ch 23: Enzyme coupled receptors
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
growth factors mostly bind to
receptor tyrosine kinase ( RTKs)
when a ligand binds to an RTK it leads to the dimerization on
tyrosines
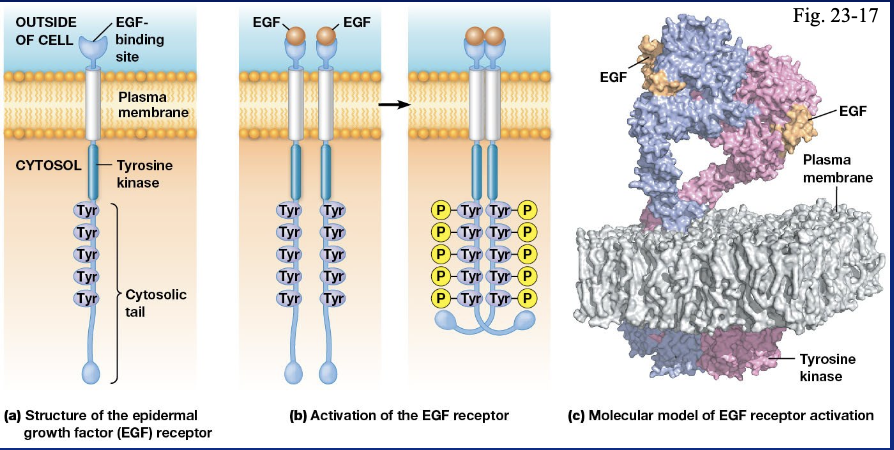
phosphorylated tyrosine residues privide bidning site for proteins with
SH2 domains
how is phospholipase C-gamma activated
it binds to phototyrosine residues using their SH2 domains
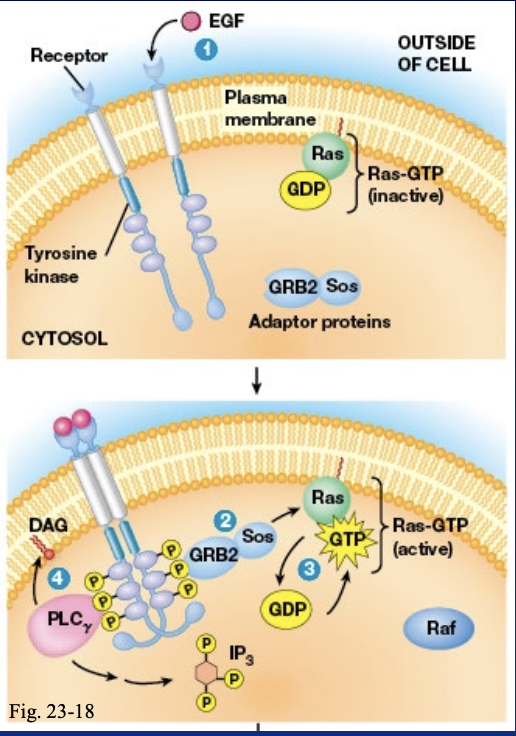
what does PLC-gama produce and how
it produces IP3 and DAG by cleaving PIP2
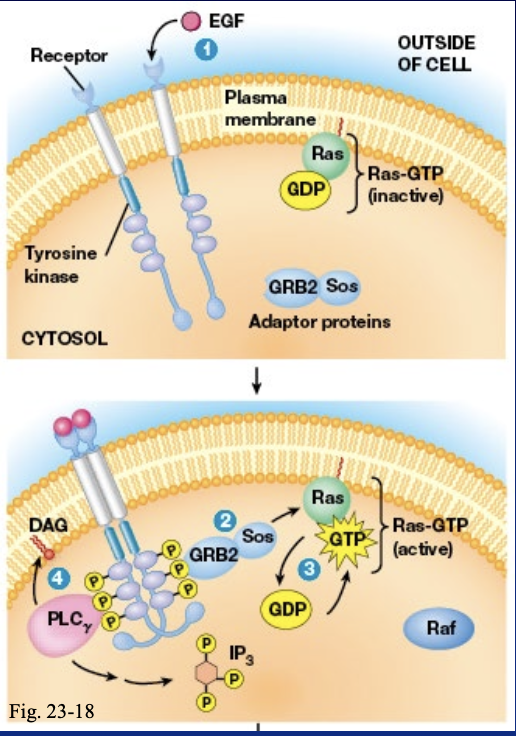
only activation of RTKs by growth factor is mitogenic and can also activate
Mitogen Activated Protein Kinase (MAP kinase)
describe how RTKs activate MAP kinase
Grb2 binds phosphotyrosine residues using SH2 domain
GRV2 uses its SH3 domain to binds to proline rich regions on Sos
Sos is a GEF for the G-protein Ras
Ras-GTP activates the protein kinase Rad
