Water and Ion Balance in Cellular Physiology
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
Na+
Sodium ion, crucial for cellular functions.
K+
Potassium ion, vital for nerve signaling.
ATP
Energy currency of the cell.
ADP
Adenosine diphosphate, lower energy molecule.
Pi
Inorganic phosphate, involved in energy transfer.
Osmolarity
Concentration of solute particles in solution.
Tonicity
Effect of solution on cell volume.
ICF
Intracellular fluid, high in potassium.
ECF
Extracellular fluid, high in sodium.
IF
Interstitial fluid, surrounds cells.
Plasma
Liquid component of blood, carries cells.
Homeostasis
Maintenance of stable internal environment.
Passive Transport
Movement across membrane without energy.
Active Transport
Movement against gradient, requires energy.
Simple Diffusion
Direct movement through membrane, no proteins.
Facilitated Diffusion
Transport via membrane proteins, no energy.
Primary Active Transport
Direct use of ATP to move substances.
Secondary Active Transport
Uses energy from primary transport indirectly.
Concentration Gradient
Difference in solute concentration across a membrane.
Diffusion
Movement from high to low concentration.
Driving Force
Force causing movement down concentration gradient.
Membrane Flux Equation
Describes solute movement across membranes.
Integral Membrane Proteins
Proteins that span the membrane, affecting permeability.
Random thermal motions
Movement of particles due to temperature effects.
Fick's law of diffusion
Describes solute movement based on concentration gradient.
Diffusion coefficient (Ds)
Measures solute mobility in a medium.
Concentration gradient (C2 - C1)
Difference in solute concentration driving diffusion.
