The Water Cycle
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|

37 Terms
What is the driving force behind the water cycle?
the sun

Which stage of the water cycle are clouds formed?
condensation

Describe a water drop in the water cycle that involves evaporation.
Water heats up, changes to water vapor and evaporates, rises into the sky. It cools, condenses, turns back into liquid water forming clouds. Then it falls back to earth as precipitation and runs down hills or mountains during runoff and returns to lakes and oceans.

*precipitation
water that falls to the ground in the form of rain, sleet, snow, hail, or freezing rain
Describe a water drop as it goes through the water cycle that involves transpiration.
Plants heat up due to sun's energy. Water heats up changes to water vapor and leaves the plants and rises into the sky. Then it follows the rest of the water cycle.
Explain the process of evaporation.
Liquid water gains energy from heat and changes states of matter into a vapor. Because vapor is less dense it rises into the sky.
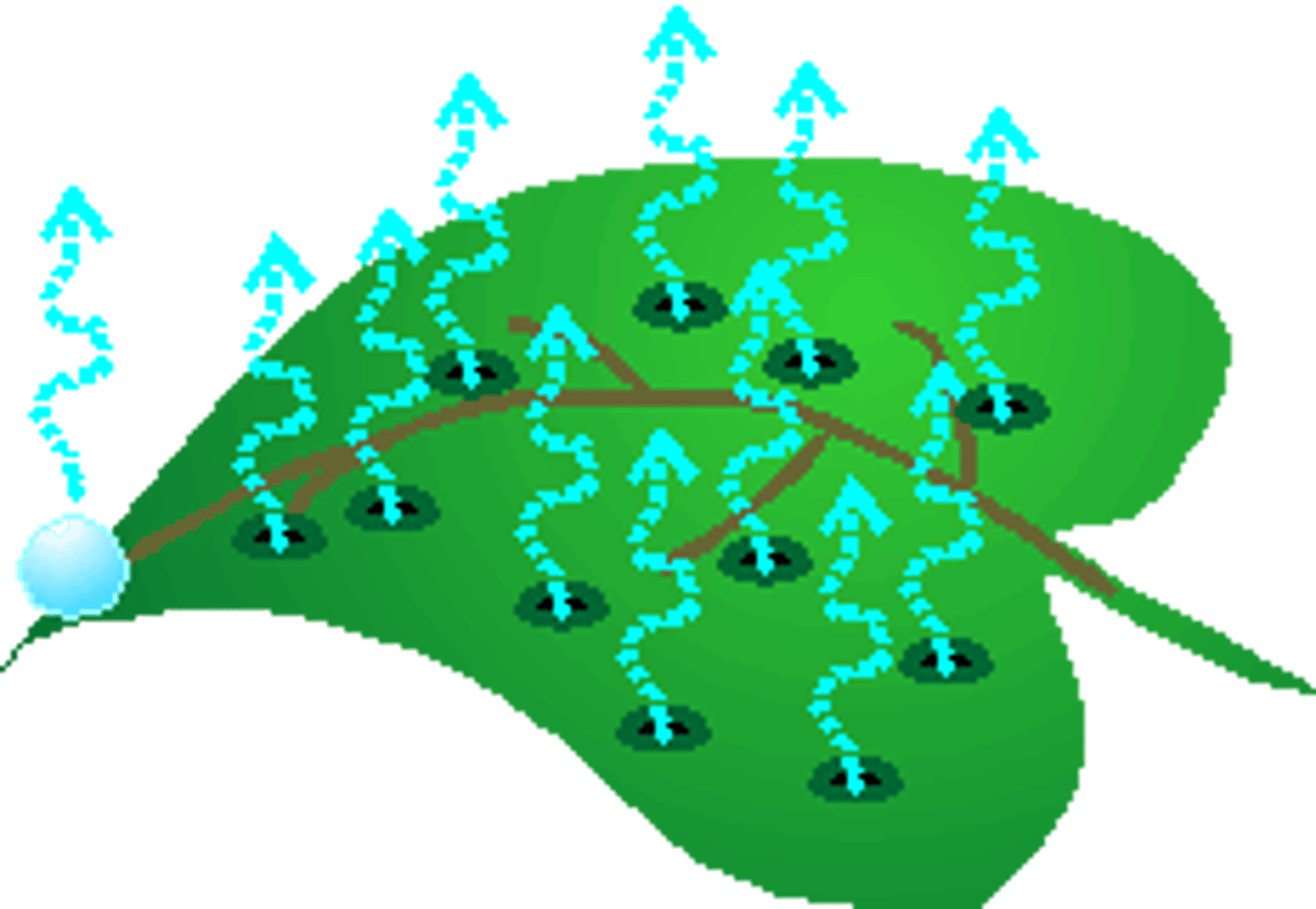
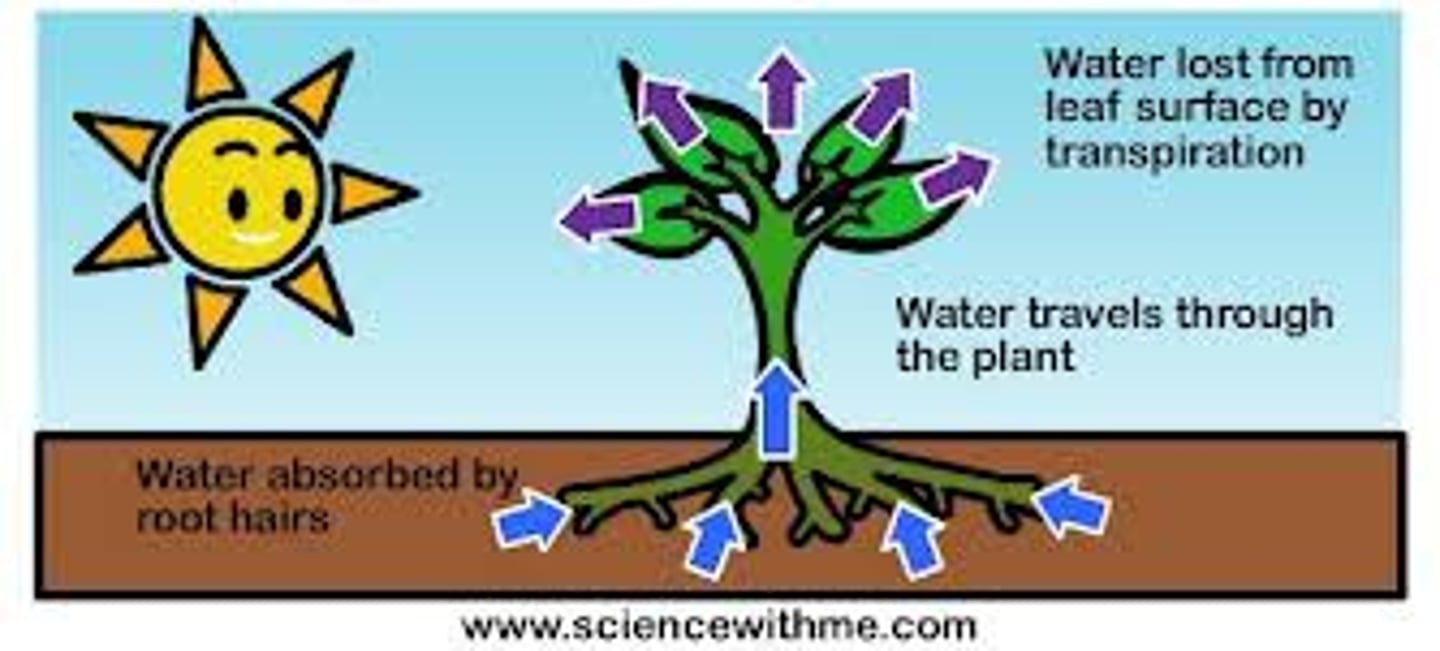
Explain the process of transpiration.
As the plant heats up, it gains heat energy from the sun, water that is absorbed changes states of matter into water vapor and is released from the plant and rises into the sky.
