COOP Quiz 13 Nervous System Anatomy and Physiology
1/82
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Parts of brain and their functions, parts of neuron and their functions, how action potentials work, how drugs affect neurons
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
83 Terms
Which structure is responsible for the autonomic centers that control blood pressure, heart rate, and digestion?
medulla oblongata
The ________ filters and routes sensory information to the cerebral cortex.
Thalamus
Joe begins to experience mood swings and disturbed thirst and hunger. Imaging studies indicate that a brain tumor is the likely cause of these disorders. In what part of the brain is the tumor most likely located?
hypothalamus
Which of the following brain parts is NOT correctly paired with its function?
Occipital lobe: taste and smell
After suffering a stroke, Mary finds that she cannot move her right arm. This would suggest that the stroke damage is in the area of the ________ lobe.
left frontal
After suffering a blow to the back of the head, Phil loses his vision. The blow probably caused damage to the
occipital lobe
Which of the following is not a division of the peripheral nervous system?
Spinal Division
The ________ nervous system is composed of the brain and spinal cord.
central
Pulling your hand back from a hot stove would involve____________neurons.
Somatic motor
What is the site of communication between neurons (the gap between 2 neurons) called?
synapse
Which of the following describes the transport of Na-K ions at the normal resting potential of a typical neuron?
3 sodium ions for 2 potassium ions
Which of the following is not true about the resting potential of a neuron?
+30 mV membrane potential
Puffer fish poison blocks voltage-gated sodium channels like a cork. What effect would this neurotoxin have on the function of neurons?
The axon would be unable to generate action potentials.
Which of the following is the result of opening of sodium channels in the axon membrane?
Both depolarization and increased positive charge inside the membrane
Which of the following would happen if the potassium continues to pass out of the membrane after the resting potential has been reached?
The inside of the membrane will become more negative.
Put the following steps of the generation and recovery of an action potential in the correct order.
Sodium channels are opened.
Voltage-gated potassium channels open and potassium moves out of the cell, initiating repolarization.
A temporary hyperpolarization occurs.
Sodium ions enter the cell and depolarization occurs.
The membrane potential drops from 30mV to -70mV.
1, 4, 2, 5, 3
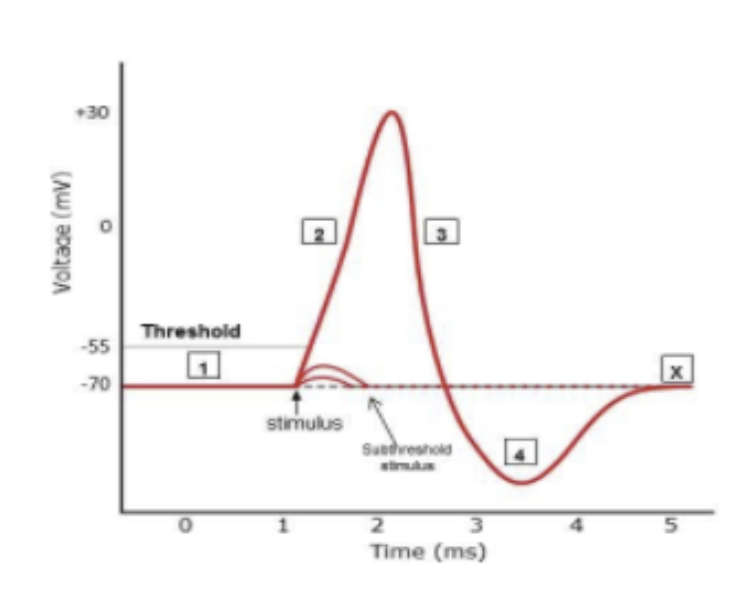
Match the number to the correct description (you can repeat numbers).
depolarization: 2
sudden rush of sodium ions: 2
shows effect of prolonged opening of potassium gate: 4
potassium outflow exceeds sodium inflow: 3
hyperpolarization: 4
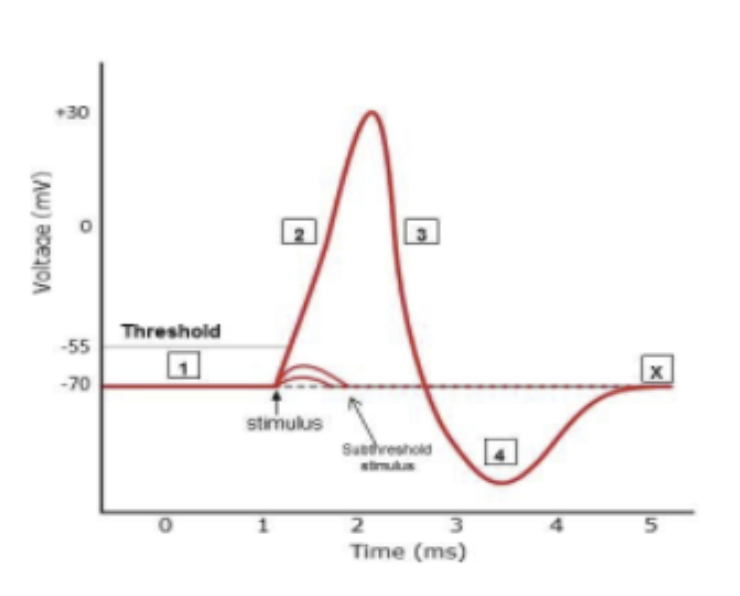
Which of the following statements about the action potential is false?
The rapid depolarization phase is caused by the entry of potassium ions.
Which of the following is the result of hyperpolarization of the axon?
it makes it more difficult for the neuron to generate an action potential
Which of the following does not describe threshold level?
is met when potassium leaves the cell
Describe a stimulus that would not reach the threshold for an action potential to occur. Why is it important that we do not experience all stimuli we experience?
One example of a stimulus that wouldn't reach the threshold, would be the hair touching your body constantly. It's important to not experience all the stimuli because that would be a sensory overload leading to the nervous system being overloaded constantly with signals and making us unable to function.
Why is it important that we do not experience all stimuli we experience?
Limited Capacity for processing sensory information, if we tried to process all of it consciously it would lead to sensory overload
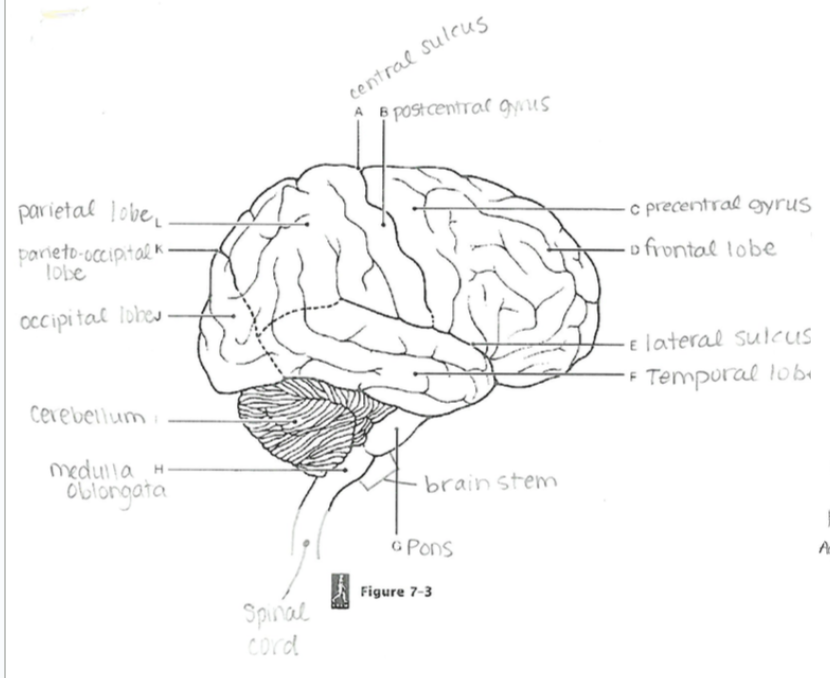
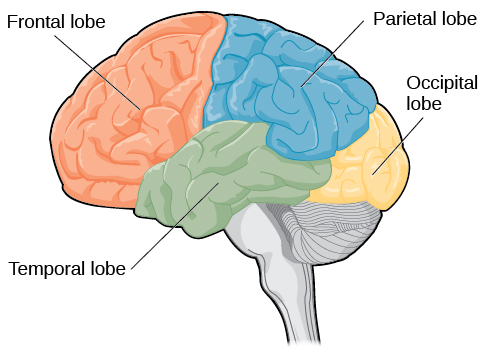
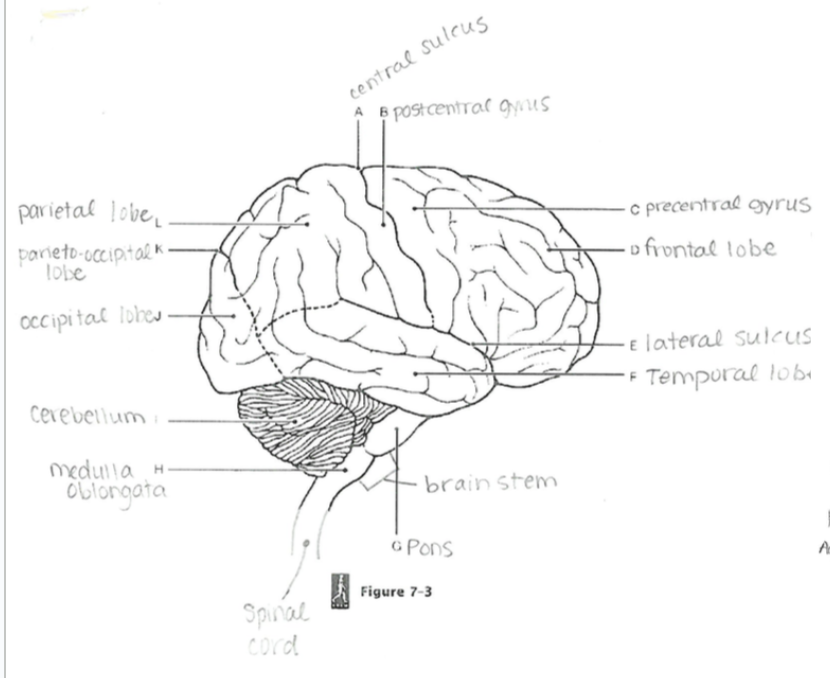
Frontal Lobe
Controls voluntary movement, reasoning, problem-solving, planning, emotions, and parts of speech.
