English Lang-CLA-Theories
1/7
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Theories of Skinner's Behaviourism, Chomsky's LAD, Bruner's LASS, Vygotsky's Zones of development, Halliday's Functions of Language, Piaget's stages of language etc.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
Skinner’s Behaviourism Theory
consists of how language is attained through nurture, not nature. Talked of how behaviour/language use changed through resultant stimulus (praise or punishment etc). This theorist outlined some aspects of this, such as:
operant conditioning:
positive reinforcement
negative reinforcement
imitation
modelling
Chomsky’s LAD Theory
Short for Language Acquisition Device, this theorist believed that there is an innate understanding of the rules of language in a child’s mind right from the beginning. Proofs of this were:
Stages of children all occur at a similar time
There is a similar pattern of CLA across different cultures
Children learn language quickly and effortlessly
Deaf children may take up their own form of language
Virtueous errors where grammar rules etc should be applied, are shown by children-noone taught them these rules
The SV (subject-verb) form of sentence is innately used by children when making their own language
Overall, he believed in nature over nurture.
Bruner’s LASS Theory
short for Language Acquisition Support System (also a linguistic joke with the LAD and LASS), this theorist suggested that language is both innate, and learned through support from others. his main points for nurture were:
scaffolding
joint attention
CDS (child-directed speech) such as exaggerated intonation, slower tempo, simplified vocabulary
feral children show near to none of the understanding of language
this theory could be considered a joint of LAD and Behaviourism.
Piaget’s Cognitive Development Theory
This theorist believed that language walked hand in hand with cognition. He believed in 4 stages of development:
Sensorimotor stage: newborn-2yrs, learn to use 5 senses, reflexes, don’t know object permanence
Preoperational stage: 2-5yrs, egocentric, learn symbolic play, categorised thinking, imagination,
Concrete Operational stage: 5-10yrs, less egocentric, learn logic, cognitive operations and can only handle concrete situations
Formal Operational stage: 11+ yrs, can handle theoretical situations/thinking, have advanced grammar, Learn abstract ideas such as identity, philosophy, success and failure
note: those of formal operational stage do not often appear in transcripts
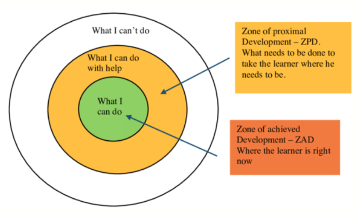
Vygotsky’s MKO Theory
short for More Knowledgable Other, this theorist challenged Piaget and believed that another more experienced individual could help to speed up the process of CLA. A similar view to that of LASS, he believed in 3 zones of development.
ZAD: Zone of Achieved Developmant
ZPD: Zone of Proximal Development
ZDD: Zone of Desired Development
Halliday’s 7 Functions of Language Theory
This theorist believed that there were 7 functions of language for CLA:
Instrumental: language used to fulfill a need: ‘mummy, want food’.
Regulatory: language used to demand action: ‘give ball!’
Interactional: language used to develop relations: ‘love you mummy’
Personal: language used to express personal thoughts: ‘he did naughty thing’
Heuristic: language used to explore something or a running commentary of what the child is doing: ‘what’s that?’
Imaginative: language used to tell a story, or relay events currently happening: ‘then train fall down(.)then(.)oh no(1)train fall down(.)’
Representational: language used to relay/request info: ‘granny sitting down’
Grice’s Maxims and Lakoff’s Politeness Principle
This theorist believed that there were certain maxims to be adhered to when in conversation. This can be used to show which stages of these children in the transcript are at. They are as follows:
Maxim of Quantity: information given should be neither too much or less
Maxim of Manner: one sould be clear and unambiguous
Maxim of Quality: one should not lie in conversation
Maxim of Relation (relevance): one should talk relevantly to the current topic
Another theorist also added to these maxims, regarding politeness. They are as follows:
Maxim of Tact: one should be polite and respect others in conversation
Maxim of Generosity: one should minimise self-benefit
Maxim of Approbation: one should minimise criticism of others
Bernstein’s Elaborated and Restricted Code Theory
This theorist believed that two types of code are used:
Restricted Code: context mentioned which only close family/friends would know
Elaborated Code: context given in a more general manner so everyone understands
He also dicussed the concepts of a context-board, which related to the context of a particular situation and code-switching, which is to switch one’s syntax of speaking