Visual Culture Final
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Imagined community
a concept where individuals who may never meet share a sense of belonging to a larger group based on a shared identity, history, or culture
how it is visualized depends on the shared political values/ideals of the specific nation
Print Capitalism
describes the rise of nation-states in Europe, fueled by the printing press and the capitalist market
theory proposes that the business of printing first fueled the rise of nation-states and nationalism in 15th-century Europe
interpellation
the process by which we encounter a culture's or ideology's values and internalize them
Interpellation as national subjects
refers to the process by which individuals are hailed or addressed as national subjects, internalizing and accepting a specific identity and role within a nation-state
Effect of political ideology on representation and interpellation
impacts how individuals are portrayed and how they understand their place in society.
Ideology shapes how individuals are represented, often leading to stereotypes or biased portrayals
influences the process of interpellation
Race as a social construction/ontology
consists of the all the assumptions, stereotypes, value systems that different societies attach to physical differences
there is no biology of it, only a sociology
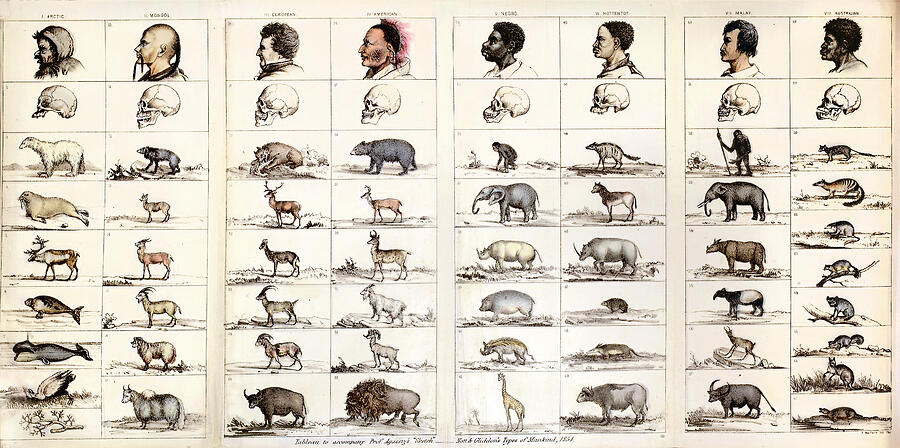
19th century theory of race
There is a hierarchy of races based on the characteristics and capabilities
Taken as. biological fact at the time
Theories of Biological Race
Dutch Brazil
mid-1600s
Dutch West India Company
colonizers of Dutch West Indies (ex: Brazil, Caribbean, North America)
Johan Maurits, governor
Paintings eventually given to the King of Denmark
8 paintings of people in Brazil with different clothes, cultures, & backgrounds
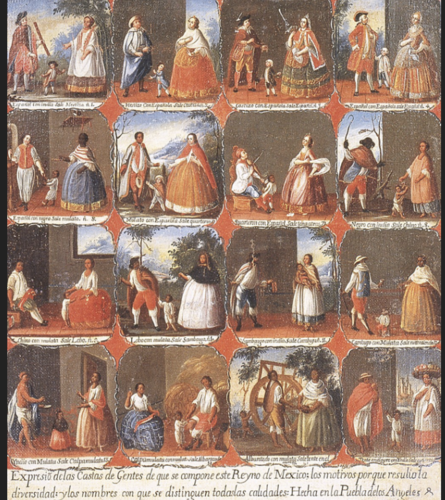
Colonial Mexico
1700s
Casta paintings
Ethnographic portrait
a visual representation, typically a photograph, painting, or drawing, that captures an individual's characteristics and cultural context

Casta Painting
originating in 18th-century colonial Mexico, were a unique artistic genre that illustrated the complex racial hierarchies and social structures of the time

4 continent allegories
humans are one species, 4 “varieties” characterized by “color” difference in temperament caused by climate
Africa, America, Europe, Asia
polygenism
the doctrine or belief that existing human races have evolved from two or more distinct ancestral types

Stereotype
a stock-cut image that could be used over and over again with print text
considered to be a method of visual shorthand, and were used by advertisers to promote products

