Radiographic Procedures 2 (155) Cranium Anatomy
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
87 Terms
Skull
composed of 22 bones, separated into:
cranial bones (8)
facial bones (14)
cranial bones further divide into:
calvaria
floor
Diploe
inner layer of spongy bone separating two outer plates of compact tissue
Sutures
fibrous joints that connect the bones of the skull; immovable
Coronal suture
between the frontal and parietal bones
Sagittal suture
between the two parietal bones
Squamosal suture
beteen the temporal bone and parietal bones
Lambdoidal suture
between occipital and parietal bones
Cranial bones
calvaria:
frontal
occipital
right parietal
left parietal
floor:
ethmoid
sphenoid
right temporal
left temporal
Bregma
junction of coronal and sagittal sutures
Lambda
junction of sagittal and lambdoidal sutures
Pterion
junction of the parietal bone, squamosal suture, and greater wing of the sphenoid
Fontanels
areas of incomplete ossification in infant skulls
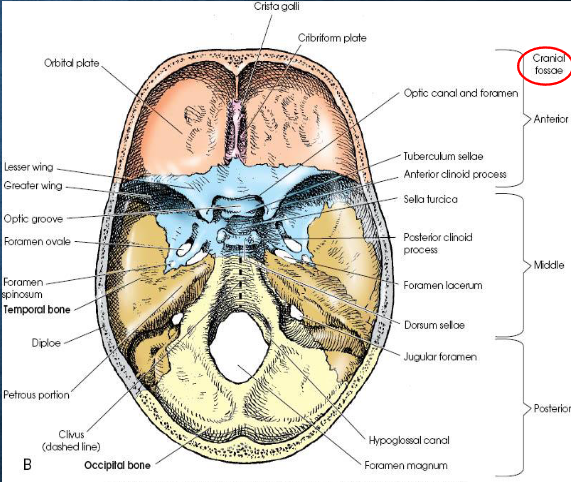
Cranial floor
internally, divided into three regions
anterior cranial fossa: houses the frontal lobes of the cerebrum; extends from anterior frontal bone to lesser wings of sphenoid
middle cranial fossa: houses temporal lobes; extends from lesser wings of sphenoid to apices of petrous ridges
posterior cranial fossa: deep depression posterior to petrous ridges; protects cerebellum, pons, and medulla oblongata
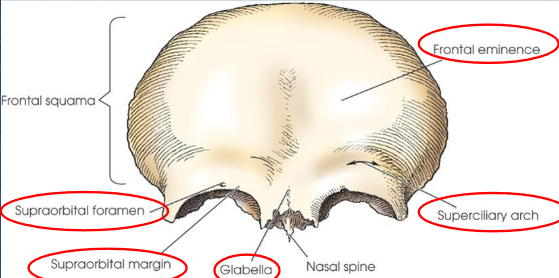
Frontal bone
landmarks:
frontal eminence
supraorbital margins
supraciliary arches (eyebrow ridges)
supraorbital foramina
glabella
articulates with right and left parietals, sphenoid, ethmoid, nasal bones, and zygoma
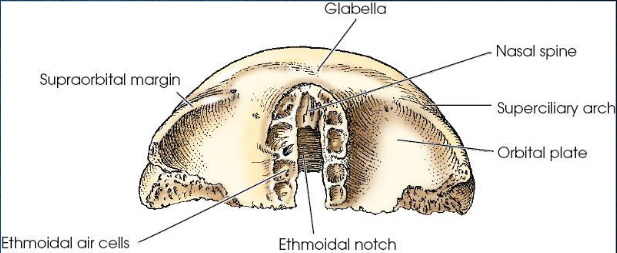
Posterior view of frontal bone
Ethomoid bone
consists of:
horizontal plate (cribriform plate)
vertical plate (perpendicular plate)
two labyrinths - light, spongy masses
articulates with frontal, sphenoid, lacrimal, maxilla, and vomer
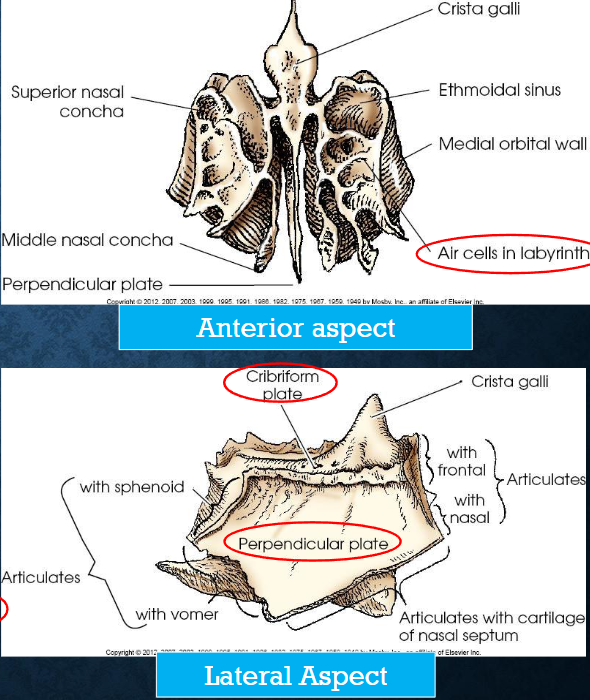
Cribriform plate
contains numerous foramina for transimission of olfactory nerves; horizontal plate of ethmoid bone
