AP Psychology: Topic 4.4 - Psychodynamic and Humanistic Theories of Personality
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Psychodynamic theory
Freudian theory that unconscious forces determine behavior
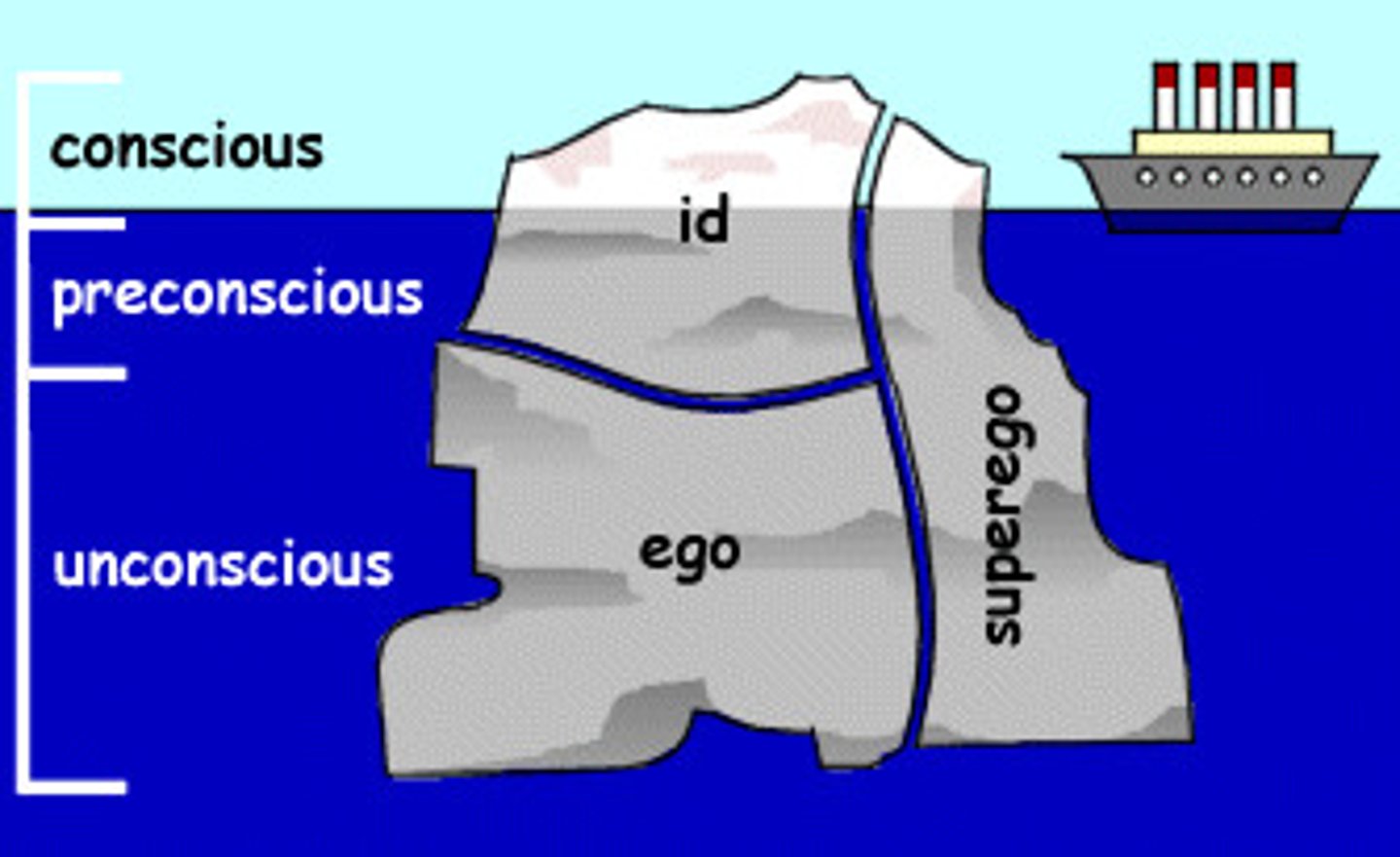
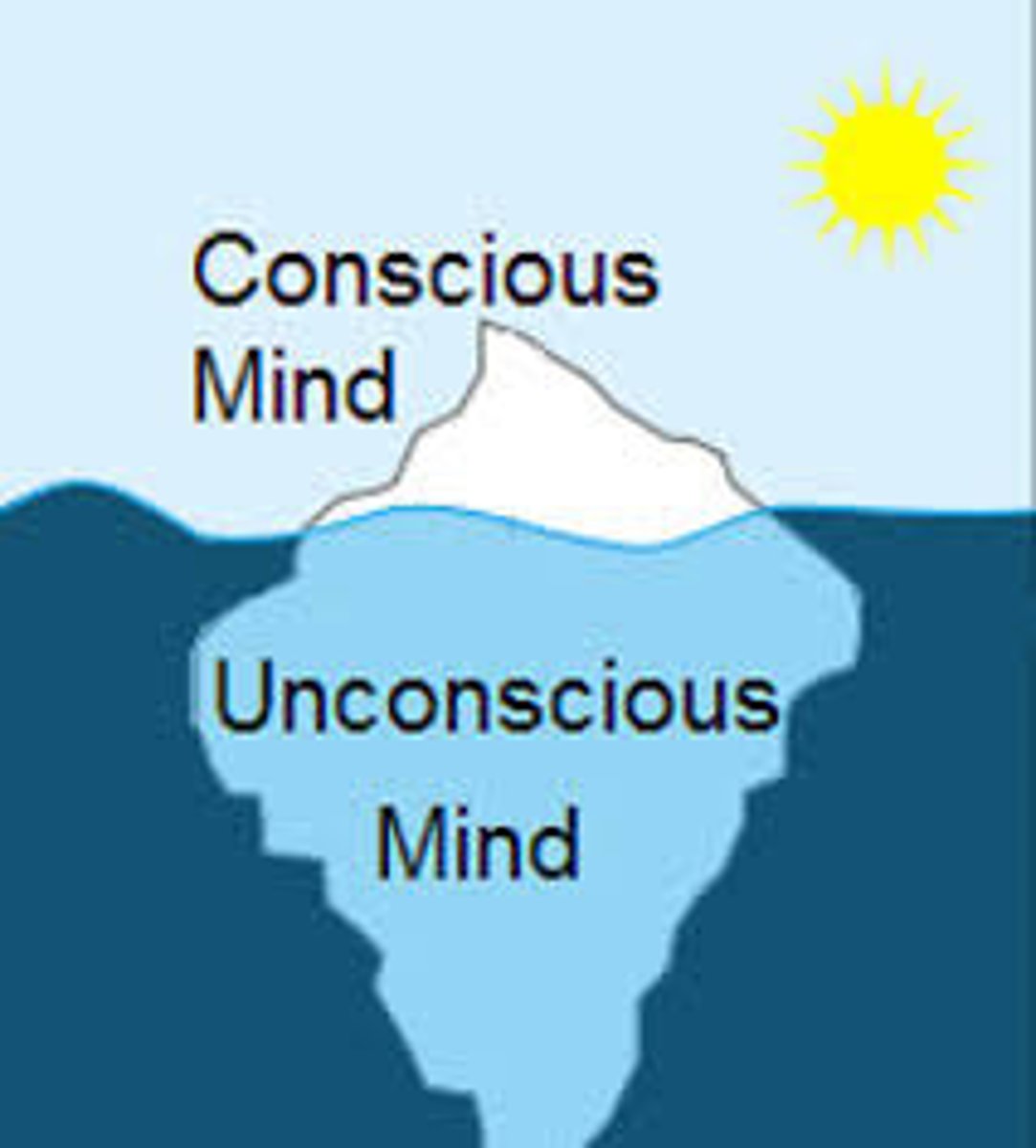
Unconscious processes
mental activities that occur outside of a person's awareness, such as thoughts, desires, and memories that are hidden from conscious thought
Ego defense mechanisms
things that protect the conscious mind from the anxiety that arises from unacceptable impulses

