2024: We the People Chapter 2 and 3
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
House of Representatives
the lower house of Congress, consisting of a different number of representatives from each state, depending on population. Must be 25 elected for 2 year terms.
The United States Senate
The upper house of Congress. Composed of 100 members, 2 senators are elected from each state for 6-year terms
Commerce Clause
The clause in the Constitution (Article I, Section 8, Clause 1) that gives Congress the power to regulate all business activities that cross state lines or affect more than one state or other nations.
Necessary and Proper Clause
Constitutional clause that gives congress the power to make all laws "necessary and proper" for executing its powers aka as the elastic clause.
expressed or enumerated powers
specific powers granted by the Constitution to Congress (Article 1, Section 8) such as: Coin money, declare war, etc..
Implied Powers
Powers inferred (not written down) from the express powers that allow Congress to carry out its functions. (such as create a draft because they have the expressed power to create an army and navy)
Anti-federalists
Opponents of the American Constitution. Their greatest fear was that a strong national government would infringe on the liberties of the people.
French and Indian War
Caused the British to raise taxes on the colonists due to the debt they had accumulated
Stamp Act
an act passed by the British parliament in 1756 that raised revenue from the American colonies by a duty in the form of a stamp required on all newspapers and legal or commercial documents
Sugar Act
law passed by the British Parliament setting taxes on molasses and sugar imported by the colonies
American Revolution Cause
There were many but ultimately increasing the taxes on the colonists led to them declaring their independence
Articles of Confederation
America's first written constitution; had a one house congress only. Primarily concerned with limiting the powers of the national government.
Articles of Confederation weaknesses
No Executive and Judicial branches, lacked power to tax and regulate trade, could be amended only with a unanimous vote, states had all the power
Shay's Rebellion
Convinced many people that the government under the Articles of Confederation had become dangerously inefficient and indecisive.
Confederation
an alliance of independent states
Bicameral
Two house legislature
Bill of Rights
the first 10 amendments to the constitution; they ensure certain rights and liberties to the people.
checks and balances
mechanisms through which each branch of government is able to influence the activities of the other branches
consent of the governed
People are the source of any and all governmental power
The Constitution
Created a federal system of government.
Article I: Let's-Legislative
Article II: Eat-Executive
Article III: Jolly-Judicial
Article IV: Ranchers-Relations among states
Article V: And-Amendment
Article VI: Some-Supremacy Clause
Article VII: Reese's-Ratification
Article I of the Constitution
Establishes Congress as the legislative branch of the Federal Government and lists the powers of Congress.
Article II of the Constitution
establishes the executive branch of the federal government, which carries out and enforces federal laws
Article III of the Constitution
creates only the Supreme Court and allows Congress to establish lower courts.
Article IV of the Constitution
STATES: each state has to recognize laws, records and rulings of other states. Respect people from other states while in their state.
Article V of the Constitution
describes the process for amending the Constitution (2/3rds of both houses must propose and 3/4th of state legislatures are needed for ratification)
Federalism
Division of power between the federal government and the states. The United States was the first nation to adopt federalism as its governing framework.
Federalists
those who favored a strong national government and supported the Constitution

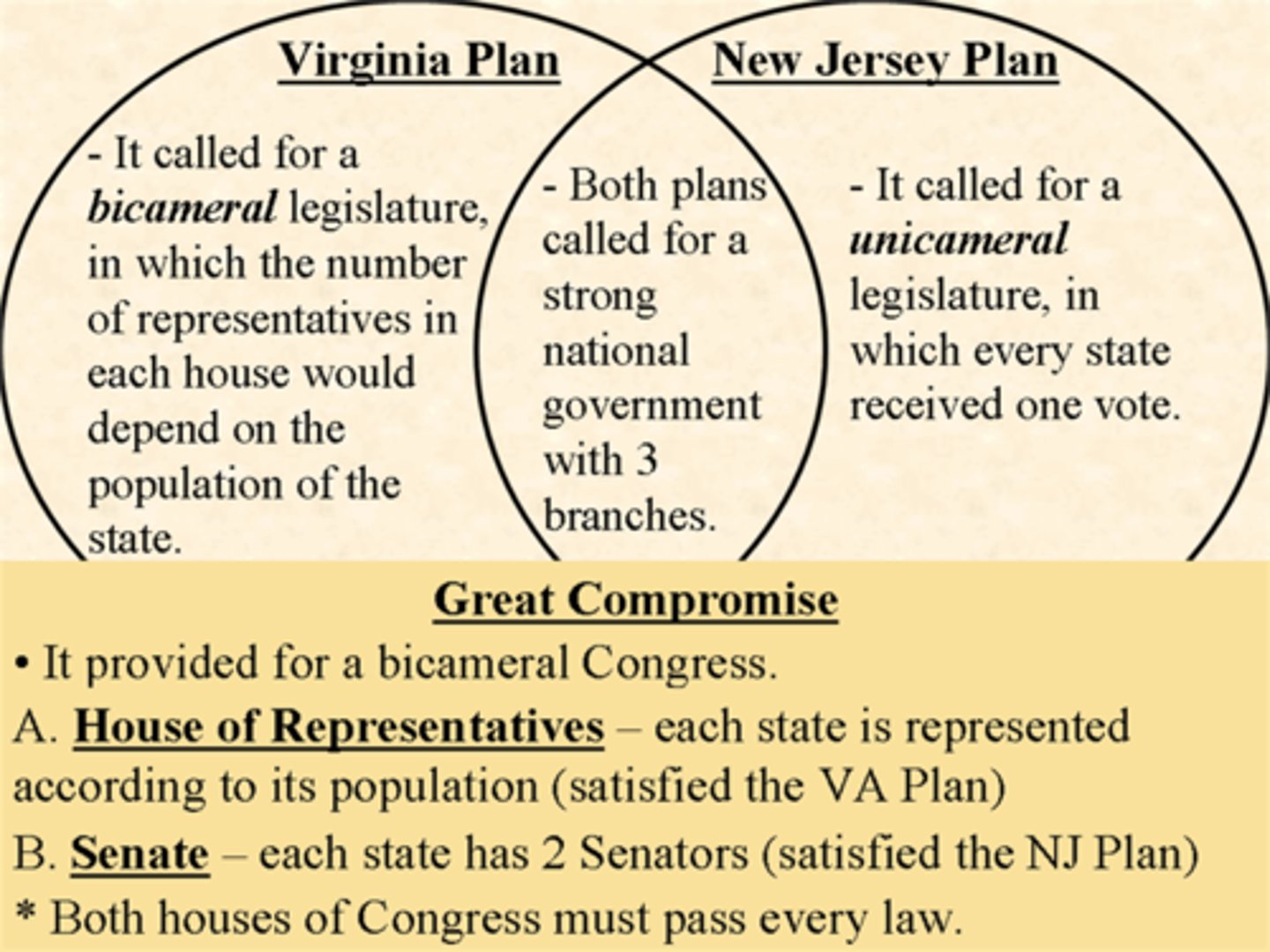
Great Compromise (Connecticut Compromise)
the agreement reached at the Constitutional Convention of 1787 that gave each state an equal number of senators regardless of its population, but linked representation in the House of Representatives to population
