lec 20 - pediatric PK (robinson)
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
challenges children pose
weight based dosing
involves more calculations than for adults
necessity for alterations
commercially available products are adult focused
absent/limited communication skills
young children do NOT have communication skills to warn about potential errors or adverse effects
limited capacity to buffer errors
more limited internal reserves than adults
terminology
gestational age
1st day of mom’s last menstrual cycle → birth
chronological or post natal age
birth → present
post-menstrual age
gestational age + chronological age
neonate
birth to 1 month
pre-mature = <37 weeks
full term = 37-42 weeks
infant
1 month - 1 year
child
1-12 years
adolescent
13-18 years
example of age
baby born at 28 weeks gestation is now 21 days old
gestational age?
full mature or preemie?
post-menstrual age?
neonate, infant or child?
gestational age = 28 weeks
preemie
post-menstrual age = 28 weeks + 21 days = 31 weeks
neonate
gastric absorption
gastric emptying and intestinal motility
most drug absorption takes place in the duodenum
gastric emptying
significantly delayed in neonates/infants (6-8 hours)
adult values (20-50 minutes) by 6-8 months
intestinal motility
prolonged and irregular peristalsis
infantile diarrhea (shortens transit time)
delayed and possibly enhanced absorption
gastric mucosal integrity
neonates at higher risk of intestinal damage
due to poor oxygenation
subject to intestinal injury and necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) from hypertonic solutions
avoid high osmolality drugs and oral drugs until full enteral feeding
minimize osmolality load
minimizing osmolality load
american academy of pediatrics recommends formulas not exceed 450 mOsm/kg
what about medications?
poly-vi-sol: 10,853 mOsm/kg
acetaminophen suspension: 5,017 mOsm/kg
ferrous sulfate: 3,117 mOsm/kg
calcium glubionate syrup: 2,034 mOsm/kg
calcium gluconate injection: 302 mOsm/kg
percutaneous absorption
immature epidermal barrier in premature neonates
mature stratum corneum in full-term neonates
increase skin hydration and increased BSA:weight
increased absorption up to 6 years (vs adults)
inadvertent poisoning
use caution in application of any topical agents in young patients, especially premature neonates in the first 2-3 weeks of life
intramuscular absorption
variable and unpredictable in premature neonates and newborns
decreased muscle mass
insufficient muscle tone and contraction
decreased blood flow
painful
AVOID IM injection whenever possible
distribution: Vd:body composition
Vd:body composition
total body water
infant > younger children > adults
premature (85%) > full term (70%)
larger Vd for water-soluble drugs
total body fat
infants < adults
premature (1%) < full term (15%)
smaller Vd for lipophilic drugs
in general
larger doses (mg/kg) of water soluble drugs
neonates have higher total body water percentage so Vd is larger b/c drug distributes into that extra body water so to achieve same plasma concentration you need higher dose
