Organic Chemistry II Exam 3: Chapter 20, 21, 22, 23
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
what are the three ways we learned to synthesize carboxylic acids
1. hydrolysis of nitriles
2. carbonaiton of organometallics
3. oxidation
What is the the reaction for the hydrolysis of nitriles
RCN ----> (1. NaOH, H2O, 2. H3O+) --> RCO2H
RCN --- (H3O+) --> RCO2H
What is the mechanism for the acidic hydrolysis of the nitrile
1. protonate the nitrogen
2. attack the triple bond with water and then transfer one of the pi bonds onto the nitrogen (should be left with OH2, R, and NH)
3. protonate the nitrogen with one of the H2 of OH2
4. attack with water and transfer electrons onto the nitrogen
5. protonate NH2 with an H from OH2
6. have electrons from OH go down and then have NH3 leave
7. deprotonate
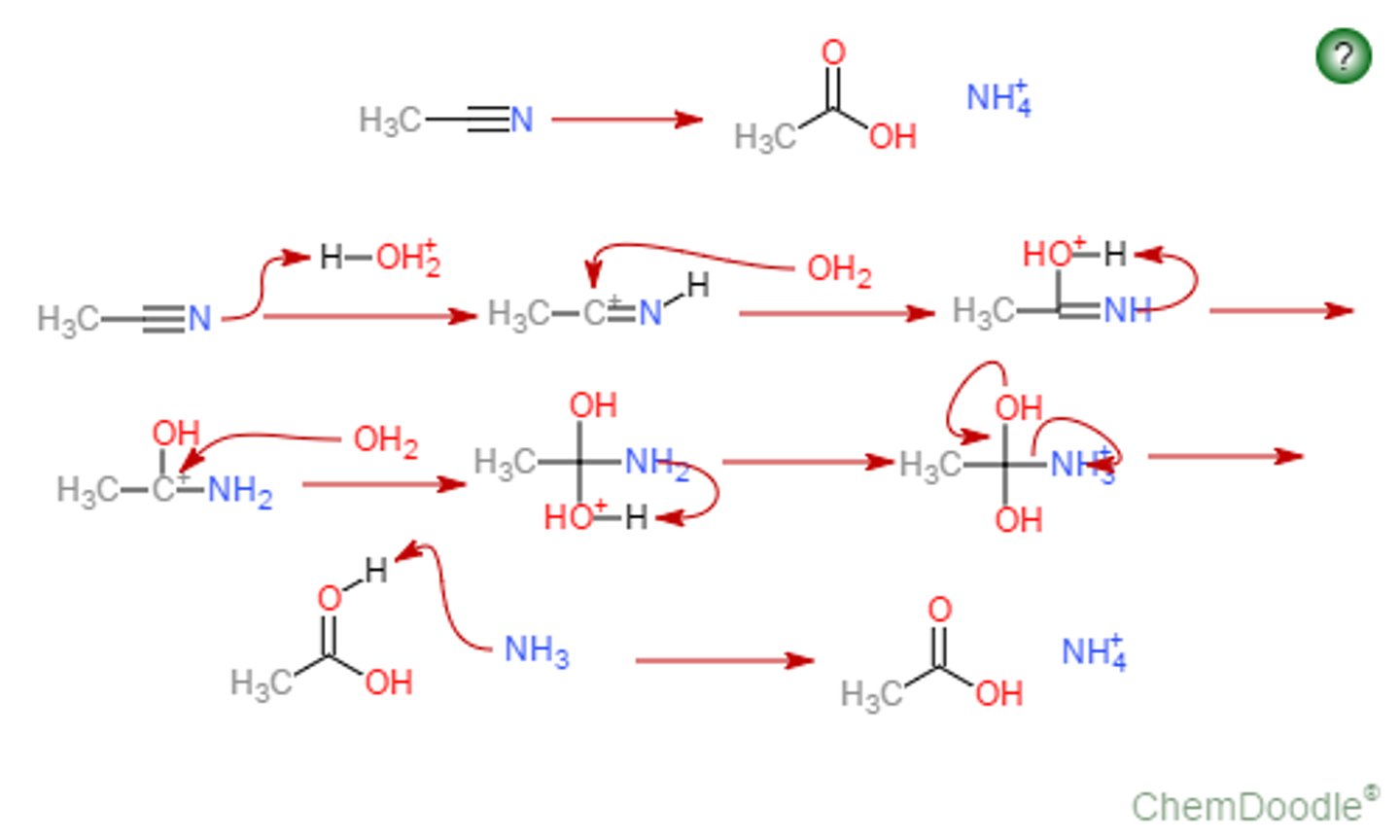
What is the mechanism for the basic hydrolysis of nitriles
1. attack triple bond with OH and then have the pi bonds move onto the nitrogen
2. protonate the nitrogen (should have a negative charge) and then form OH-
3. depronate the OH and put electrons onto the oxygen
4. transfer the electrons from the oxygen down and then have the double bond be protonated by water - will be left with an amide
