Clinical Medicine of Gastrointestinal System: Oral Manifestations of the GI Disease and Diseases of the GI Tract, pt.1
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
Why are there oropharyngeal presentations of the GI Tract disease?
b/c the oral cavity is the window of the gut
aphthous stomatitis
ulcers = canker sores
-solitary or multiple
-RAS = recurrent aphthous stomatitis
-associated with crohn's disease **
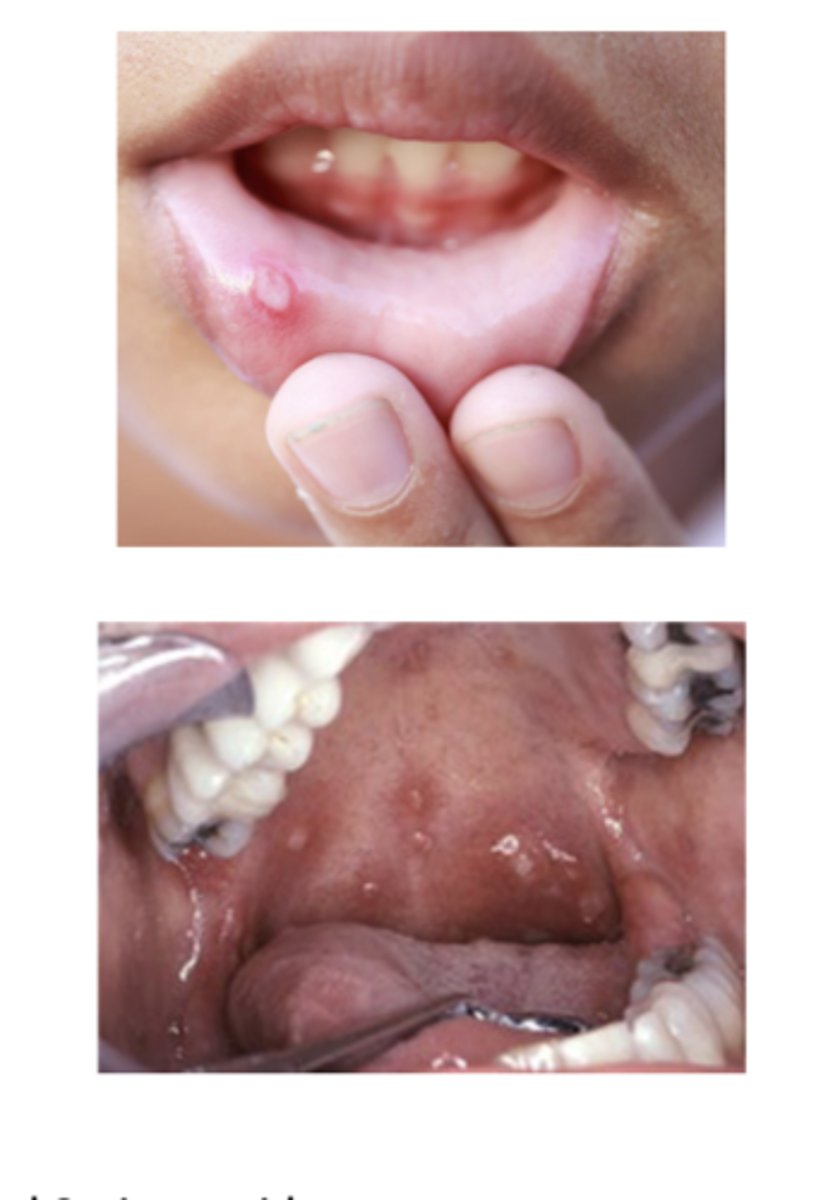
What are the predisposing factors for aphthous stomatis?
-stress
-viral illness
-hormonal changes
-food/drug hypsersenstivity
-familial
-trauma
-immunodeficiency
What is the likely etiology for aphthous stomatitis?
immune response
What are the GI diseases associated with aphthous stomatitis?
-crohn's disease --> aph ulcerations throughout the GI tract
-iron deficiency anemia --> multiple GI and non-GI etiologies
-celiac disease (less common)
cheilitis
inflammation of the lips
angular cheilitis
dryness at the corners of the mouth leading to skin breakdown, redness, crusting, & fissures
*may become infected
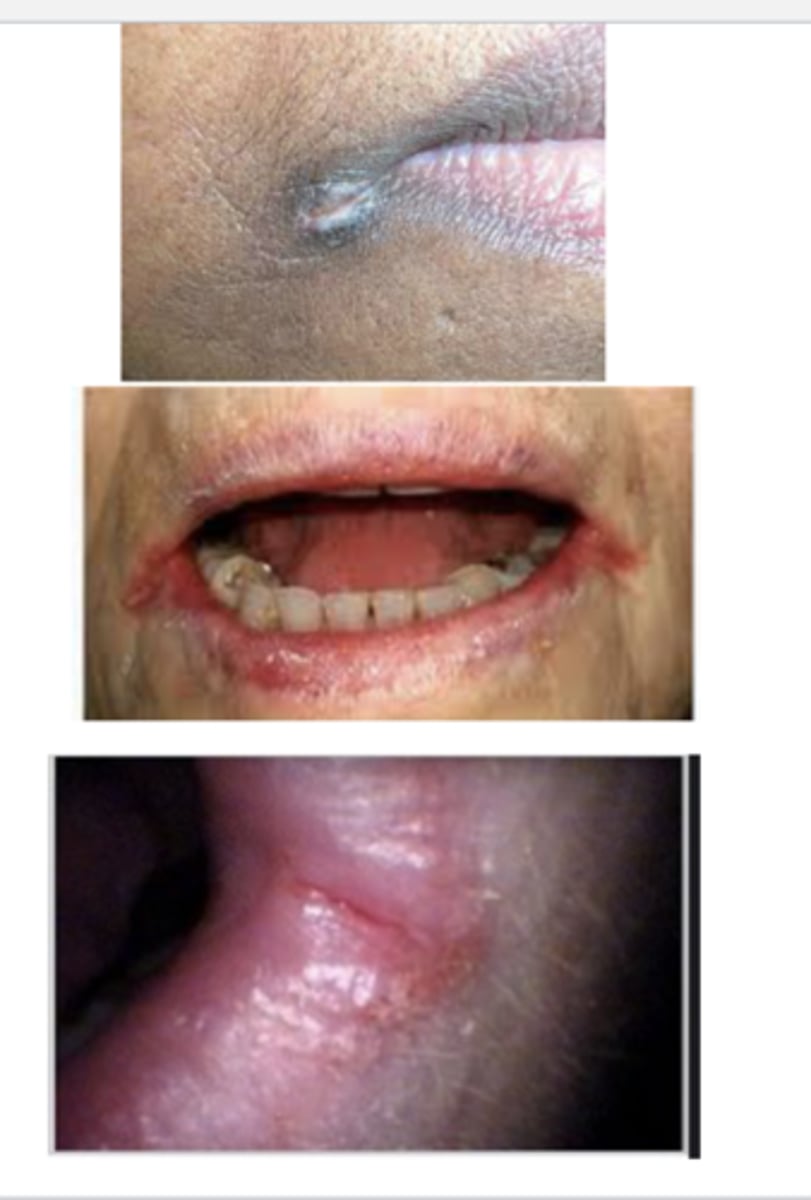
What are common causes of angular cheilitis?