smaller doses (mg/kg) of lipophilic drugs
neonates have less body fat so lipophilic drugs have less tissue to distribute into so Vd is smaller → smaller doses needed to avoid high plasma concentrations
Vd examples
aminoglycosides = water soluble so more absorption in neonates and less in adults
benzodiazepines = lipophilic so more absorption in adults vs neonates

distribution: protein binding
protein binding
decreased plasma protein binding in neonates and infants
decreased affinity and binding capacity of albumin binding sites
risk of displacing bilirubin from albumin
highly protein bound drugs may have higher free fraction in neonates
avoid drugs known to compete for albumin sites in the neonatal period
this is bc plasma protein binding is so weak to begin with if you introduce a competitor theres going to be like no plasma protein binding which is BAD
protein binding example
phenytoin
~90% protein bound in adults
~80% protein bound in neonates
therapeutic range
adults: 10-20 mcg/mL
neonate: 6-15 mcg/mL
therapeutic free level: 1-2 mcg/mL
metabolism: phase I rxns
oxidation, reduction, hydrolysis
total quantities of P450 enzymes
neonates < adults
maturation correlates with postnatal age
adult values by 6 months
p450 subfamilies mature at different rates
metabolizing capacity
older infants and children (peaks at 2-3 years) >> adults
different pathways
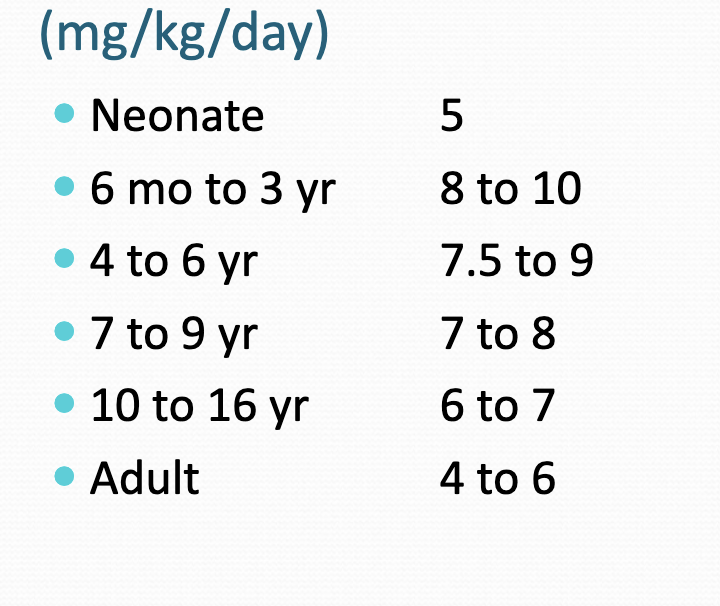
age related phenytoin dosing
increases then decreases b/c neonates have less metabolizing capacity than adults but then…
peak at 6 mo to 3 year b/c thats when metabolizing capacity is the greatest and then starts decreasing
metabolism: phase II reactions
glucuronidation
limited during the neonatal period
adult values by 18-24 months; up to 48 months
sulfation
well developed at birth
may compensate for limited glucuronidation
metabolism
recommended dosing schedules in children are based on population based estimates of CL; careful monitoring of pediatric dosing, serum concentrations and potential toxicity should be emphasized
excretion
glomerular filtration
matures quickly after birth
adult values by 6-12 months
tubular functions
maturation proceeds more slowly
adult levels by 6-8 months; up to 2 years
lower doses of renally cleared drugs during the 1st week of life, then increases with age
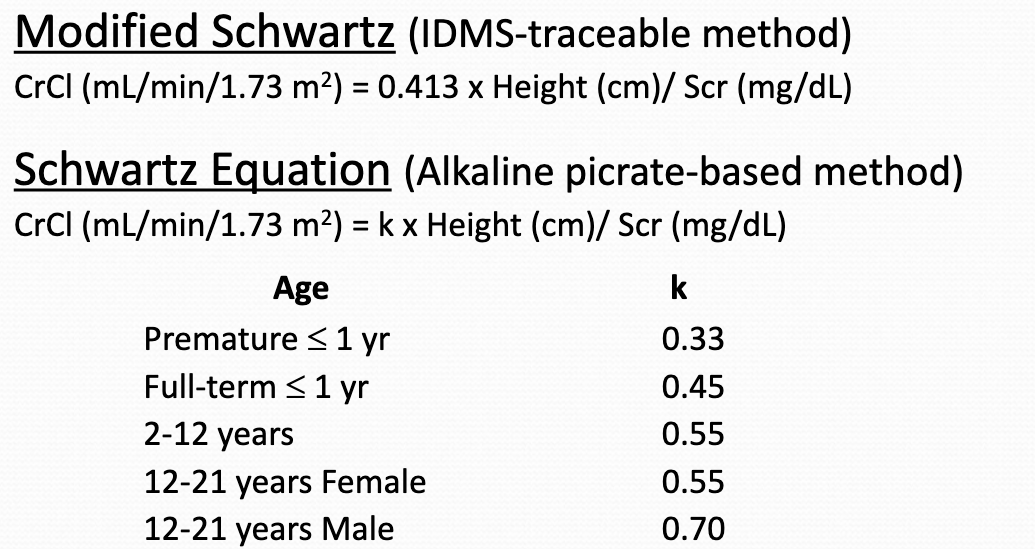
creatinine clearance
modified schwartz/schwartz equation
may NOT provide an accurate estimation of creatinine clearance for infants < 6 months of age or for pts with severe starving or muscle wasting
special considerations in children
age specific dosing regiments
drug delivery
blood sampling
interpretation of drug levels
age specific dosing regimens
NO standard dosing for peds
pediatric references
pediatric and neonatal dosage (lexicomp)
neofax (micromedex)
teddy bear book
more
rutgers resources
pediatric and neonatal→ lexicomp
neofax → microedex
red book (AAP) → STAT!ref

which dose to choose?
