of molecules against their concentration gradient, requiring ___ to provide energy.
ATP
What is the function of the cell wall?
Provides structural support and protection to the cell.
What is the role of chloroplasts?
Responsible for photosynthesis, converting light energy into chemical energy.
What is chromatin?
Complex of DNA and proteins that forms chromosomes within the nucleus.
What are chromosomes?
Thread-like structures made of DNA that carry genetic information.
What are cilia?
Hair-like structures that help in movement and sensing the environment.
What is cytoplasm?
Jelly-like substance within the cell membrane that contains organelles.
What is cytosol?
Liquid component of the cytoplasm, excluding organelles.
What is diffusion?
Process by which molecules spread from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration.
What is endocytosis?
Process by which cells take in substances by engulfing them in a membrane.
What is the role of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER)?
Involved in protein and lipid synthesis; comes in two forms: rough and smooth.
What is exocytosis?
Process by which cells expel substances using vesicles.
What is extracellular fluid?
Any body fluid that is not contained within cells.
What is facilitated diffusion?
Process of passive transport of molecules across a cell membrane via a protein channel.
What is the function of a flagellum?
Long, whip-like structure that aids in the movement of cells.
What is the fluid mosaic model?
Describes the structure of the plasma membrane as a mosaic of various components that move fluidly.
What is the Golgi apparatus?
Organelle responsible for modifying, sorting, and packaging proteins and lipids.
What is the function of lysosomes?
Contain enzymes that break down waste materials and cellular debris.
What is the role of mitochondria?
The powerhouse of the cell, generating ATP through cellular respiration.
What is the nuclear envelope?
Double membrane that surrounds and protects the nucleus.
What are nuclear pores?
Openings in the nuclear envelope that allow the transport of materials in and out of the nucleus.
What is osmosis?
Diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane.
What is the plasma membrane?
Biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of the cell from the outside environment.
What are prokaryotes?
Single-celled organisms that lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles.
What are ribosomes?
Molecular machines that synthesize proteins by translating messenger RNA.
What is rough ER?
Part of the endoplasmic reticulum studded with ribosomes, involved in protein synthesis.
What is smooth ER?
Part of the endoplasmic reticulum that is not associated with ribosomes, involved in lipid synthesis and detoxification.
What are vacuoles?
Storage sacs within cells that can hold various substances, such as nutrients and waste products.
What are vesicles?
Small membrane-bound sacs that transport materials within the cell.
What are the two types of cells found on Earth?
Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
A scientist notices a cell wall, ribosomes, and a nucleoid region in a water sample from Lake Huron. Which type of cell is it likely to be?
A) Prokaryote
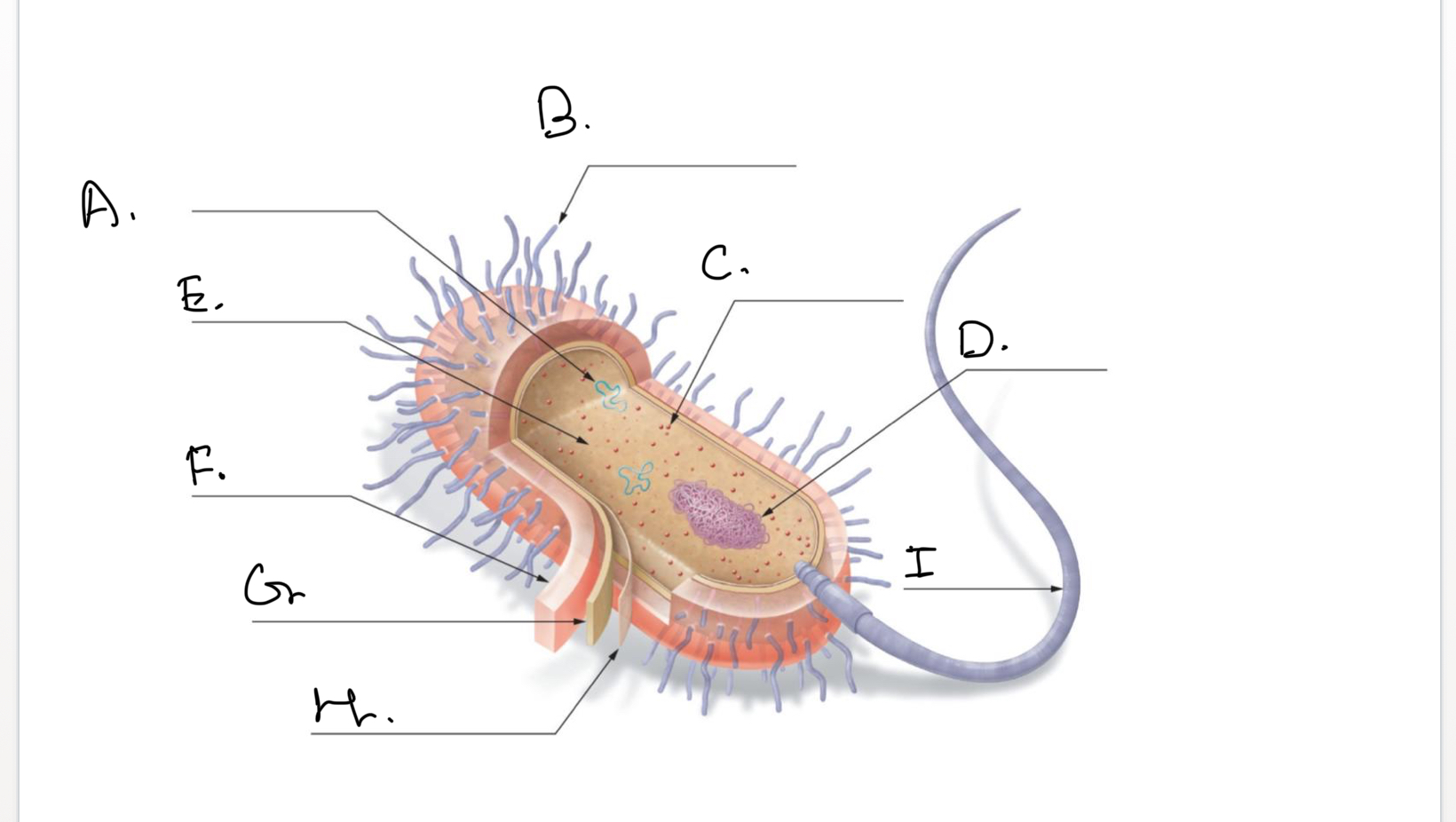
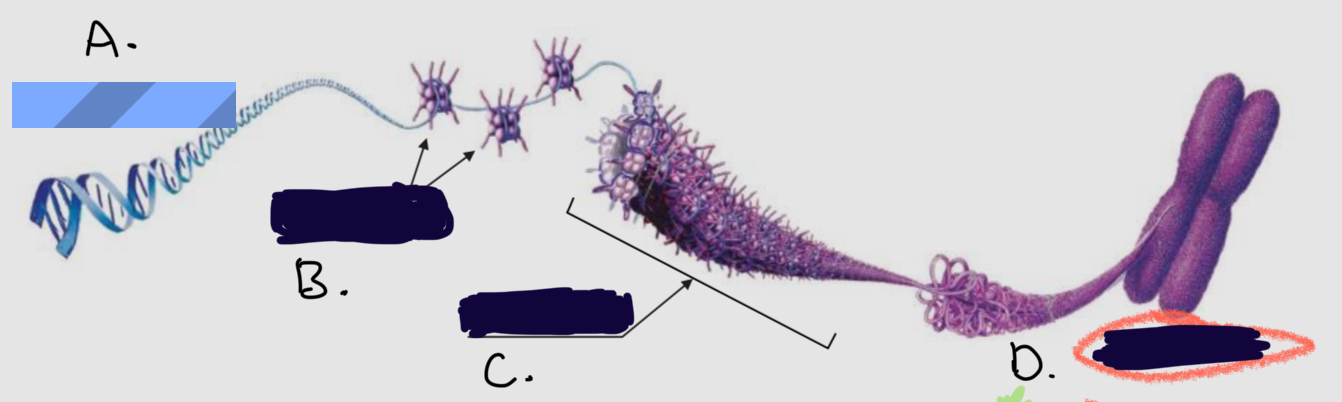
Complete the following diagram of a prokaryotic cell.:
A.
Plasmids
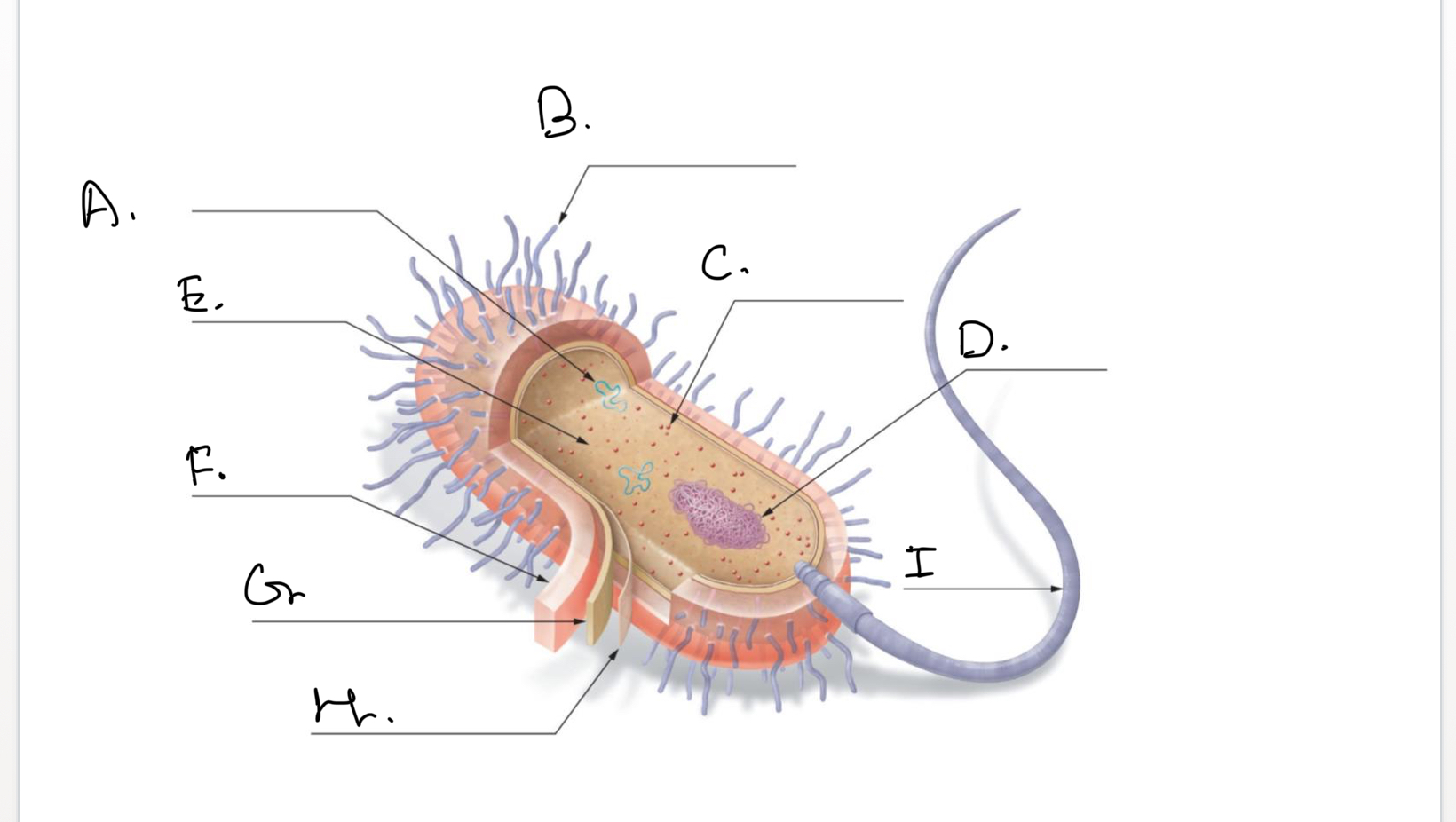
Complete the following diagram of a prokaryotic cell.:
B.
Short Projections (Pili)
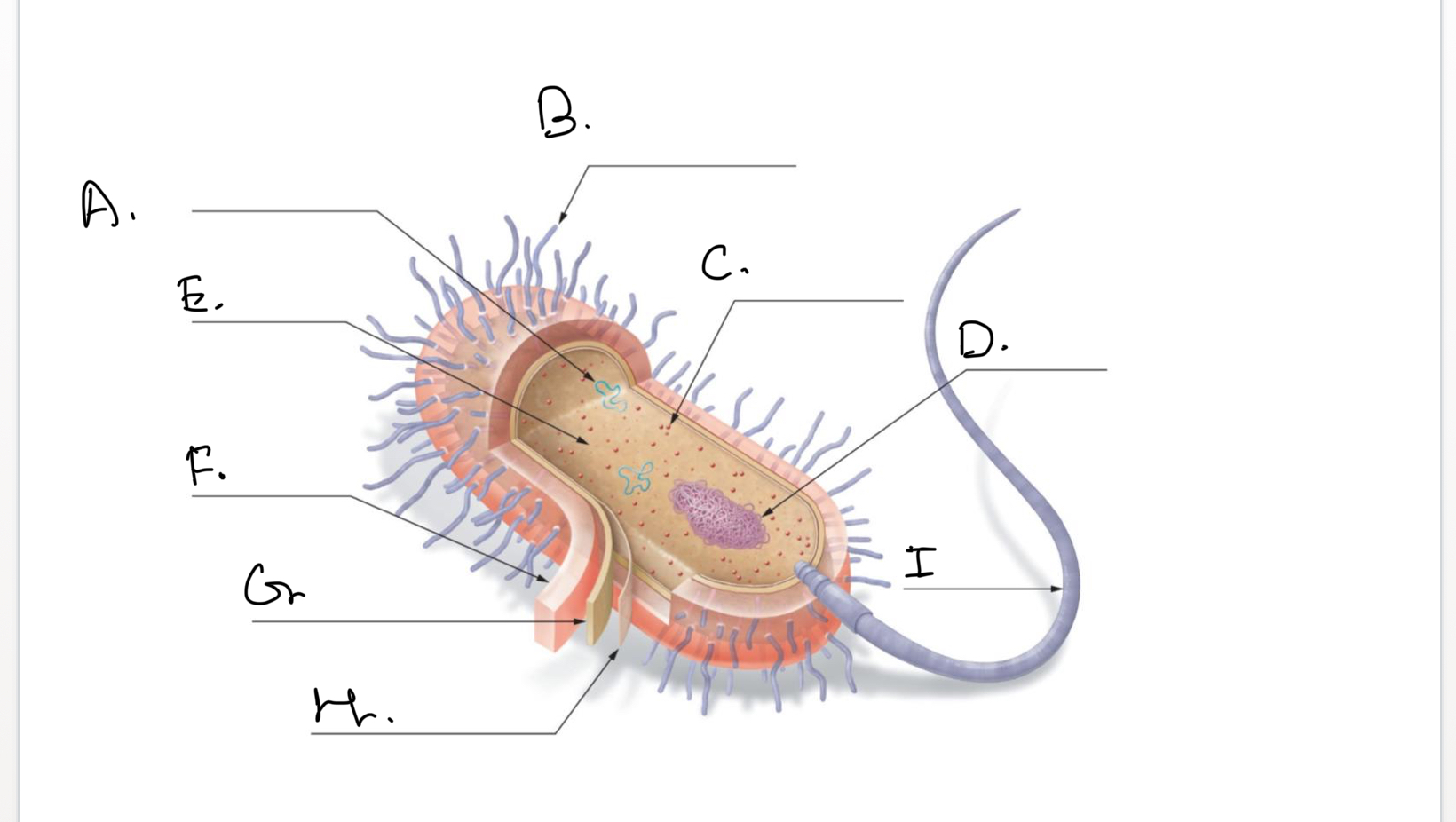
Complete the following diagram of a prokaryotic cell.:
C.