Crista galli
conical projection at anterior midline of cribriform plate
Perpendicular plate
forms superior portion of bony nasal septum; vertical plate of ethmoid bone
Labyrinths
contain ethomoid sinuses or air cells
walls form part of medial walls of orbits and lateral walls of nasal cavities
have two thin, scroll-shaped projections called the superior and middle nasal conchae
Parietal bones
right and left
convex external surface and concave internal surface
articulate with each other at the sagittal suture, the frontal, temporal, occipital, and sphenoid bones
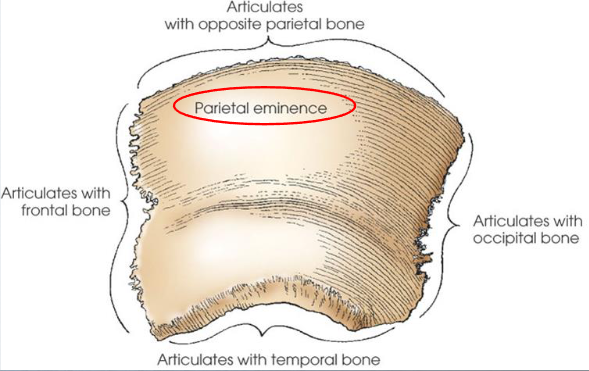
Parietal eminence
prominent bulge near center of external surface of each parietal bone; the point where the width of the skull is measured to set technique
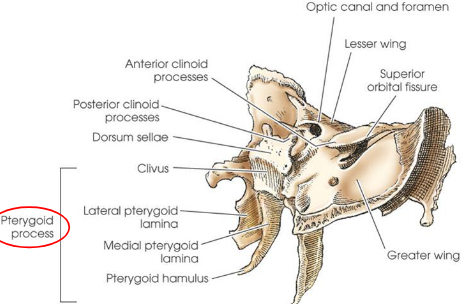
Sphenoid bone
wedge-shaped bone
located in base of cranium, anterior to temporal bones and basilar portion of occipital bone
consists of:
body
two lesser wings
two greater wings
two pterygoid processes
articulates with
all cranium bones and the zygoma
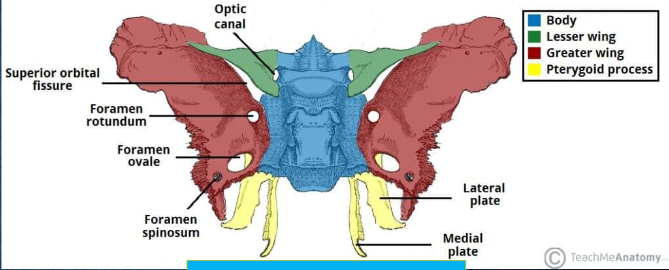
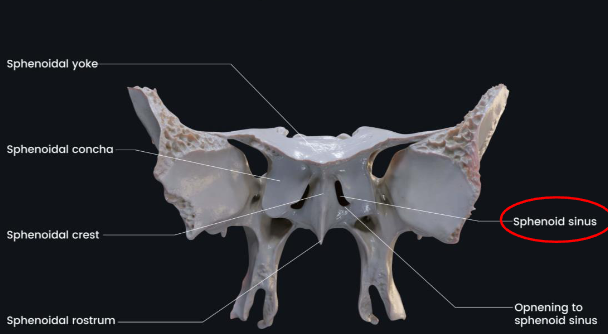
Body of sphenoid bone
contains two sphenoid sinuses and forms posterior bony wall of nasal cavity
Sella turcica
deep depression on superior surface of sphenoid body
houses pituitary gland
located in MSP of cranium, 3/4” anterior and superior to EAM
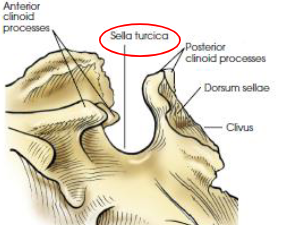
Tuberculum sellae
anterior broder of sella turicica
Dorsum sellae
posterior border of sella tucica
Posterior clinoid process
top borders of dorsum
Clivus
slanted area of bone posterior and inferior to dorsum sellae
continous with basilar area of occiptal bone
supports pons of the brain
Optic groove
chiasmatic groove; extends across anterior portion of tuberculum sellae
groove ends on each side at the optic canal
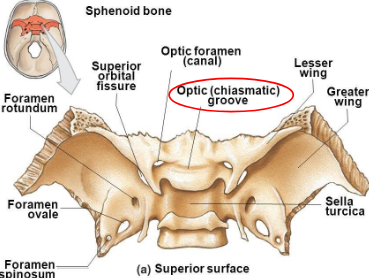
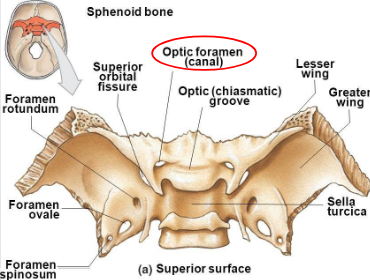
Optic canal
opening into the apex of the orbit for transmission of the optic nerve and ophthalmic artery; actual opening is termed optic foramen
Lesser wings