5. then you will have OH- come in and attack and form CR, NH2, OH, O
6. have the electrons go down the O- and then have NH2 leave
7. because basic conditions should be R-C=O,OH
what is the general formula for carbonation of organometallics
RMgX/RLi
1. CO2
2. H3O+
RCO2H
what is the mechanism for the carbonation of organometallics
1. form the grignard reagent
2. have the grignard attack O=C=O
3. protonate the oxanion
What is oxidation for forming carboxylic acid
1. alkyl benzene - can react with KMNO4 H2)
2. primary alcohol can react with CrO3 and H3O+
what are the three ways we learned how to synthesize nitriles
1. SN2 displacement
2. cyanohydrins
3. dehydration of amids
what is the reactant necessary for the formation of a cyanohydrin from a ketone
KCN, H2SO4 or HCN
What happens when you react RCN with 1. LiAlH4 and H2O
RCH2NH2
what happens when you react RCN with 1. R'Li and 2. H3O+
forms a ketone
What is the mechaism for RCN + 1, LiALH4 2. H3O+
1. the n itrile takes an H from AlH4 and then transfers an electron onto the N
2. then the nitrogen is negatively charged and then AlH3 attaches to the N
3. add water
What is the mechanism for adding a grignard to an ester
3 main steps: nucleophilic addition, imine formation, and hydrolysis
1. girgnard attacks and the pi electrons transfer onto the n
2. and then protonate the nitrogen
3. then protonate the nitrogen again and then have the h3O+ say that is not positive and then the electrons transfer onto the nitrogen n
4. protonate the H of NH2 with the OH2
5. then OH with left with chain -
6. then have the OH go down and have NH3 leave
7. depronate the oxygen
how do you form an acid chloride
carboxylic acid + SOCl2
mechanism for the formation of the acid choride from carboxylic acid
carboxylic acid + SOCl2
mechanism for the formation of an acid chloride
so the Cl- attacks C and then puts electrons on oxygen for negative charge
then the oxygen moves it down and then the other bond goes to the other side so pretty similar to th eoutcomes
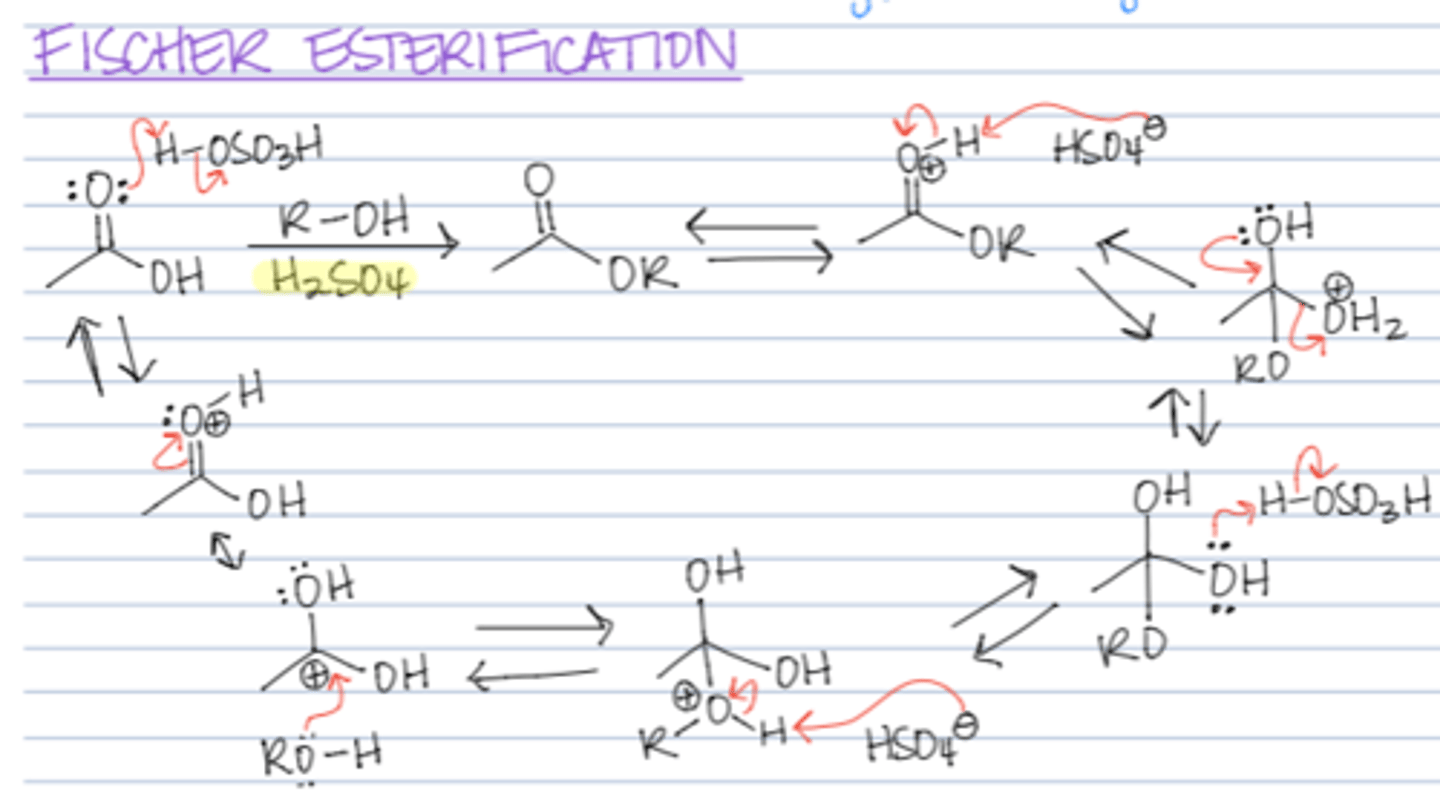
Fischer esterification - which reactants
ROH in HCl `
what is the mechanism for fischer esterification
1. protonate oxygen
2. attack with R OH
3. then oxygen goes down adn the Oh2 moves away
4. OH2 gets rid of hydrogen
5. protonate the oxygen
6. the Oh2 goes again
