organisation: plant tissues, organs and systems
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
aqa triple higher
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
stomata in the day and why
take in water by osmosis, becomes turgid, stomata open
this is to allow for greater gas exchange for photosynthesis
stomata at night and why
lose water by osmosis, becomes flaccid, stomata close
to prevent water loss when no photosynthesis is occurring as no CO2 is needed
how does high temperature affect the rate of transpiration?
kinetic energy of water particles increases
rate of osmosis out of leaf increases
so concentration gradient increases
so rate of transpiration increases
how does wind/air movement affect the rate of transpiration?
kinetic energy of water molecules increases
moving water molecules away
rate of osmosis out of leaf increases
so concentration gradient increases
so rate of transpiration increases
translocation
movement of food molecules (such as sucrose) through phloem tissue (up and down the plant)
compare the structure and function of the xylem and phloem
xylem consists of dead cells, phloem consists of alive cells
xylem transports water during transpiration, phloem transports sucrose during translocation
phloem transports substances in both directions but xylem only transports substances upwards
translocation in the phloem requires energy but transpiration in the xylem is a physical process so does not require energy
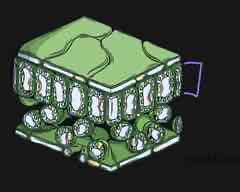
what is this part of the leaf called and what is its function?
palisade mesophyll tissue - contains lots of chloroplasts which contain chlorophyll for photosynthesis and the enzymes needed for photosynthesis
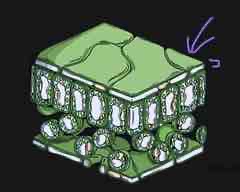
what is this part of the leaf called and what is its function?
upper epidermis - transparent so light can pass through to the palisade layer for photosynthesis
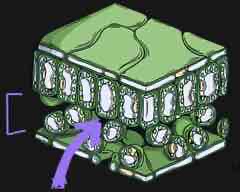
what is this part of the leaf called and what is its function?
spongy mesophyll tissue - contain large air spaces to increase the SA:V and therefore rate of diffusion of gases such as O2 and CO2 in and out of the leaf
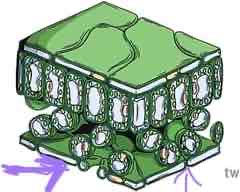
what is this part of the leaf called and what is its function?
lower epidermis - contain lots of stomata and guard cells so CO2 can diffuse into the leaf and O2/water can diffuse/osmose out of the leaf
where is the waxy cuticle and what is its function?
situated at the top and bottom of the leaf
reduces water loss
what are the roles of the stomata?
to control gas exchange and water loss
how does high humidity affect the rate of transpiration?
decreases rate of transpiration
the drier the air around the leaf, the higher the rate of transpiration
humid air causes conc gradient of water between air and leaf to decrease
so rate of osmosis out of leaf decreases
how does high light intensity affect the rate of transpiration?
increases rate of photosynthesis
so stomata open
so water osmoses out of leaf
how are root hair cells adapted for their function?
large SA:V to increase rate of osmosis/active transport of water/mineral ions and provide contact with soil water
thin walls so as not to restrict movement of water

(not required) how could a student investigate factors affecting transpiration?
measure change in mass over time:
air movement - direct fan on leaves
temperature - heater
obstructing stomata - e.g. using petroleum jelly
light intensity - artificial lighting
(not required) how could a student investigate the rate of transpiration?
using a potometer:
fill w water
cut shoot underwater and insert into rubber tubing
raise potometer so air bubble is taken up
lower back into water and record distance travelled over a period of time
repeat
plot graph excluding any anomalies
(not required) how could a student investigate the distribution of stomata and guard cells?
paint surface of leaf a clear nail varnish
wait to dry
peel off w forceps
place on dry microscope slide and examine
calculate density of stomata per unit area