arise frome anterior and superior portion of the body and lie horizontally on each side
form posteromedial portion of orbital roofs, posterior portion of anterior cranial fossa, upper margin of superior orbital fissure, and optic canals
medial ends form the anterior clinoid processes
Greater wings
arise from side of the body and curve laterally, posteriorly, anteriorly, and superiorly
form part of middle cranial fossa and posterolateral walls of orbit
sphenoid foramina
rotundum
ovale
spinosum
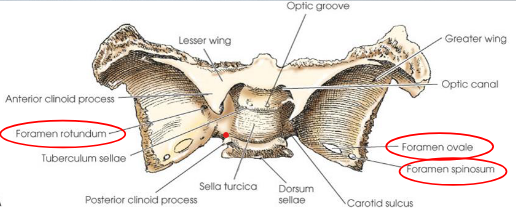
Pterygoid processes
arise from lateral portions of inferior surface of body and medial portions of inferior surfaces of greater wings
articulate with:
palatine bones anteriorly
vomer as part of the nasal cavity
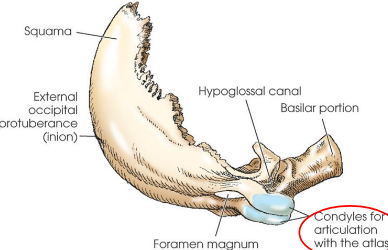
Occipital bone
situated at posteroinferior part of cranium
forms posterior half of cranial base and greater portion of posterior cranial fossa
four parts:
squama
occipital condyles (2)
basilar portion
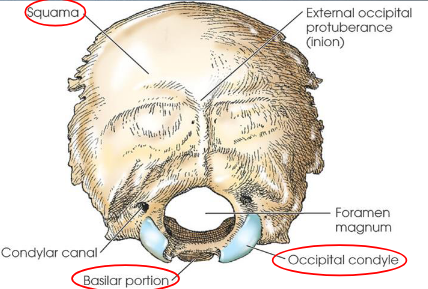
Foramen magnum
large opening through which the medulla oblongata of the brain passes as it exits the cranium
External occipital protuberance
prominent process on squama
also called inion
corresponds to internal occipital protuberance
palpable bump on back of skull
Occipital condyles
project anteriorly from each side of squama
fuse at basilar portion to complete foramen magnum
articulate with both parietals, both temporals, the sphenoid bone, and the atlas (C1)
Temporal bone
paired, irregular in shape
situated on each side of cranial base between greater wings of sphenoid bone and occipital bone
form large part of middle cranial fossa and a small part of posterior cranial fossa
consists of
squamous oortion
tympanic portion
styloid process
zygomatic process
petromastoid portion (petrous bone), contains the organs for hearing and equilibrium
articulates with
pariteals, occipital, sphenoid, zygoma, and mandible
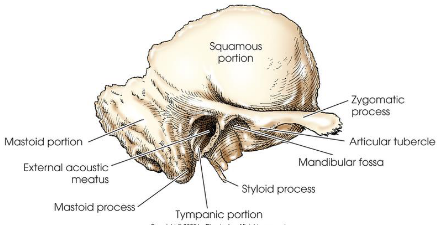
Squamous portion
thin upper portion of temporal bone
forms part of side wall of cranium
Zygomatic process