Denial
a defense mechanism by which people refuse to believe or even to perceive painful realities

Displacement
defense mechanism in which a person redirects a negative emotion from its original source to a less threatening recipient (e.g., a person angry at their boss may "take out" their anger on a family member)

Projection
a defense mechanism that directs things a person doesn't like about themself toward someone else (e.g., a cheating spouse suspects their partner is being unfaithful)

Rationalization
a defense mechanism in which people justify unwanted feelings with seemingly logical explanations (e.g., a student who is rejected from their dream college may say they are happy to attend a school that's less competitive and more welcoming)

Reaction formation
a defense mechanism in which a person expresses an exaggerated, opposite version of how they actually feel

Regression
a defense mechanism in which an anxious individual retreats to an earlier stage of development (e.g., a first grader reverts to thumb sucking because they have anxiety about school)

Repression
a defense mechanism in which anxiety-provoking thoughts and feelings are forced to the unconscious

Sublimation
when a person redirects unacceptable feelings into a socially acceptable activity (e.g. after being fired, a person puts more effort into caring for their family)

Projective tests
personality assessments that present ambiguous visual stimuli to a person and asks them to respond with whatever comes to mind

Preconscious mind
Freud's term for memories that are not presently at the level of awareness but can accessed
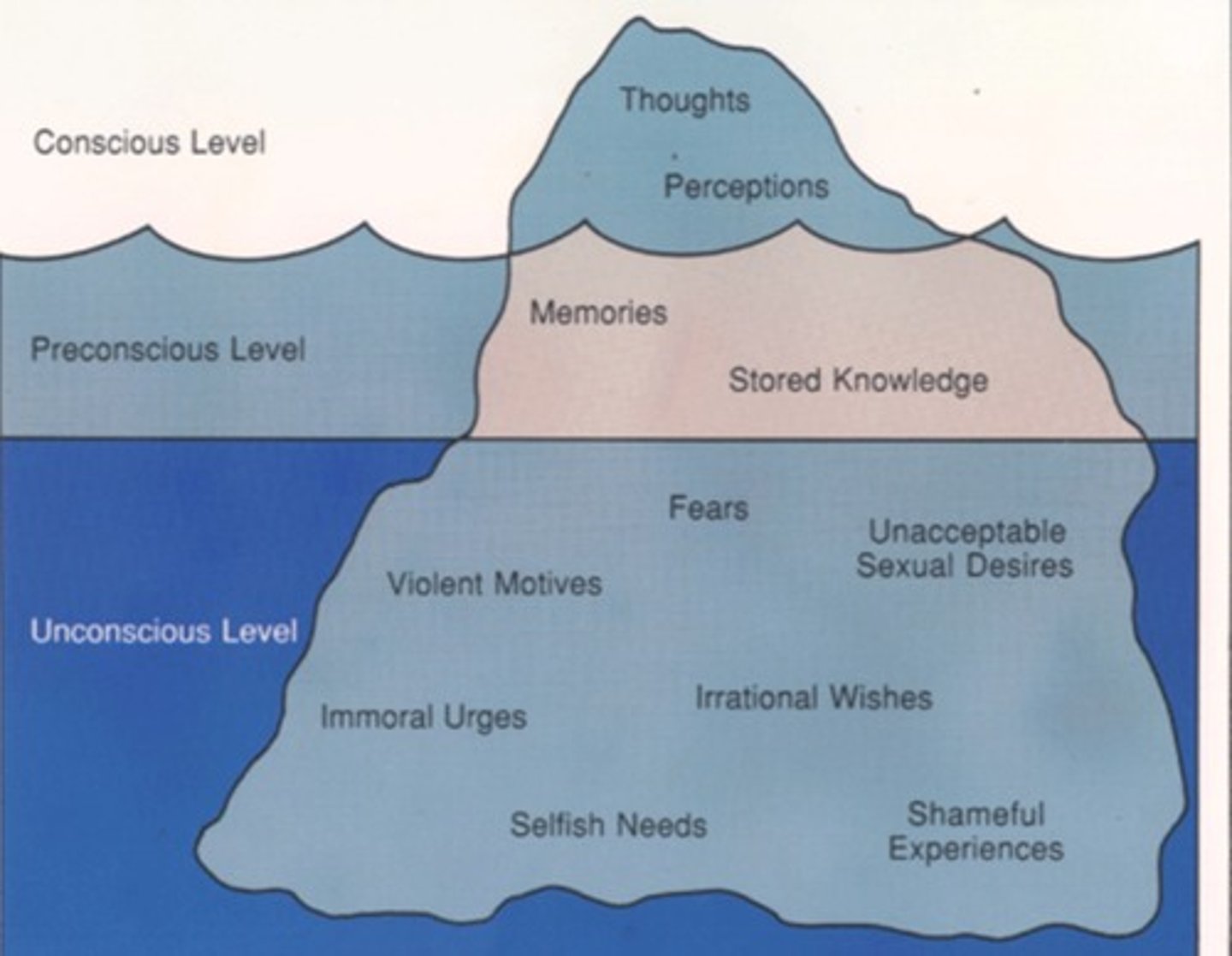
Unconscious mind
Freud's term for the thoughts, desires, and urges that are actively repressed from consciousness and that affect mental activity outside of active awareness