-irritation--> chemical, dry mouth, poor fitting dentures, edentualism
-iron deficiency, riboflavin deficiency, poor nutrition
-infection
-allergies
-decreased immune function
How does edentualism (of having lost one or more teeth, whether partially or fully) cause angular cheilitis?
leads to more saliva exposure at the corners of the mouth --> repetitive exposure to saliva leads to skin breakdown = form of contact dermatitis
Peutz-Jeghers Syndrome
mucocutaneous hyperpigmentation that presents as pigmented macules on lips and buccal mucosa
-autosomal dominant
-presents in 1st-3rd decade
-can fade after puberty
-can also have lesions on fingers, soles, & around the eyes
-associated with polyps of the GI tract **
-risk for multiple cancers
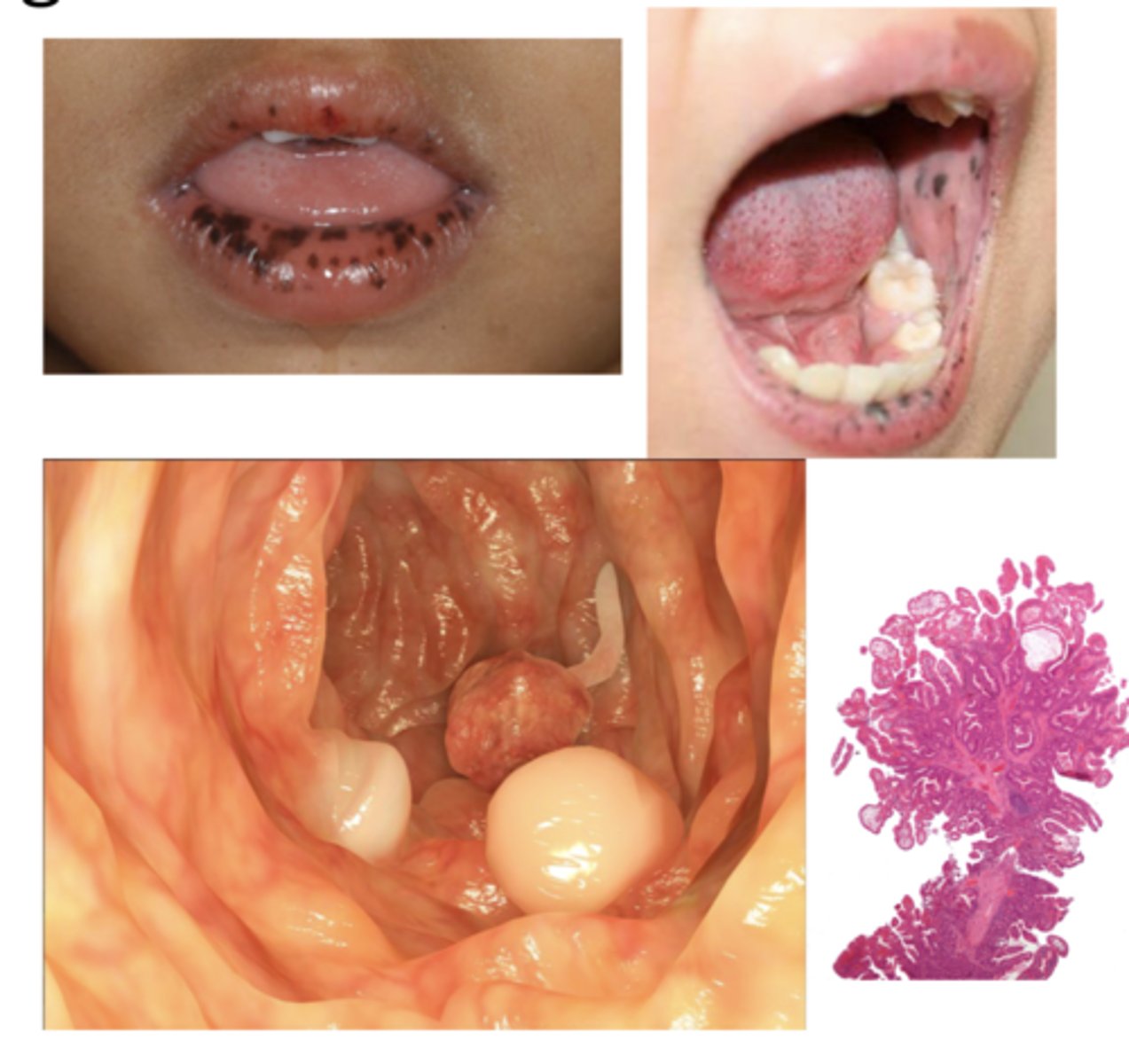
What GI disorder is Peutz Syndrome associated with?
hamartomatous Peutz-Jeghers Polyps (PJPs) --> associated with multiple polyps of GI tract
Peutz Syndrome increases the risk for which cancers?
-38-66% risk GI cancer --> stomach, small intestine, colon, pancreas
-increased risk for lung, breast, ovarian/testicular
What are the complications of the GI polyps that are associated with Peutz Syndrome?
-intestinal onstruction
-abdominal pain
-GI bleeding
-malignant transformation
-rectal prolapse
Mucocutaneous Telangiectasia/Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia
vascular malformation of the skin and internal organs (GI tract, lungs, brain) ==> AKA Osler-Weber-Rendu Syndrome
-presents in 2nd or 3rd decade
-autosomal dominant
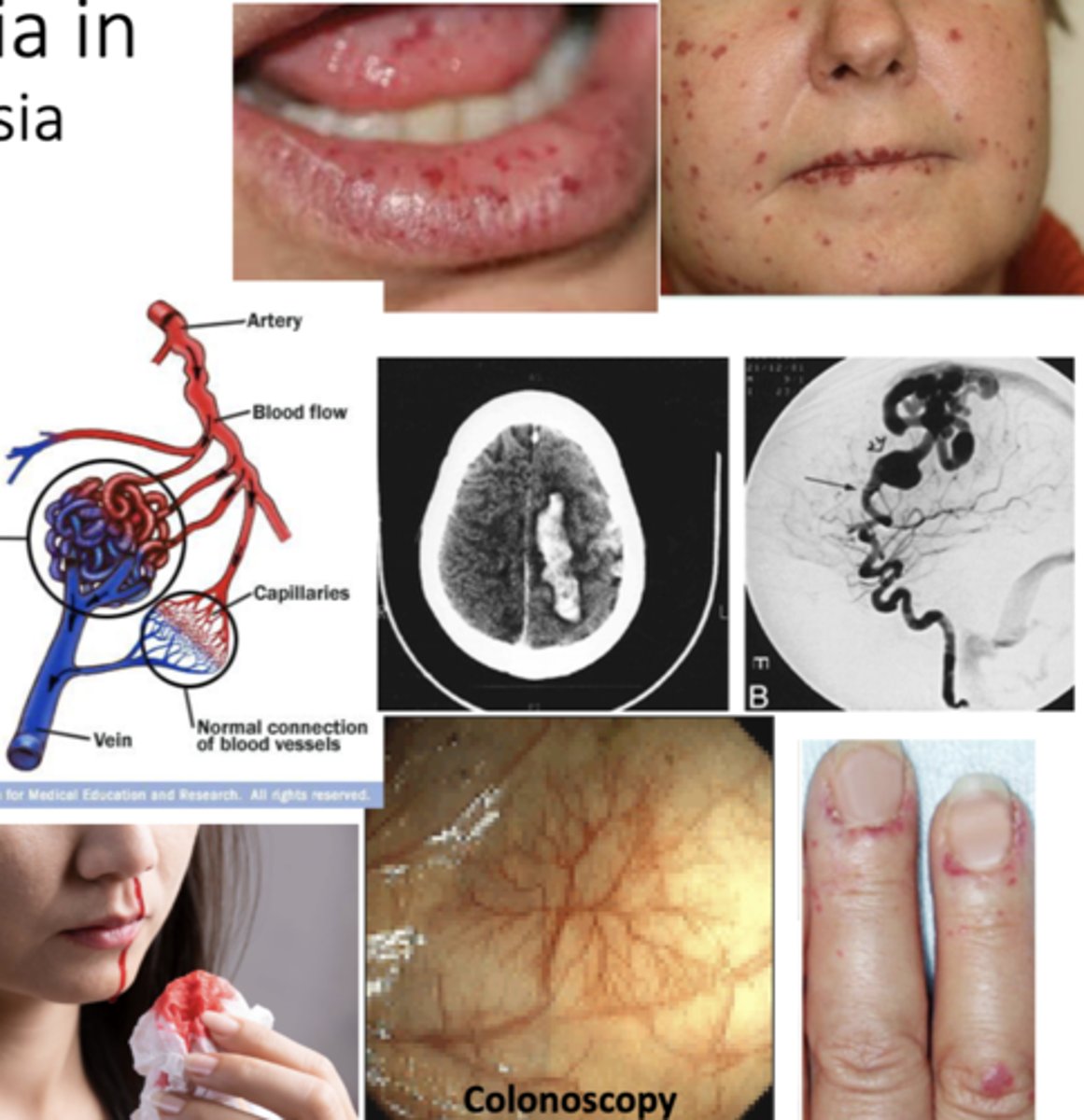
Telangiectasia
small, dilated blood vessel near surface of skin/mucous membranes.
