Topic 5A.2: Chloroplasts and Chlorophyll
1/33
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Pg. 17
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
What are chloroplasts?
Chloroplasts the organelles in plant cells where photosynthesis occurs
Each is surrounded by the chloroplast envelope
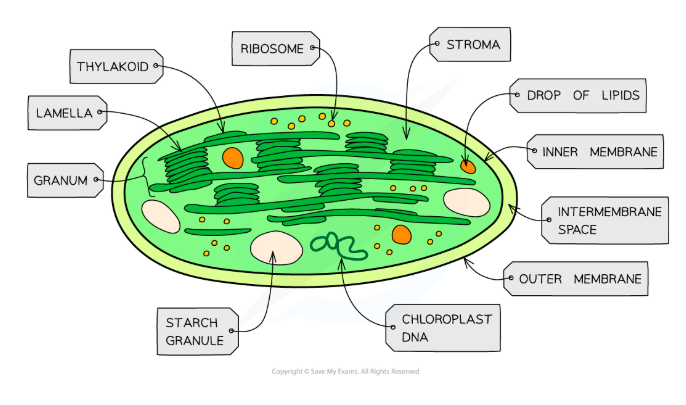
What is the chloroplast envelope?
The chloroplast envelope is the outer and inner membranes of a chloroplast including the intermembrane space that surrounds each chloroplast
Each of the envelope membranes is a phospholipid bilayer
What are thylakoids?
Thylakoids are membrane systems that consist of a series of flattened fluid-filled sacs/discs, each surrounded by a thylakoid membrane
They stack up to form grana
The thylakoid membrane is the sight light dependant stages of photosynthesis
Where are the photosynthetic pigments found?
The photosynthetic pigments are found in the thylakoid membranes
The pigment molecules are arranged on the membranes in the best possible position for capturing light energy
What are the grana? (pl. granum)
The grana are the layers of thylakoid membranes within a chloroplast
The grana are joined together by lamellae to ensure the stacks of sacs are connected but distanced from each other
What is a single granum made up of?
A single granum is made up of layers of membrane discs known as thylakoids
What doe sit mean if a chloroplast has many grana?
If a chloroplast has many grana this means that there is lots of photosynthesis occurring
What are the lamellae?
The lamellae are extensions of the thylakoid membranes which connect two or more grana and act as a supporting skeleton in the chloroplast
They maintain a working distance between the grana so that these receive the maximum light and function as efficiently as possible
What is the stroma?
The stroma is the cytoplasm-like fluid which surrounds the grana
It contains all the enzymes needed to complete the process of photosynthesis and produce glucose
It also contains sugars, ribosomes and chloroplast DNA
If the chloroplast has been photosynthesising there may be starch grains or lipid droplets in the stroma
It is the site for light independent stages of photosynthesis
Describe the DNA found in chloroplasts
Chloroplast DNA is circular (ie. Circular DNA)
It has genes for proteins (eg. enzymes) used during photosynthesis
What is chlorophyll?
Chlorophyll is is a light-capturing, photosynthetic pigment
It is a mixture of closely related pigments, not a single molecule, namely:
Chlorophyll a
Chlorophyll b
The chlorophyll carotenoids
Phaeophytin
What is chlorophyll a?
Chlorophyll a is a blue-green photosynthetic pigment, found in all photosynthesising green plants
It is in the highest quantity of the five pigments
What is chlorophyll b?
Chlorophyll b is a yellow-green photosynthetic pigment
What are chlorophyll carotenoids?
Chlorophyll carotenoids are photosynthetic pigments consisting of orange carotene and yellow xanthophyll
What is phaeophytin?
Phaeophytin is a grey pigment which is produced by the breakdown of the other photosynthetic pigments
What gives the leaves of plants their great variety of different greens?
The varying proportions of the pigments (other than chlorophyll a) are found in in different plants
Each of the pigments absorbs and captures light from particular areas of the light spectrum
How are the different proportions of the photosynthetic pigments an adaptation?
Different proportions of the photosynthetic pigments will produce a different colour of leaf - his can be a major adaptation to habitat
Example: many aquatic plants are red or brown
These colours absorb the blue light that penetrates water easily.
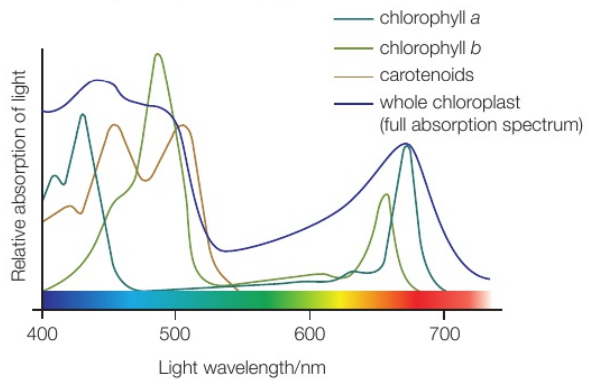
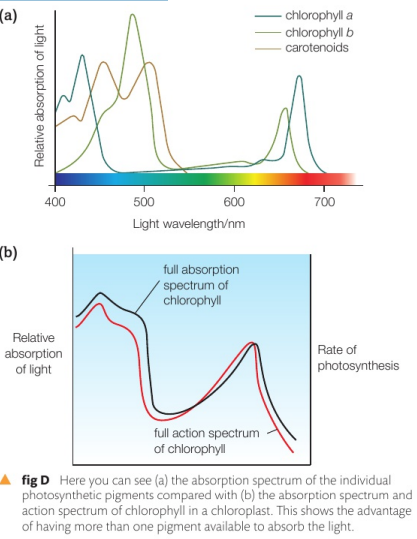
What is the absorption spectrum?