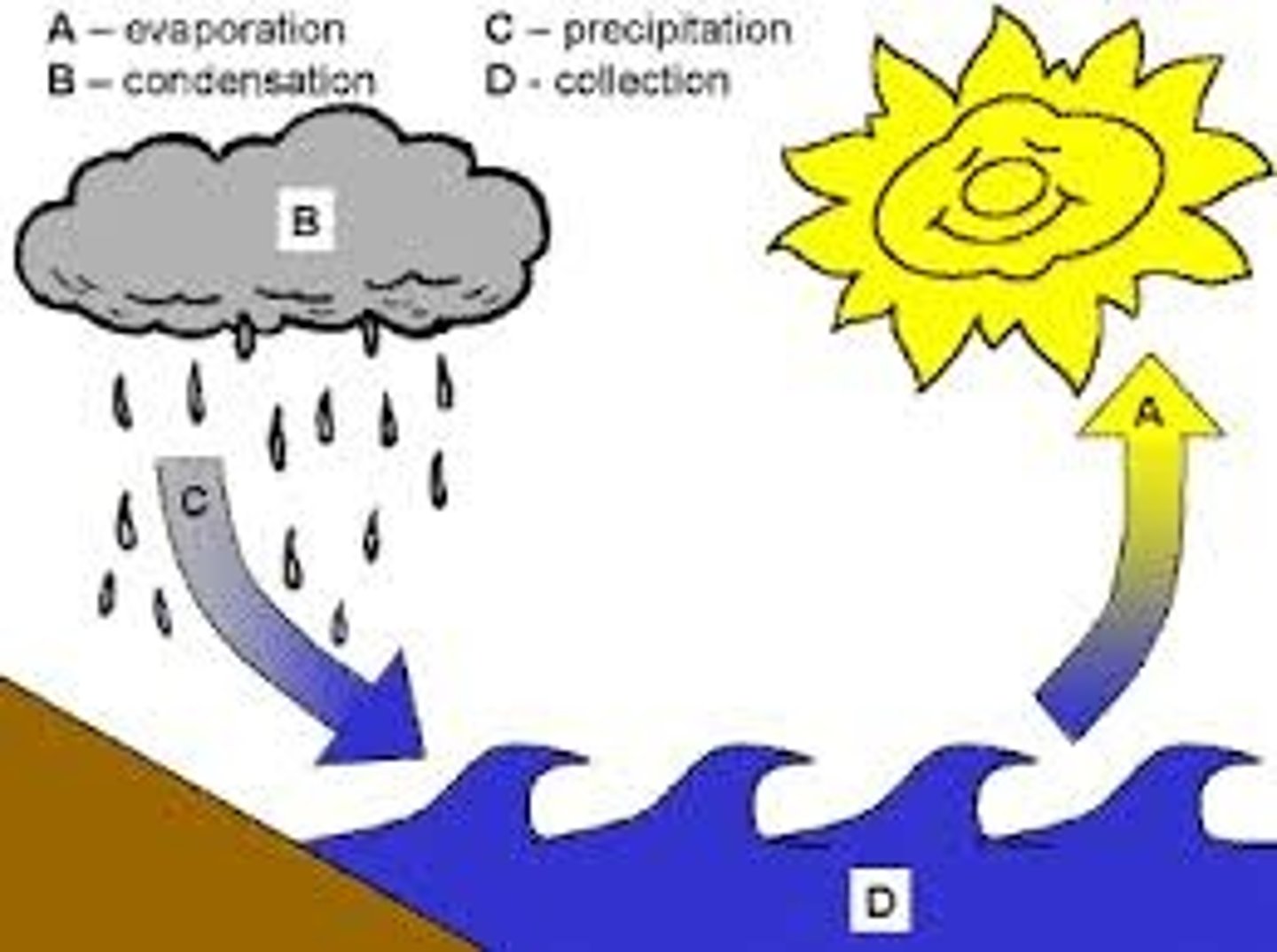
Explain the process of condensation.
Water vapor cools as it rises higher into the atmosphere and turns back into liquid water. Water droplets come together to form clouds.

Explain run off.
As precipitation falls, due to the force of gravity, it runs down hills and mountains back into other bodies of water. It can also seep into cracks in the ground and collects in aquifers under the ground.

What force cause run off?
gravity
Compare and contrast evaporation and transpiration.
Evaporation and transpiration are both examples of water changing states from a liquid to a gas and rising into the atmosphere. Evaporation happens from bodies of water and transpiration happens from plants.
What role does changing temperature play in the water cycle?
Water cooling or losing heat energy causes condensation and water gaining heat energy or heating up causes evaporation.