*common on lips, tongue, face, chest, fingers, GI tract
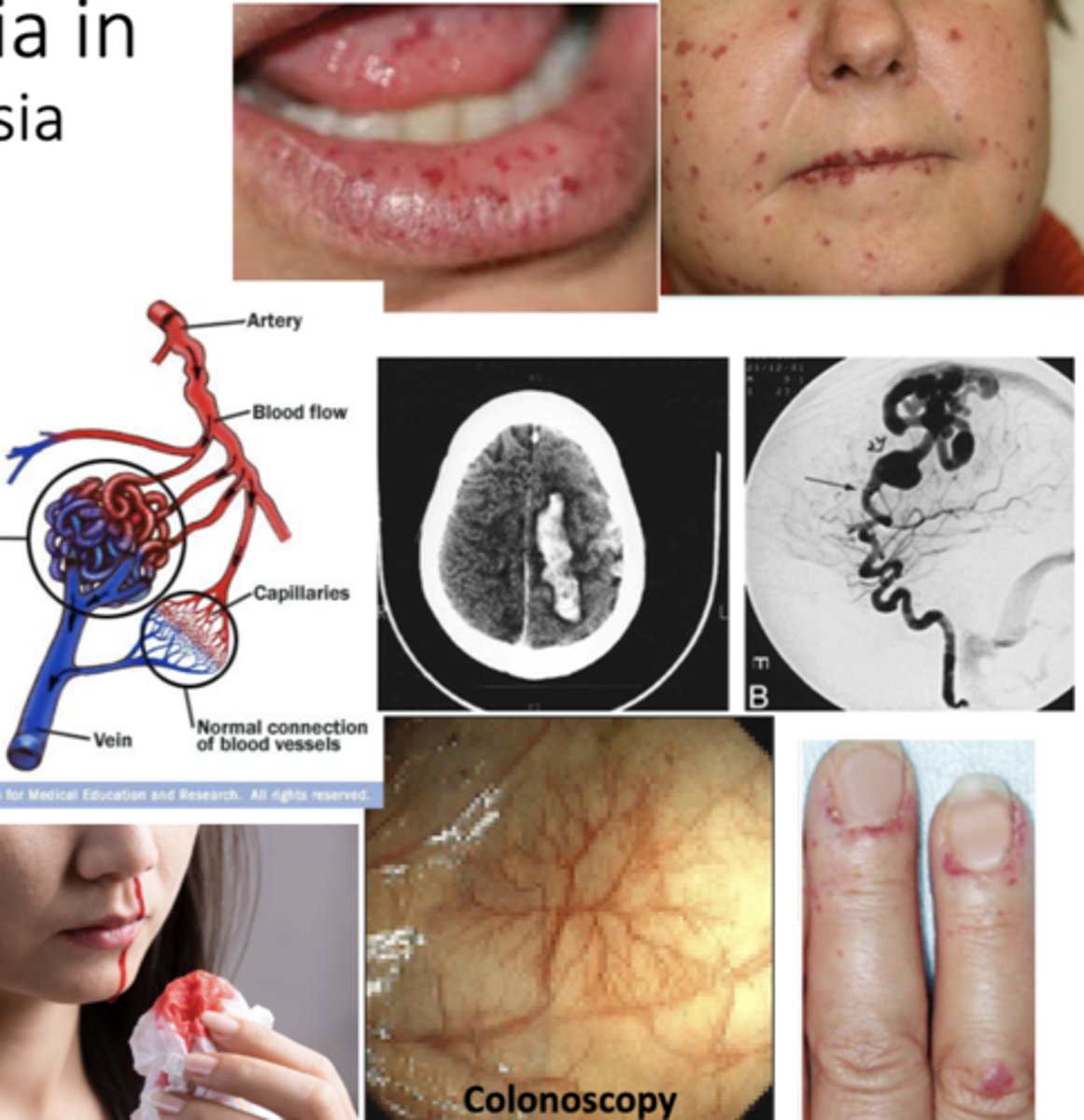
Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia?
-telangiectasia --> small, dilated blood vessel near surface of skin/mucous membranes (lips, tongue, face, chest, fingers, GI tract)
-Arteriovenous shunts/malformations (AVMs) --> Liver (60%), brain (10%), respiratory system
What are the complications of hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia?
-epistaxis --> nosebleeds (97%)
-GI bleeding (33%)
-iron deficiency
-stroke
-pulmonary hemorrhage/embolism
oral candidiasis
oral mucocutaneous candida infection = oral thrush --> fungal infection, can be chronic or acute; local or systemic
*presents as creamy white/yellow curd like plaques on the tongue/oral mucosa
-often asymptomatic
-symptoms --> "cotton mouth", loss of taste, odynophagia
-can accompany esophageal candidasis
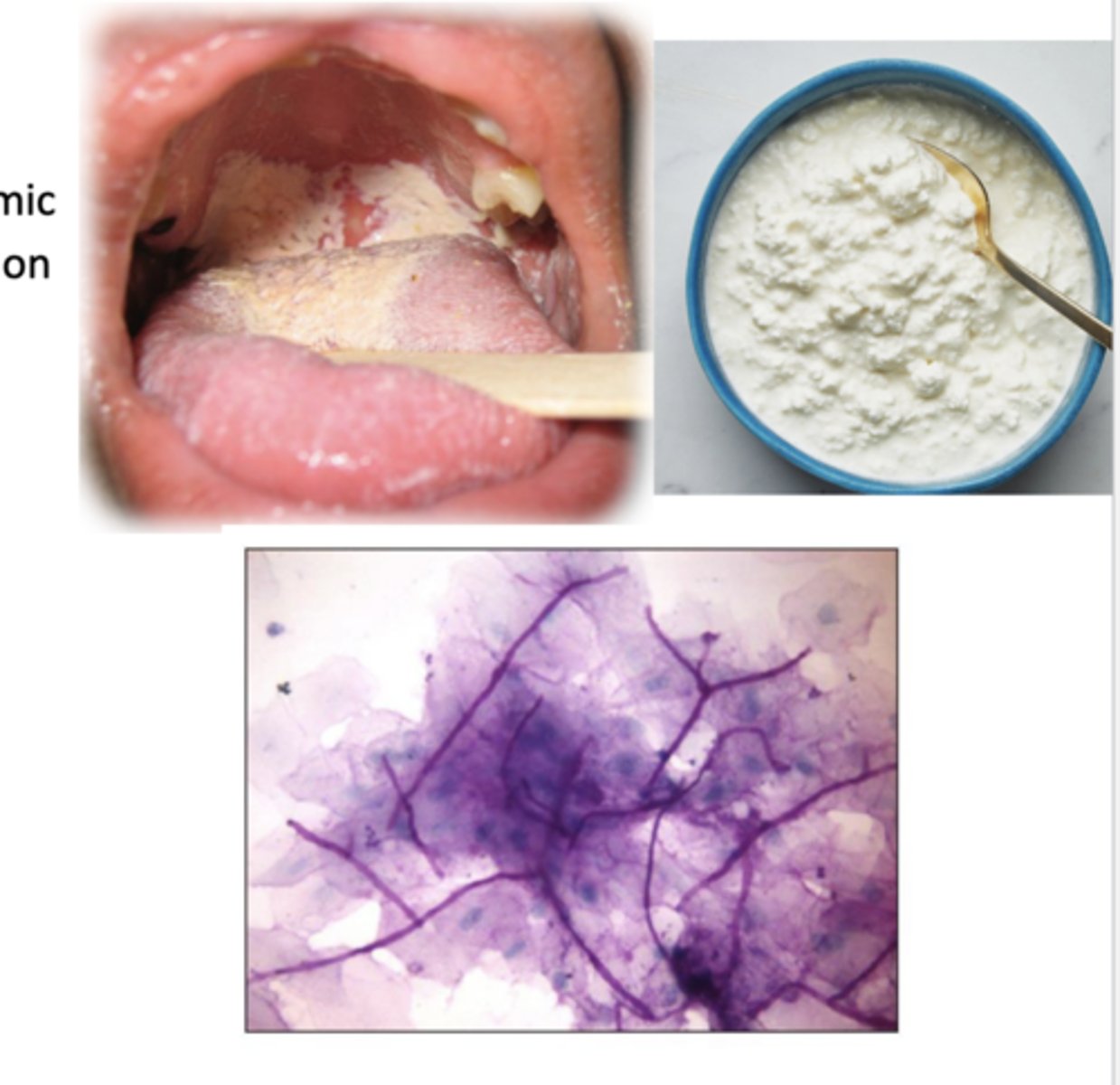
How is oral candidiasis diagnosed?