prominent arched process that projects anteriorly to articulate with zygoma and complete the zygomatic arch
Articular tubercle
located on inferior border of zygomatic process of the temporal bone
forms anterior boundary of mandibular fossa
Mandibular fossa
receives condyle of mandible to form temporomandibular joint (TMJ)
Tympanic portion
located below squama and in front of petromastoid portion
forms anterior wall, inferior wall, and part of posterior walls of EAM
Styloid process
slender, pointed bone projecting inferiorly, anteriorly, and slightly medially from inferior surface of tympanic portion of the temporal bone
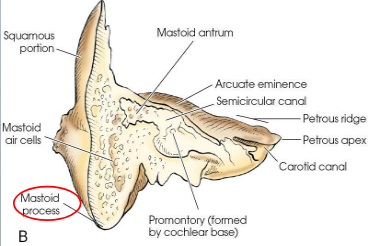
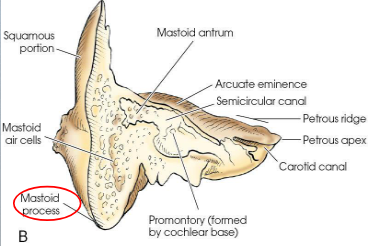
Petromastoid portion
combines petrous and mastoid portions
forms the inferior posterior part of the temporal bone
articulates with parietal bone at its superior border and with occipital bone at its posterior border
usually contains air cells, which vary greatly in size, number, and pneumatization
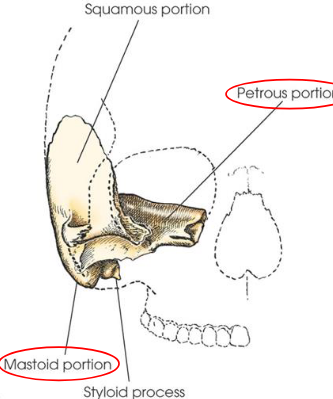
Mastoid process
conical process projecting from mastoid portion
Petrous portion
projects medially and anteriorly between greater wing of sphenoid and occipital bone
also called petrous pyramid
consical or pyrimidal in shape
thickest and densest portion of cranium
contains the organs of hearing and balance
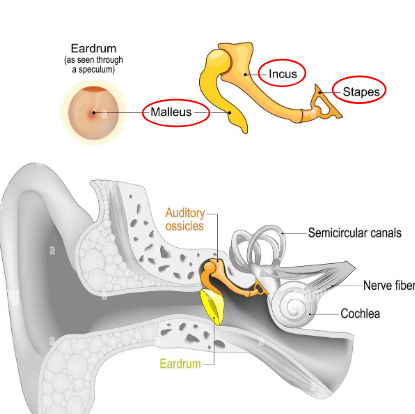
Auditory ossicles
bones of the middle ear
malleus (hammer)
incus (anvil)
stapes (stirrup)
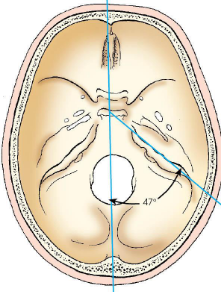
Mesocephalic
typical skull; petrous pyramids project anteriorly and medially at 47-degree angle from MSP
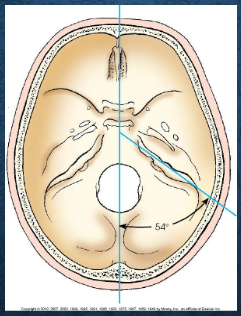
Brachycephalic
petrous pyramids project anteriorly and medially at 54-degree angle from MSP
short from front to back, broad from side to side, and shallow from vertex to base
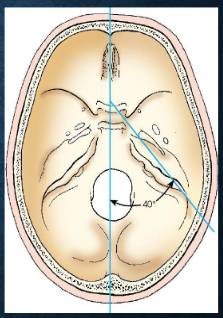
Dolichocephalic
petrous pyramids project anteriorly and medially at 40-degree angle from MSP
long from front to back, narrow from side to side, and deep from vertex to base
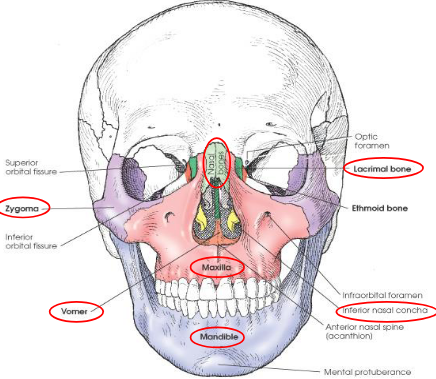
Facial bones
14 total
right and left nasal