How is the water cycle an example of matter changing states.
Due to gaining or losing heat energy from the sun, water changes from liquid water into gas (evaporation) and from water vapor, gas, into liquid water (condensation)
Explain how water is recycled on earth.
The Water Cycle
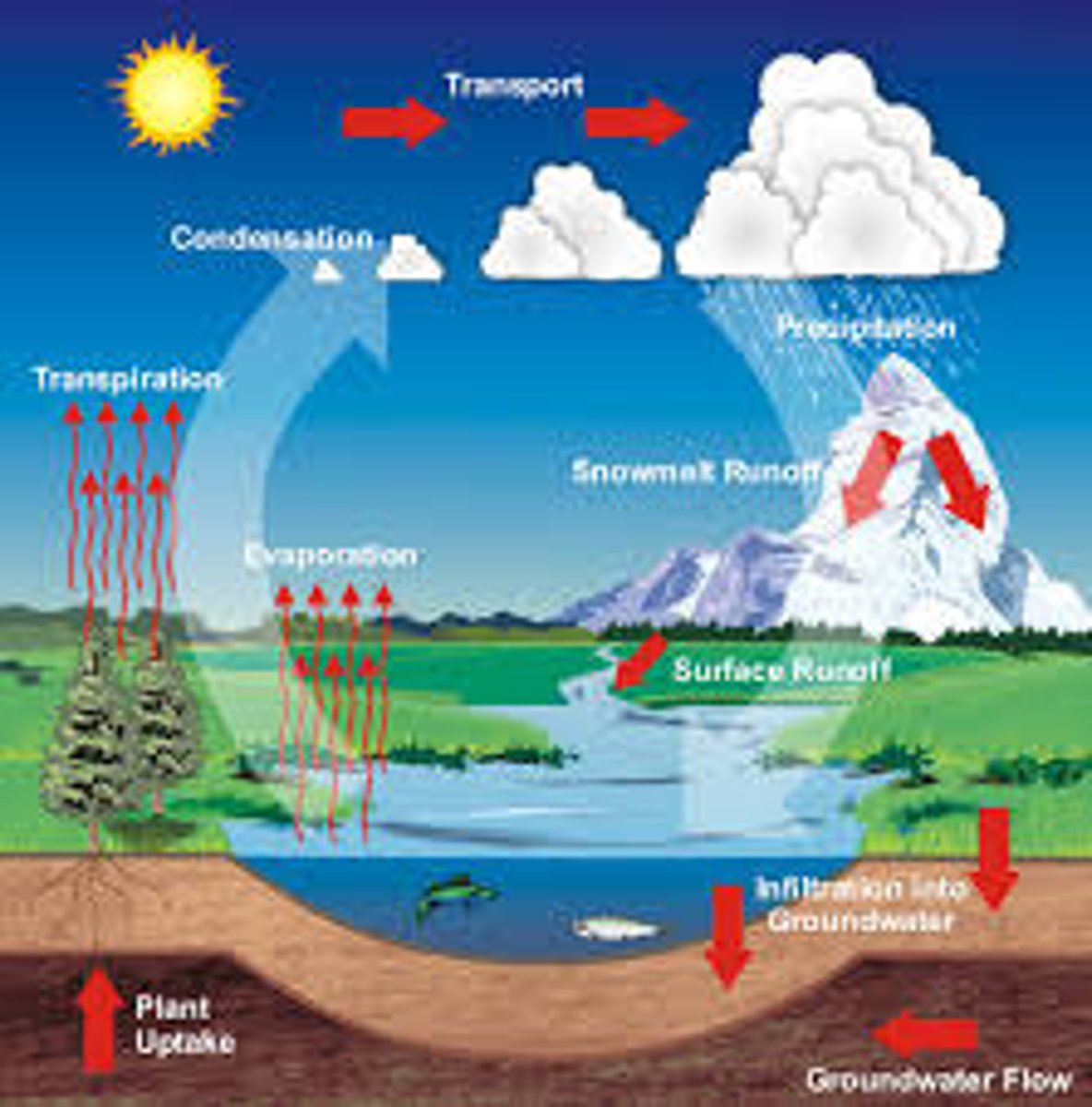
Explain 2 things that can happen to water after the precipitation stage.