Raf phosphorylates MEK to activate it
MEK phosphorylates MAP kinase to activate it
MAP kinase phosphorylates transcription factor which activate the immediate early response genes
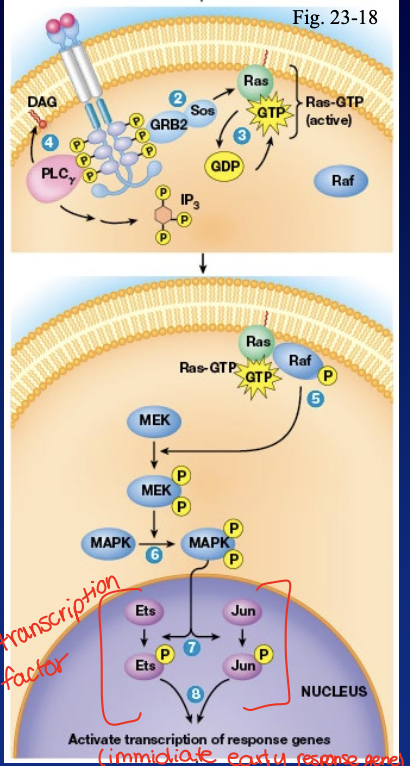
what are immediate early-response genes
transcribed first and transiently on response to growth factor simulation
what are some transcription factors
c-fos, c-jun, c-myc
after the immediate early response genes are transcribed the ___ is made
protein
what are the two sexes of yeast?
alpha and beta
describe yeast mating
haploid cells of the opposite sex fuse to become diploid
how is mating of yeast done
mating pheromones are released by one cell type and binds receptors on the opposite cell type leading to mating
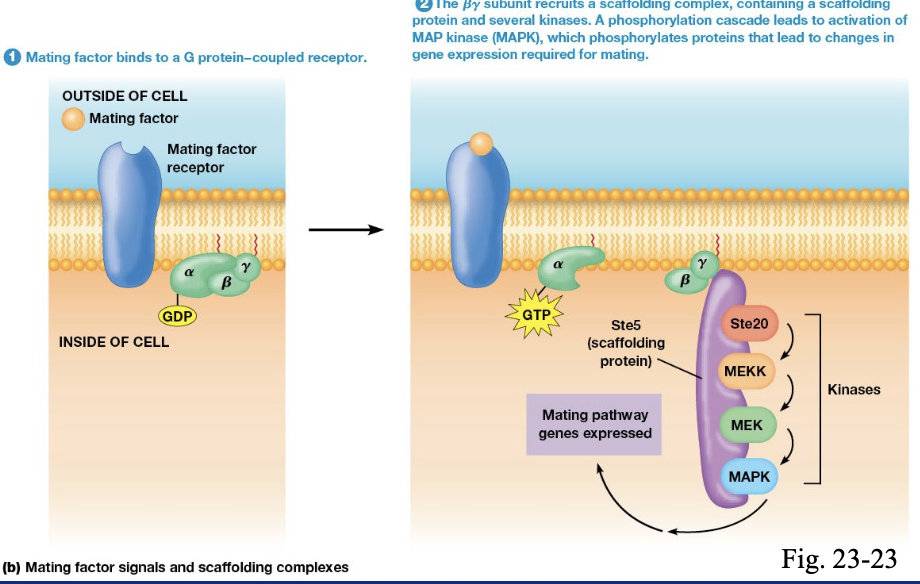
how do yeast use MAP pathway to mate
mating pheromone binds to G-protein coupled receptor.
the beta gamma subunit recruits a scaffolding complex which contains several kinases.
