ornithology test 1
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
the spruce grouse
adapted to live in the northern coniferous forest
the jacamar is specifically adapted for its what?
prey
penguins-
have musculature and specific physiological adaptions to allow it to inhabit the water, but also to withstand the extreme temperatures and find enough food sustain it
the bed bellied leiothrix
captured and bred for the pet trade, populations have been springing up in other locations than its native Asia
why are birds important?
you can found them anywhere, learn by observing where they go an what they do, indicators of environmental conditions as we change the planet how do they adapt,
how it one way that we can be a part of the solution?
citizen science
the paradigm-
avian biology is common ancestry
study skins-
used to be more common in ornithology
what is used to explain similarities of taxonomic groups that are unrelated?
convergence
some species have distinctly different what?
colors and patterns
relatedness-
implied in the binomial nomenclature, those that share the same Genus name are closely related
are new birds being found rather frequently?
yes
what occurs when scientists dont agree?
lumping and splitting
for some species there is quite a range of plumage variation which could result in what?
speciation or further adaptive radiation
what do new cladograms represent?
relatedness using DNA evidence, some ornithologists are not convinced these phylogenies are correct.
what does circular evolutionary tree track?
rates of speciation across space and time and is one of the first to include all recognized species of extant birds. reddish branches indicate groups with particularly high speciation rates.
what happens if a genus includes more than one species?
then they are distributions are distinguished with different colors
morphology can be …?
misleading for example the hume ground jay is not actually a jay but rather an unusual member of the chickadee and tit family
species with fragmented ranges often show genetic variation among their consistuent populations for example?
the white starred robin breeds only in montane regions above 1500 meter
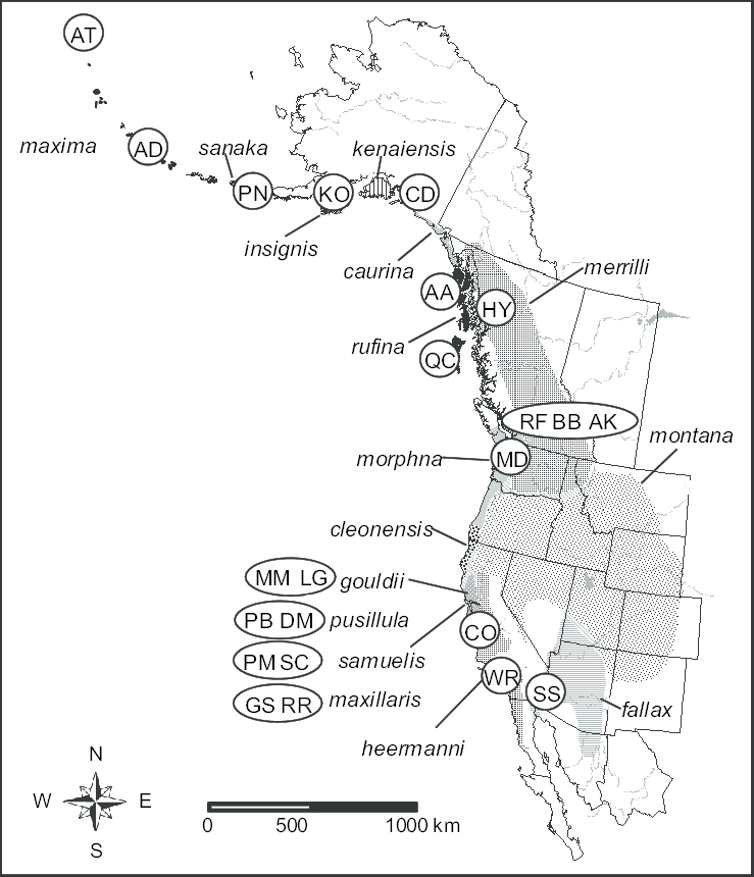
song sparrow subspecies distribution maps
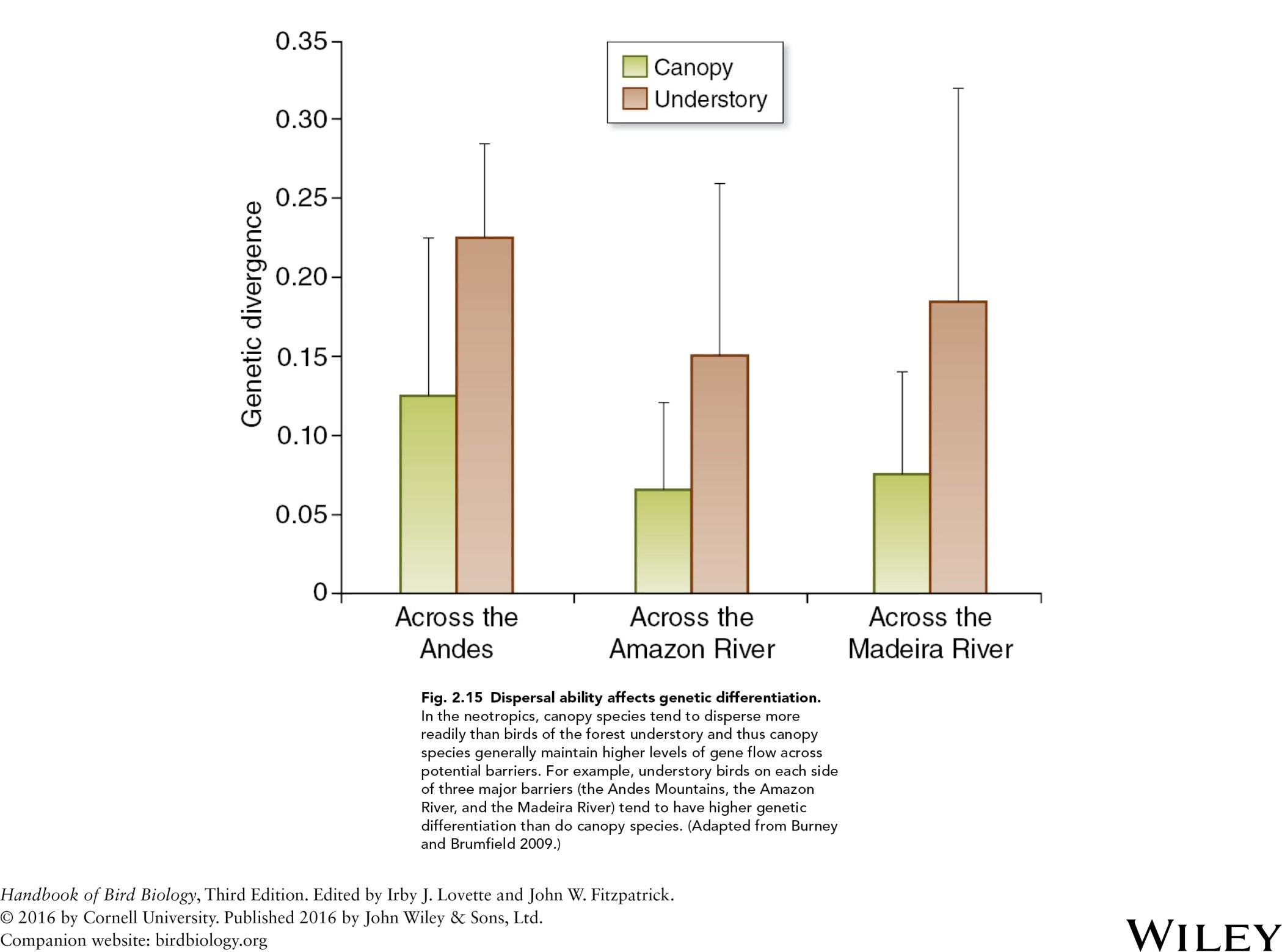
dispersal ability genetic differentiation-
in the neotropics, canopy species tend to disperse more readily than birds of the forest understory and thus canopy species generally maintain higher levels of gene flow across potential barriers. for example understory birds on each side of three major barriers tend to have higher genetic differentiation than do canopy species
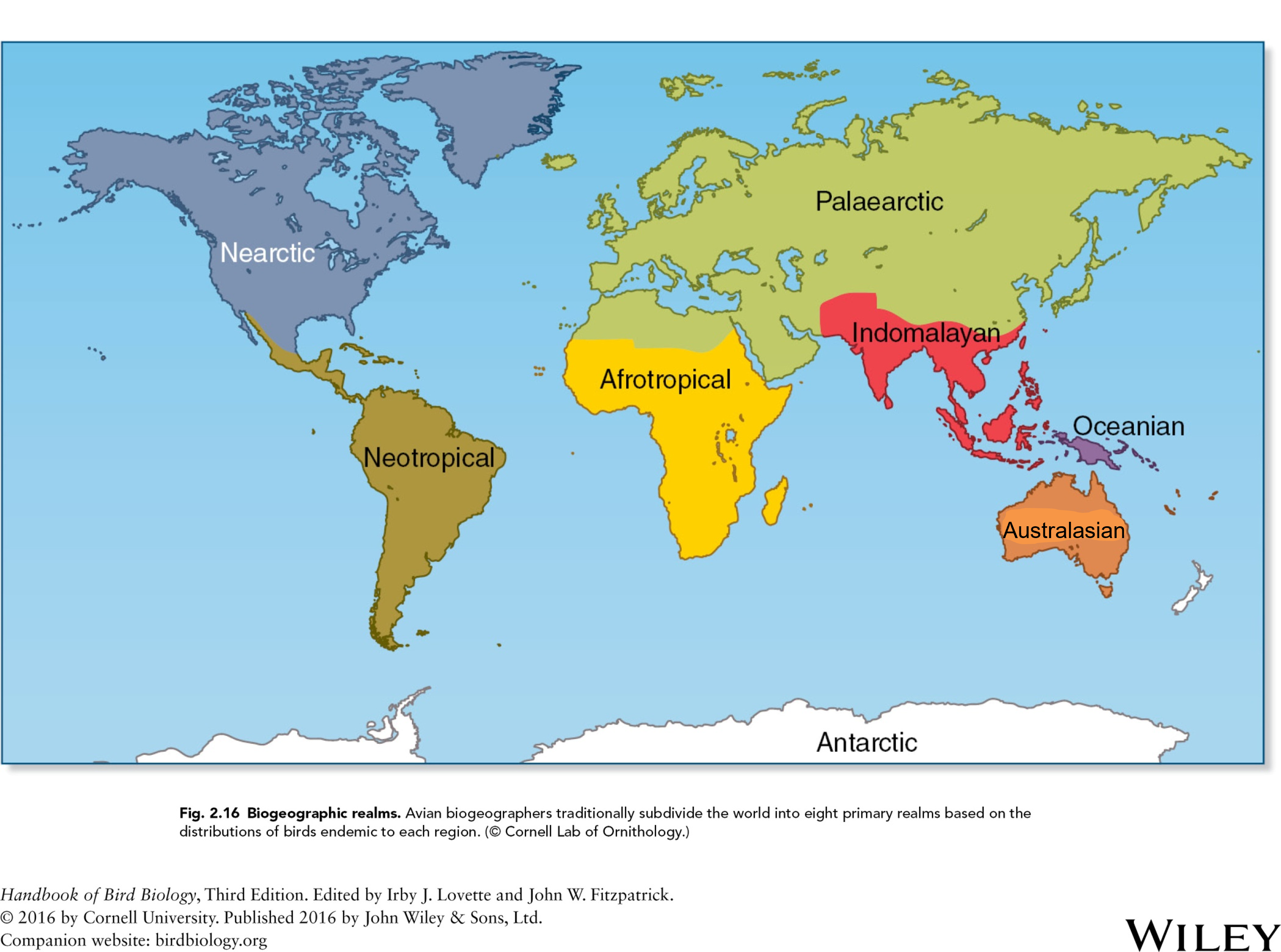
biogeographic realms-
traditionally subdivide the world into eight primary realms based on the distribution of birds endemic to each region
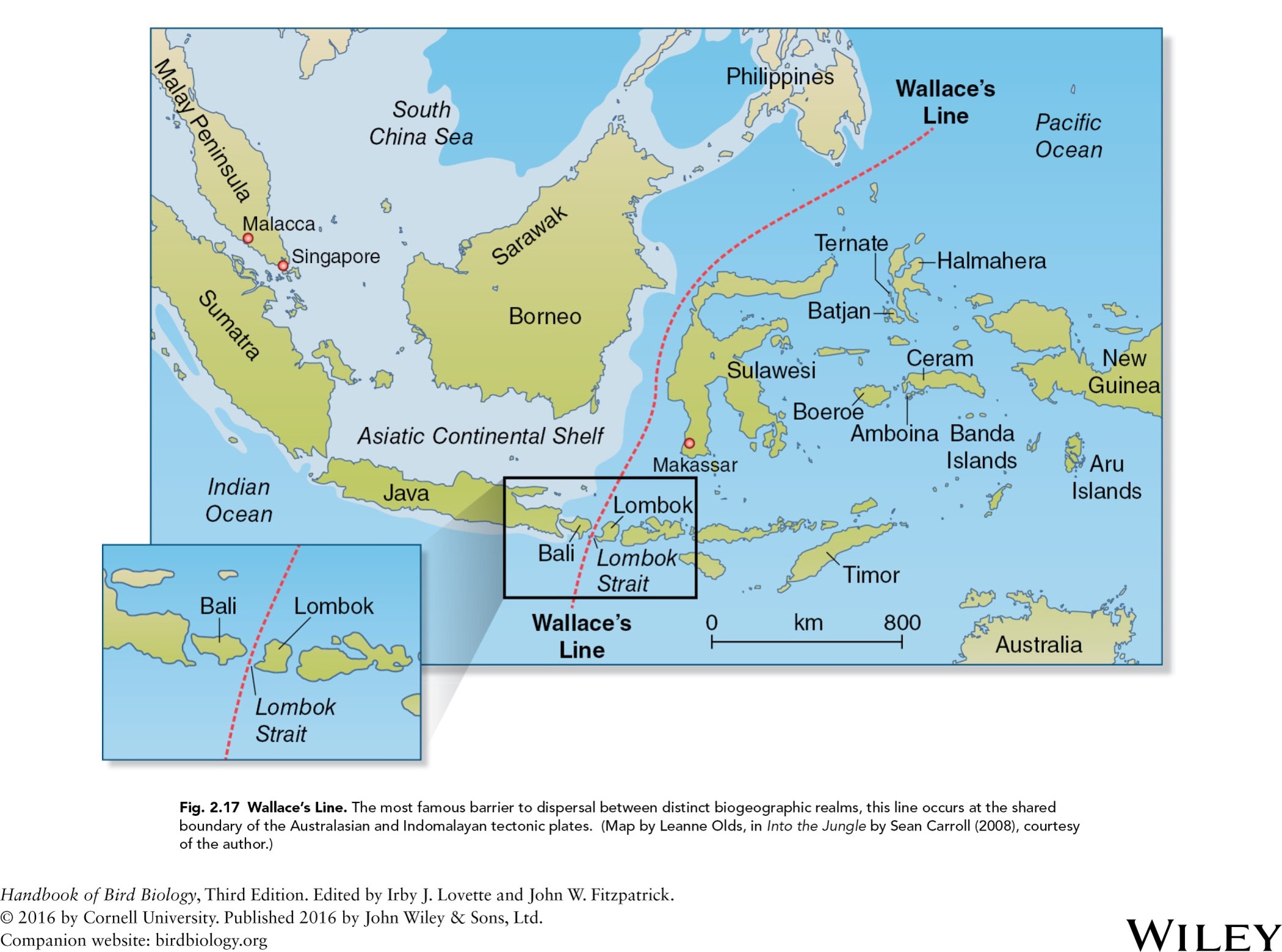
where is the most famous barrier that distinct biogeographic realms?