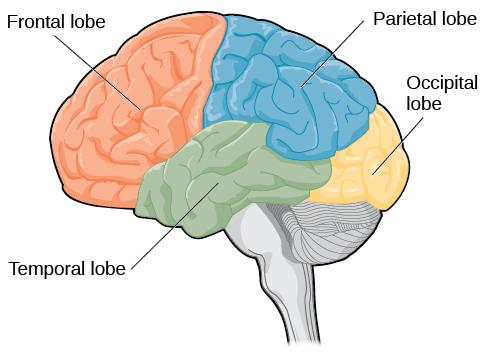
Occipital Lobe
Responsible for processing visual information/sight
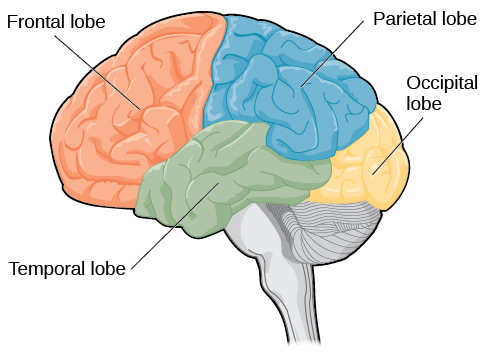
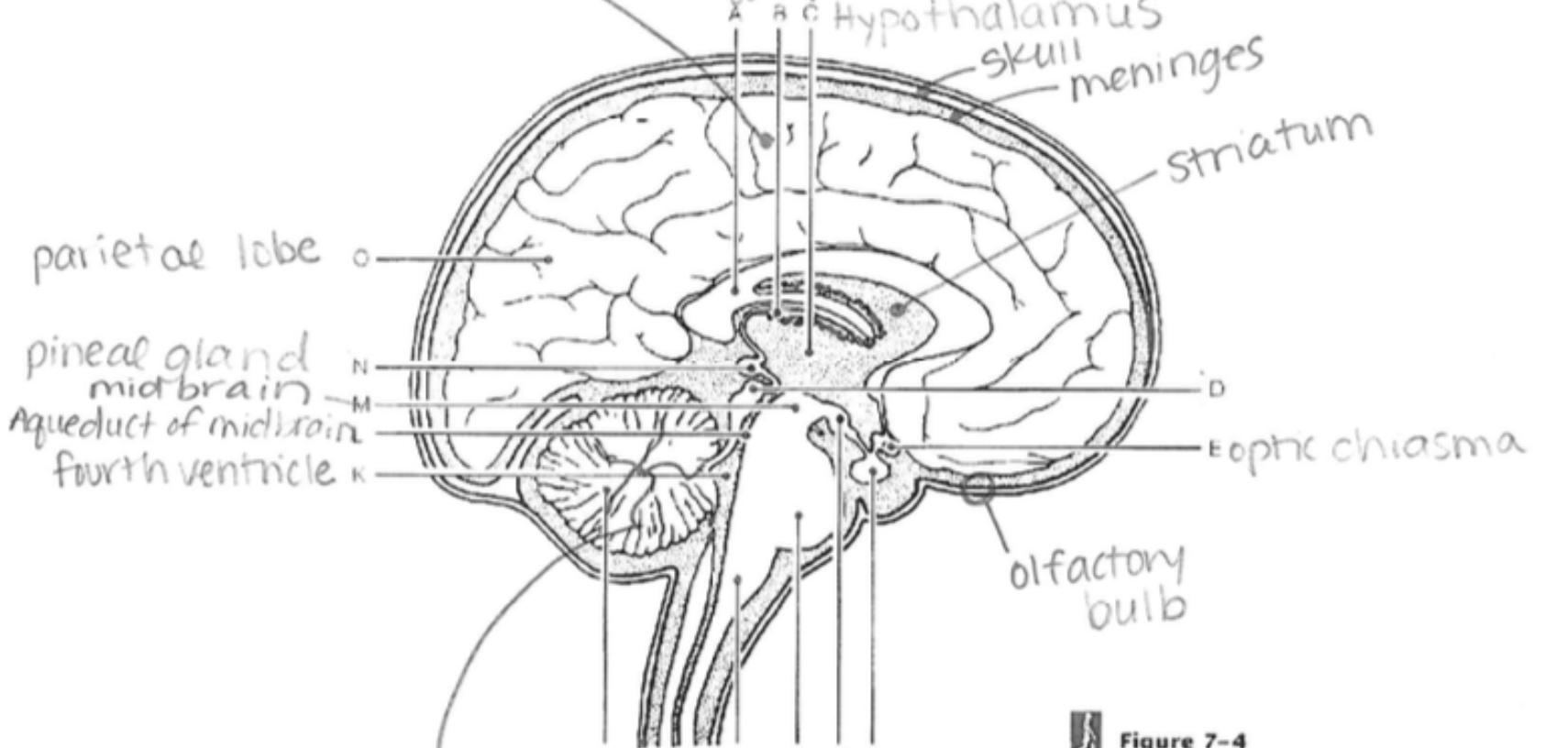
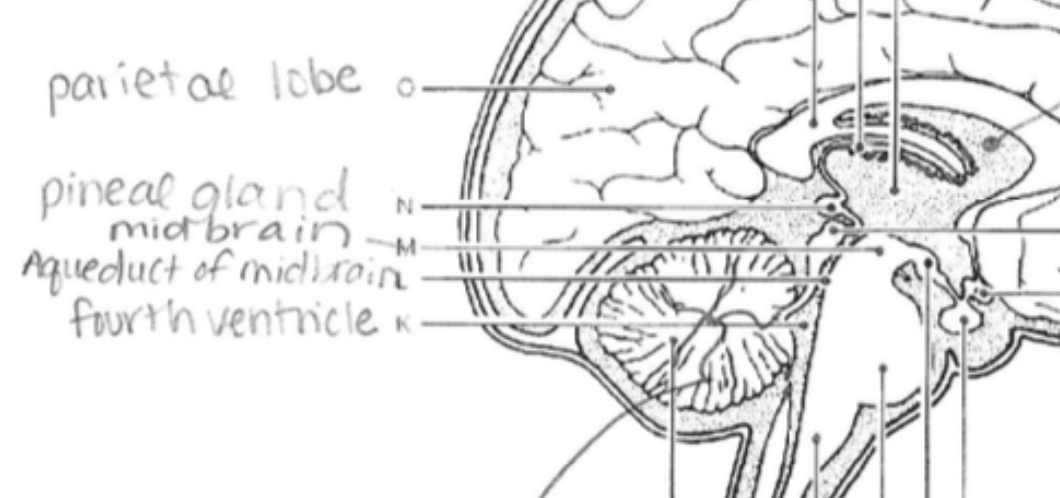
Parietal Lobe
Processes sensory input such as touch, temperature, and pain
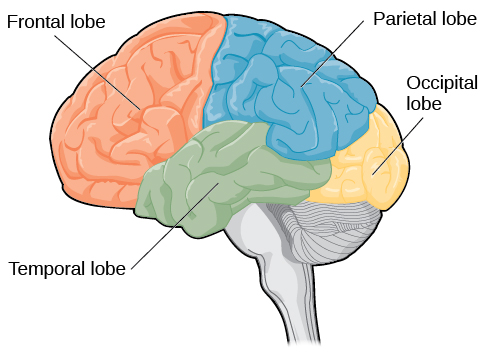
Temporal Lobe
Involved in auditory perception (hearing), memory, and speech
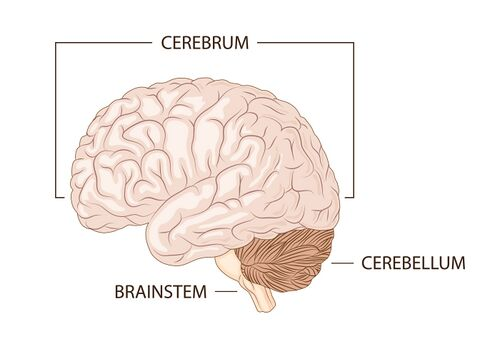
Cerebellum
Coordinates fine motor movement, posture, and balance.
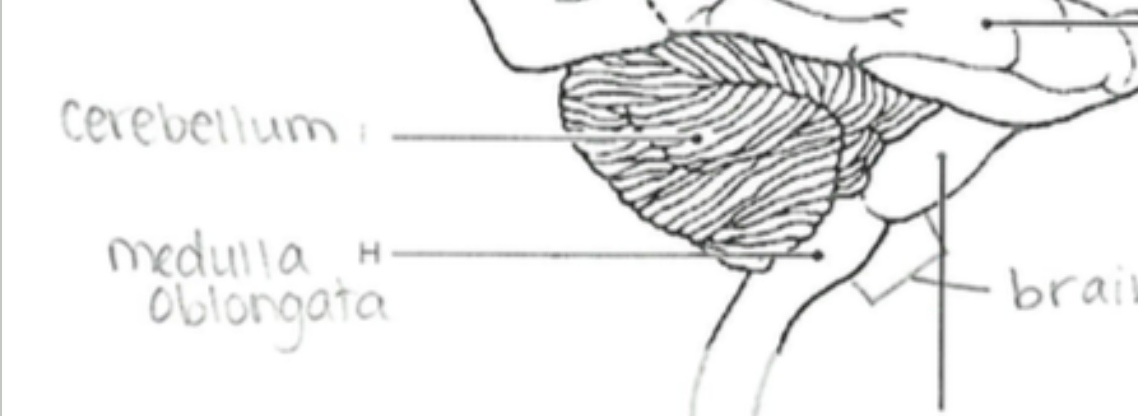
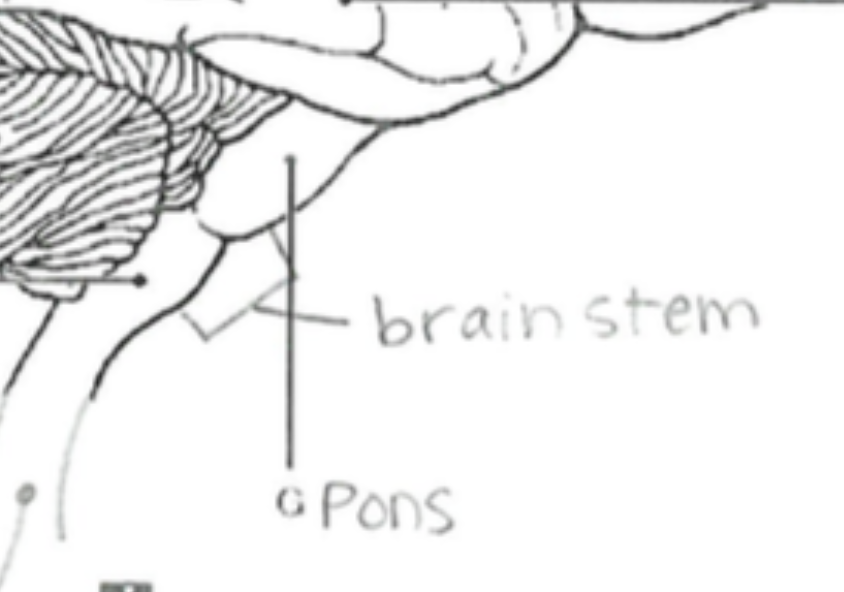
Brain Stem
Connects the brain to the spinal cord; controls basic life functions like breathing, heartbeat, and blood pressure.
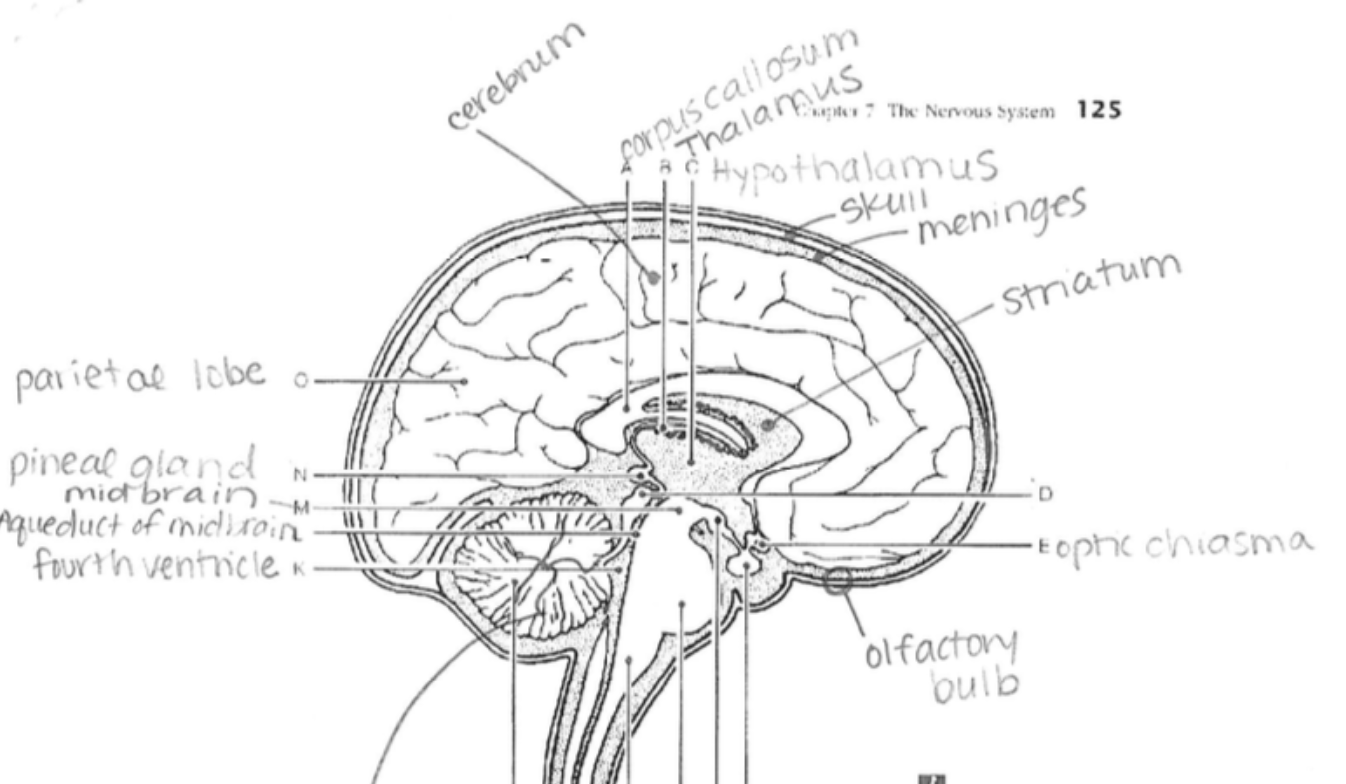
Cerebrum
The largest part of the brain, responsible for higher brain functions including thought, action, and sensory processing.