7. electrons go down
8. depronate the oxygen
what reactants are used to form an amide from a carboxylic acid
1. DCC
2. R'NH2
what is the mechanism for formation of an amide from carboxylic acid
(review the sheet page 4)
what are the reactants for reduction of RCO2H + RCH2OH
if react with 1. BH3, THF 2. H2O - faster
if react with lialh4 2. h3O+
what is needed to hydrolyze acid chloride
react with water
what is mechanism for hydrolyis s of acid chloride
add water
2. electrons from O- go down adn cl leaves
3. Cl- deprotonates Oh2
estherification of acid chloride - what are the reactants
r'OH and pyridine
ihow do you replace a primary OH with AcO
1. CH3OCl 2. pyridine
what reactants are necessary for aminolysis of an acid chloride
2 equivalents of 2 R'NH2
what is mechanisms of aminolysis - amide formation
1. pyridiine deprotonates the H from NHR1
2. nitrogen attacks
3. electrons shift down forming a dance arena
how do you reduce an acid chloride
1. add LiAlH4
2. add RMgX
what is ketone synthesis from acid chloride
have the oxgen come down and Cl leave
have it go away
what happens with Ac2O + ROH --pyridine --> RoAC + ACO
What happens with Ac2O +RNH2 ---> RNHAC + ACO -