shared boundary of the Australasian and Indomalaya tectonic plates
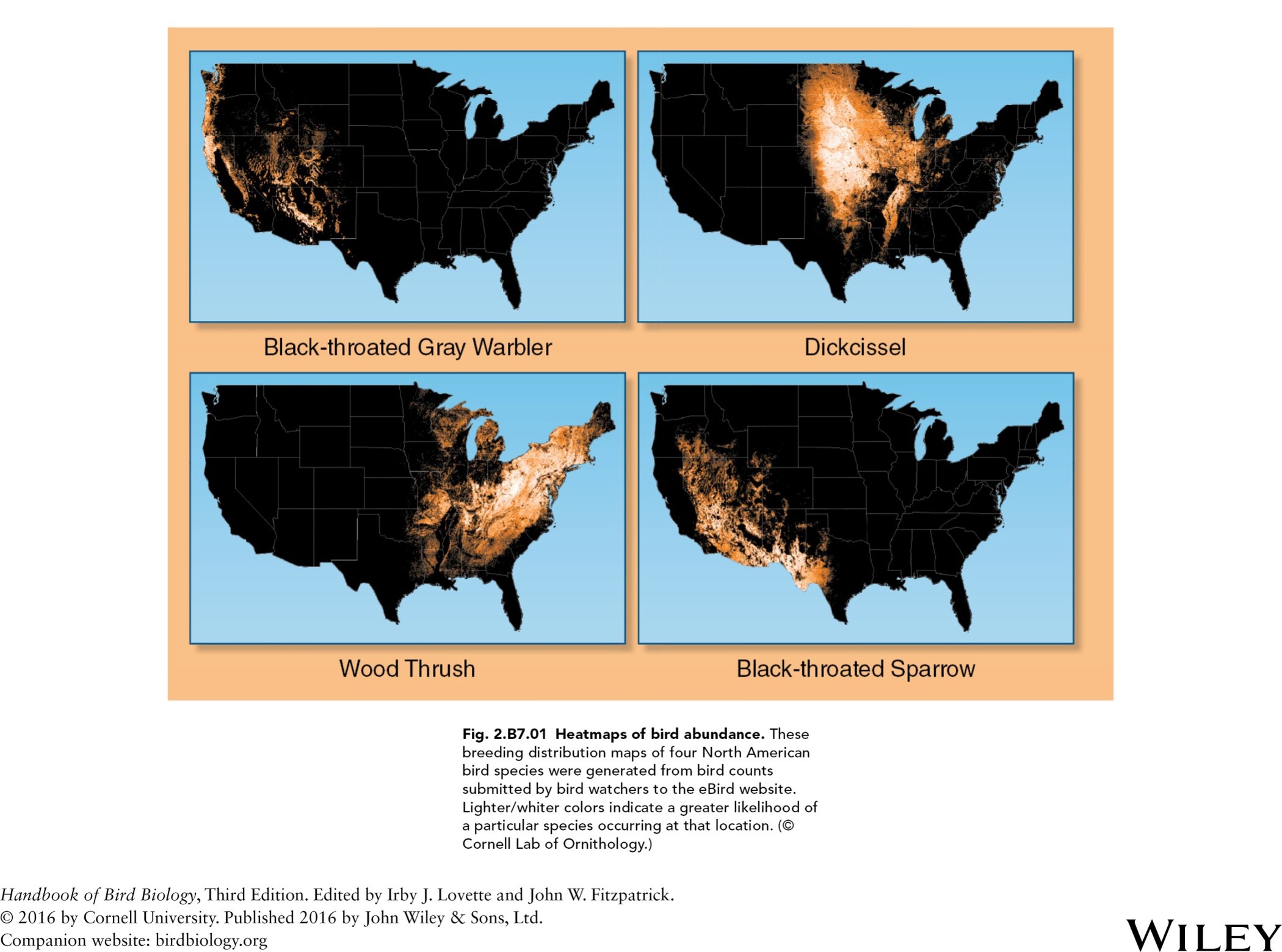
heatmaps of bird abundance
what gave rise to birds?
the maniraptorans- dinosaur that had many bird-like features
what is the nearest living relative to the archosaurs?
crocodiles
feather impression have been found on…?
fossils in china
birds and other theropod dinosaurs have small what?
genomes
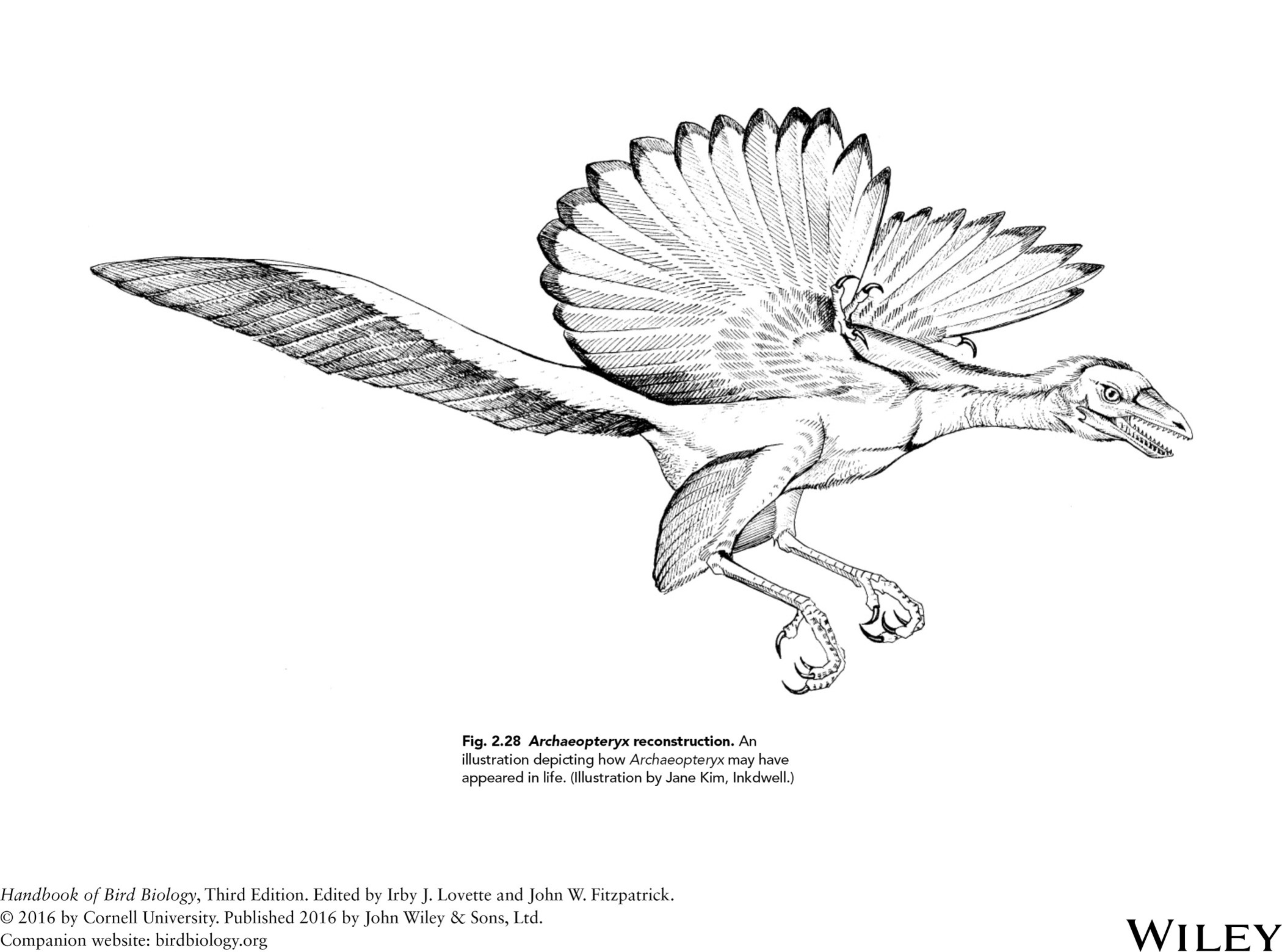
an early bird fossil?
