A&P Exam 2: Chapter 6 The skeletal system (unfinished)
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
functions of skeletal system
support, protection (skull, vertebrae, rib cage), allows movement, stores minerals (CA+P) and fat (yellow bone marrow), hematopoeisis (blood cells & platelets produced in red bone marrow)
tendons
band/cord of dense regular CT. connects muscle to bone. contain bundles of collagen fibers & have few nerves/blood vessels
ligaments
dense regular CT. connects bone to bone. contain bundles of collagen fibers & have few nerves/blood vessels
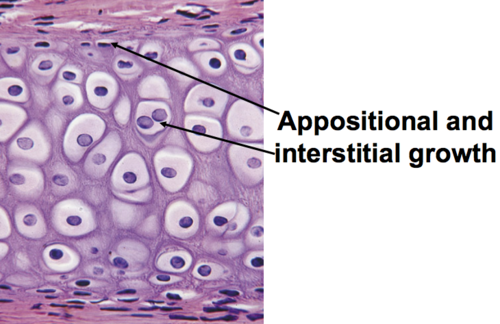
appositional growth
the process by which bones increase in diameter through the addition of new bone tissue matrix/cells to the OUTSIDE/surface
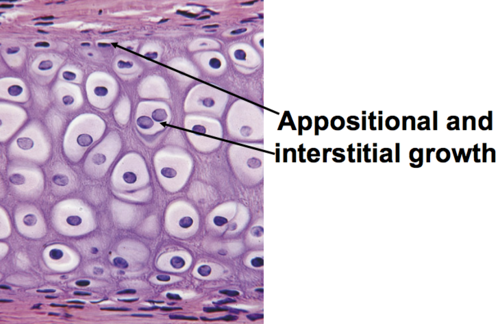
interstitial growth
the process by which bones increase in length. cells within tissue divide & add more matrix from the INSIDE
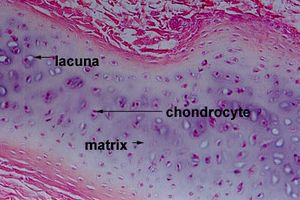
hyaline cartilage
chondroblasts turn into chondrocytes which are found in the lacuna. grows by appositional&interstitial growth. matrix consists of collagen (provides flexible strength) and proteoglycan (traps water & provides resiliency/strucural support. returns to original shape after compression.) found on articular surfaces. is replaced by bone in fetal skeleton. avascular (diffusion through matrix occurs to get nutrients).
Bone
classified by shape
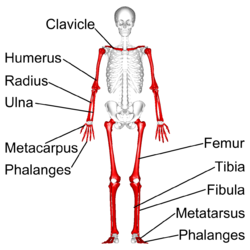
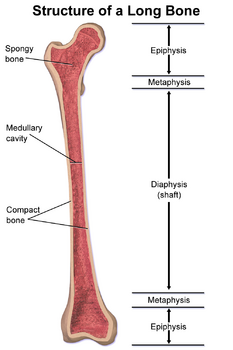
long bone