right and left lacrimal
right and left maxilla
right and left zygoma
right and left palatine
right and left inferior nasal conchae
vomer
mandible
Nasal bones
two small, thin bones
vary in size and shape in individuals
form superior bony wal of nasal cavity
commonly called “bridge of nose”
articulates with:
each other in MSP
frontal bone, superiorly
perpendicular plate of ethmoid bone, posterosuperiorly
maxillae, on each lateral side
Lacrimal bones
two smallest bones in the skull
located in anterior part of medial wall of orbits between labyrinth of ethmoid and maxilla
each bone contains a lacrimal foramen through which the tear duct passes
articulates with
frontal
ethmoid
maxilla
inferior nasal concha
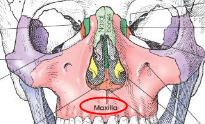
Maxillary bones
largest immovable bones of the face
articulates with all other facial bones, except for mandible
also articulates with frontal and ethmoid bones
form part of lateral walls and most of floor of nasal cavity
form part of floor of orbit
form ¾ of roof of mouth
have zygomatic process that articulates with zygoma to form part of cheek
contains maxillary sinus
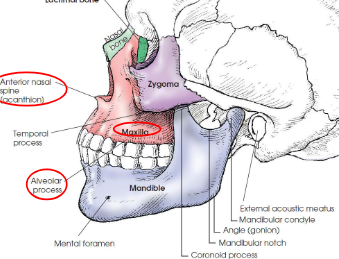
Infraorbital foramen
located under each orbit for passage of infraorbital nerve and artery
Alveolar process
superior (mandible) and inferior (maxillae) borders of spongy bone that support roots of teeth
Anterior nasal spine
forward, pointed process at the midline junction of maxillae; acanthion is the midpoint of this junction
Zygomatic bones
forms prominence of cheeks
form part of side wall and floor of orbits
articulates with:
frontal bone, superiorly
zygomatic process of temporal bone, laterally
maxilla, anteriorly
sphenoid bone, posteriorly
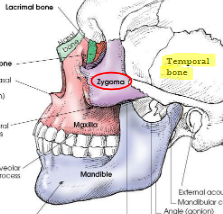
Zygomatic arch
formed by union of temporal process of zygoma and zygomatic process of temporal bone
Temporal process
extends posteriorly to join zygomatic process of temporal bone
Palatine bones
two L-shaped bones composed of vertical and horizontal plates
horizontal plates articulate with maxillae to complete the posterior ¼ of the roof of the mouth