Water can return to bodies of water like lakes and oceans or it can seep into the ground and return to aquifers.
List 4 types of precipitation.
rain, sleet, snow or hail
*condensation
Water vapor cools as it rises higher into the atmosphere and turns back into liquid water because it loses heat energy; Water droplets come together to form clouds
What determines the type of precipitation that will fall?
temperature of air near the ground
Has Earth gained or lost water throughout time?
Same amount as millions of years ago. It is constantly recycled.
Where does the most evaporation happen?
Over the oceans

Over the summer you notice less water in your pool than last week. Explain what happened.
It is hot in the summer so the water evaporated.
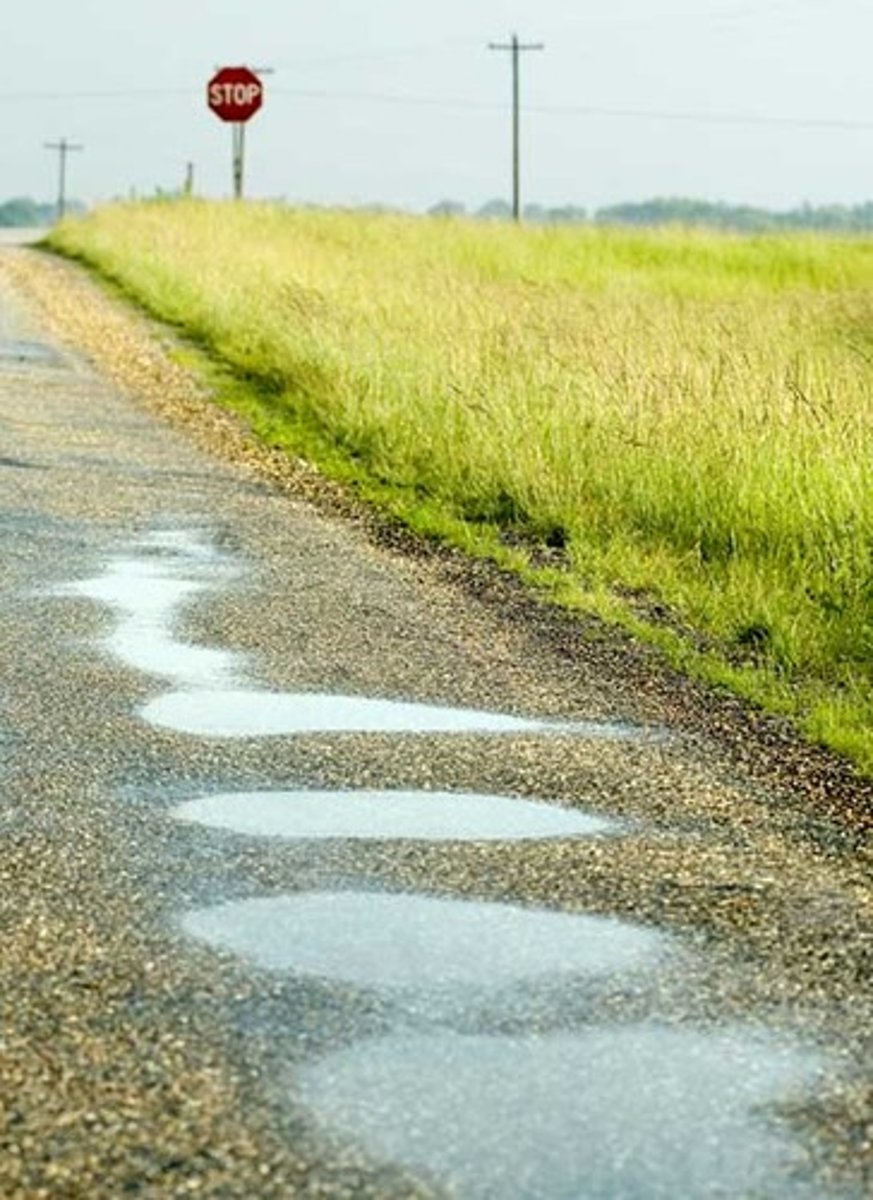
After a heavy rain there was a large puddle in your lawn. The next day the puddle is gone. What happened?
The water evaporated.