-clinical
-yeast seen on smear
What underlying conditions associated with oral candidiasis?
-diabetes
-HIV/AIDS
-cancer
-medications --> chemotherapy, steroids, antibiotics
-smoking
-other immunocompromised states
How is oral candidasis related to underlying GI disease?
seen when GI diseases are treated with steroids in advanced GI cancer or chemotherapy for GI cancers
hyperdontia
supernumerary teeth ==> extra permanent teeth (1-4% of population)
What diseases are associated with hyperdontia?
-cleidocranial dysplasia
-ehlers-danlos syndrome
-cleft lip and palate
-gardner syndrome
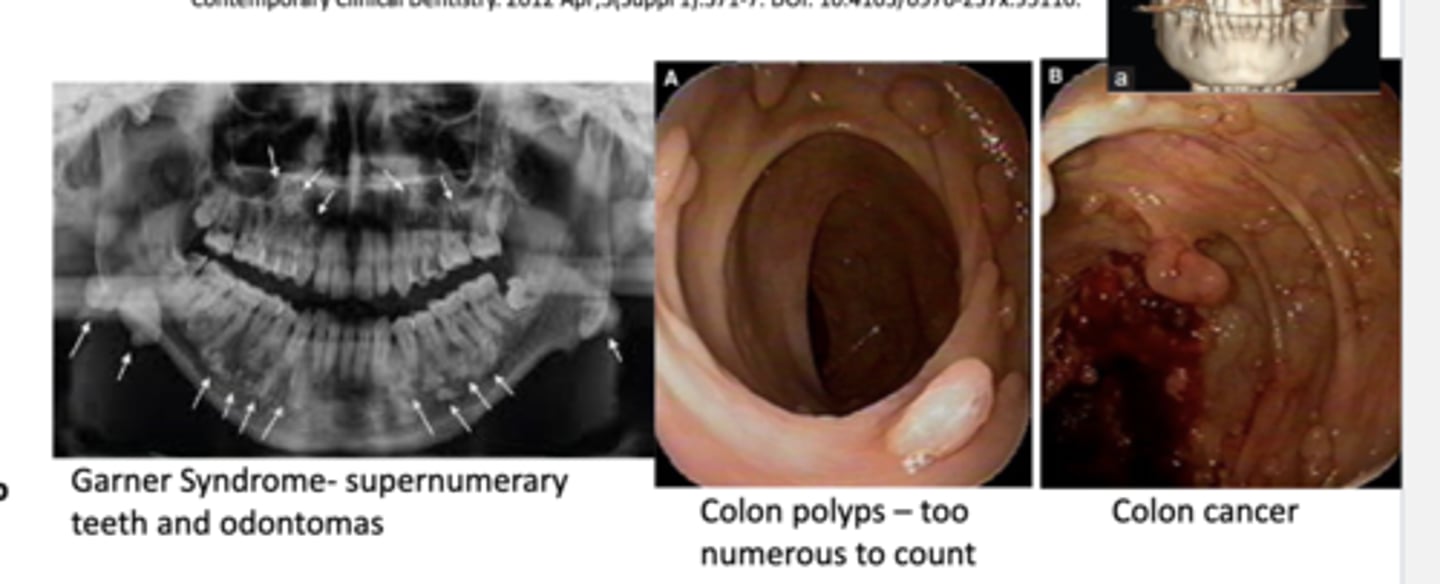
Garner Syndrome
-autosomal dominant
-supernumerary teeth
-osteomas
-odontomas
-many colon polyps w/ 100% chance of malignant change--> variant of familial adenomatous polyposis
-colon cancer at 20-40 years old without treatment
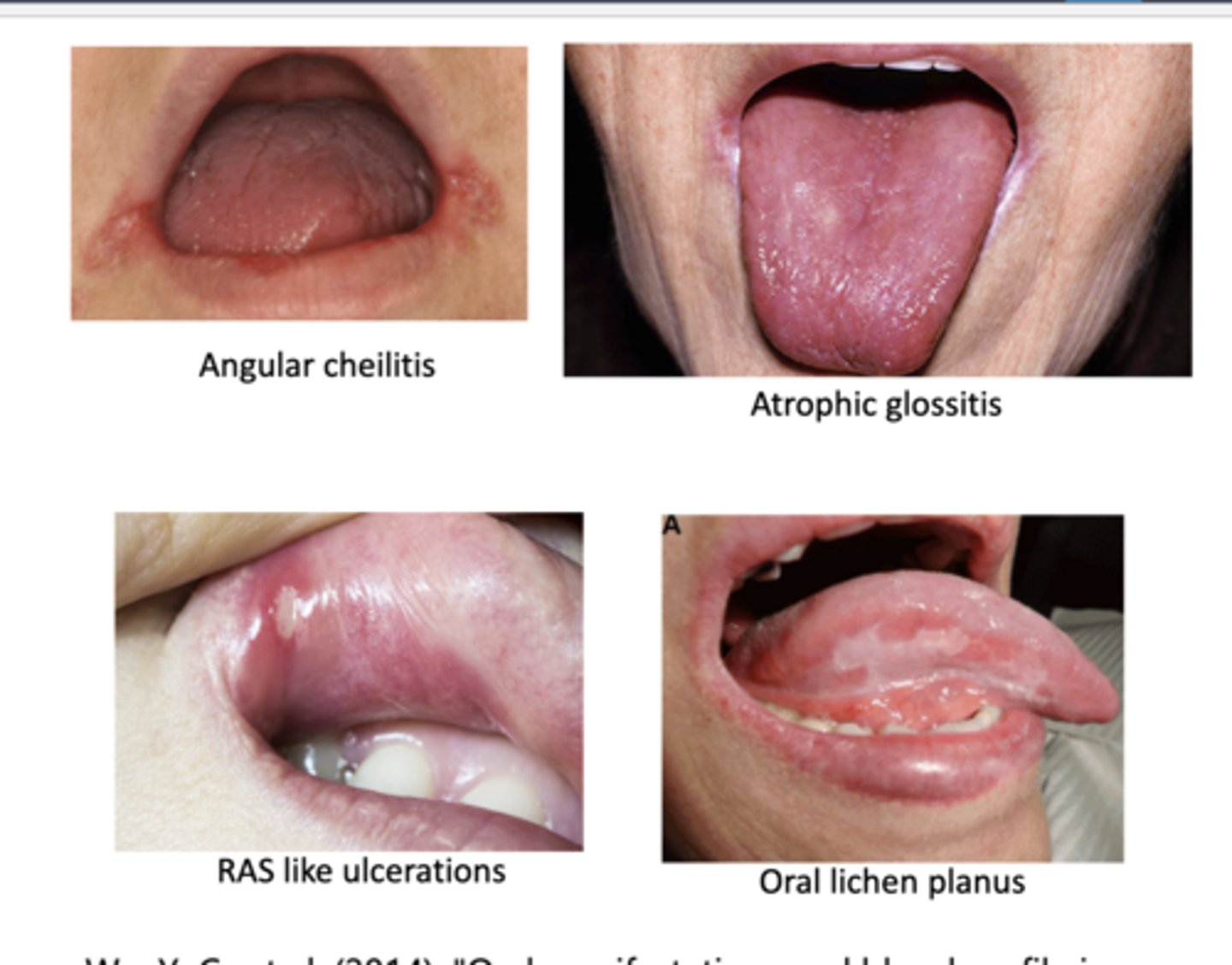
What are signs of anemia in the mouth?