vertical portions extend upward between maxillae and pterygoid process of sphenoid in posterior nasal cavity
superior tips of vertical plates assist in forming posteromedial orbit
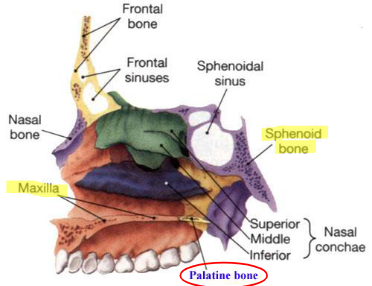
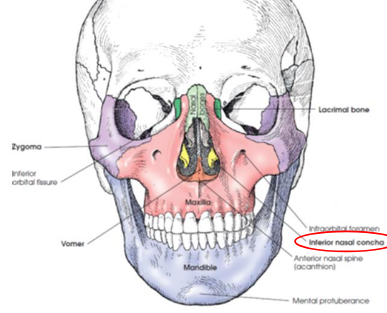
Inferior nasal conchae
extend diagonally and inferiorly from lateral walls of nasal cavity at its lower third
long, narrow, very thin bones with a lateral curl
gives scroll-like appearance
3 nasal conchae on each side
superior middle
inferior
upper two nasal conchae are processes of the the ethmoid bone
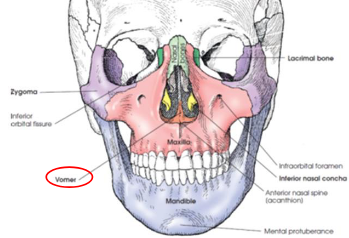
Vomer
thin plate of bone situated in MSP of floor of nasal cavity
forms inferior nasal septum
superior broder articulates with body of sphenoid bone
superior part of anterior border articulates with perpendicular plate of ethmoid bone
posterior border is free
Mandible
largest and densest bone of the face
body is curved and horizontal portion
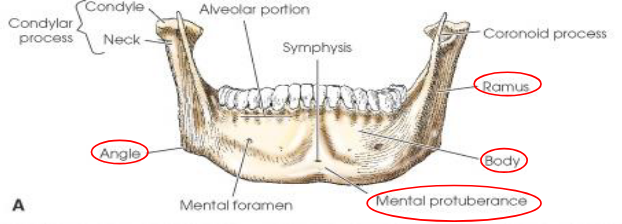
Mandibular rami
two vertical portions on each side of body
Gonion
junction of body and ramus, called angle of mandible
Mental protuberance
anterior, triangular prominence on anterior body of mandible
Mandibular symphysis
most anterior and central part where left and right halves of mandible fuse
Mental foramina
small openings on each side below the second premolar; transmit nerves and blood vessels
Coronoid process
anterior process on top of ramus
Condylar process
posterior process on top of ramus; articulates with mandibular fossa of temporal bone to form temporomandibular joint (TMJ)
Mandibular notch
concave area at top of ramus between coronoid and condylar processes
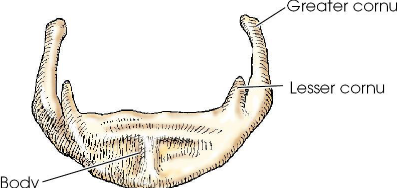
Hyoid bone
small U-shaped bone situated at the base of the tongue
accessory bone of axial skeleton; not a facial or cranial bone
only bone in the body that does no articulate with another bone
Orbits
each is composed of seven bones
cranial:
frontal
ethmoid
sphenoidal
facial:
lacrimal
palatine
maxillary
zygomatic
parts:
roof
medial wall
lateral wall
floor
serve primarily as bony sockets for the eyeballs