Making & Challenging the Mammy Stereotype
Stereotype of a Black woman used on products (pancake mix)
Shown to be old, large/overweight, and extremely dark (like back face), and content as a servant
Challenged by being presented like a real Black woman with nice clothes, married, average weight, turned into a statue in old sugar factor, and made to look liberated through art
Appropriation
the action of taking something for one's own use, typically without the owner's permission
typically related to culture
Orientalism in 19th century European art
the depiction of the "Orient" (primarily the Middle East, North Africa, and parts of Asia) by Western artists, often with a romanticized and idealized, yet sometimes inaccurate, portrayal of Eastern culture and customs
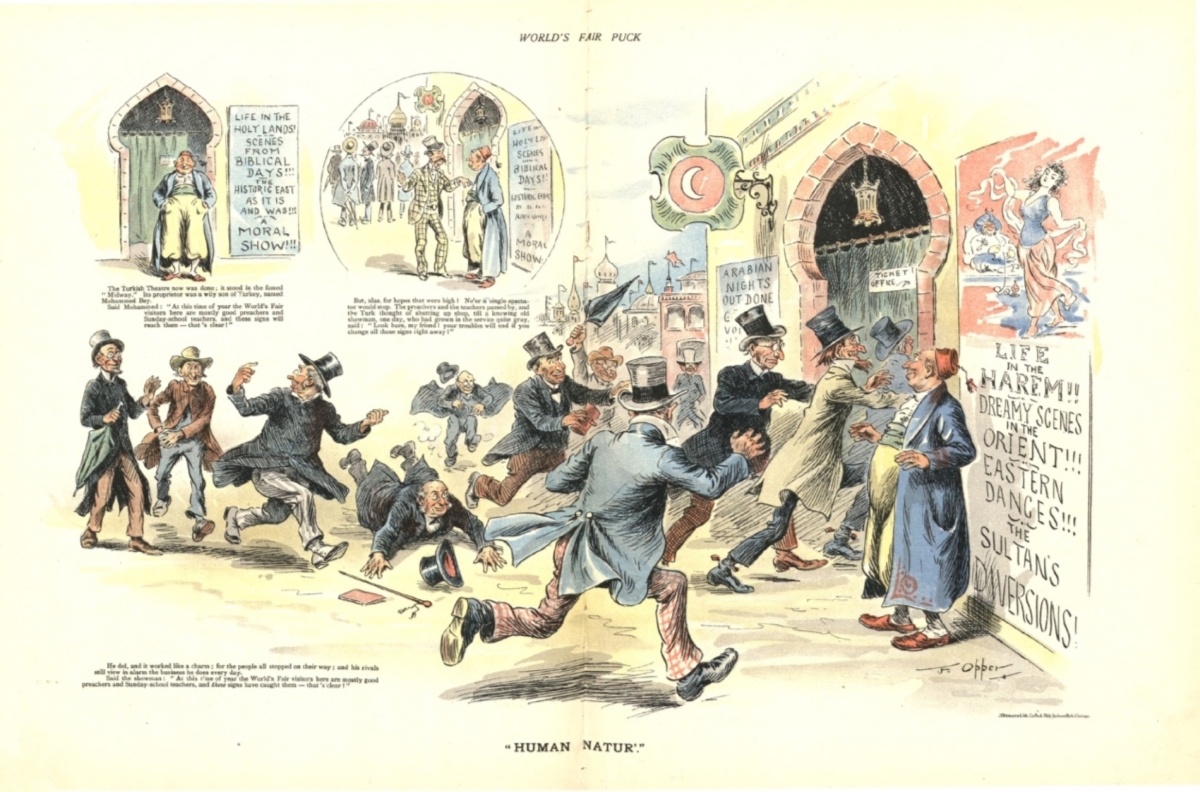

Legacies of Orientalism in 20th & 21st century popular culture
Hollywood movies
Inaccurately depicts those of Oriental culture
White male heroes, white women often captured or sexualized by an Orient man, Oriental men portrayed as villains
Mostly white actors, like white women playing oritenal women
Orientalism and contemporary political implications
After 9/11, middle eastern people have been stereotyped as terrorists
stereotypes have harmfully impacted middle eastern Americans and middle eastern people
We are taught that middle eastern culture is dangerous and bad
Clothing as a signifier for identity
gender, class, culture, ethnic identity, race
We judge and interpret people based on their clothes
Moralizing architecture
the idea that buildings and the built environment can carry moral connotations and judgments, and that architecture can be used to promote or reflect certain values or beliefs
Banyan
a loose-fitting garment, often a dressing gown or jacket, with origins in India and later adopted in Europe
symbolized wealth, sophistication,
cosmopolitanism

qipao/cheongsam
Traditional Chinese dress that is considered dignified and elegant and formal
has changed over time from wide and covering most if body to fitted and shortened (western influence)
It is traditional & modern and authentically Chinese & global commodity

