DNA test Pre-AP Biology 9
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
What is transcription?
The process of turning DNA into mRNA molecules
What is translation?
The ribosome reads the mRNA and translates it into the right amino acids, which make up/ “code for” proteins.
What does helicase do?
Unwinds parental helix at replication forks.
What does topoisomerase do?
Relieves overwinding strain ahead of replication forks by breaking, swiveling, and rejoining DNA strands (to relieve pressure)
What does primase do?
Lays down mRNA so it can tell polymerase which base to put down (ex: guanine)
What does ligase do?
Joins okazaki fragments at the end of a lagging strand.
What does DNA polymerase 3 do?
Puts the new nitrogen bases that MRNA requests down on top of the primer. It builds the complementary strand.
What’s a codon?
A sequence of three nucleotides in mRNA that corresponds to a specific amino acid or stop signal during protein synthesis.
Where does DNA replicate from?
5’ to 3’
Where does transcription happen?
The nucleus
Where does translation happen?
The ribosomes in the cytoplasm.
What is this model, and what is each label?
The blue thing is a ribsome, which has a codon that reads three nucleotides at a time. The “stop” codons then tell the ribosome that the protein is complete.

What is this photo, and what is happening?
Inversion. When a broken chromosome segment gets inverted and put back on the chromosome.

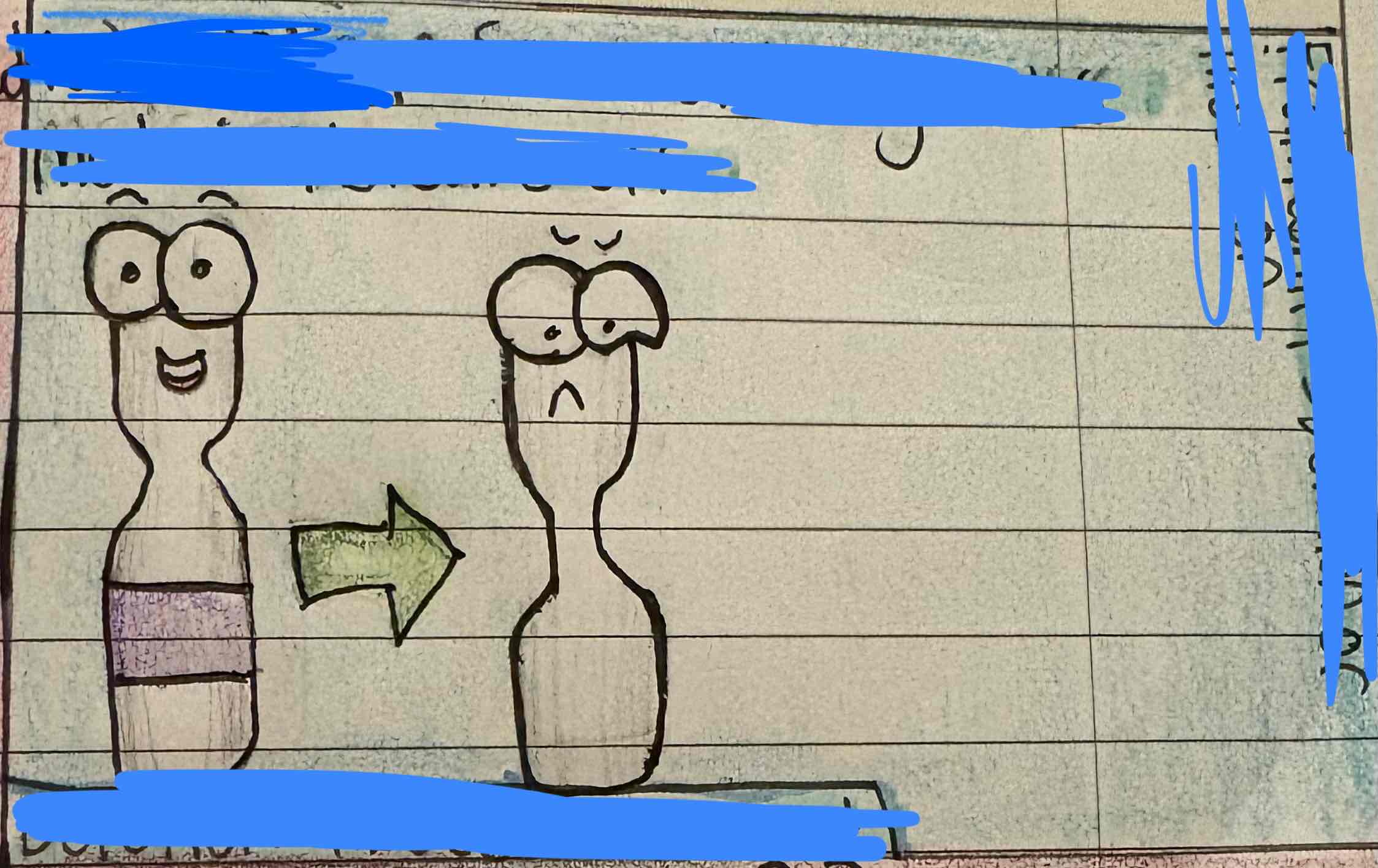
What is this photo, and what is happening?