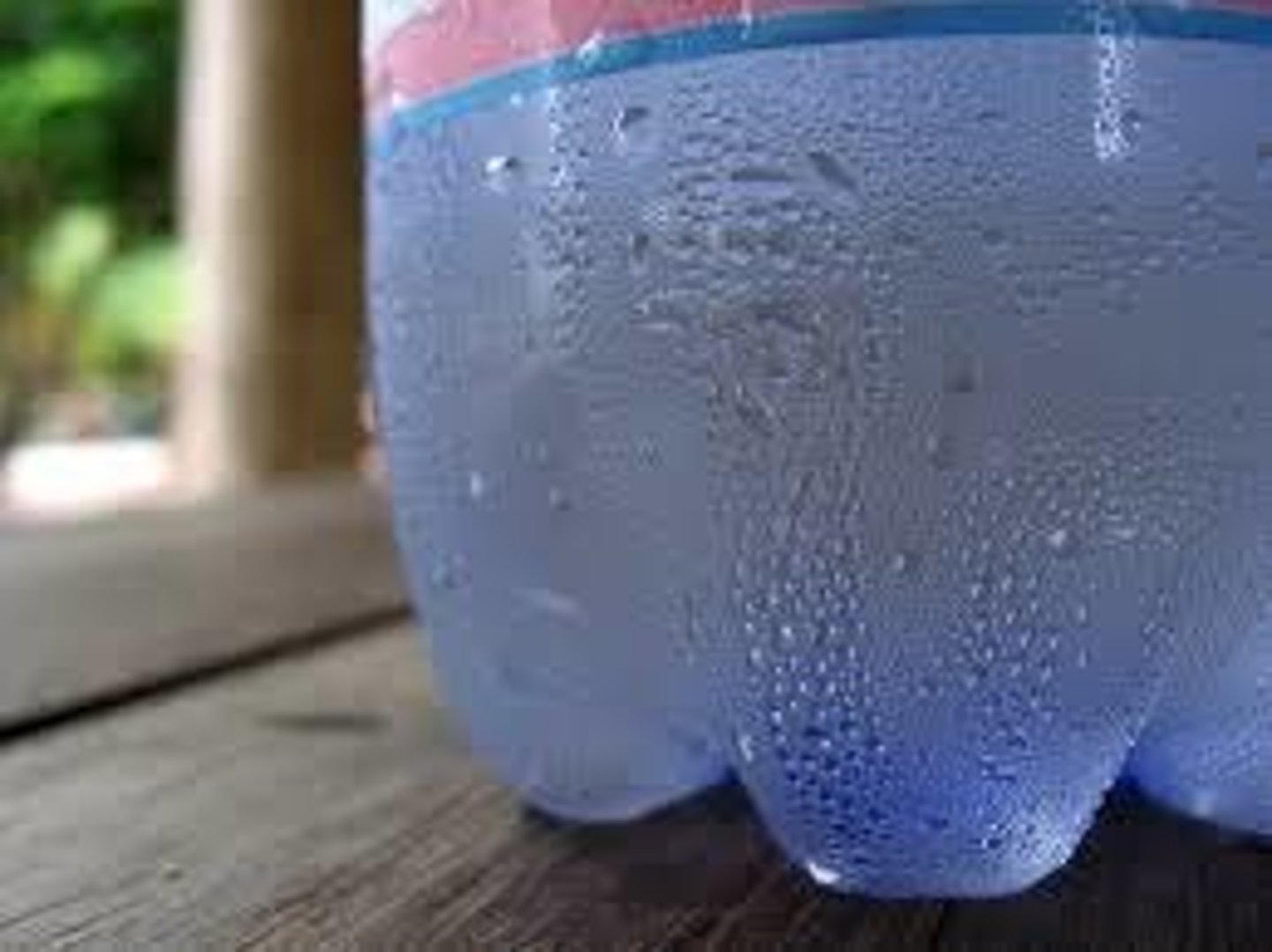
On a hot day you take a cold glass of Kool-Aid outside and you notice moisture on the outside. Explain what caused this.
Condensation caused by the difference in temperature between the cold liquid and the hot air.