femur. metacarpals, metatarsals, phalanges.
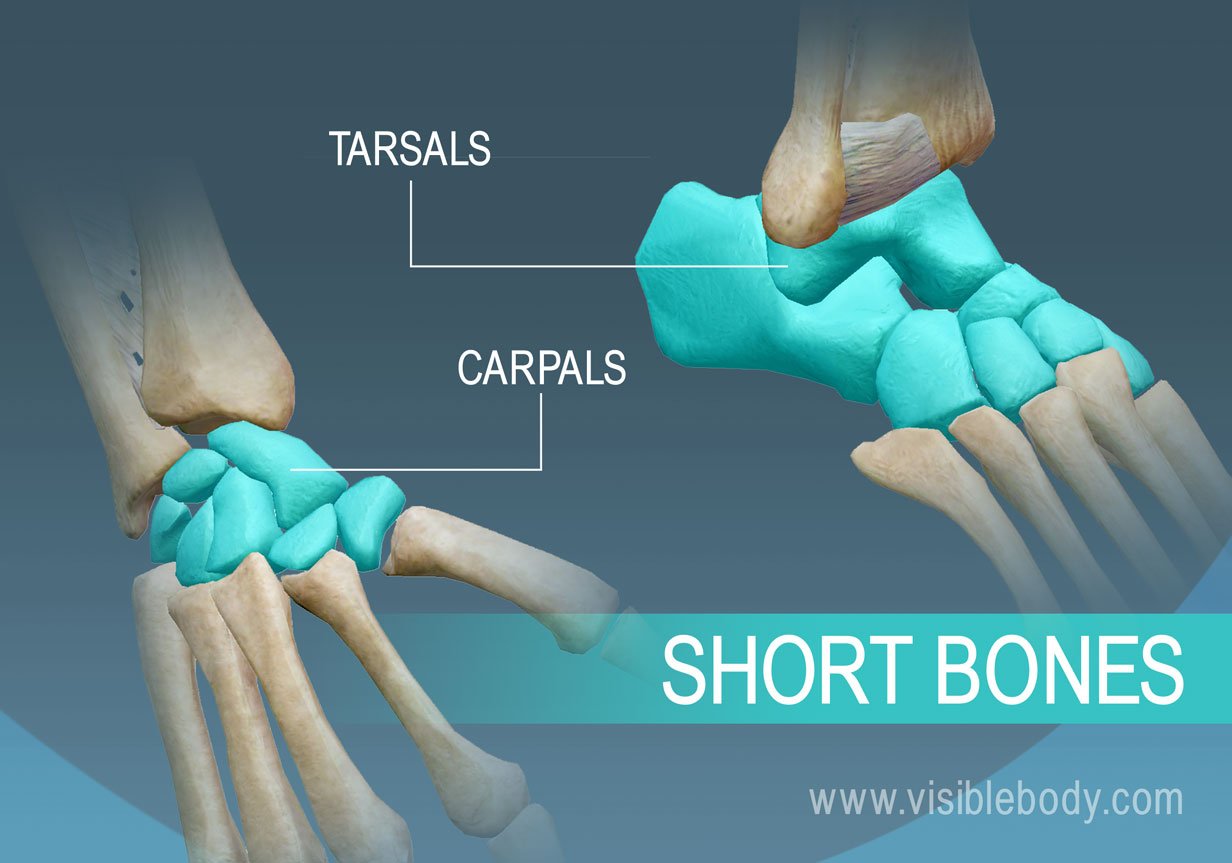
short bone
carpals & tarsals
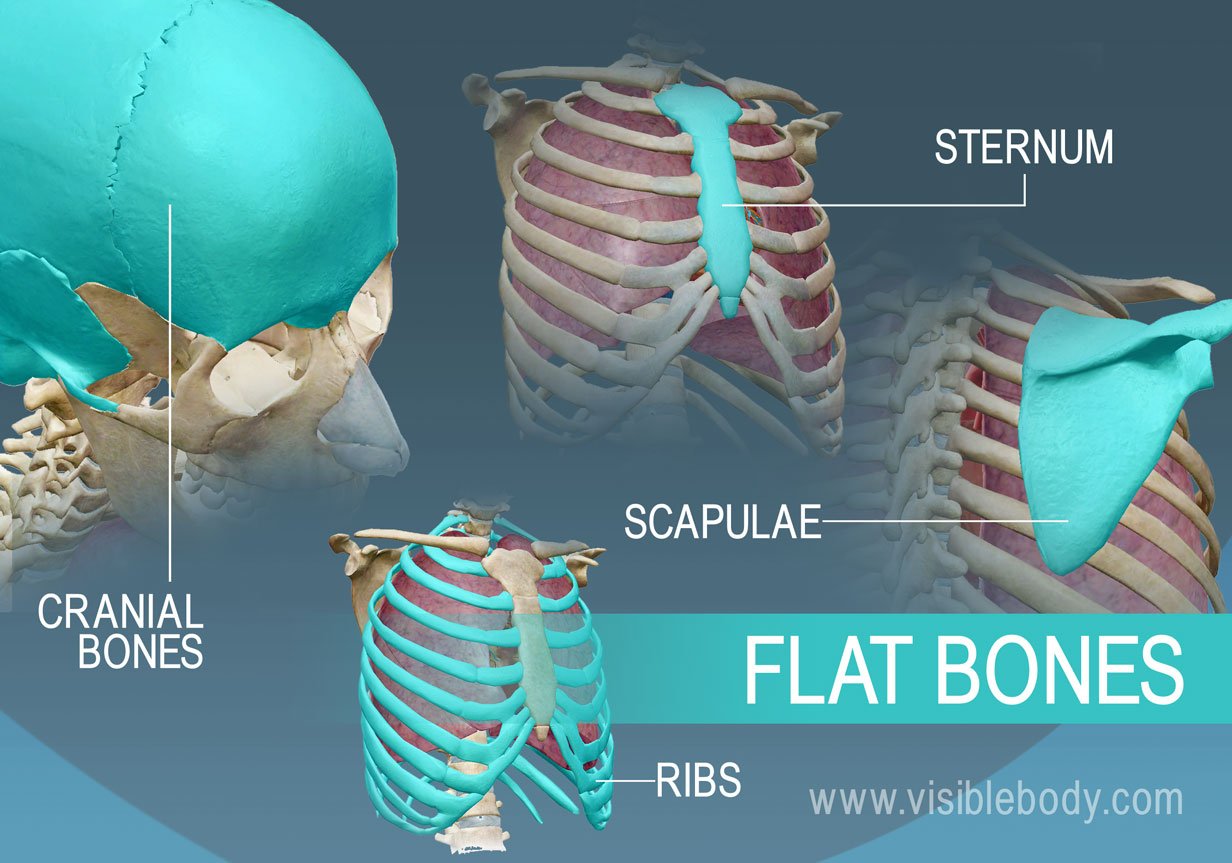
flat bones
skull, ribs, sternum
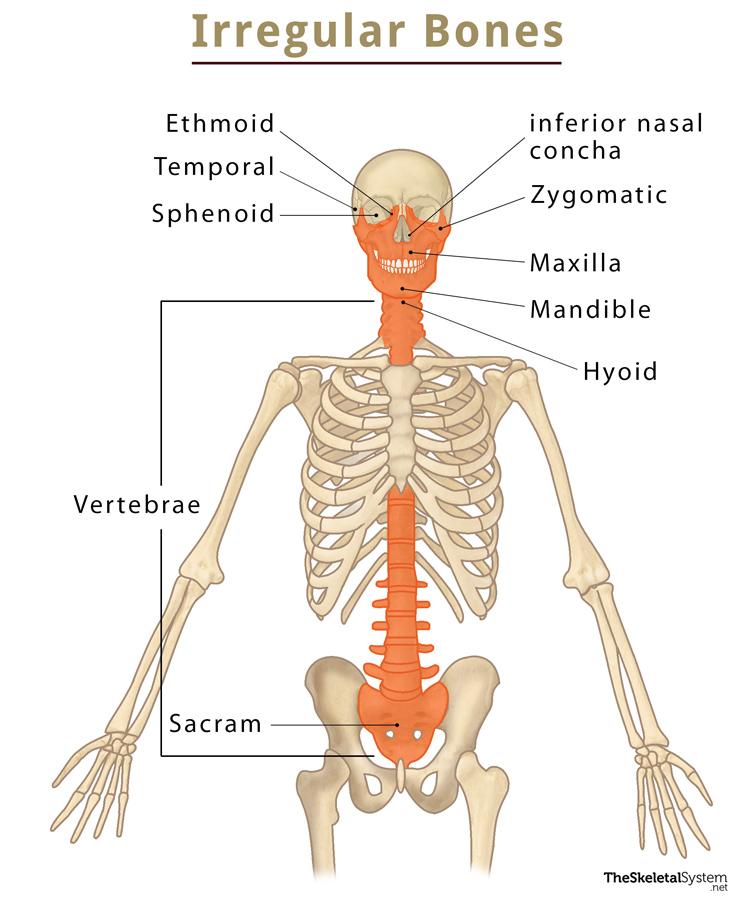
irregular bones
vertebrae, sphenoid, facial bones, sacrum
bone matrix
35% organic, collagen for flexible strength (mechanical strength) & proteoglycan for regulization of homeostasis&organization of ECM. 65% inorganic, hydroxypatite (CA+P) for hardness & weight bearing strength (compressive strength)
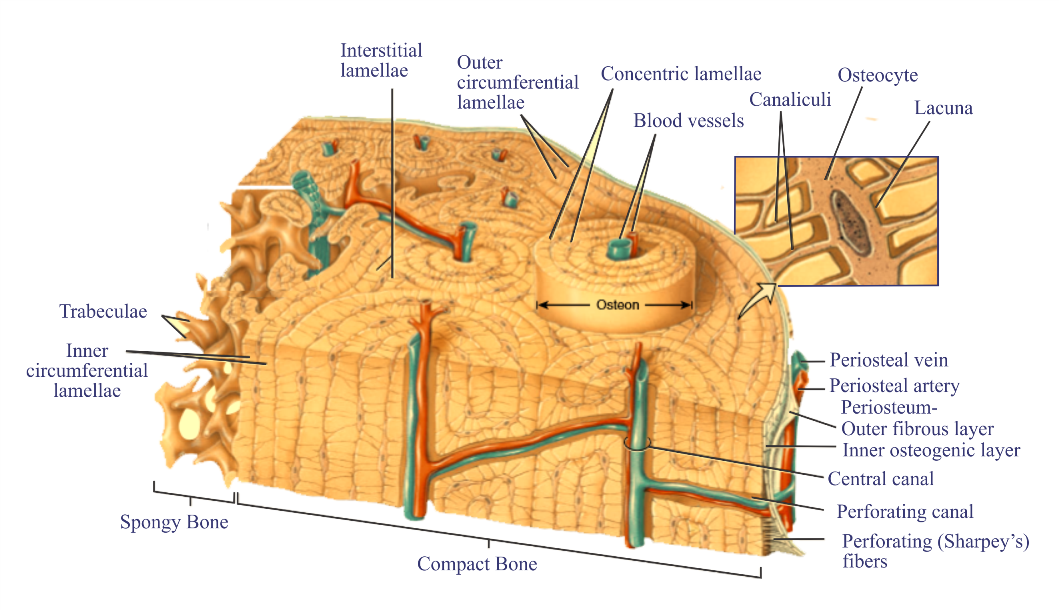
concentric lamellae
layers of lamellae that surround haversion canal
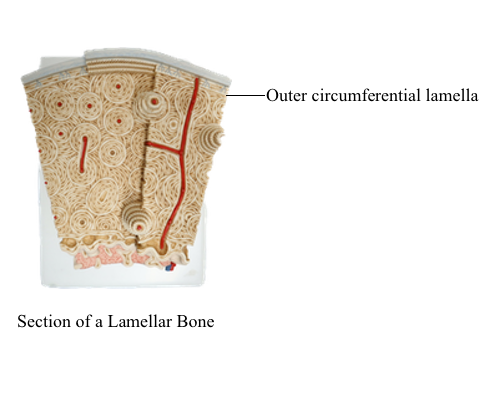
circumferential lamellae
layers of lamellae that wrap around the periosteum & endosteum.