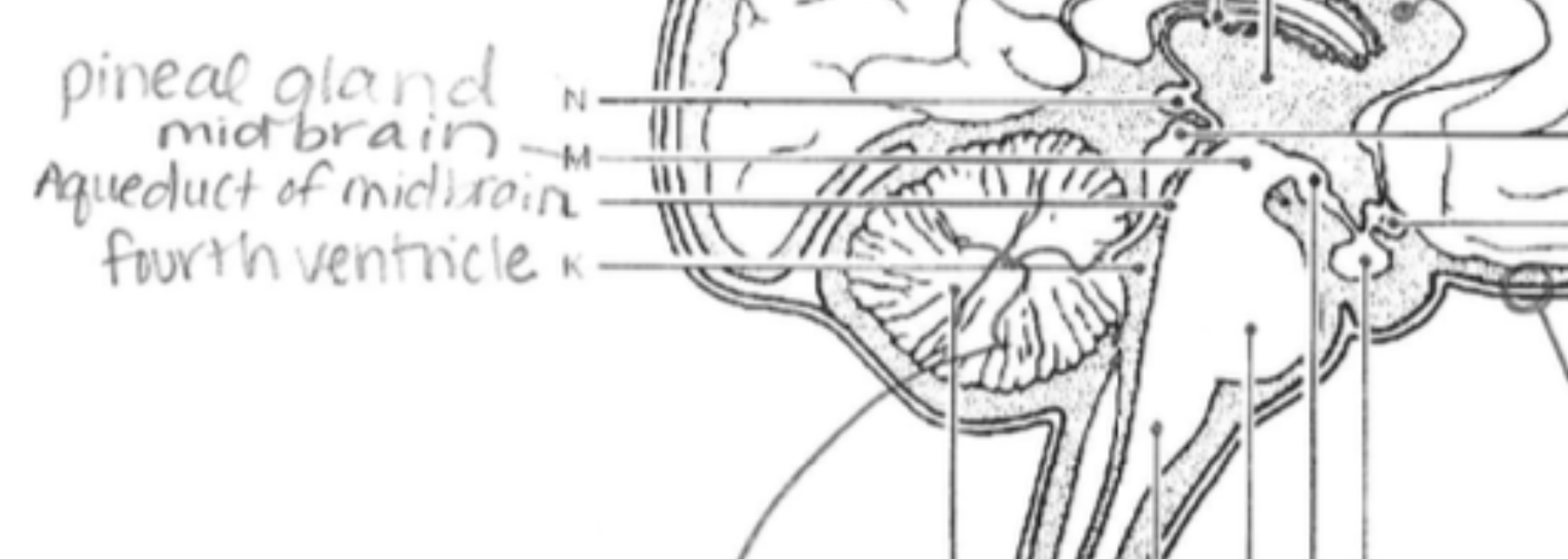
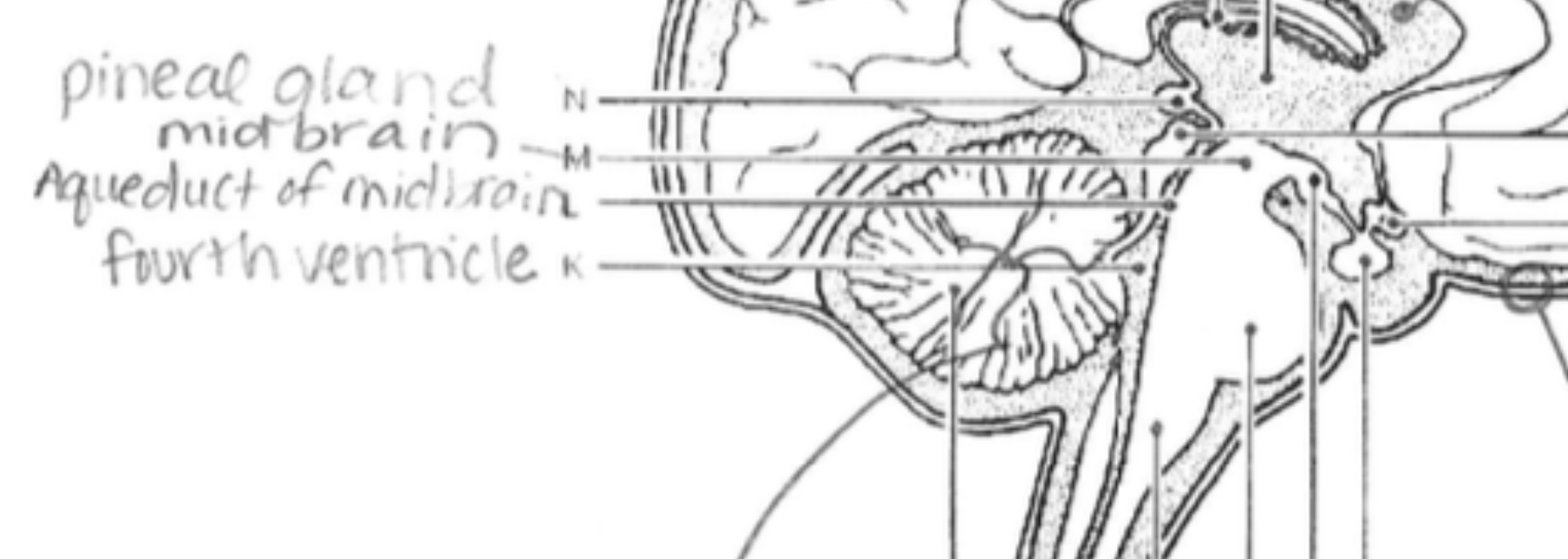
Midbrain
Controls eye movement and processes auditory and visual information.
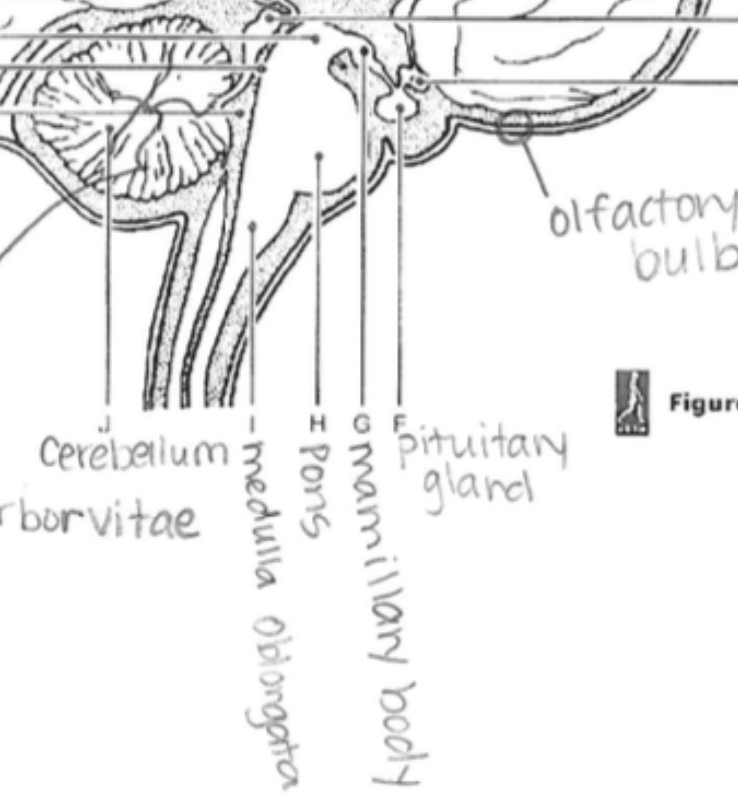
Pons
Relays messages between the cerebrum and cerebellum; involved in sleep and respiration.
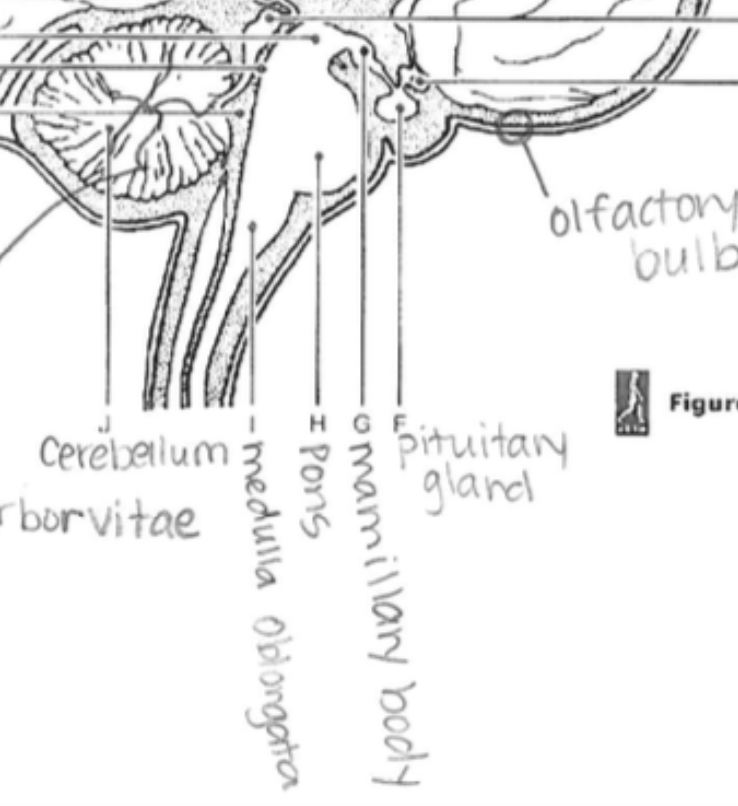
Medulla Oblongata
Regulates autonomic functions, like heartbeat, breathing, and blood pressure.
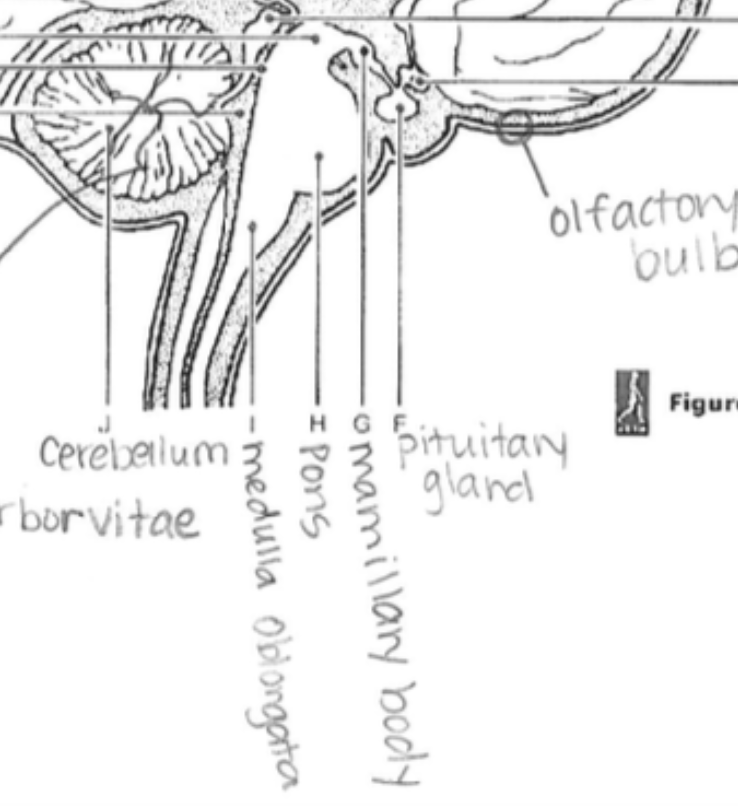
Mamillary Body
Involved in memory and recollection.
Pineal Gland
Produces melatonin, regulating circadian rhythms (sleep-wake cycles).
Pituitary Gland
The "master gland"; regulates various hormones affecting growth, metabolism, and reproduction.
Hypothalamus
Regulates hunger, thirst, body temperature, emotions, and links the nervous system to the endocrine system
Corpus Callosum
Connects the two cerebral hemispheres, allowing communication between them.
Thalamus
Relays sensory and motor signals to the cerebral cortex; involved in consciousness and alertness.
Brain’s relay center
filters and routes sensory information to the cerebral cortex.