Semi-permeable membrane
Allows selective passage of certain substances.
Permeable
Substances can pass through the membrane.
Impermeable
Substances cannot pass through the membrane.
Hydrophobic solutes
Substances that diffuse through lipid membranes easily.
Hydrophilic solutes
Substances that require pores to diffuse through membranes.
Membrane permeability
Defines ease of substance crossing the membrane.
Transmembrane proteins
Integral proteins spanning the lipid bilayer.
Ion channels
Proteins that regulate ion movement across membranes.
Open state of ion channels
Allows ions to pass through the membrane.
Closed state of ion channels
Prevents ion passage through the membrane.
Na+-K+ ATPase
Enzyme maintaining Na+ and K+ concentration gradients.
Osmosis
Movement of water across a semi-permeable membrane.
Colligative property
Depends on solute concentration, not solute type.
Boiling point elevation
Increase in boiling point due to solute presence.
Freezing point depression
Decrease in freezing point due to solute presence.
Vapor pressure elevation
Increase in vapor pressure due to solute presence.
Hydrophobic core
Barrier preventing hydrophilic substances from passing.
Concentration of pure H2O
55 M or 55,000 mM in 1 liter.
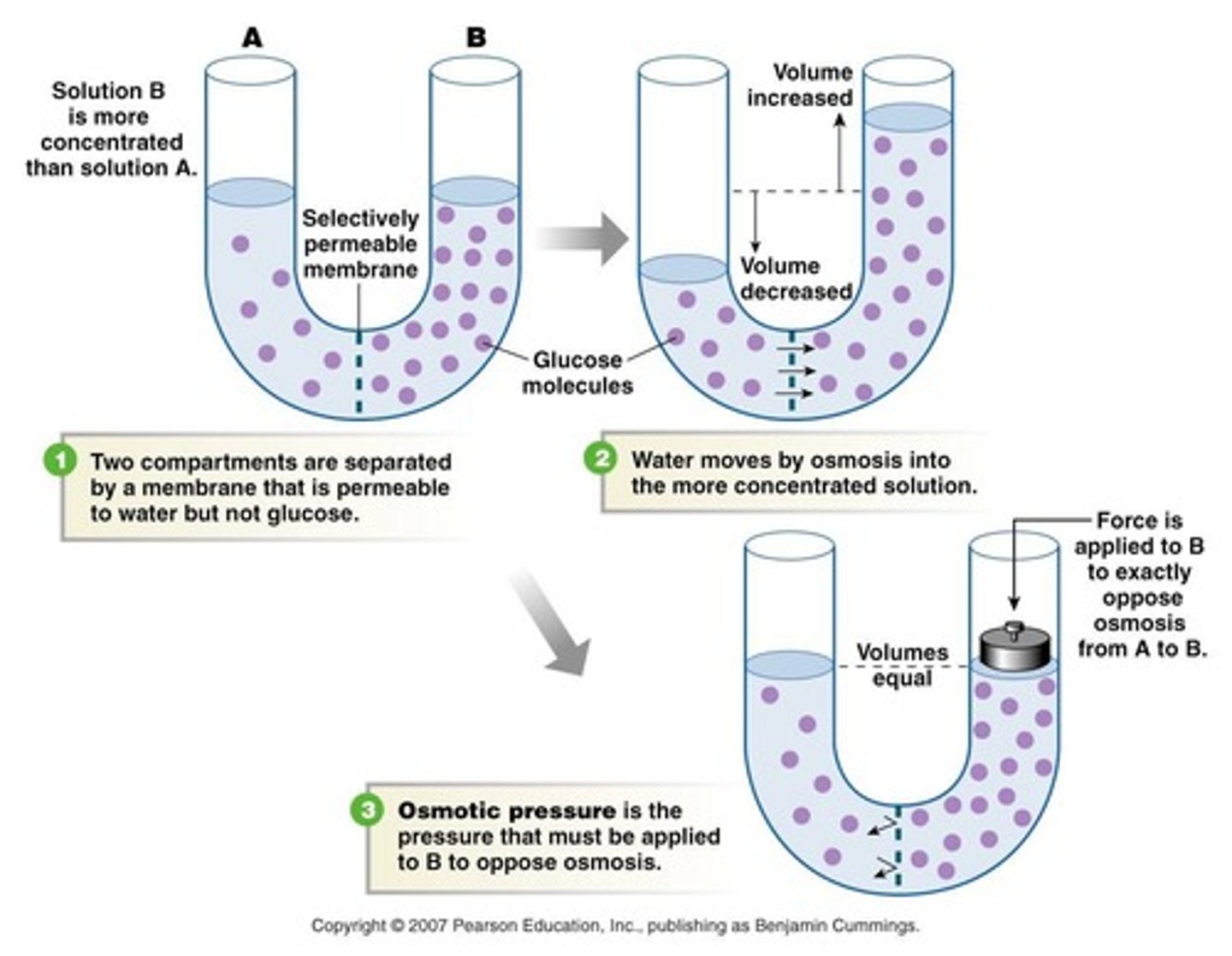
Osmotic Pressure
Hydrostatic pressure generated by osmosis.
1 Molar
1 mole of solute per 1 liter solution.
1 osmolar
1 mole of solute per 1 liter solution.
1000 milliosmolar
Equivalent to 1 osmolar.
Dissociation in H2O
Solutes like NaCl dissociate into ions.
Osmolarity Calculation
Total osmolarity adds independently from solutes.
Hypertonic Solution
Higher osmolarity than cell, causes water efflux.