phosphorylation cascade leads to activation of MAP kinase which phosphorylates proteins that lead to changes in gene expression required for mating
insuline secretes in response to
elevated blood glucose
insuline causes cell to take up glucose which causes
increase storage of glucose and increase metabolism glucose
the insuline receptor is a
tyrosine kinase
in insulin signaling the tyrosine kinase recruits and phosphorylates
Insuline Receptor Substrate 1 (IRS 1)
what happens after IRS 1 is phosphorylated
GRG2 binds phosh\photyrosine residues on IRS 1 leading to activation of the MAP kinase
T or F Insulin is a growth hormone
F. it is not
T or F insuline has complete effect to the amount of glucose that is uptaken
F. it has none
IRS-1 is alos bound to PI 3-kinase via
SH2 domain
PI 3-kinase phosphorylates phosphatidylinositol 4,5 bisphosphate on it’s #3 carbon to produce
PIP3
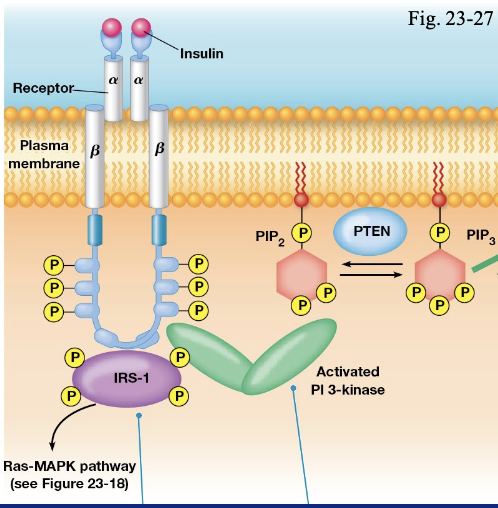
what does PIP3 provide?
binding sites for proteins with a plekstrin homology domain
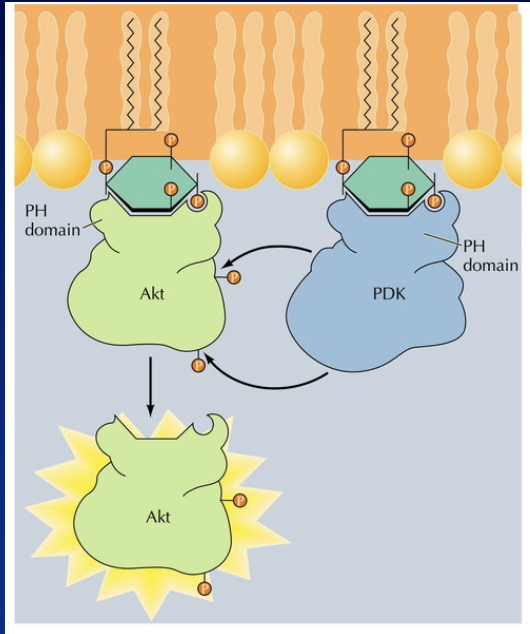
two enzymes that have plekstrin homology domain are
phosphinositide dependent kinase (PDK) and akt (protein kinase B)
PDK and its substrate Akt binds near each other at the plasma membrane and once PDK phosphorylates
Akt is activated
Akt phosphorylates multiple proteins leading to the translocation of vesicles containing glucose transport proteins to the plasma membrane leading to
glucose uptake
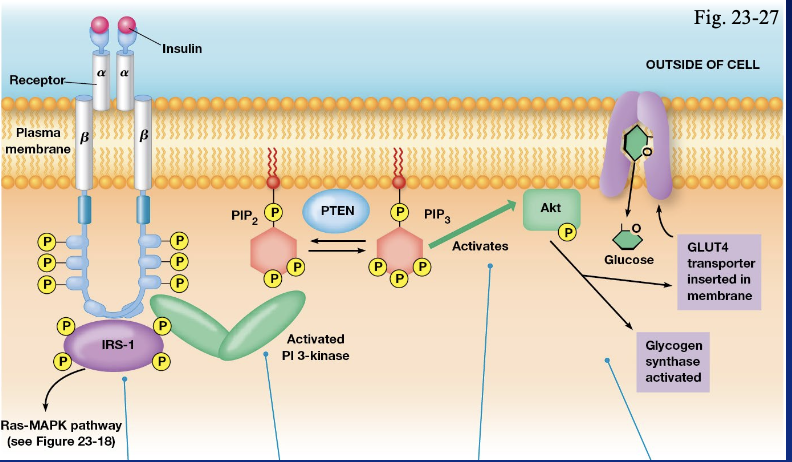
Akt also phosphorylates proteins leading to increased ___ synthesis
glycogen
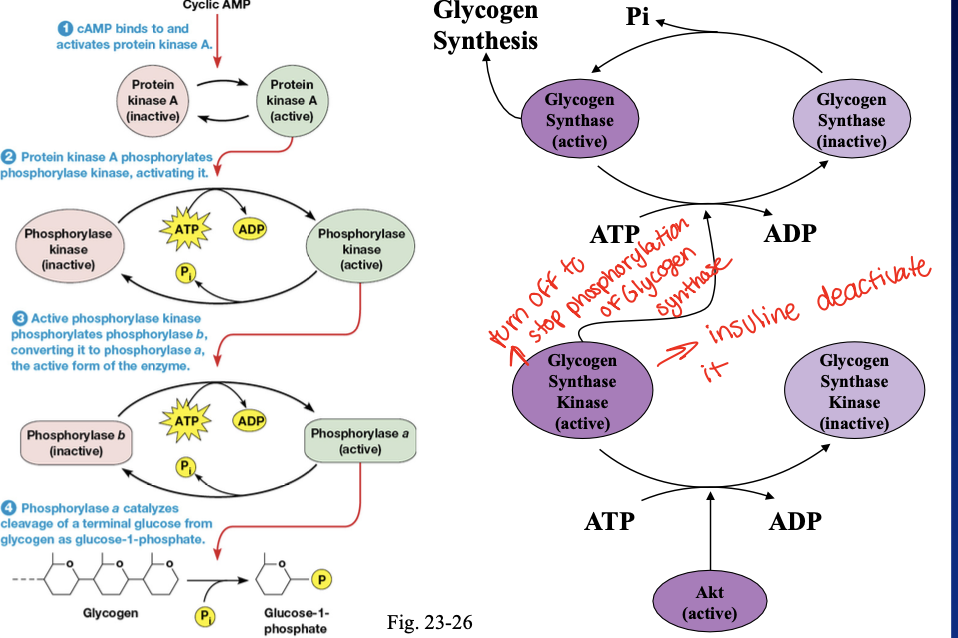