Meninges
Protective membranes that cover the brain and spinal cord
Optic Chiasma
The point where optic nerves cross; essential for visual field processing
Olfactory Bulb
Processes information about odors and is involved in the sense of smell
Arbor Vitae
The tree-like white matter structure inside the cerebellum that brings sensory and motor information to and from the cerebellum
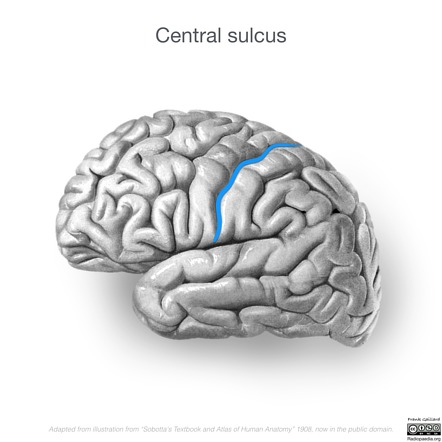
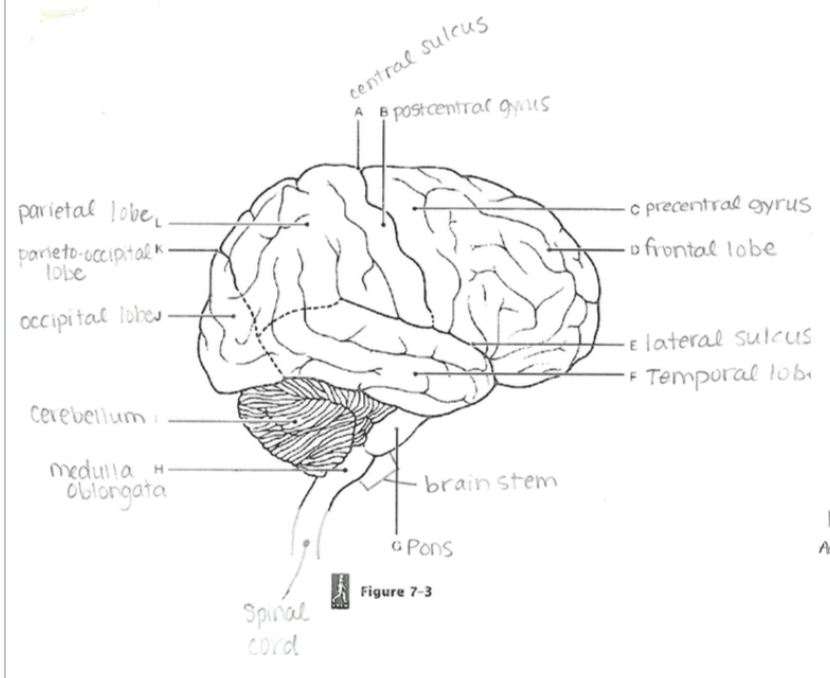
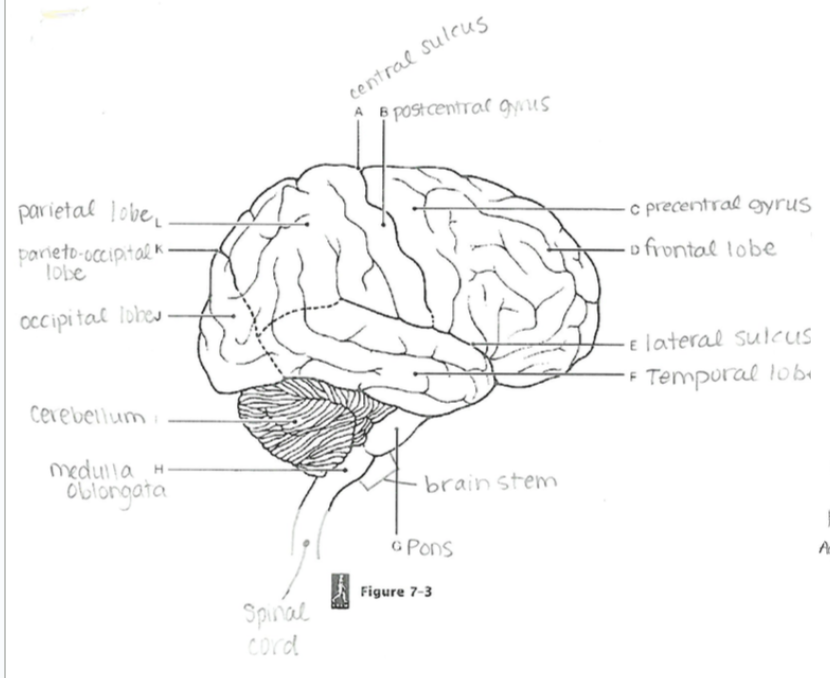
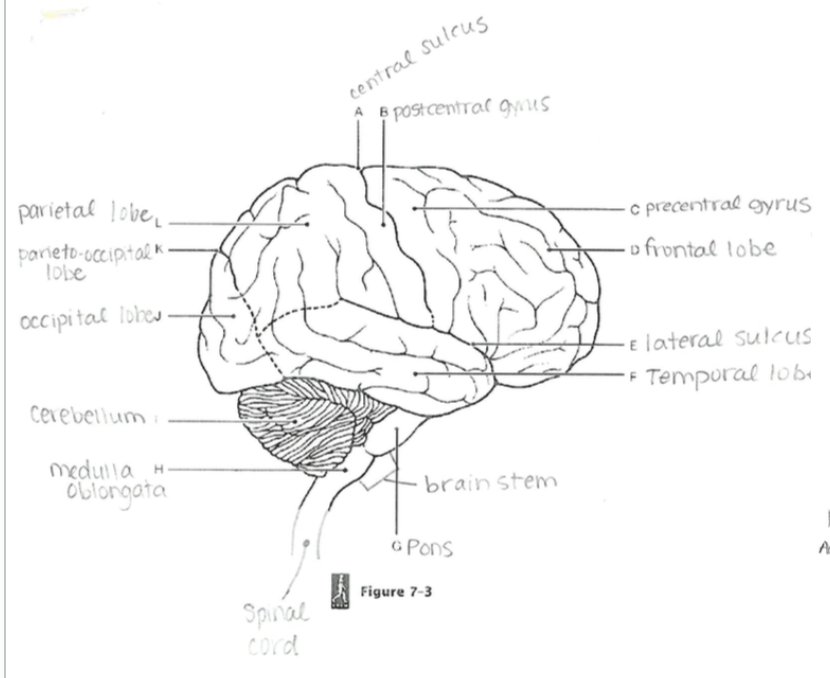
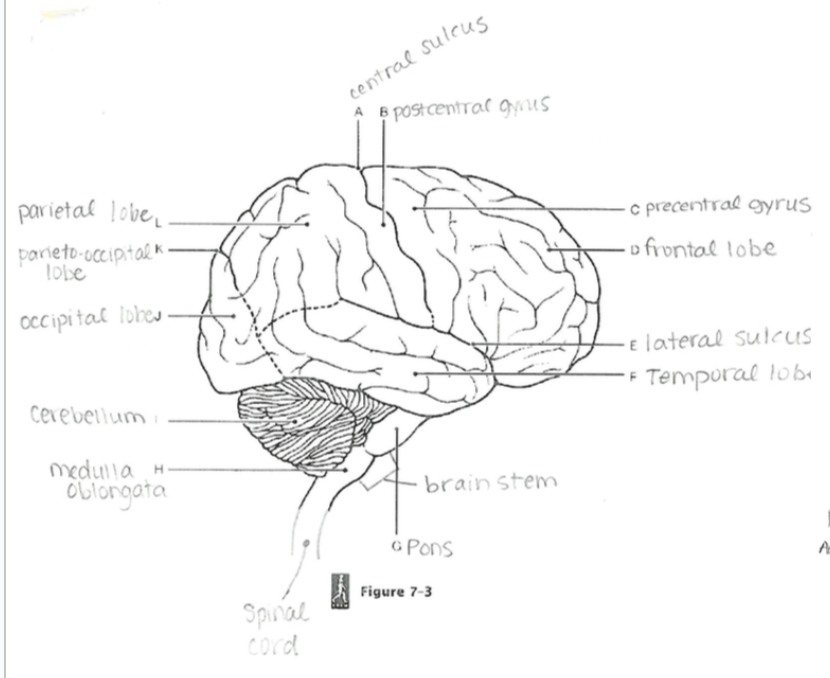
Central Sulcus
A groove separating the frontal and parietal lobes; divides motor and sensory regions.
Parieto-occipital Sulcus
Separates the parietal lobe from the occipital lobe.
Lateral Sulcus
Separates the temporal lobe from the frontal and parietal lobes
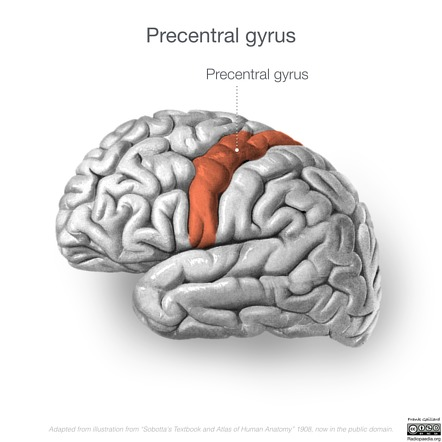
Precentral Gyrus
Primary motor cortex; controls voluntary movements.
Postcentral Gyrus
Primary somatosensory cortex; processes tactile sensory information.
Skull
Bone structure that encases and protects the brain.
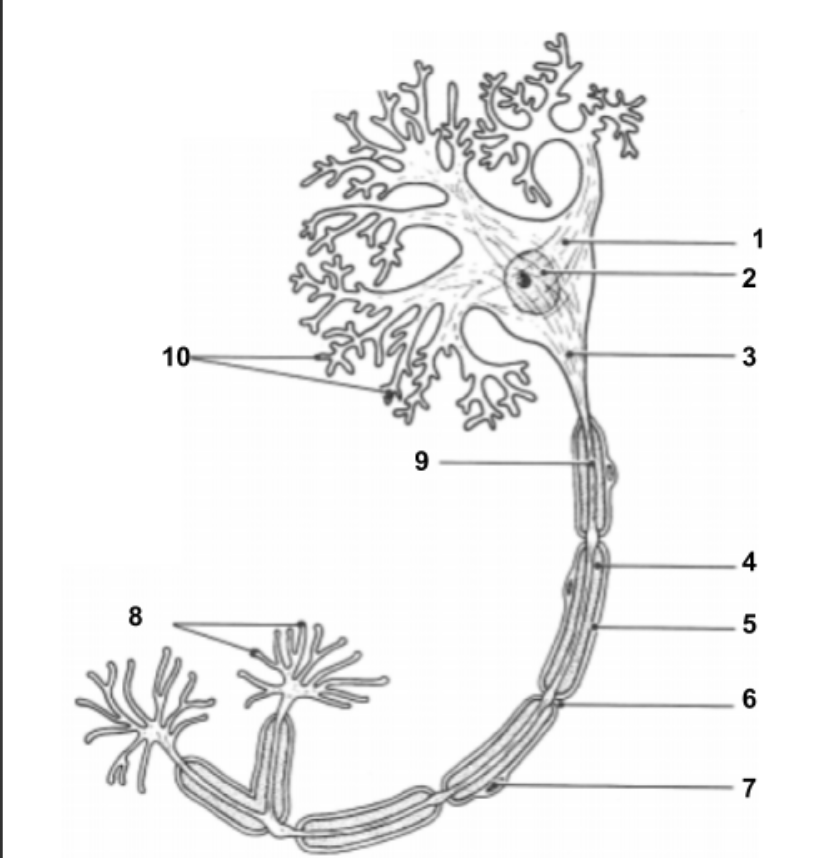
Dendrites
conduct impulses toward the cell.
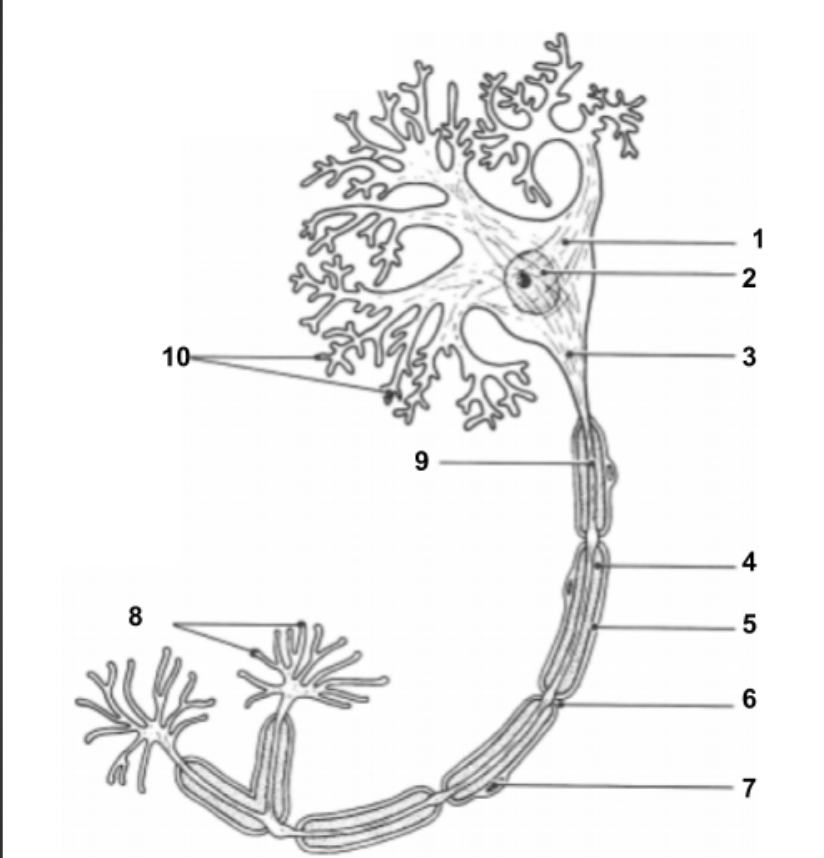
Cell Body (1):
Impulse travels through here to reach Axon.
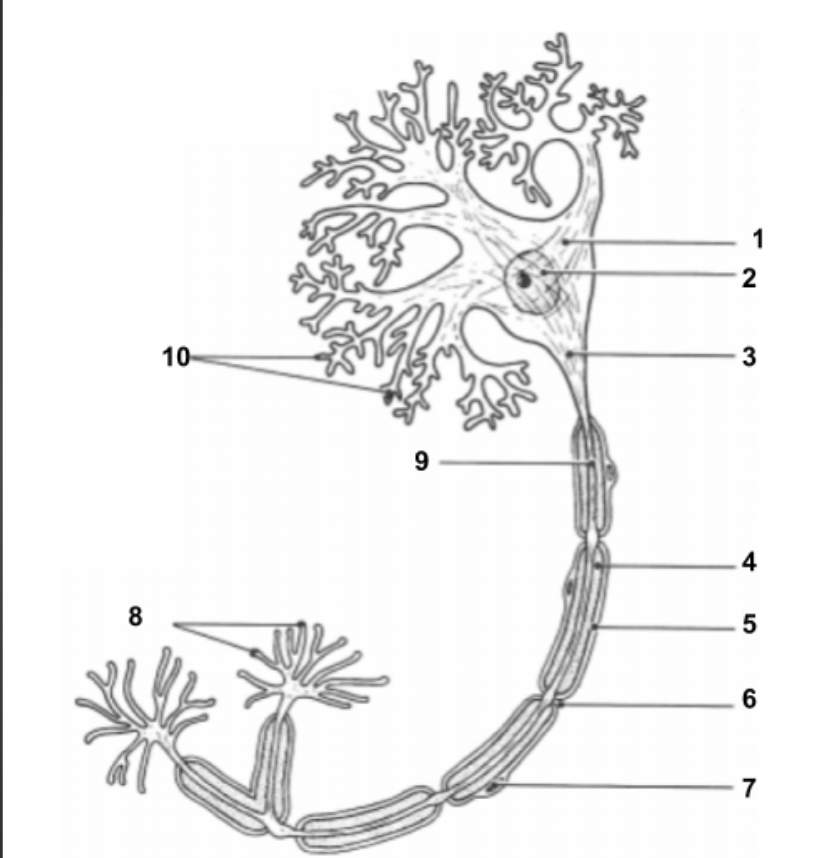
Nucleus (2)
Holds all genetic information.