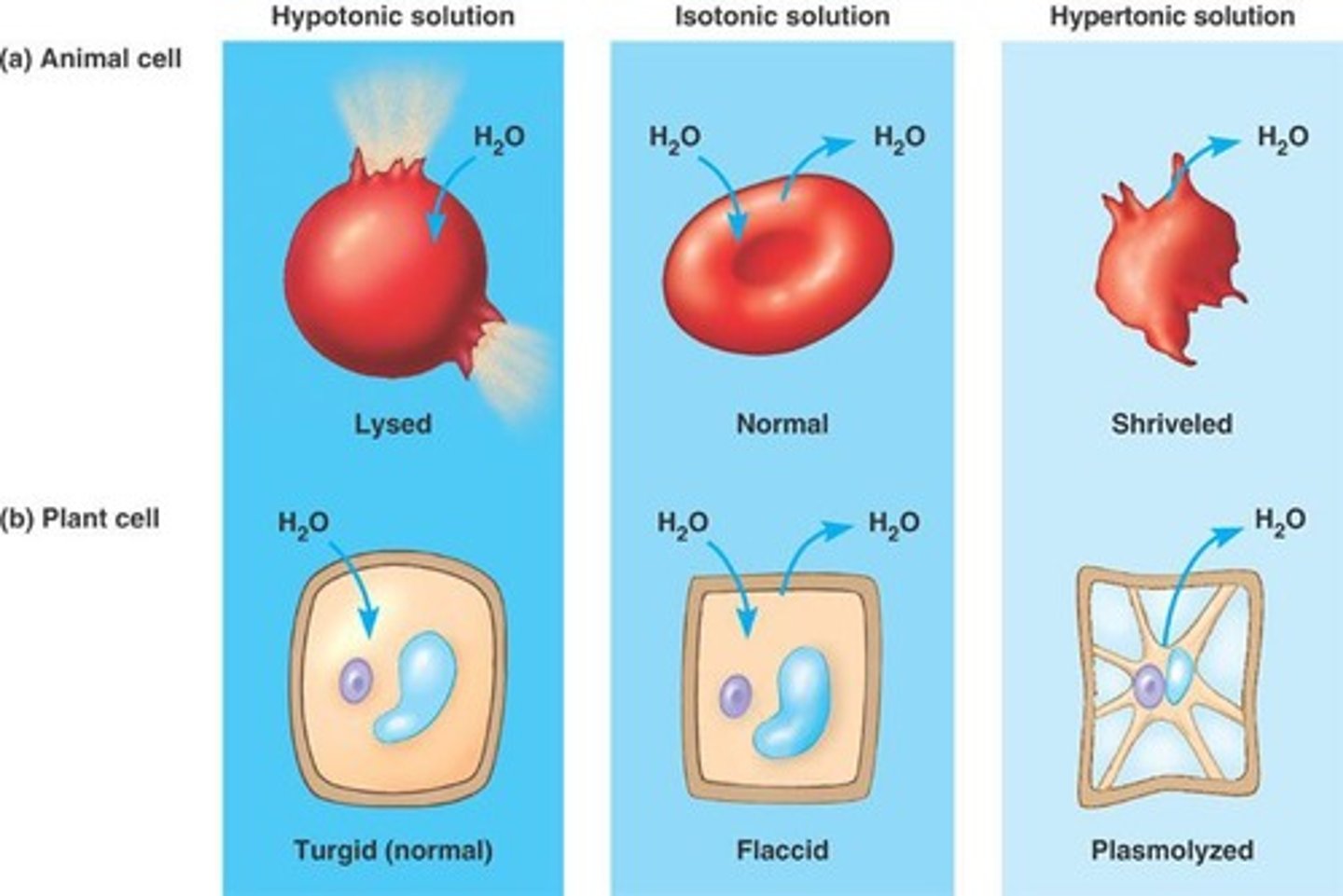
Isotonic Solution
Equal osmolarity inside and outside cell.
Hypotonic Solution
Lower osmolarity than cell, causes water influx.
Osmoregulator
Maintains stable body fluid osmotic concentration.
Osmoconformer
Body fluid concentration matches environmental osmotic concentration.
Euryhaline
Survives wide range of osmotic concentrations.
Stenohaline
Tolerates limited osmotic concentration range.
Transcellular Transport
Movement through cell membranes.
Paracellular Transport
Movement between adjacent cells.
Transport Epithelia
Specialized cells for solute and water transport.
Channel Proteins
Membrane proteins facilitating passive transport.
Carrier Proteins
Membrane proteins facilitating active transport.
Water Budget
Balance of water intake and loss in organisms.
Body Fluid Osmotic Concentration
Osmotic concentration of body fluids, ~300 mOsm.
Environmental Osmotic Concentration
Osmotic concentration of surrounding environment.
Passive Regulation
Water movement without energy expenditure.
Regulated Gain/Loss
Active control of water and ion levels.
BFOC
Body fluid osmotic concentration, e.g., 300 mOsm.
Osmoregulators
Organisms that maintain constant internal osmotic pressure.
Aquatic Environment
Habitat with water as the primary medium.
Terrestrial Environment
Land habitat with varying water availability.
Cutaneous Evaporation
Water loss through the skin.