Deletion. Some of the genetic material breaks off the chromosome.
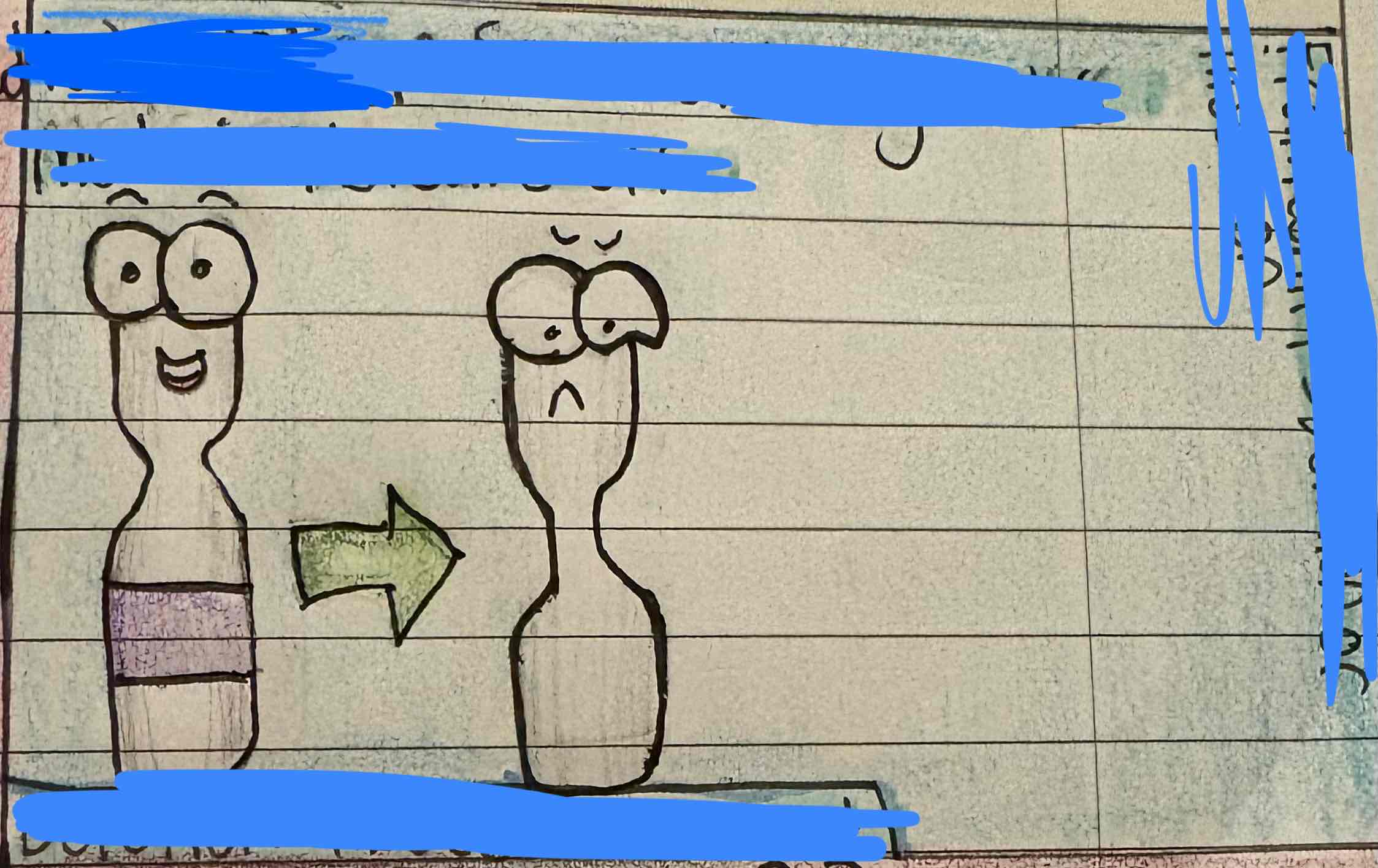
What is a point change?
