Signal Detection Theory
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
What is signal detection theory? (very general)
psychological theory explaining how people detect stimuli in their environment
What is a signal in SDT?
refers to the true sensory information coming from external world
What is noise in SDT?
refers to various physiological and psychological processes influencing our perception of a signal (external stimulus) in an unpredictable manner
physiological noise could be spontaneous activity in sensory nerves
psychological noise could be spontaneous fluctuations in attention
noise = whatever is not measured + contributes to variability in participants’ responses
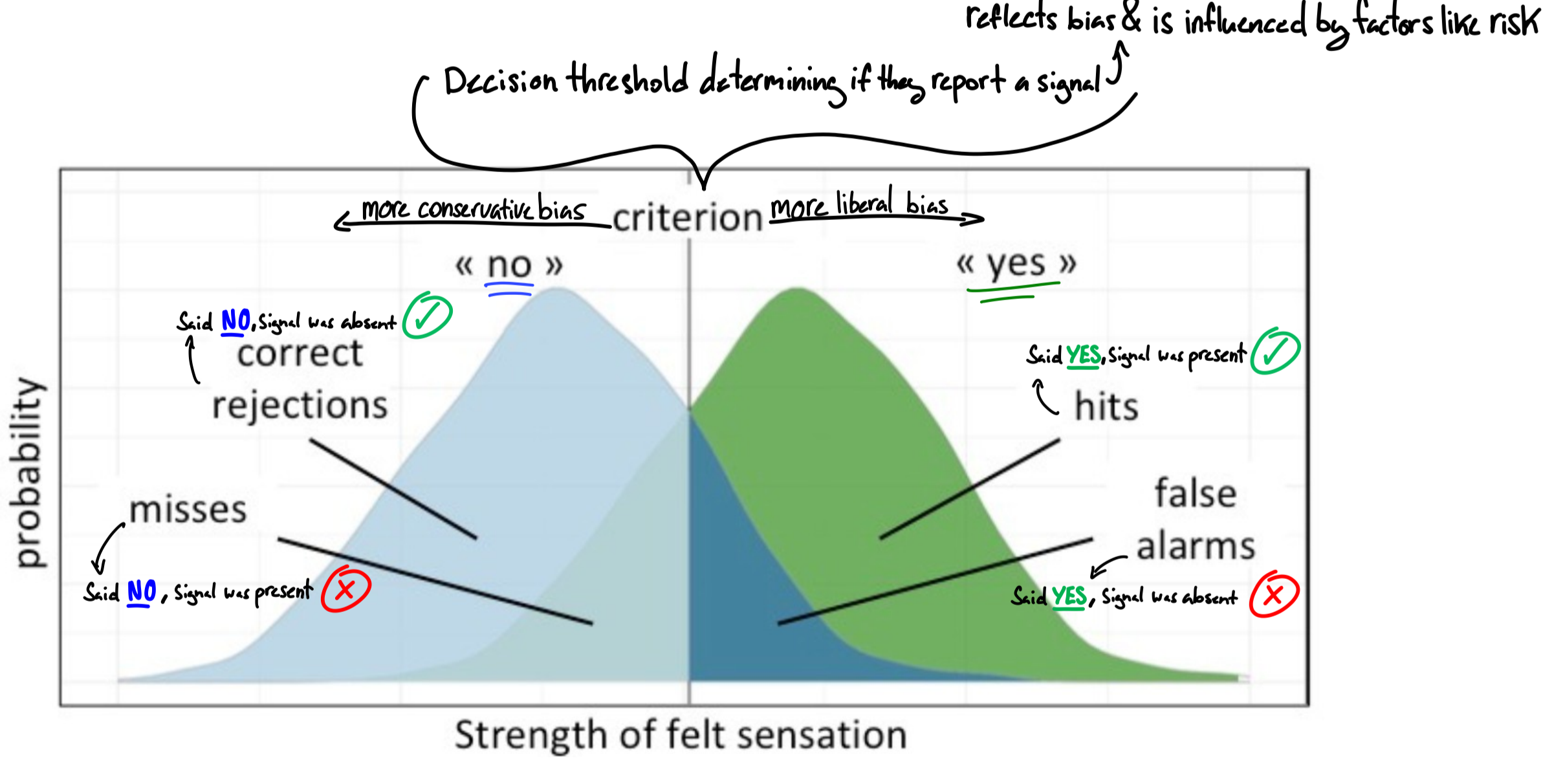
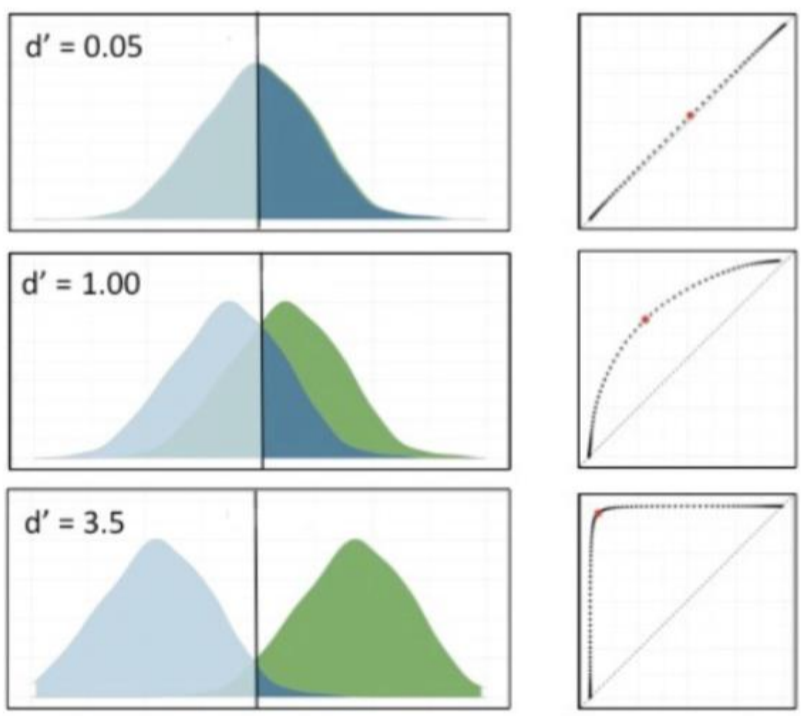
What is sensitivity (d’) in SDT?
individual's ability to distinguish between signal and noise (regardless of response bias)
reflets how well they can detect target stimulus
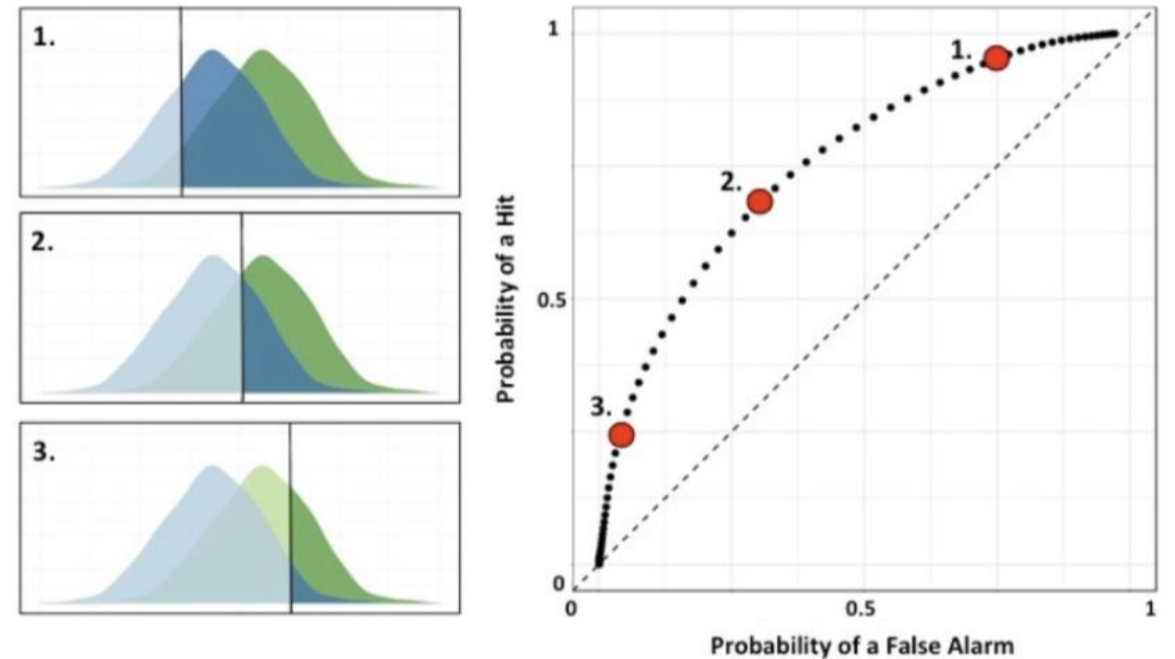
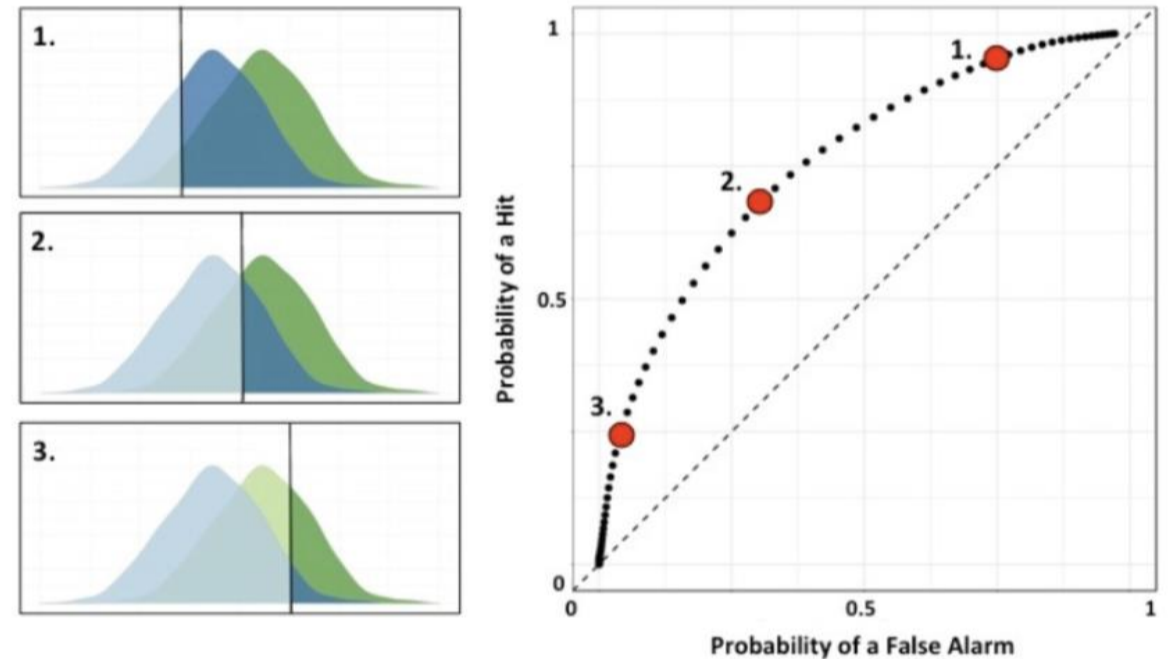
What is the criterion in SDT?
strength of felt sensation where an individual says yes vs no that they felt stimulus
determines an individual’s bias
(intensity required for them to report “yes”)
What is a more conservative bias?
more likely to withhold detections until certain they perceived
higher intensity needed to meet detection “criteria”
may occur when you lose something from false alarms
(minimizing false alarms rather than maximizing hits)
What is a more liberal bias?
more likely to report a detection
lower intensity needed to meet detection “criteria”
may occur when you lose something from misses
(maximizing hits rather than minimizing false alarms)
What is an ROC curve?
used to plot the probability of a hit / false alarm
criterion determines where points are on curve
sensitivity impacts shape of curve