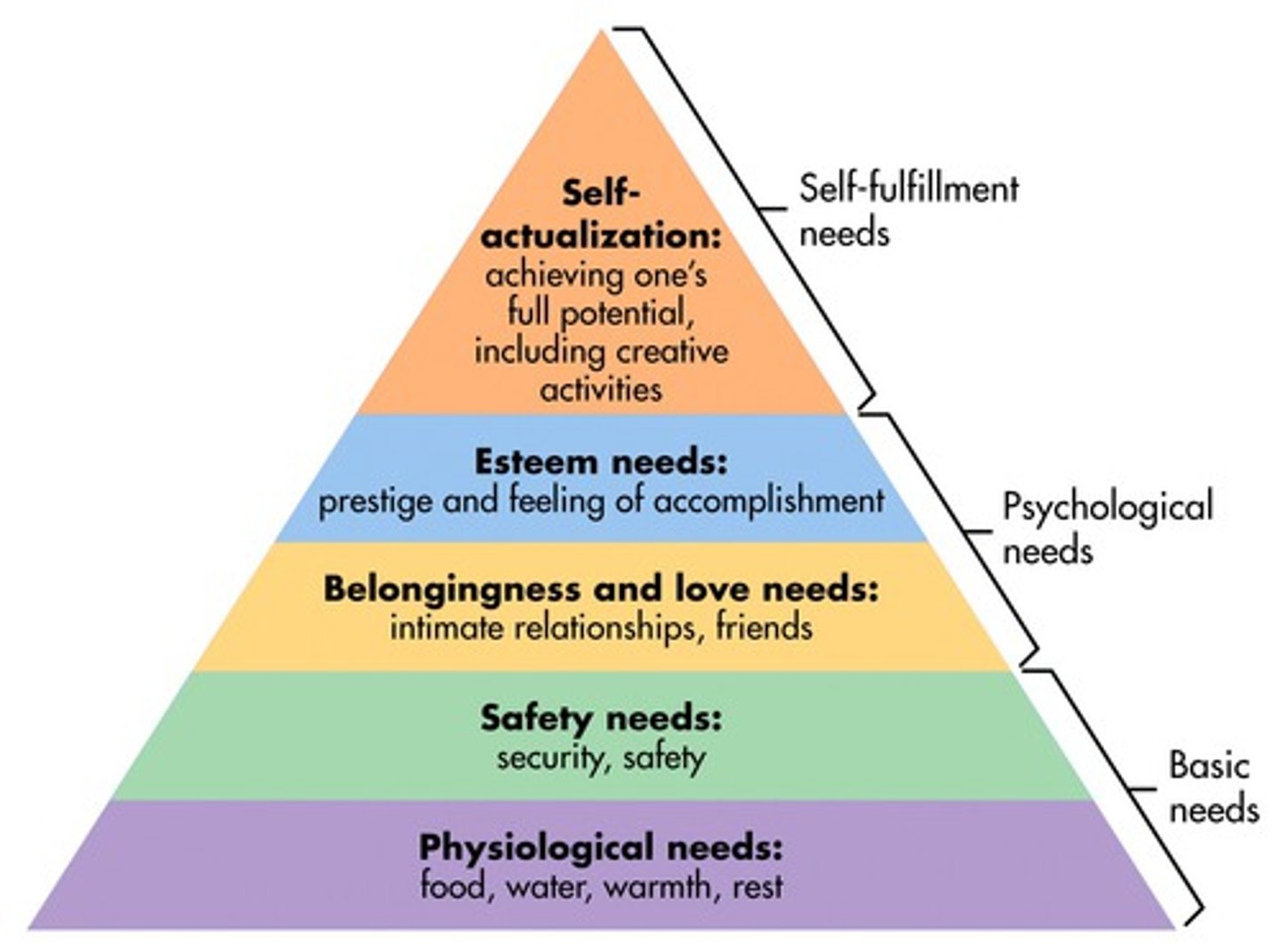
humanistic psychology
studies the whole person by looking at behavior through the eyes of the person doing the behaving with the goal of developing a healthy sense of self
Unconditional regard
a client-centered technique in which a therapist shows positive feelings and acceptance to the client, regardless of what the client says or does

Self-actualizing tendency
a desire that pushes a person to grow, to be creative, and to reach their full potential