clin med M13 Somatic symptom disorders & preventative healthcare:
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
what are the 3 somatic symptom disorders?
Illness anxiety disorder
Somatic symptom disorder
Functional neurological symptom disorder
illness anxiety disorder:
Excessive preoccupation with possibility of illness or symptoms
Symptoms typically absent or mild at the time of the encounter
High level of anxiety with health related topics & worry about developing symptoms in the future
Increased self examination or obsessive online research
Symptoms present for ≥6 months
illness anxiety disorder key differentiators:
excessive worry about having a serious illness with little to no sxs
Ex: terrified about the prospect of breast CA so doing several breast checks each day
Previously called “hypochondria”
1st line tx for illness anxiety disorder:
CBT
2nd line treatment for illness anxiety disorder:
SSRIs
prozac
somatic symptom disorder:
≥ 1 physical symptom that causes either distress or functional impairment
≥ 1 abnormal thought or behavior
Excessive & pervasive thoughts about sxs
Persistently ↑anxiety about health
Excessive time spent addressing sxs
Symptoms present for ≥6 months
s/s of somatic symptom disorder:
Focal weakness
GI distress
Fatigue
Pain
Abnormal thoughts (excessive worry or obsession)
Abnormal behaviors (frequent self examination or frequency ER visits)
Or avoidance of appointments due to anxiety
tx for somatic symptom disorder:
Regular follow-up w PCP q4-8 weeks
+/- psychotherapy
what is functional neurologic disorder?
≥ 1 symptom involving involuntary motor or sensory function:
Voluntary muscle dysfunction:
Tremor
Weakness
Paralysis
Gait disturbance
Seizure-like limb movements
Sensory dysfunction:
Numbness
Paresthesia
Visual changes
Hearing loss
Change to taste or smell
Evidence that sx are incompatible w other conditions
Symptom must cause distress or impairment
acute vs persistent functional neuro disorder:
Acute episodes: symptoms present for <6 months
Persistent: symptoms present for ≥6 months
for what condition may you see “La belle indifference”?
functional neurological disorder
what is la belle indifference?
Pt may be too chill about what's going on
EX: “the drs will figure it out eventually”
what is functional neurological disorder often related to?
stress
treatment for functional neurological disorder?
Condition education
CBT
PT
+/- OT & SLP
2nd line: Meds if comorbid mental illness
what is malingering?
When individuals are intentionally faking or exaggerating their symptoms in order to achieve some secondary gain or external goal
May include: getting money, housing, time off from work, access to medications, escaping jail time
can malingering be imposed on someone else?
yes
Ex: mom did this to child to get out of work
clinical manifestations of malingering:
Conscious of motivation
For reward!!
Uncooperative
demand an extensive workup, but are not satisfied with negative results and don’t adhere to the diagnostic follow-up or treatment plan
Not satisfied with negative results
Symptoms stop once they achieve their goal
what is factitious disorder?
Individuals are intentionally faking or inducing symptoms, w the goal of getting attention and sympathy that is often given to someone who’s sick
who is factitious disorder MC in?
those w HC experience
females
clinical manifestations of factitious disorder:
usually unconscious or unaware of their motivation, which means that individuals often don’t even realize why they fabricate their symptoms
pretend symptoms persist even after they get the attention, sympathy, or even medical care
factitious disorder imposed on self:
(Munchausen syndrome)
Falsification on physical or psychological symptoms or induction of injury or disease, associated w identified deception
Pt presents themselves as ill, impaired, or injured
The deceptive behavior is evident even in the absence of obvious external rewards
Behavior not better explained by another mental disorder
individuals mainly pretend to have physical signs and symptoms of a disease
these individuals typically have a medical record of recurrent hospitalizations, and are overeager to go through invasive interventions, like surgical procedures
factitious disorder imposed on another:
(Munchausen syndrome by proxy)
Falsification of physical or psychological symptoms, or induction of injury or disease in another person, associated w identified deception
Individual -presents the victim (typically a dependent, such as a child or elder) to others as ill, impaired, or ill
The deceptive behavior is evident even in the absence of obvious external rewards
The behavior is not better explained by another mental disorder, such as delusional disorder or another psychotic disorder
The diagnosis is applied to the perpetrator, not the victim
person deliberately makes a second person ill without that person’s knowledge
Often, the 2nd person is someone they’re responsible for, like a child, an elder, or even a pet
this is considered a type of child or elder abuse
how do u diagbose factitious disorder?