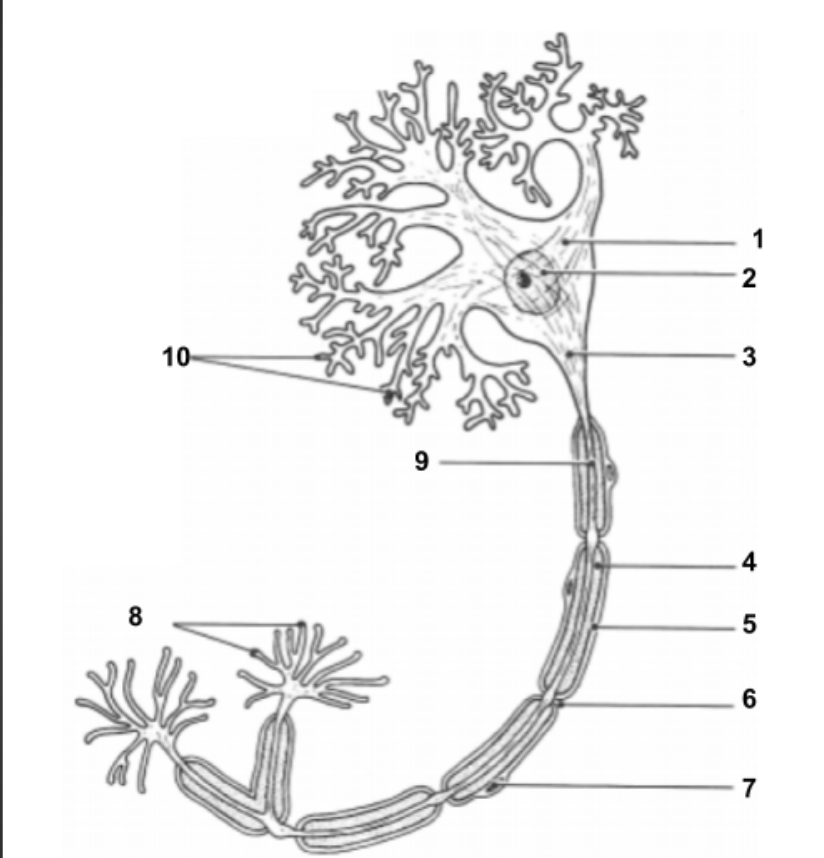
Axon Hillock (3)
Impulse is funneled through here to reach axon.
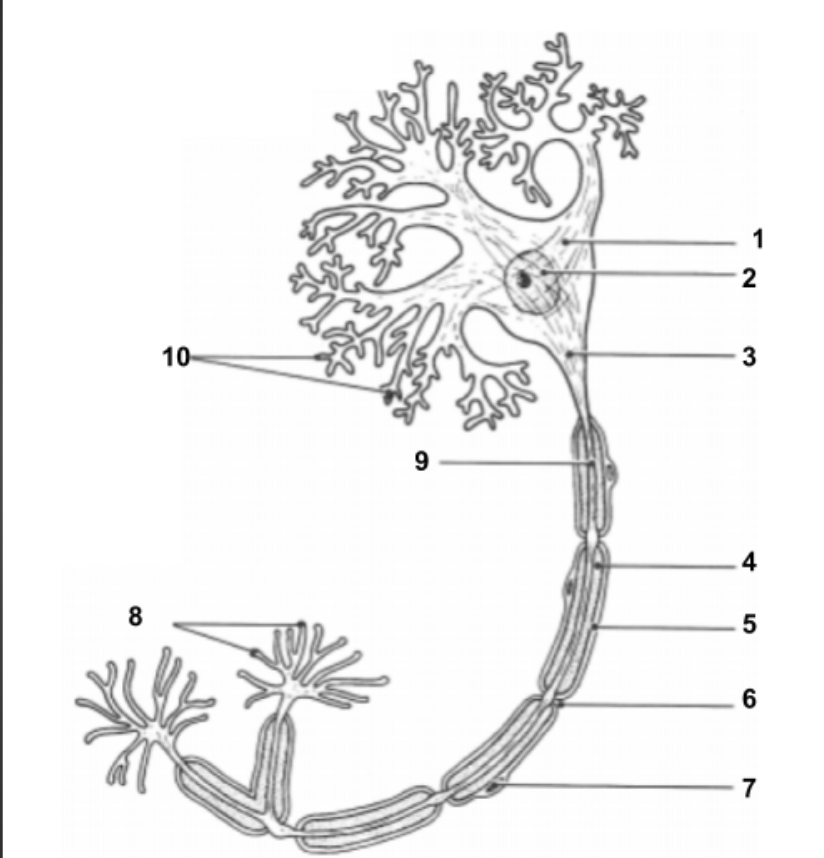
Axon (9)
conduct impulses away from the cell.
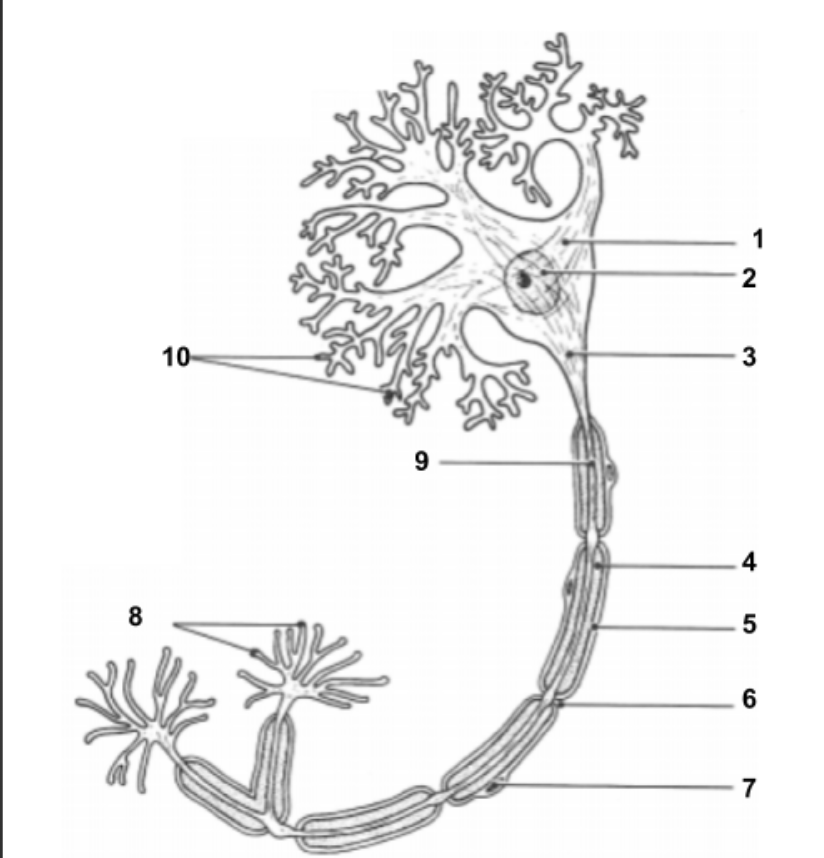
Myelin Sheath (4):
protective layer around axon.
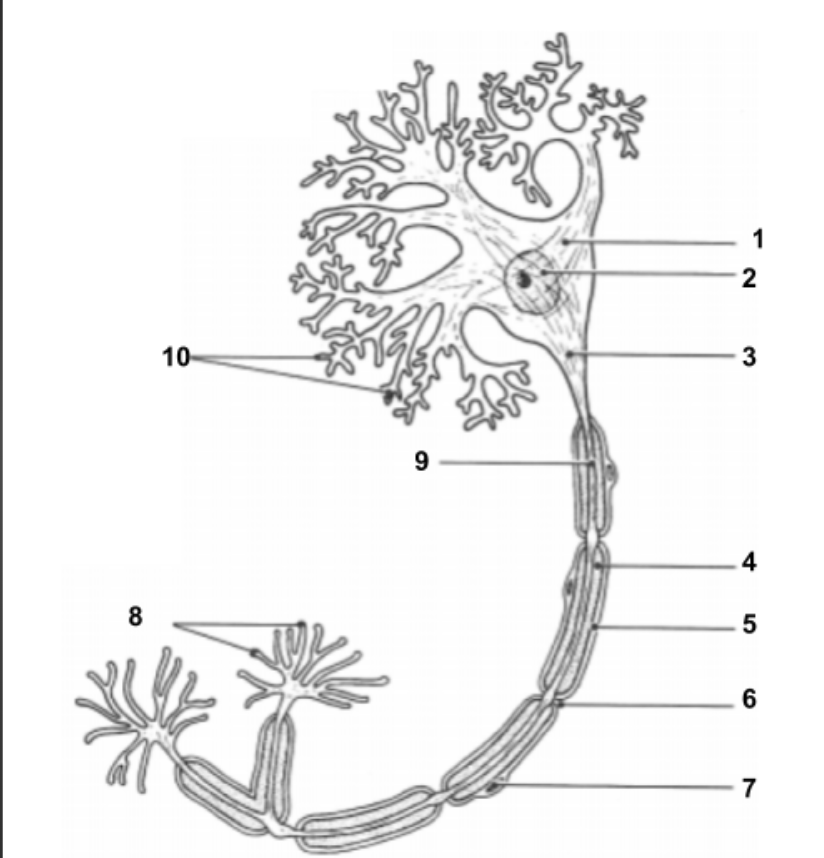
Neurilemma (5):
cell membrane for myelin.
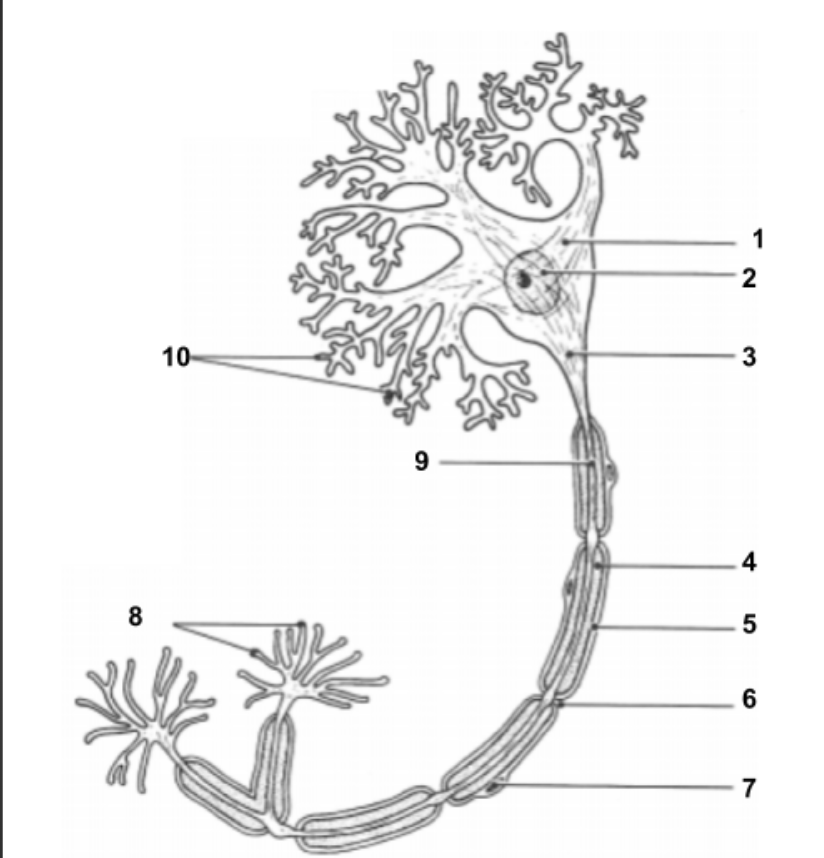
Schwann Cells (7):
produce myelin sheath around axon for protection.