A change in a single nucleic acid. Example: substitution
What is deletion?
A base is removed
What is insertion?
An extra base is added in
What is a frameshift?
The removal or addition of a nitrogen base, which makes everything else shift. This can result in the wrong codon, which makes the wrong amino acids.
What causes a frameshift?
Deletion or insertion.
What is a mutation, and where does it happen?
A change in genetic material (specifically a nucleic acid. It happens in one of the DNA bases (A, T, C, G)
Are mutations random?
Yes
Can mutations be genetically inherited?
Yes
Can mutations occur in both DNA and RNA?
Yes, because they’re both nucleic acids
Can mutations only occur during interphasE?
No, they can occur at any part in the cell cycle.
Are not all genes “turned on” at a given time?
Yes
Whcih types of organisms can experience a genetic mutation?
All living ogranisms
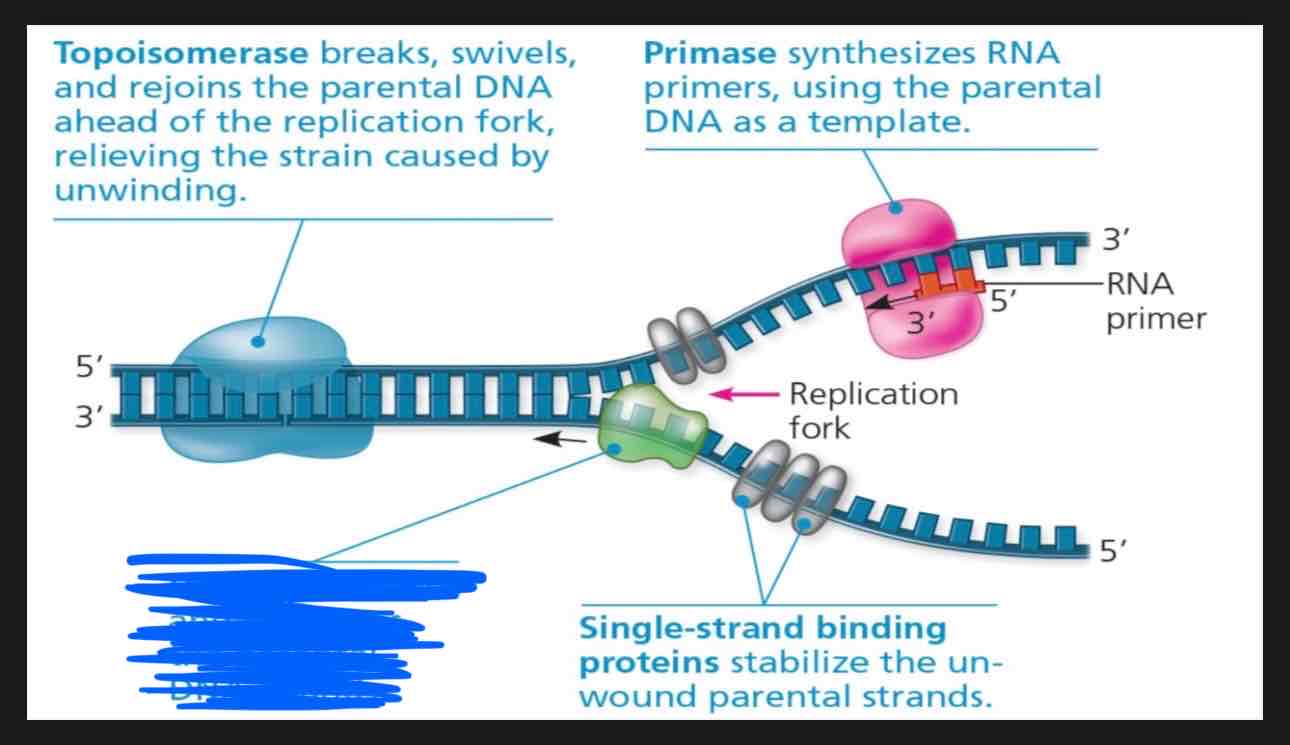
What is going on in this photo?