archaopteryx
archaopteryx reconstruction
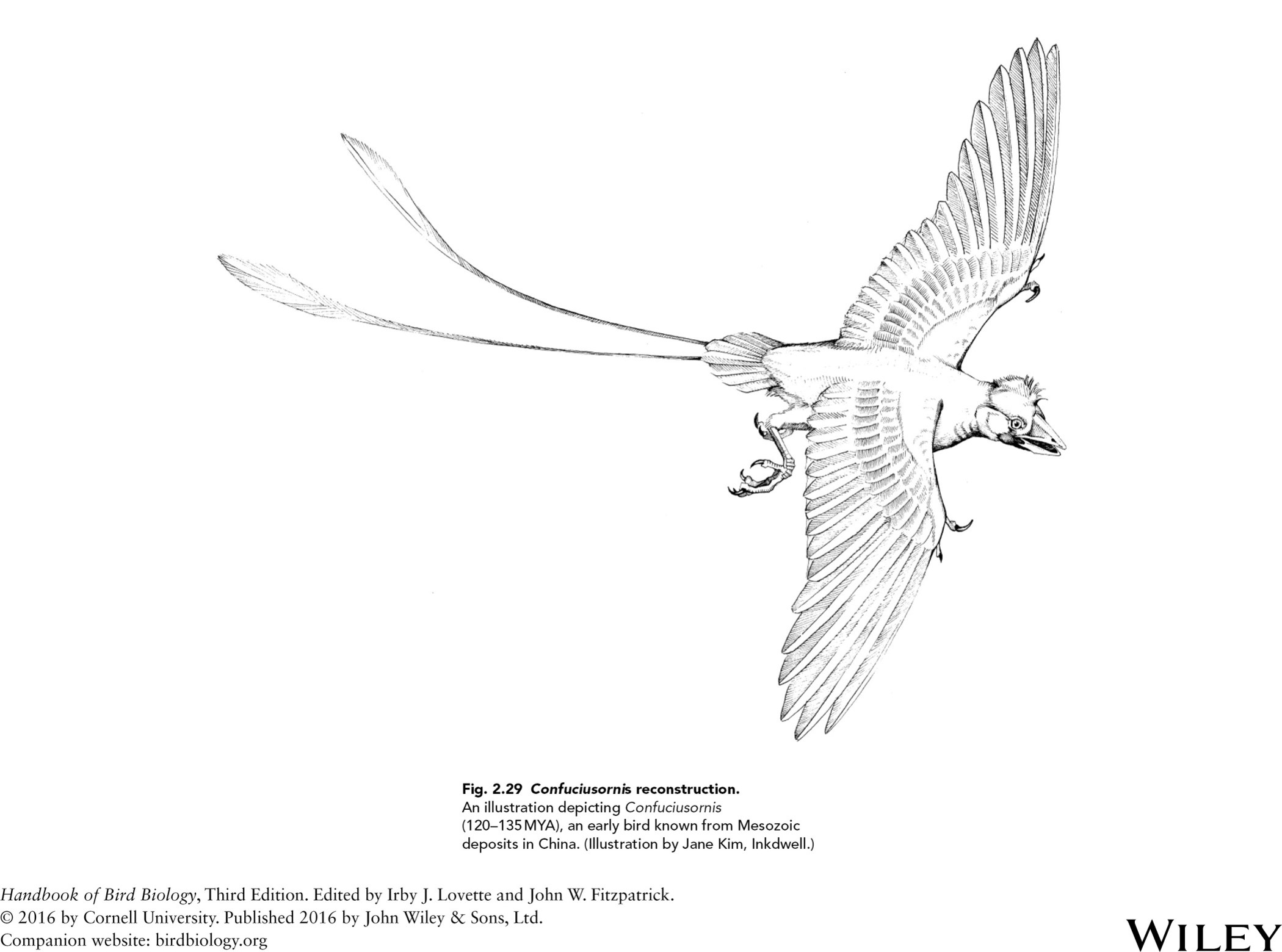
confusiusornis reconstruction-

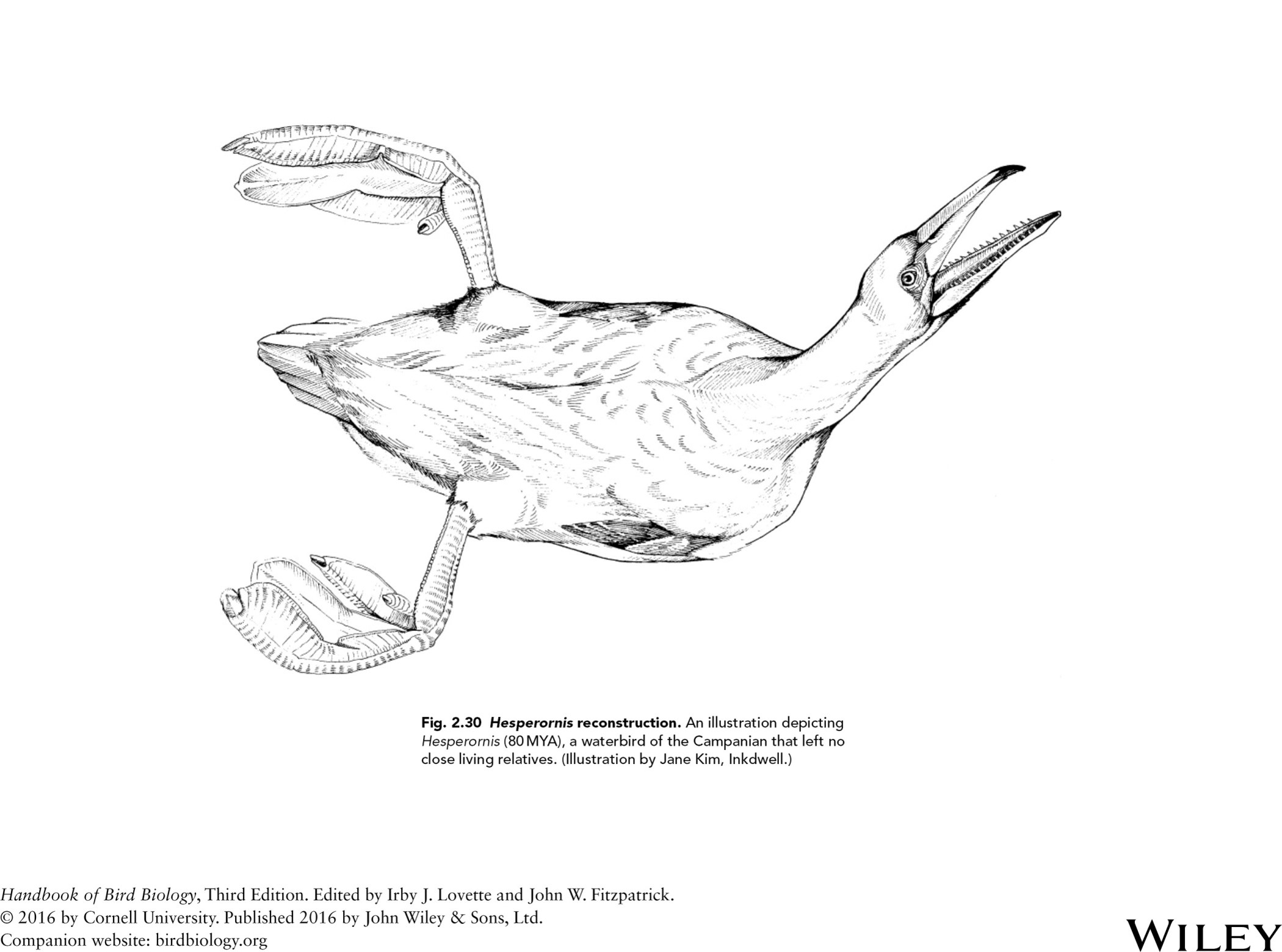
hesperonis reconstruction
waterbird that left no close living relatives
birds diversity before the what period?
tertiary period
what are two examples of living ratites?