Ribosomes
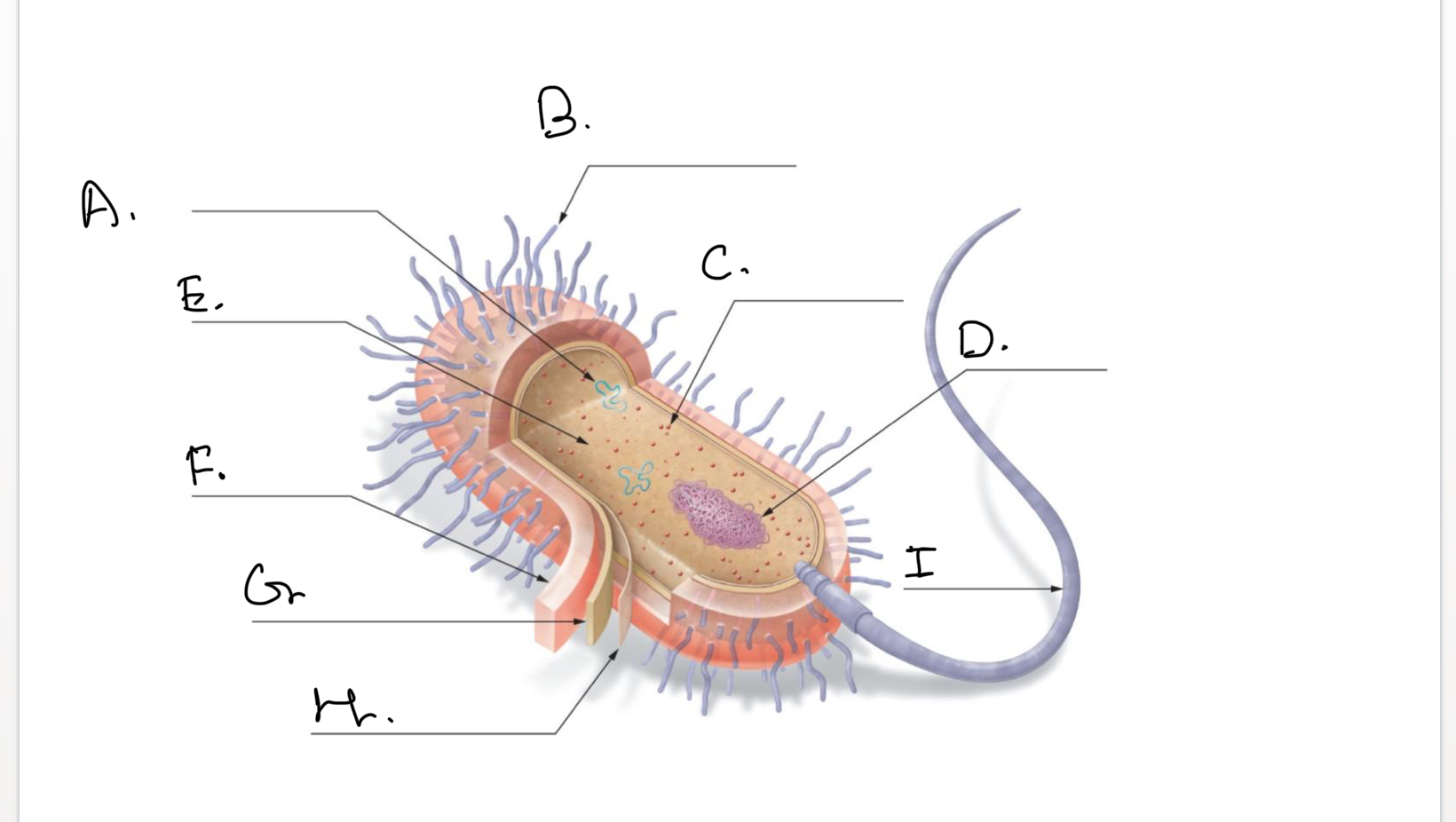
Complete the following diagram of a prokaryotic cell.:
D.
Nucleoid Coiled DNA
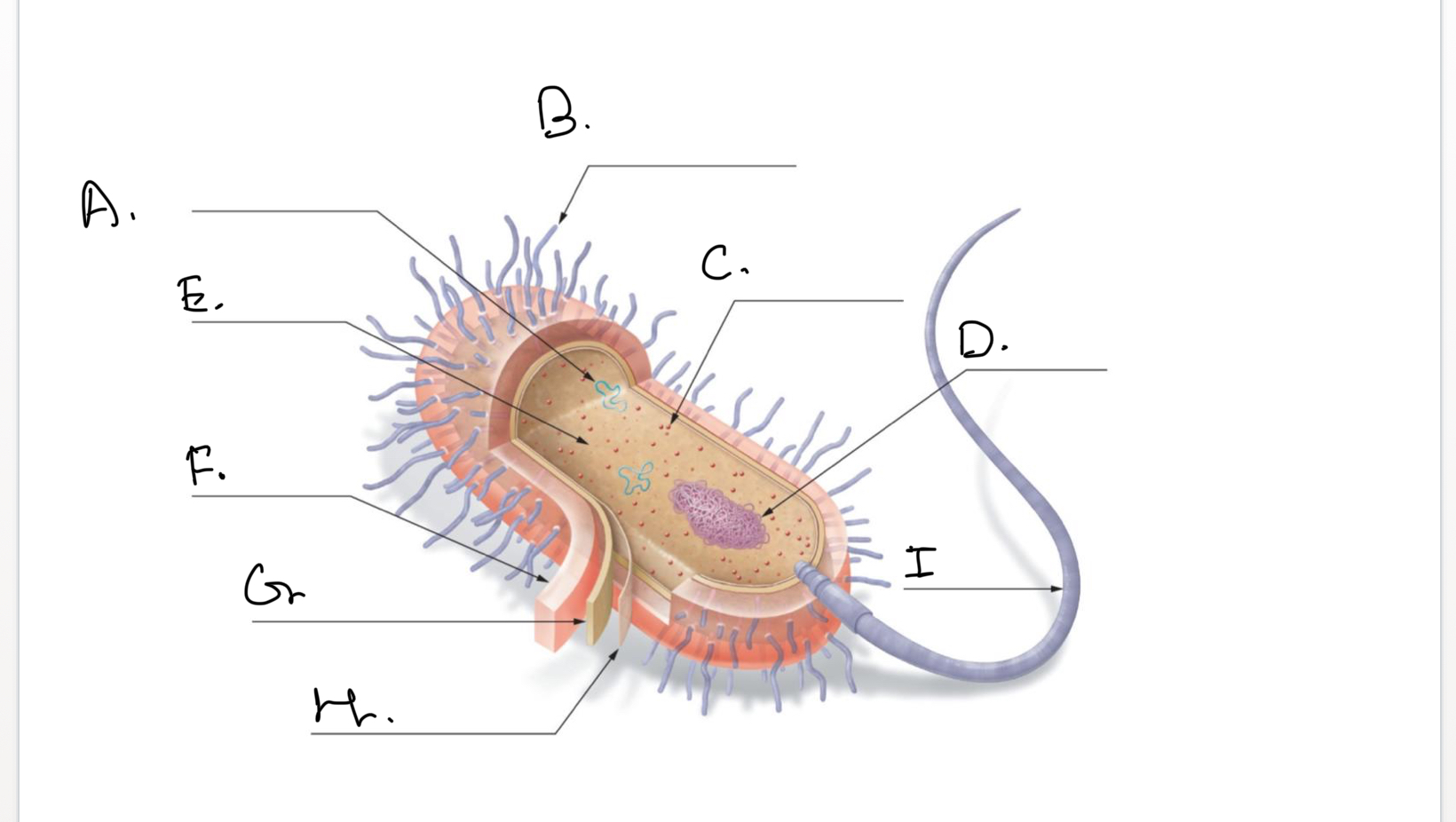
Complete the following diagram of a prokaryotic cell.:
E.
Cytoplasm
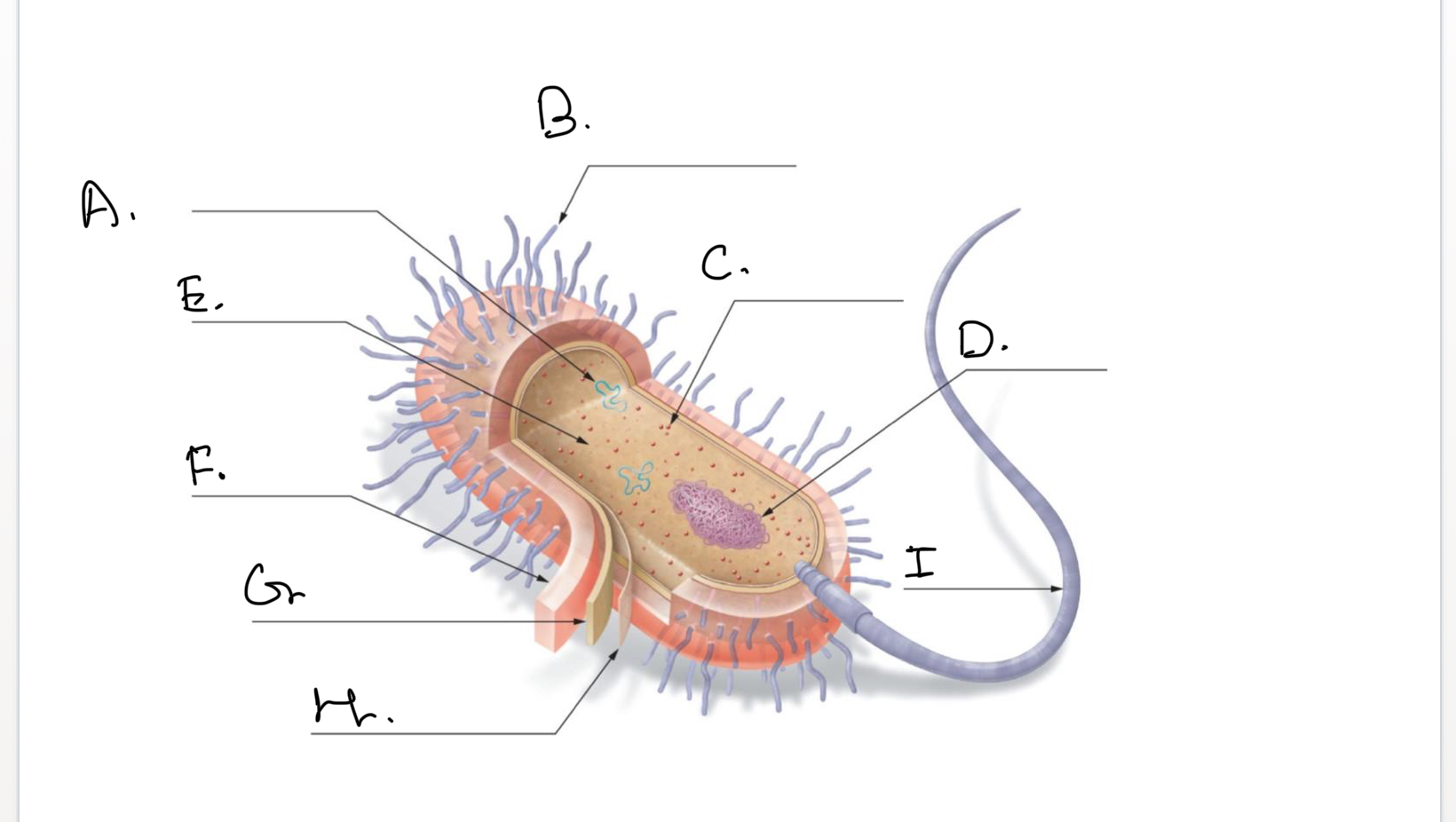
Complete the following diagram of a prokaryotic cell.:
F.
Capsule
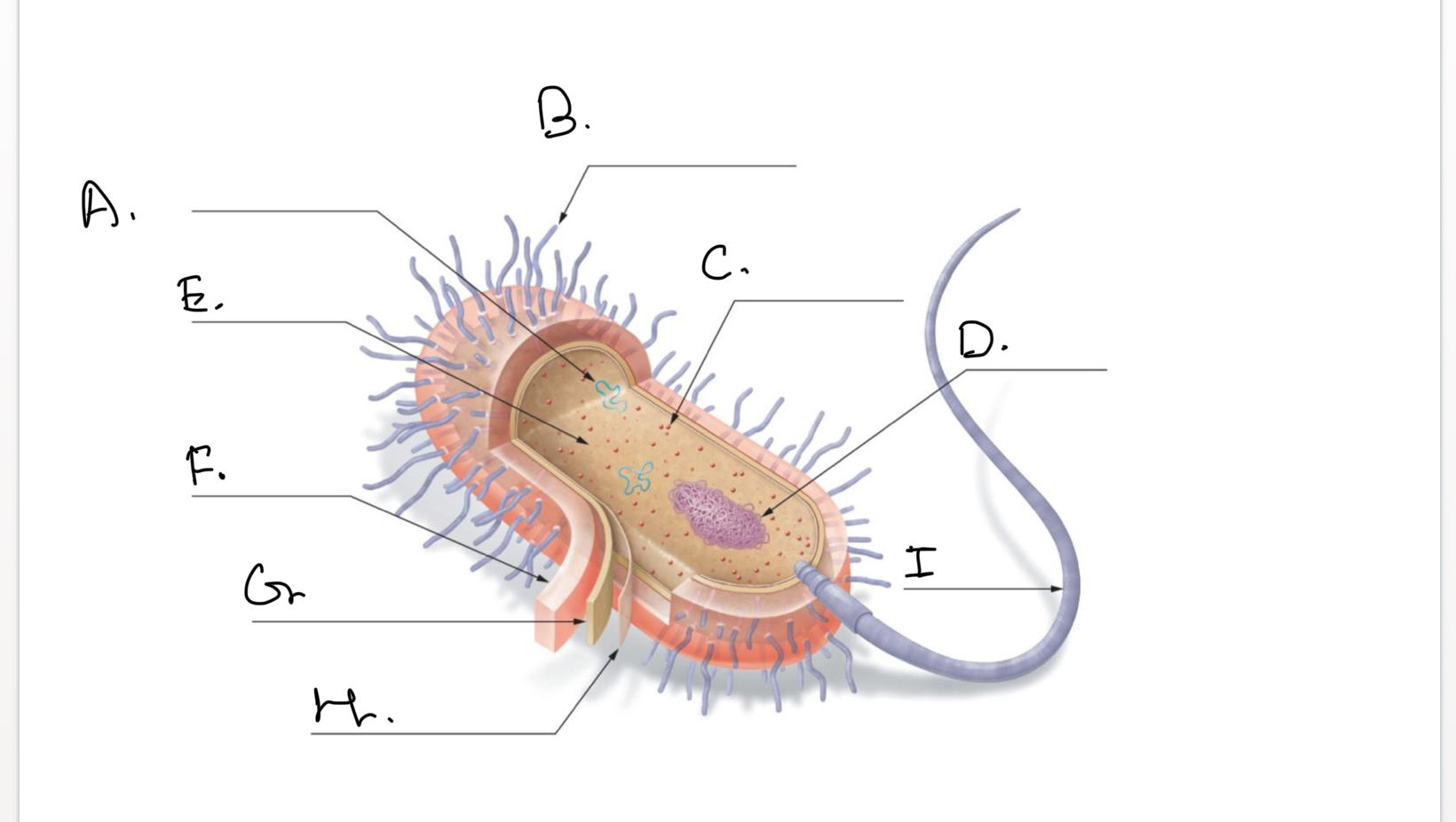
Complete the following diagram of a prokaryotic cell.:
G.
Cell Wall
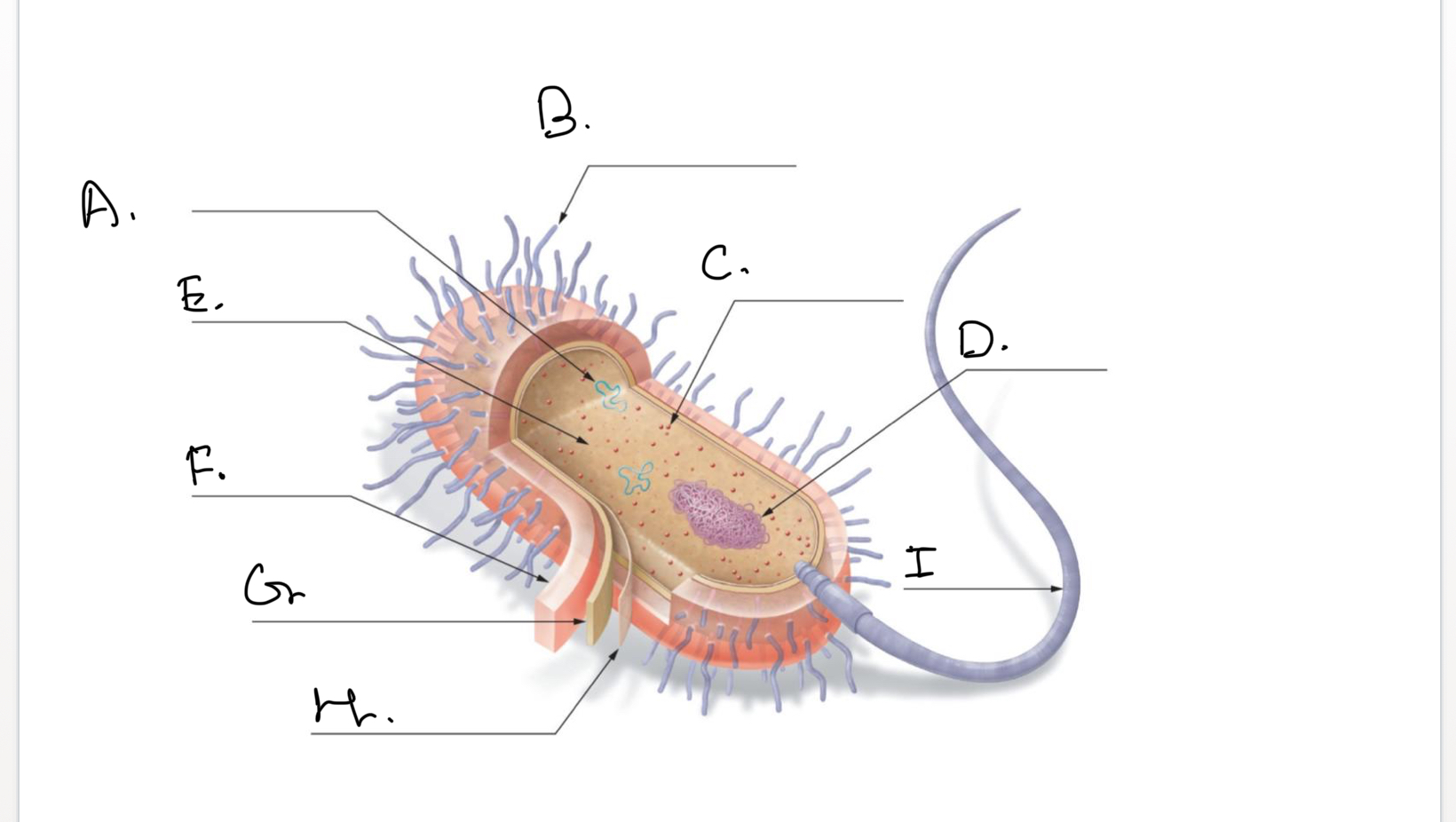
Complete the following diagram of a prokaryotic cell.:
H.