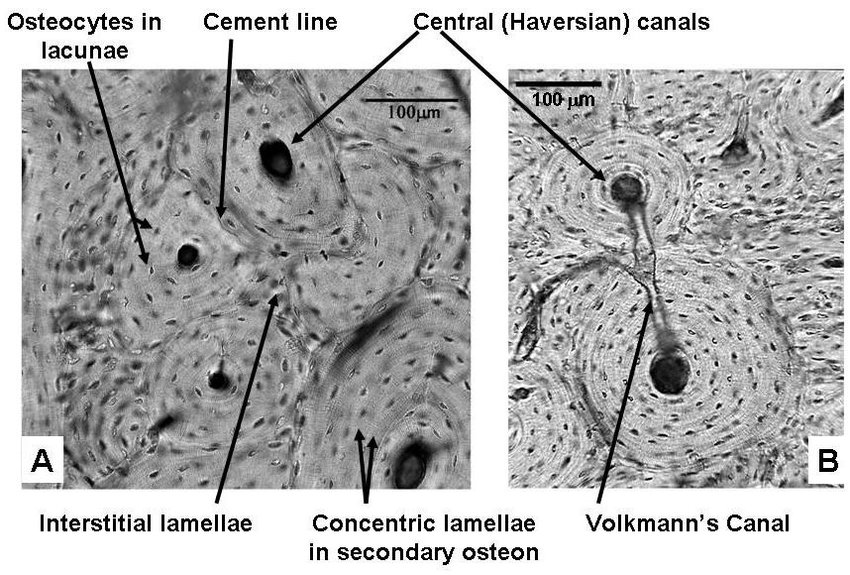
interstitial lamellae
irregular shaped bony plates BETWEEN OSTEONS.

periosteum
doubly layer of dense fibrous CT. site of growth in diamter. inner layer has osteoblasts.
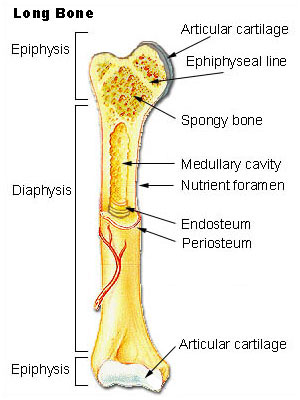
endosteum
lines medullary cavity. contains osteoblasts.
cortical bone
dense bone arranged into osteons. found in diaphysis & covering cancellous bone.
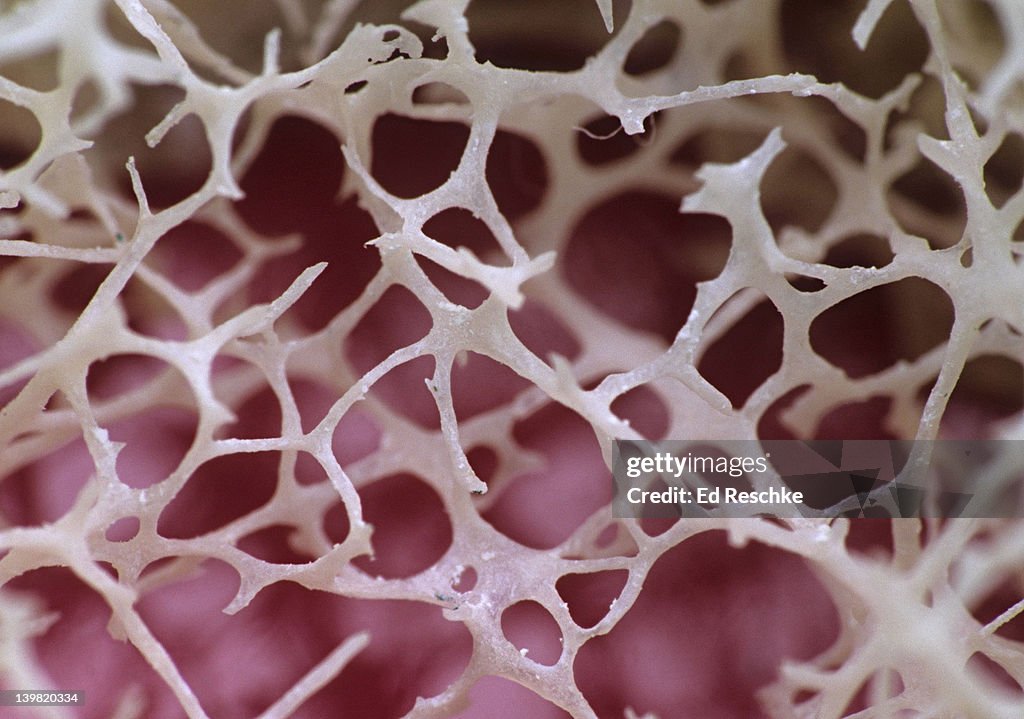
red bone marrow
found within trabeculae. site of hematopoeisis (blood cell production.