major openings:
optic foramina
superior and inferior orbital fissures
Base of orbits
orbital rim or orbital margin; easily palpable, quadrilateral-shaped anterior circumference
Apex of orbits
corresponds to the optic foramen
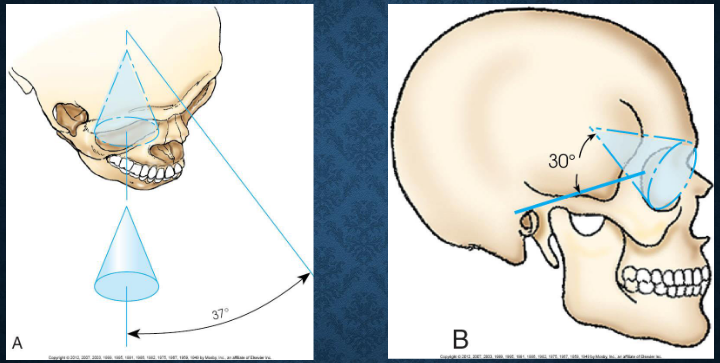
Long axis of orbits
directed obliquely, posteriorly, and medially at 37 degrees to the MSP and superiorly at a 30 degree angle from the OML
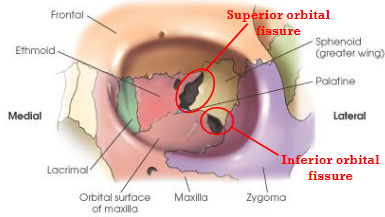
Superior orbital fissure
cleft between greater and lesser wings of sphenoid
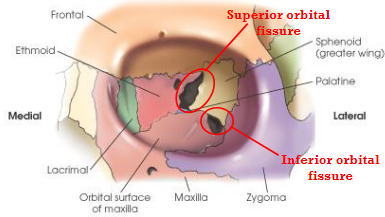
Inferior orbital fissure
narrow cleft extending from the lower anterolateral aspect of the sphenoid body anteriorly and laterally between the floor and lateral wall of the orbit
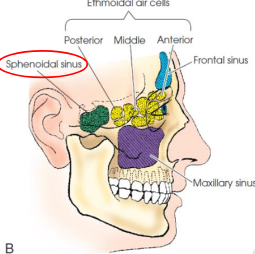
Paranasal sinuses
air-filled cavities located in the frontal, ethmoid, and sphenoid bones of the cranium, as well as the maxillae of the fce
functions:
resonating chamber for the voice
decrease weight of skull
aid in warming and moisturizing inhaled air
act as shock absorbers in trauma
possibly control the immue system
development:
begins in fetal life
maxillary sinuses are usually the only ones developed enough to be demonstrated radiographically at birth
by 6-7 years, frontal and sphenoid are distinguishable from ethmoids
do not fully develop until 17-18 years
Maxilllary sinuses
largest and most symmetric
paired
vary in size and shape, but are approximately pyramidal
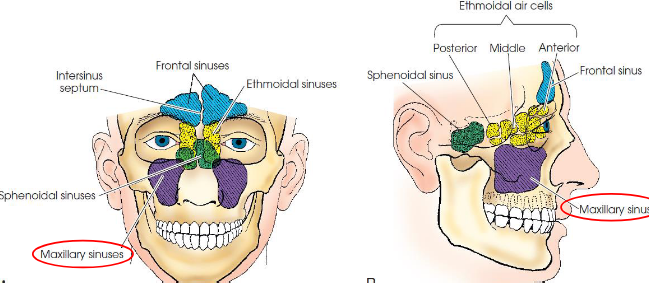
Frontal sinuses
second largest sinus
paired
located between vertical plates of frontal bone
vary greatly in size and shape
occasionally absent
rarely symmetric
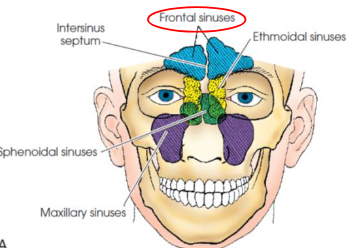
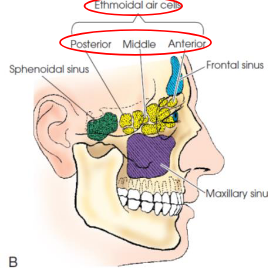
Ethmoid sinuses
located within lateral masses
composed of air cells divided into three main groups
anterior
middle
posterior
Sphenoid sinuses
normally paired
occupy body of sphenoid bone
often only one sinus develops, but never more than two
vary in size and shape
usually asymmetric
located below sella turcica and extend between dorsume and posterior ethmoids