Plasma Membrane
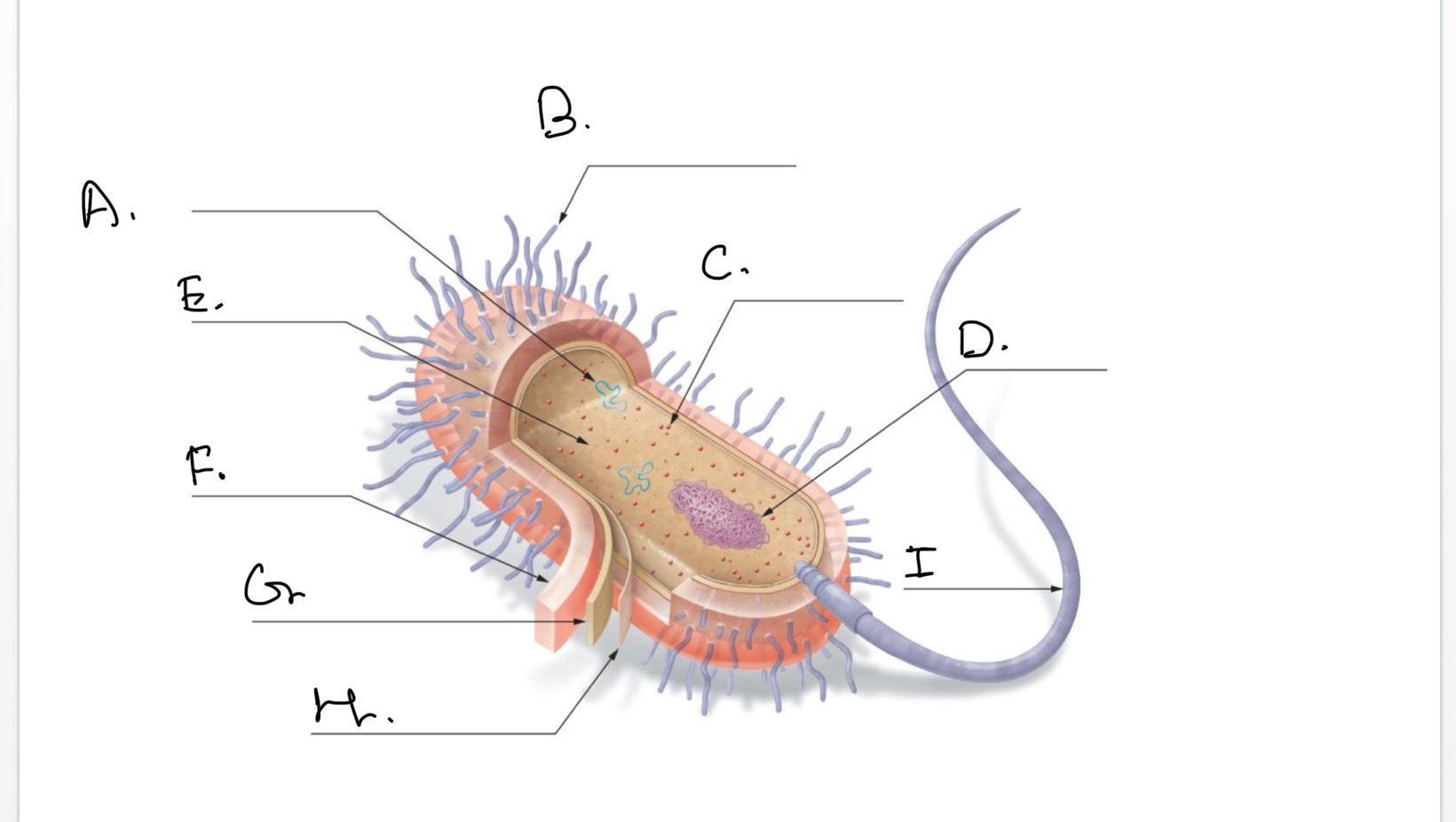
Complete the following diagram of a prokaryotic cell.:
I.
Flagellum
Prokaryote vs. Eukaryote
• Eukaryotes are larger_ than a prokaryotic cell (about 10X)
• In addition to prokaryotic components, eukaryotes have additional Structures:
-Nucleus - contains the DNA
-Organelles- tiny structures with special
functions
• Mitochondria, Lysosome, etc..
The ___________________ is an organelle that houses most of a eukaryotic cell’s DNA.
Nucleus
______________ are membrane-bound structures that perform specific cellular functions.
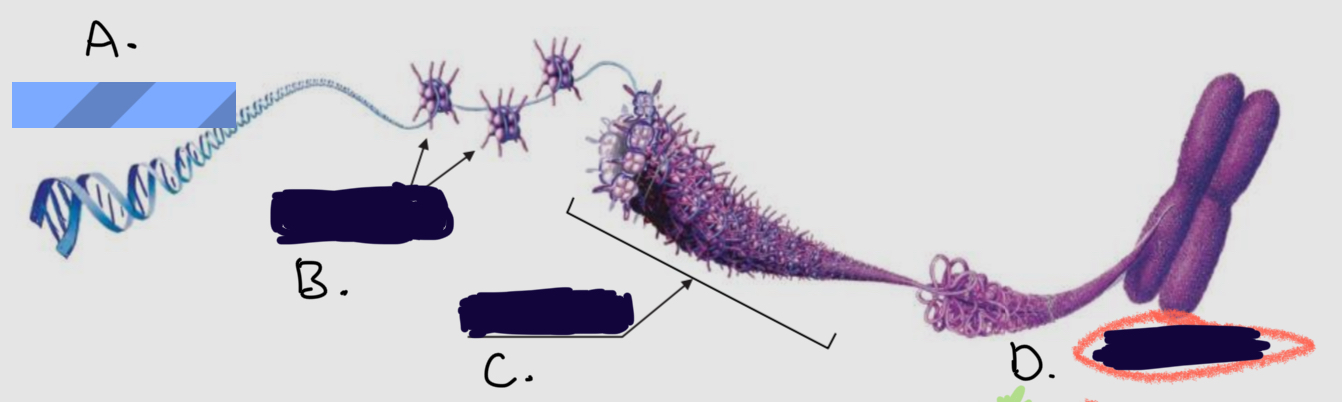
What is
A.
Dna molecule
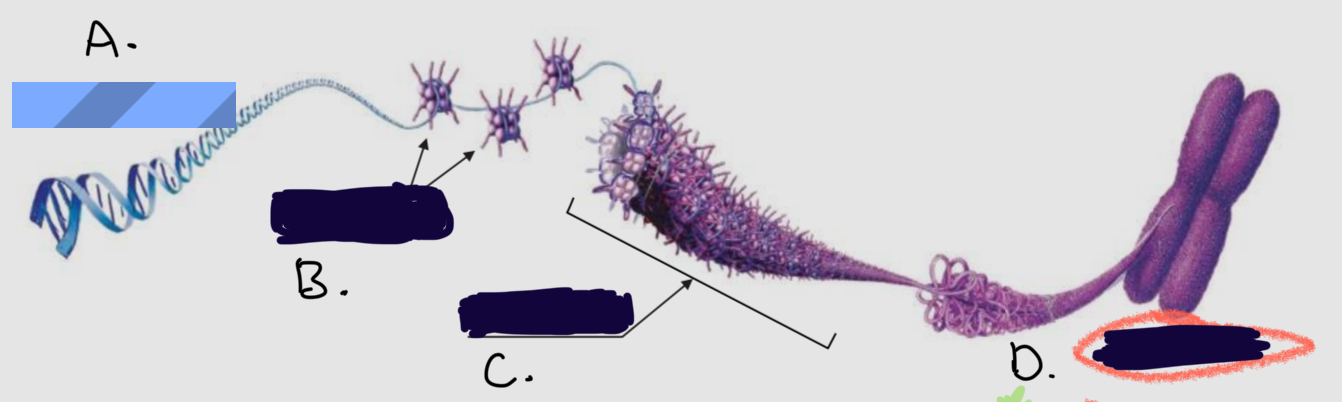
What is
B.
Proteins
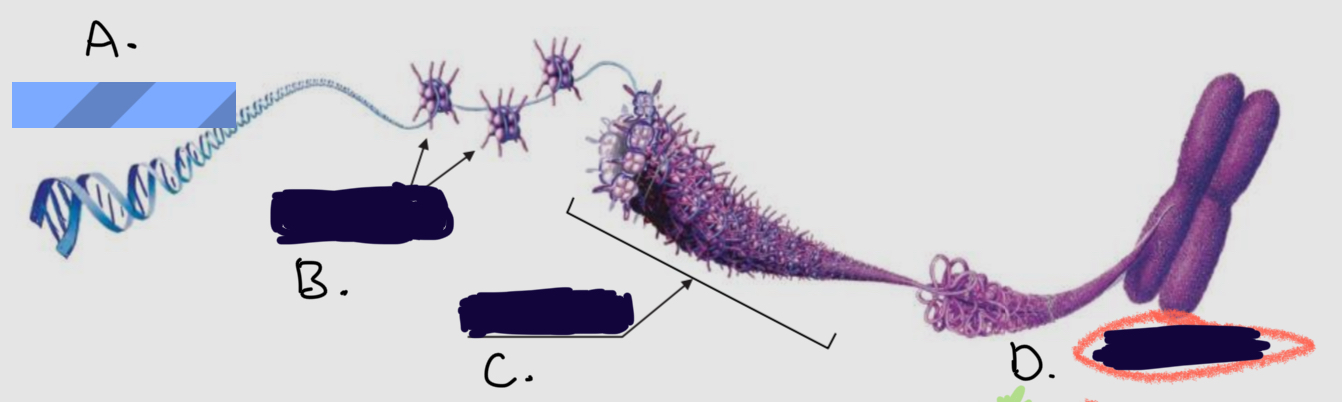
What is
C.
Chromatin fiber
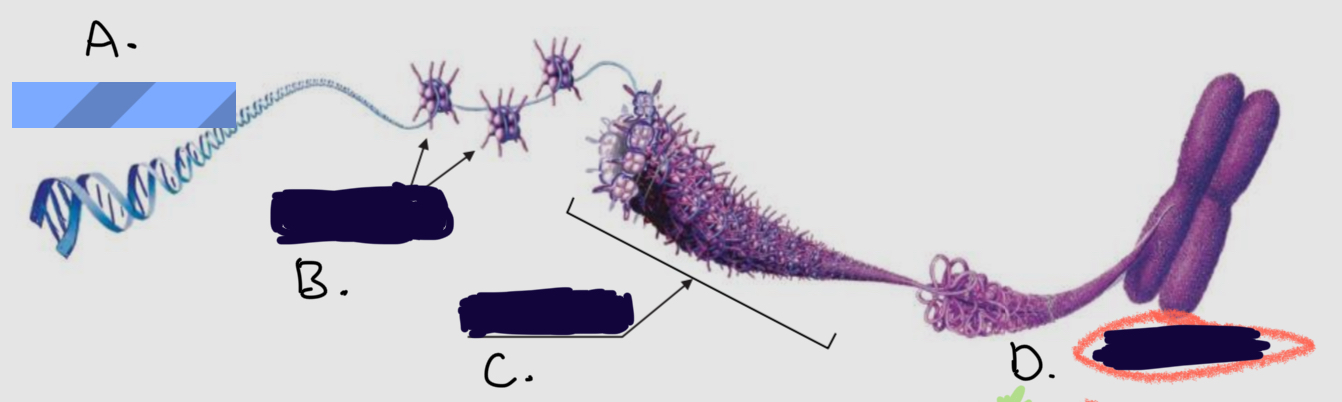
What is
D.
Chromosome
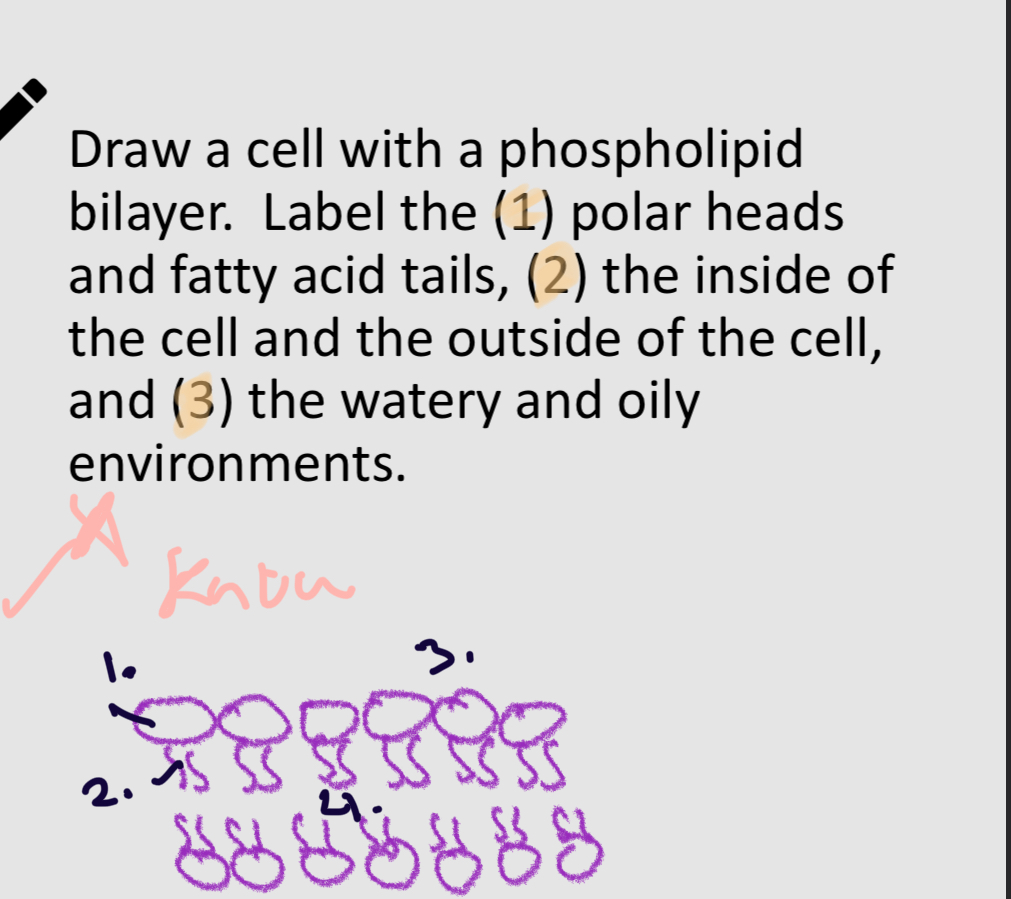
Phospholid bilayer.
1:
polar head
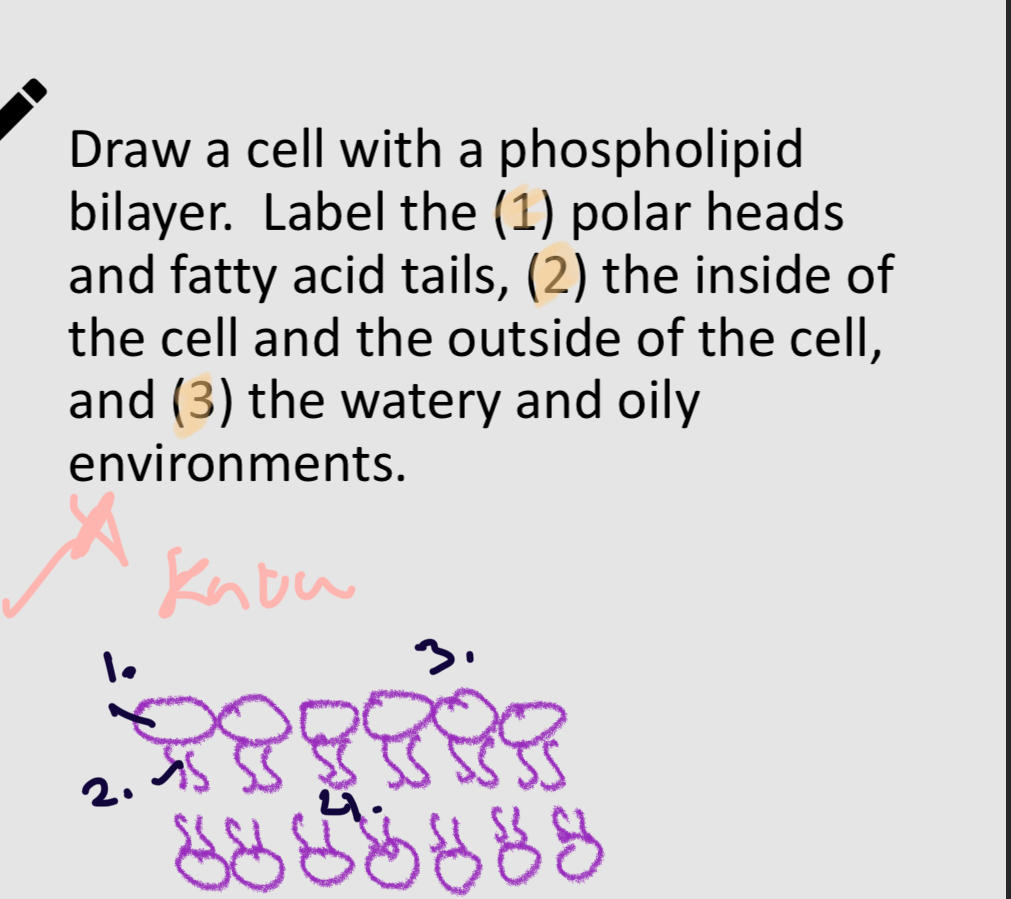
Phospholid bilayer.