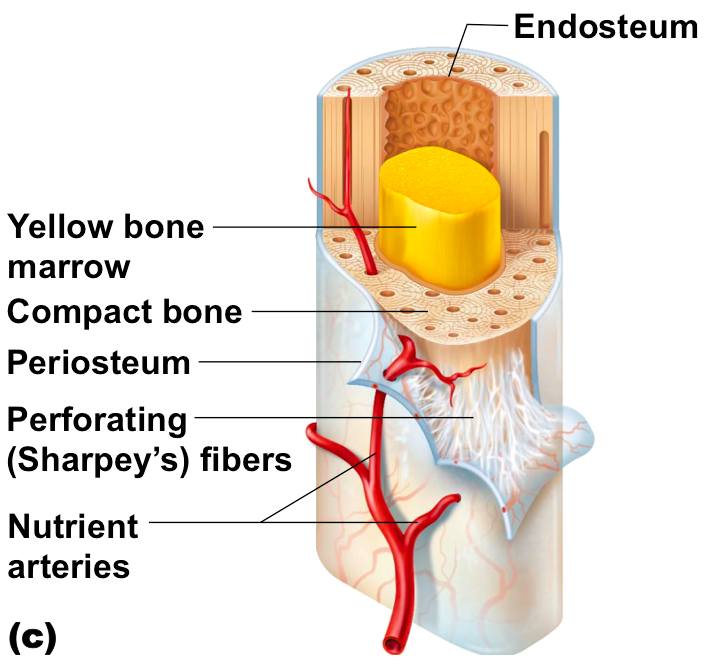
yellow bone marrow
fat stored within medullary cavity
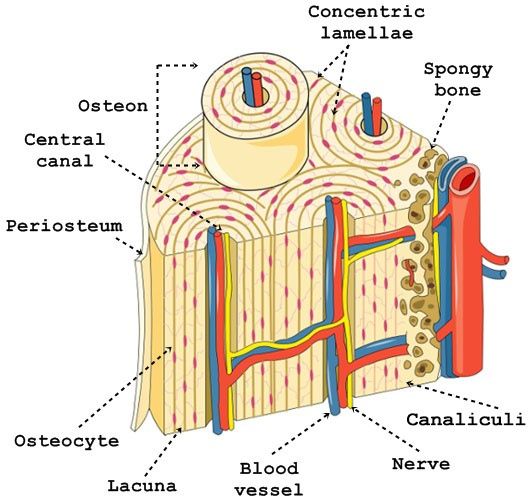
canaliculi
connects osteocytes in lacuna. communicate the change from osteoblasts or osteoclasts. communication, supply nutrients, & remove waste.
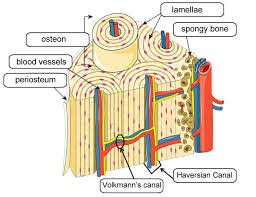
volkmann’s canal
connects osteons. allows blood to travel up into haversion canal.
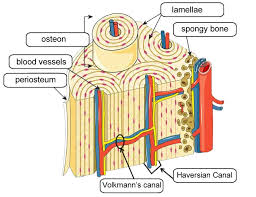
haversion canal
contains blood vessels&nerves.
ossification
process of bone formation. osteoblasts produce organic & inorganic matrix. intramembranous&endochondral ossification form both cancellous and cortical bone.
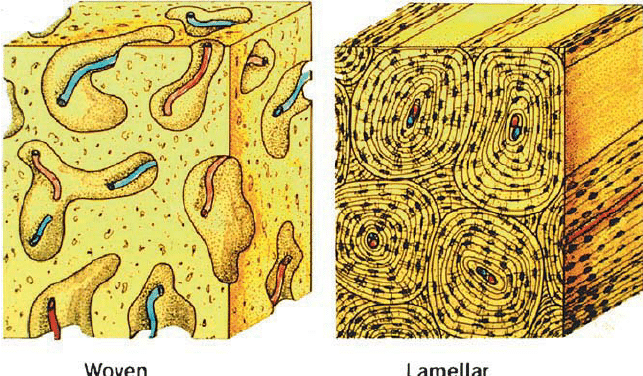
woven bone
immature bone. collagen fibers are orientated in different directions. it is eventually replaced by lamellar (mature) bone with organized collagen fibers AKA remodeling.