Topoisomerase is breaking, swiveling, and rejoining the parental DNA ahead of the replication fork to relieve strain caused by unwinding
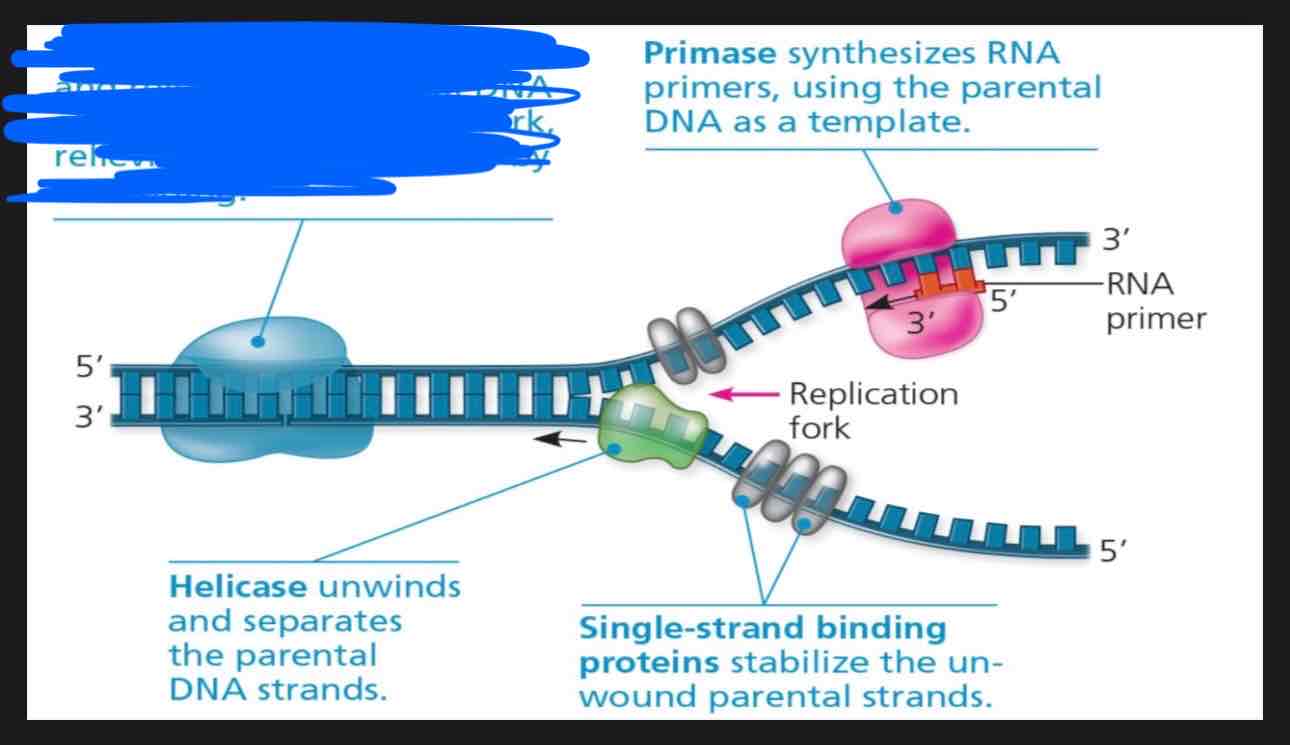
What is going on in this photo?