Chloride Cell
Cell type for ion transport in fish gills.
Pavement Cell
Cell type in fish gills for passive transport.
Loop of Henle
Kidney structure for water reabsorption.
Temporal Counter-Current Exchange
Mechanism to minimize respiratory water loss.
Hyperosmotic Urine
Urine with higher osmolarity than body fluids.
Hypoosmotic Urine
Urine with lower osmolarity than body fluids.
Dietary Influence
Food intake affecting water and ion balance.
Excretion Mechanisms
Processes for removing excess water and ions.
Metabolic Water
Water produced from metabolic processes.
Environmental Osmotic Concentration (Env OC)
Osmotic concentration of surrounding water.
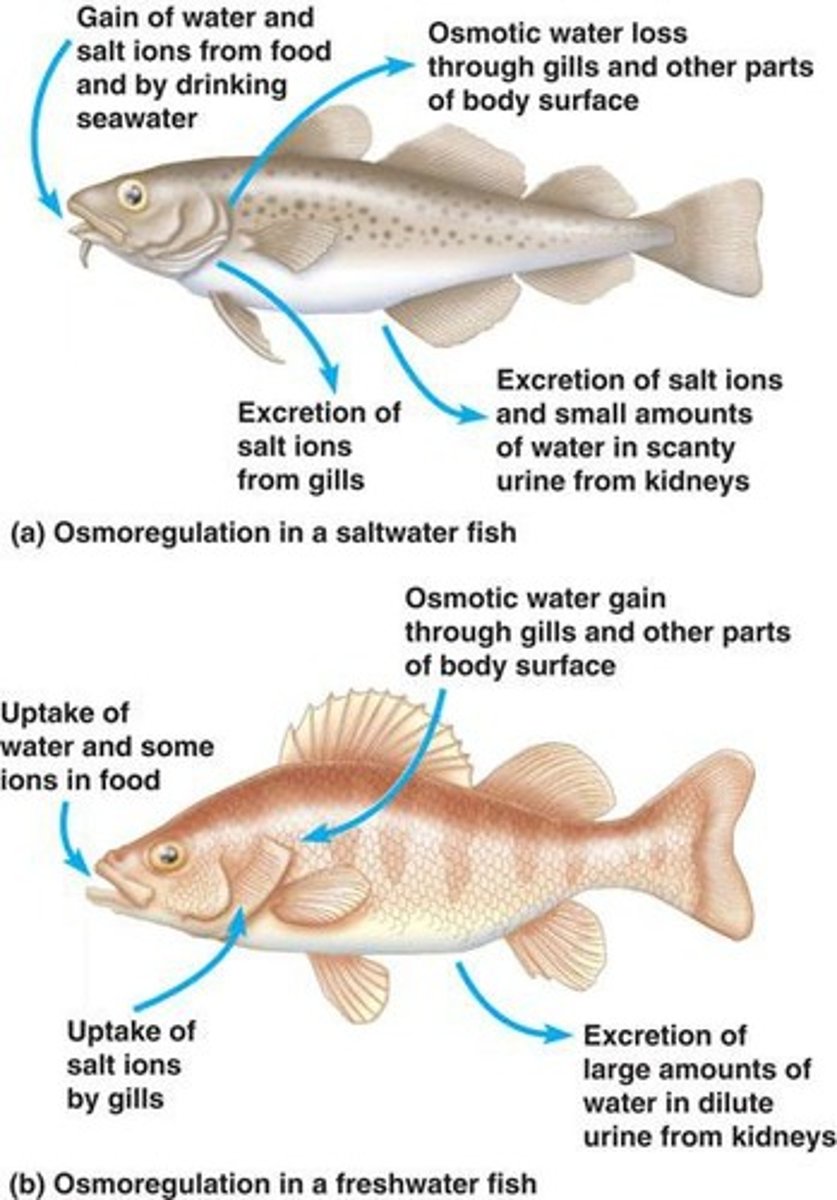
Freshwater Fish Adaptation
Gain water osmotically, do not drink.
Saltwater Fish Adaptation
Drink seawater, excrete excess ions.
Behavioral Adaptation
Strategies to minimize water loss in animals.