science weathering and soils unit
1/101
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
102 Terms
Porosity
amount of open space in a rock
Amount of Cement
the more cement between the particles the less pore space
sorting
well sorted soils have more pore space than unsorted soils
fracturing
Bedrock with more fracture or cracks has more pores than bedrock without many cracks
equal volumes of sorted sediment
has equal pore space
Permeability
ability of water to flow through a soil
impermeable
the inability of water to flow
what does permeability depend on?
soil composition
large particles
-More Permeable
-Water flows easily from space to space
small particles
-Less Permeable
-Its hard for water to find a path through the soil
sorted particles
-More Permeable
-Plenty do open spaces that connect to each other
unsorted particles
-Less permeable
Small particles fill up the spaces leaving little room for water to move
capillarity
the ability of water to rise in small openings
mass movement(gravity)
unsorted/angular
wind causes what type of sorting?
sorted/rounded
waves
sorted/rounded
what are glaciers?
thick masses of ice that form over thousands of years
valley glacier
ice that flows down mountain valleys at high latitudes
ice sheet
ice that covers a large region where the climate is extremely cold
plucking
Frost Action loosens blocks of rock and the glacier then lifts them away
Abrasion
the ice slides over the rocks like sandpaper
striations
scratches left on the bedrock as the glacier moves over it
deposition due to glaciers results in
random arrangement
angular sediments
U-shaped valley
ice carves a wide valley pushing everything in its way
kettle lake
small lake formed when a chunk of ice becomes dislodged and then melts
glacial erretic
large boulders dropped by melting ice
till
unsorted sediments left behind from a glacier
moraine
ridges of till
drumlin
an oval shaped mound of till
erosion
picking up sediment
depositional
putting down sediment
erosion with equal deposition is called
dynamic equalibrium
five major agents of erosion
gravity
wind
waves
glaciers
running water(streams)
What is mass movement(gravity)
the transfer of rock and soil in a downward slope due to gravity
what causes mass movement to happen?
water-heavy rains or melting snow over
saturates the surrounding surface materials with water
deposition due to gravity leaves behind…
unsorted and angular rock fragments
deflation
the lifting or removing of small loose particles
abrasion
wind blown sand blasts exposed rock smoothing and polishing them
wind erosion is more effective in
desert locations(arid=dry)
wet sediment
heavier
dry sediment
easier to pick up
graded bedding
large particles are dropped first then smaller particles
deposition by wind results in
small, sorted particles
waves along the shoreline are constantly
weathering
eroding
and depositing sediment
deposition due to waves is
sorted(large to small) and rounded
time- the more time a rock is exposed
the more weathering will occur
surface area- the more surface area a rock has exposed
the more weathering will occur
a solid rock has the least surface pressure
the interior is protected
a ground up rock has greatest surface area- exposed
the interior can now be attacked
mineral composition
a minerals hardness determines its resistance to weathering
types of climate weathering
physical, chemical
factors that affect weathering
climate and surface area
weathering
the break down of rock at or near earth’s surface
sediments
smaller pieces of rock that have undergone weathering
when does weathering occur in rocks?
when the rocks are exposed to air or water
chemical weathering
the breakdown of rock through a charge in mineral or chemical composition
chemical weathering increases in
warm and moist climates
oxidation(type of chemical weathering)
when iron combines with O² to make rust
another name for water is “blank” because it can resolve almost anything
universal solvent
what does water combine with for form carbonic acid?
CO²
carbonic acid can blank most rocks
dissolve
sinkhole
a natural depression in a land surface formed by the collapse of a cavern roof
physical weathering
the breakdown of rock into smaller pieces without chemical change
abrasion(type of physical weathering)
occurs when rock particles grind against rock
frost action(frost wedging)
weathering process caused by cycles of freezing and thawing of water in rock openings
infiltration
the process which water seeps into soil or rock
plant root growth(root action)
as plants grow they can also spread cracks apart even farther
what happens to rocks when temperatures increase
rocks expand and fracture
humus
part of the soil that serves as a source of plant nutrients
streams erode their channels which does what to loose particles?
