Unit 3A 2: Microeconomic decision makers
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/19
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
1
New cards
Total cost
Total cost = fixed cost+variable cost
2
New cards
fixed cost + variable cost
**Fixed cost**: One of the costs that firms have to pay to work. Fixed costs are costs that are fixed no matter what the firm is producing.
* Rent
* employee salaries
**Variable cost:** The cost that varies depending on output. Depends on how much the firm is producing because it’s not always producing the same.
* Overtime payment to workers
* utilities depending on how much you produce.
* Rent
* employee salaries
**Variable cost:** The cost that varies depending on output. Depends on how much the firm is producing because it’s not always producing the same.
* Overtime payment to workers
* utilities depending on how much you produce.
3
New cards
how do sales affect revenue
Increased sales = increased revenue
4
New cards
objectives of firms
* Increase profits
* Eliminate competitors
* Achieve economies of scale
* Become a monopoly to control prices
* Eliminate competitors
* Achieve economies of scale
* Become a monopoly to control prices
5
New cards
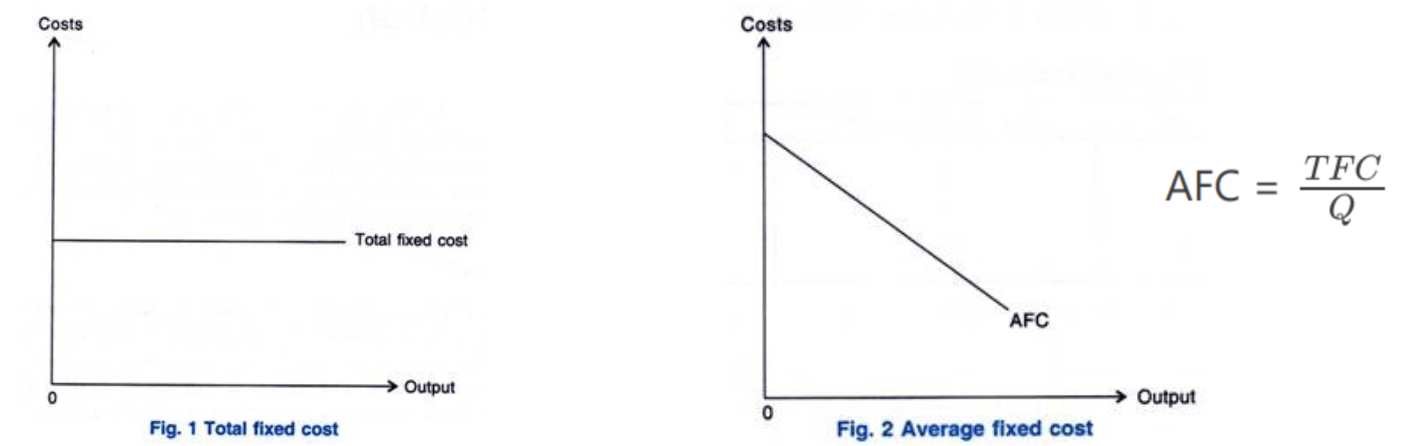
Fixed cost + average fixed cost diagram
For AVC fixed costs get smaller as output increases
6
New cards
Average revenue
Average revenue=price per product
7
New cards
profit maximisation
It cannot increase its profit by changing its output
8
New cards
Advantages of small firms
* More personal relationship with customers
* Easier to make changes due to feedback
* Can be very profitable with certain, personal services
* Easier to make changes due to feedback
* Can be very profitable with certain, personal services
9
New cards
Disadvantages of small firms
* Difficult to raise finance if needed
* Owners have a hard to taking holidays
* Difficult to get staff
* Owners have a hard to taking holidays
* Difficult to get staff
10
New cards
Internal growth
When firms grow slowly and use profit to increase market share and expand over time.
11
New cards
External growth
When firms carry out takeovers or mergers to rapidly increase size.
12
New cards
advantages + negatives of external growth
A: Gain knowledge and skills from the other firm, firms increase in assets, market share and income
N: Managers have to work harder, might not have enough experience, different working cultures
N: Managers have to work harder, might not have enough experience, different working cultures
13
New cards
advantages + negatives of internal growth
A:Allows owners to progress consistently and gain more knowledge about company, workers can be more committed if they are part of its growth for a long time
N: There might be limited resources to grow, takes longer, workers have little opportunity for promotion.
N: There might be limited resources to grow, takes longer, workers have little opportunity for promotion.
14
New cards
Mergers
A type of external growth, when two firms join together to increase market share, income and size.
15
New cards
Takeover
A type of external growth when a firm starts buying shares of another firm. If that firm buys more then 50% of the shares, it can carry out a takeover.
16
New cards
Horizontal integration
When two firms in an industry at the same stage of production join together. E.g if two bakeries join merge.
17
New cards
Vertical integration
When two firms of the same industry but in different stages of production join together. This can be v**ertical-backwards integration**, when a firm joins with a firm in an earlier stage, or **vertical forwards integration**, when a firm joins with a firm in a later stage.
E.g if an orange farm merges with a juice manufacturer, vertical forwards integration.
E.g if an orange farm merges with a juice manufacturer, vertical forwards integration.
18
New cards
Conglomerate integration
When two firms in different industries merge
19
New cards
Economies of scale
When a firm lowers its average total cost by increasing in scale. Firms are often able to increase their scale of production, when they do this they can lower cost and generate efficiencies.
20
New cards
Diseconomies of scale
When a firm increases its average total cost, while also increasing its scale of production. DOS’s are caused by miscommunication, lack of control and coordination.