-angular cheilitis
-atrophic glossitis
-RAS like ulcerations
-oral lichen planus
-xerostomia
-numbness
-burning sensation
-dysgeusia--> altered taste perception
dysgeusia
altered taste perception
How does the signs of anemia in the mouth relate to the GI?
many GI disorders are associated with anemia due to malabsorption or blood loss
crohn's disease
inflammatory bowel disease characterized by bouts of abdominal pain, diarrhea, weight loss, nutritional deficiencies due to lesions anywhere in the GI tract-- including the oral cavity
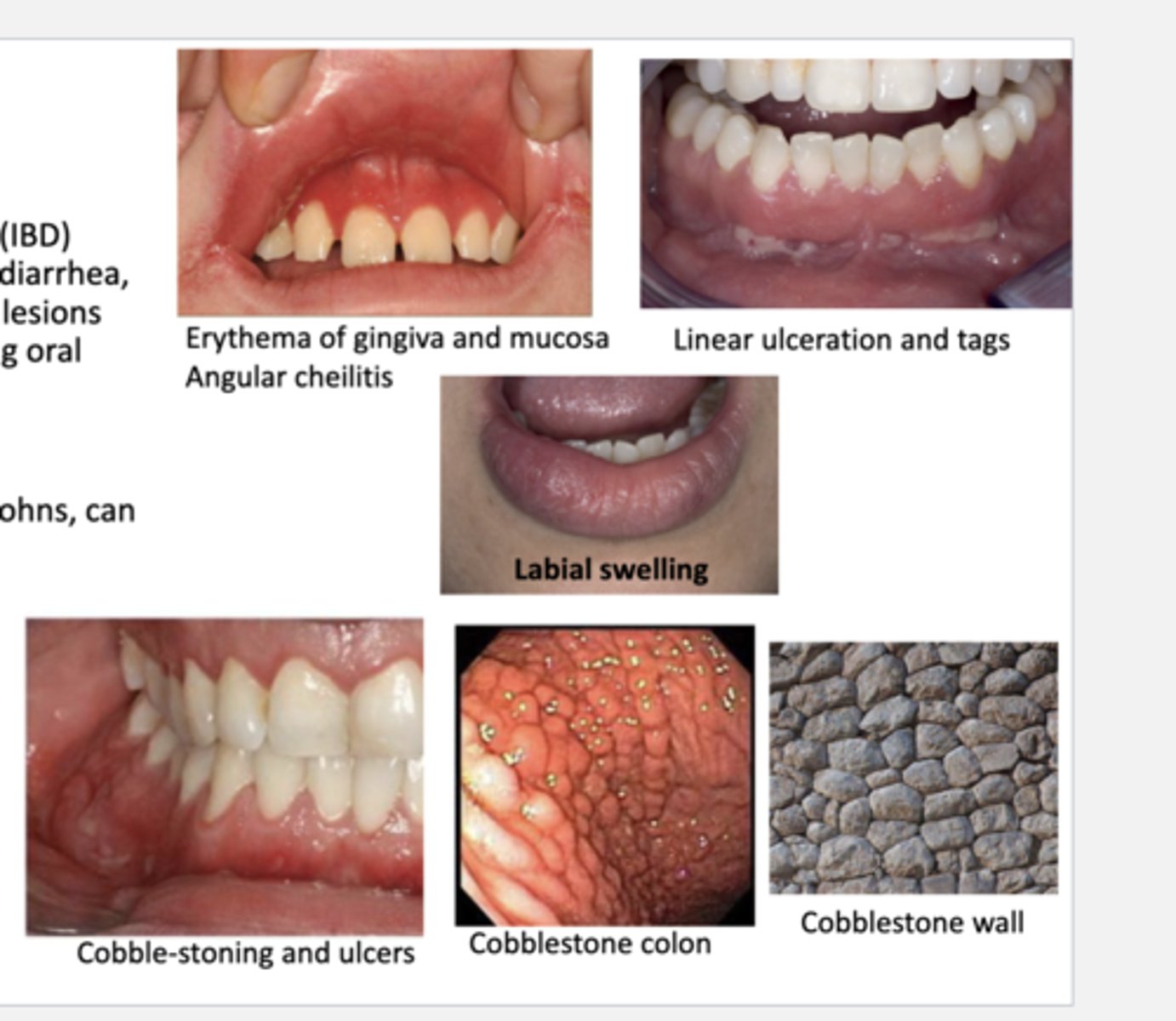
What are the oral manifestations of crohn's disease?
-cobble-stone appearance (specific to crohn's)
-linear ulceration
-mucosal tags
-mucositis & gingivitis
-labial & facial swelling
-angular cheilits
-aphthous ulcers
What are the signs & symptoms of crohn's disease?
-chronic abdominal pain
-diarrhea--> 70% bloody, 30% non-bloody
-weight loss
-extra-intestinal manifestations
-onset around 15-25, but can be later
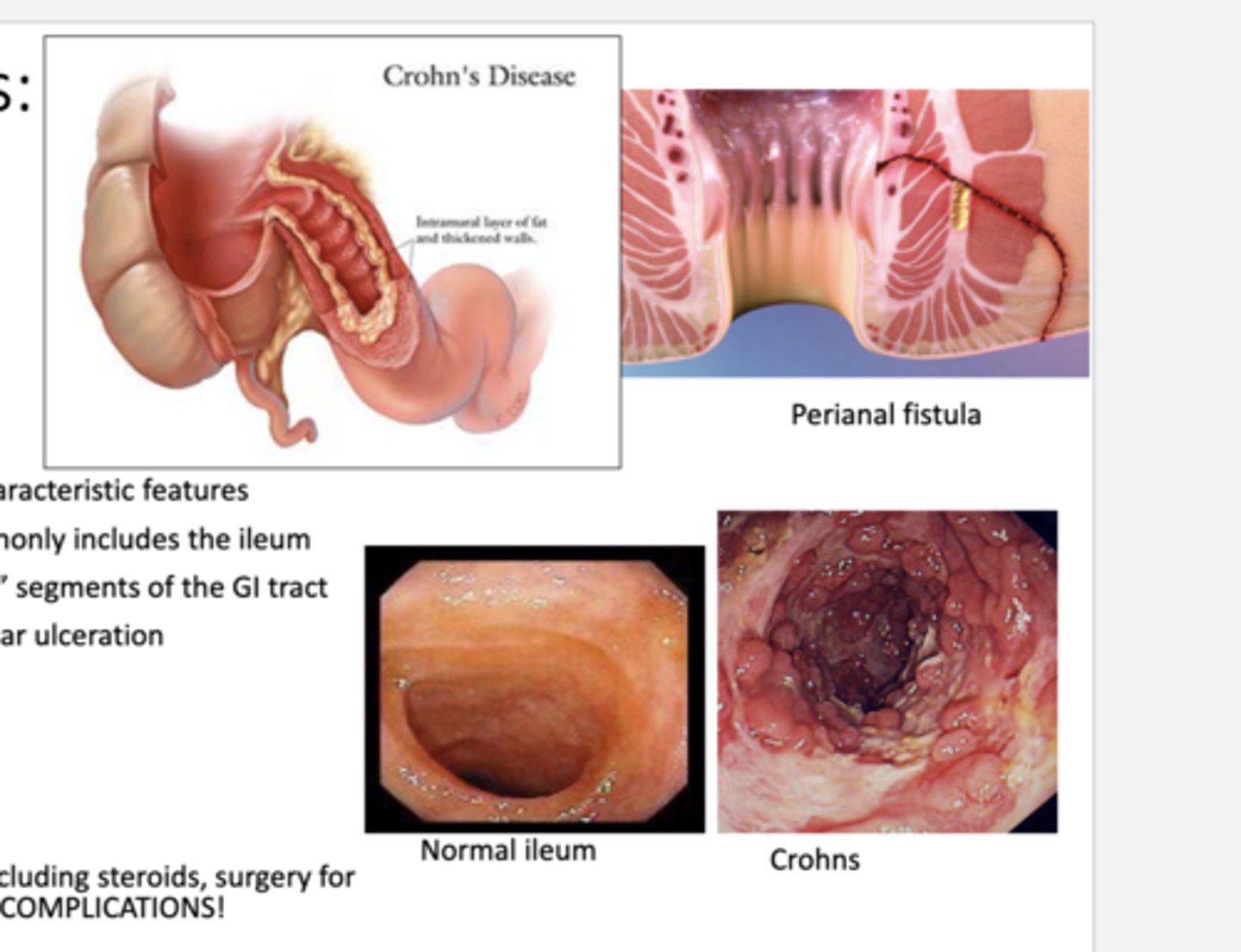
Describe the pathology of crohn's disease.
-transmural inflammation of bowel wall
-can affect anywhere in the GI tract--> most commonly includes the ileum
-lesions tend to spare the rectum & skip segments of GI tract
What would you expect to see in an endoscopy of a patient with crohn's disease?
cobblestone appearance w/ linear ulceration (discontinuous)
What are the common complications of crohn's disease?