lifts loose particles
the stronger the current
the more erosional power it has
capacity
the maximum load a stream can carry
stream deposition
streams deposit sediment in a sorted pattern. largest particles settle out first, smallest particles settle out last
hydrosphere
all water on plant earth
water cycle
the constant movement of water among the oceans, the atmosphere, the solid earth and the biosphere that does not stop or end
evaperation
the process of converting liquid water to a gaseous form in the environment
transpiration
the release of absorbed water by plants into the atmosphere
condensation
water vapor changing back into liquid water clouds are formed by condensation
precipitation
droplets join together until they are too heavy. any form of water that falls from a cloud
infiltration
the movement of surface water into rock or soil through cracks and spaces.
run off
water that does not infiltrate flows over the land into rivers and lakes
saturated
filled to capacity, can’t hold more
unsaturated
not filled, can hold more
permeable
having pores or openings that permit liquids or gases to pass through
impermeable
not permitting passage (as of a liquid)
larger particles drop
first
smaller particles drop
last
maximum velocity occurs on the blank of channel bends
outside
minimum velocity occurs on the blank of bends
inside
straight section
stream bed is symmetrical
highest speed in direct center
left meander
steeper on the left(erosion)
gentle on the right(deposition)
faster in the center of the deepest location
right meander
steeper on the right(Erosion)
gentle on the left(deposition)
faster in the center of the deepest location
deposition occurs as
stream flow decreases
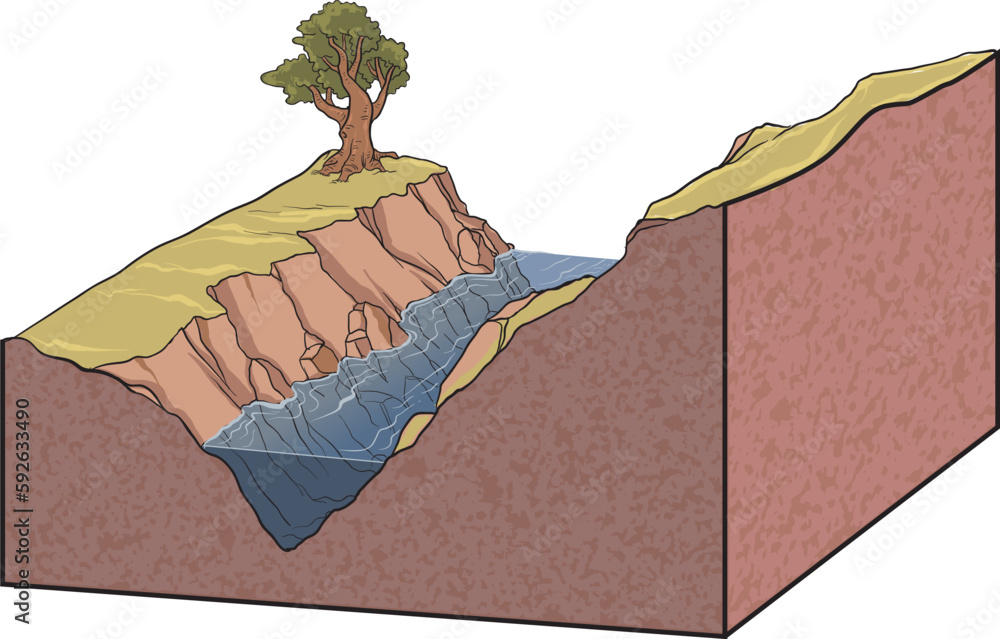
V-shaped Valley
a narrow v-shaped valley shows that a stream primarily cuts down toward the base level
common features are rapids and waterfalls
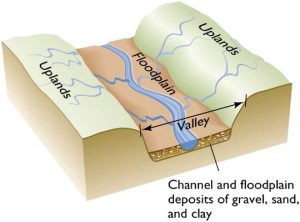
floodplain
a wide valley is created when a river erodes the banks of its stream channel
this side to side cutting creates a flat valley floor
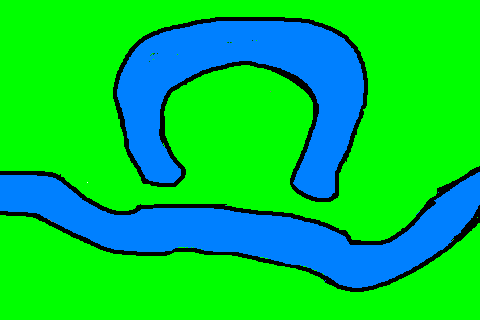
oxbow lake
most erosion occurs on the outside of the meander
when deposition cuts off these bends an oxbow lake is formed