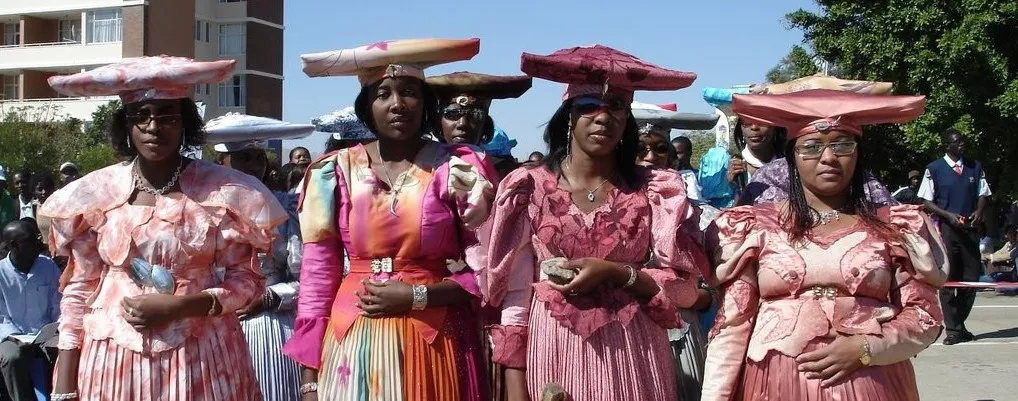
Herero long dresses
Traditional Namibia dress
inspired by victorian era dresses & forced into Namibia culture by colonizers
has head piece goes with it reprsenting cow horns

Classic (advertising logic)
Traditional method of advertising
Sells you the product as well as an idea (like a lifestyle) that the product can give you

Postmodern (advertising logic)
Often makes fun of traditional advertising
used to engage viewers in a more playful way
recognizes that consumers are not passively manipulated by ads
addresses that celebrities in ads are being paid to promote products and you shouldn’t buy something because of them

Affirmational (advertising logic)
empowering the consumer in their current state.
It emphasizes acceptance of the consumer as they are, rather than trying to get them to want something different.
promotes self-acceptance and authenticity
Values Signalining (advertising logic)
a brand conveys its core values or beliefs to potential customers, often through specific actions or messages rather than explicitly stating them
aims to attract customers who align with the brand's values and build a stronger connection.

Compassionate consumerism (advertising logic)
leverages emotional appeals to connect with consumers by highlighting a brand's concern for their well-being and social responsibility.
It aims to create a sense of shared values and ethical alignment
encourages purchasing decisions that benefit both the consumer and the greater community

Charles Mills main points
Critical Race Theory
Race can be socio-politically real while being anthropologically and biologically unreal
Social ontology (our natural being or identity is shaped by social contexts)
Racially categorized (illustrates that race and other identity components are social constructs)
Morgan main points
Stereotypes (original and contemporary meaning)
Characteristics of stereotypical Mammy figure
Mammy helped unite the whites in the North and South
by being illustrated in Southern stories meant to reunite the North and South
was romanticized by showing her voluntarily staying to serve (symbol of forgiveness and redemption for confederates)
Said main points
Orientalism:
Homogenizes (make uniform), Stereotypes & Justifies Colonialism
Nochlin main points
voyeurism and the gaze
European gaze of the Orient is one of objectification & dominance (like male gaze)
4 absences related to Oriental art
History
Westerners/colonial presence
Art (in the sense that the Western paintings of the Orient look like documents, not fictions
or interpretations)
Work and Industry
Khalid main points
War on Terror
Muslim women depicted as voiceless victims & oppressed
Muslim men are depicted as barbaric and oppressive
American men & women characterized as equal by media but not true.
Zhang main points
Asian style clothing being used for profit
stereotyping & misrepresentation of culture and people
clothes we wear tell others about us
Clothes can attract negative or positive attention
Wang main ideas
Cultural appropriation & fashion
isn’t always bad; it’s universal
can be used as form of communication or rebellion
makes people appriciate cultures they typically would ignore (ex. fashion)
Berger main ideas
“Publicity is about social relations, not objects”
products make people perceive or envy someone
"All publicity work(s) upon anxiety"
fear of not having anything or being able to buy things
consumption into a substitute for democracy
advertising distracts & hides political issues
Sturken and Cartwright
"Therapeutic ethos"
shift in values led to shift to consumerism
“Advertising speaks the language of transformation.”
consumers promised their lives will be better by buying a product
ads sell a sign/company so that consumers want to develop a relationship with the company
“selling social awareness?”
products promote ideologies