Helicase is unwinding and separating the parental DNA strands at the replication fork
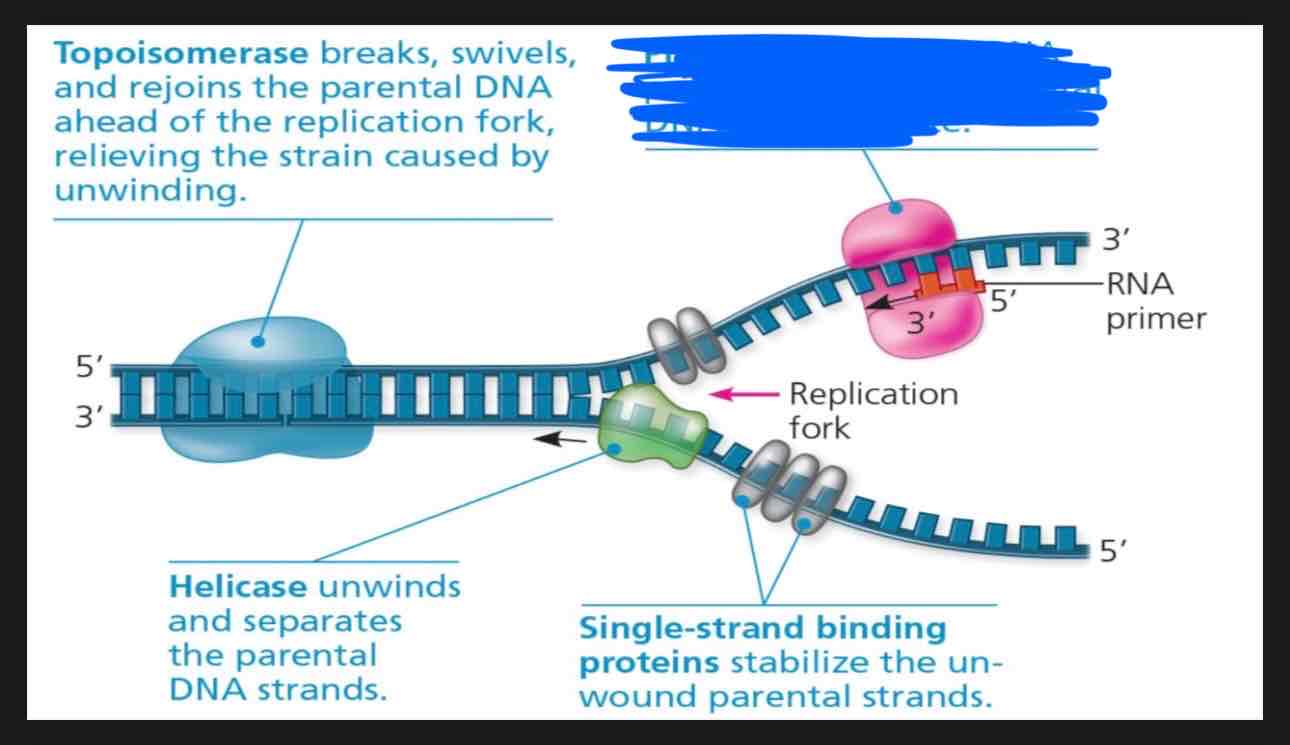
What is going on in this photo?
Primase is making the RNA primer using the parental DNA as a template