the greater rhea and the emu
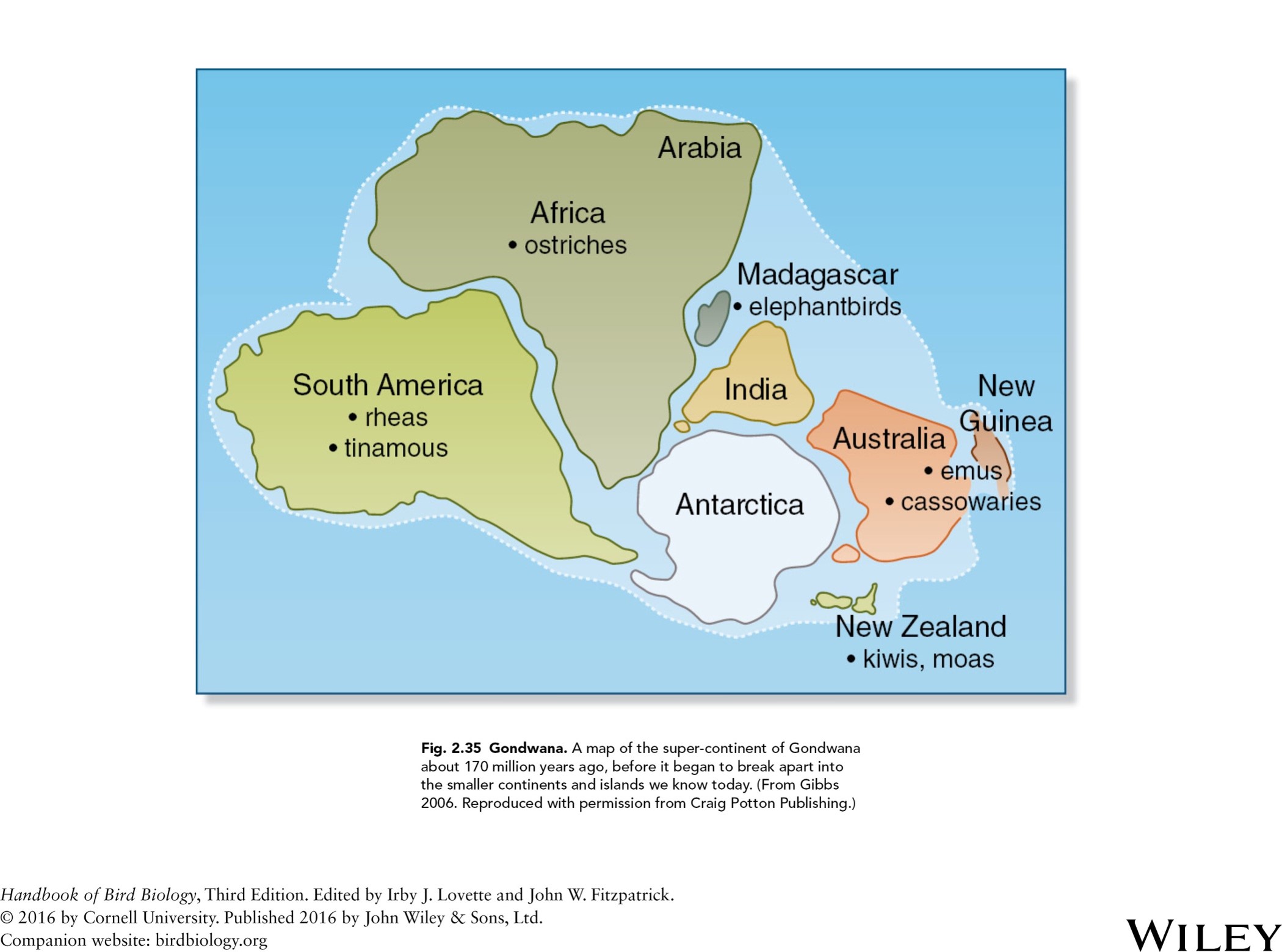
map of the super continent of Gondwana
basic features of a feather
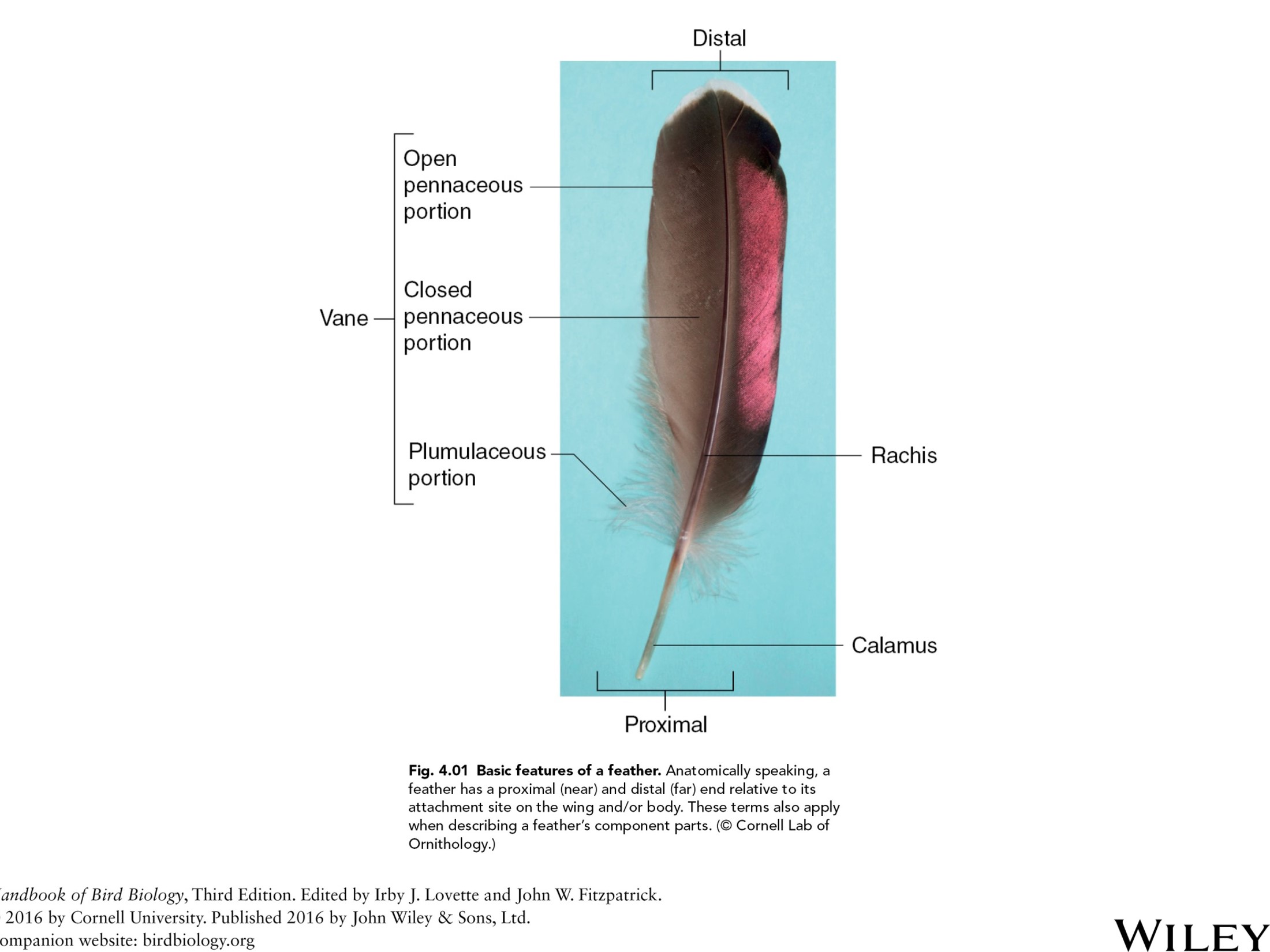
what is the ultimate waterproofing substance?