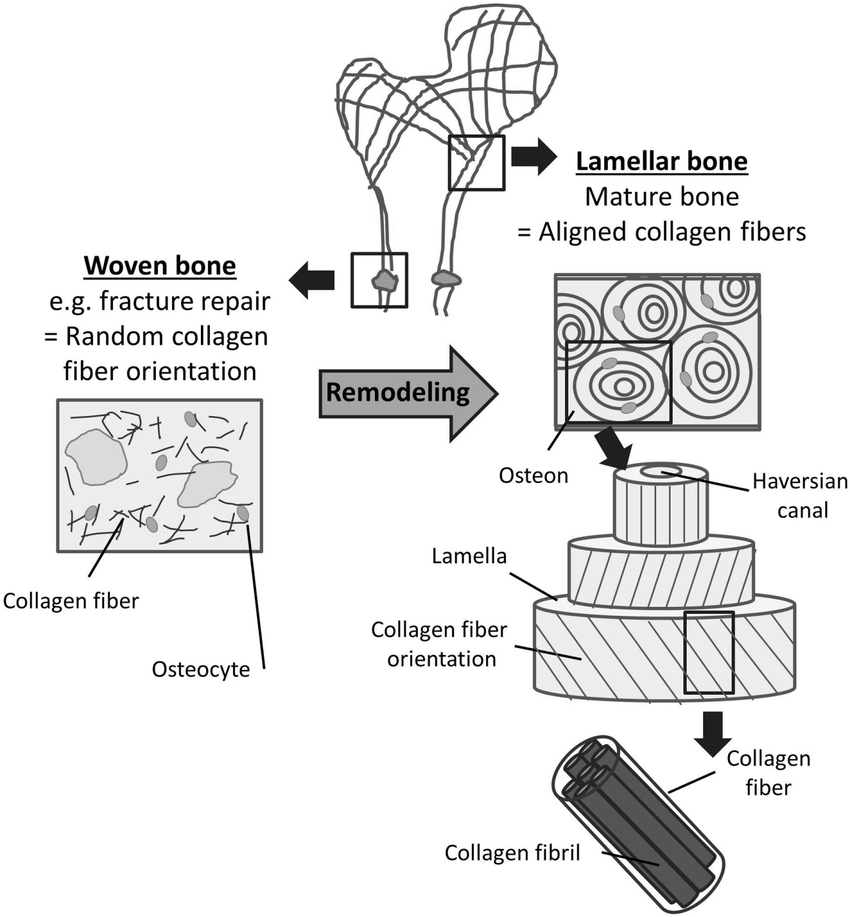
lamellar bone
have collagen fibers facing opposite directions to adjacent lamellae in order to distribute weight
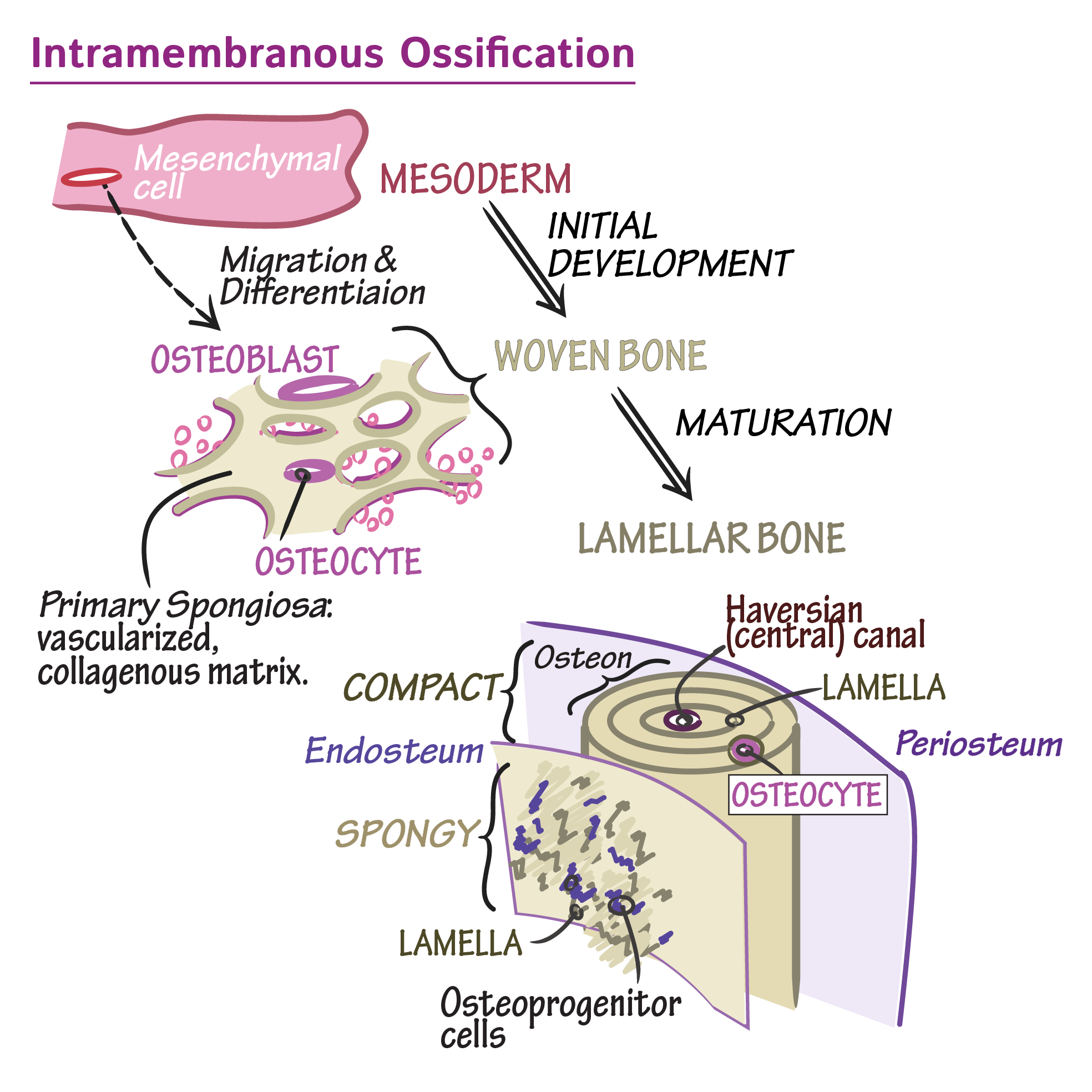
intramembranous ossification
results in flat bones. takes place in CT. occurs within membranes. osteoblasts produce cancellous bone. beneath periosteum, osteoblasts lay down cortical bone to form outer cell.
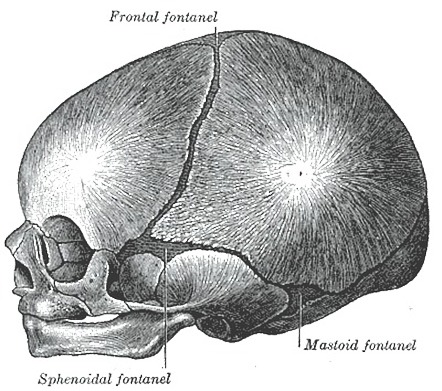
fontanels
“soft spots”. regions of incomplete intramembranous ossification (cortical bone hasn’t formed yet) in fetal/newborn skull.
endochondral ossification
produces long bones. bones develop from within a cartilage model/template, cartilage is then calcified&dies which forms spongy bone, cortical bone is formed beneath periosteum, primary ossification forms in diaphysis during fetal development, secondary ossification forms in epiphysis which forms epiphyseal plates.