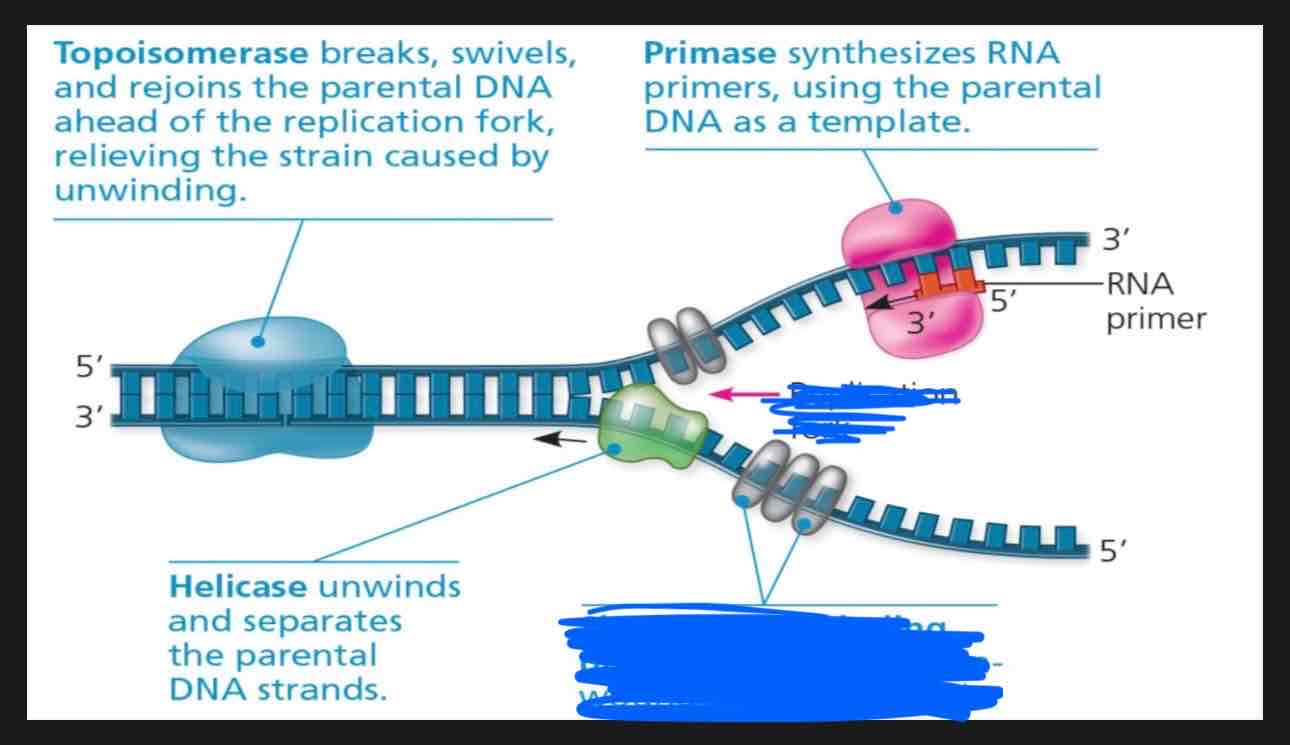
What is going on in this photo?
Single-strand binding proteins stabilize the unwound parental strands
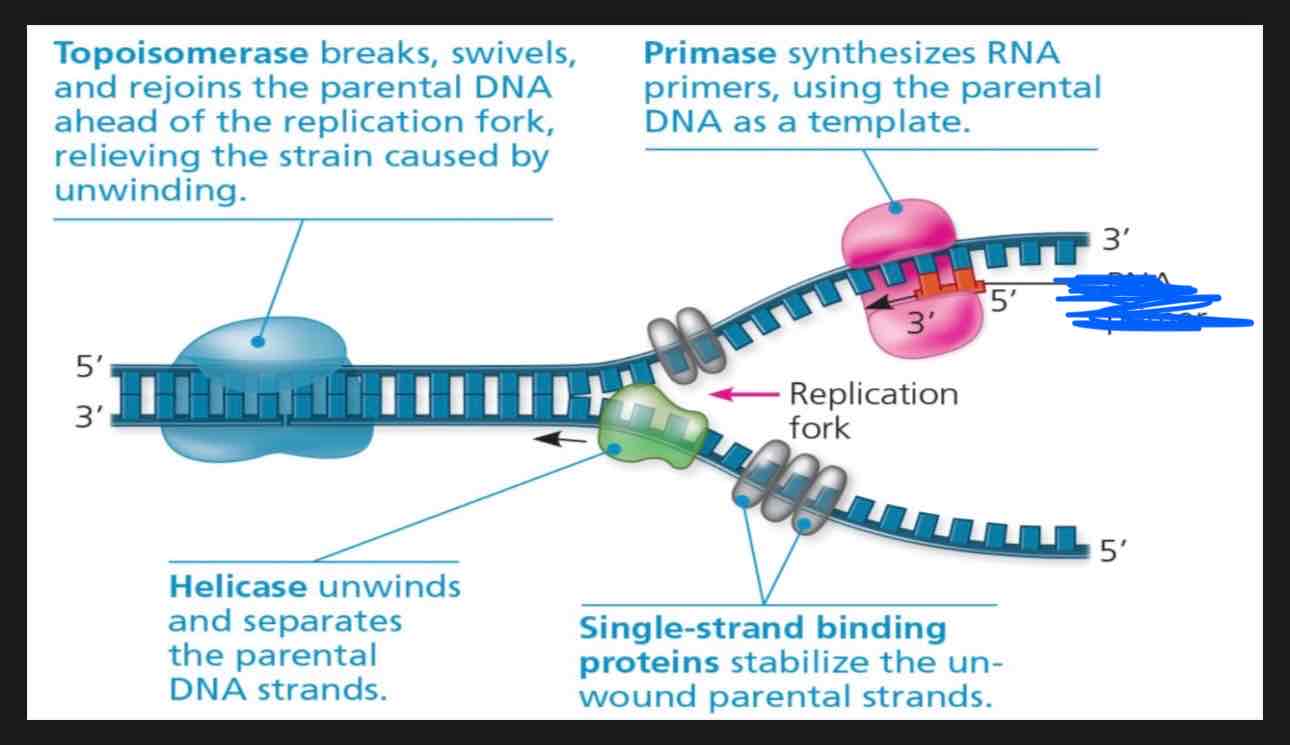
What is the term for the thing covered in blue?