keratin
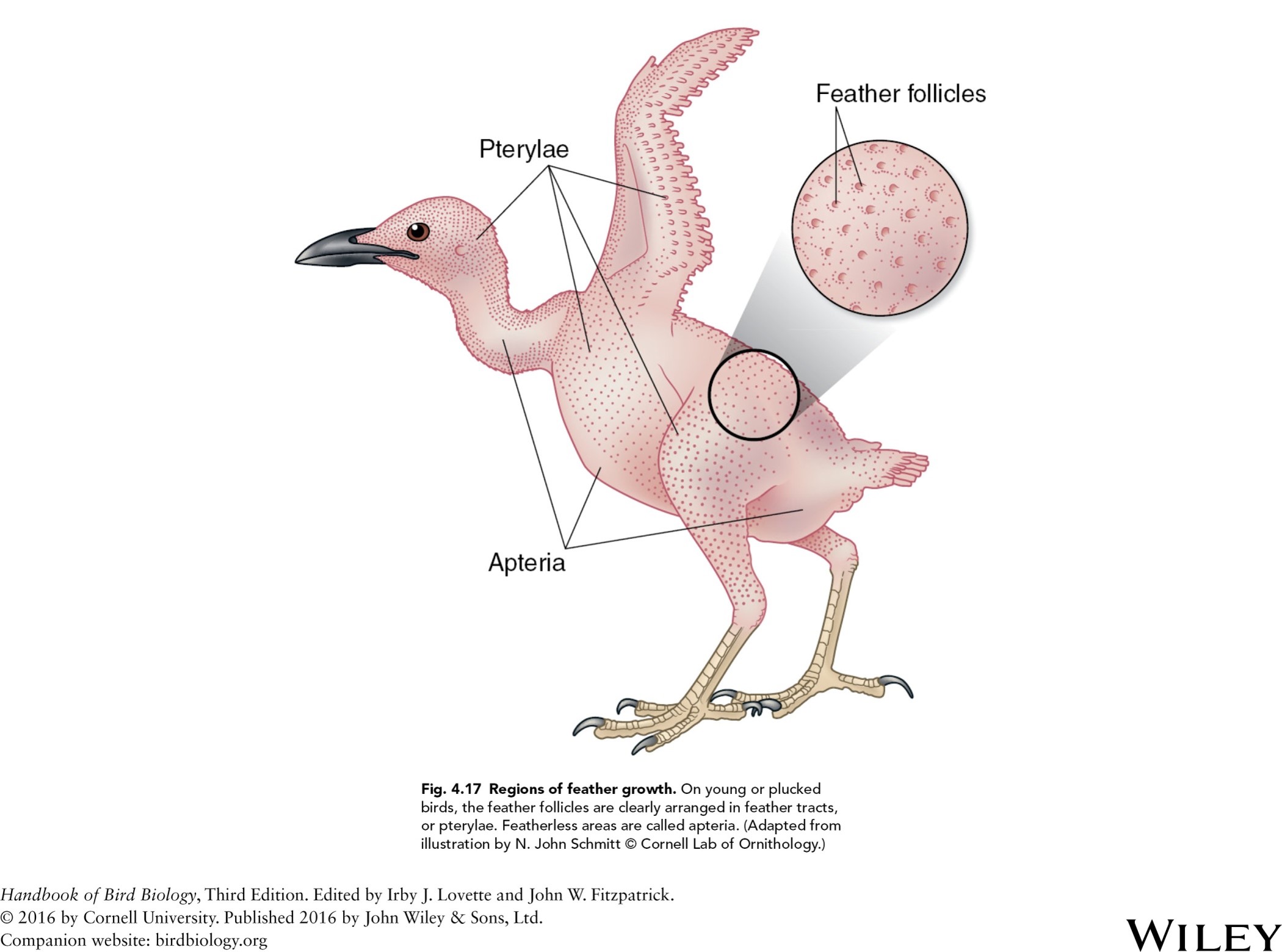
bear skin of a chicken with feather follicles?
the pterylae
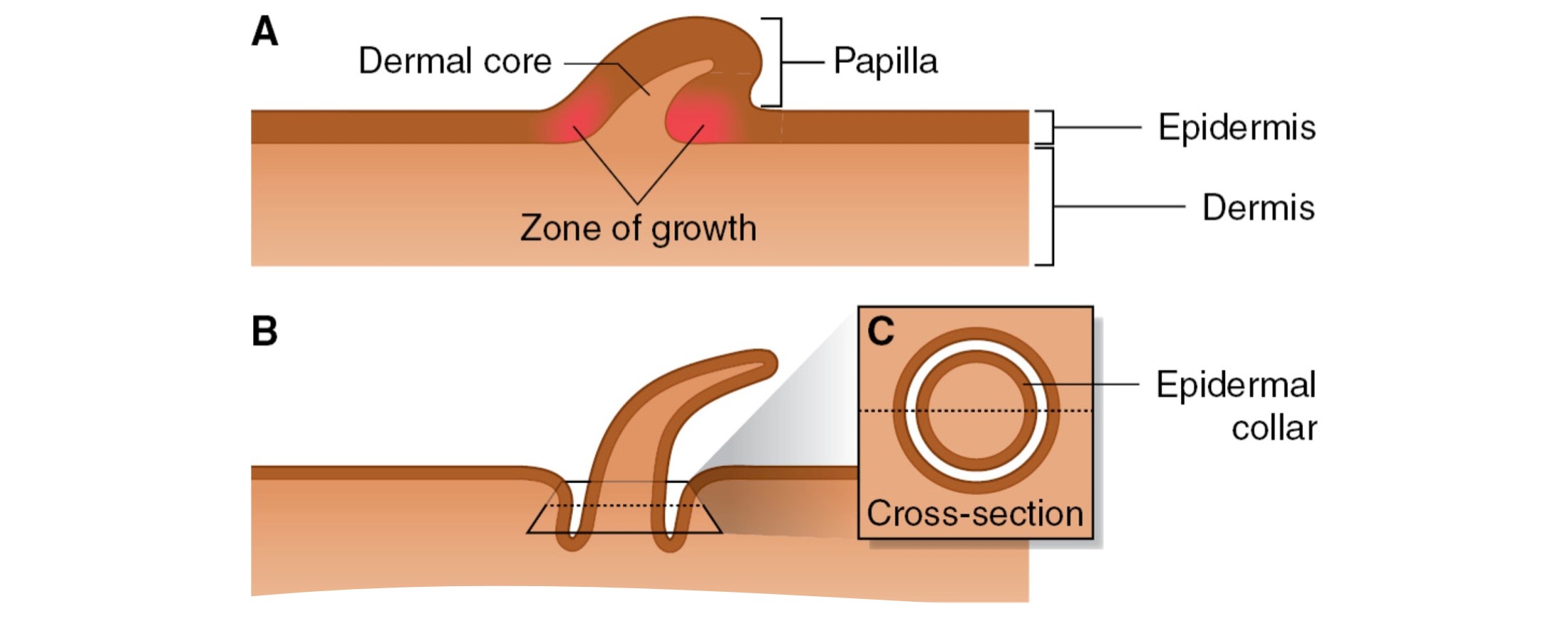
origin of feathers from the dermal papilla
ventral surface=
underside of feather
when a feather unfurles completely its ventral surface is what
concave and its dorsal surface is convex