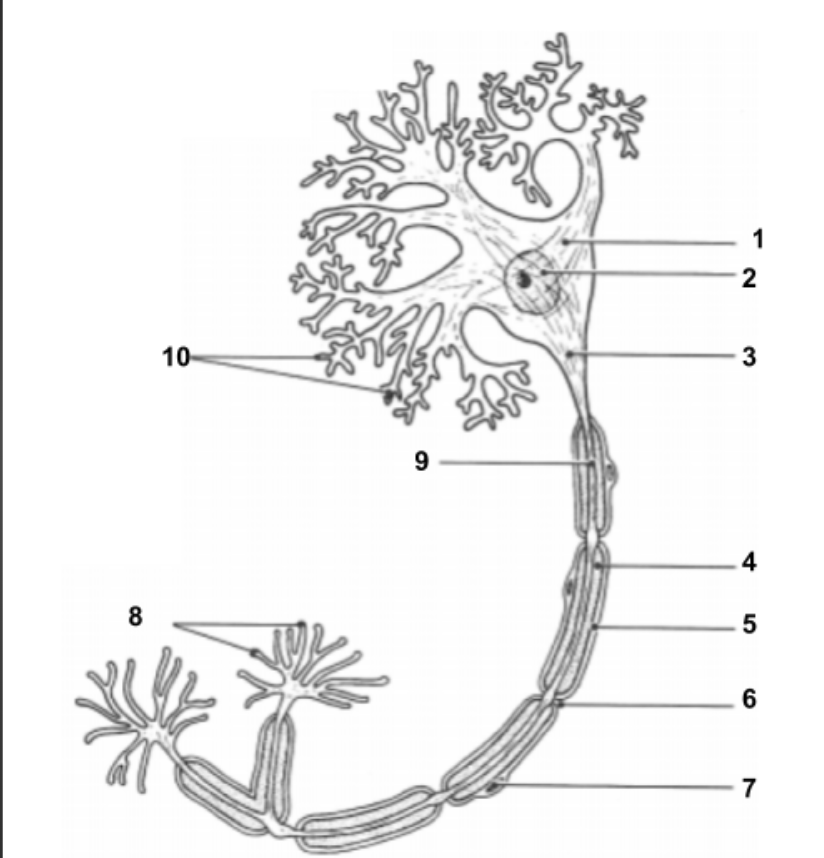
Node of Ranvier (6):
gaps in myelin sheath along the axon
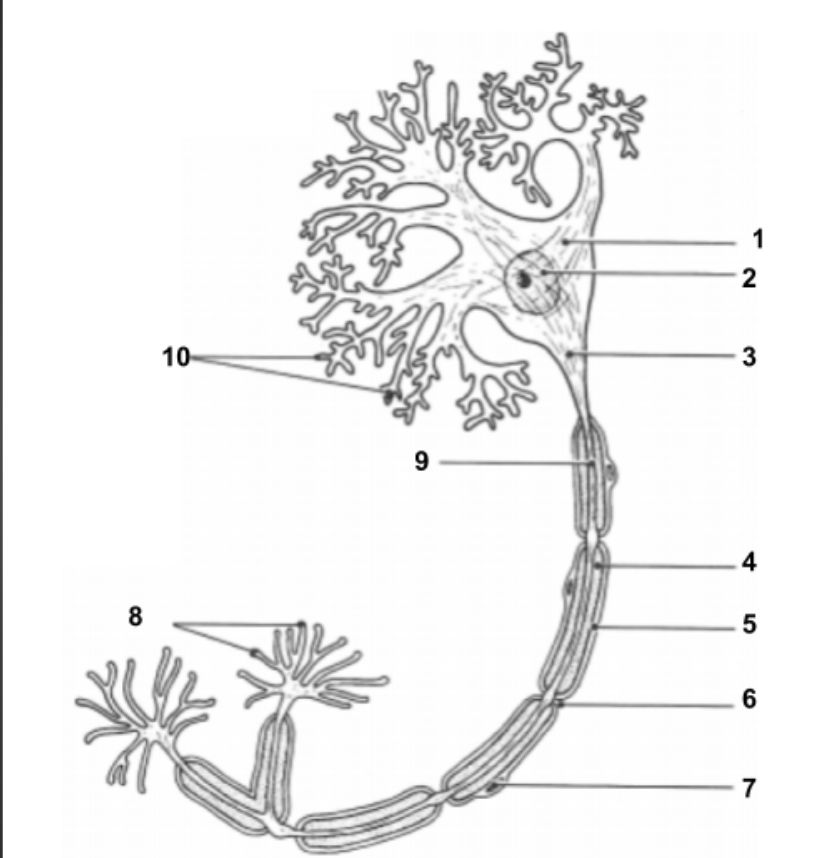
Axon Terminals (8):
Impulse leaves the cell here to move into the synapse to communicate with other neuron cells.
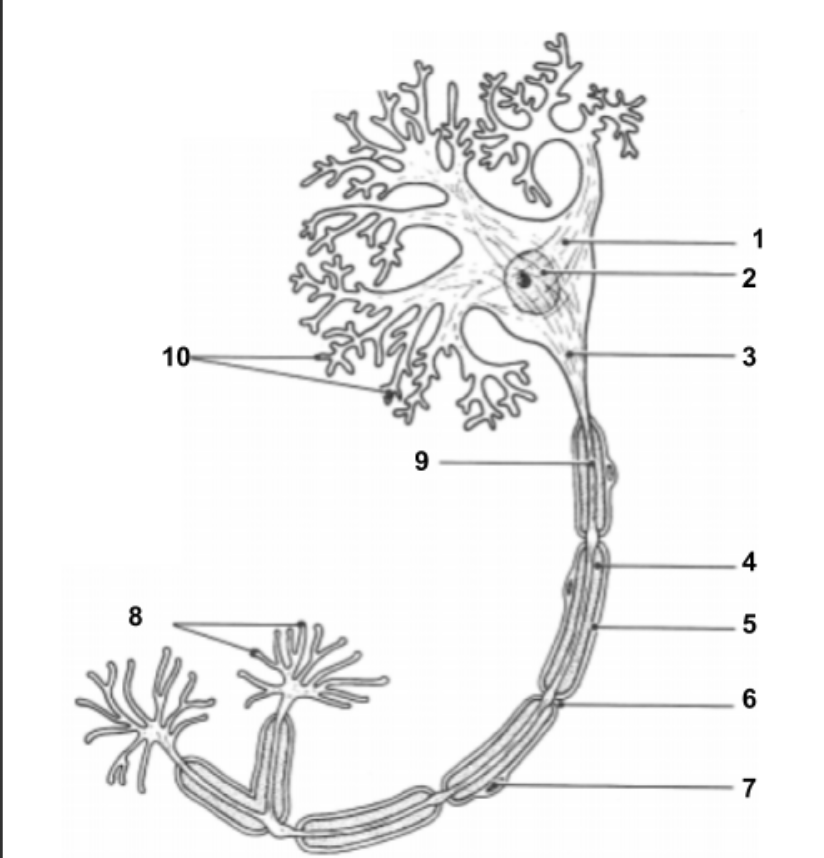
Synapse:
space between axon terminals and dendrites of another neuron cell.
Functions of the Nervous System
To monitor changes occurring inside and outside the body (sensory input).
To interpret the changes.
Affect a response in muscles or glands (motor output).
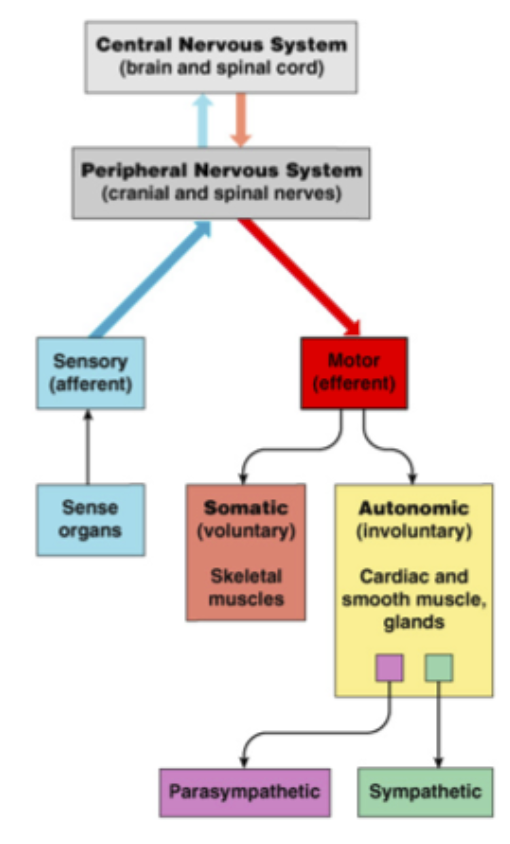
Central nervous system (CNS)
Brain
Spinal cord
Peripheral nervous system (PNS)
Outside CNS
12 pairs of cranial nerves and 31 pairs of spinal nerves
Splits into the Sensory & Motor
Further splits from motor into somatic and automatic
Further splits from automatic to Parasympathetic and sympathetic
Sensory (afferent division)
Towards the CNS
Sense organs/receptors
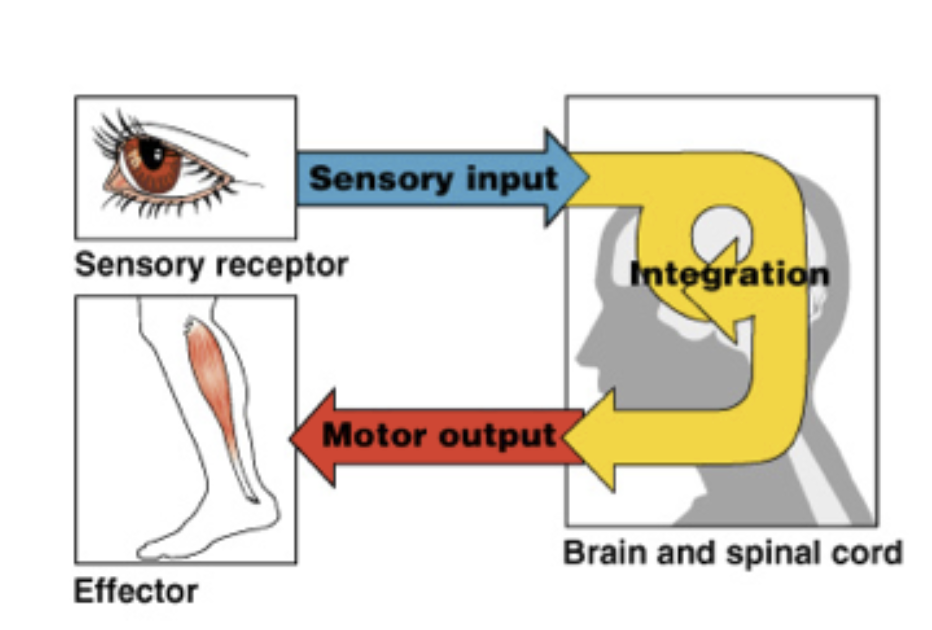
Motor (efferent division)
Exits the CNS
Somatic (Voluntary): Skeletal Muscles
Automatic (Involuntary): Cardiac, smooth muscles, and glands.