Constitutional compromises
two houses, electoral college
New Jersey Plan
The proposal at the Constitutional Convention that called for equal representation of each state in Congress regardless of the state's population.
Virginia Plan
Constitutional plan that called for representation in Congress to be based on a state's population
Declaration of independence
Breakup with a list of all the things King George had done to the colonists; defined rights of colonists and all humans. It was a political document because it explained why the colonists rebelled against Great Britain and sought self-government. It was philosophical document because it included "unalienable rights" which are Life, Liberty, and the pursuit of happiness.
Natural rights
Rights inherent in human beings, not dependent on governments, which include life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness.
John Locke
English philosopher who argued that people have natural rights (life, liberty and property) ideas and thoughts copied by the founders. Believed that the main purpose of government is to protect our natural rights.
Thomas Hobbes
Advocated the idea of a limited government
Barron Montesquieu
His discussion of separation of powers and checks and balances profoundly influenced the American Founders and the design of the U.S. Constitution.
concurrent powers
authority possessed by both state and national governments, such as the power to levy taxes
Full Faith and Credit Clause
Constitution's requirement that each state accept the public acts, records, and judicial proceedings of every other state
Defense of Marriage Act
1996 (Bill Clinton) Declares that states are not obligated to recognize any same sex marriages that might not be legally sanctioned in other states, also defined marriage and spouse in heterosexual terms for federal law as well.
Judicial Review
The power of the courts to declare laws unconstitutional
Windsor vs US
Ruled section 3 of the Defense of Marriage Act unconstitutional.
Obergefell v. Hodges
Ruled section 2 of Defense of Marriage Act unconstitutional. In addition legalized gay marriage in every state (example of judicial activism)
Privileges and Immunities Clause
Part of Article IV of the Constitution guaranteeing that the citizens of each state are afforded the same rights as citizens of all other states, helps prevent discriminating against non-residents. Exception: tuition
grants-in-aid
federal money provided to states to implement public policy objectives
categorical grants
Federal grants for specific purposes, such as building an airport. Can come with strings by requiring states to meet a certain criteria
unfunded mandates
Programs that the Federal government requires States to implement without Federal funding. (Americans with Disabilities Act, NCLB, Clean Air Act, Motor Voter Act)
Devolution
the transfer of powers and responsibilities from the federal government to the states
block grants
federal grant that allows states considerable discretion in which the funds are spent
The Welfare Reform Act
An example of devolution, giving states the authority to determine how to implement Welfare Programs and determine eligibility locally.
Supremacy Clause
Article VI of the Constitution, which makes all laws made under it superior to any state laws
What amendment established the reserved powers?
10th Amendment
1st Amendment
Freedom of Religion, Speech, Press, Assembly, and Petition
2nd Amendment
Right to keep and bear arms
3rd Amendment
No quartering of soldiers
4th Amendment
Freedom from unreasonable searches and seizures
5th Amendment
Criminal Proceedings-Double Jeopardy; Protection from Self incrimination (right to remain silent)
6th Amendment
The right to a Speedy Trial by jury, representation by an attorney for an accused person
Recall election
a special election called by voters to remove an elected official before his/her term expires.
Initiative
a process that allows citizens of many U.S. states to place new legislation on a popular ballot
Referendum
A state-level method of direct legislation that gives voters a chance to approve or disapprove proposed legislation