Lecture 14 Key Concepts/Terms
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/63
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
1
New cards
what are the major ways plants differ from protists?
protists are unicellular, plants are multicellular
protists are microscopic
move protists can move, plants cannot
protists are microscopic
move protists can move, plants cannot
2
New cards
challenges of land living
drying out, structural support, reproduction
3
New cards
adaptations to land dwelling
embryophytic
cuticle
stomata
pigmentation
fungal relationship
tracheid cells
seeds
cuticle
stomata
pigmentation
fungal relationship
tracheid cells
seeds
4
New cards
embryophytic
plants that have structures to protect the developing embryo
5
New cards
cuticle
The waxy, waterproof layer that covers the leaves and stems of most plants.
6
New cards
stomata
the small openings on the undersides of most leaves through which oxygen and carbon dioxide can move
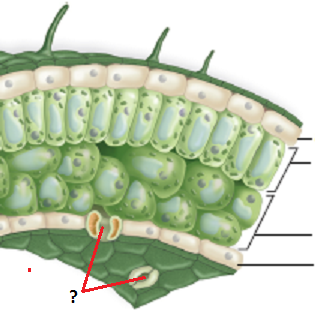
7
New cards
tracheid cells
Water-conducting and supportive elements of xylem
8
New cards
diplontic life cycle
a life cycle in which only the diploid phase is multicellular (e.g. human life cycle)
9
New cards
sporangia
located on the tip of the mature sporophyte, where meiosis occurs, producing haploid spores
10
New cards
spore mother cells
The cells that undergo meiosis and generate haploid spores within a sporangium.
11
New cards
spores
Produced by meiosis. Grow into haploid organisms by mitosis.
12
New cards
Zygote (plant)
diploid
13
New cards
embryo (plant)
Immature sporophyte stage
14
New cards
sporophyte
Diploid, or spore-producing, phase of an organism
15
New cards
gametophyte
Haploid, or gamete-producing, phase of an organism
16
New cards
haploidiplontic life cycle
an alternation between a multicellular haploid generation and a multicellular diploid generation
17
New cards
how do the events of meiosis and syngamy (fertilization) shape the haplodiplontic life cycle?
the fusion of gametes (syngamy) produces diploid cells and meiosis produces haploid cells
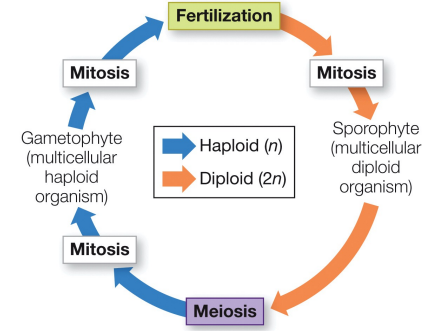
18
New cards
dominant life stage of moss
gametophyte
19
New cards
dominant life stage of ferns
sporophyte
20
New cards
is there a clear definition of plants?
Any of the eukaryotic organisms of the biological kingdom Plantae, characterized by being photosynthetic and having a rigid cell wall
21
New cards
the haploid phase gets _____ as plants evolve
shorter
22
New cards
syngamy
the fusion of two cells, or of their nuclei, in reproduction.
23
New cards
antheridium
male reproductive structure in some plants that produces sperm
24
New cards
archegonium
structure that produces eggs, develops on the gametophyte
25
New cards
red algae is the _______ of the plantae
outgroup
26
New cards
Red Algae (Rhodophyta)
marine algae in which the chlorophyll is masked by a red or purplish pigment
27
New cards
chloroplasts are a result of process
primary endosymbiosis
28
New cards
primary endosymbiosis
the process in which a eukaryote engulfs another living prokaryote
29
New cards
secondary endosymbiosis
when a living cell engulfs another eukaryote cell that has already undergone primary endosymbiosis
30
New cards
what group of stramenopiles is an example of secondary endosymbiosis
brown algae
31
New cards
land plants all arose through the ______ _______ lineage
green algae
32
New cards
land plants are photosynthetic due to what process
primary endosymbiosis
33
New cards
red algae has chlorophyll __
a
34
New cards
brown algae has chlorophyll __ and __
a; c
35
New cards
green algae has chlorophyll __ and __
a; b
36
New cards
land plants have chlorophyll __ and __
a; b
37
New cards
chlorophytes
most green algaes
similar cell form to land plants
monophyletic clade
similar cell form to land plants
monophyletic clade
38
New cards
stoneworts
sister to land plants
filamentous cell form
many homologous traits with land plants
cell structure
mitosis style
branching apical growth
filamentous cell form
many homologous traits with land plants
cell structure
mitosis style
branching apical growth
39
New cards
branching apical growth
grows vertically
40
New cards
what are the non-vascular plants
liverworts, hornworts, mosses
41
New cards
what are the seedless vascular plants
lycophytes, horsetails, ferns
42
New cards
what are the non-flowering seed plants
gymnosperms
43
New cards
what are the flowering plants
angiosperms
44
New cards
other name for nonvascular plants
bryophytes
45
New cards
what does it mean to be nonvascular?