-intestinal obstruction
-fistulas
What are some common treatments of crohn's disease?
-steroids & other meds to modify disease
-surgery for bowel obstruction
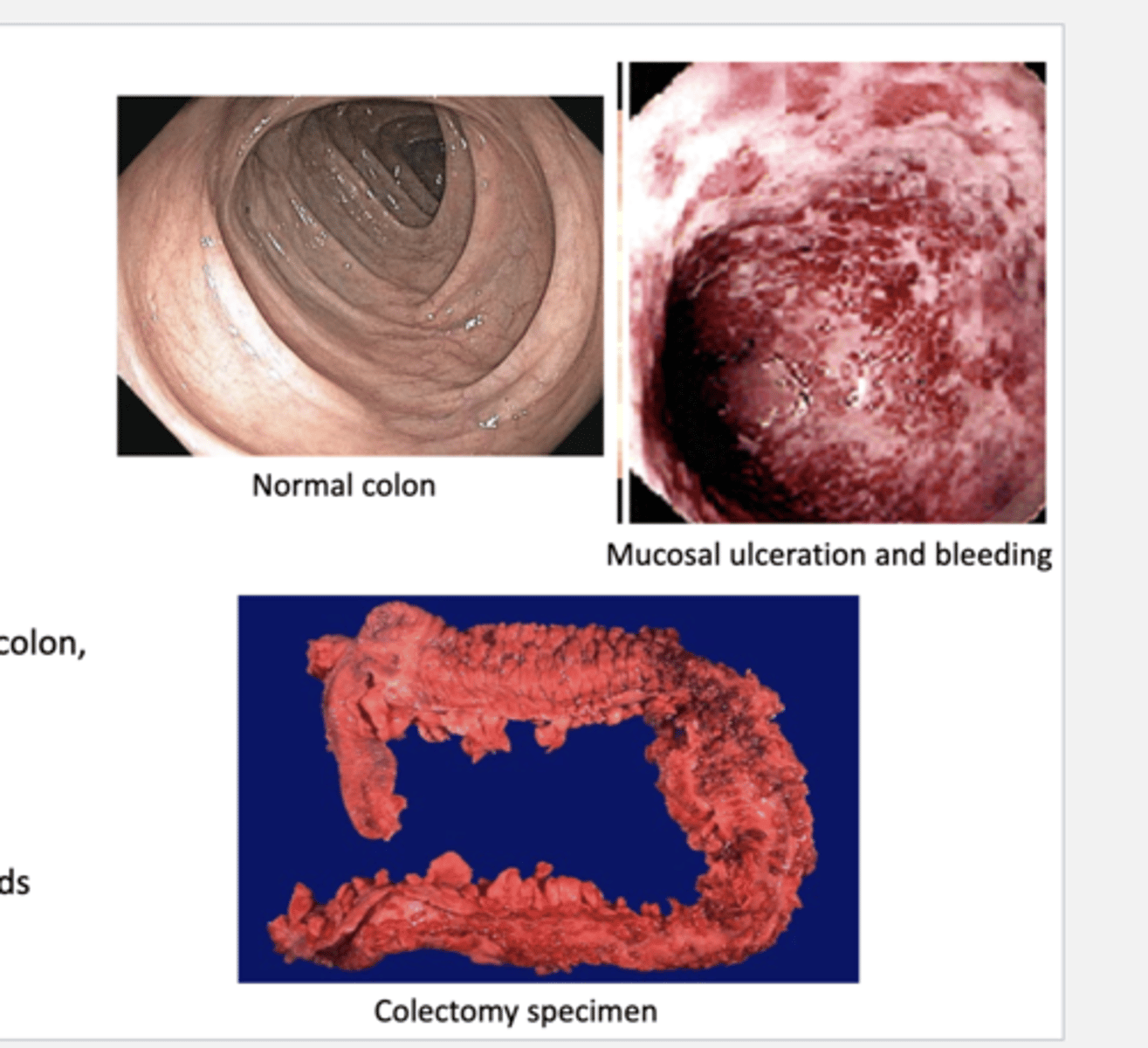
ulcerative colitis
inflammatory bowel disease characterized by bouts of bloody diarrhea
-often bloody mucosal ulceration of the colon.
-anemia common
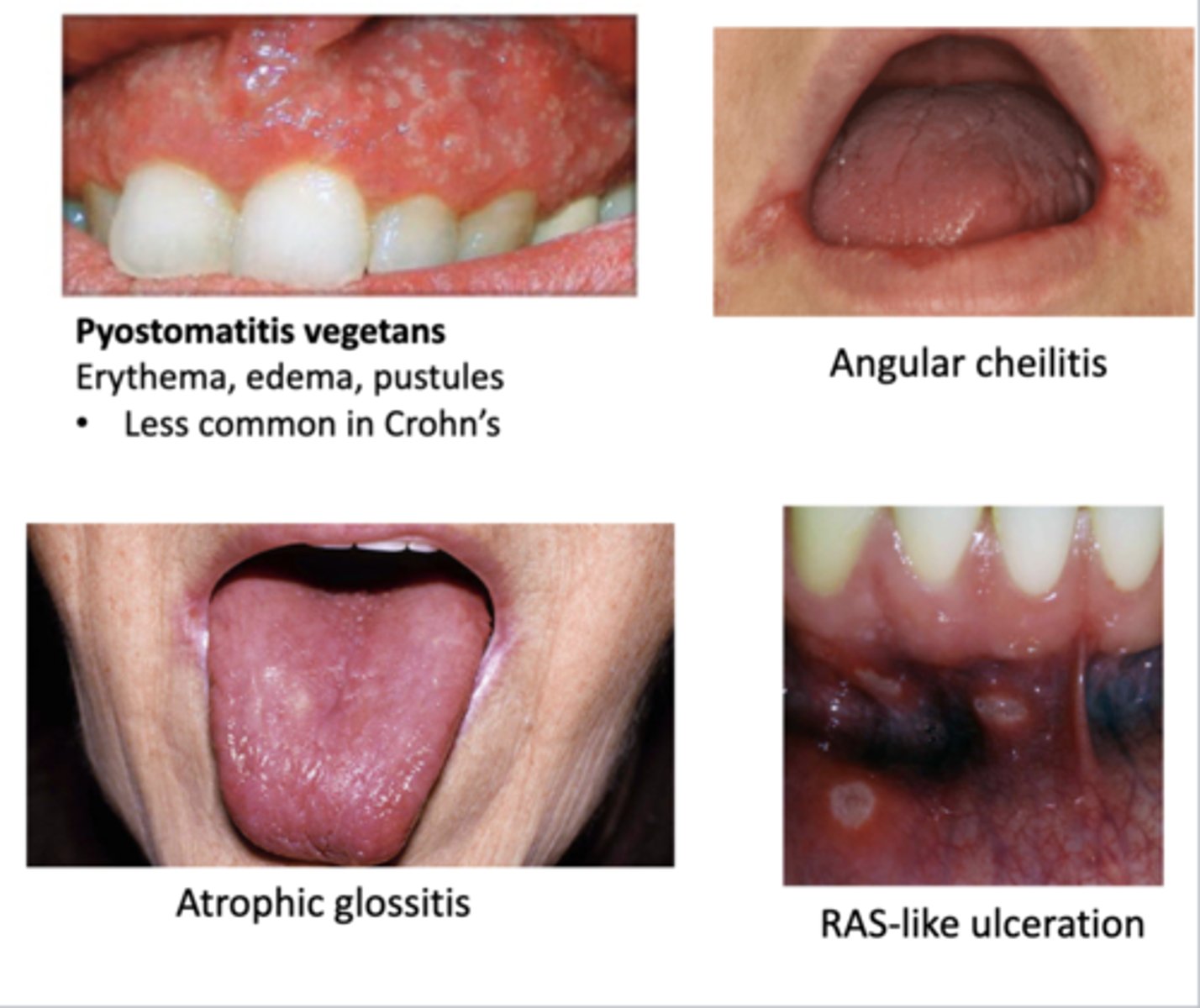
-oral manifestations
>pyostomatis vegetans--> low occurence but more common here than in crohn's disease
>RAS-like ulceration
>angular cheilitis
>atrophic glossitis
>other anemia findings
What are the oral manifestations of ulcerative colitis?