2:
non-polar head
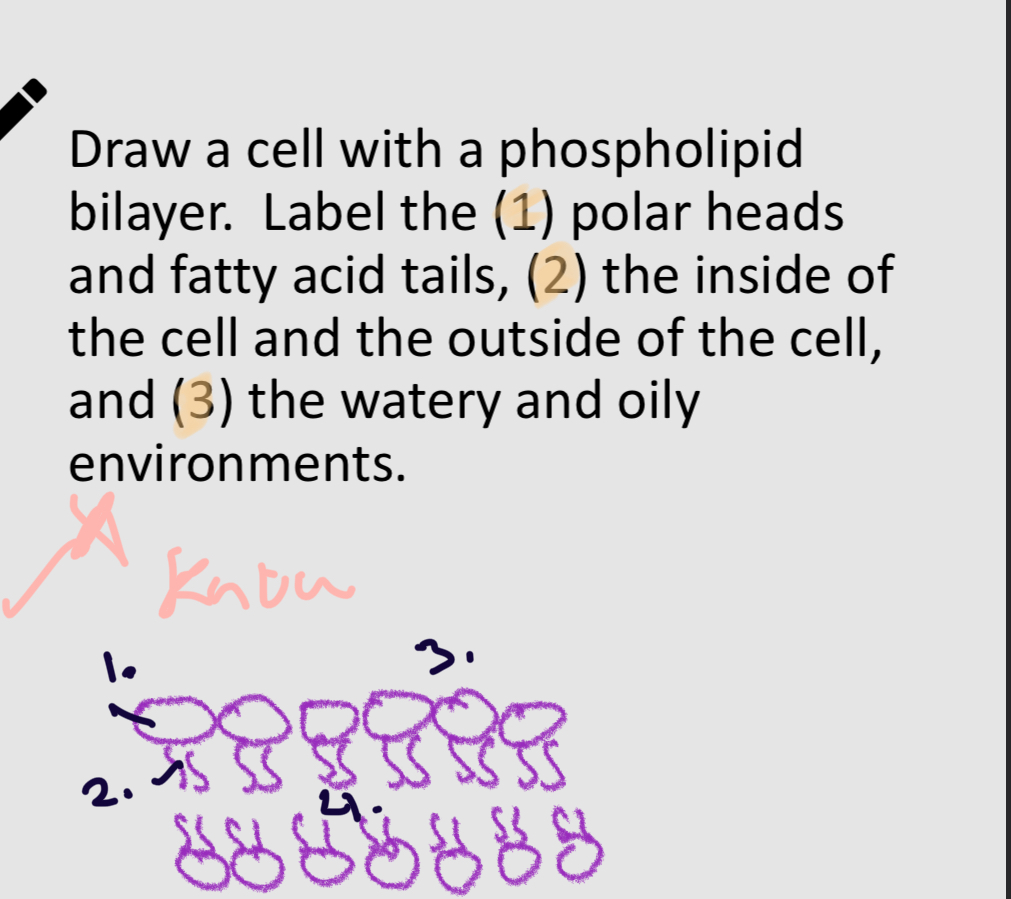
Phospholid bilayer.
3:
H2O
Phospholid bilayer.
4:
Oliy
What is 1. in the receptor protein?
Membrane proteins
What is 2. in the receptor protein?
Substance being transported
3. Which of the following cellular features would be shared by all eukaryotic cells?
A) A plasma membrane
B) A nucleus
C) Cytoplasm
D) All of the above would be found in eukaryotic cells
D) All of the above would be found in eukaryotic cells
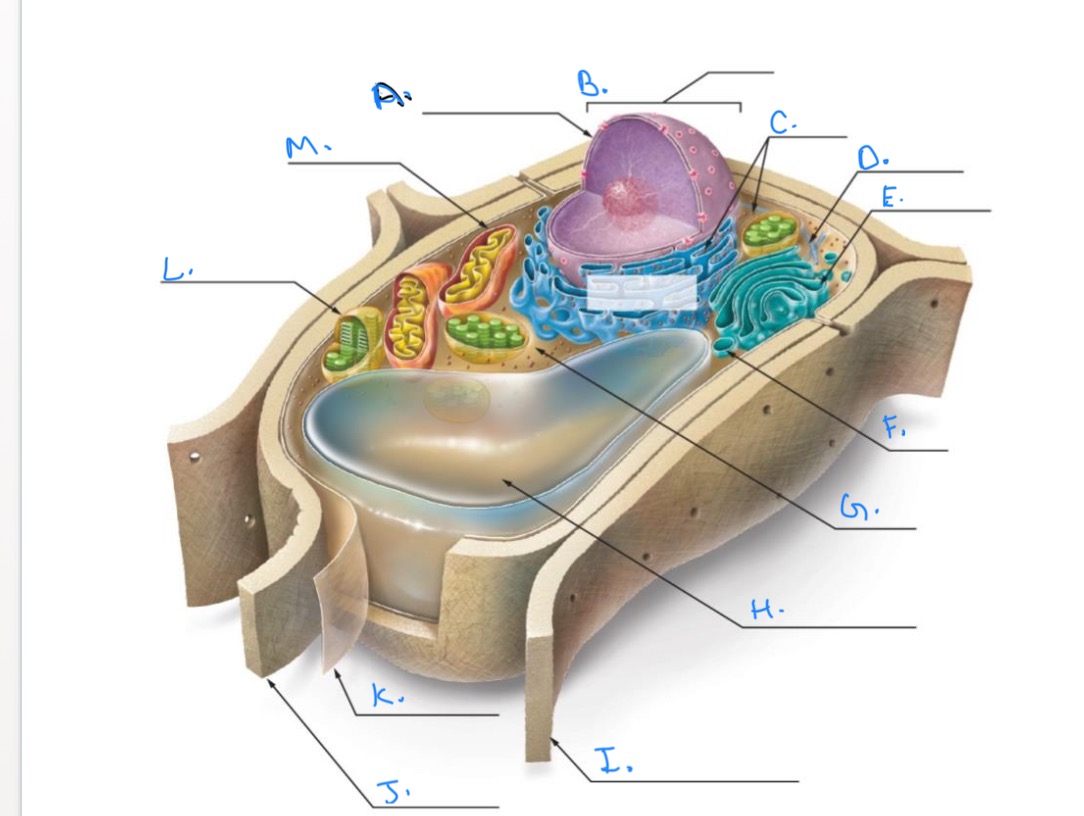
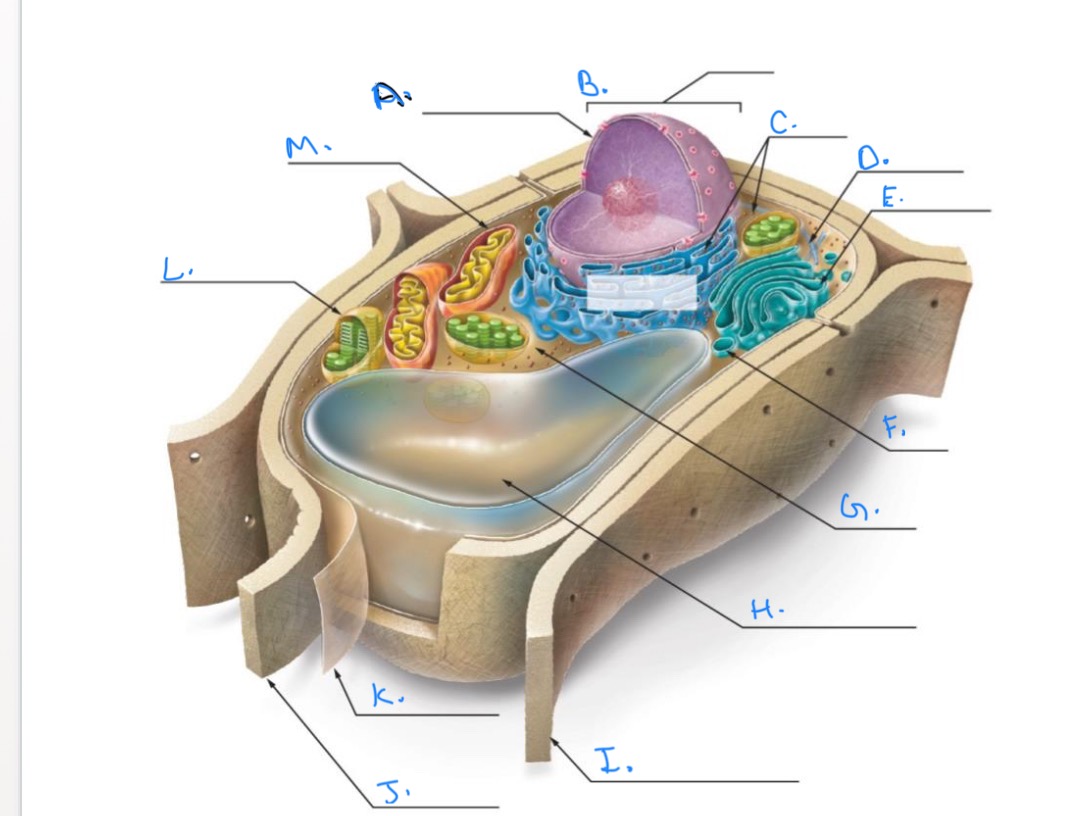
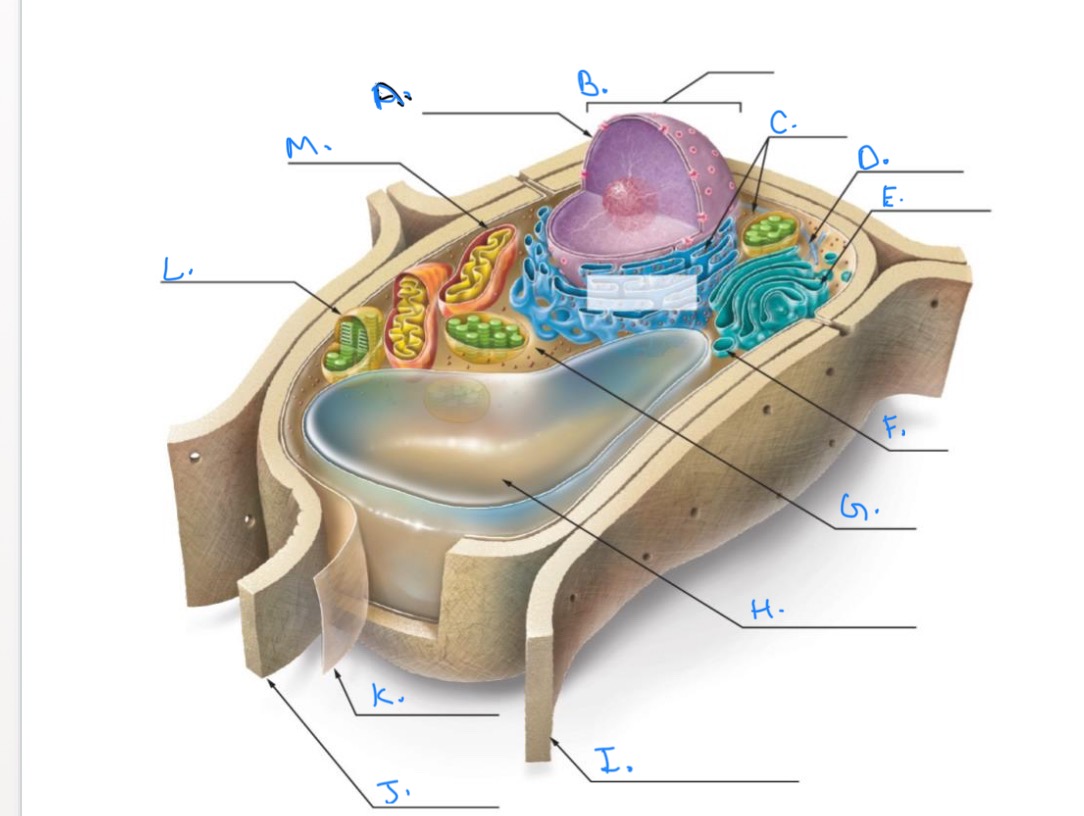
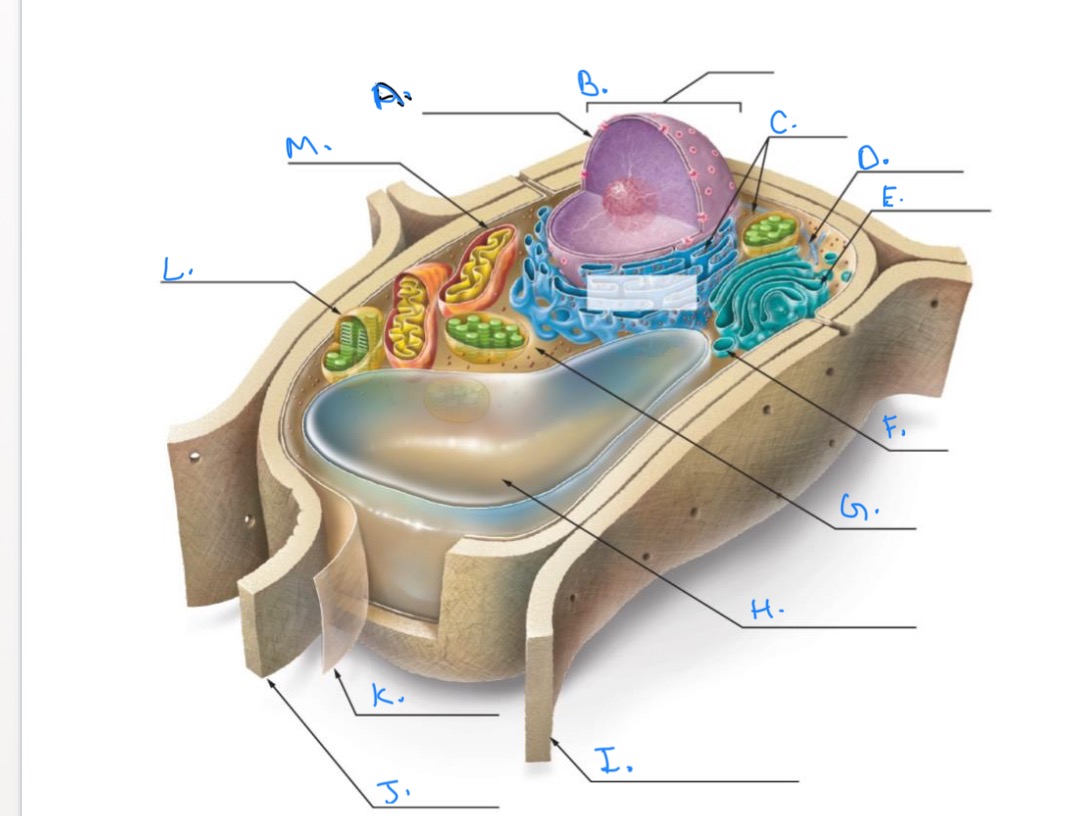
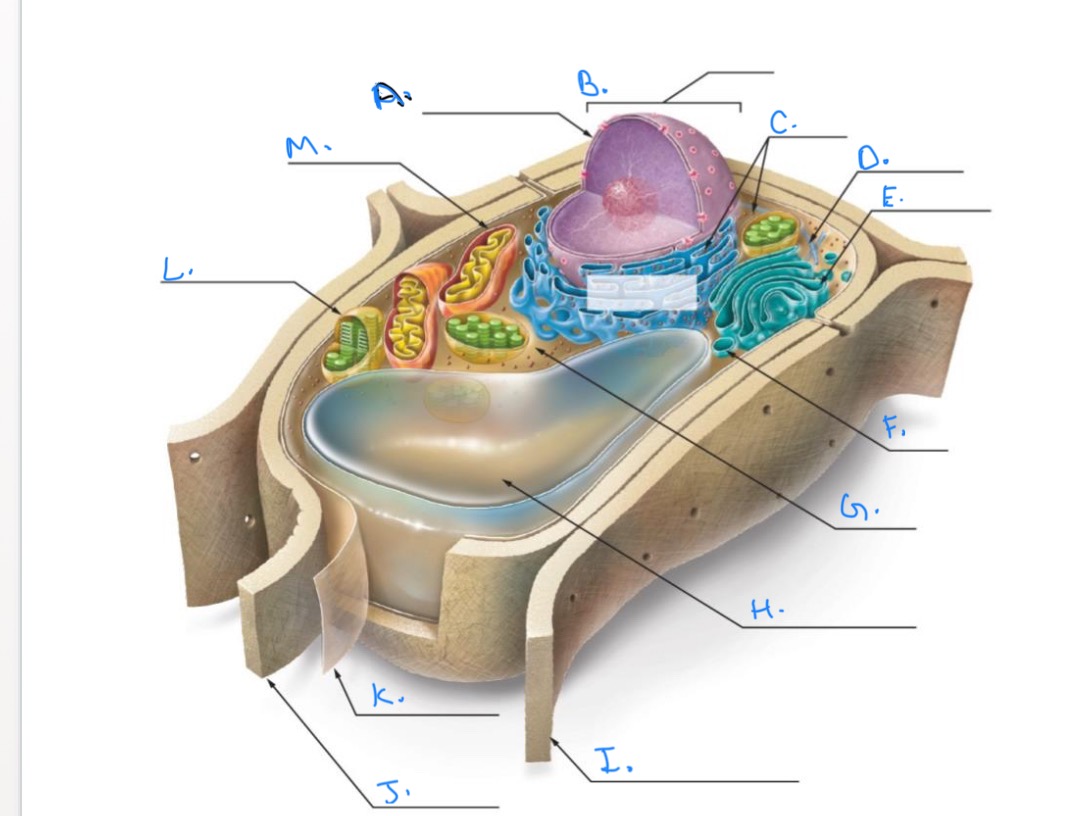
Label the Plant Cell.