NO tracheid cells
46
New cards
features of byrophytes
embyrophytic
gametophyte dominant
sporophyte dependent on gametophyte
require water for sexual reproduction
gametophyte dominant
sporophyte dependent on gametophyte
require water for sexual reproduction
47
New cards
moss life cycle
ungerminated spore --> germinating spore --> gametophyte --> antheridium or archegonium (water necessary) --> fertilization --> sporophyte --> sporangium --> meiosis --> ungerminated spore
48
New cards
what are the benefits of tracheids?
allows plants to grow tall because water and minerals can move upwards and sugar and nutrients can move downward. taller plants survive better because they are closer to the sun and receive more light for photosynthesis
49
New cards
other name for seedless vascular plants
tracheophytes
50
New cards
features of tracheophytes
embyrophytic
sporophyte dominant
free-living gametophyte
can get very large
sporophyte dominant
free-living gametophyte
can get very large
51
New cards
lycophytes (club mosses)
most primitive tracheophytes
generally small
have microphylls (seeds without vasculature)
generally small
have microphylls (seeds without vasculature)
52
New cards
microphylls
The small leaves of lycophytes that have only a single, unbranched vein.
53
New cards
megaphylls
leaves with a highly branched vascular system
54
New cards
are the monilophytes paraphyletic or monophyletic?
monophyletic
55
New cards
monilophytes
ferns, horsetails
56
New cards
sori
fern structures in which spores are produced (enclose sporangia)
57
New cards
fern life cycle
broken sporangium releases germinating spores --> mature gametophyte (heart shaped) --> antheridium or archegonium produce sperm or egg --> fertilization --> embryo --> sporophyte --> mature sporophyte
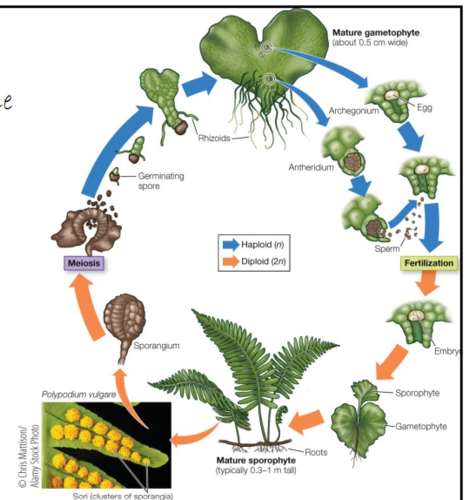
58
New cards
Sequoiadendron giganteum (giant sequoia)
tracheophyte and gymnosperm (excellent example of plant adaptation)
59
New cards
Sequoia sempervirens (coast/california redwood)
largest gymnosperm
60
New cards
Chlamydomonas
unicellular green algae
61
New cards
Volvox
colonial green algae
62
New cards
Nori (red algae)
dried edible seaweed used in japanese cuisine
63
New cards
Chara
green algae
64
New cards
Which of the following statements about the haplodiplontic life cycle of land plants is/are TRUE?
A) during the sporophyte stage, sporangia house diploid mother cells that will eventually undergo meiosis
B) sperm develop from mitosis in the archegonium
C) spores grow by mitosis into mature haploid gametophytes
D) the gametophytic stage begins with a diploid spore
E) A and C are both true
A) during the sporophyte stage, sporangia house diploid mother cells that will eventually undergo meiosis
B) sperm develop from mitosis in the archegonium
C) spores grow by mitosis into mature haploid gametophytes
D) the gametophytic stage begins with a diploid spore
E) A and C are both true
E) A and C are both true