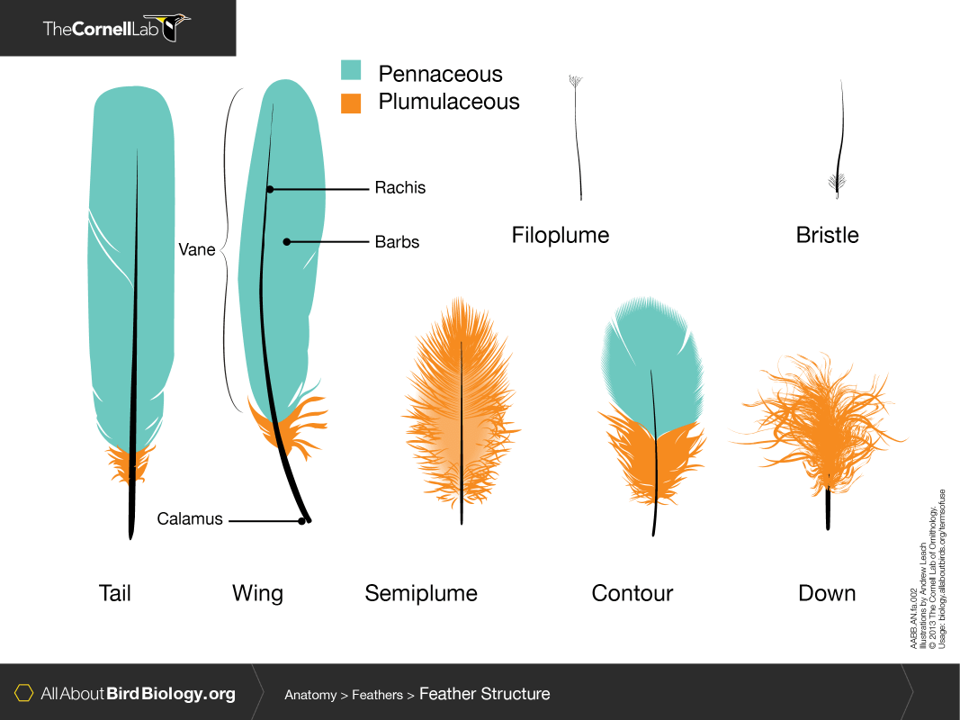
types of feathers
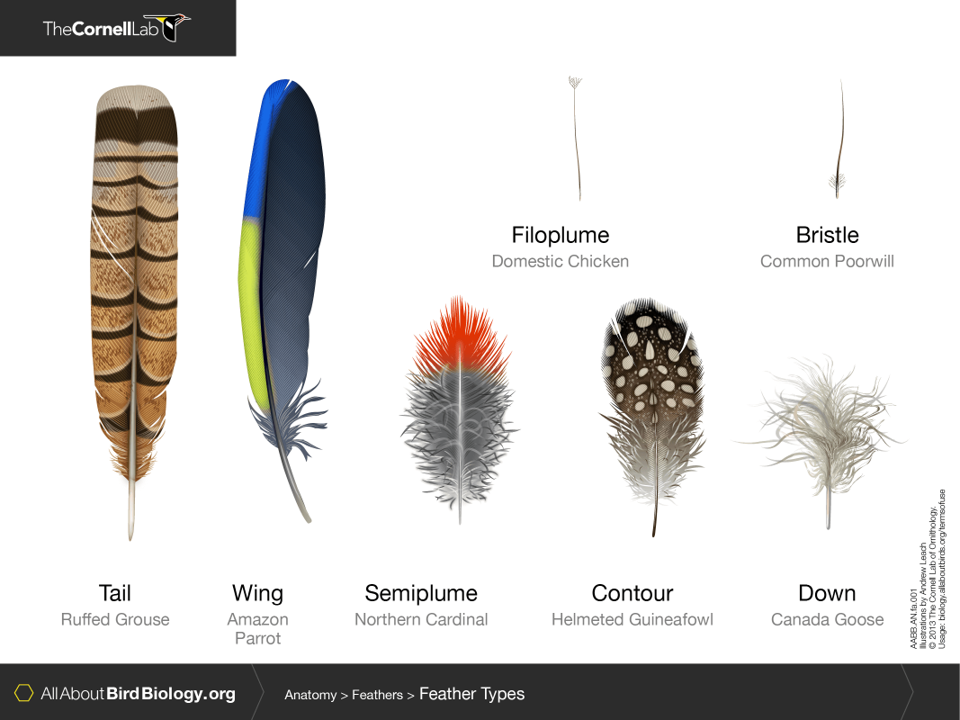

pennaceous vs. plumulaceous
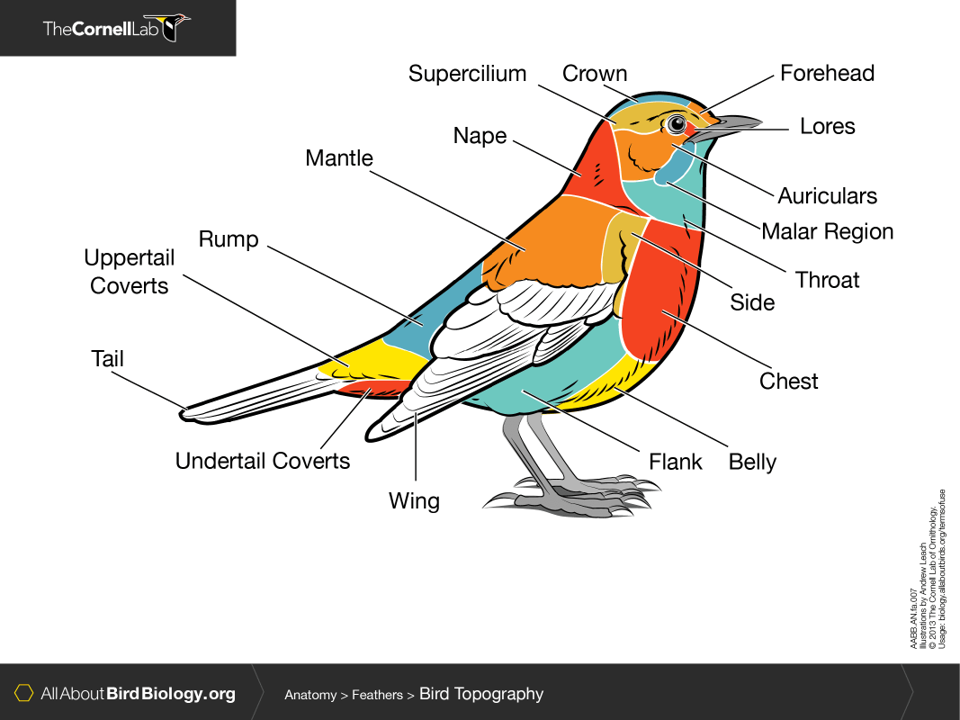
anatomy of a bird?
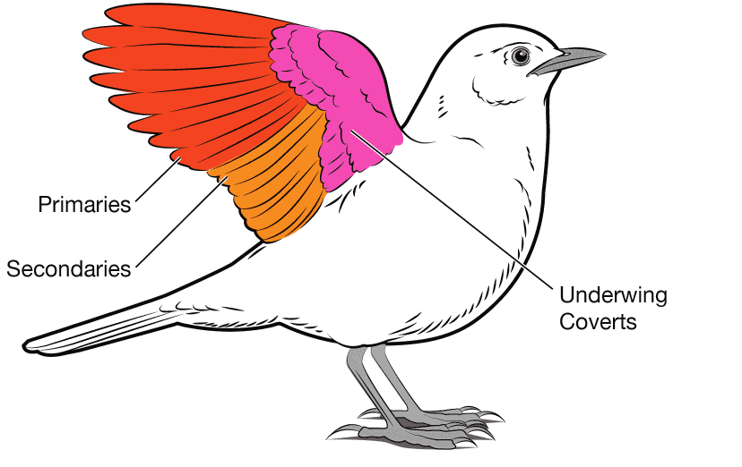
wing of birds
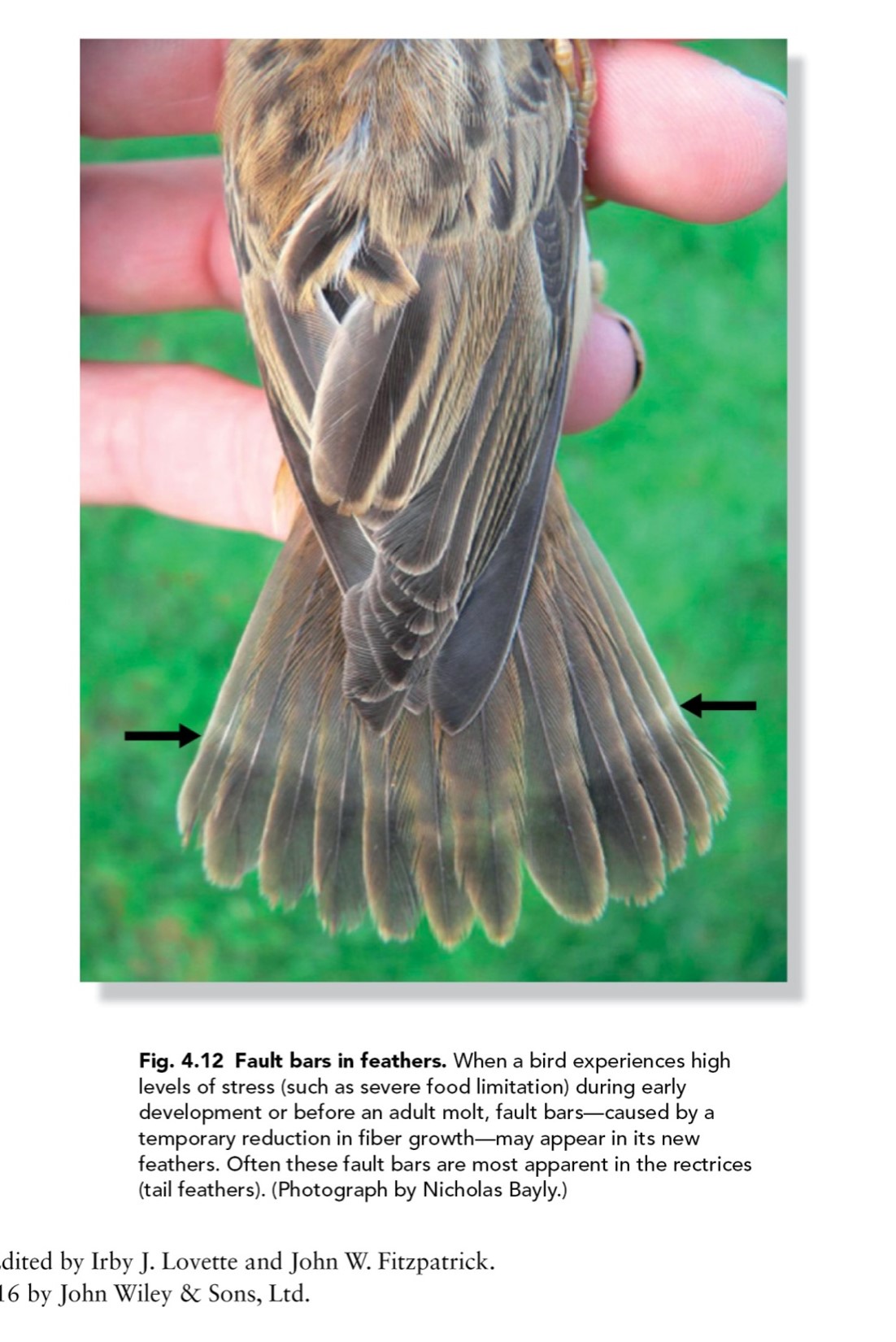
fault bars and due to what?