Classification of Neurons in PNS
Visceral: impulses carried to or from a body organ
Somatic: impulses carried to or from the skin or a muscle.
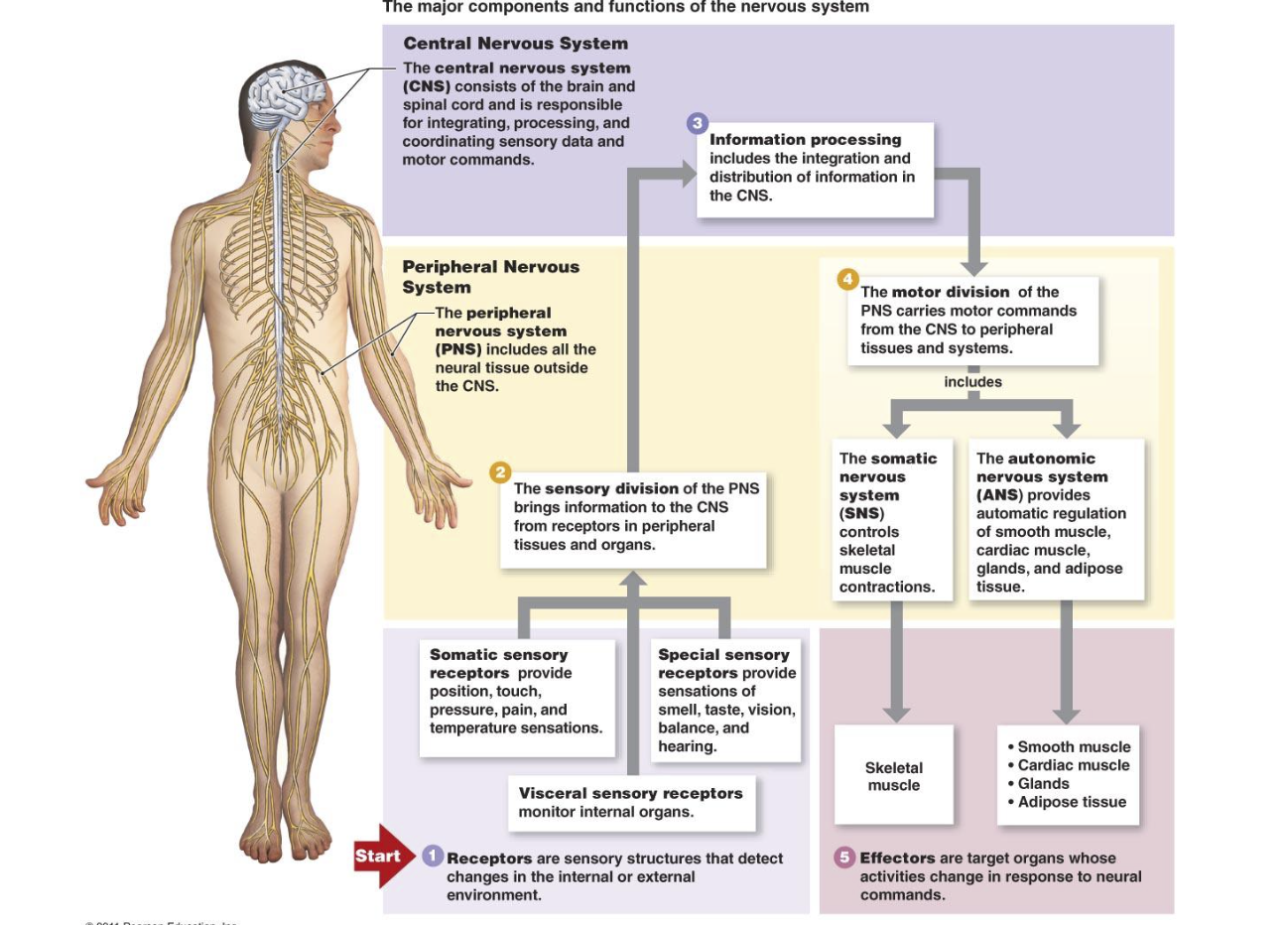
Major components of the nervous system
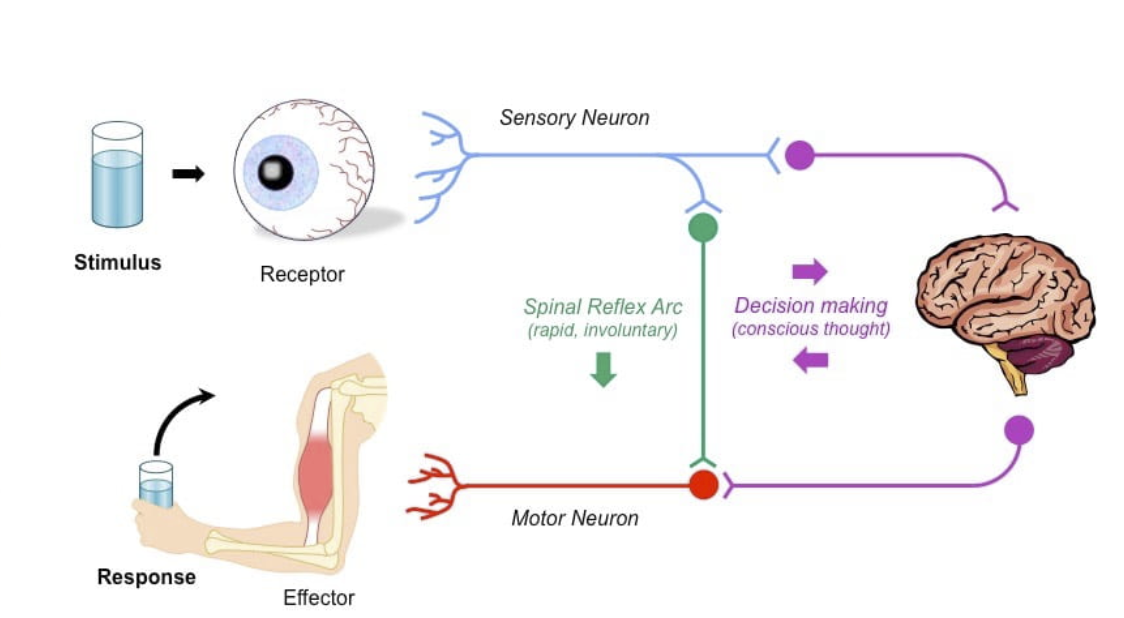
Pick a stimulus and explain how information travels through the nervous system
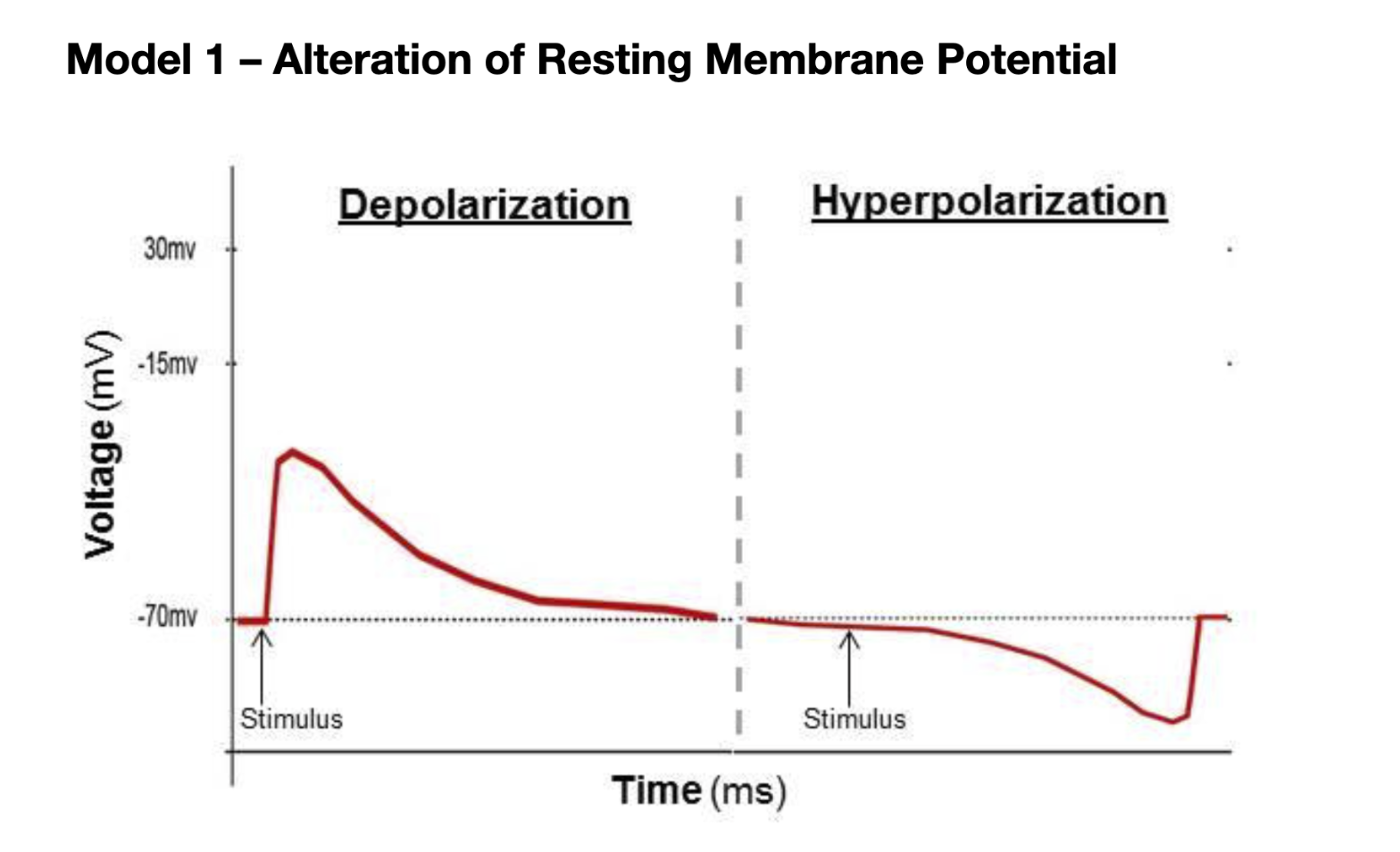
Resting Membrane Potential (RMP) is the potential difference that exists across a membrane of a cell.
Typically it is -70mv
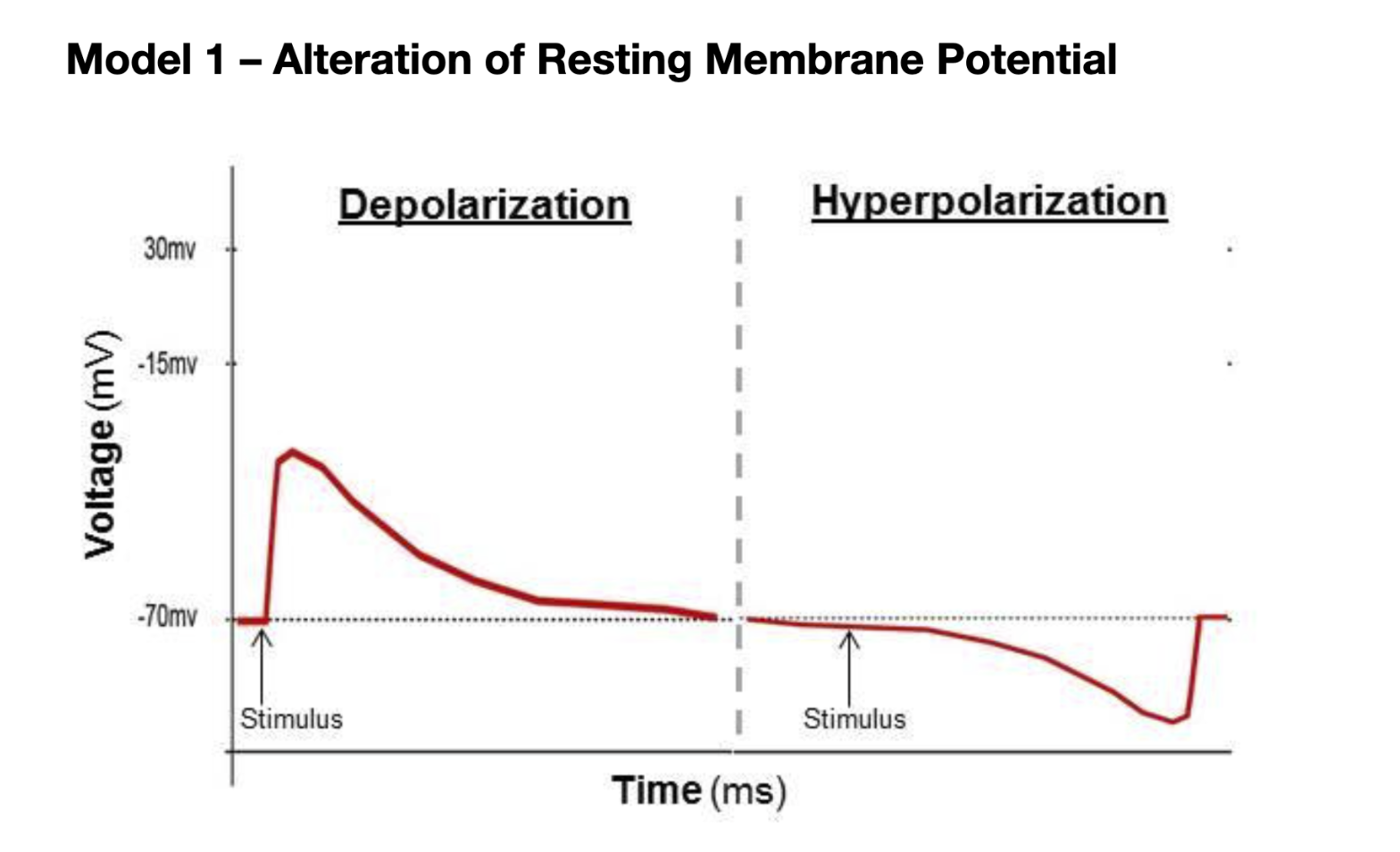
Depolarization
When the voltage is above -70, the process where the inside of the cell becomes more postive/less negative than outside of the cell
A wave of depolarization is the nerve impulse/action potential
Hyperpolarization
When the voltage is below -70, the inside of the cell becomes more negative/less positive than outside of the cell
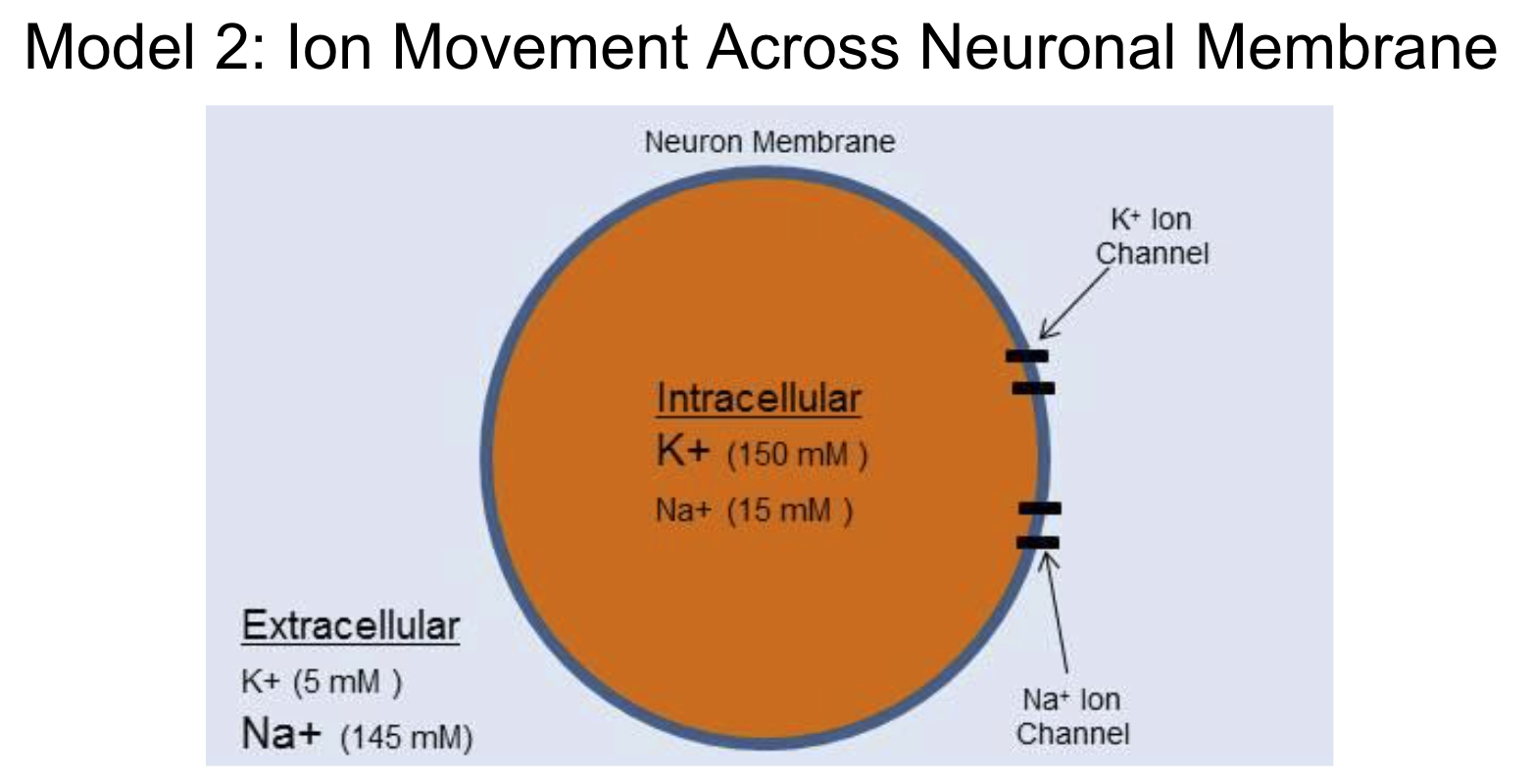
Neurons use changes in membrane potential as communication signals (nerve impulses). The RMP changes are due to ions crossing the plasma membrane through specific ion channels.