It’s the RNA primer that primase makes
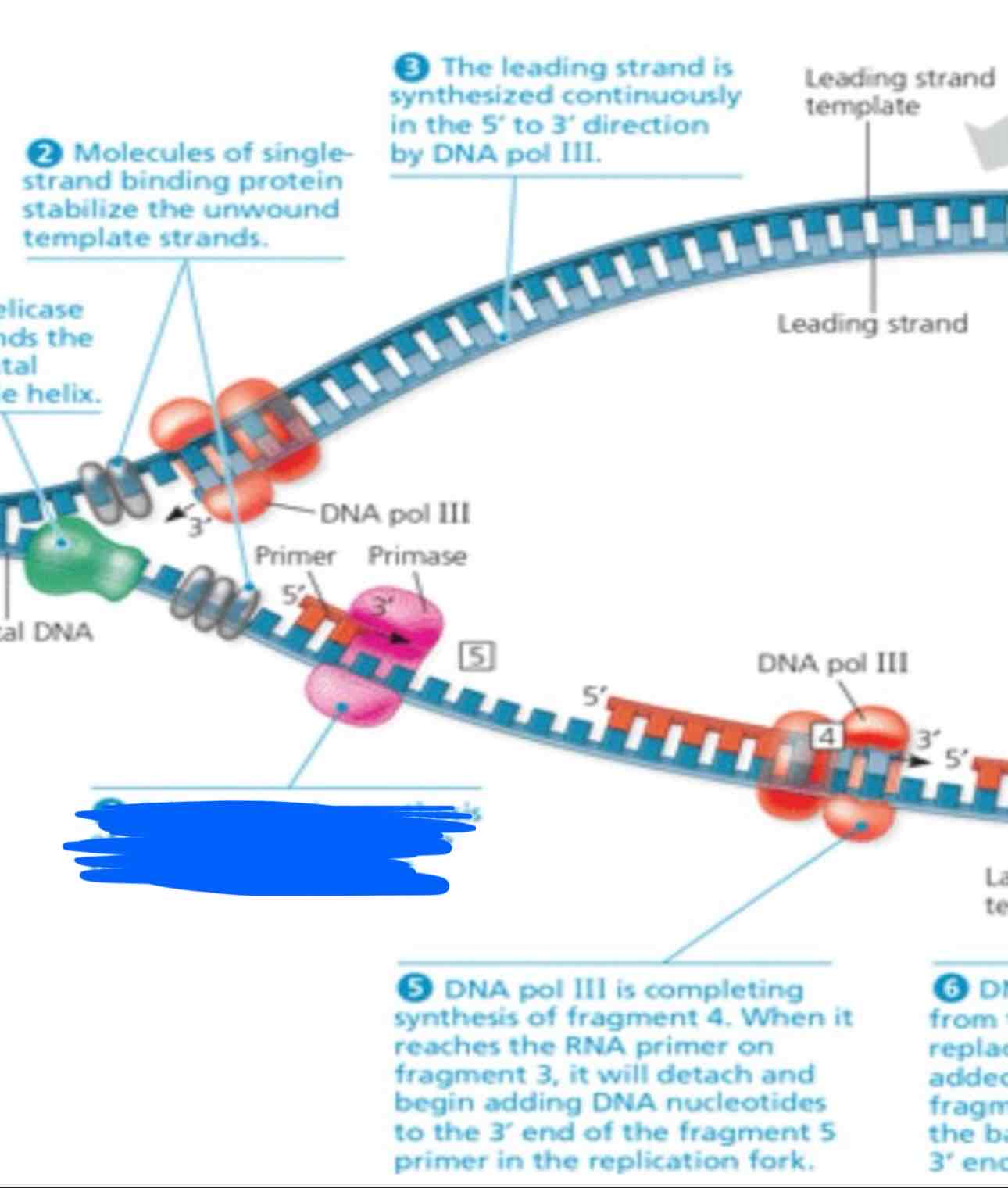
What is going on in this photo?