*evaporation
Water heats up, changes to water vapor and evaporates, rises into the atmosphere; mostly happens over oceans; liquid water gains energy and changes to water vapor
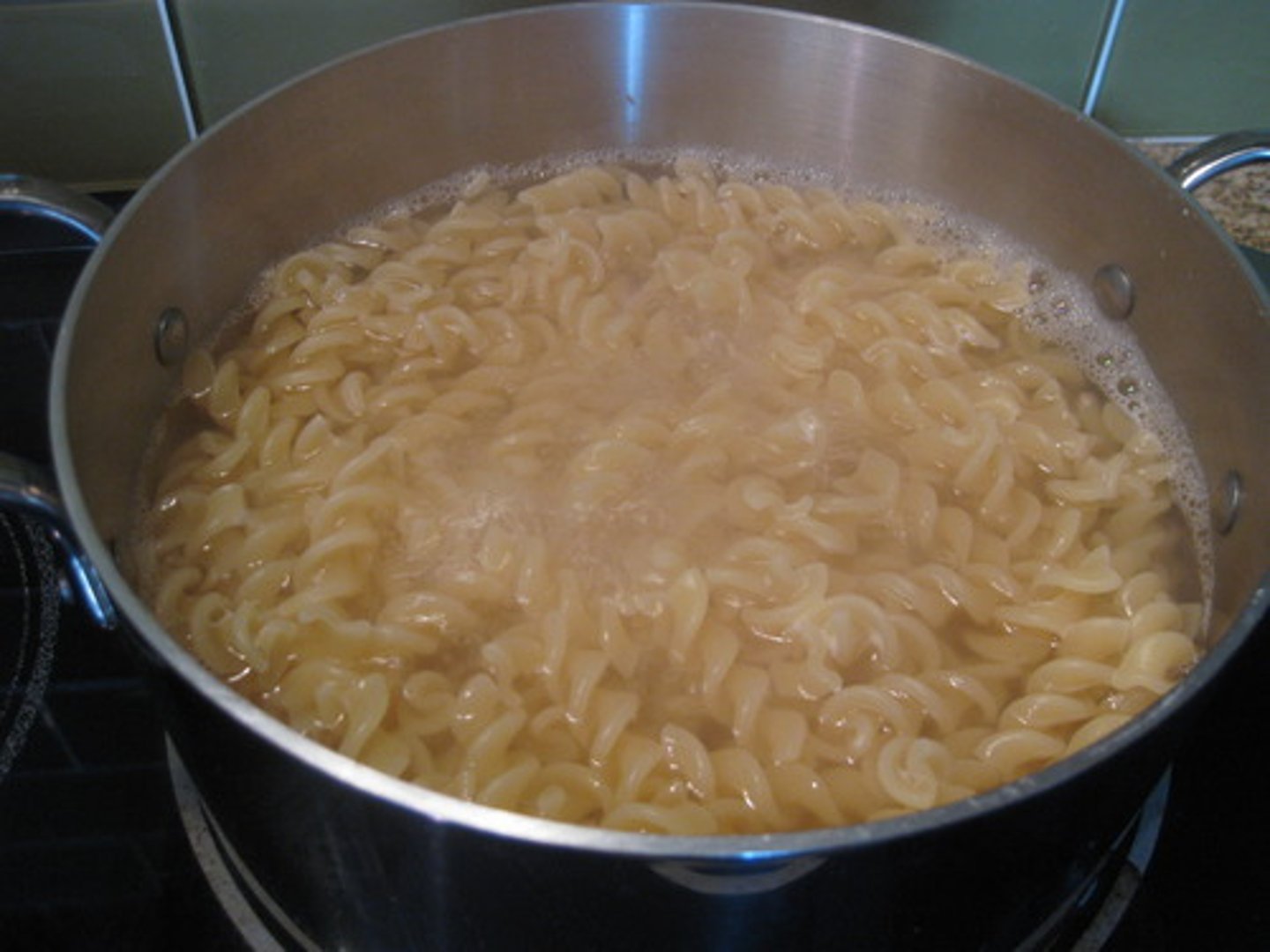
Mom is boiling pasta and after 10 minutes some of the water is missing. What happened to the water?
Water evaporated due to the heat from the stove.

Your neighbor is watering his yard in the middle of the day when it is hot. What would you say to him to make him water his yard in the evening?
Since it is hot outside most of the water is evaporating.
Explain cloud formation.