Sodium Ion movement
Sodium is more concentrated on the outside of the cell membrane
It will diffuse into the cell
Makes the membrane potential (inside) less negative leading to depolarization
Potassium Ion Movement
Potassium is more concentrated on the inside of the cell membrane
It will diffuse out of the cell
Makes the membrane potential (inside of neuron cell) more negative
In a resting neuron there is greater K+ permeability than Na+ permeability. What would happen to the RMP if Na+ and K+ permeability were the same?
It would neutralize and stay at -70mV
Resting potential
No action potential
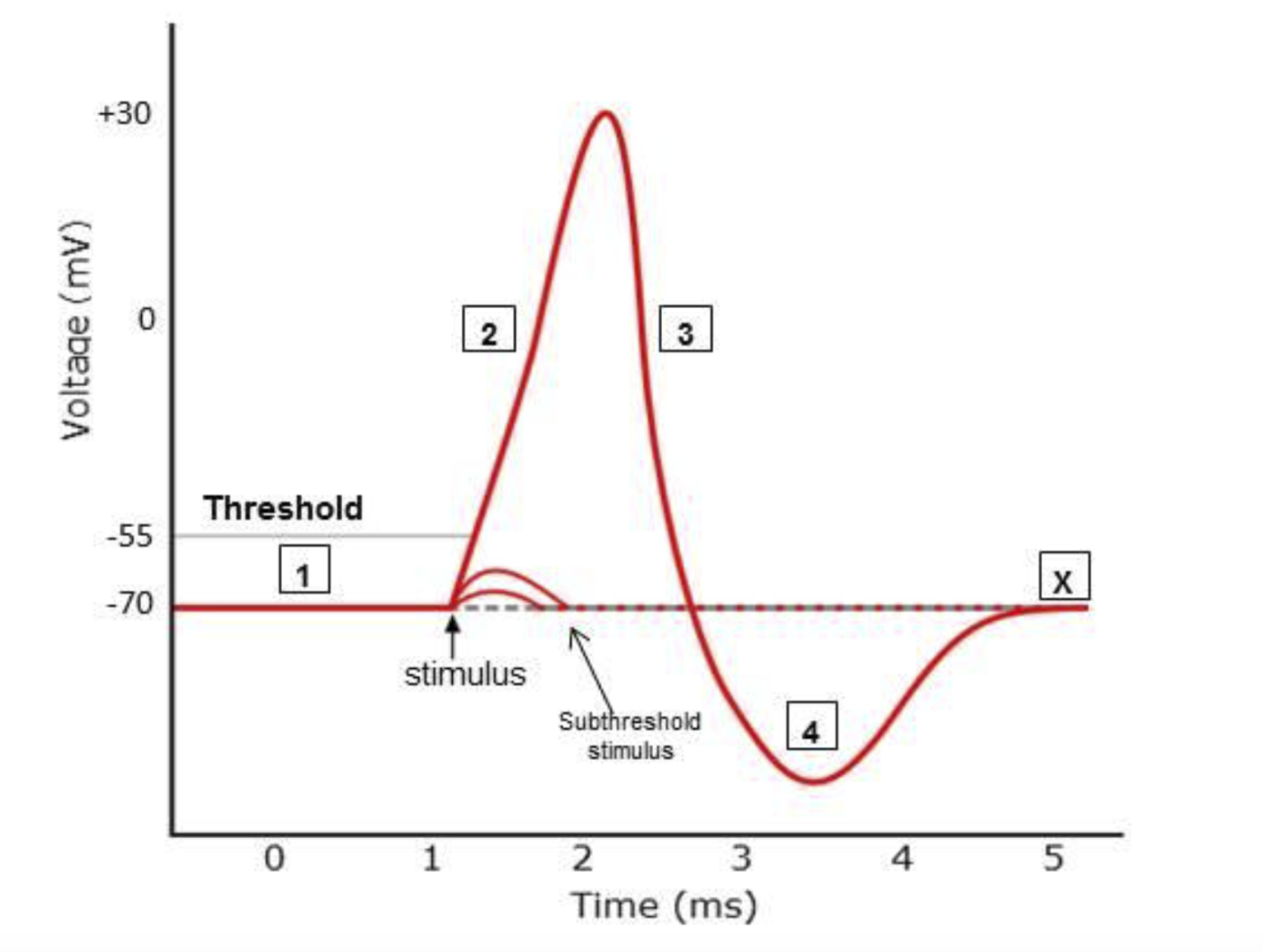
Action potentials
brief reversals of membrane potential in response to a stimulus. Action potentials travel along the axon, and method of how neurons communicate.
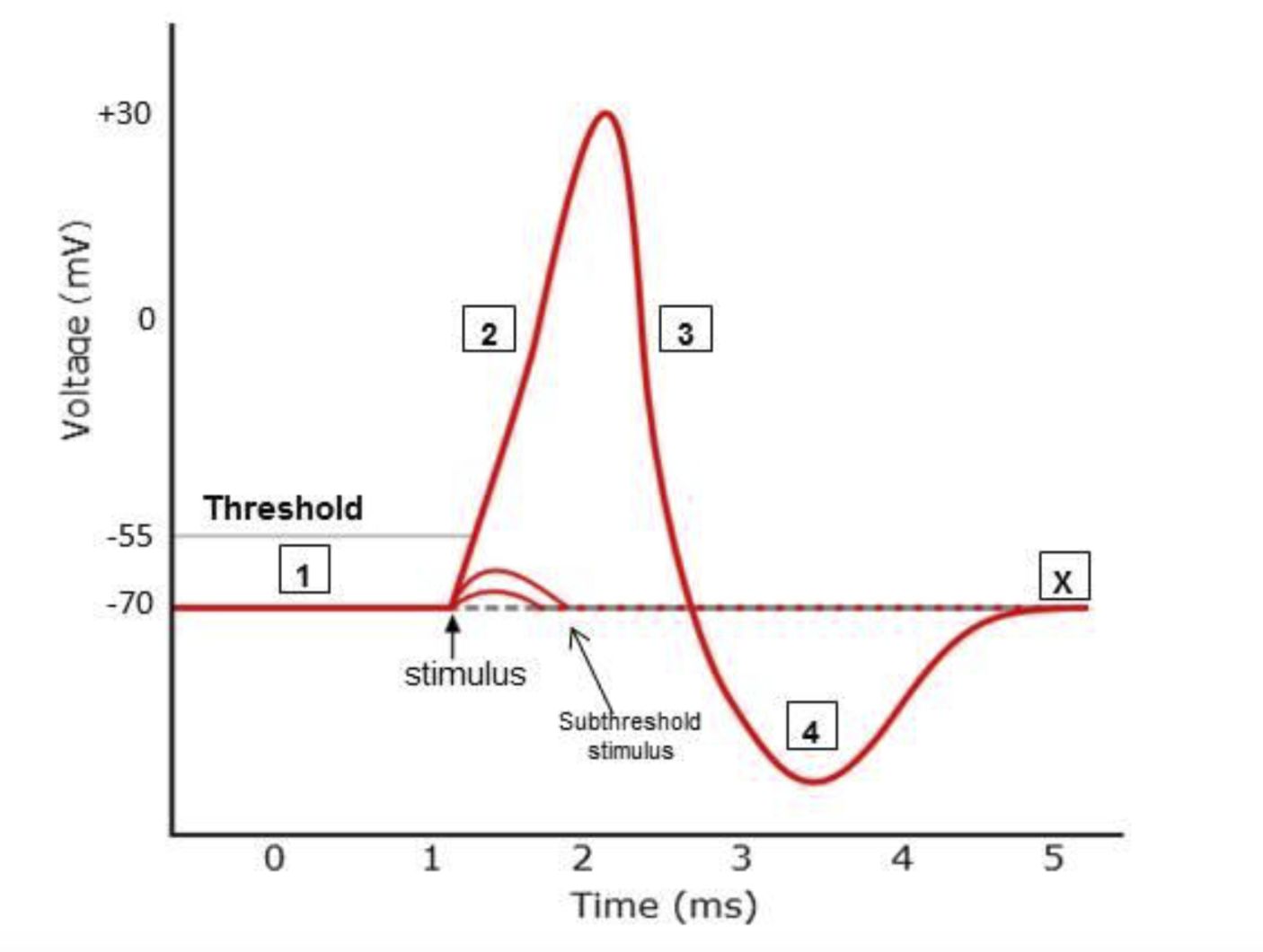
Four phases of the action potential.
Resting = -70
Depolarization = From -70 to 30
Repolarization = 30 to -70
Hyperpolarization = -70 to below -70
Action potentials traveling along a neuron are due to the opening and closing of sodium and potassium ion channels.
# | Action Potential Phase | Sodium (Na+) | Potassium (K+) |
1 | Resting | Closed | closed |
2 | Depolarization | Open | closed |
3 | Repolarization | closed | open |
4 | Hyperpolarization | closed | open |
What must be reached to initiate an action potential
The threshold, -55mV
Although a stimulus originates at the dendrite and travels through the cell body, an action potential does not start until the axon hillock.
Postulate why action potentials do not occur on dendrites (even with a very strong stimulus) and why action potentials first start at the axon hillock.
Dentrites receive chemical signals, not ions
In the axon hillock there are due to the lack of a high concentration of voltage-gated sodium channels, which are necessary for the rapid depolarization that characterizes an action potential.
What happens to neurons during an impulse?: Salty Banana
Resting membrane is polarized by Na-K Pump.
Stimulus reverses the polarization causing depolarization.
The wave of depolarization is known as nerve impulse or action potential.
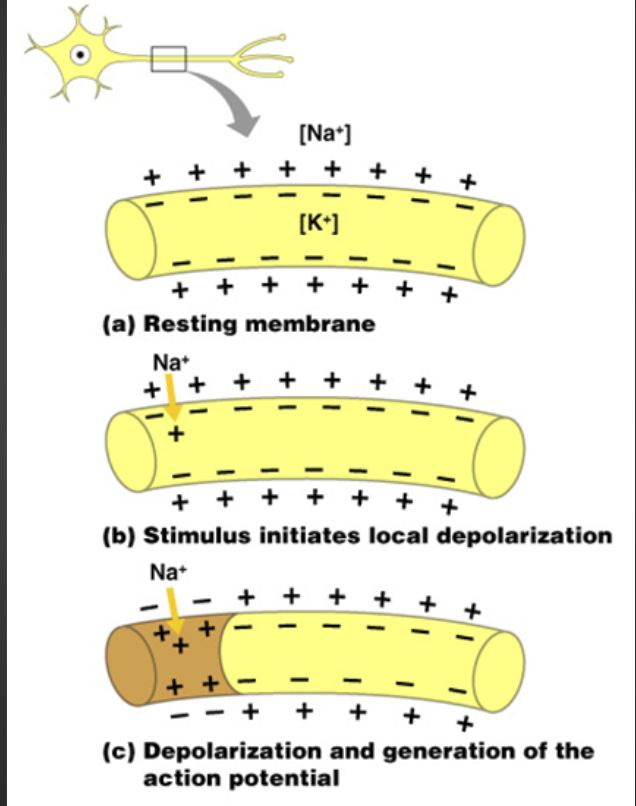
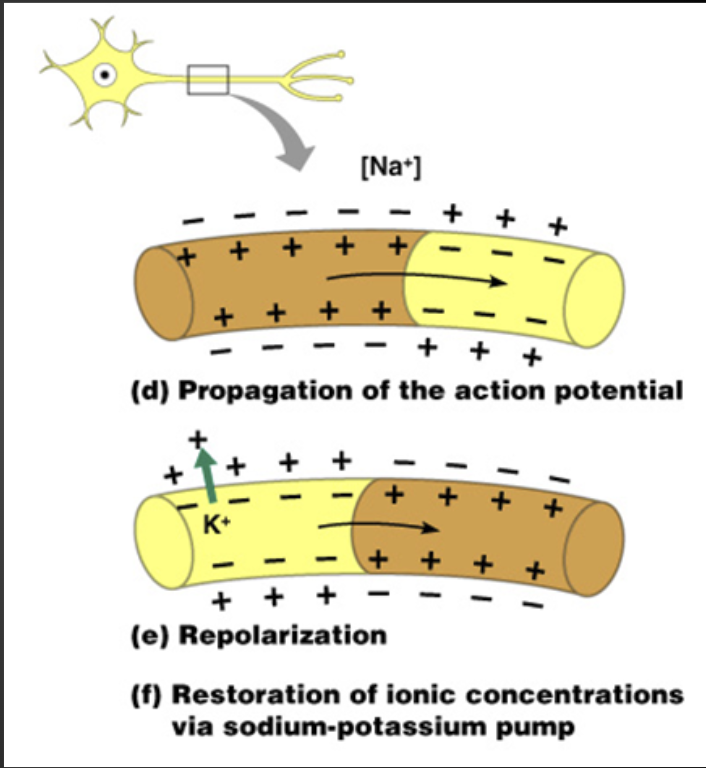
Salty Banana
4. Action potential continues down length of axon.
5. The axon repolarizes to restore polarization.
6. Axon is in refractory/resting period.
A drug that opens sodium channels in a motor neuron would depolarize the membrane.
Predict how this drug would affect the probability of generating an action potential.
It would increase in generating a action potential
Novocaine and lidocaine are two local anesthetic drugs used in dentistry. Anesthetics block nerves from sending action potentials to the nerve. D
etermine possible mechanisms of action for novocaine.
Drugs blocks signals during the synapse, leading to the chemical receptors not receiving the message and it blocks sodium channels from opening up.