A.
Nuclear Envelope
Label the Plant Cell.
B.
Nucleus
Label the Plant Cell.
C.
Ribosomes
Label the Plant Cell.
D.
Label the Plant Cell.
E.
Golgi Apparatus
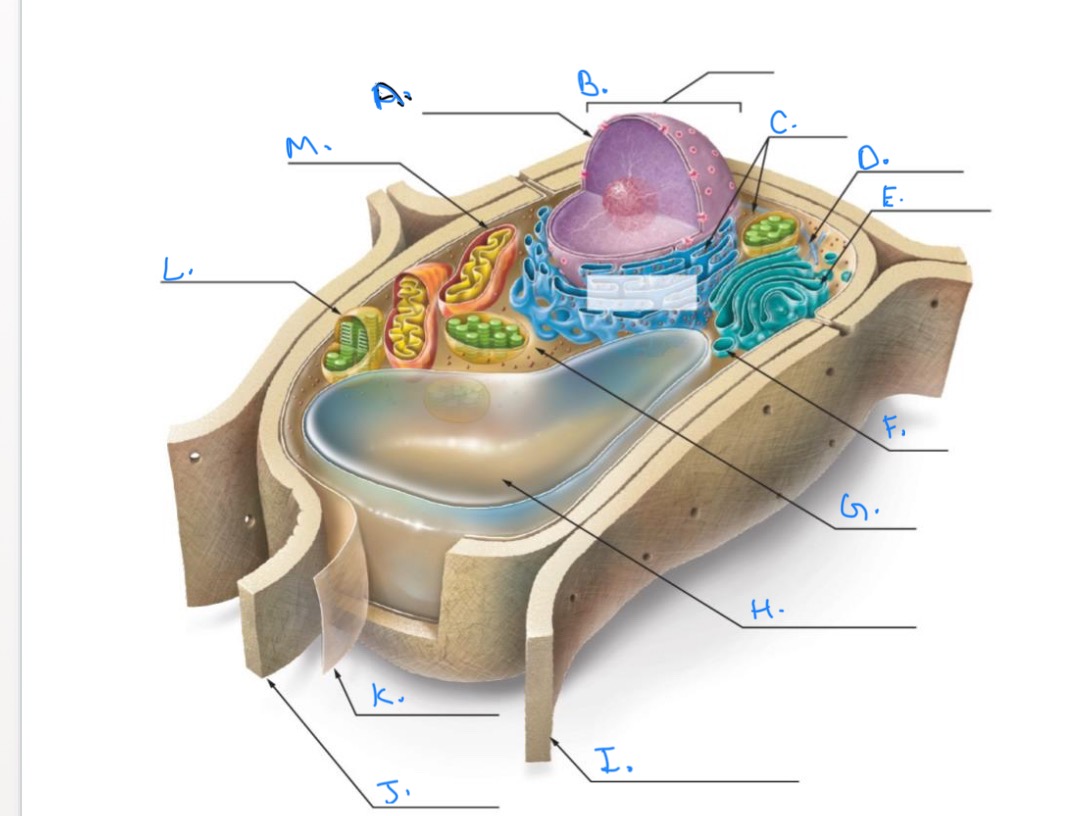
Label the Plant Cell.
F.
Vesicle
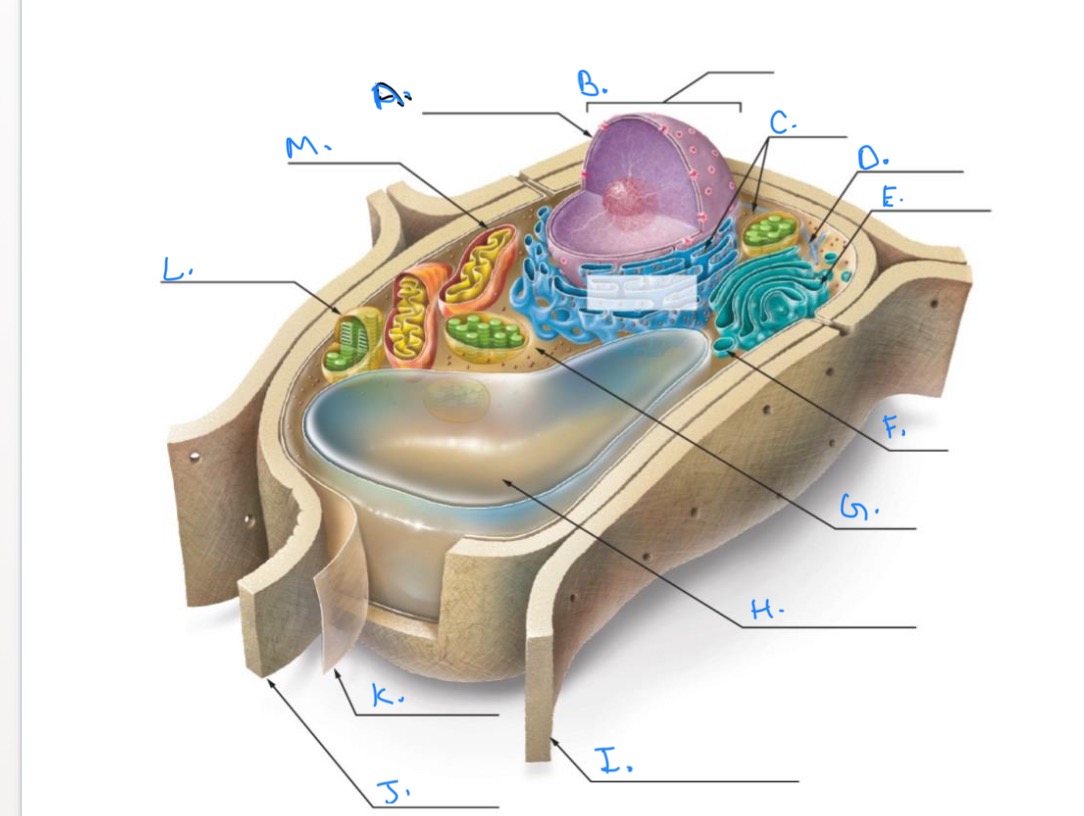
Label the Plant Cell.
G.
Cytpplasm
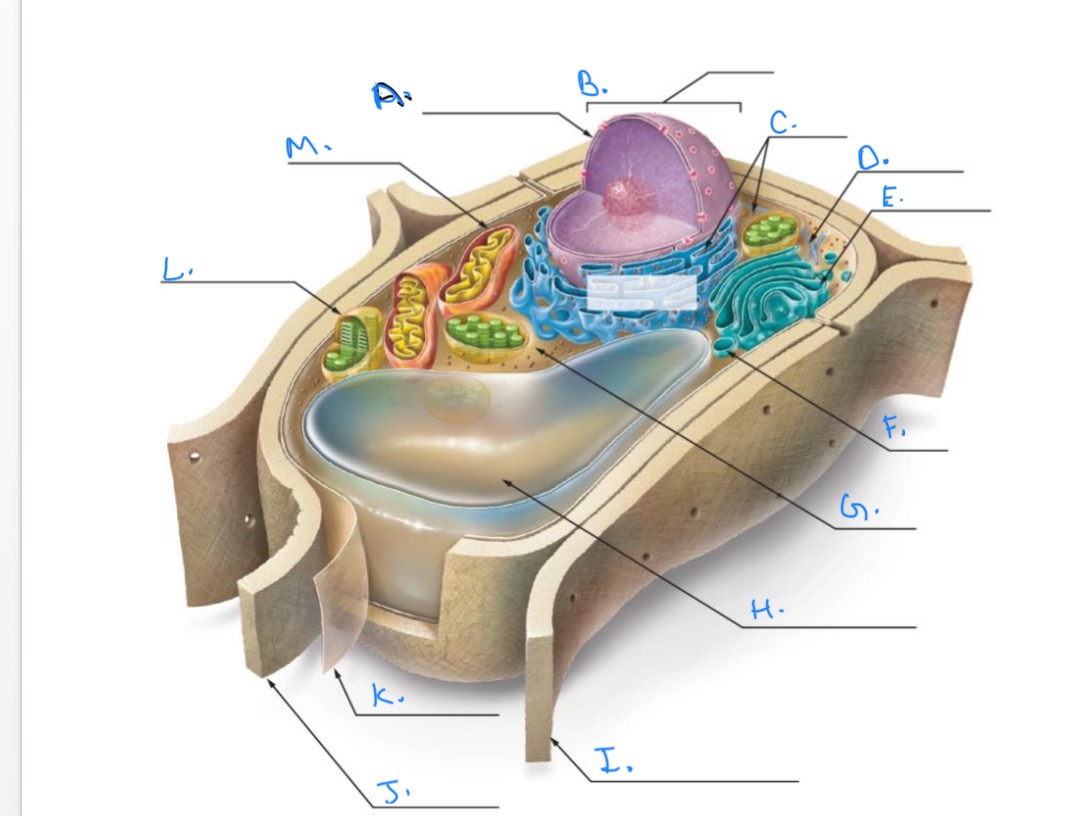
Label the Plant Cell.
H.
Central Vacuole
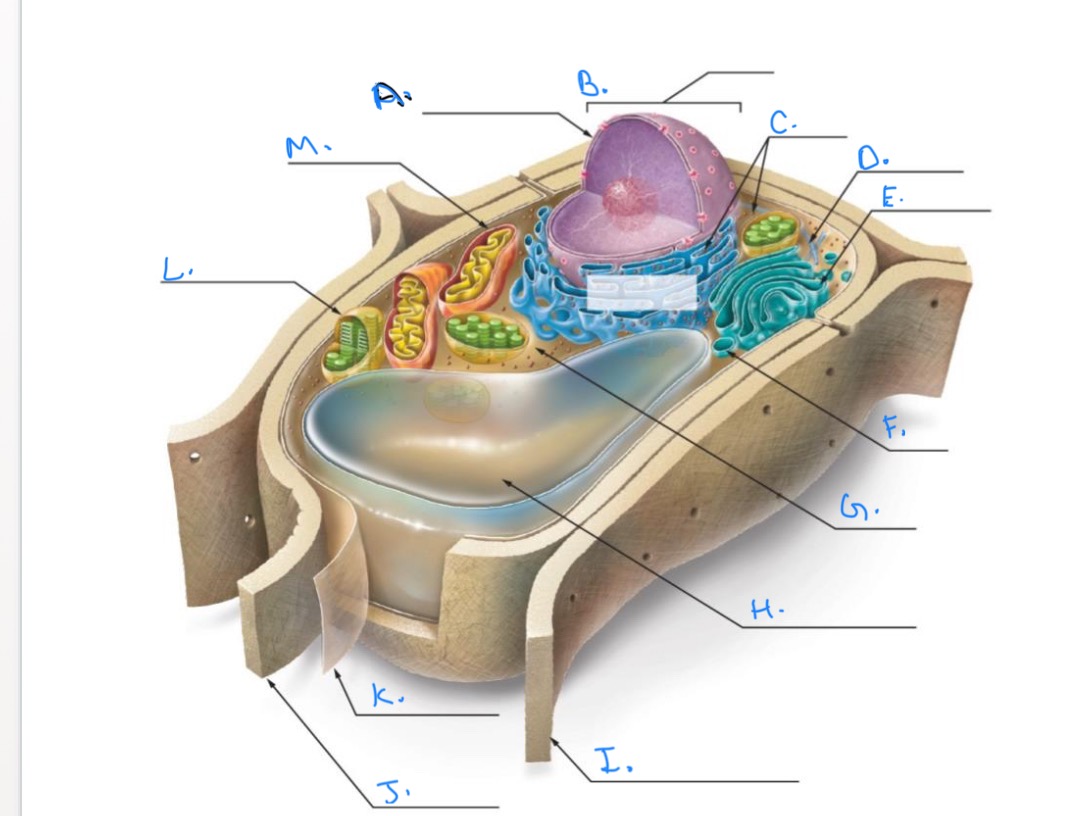
Label the Plant Cell.
I.
Cell Wall of Adjoining Cell
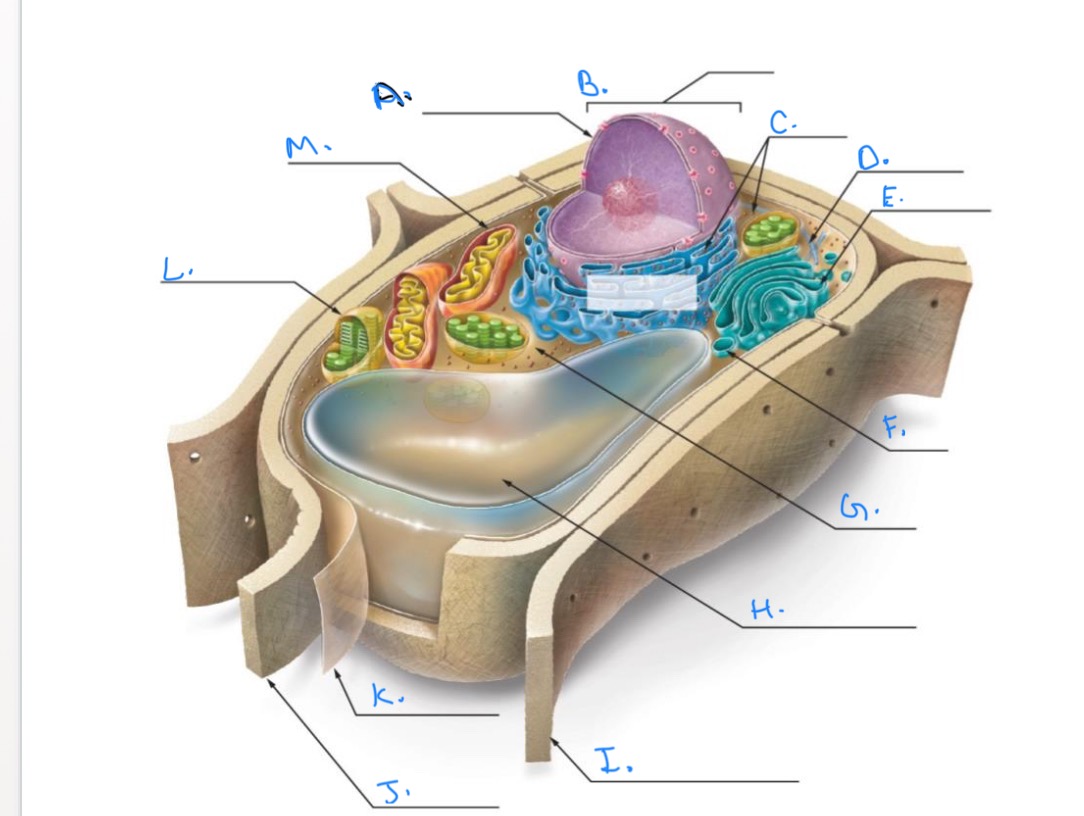
Label the Plant Cell.
J.