when is glycogen synthase active
when it’s dephosphorylated
PKA can inhibit glycogen synthase only when
PKA activity is really high
describe how Akt inhibits inhibition of glycogen synthase
Akt phosphorylates glucogen synthase kinase. Glycogen synthase kinase will inhibit glycogen synthase causing the phosphorylation of glycogen synthase making it inactive
how is focal adhesion able to be a binding site for so many pathways?
integrin binds to ecm and recruitsfocal adhesion kinase will be binding site for Src which is a soluble tyrosine kinase that phosphorylates additional tyrosine on FAK. Since PI 3-kinase, PLC-gamma and Grb2 use tyrosine to bind to them they can all bind in one site
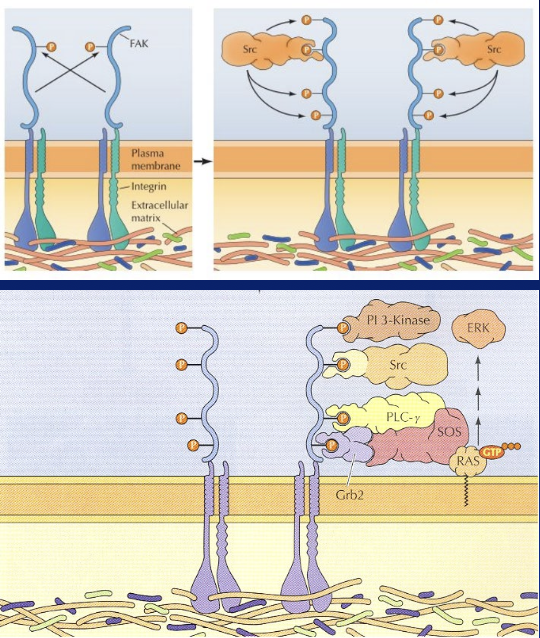
growth and survival of cell is due to FAK and Src family being overreactive and over expressed leading to
cancer
focal adhesion signal and FAK signal lead to development and migration which regulates ___, ____, ____ to modify actin polymerization and organization
rho,rac,cdc42
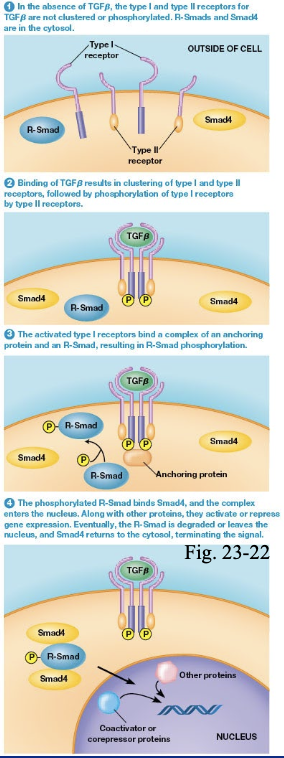
what are serine/threonine kinases
transforming growth factor
what is the purpose of serine/threonine kinases
inhibits growth of most cells types and promotes tissue maturation by promoting synthesis of ECM component s
how is serine/threonine kinase activated
transforming growth factor beta binds recepto somposed of 2 type I and 2 type II
type II are going to bind to type II and they are activated
type II is going to phosphorylate type I receptors to activate them
activated receptor is a serine/threonine kinase which phosphorylates Smad transcription factor and inhibit growth