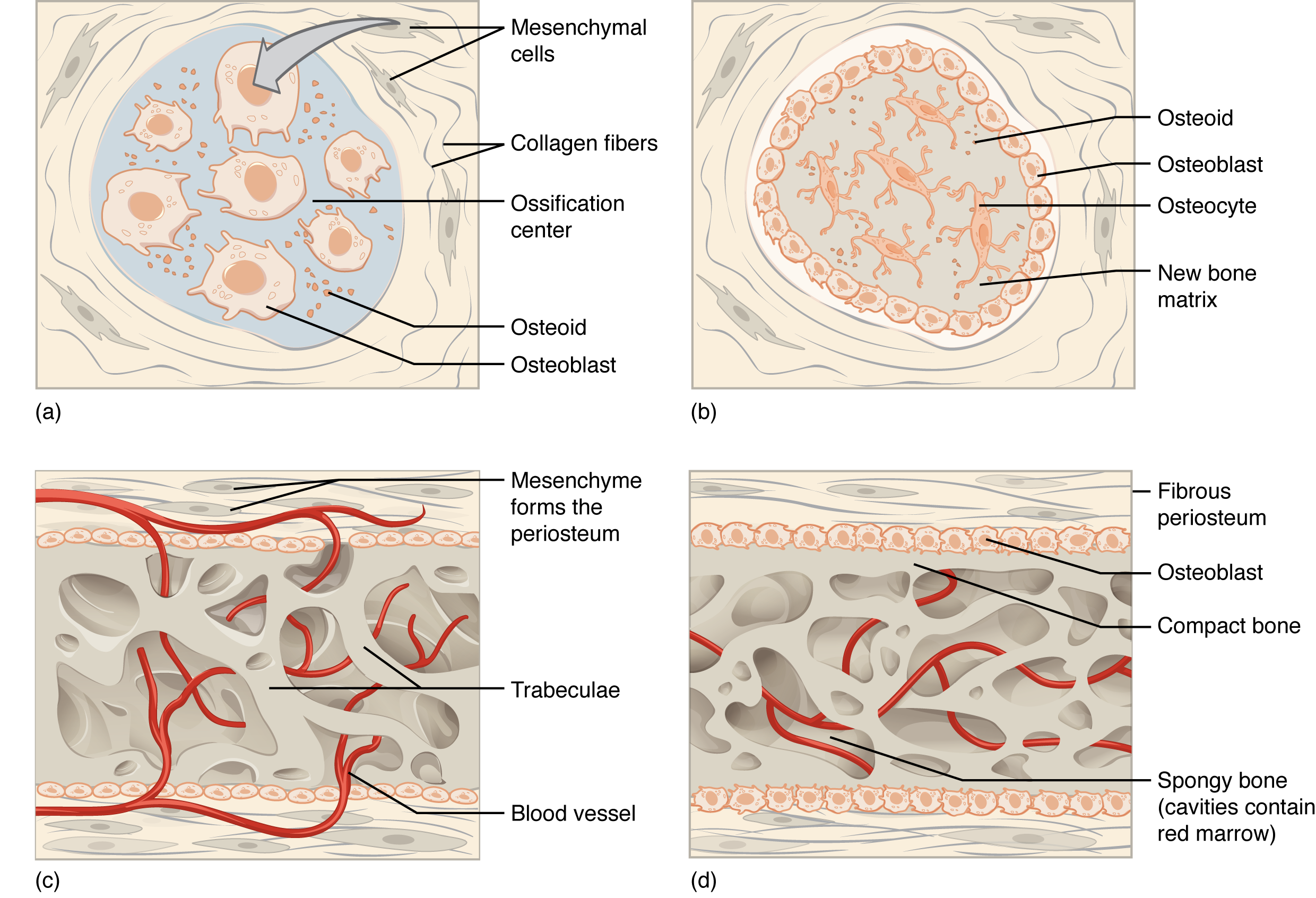
cancellous bone
formed when osteoblasts form bone on calcified (dead) cartilage
when do epiphyseal plates close completely?