DSM-5
treatment of factitious disorder:
pharmacotherapy
Pts should be managed by one physician and have a close relationship w them
what is preventative medicine?
The act of improving and maintaining patient well being in order to prevent disease, illness, disability, or untimely death
primary prevention:
focusing on interventions b4 the onset of disease to reduce risk of developing health problems
Ex: vaccination against a disease, health education
secondary prevention:
targeting individuals w existing RFs or early signs of disease to halt or slow progression
Ex: W screen for mammograms to secondarily prevent breast CA
what is the recommended screening for prostate cancer?
PSA screening
are digital rectal exams recommended for screening of prostate ca?
NO!
DRE not recommended as screening test due to lacking evidence of benefits
ages & recs for prostate cancer screening:
men aged 55-69 should undergo periodic PSA screening
***for 55yo, discuss the risks & benefits of PSA screening & proceed based on the patient’s preferences
>70 yo PSA-based screening not recommended
consider 40-45yo for high risk pts
repeat every 1-2yrs -3
what are the ages & screening recs for breast cancer?
Younger than 30:
US is the preferred initial modality. Incidence of breast cancer is <1% in this group.
30–39:
Either is okay but recommended to do both as initial
40 years and older:
Diagnostic mammography is the best initial diagnostic test
+/- PRN US
protocol for women aged 50-74 who are at average risk for breast cancer:
recommended mammograms every 2 years
think- 2 boobs, so every 2 yrs
if pt has famhx & noticed a lump, what should u do (breast CA)?
obtain diagnostic digital mammogram
75 or older breast ca screening:
dont necessarily need it; talk w provider
what is BI-RADS 3 & what do u do for it?
probably benign; short-interval (6month) follow up
what is BI-RADS 4&5 & what do u do for it?
4= suspicious
5= highly suggestive
both require biopsy for tissue diagnosis
what is BI-RADS 6 & what do u do for it?
6= biopsy-proven malignancy
requires surgical excision
at what age should u start colorectal cancer screening?
45yo
what ages require colorectal cancer screening?
45-75
Guaiac-based fecal occult blood test (gFOBT):
uses chemical guaiac to detect blood in the stool
Recommended annually

Fecal immunochemical test (FIT):
uses antibodies to detect blood in the stool; sensitivity not amazing
Recommended annually

FIT-DNA test:
also known as stool DNA test(cologuard). Combines the FIT with a test that detects altered DNA in the stool; great sensitivity
Recommended once every 3 years
think- DNA=3 letters→ Q3 yrs
Flexible sigmoidoscopy:
A short, thin, flexible, lighted scope inserted into the rectum to visualize the lower third of the colon; (doesn’t go as proximal as colonoscopy)
Recommended Q5 years OR Q10 years w FIT every year
think- flexible bc can do Q5 or Q10yrs
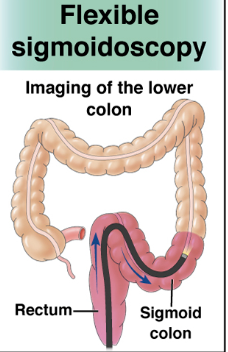
when can u get flexible sigmoidoscopy every 10 years?
if you do a FIT test annually
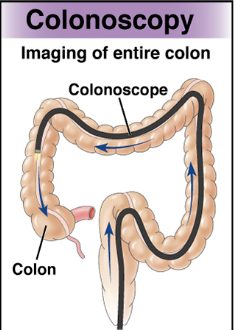
Colonoscopy:
Longer, thin, flexible lighted scope to visualize the entire colon
Recommended Q10 years for people at average risk of colorectal cancer
Most sensitive for lesions
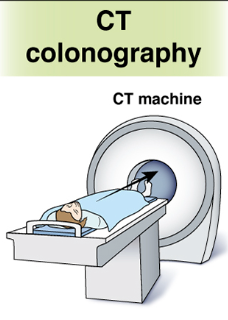
CT colonography (virtual colonoscopy):
Uses X-rays and computers to produce images of the entire colon which are displayed on a computer screen; good sensitivity for lesions
Recommended Q5 years
how often is each test option for colorectal cancer screening?