This is condensation. Water vapor cools, turning back into liquid water drops. The water drops come together to form clouds.
During a storm hail falls to the ground. Which stage of the water cycle was this an example of?
Precipitation
What happens to liquid water when it evaporates? What caused this?
Changes from liquid water into water vapor because it gains heat energy.
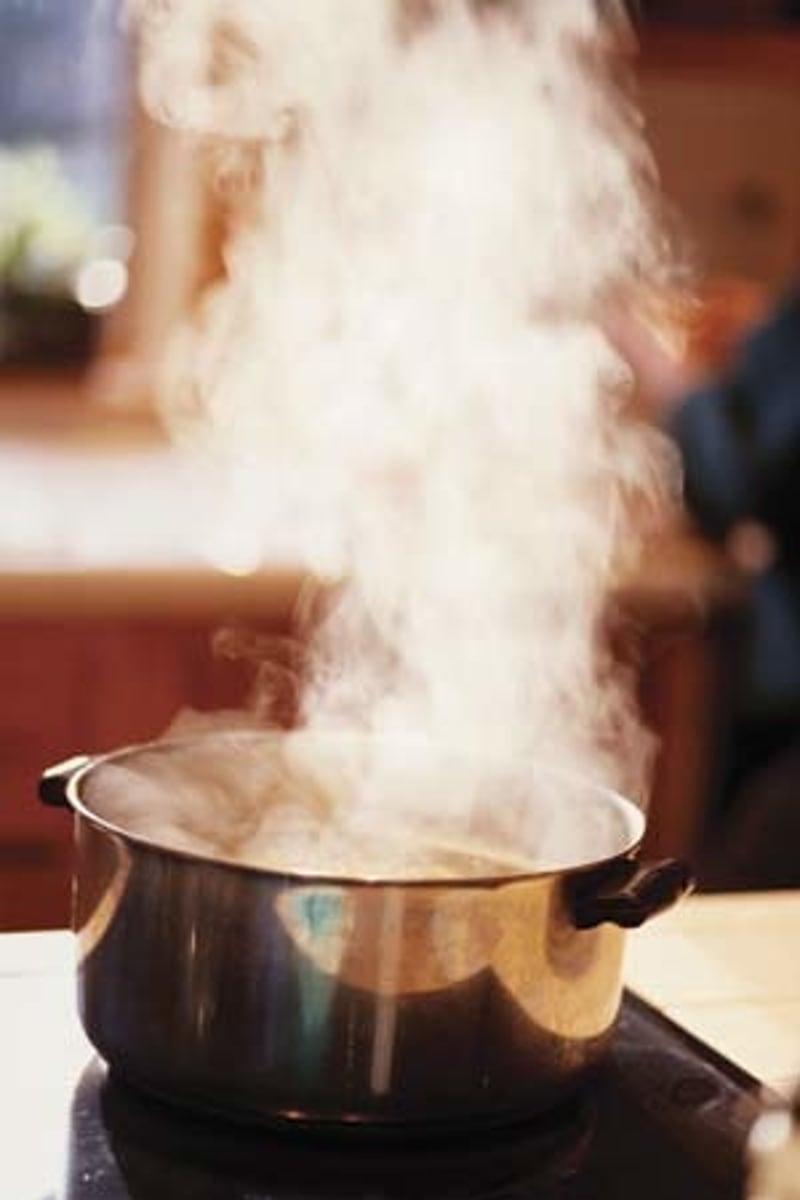

What happens to liquid water when it condenses? What causes this to happen?
It loses heart energy and cools, turning from water vapor into liquid water.
Liquid water gains heat energy and turns into water vapor. Name this stage of the water cycle.
Evaporation
Water vapor cools and turns into liquid water. Which water cycle stage is this?
Condensation
*transpiration
Plant heats up and gains heat energy from the sun, liquid water that is absorbed in the plant changes into water vapor and is released from the plant and rises into the atmosphere
Water fall to the earth as sleet. Name the stage of the water cycle.
Precipitation
Water leaves a plant and rises into the atmosphere. Name the water cycle stage.
Transpiration
Explain why transpiration would be faster during the day than at night.
It is faster during the day because there is more heat from the sun.
Explain why evaporation is faster during the day than at night.
Evaporation happens faster because there is more heat from the sun.