Unit 2: Lecture 11: Neurophysiology Pt 2
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
Graded Potentials
temporary, short lived localized change in the RMP
Caused By Stimulus
Localized= does not travel far from site
Goal: Axon Hillock reaches threshold at -60 mv to fire AP
Strength varies in magnitude depending on stimulus

Local Potentials
Neurons stimulating another neuron
ligand/ions bind to a chemical regulated channel
Physical shape changes in a mechanical gated channel
small local disturbances in MP
Characteristics of a Local Potential
Graded
Decremental
Reversible
Excitatory/Inhibitory
Graded
Strength varies in magnitude depending on stimulus
open more channels
length of opening
Decremental
Signal weakens the further it travels
Distal from the axon hillock as it works towards the axon hillock
Reversible
Removal of signal can restore RMP
Excitatory/Inhibitory
Open Na+ channels will EXCITE; Depolarize
Open K+ channels will INHIBIT; Hyperpolarize
Depolarization
Na+ moves into the cell
Raises MP to approx -60 mv
Makes cell more (+)
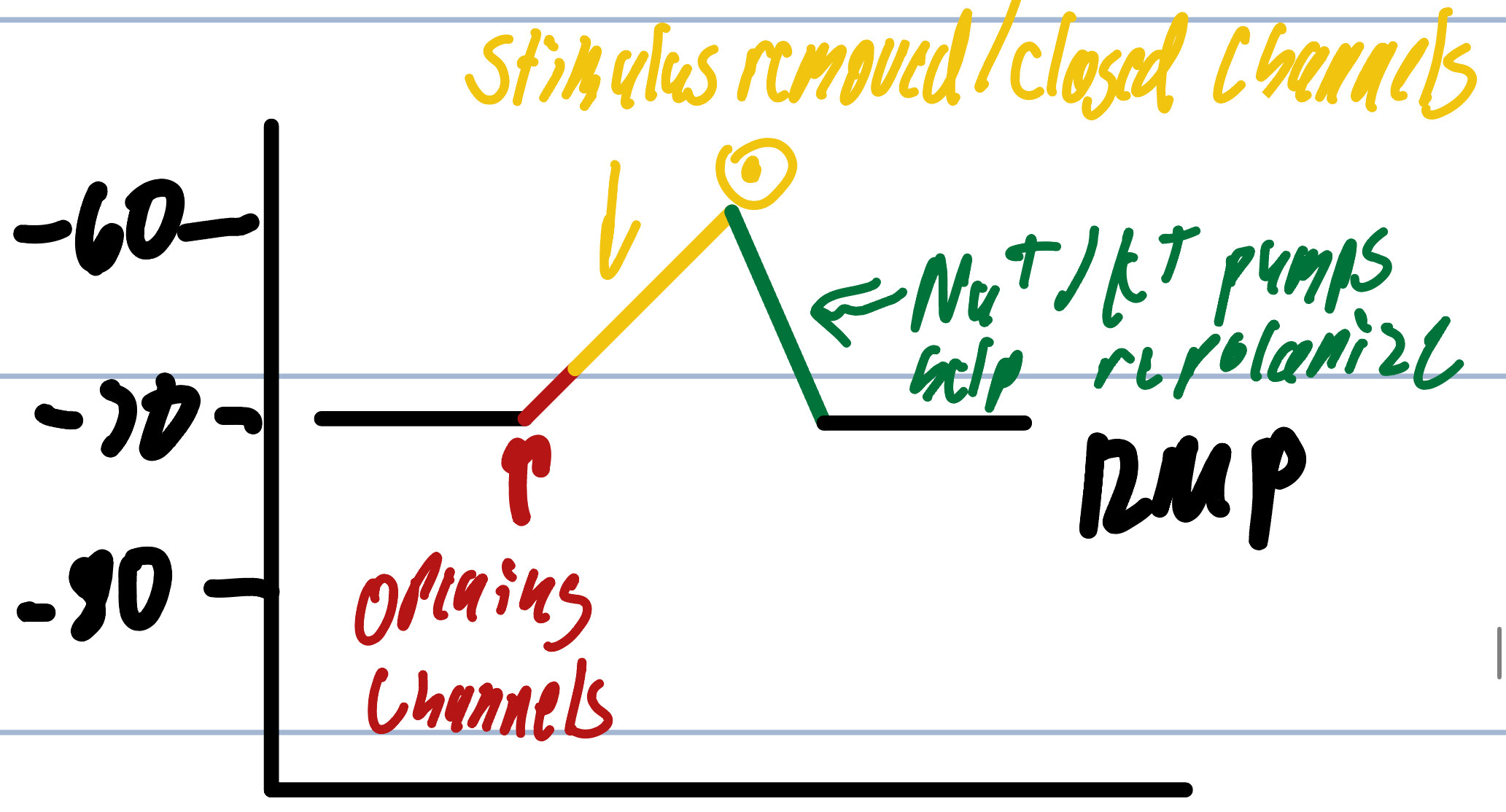
Steps for Depolarization
1. Na+ gated channels open due to stimulus
2. Flow of Na+ ions enter cell and causes MP to increase since gate is open
3. Na+ gated channels close once stimulus is removed
4. Na+/K+ ATPase pumps Na+ out of the cell causing MP to decrease
5. RMP is established due to Repolarization
Hyperpolarization
K+ moves out of the cell
Lowers MP to approx -80mv
Makes Cell more (-)
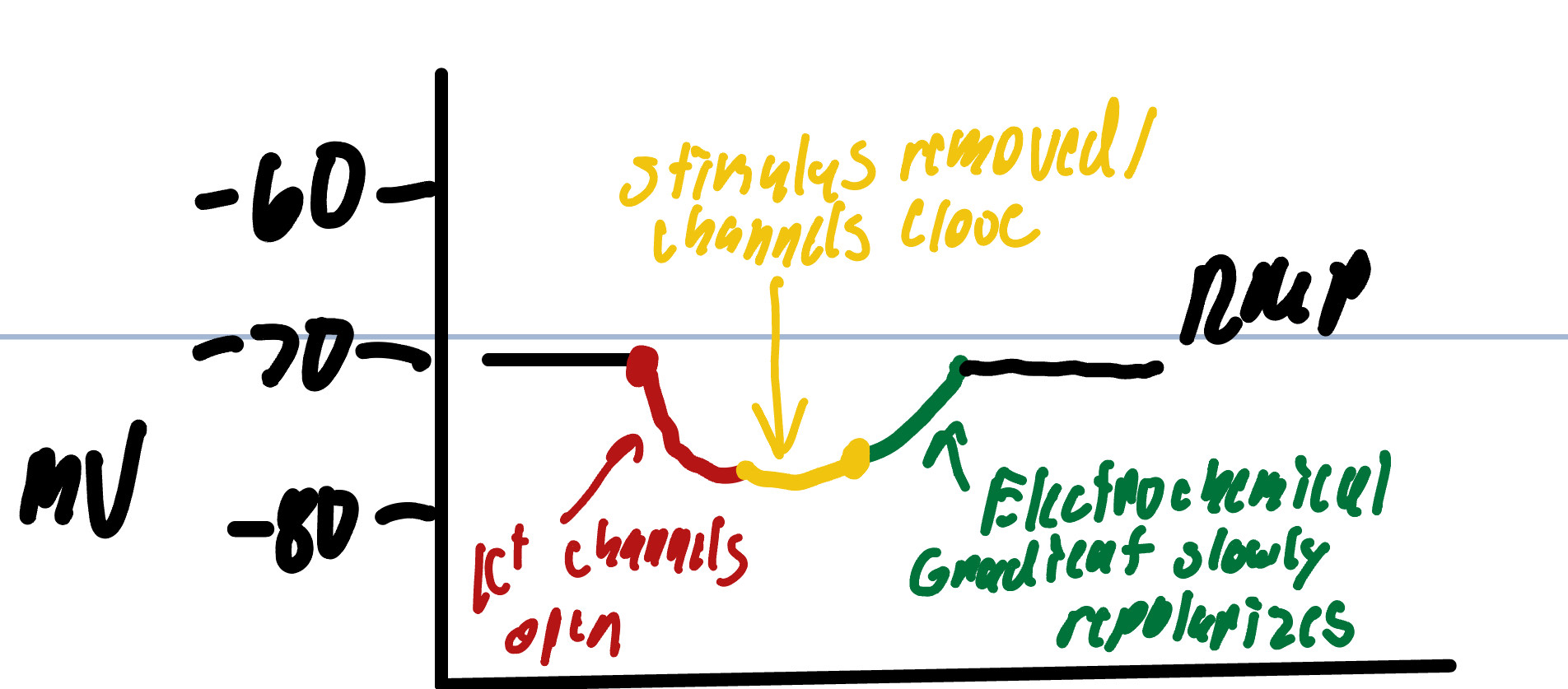
Steps of Hyperpolarization
1. K+ gated channels open due to stimulus
2. Flow of K+ ions leave the cell and causes MP to decrease since gate is open
3. K+ gated channels close once stimulus is removed
4. Cells work on chemical and electrical gradient by letting K+ enter the cell causing MP to increase
5. RMP is established due to Repolarization