Primase begins making the RNA primer
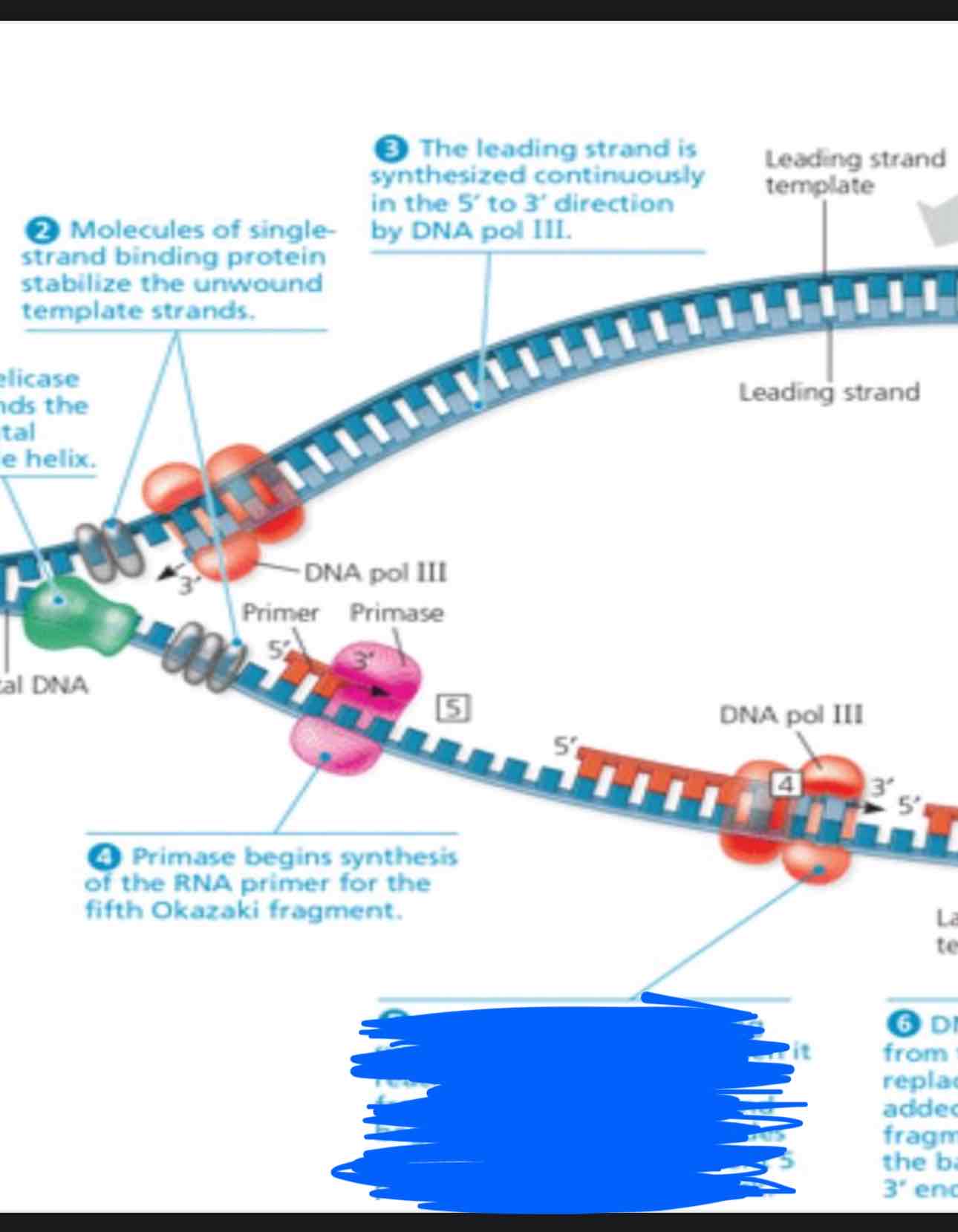
What is going on in this photo?
DNA pol 3 is finishing making fragment 4. When it reaches the RNA primer on fragment 3, it will detach and begins adding nucleotides to the 3’ end of the fragment 5 primer in the replication fork