-pyostomatitis vegetans --> erythema, edema, & pustules of gingiva (low occurrence but more likely here than in crohn's)
-RAS-like ulceration
-angular cheilitis
-atrophic glossitis
-other anemia findings
What are the signs and symptoms of ulcerative colitis?
-fever
-abdominal pain
-bloody diarrhea --> can be nocturnal
-extra-intestinal manifestations --> skin & joints
-signs of anemia
-onset 15-25 years old (can be later)
what is the pathology/endoscopy of ulcerative colitis?
continuous mucosal inflammation & ulceration of the colon
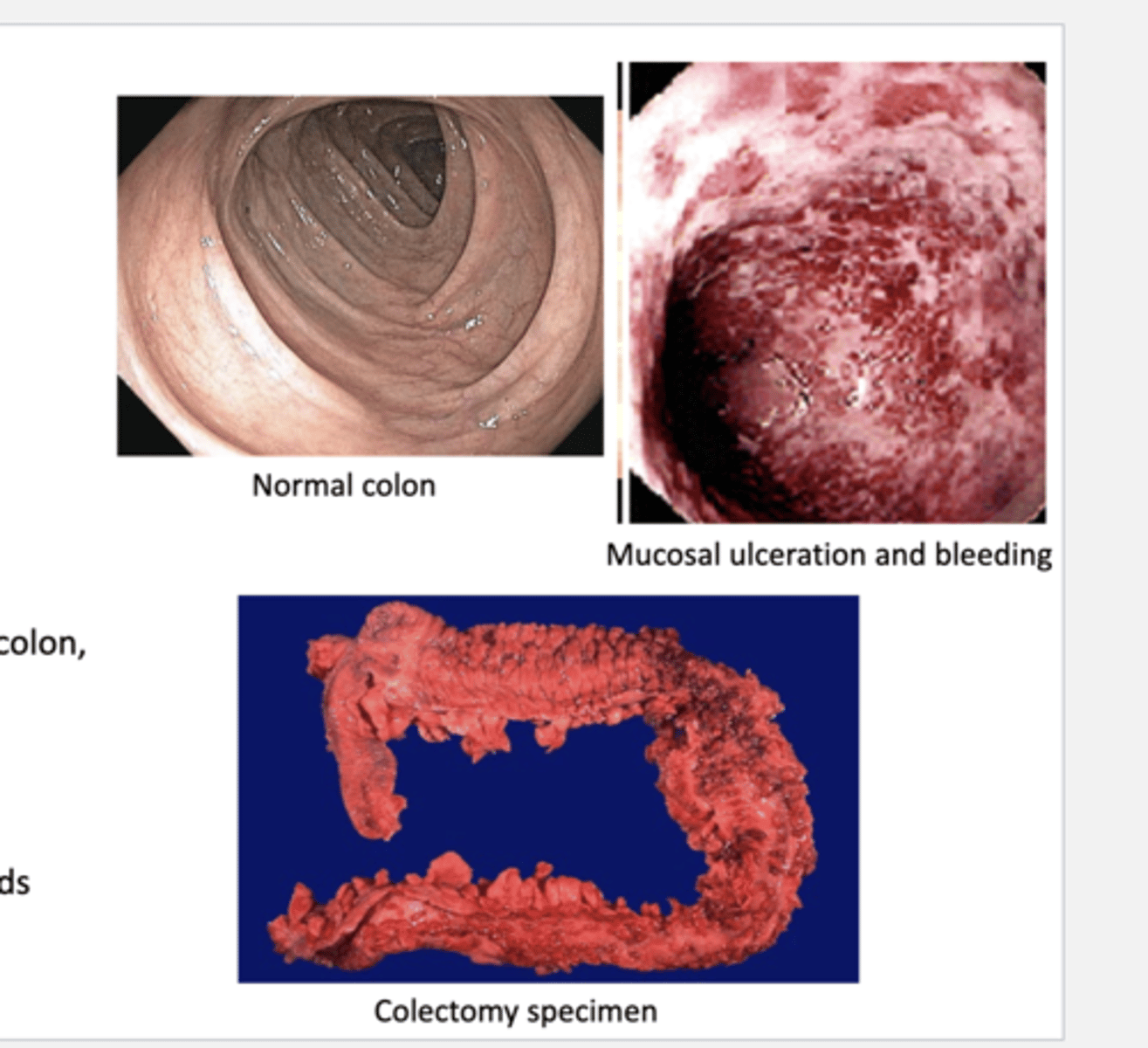
What are common treatments of ulcerative colitis?
-total colectomy can be curative
-medications to modify disease, including steroids
celiac disease
gluten sensitive enteropathy==> immune-mediated disease w/ diverse presentation
-oral manifestations may be a early sign in childhood or the only sign
>enamel defects--> hypoplasia w/ discoloration & banding
>aphthous ulcers
-severe disease can lead to malnutrition through malabsorption
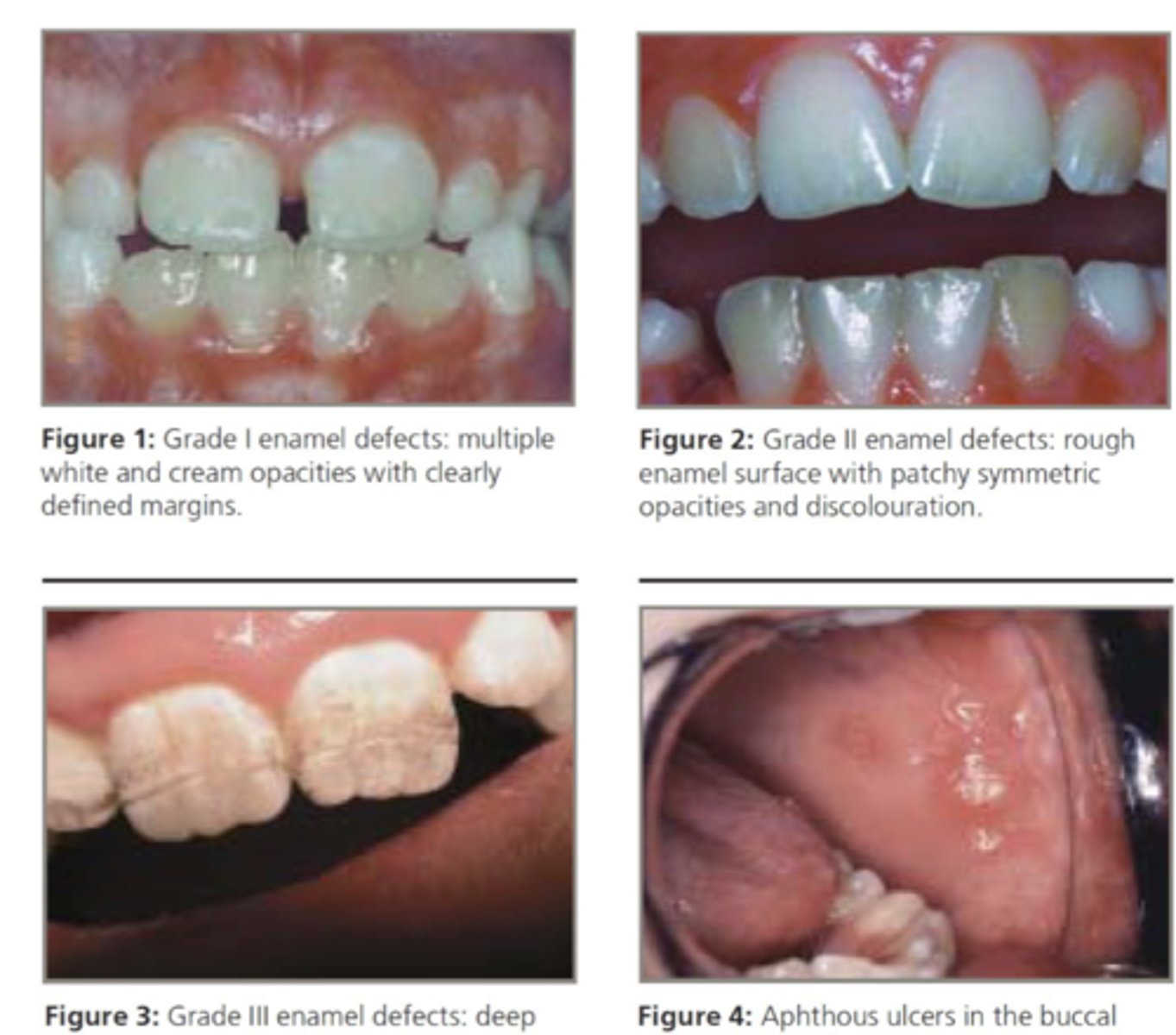
What are the oral manifestation of celiac disease?