Cell Wall
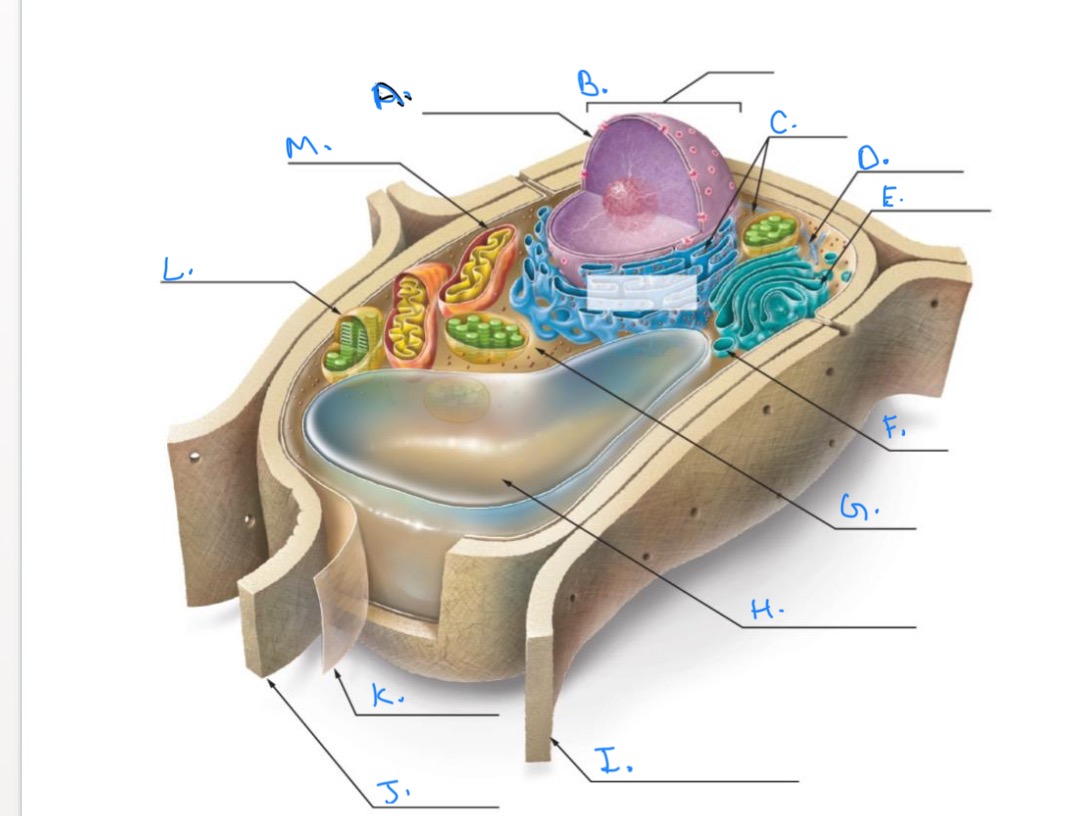
Label the Plant Cell.
K.
Plasma Membrane
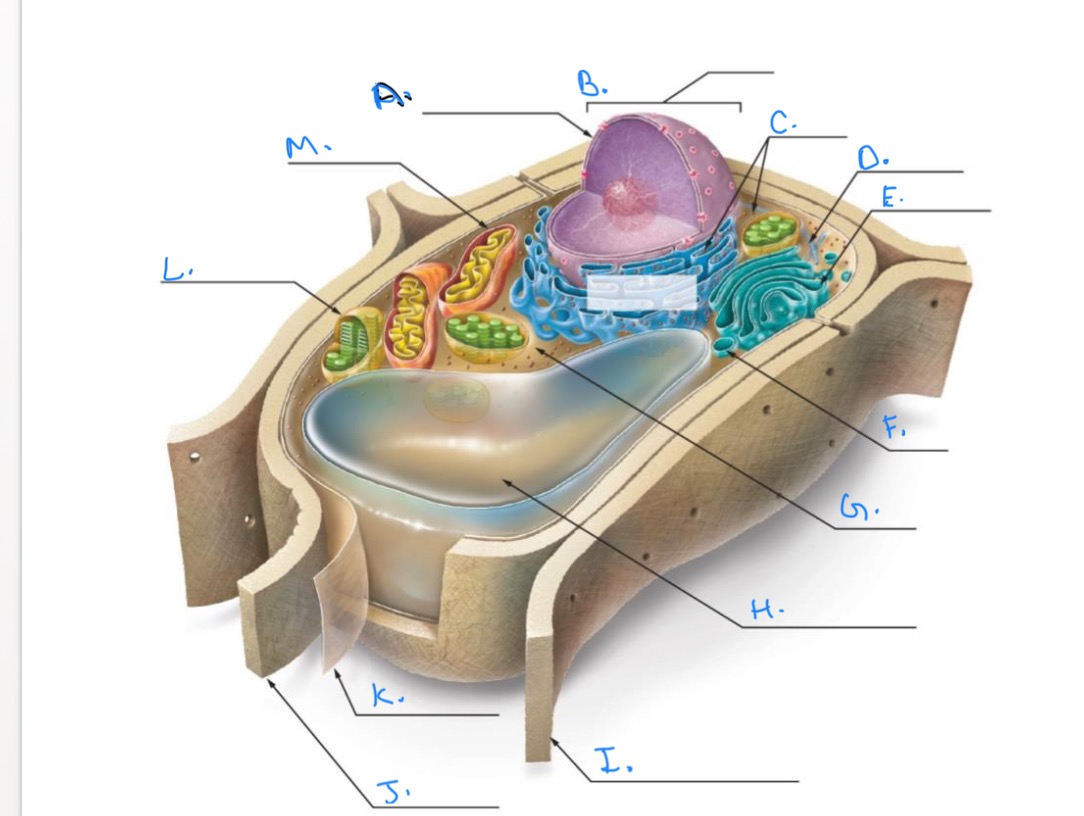
Label the Plant Cell.
L.
Chlorplast
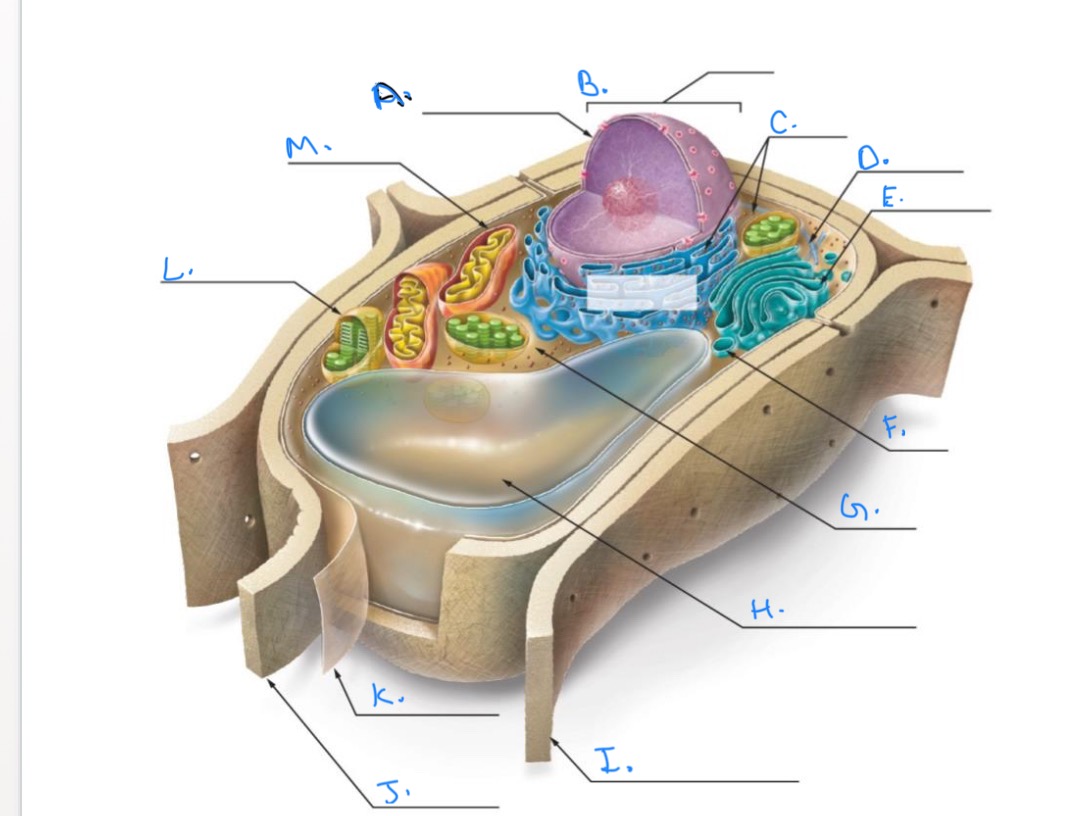
Label the Plant Cell.
M.
Mitochondrion
_________________ are organelles that are found only in animal cells.
Centrosomes and lysosomes
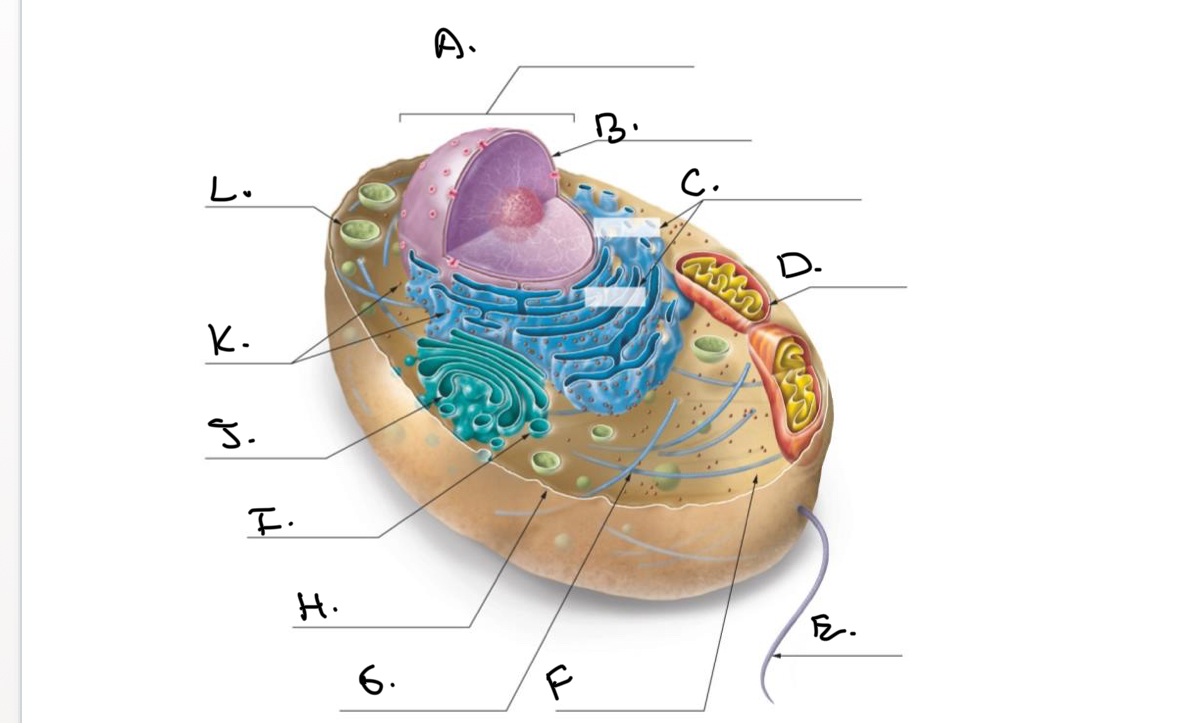
Label the Animal Cell.
A.
Nucleus
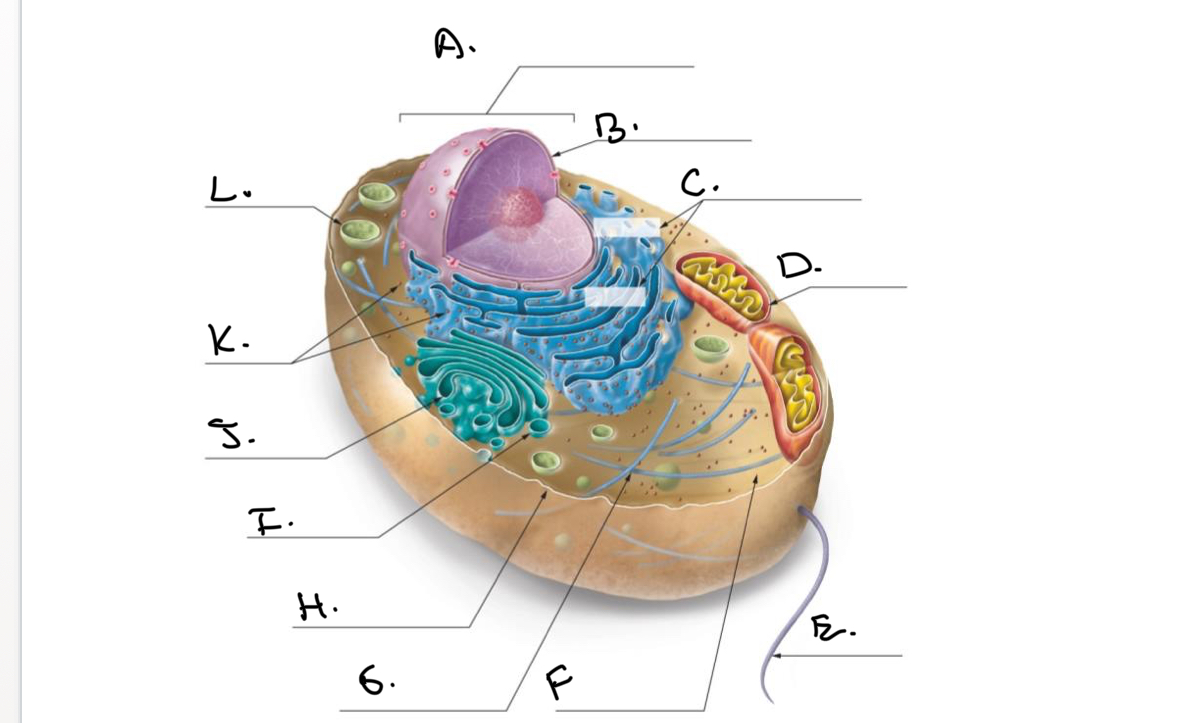
Label the Animal Cell.
B.
Nucleolus
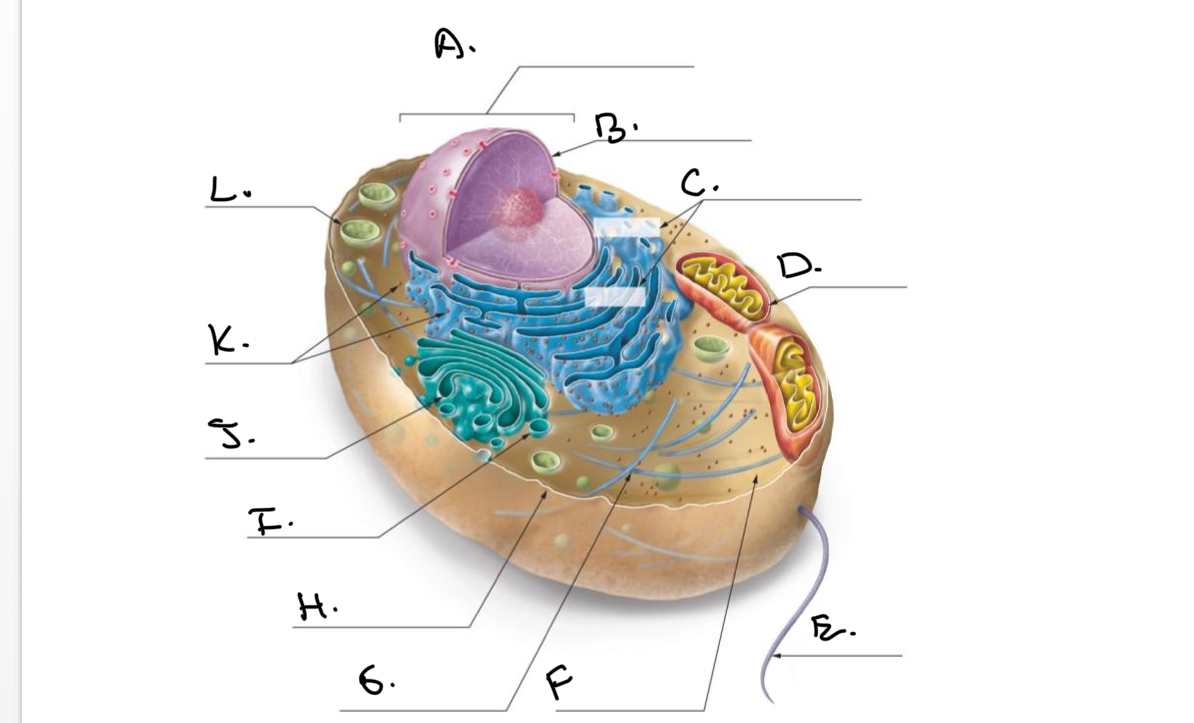
Label the Animal Cell.
C.
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (Rough ER)
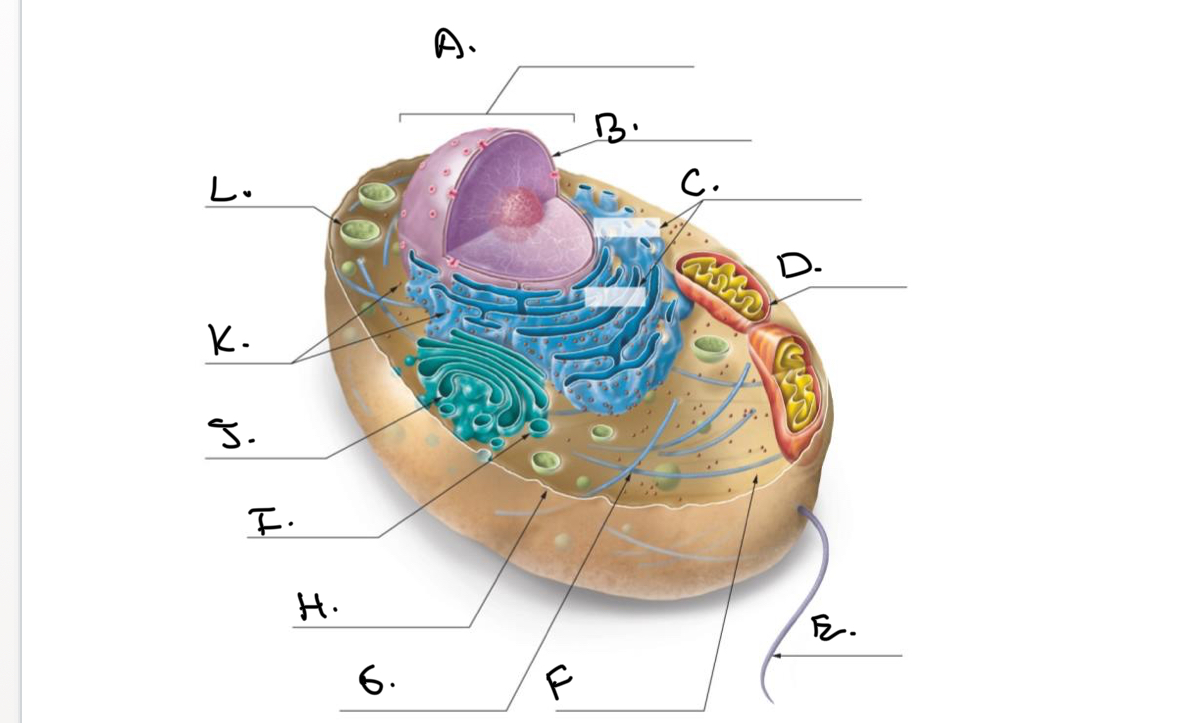
Label the Animal Cell.