stress

regions of feather growth-
precocial vs altricial feather differences?

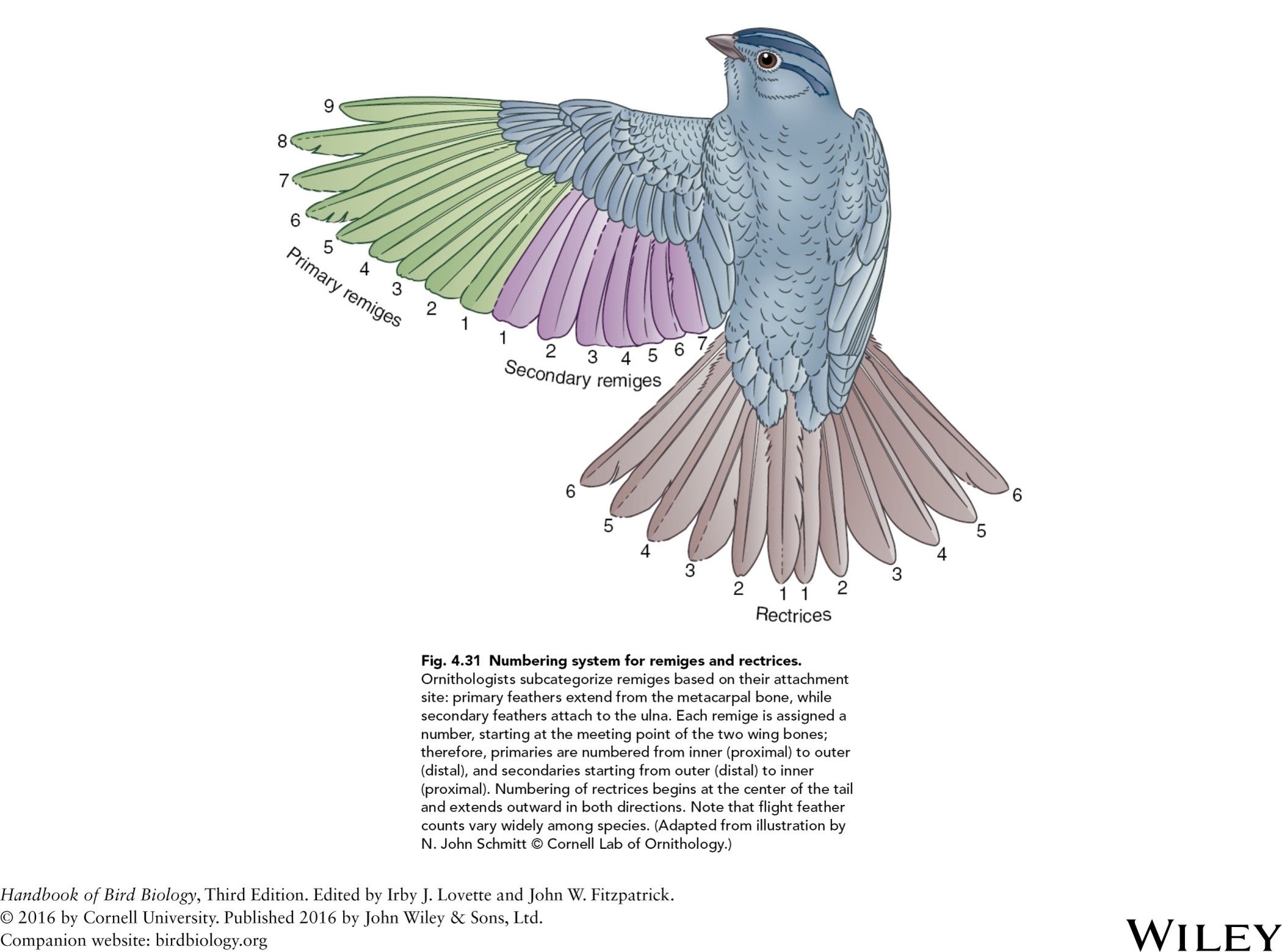
placement of remiges and rectrices

numerbing system for understanding molting patterns-
specialized feathers of owls
they have a soft pile coat and fringed tips helps move through the air better
semiplumes-
lack barbule hooks like down but have barbs shorter than the rachis as in contour feathers
bristle feathers-
eyelashes that provide extra protection
filoplumes-
the smallest feather type
eclipse versus alternate molts in adult waterfowl

feather preening-
when a bird spends a great deal of time maintaining their feathers to remove dirt and ectoparasites spread protective oils and rezip barbs and barbules
why dust bath?
a practice that may remove excess oils that ATTRACT ECOTPARASITES may desiccate or clump ectoparasites already in the oils making it easier to preen them off
passive anting-
remove ectoparasites by allowing ants to crawl through their feathers
carotenoid pigments-
obtained from the diet carotenoids create warm red orange and yellow hues as featured
when does constructive interference occur -
two waves of equal frequency rise and fall at the same timetheir energy combines and the amplitude doubles
what three elements create the green color in the barbs of wild type budgerigar fathers?
coherent scatting of blue green frequencies via the keratin air matric yellow pigment embedded in the keratin and a layer of melanin on the underside of the barb a change of any of these properties results in a different color morph
countershading for ..?
huunting success
white backed woodpecker male
red crowns
white backed woodpecker female
black crowns
flight-
fluid dynamics, discoveries in aviation, aerodynamics(the interplay between lift and drag), power fueling this activity, adaptations seen in various species
aerodynamics-
counteracting the force of gravity, airflow over a wing causes lift, the Bernoulli equation is the key to understanding pressure for flight
wingspan-
either extended or flexed influence the lift to overcome the drag changing altitude and the speed of flight
what is of ultimate importance in influencing the lift in relation to the drag?
the angle of the wing
what is another important variable in flight?
aspect ratio- wingspan divided by average width
what makes a difference in reducing drag?
tails
what does body size affect?
marginal power and flight style
low wing load=
small turn radius
high wing load=
large urn radius
large right wing effective surface area=
high right side effective lift
tails help restore what during yaw?
stability
Anseriformes
swans, geese, and ducks
Galliformes-
quail, pheasant ,grouse, and turkey
gaviiformes-
loons
podicipediformes-
grebes
procellariiformes-
strom petrals
ciconiiformes-
storks
suliformes-
frigatebirds, gannets, and cormorants
pelecamiformes-
pelicans, bitterns, herons, egrates, ibises and spoonbillls
accipitiformes-
vultures, ospreys, hawks eagles kites
gruiformes-
rails, gallinules , coots and cranes
charadriiformes-
stiles, avocets, plovers, sandpipers, gulls, terns and skimmers
columbiformes-
pigeons and doves
Cuculiformes-
cuckoos and anis
strigiformes
owls
caprimulgiformes-
might hawks and whip poor wills
apodiformes-
swifts and hummingbirds
coraciiformes-
kingfishers
piciformes-
woodpeckers
falconiformes-
falcons
psittaciformes-
parakeets
Passeriformes-
perching birds
anatidata families-
ducks, geese, and swans, cormorants and anhiges phalacrocoracisae gavidae loons