-enamel defects --> hypoplasia w/ discoloration & banding
-aphthous ulcers
What are the consequences of severe celiac disease?
-malnutrition thru malabsorption
-multiple deficiencies --> Ca2+, vitamin D, vitamin K, vitamin B12
What are the symptoms of Celiac Disease?
-abdominal pain
-bloating
-weight loss
-chronic diarrhea
-steatorrhea
-extra-intestinal manifestations
What is the pathology of celiac disease?
blunting of intestinal villi & inflammation
*common in duodenum
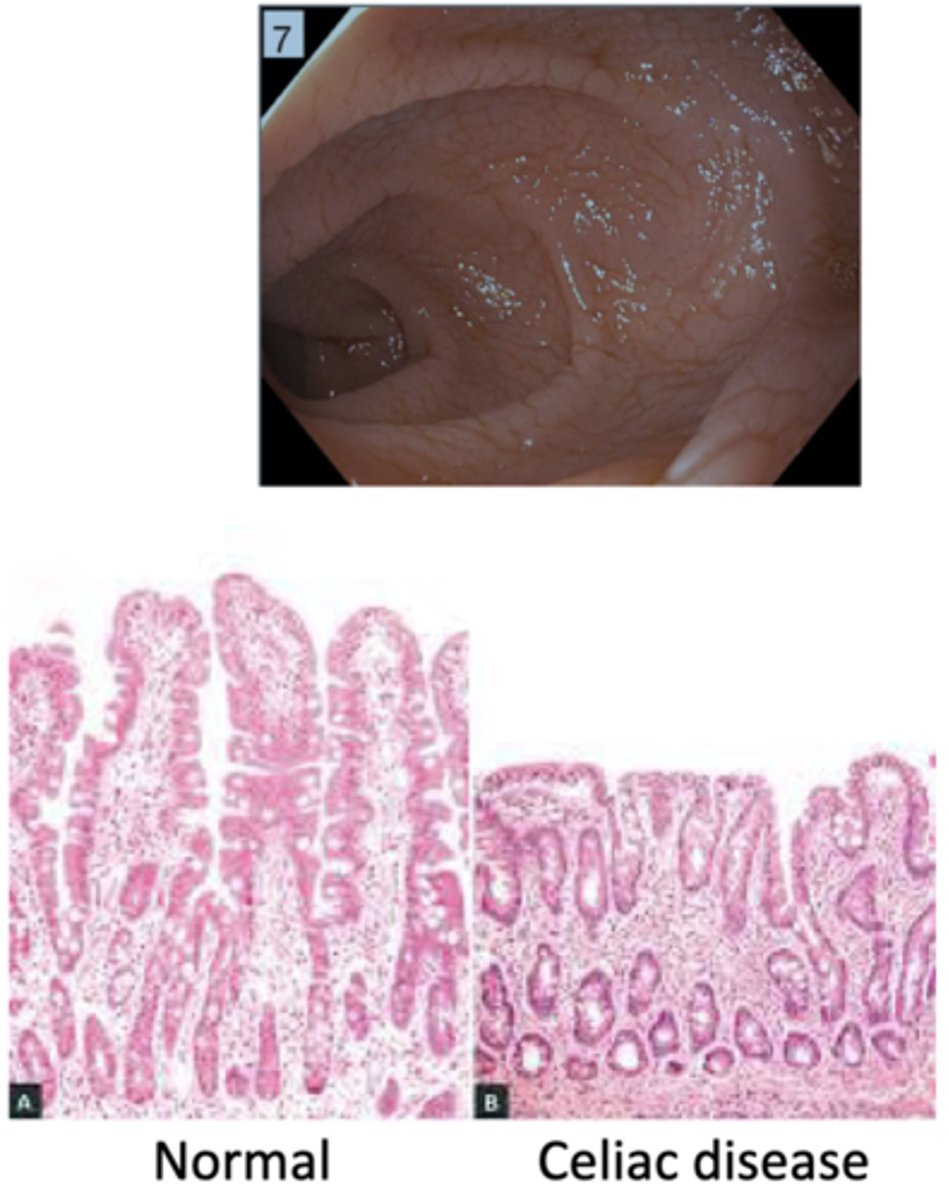
How is celiac disease diagnosed?
labs
-antibodies for tissue transglutaminase antigens
-antibodies to other specific antigens
Treatment of Celiac Disease
-gluten-free diet
-nutritional supplementation for any deficiencies
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
reflux severe enough to cause symptoms and/or tissue injury ==> causes reflux esophagitis
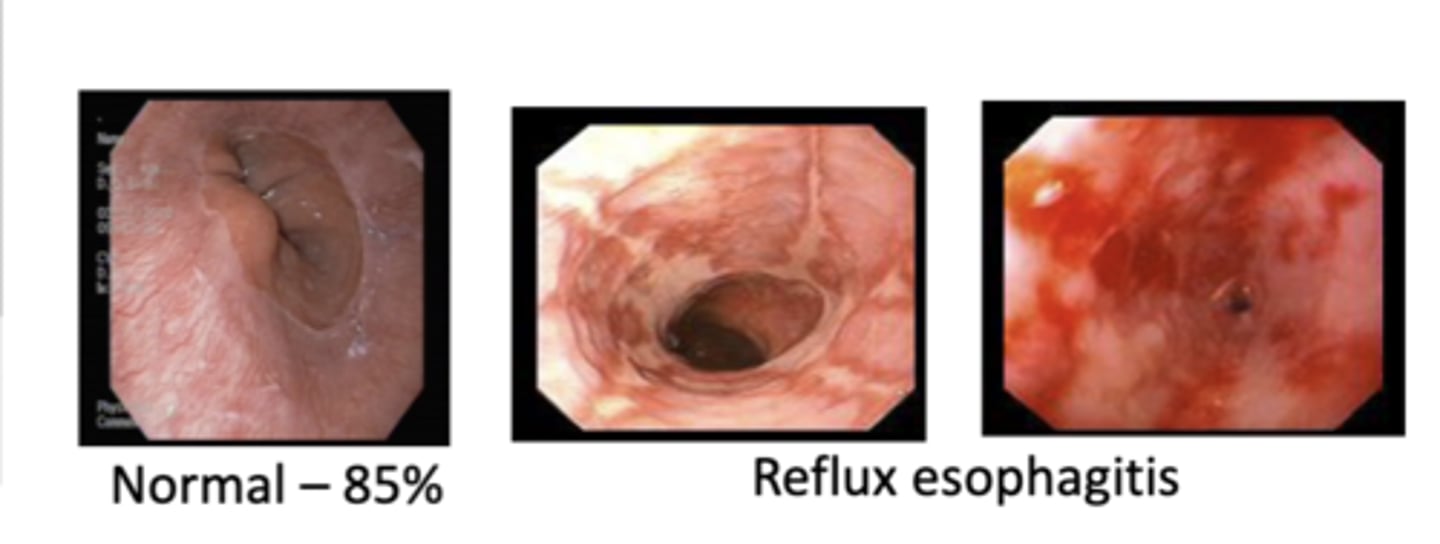
What are the predisposing factors of GERD?
-hiatial hernia
-obesity
-delayed gastric emptying
-diet
-medications
-lifestyle
What are all complications of GERD?
-developing a sour taste in the mouth
-bad breath --> due to slight regurg of acidic foods
-pain or swelling in the throat
-dysphagia
-hoarseness
-stomach noises
-nausea & loss of appetite
-dry mouth
-gum irritation including bleeding & tenderness
-tooth erosion
-heartburn behind breastbone after meal
-bloating, burping, or passing gas after meals
What are some key complications of GERD?
-severe dental disease
-esophageal ulceration
-esophageal stricture
-metaplasia to Barret's Esophagus
Treatment of GERD
-lifestyle changes
-OTC meds --> acid neutralizers, PPIs, H2 blockers