what is needed for basic esther hydrolysis
hydroxide
what is the mechanism of basic esther hydrolysis
1. oh attacks and then it only got one and it was nice
what is needed for aminolysis of esther
RNH2
what is the mechanism for it
N attacks
o shifts down and OR leaves
RO is on a run and took H from NH2
how do you do transesterhification but alcoholysis
have the RCO2Me and the ROH
what is the reduction of an esther - what is needed
LiALH4 and 2. h3o+
how many equivalents of griganrd do you need for esthers
2
what happens with grignard and esther
R-Li attacks and the O4 leaves and then the R-Li attacks again and then h3O+
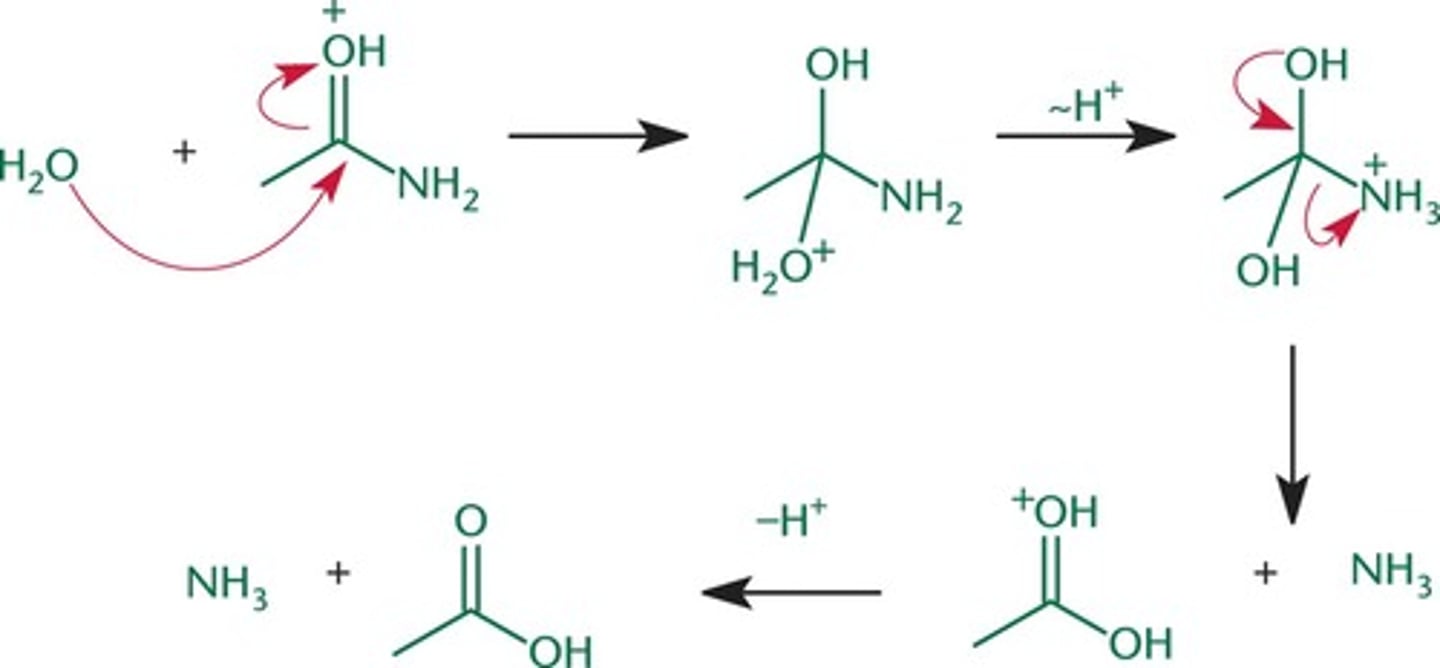
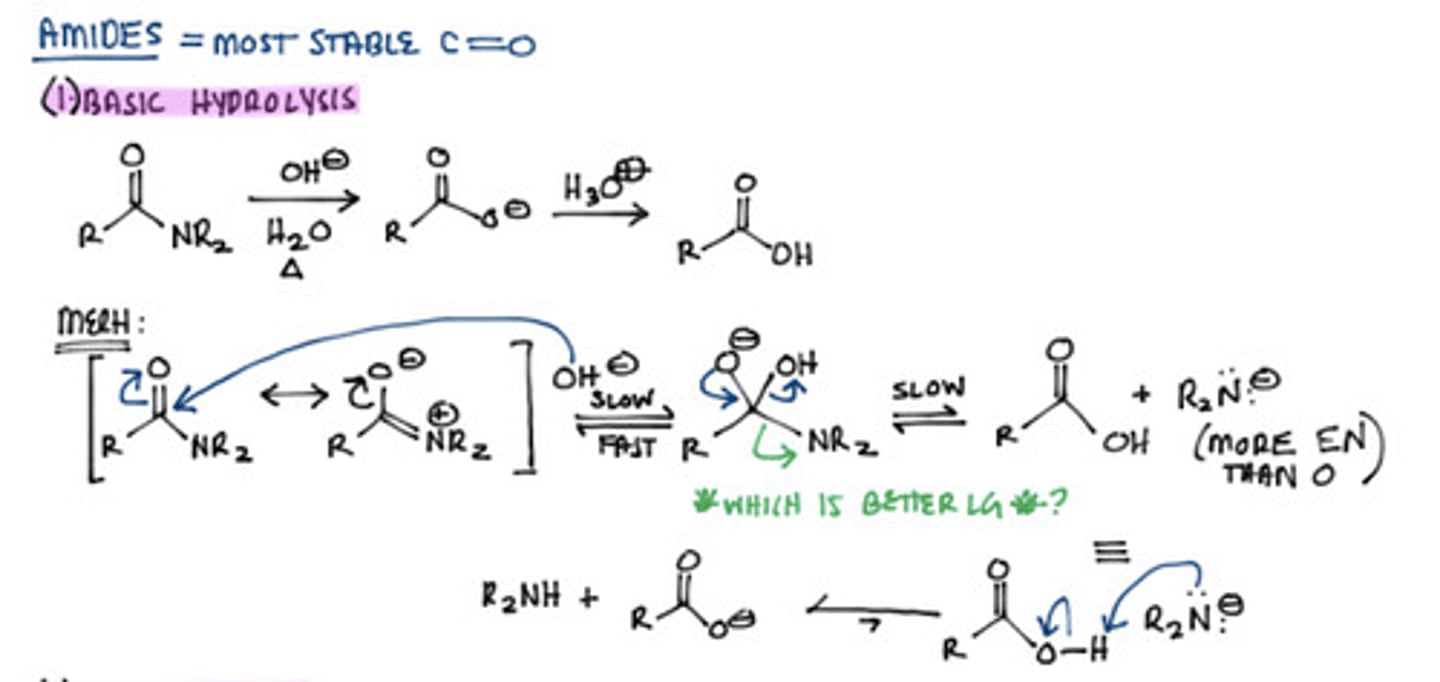
hydrolysis of amide two ways
1. H3O+
1. OH-
hydrolysis of amide (acidic
hydrolysis of amid (basic)
how do you reduce an amide
1. LIALH4 2. H2O
mechanism for reduction of amide
ALH4 enters and shifts oxygen
then the nitrogen stuff into it and onto oxygen
get rid of double bond and then it forms
if you want to reduce an esther into an alcohol which reactant should you use `
LiAlH4 H3O+
if you want to reduce an esther into an aldehyde which reactant should you use
(i-bu)2AlH
2. H3O+