The absorption spectrum is a graph showing the amount of light absorbed by a pigment against the wavelength of the light
It describes he different amounts of light of different wavelengths that a photosynthetic pigment absorbs
How can the absorption spectra of the different photosynthetic pigments be found?
By measuring their absorption of light of differing wavelengths
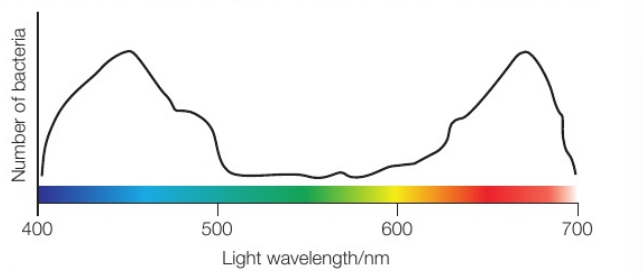
What is an action spectrum?
An action spectrum is a graph demonstrating the rate of photosynthesis against the wavelength of light
What does action spectra show us in relation to absorption?
Action spectra show us that the rate of photosynthesis is very closely related to the combined absorption spectrum of all the photosynthetic pigments in a plant
This demonstrates that having different photosynthetic pigments makes a much bigger portion of light available to plants and therefore gives them an adaptive advantage
What is chromatography?
What is the Rf value (retardation factor)?
The Rf value is the ratio of the distance travelled by the pigment to the distance travelled by the solvent alone when pigments are separated by chromatography
After chromatography is conducted on the photosynthetic pigments, their Rf values can be determined and compared to the Rf values of known pigments in the same solvent. Why is this important?
It is important to compare Rf, values using the same solvent because the pigments can have very different values with different solvents
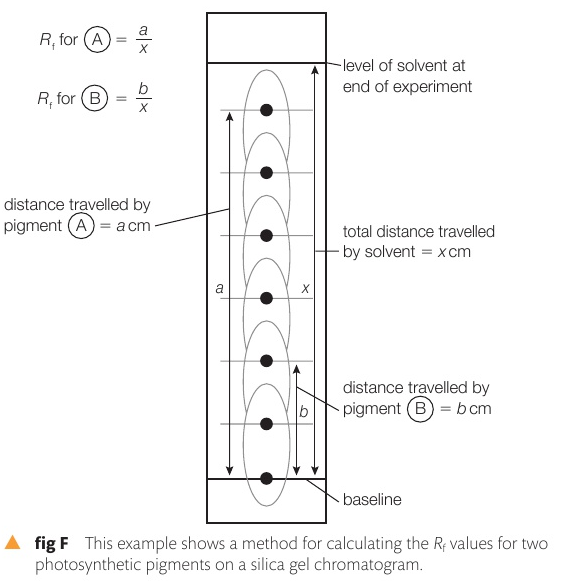
How is the Rf calculated?

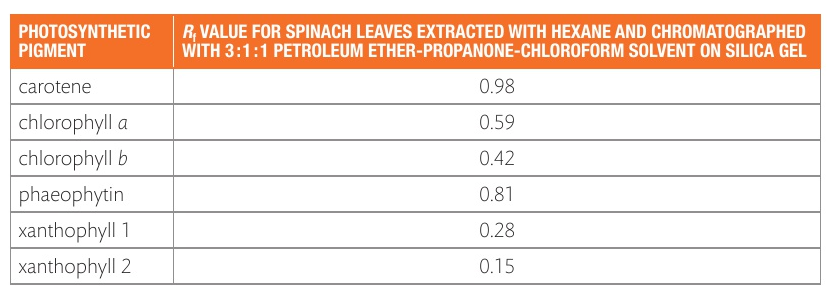
TABLE OF PHOTOSYNTHETIC PIGMENTS AND THEIR Rf VALUES
The photosynthetic pigments absorb light in two distinct chlorophyll complexes. What are they?
Photosystem I (PSI)
Photosystem II (PSII)
What are two things that make the two photosystems different?
Each system contains a different combination of chlorophyll pigments and therefore absorbs light in a slightly different area of the spectrum
Each photosystem are differently sized particles attached to the membranes in the chloroplasts
PSI particles are mainly on the intergranal lamellae, whereas PSII particles are on the grana themselves
Each have different functions
What is photosystem I (PSI)?
Photosystem I (PSI) is a combination of chlorophyll pigments which absorbs light of wavelength 700 nm and is involved in cyclic and non-cyclic photophosphorylation
What is photosystem II (PSI)?
Photosystem II (PSII) is a combination of chlorophyll pigments which absorbs light of wavelength 680 nm and is involved only in non-cyclic photophosphorylation
Each photosystem has two types of pigments. Name them
Primary pigment (reaction centre): Chlorophyll a
Accessory pigments: Chlorophyll b, carotenoids and xanthophyll
What is the difference between the primary pigment and accessory pigments?
The primary pigment is directly involved in the absorption of light to provide energy for photosynthesis
When it absorbs light an electron is lost from it in photoactivation
The accessory pigments pass energy to the primary pigment
Chloroplasts are not present in all plant cells. Explain why not
Because not all the cells carry out photosynthesis – any parts of the plant that are not directly exposed to light will not contain chlorophyll
Summarise the adaptations of chloroplasts for their role in photosynthesis, including the role of membranes.
Folded membranes give large surface area
Enzymes on membranes and in stroma to carry out reactions.
The presence of several photosynthetic pigments to absorb different wavelengths of light.