D.
Mitochondrion
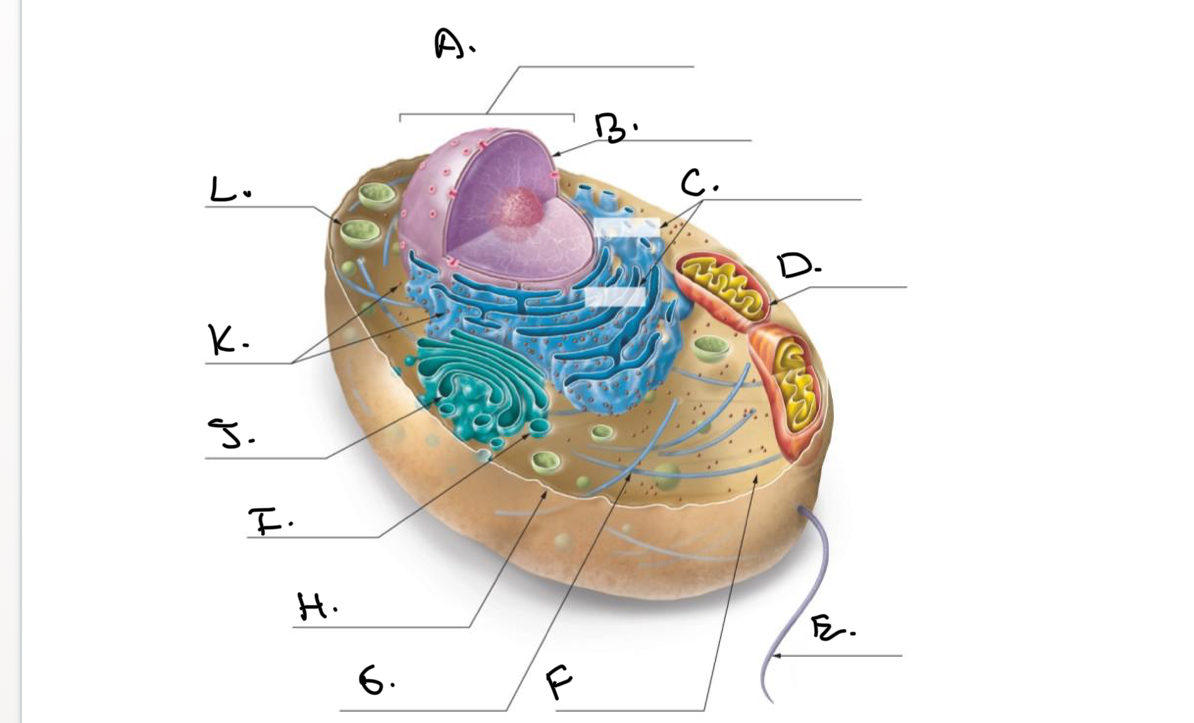
Label the Animal Cell.
E.
Flagellum
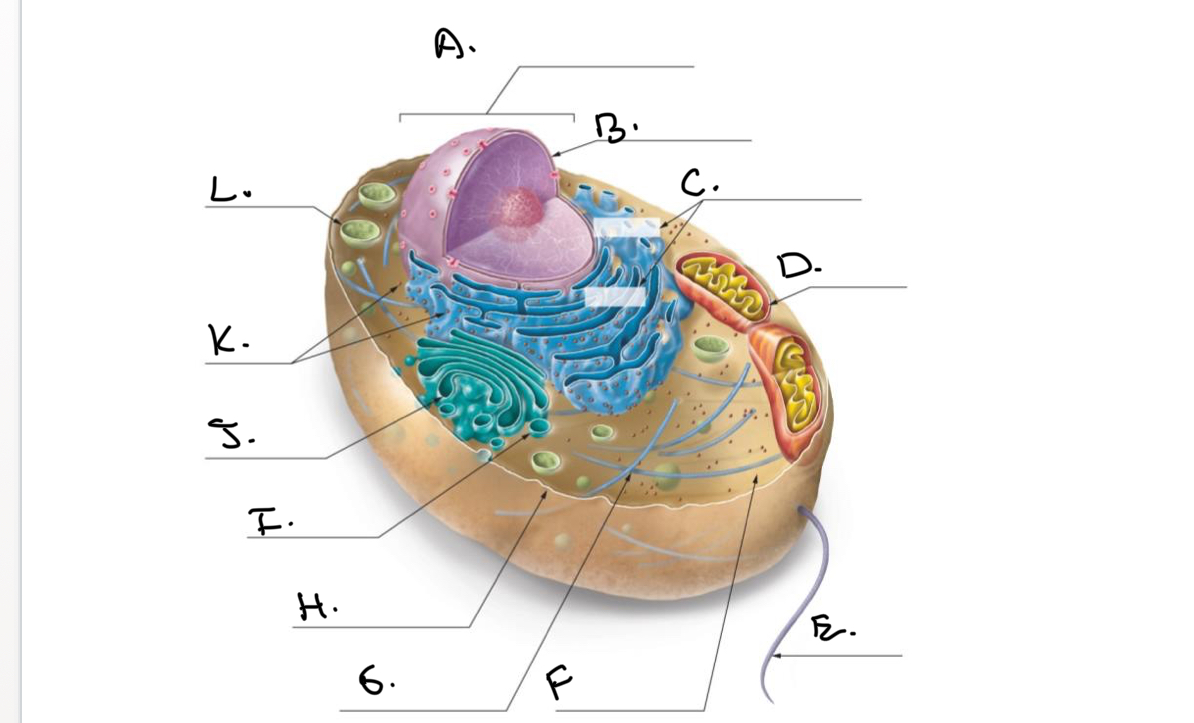
Label the Animal Cell.
F.
Cytoskeleton
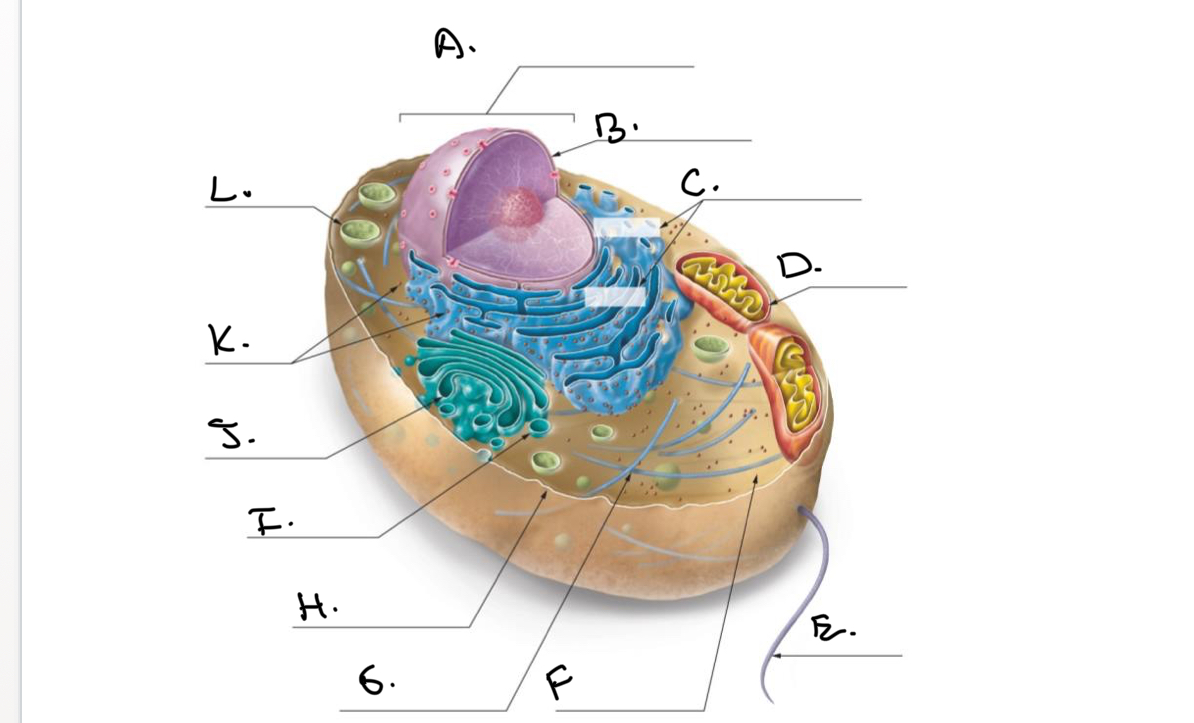
Label the Animal Cell.
G.
Cytoplasm
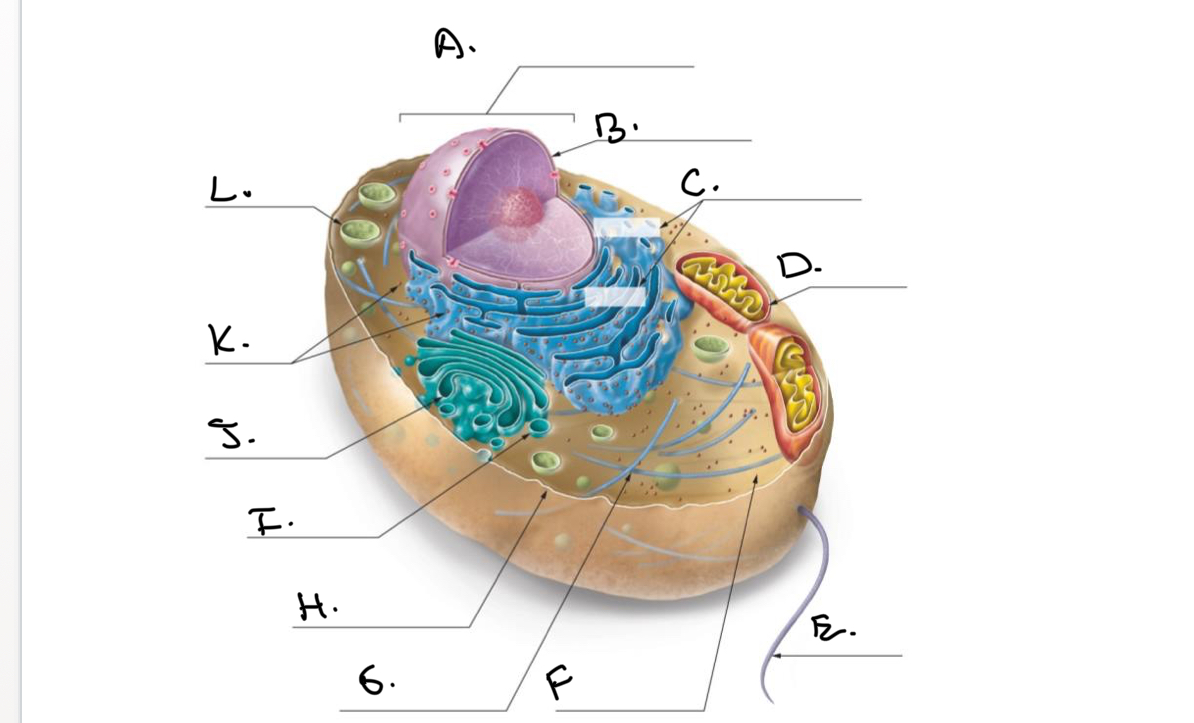
Label the Animal Cell.
H.
Plasma Membrane
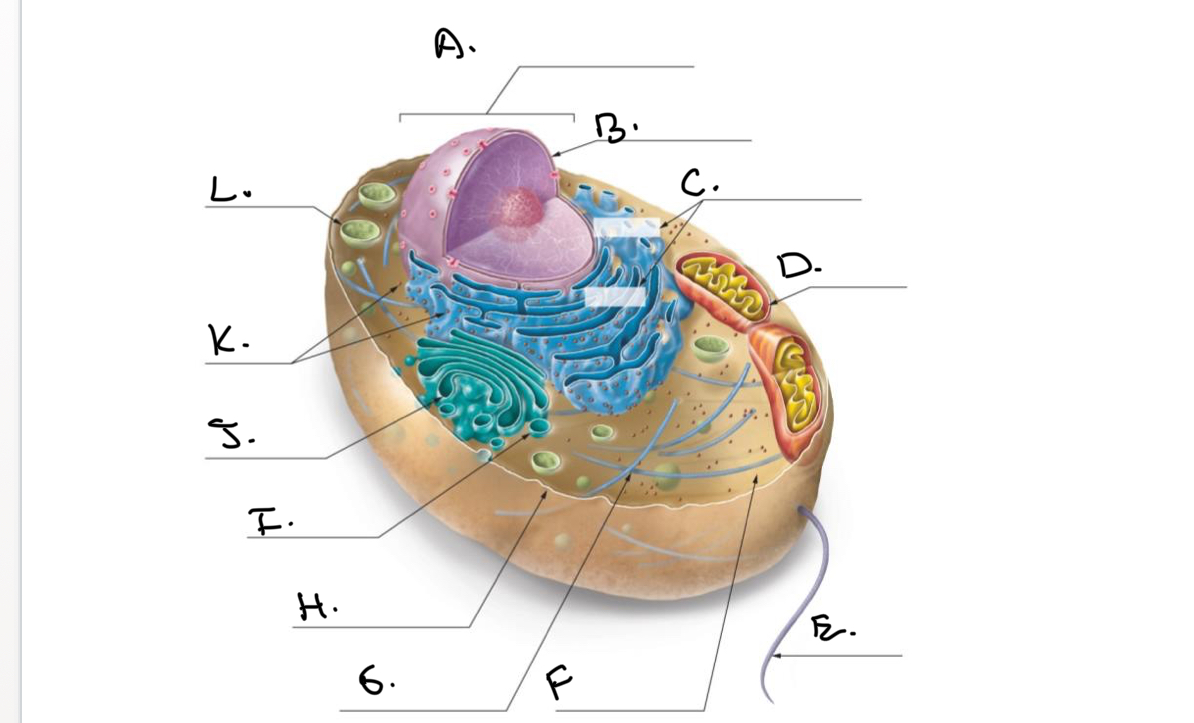
Label the Animal Cell.
I.
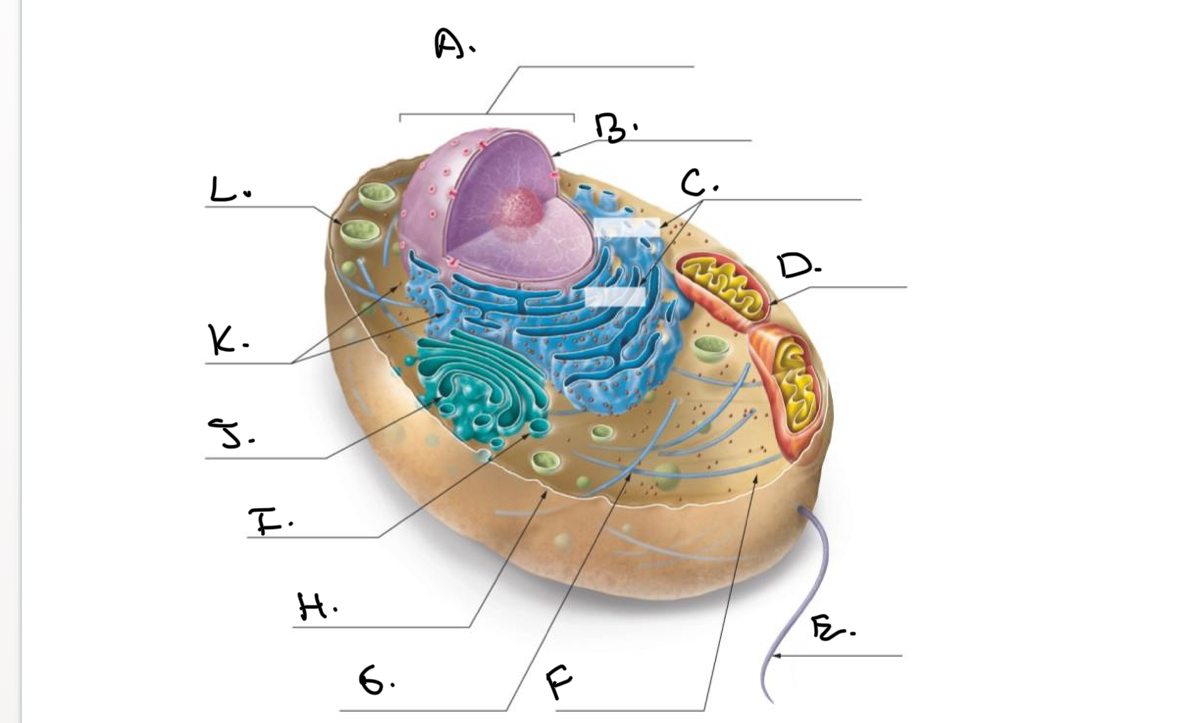
Label the Animal Cell.