between 18-21 years of age, no more vertical growth is possible
bone growth
grows by either appositional or endochondral process (not interstitial)
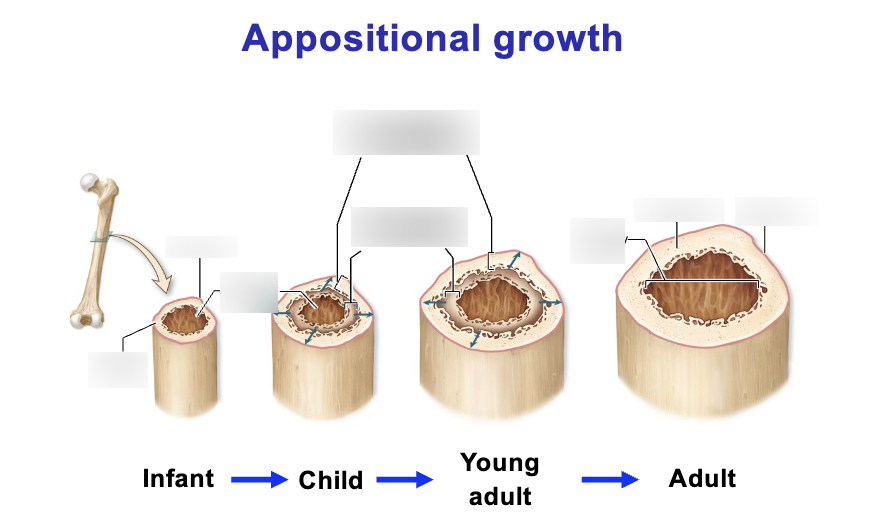
appositional bone growth
increases DIAMETER of long bone. is responsible for most growth of other bones. osteoblasts on the surface of the bone divide and become surrounded by matrix which causes them to become osteocytes in lacuna
endochondral bone growth
increases LENGTH of long bone at epiphyseal plates. articular cartilage ossifies (is replaced by bone). interstitial growth of hyaline cartilage within epiphyseal plate occurs (new cartilage forms), cartilage cells become calcified&die and are replaced by bone (AKA endochondrial ossification)
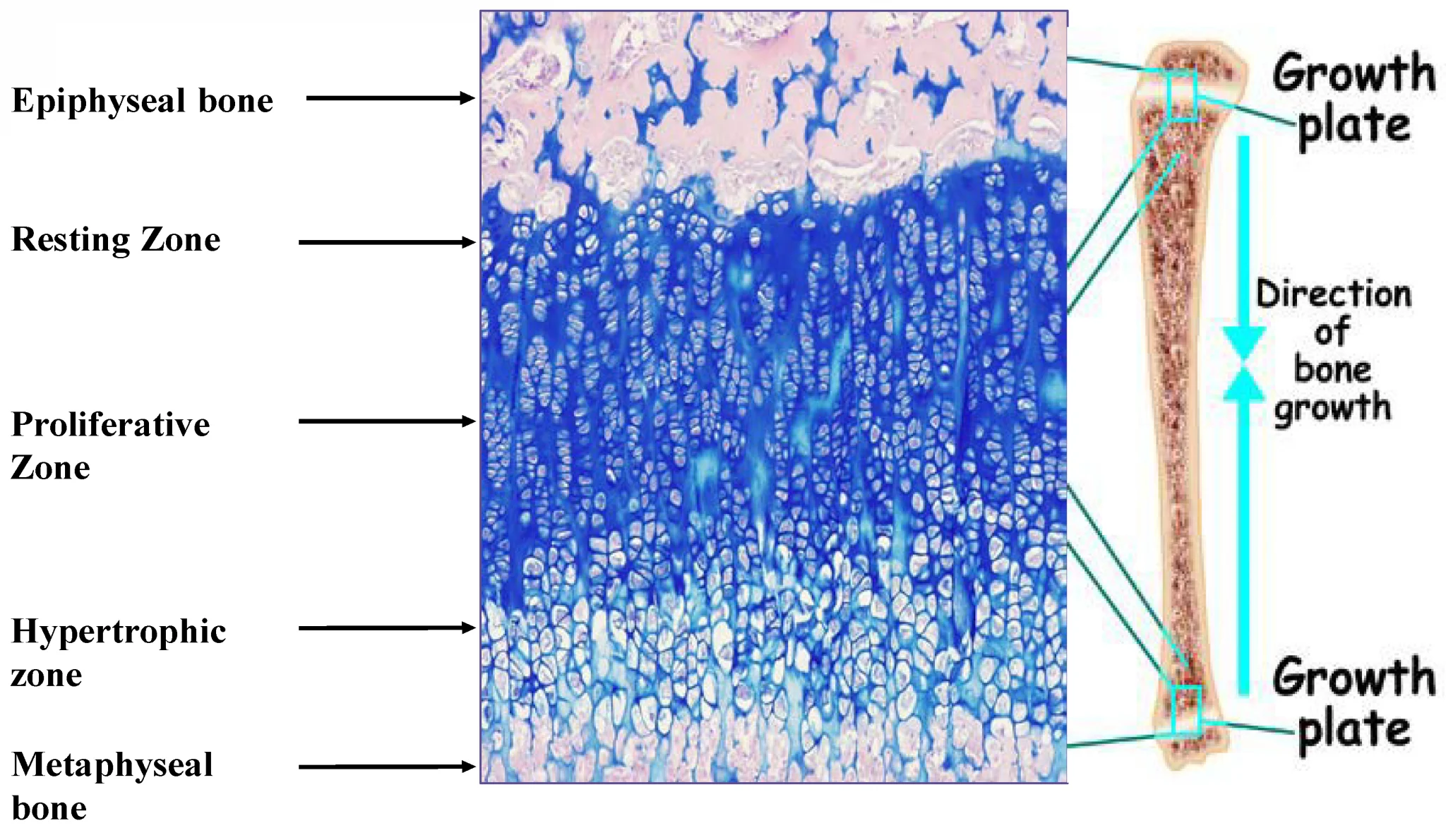
zones of epiphyseal plates
distinect regions in epiphyseal plates where cartilage proliferates, matures & calcifies, allowing for bone elongation.
zone of resting cartilage
slow dividng chondrocytes
zone of proliferation
chondrocytes divide mitotically & form stacks of cells, causing new cartilage to be produced on the epiphyseal side of the plate. stacking cells increase length.
zone of hypertrophy
mitosis ends. chondrocytes mature & enlarge.
zone of calcification
matrix is calcified & chondrocytes die.
factors affecting bone growth
vitamin D- important for calcium absorption
vitamin C- important for collagen synthesis
hormones- GH (pituitary gland), T3 & T4 (thyroid gland)
Calcium homeostasis
2 hormones that help regulate calcium concentration in. Parathyroid hormone and calcitonin