dosing ranges
age
diagnosis
meningitis vs UTI
concurrent disease states
cancer, gastroenteritis
organ function
renal or hepatic disease
what to be careful about
units
mg/kg/dose times desired frequency
acetaminophen 15 mg/kg/dose q4h prn
mg/kg/day divided by the desired frequency
ampicillin 200 mg/kg/day divided q8h
mg/m2/day
acyclovir 500 mg/m2/dose q8h
in general when a patient’s calculated dose exceeds the adult dose, the pt should be dosed according to adult medication guidelines
KNOW WHEN TO SAY WHEN
drug delivery
dosage form
route of admin
delivery system
method of admin
drug delivery: oral admin
give orally whenever possible
solid vs liquid
depends on age and developmental level
most children can safely swallow solid forms of meds by 5-6 years
younger children may be at risk of aspirating solid dosage forms
chewable tabs preferred when feasible
beware of preservatives
modify commercial products
dilute liquids with an appropriate diluent to achieve desired concentration
split tablets
if the patient’s dose is a measurable fraction
injectable drugs may be used as oral dosage forms
if oral bioavailability data exists
crush tablets or empty capsules and mix with beverages, soft foods, or enteral feeding formulas or extemporaneously prepare oral liquid
use references, if available
do NOT crush sustained release products
watch for medication/enteral nutrition interactions
drug delivery: IV delivery
ensure accurate prep and admin
choice of syringe and needle size
frequently small volumes
delayed drug delivery or underdosing may occur
FLUSH lines with adequate but min. volume
pediatric patients are susceptible to fluid overload
volumes of IV solutions need to be kept ta min
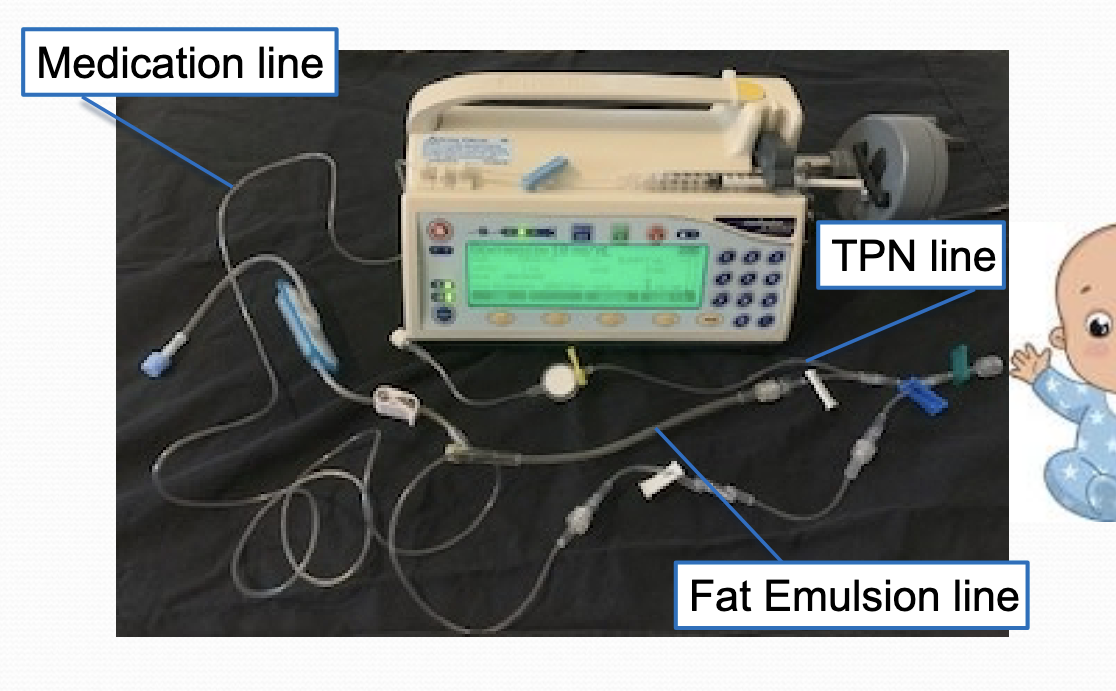
IV delivery system
syringe pumps with microbore IV tubing preferred
volumetric control devices
beware of dead space (up to 30 mL in standard IV tubing)
case study
baby boy brown is 35 week GA neonate being treated with ampicillin and gentamicin for sepsis. his nurse draws the gentamicin peak and trough levels around his 4/14 1300 dose (dose #3)
peak: 2.1 mcg/mL (drawn at 4/14 1400)
trough: 1.8 mcg/mL (drawn at 4/14 1230)
timings of the peak blood draw was incorrect
trough should be drawn right before next dose. about 30 minutes → so 1230 which is correct
peak should be drawn 30 minutes to 1 hour after the end of infusion
with this drug 30 minutes admin and 30 mins flush so anther 30 minutes after flush is when it should be measured so it should be 1430
syringe pump with microbore tubing
blood sampling
assess need to draw drug levels
NOT always necessary (empiric treatments - starting treatment on the most likely conditions before lab confirmation)
subtle signs of toxicity or lack of effect difficult to assess
ongoing maturation of renal and hepatic function
rapidly changing physiological status
weight and body compartments
minimize number of blood samples
obtain the minimal amount of blood when sampling
timing is everything
steady state, other labs, quality of life
to draw or not to draw:
mary is a 10 year old girl admitted with fever and neutropenia. she is started on cefepime and tobramycin. she is clinically stable and does NOT have any obvious sources of infection on physical exam. renal function is normal.
do we need to order tobramycin levels at this time?
probably not b/c short empiric use; stable renal function; no signs of toxicity
to draw or not to draw:
mary grows pseudomonas aeruginosa from her peripheral and central blood cultures. she is hemodynamically stable. ID recommends continuing cefepime and tobramycin for 14 days. she has received 3 doses of tobramycin to date (4/14 0400, 4/14 1200, 4/14 2000). next dose is 4/15 0400.
if and when should we draw tobramycin levels
yes we should draw b/c prolonged therapy
draw 4/15 0330 for trough and 1230 for peak
factors that are important when interpreting levels
exact time of sampling
exact time of all relevant dosing
administration and sampling method
dosing regimen
dose, frequency, duration, dosage form, route
patient characteristics
age, weight, diagnoses, organ function
concurrent medications
indication for medication and level
therapeutic range