J.
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (Smooth Er)
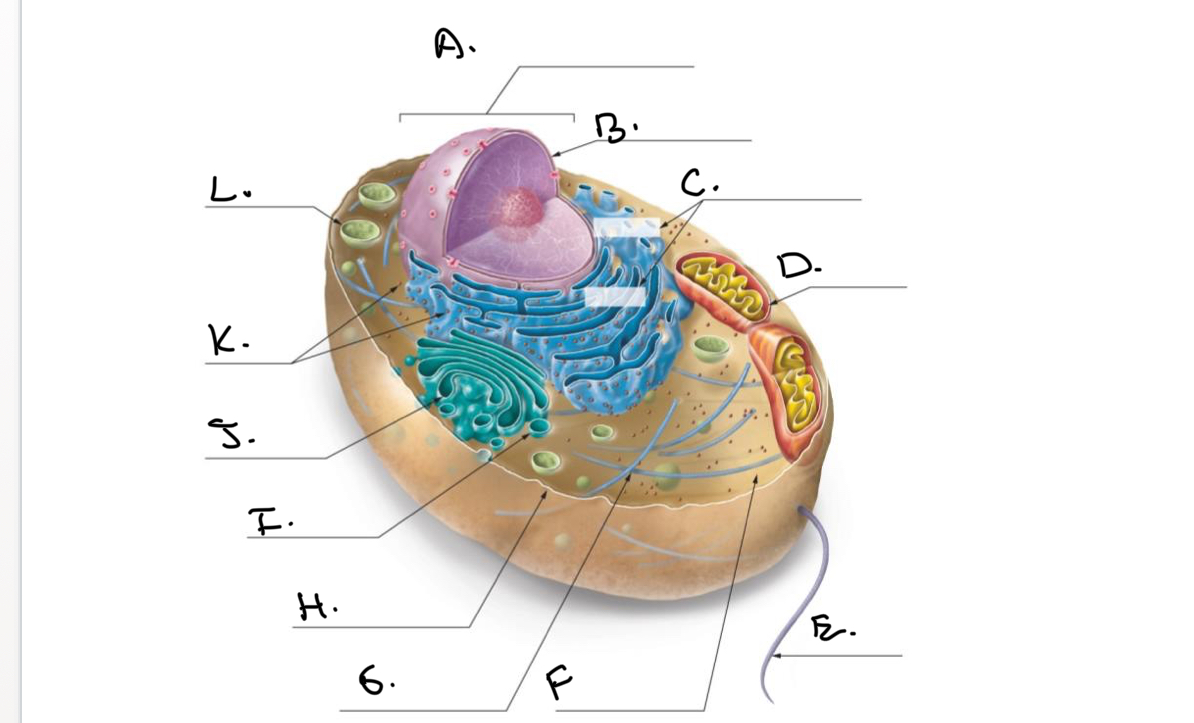
Label the Animal Cell.
K.
Ribosomes
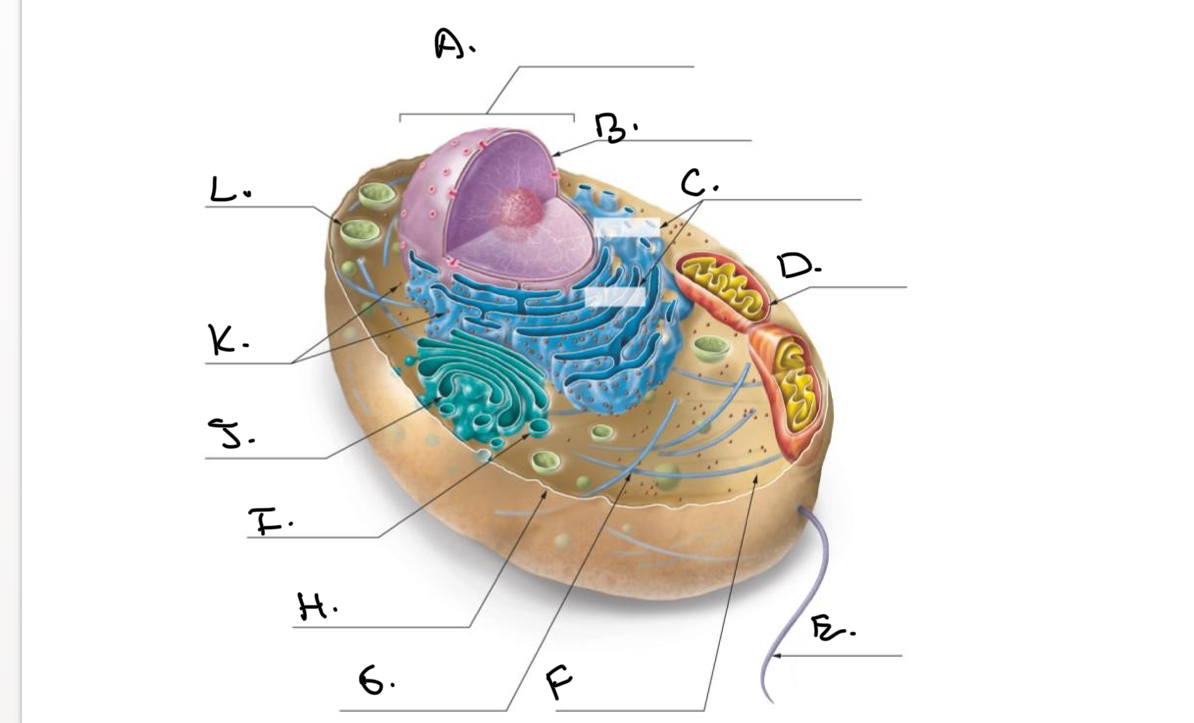
Label the Animal Cell.
L.
Lysosome
Which of the following pairs of organelles and their functions is mismatched?
A) Chloroplasts; protein synthesis
B) Nuclear envelope; regulates traffic between the nucleus and cytoplasm
C) Lysosomes; recycle foreign or worn-out cellular substances
D) Plasma membrane; regulation of substances into and out of the cell
A) Chloroplasts; protein synthesis
Every cell has a(n) _____________________________ that allows it to maintain a cellular environment that is separate from the environment in which it resides.
plasma membrane
Briefly explain what is meant by the following statement: Plasma membranes regulate the movement of substances into and out of a cell.
acts as a selective barrier, controlling which molecules can enter or exit the cell, thus maintaining the cell's internal environment.
True or false: A bacterial cell, animal cell, plant cell, and fungal cell would all have a plasma membrane. If false, correct the statement.
true
What best describes the structure of a cell’s plasma membrane?
A) Proteins sandwiched between two layers of phospholipids
B) Proteins embedded in two layers of phospholipids
C) A layer of protein covering a layer of phospholipids
D) Phospholipids sandwiched between two layers of protein
Proteins embedded in two layers of phospholipids
Biologists have described a cell’s plasma membrane as a fluid mosaic. Briefly explain what fluid mosaic means.
describes the plasma membrane of a cell, meaning it has various parts (like proteins) that move around in a flexible layer of fats (lipids).
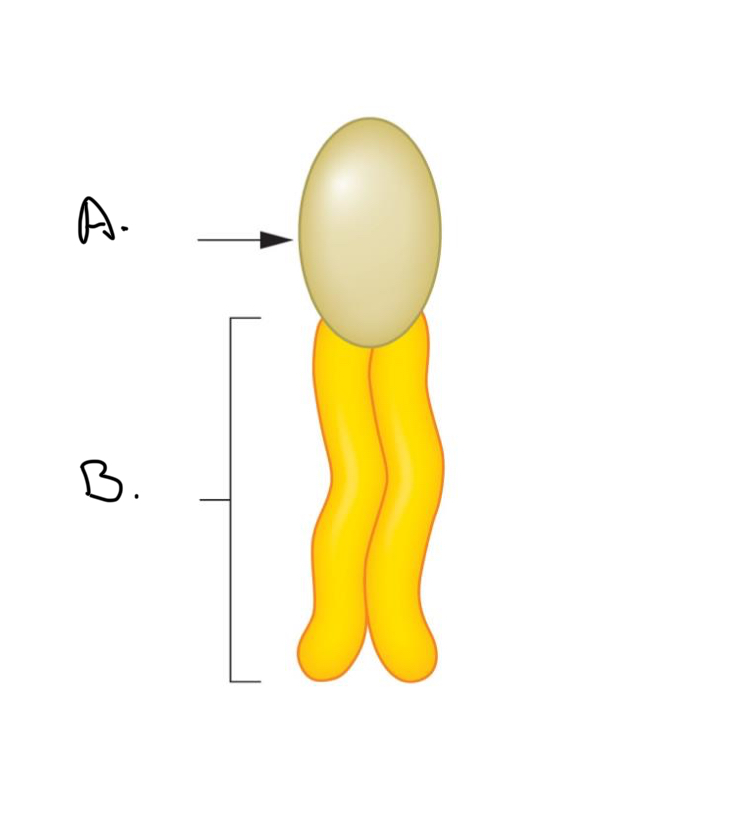
Label the Phosoholipd:
A.
Hydrophilic head
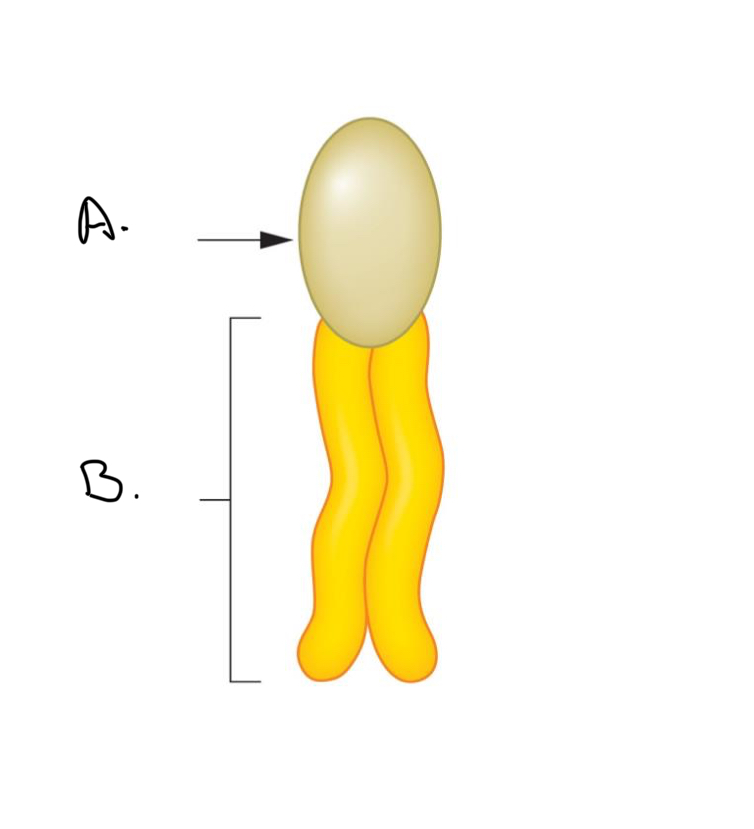
Label the Phosoholipd:
A.
Hydrophobic tail
Liquid within the cell is called ________________________.
Liquid within the cell is called __.
Cytosol.
A plasma membrane consisting of many molecules that are always moving is ****__.
Fluid mosaic.
Fatty acid tails of a phospholipid are _.
Hydrophobic.
Involved in moving substances into and out of the cell is ______________________________.
Membrane proteins.
Phosphate head of a phospholipid is ___________________________.
Hydrophilic
The structure with two layers of phospholipids arranged with the tails facing each other is
a phospholipid bilayer.
True or false: The liquid environment outside of the cell is known as the extracellular fluid. If false, please correct the statement.
true

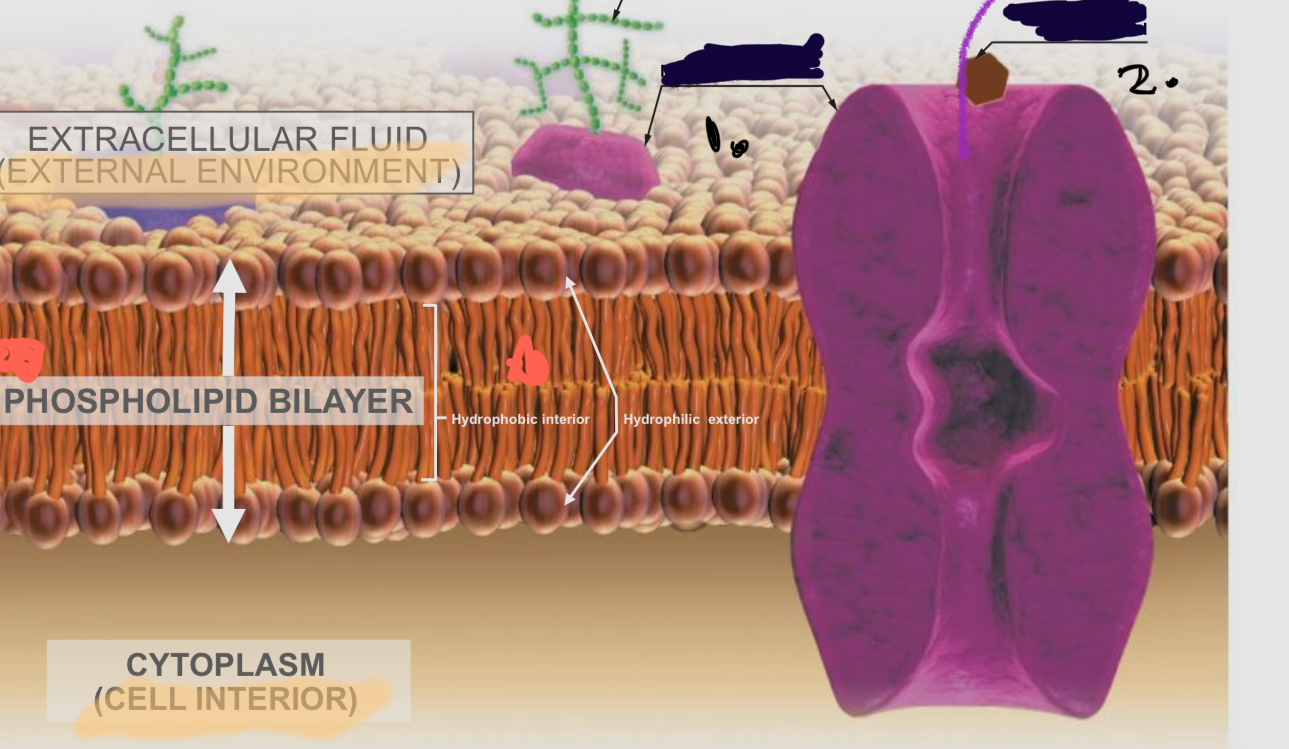
Label in the Plasma Membrane:
A.
Extracellular Fluid (External Environment)
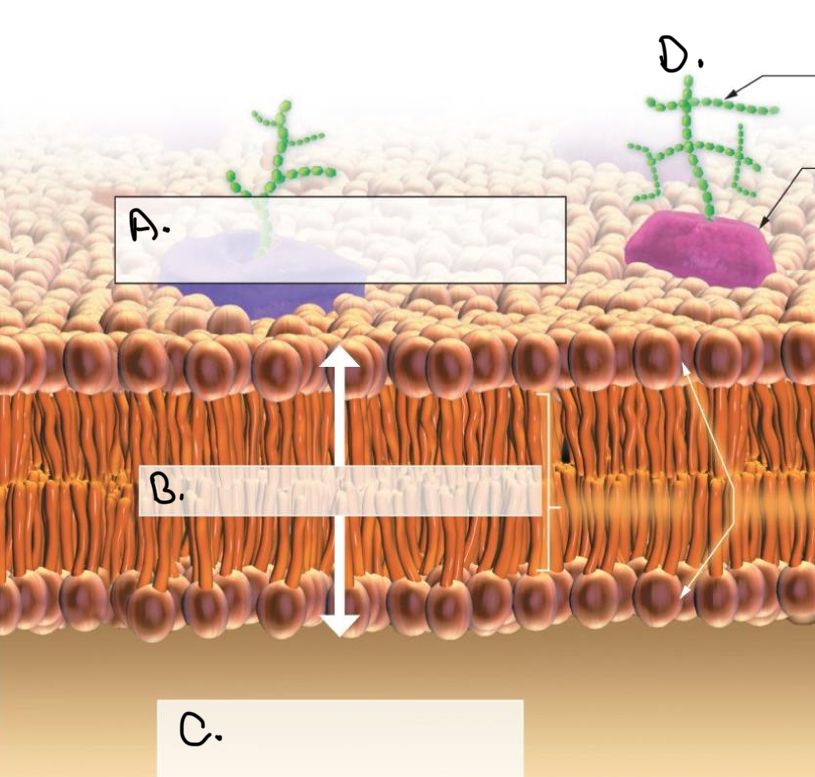
Label in the Plasma Membrane:
B.
Phospholipid bilayer