Colonoscopy Q10 years
FIT annually
gFOBT annually
FIT-DNA Q3 years
Flexible sigmoidoscopy Q5 years or Q10 years with FIT Qyr
CT colonoscopy Q5 years
which colorectal cancer screening test is LEAST expensive?
FIT ($30-90)
which colorectal cancer test is MOST expensive?
Colonoscopy ($1500-2500)
which colorectal cancer screenings are prophylactic?
colonoscopy is the only one that is diagnostic & therapeutic
prices of main colorectal cancer screening techniques:
Colonoscopy ($1500-2500)
FIT-DNA (cologuard) ($500-600)
FIT ($30-90)
CTC ($250-1000)
RFs for testicular cancer:
Undescended testicle
personal history
family history
HIV
age 20-34
what is the recommended exam for testicular cancer?
if suspicious of testicular mass, do testicular US & labs
should self-exam be done to screen for testicular cancer?
NO
recommends against screening for testicular cancer in adolescent or adult men thru self-exam or regular clinical exams
RFs for cervical cancer:
HPV, sexual activity, smoking, immunosuppression (AI disease, HIV, transplant), STDs, OCPs, >3 full term pregnancies, young age at first full-term pregnancy, socioeconomic status, DES, family history, genetic mutations
if pts mom has cervical cancer, should pt be worried ab it for themselves?
no, its not hereditary
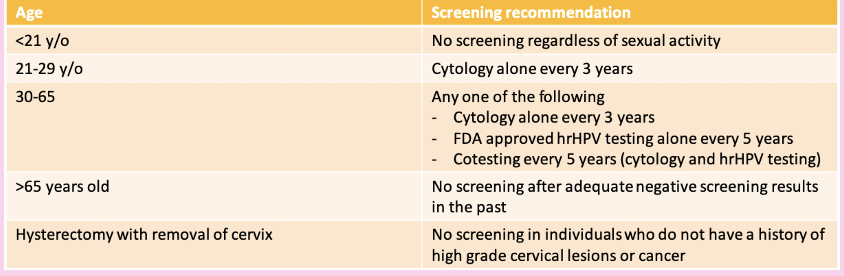
what cervical cancer screening should be done at ages 21-29?
screening Q3 years w cervical cytology alone
what cervical cancer screenings should be done at ages 30-65?
screening Q3 years w cervical cytology alone, Q5 years w high-risk HPV testing alone, or Q5 years w hrHPV testing in combination with cytology
what do the pap smear changes mean?
Normal-“negative”. Means that no cell changes were found on the cervix.
Unclear-“ASCUS”. Abnormal cervical cells. Unclear if related to HPV. Could be related to pregnancy, menopause or infection.
Abnormal–Cell changes found on the cervix. Likely caused by HPV. Often resolve on it’s own but able to develop into cancer. Can be low-grade or high-grade.
Unsatisfactory–There are not enough cells in the sample or they are clumped together and cannot be evaluated
when are pap smears done?
Pap smears begin at the age of 21 REGARDLESS of sexual activity
Then done every 3 years
cervical cancer screening guidelines:
when should clinicians screen for intimate partner violence?
in women of reproductive age
RFs of drug & alc dependence:
Family history, Availability of substance, Parental neglect, Childhood adversity, History of child, physical and/or sexual abuse, History of mood disorder, Depression, PTSD, Impulsivity
what are the screening options for alcohol?
AUDIT-C
SASQ
CAGE
TWEAK
ASCT→ Alcohol Screening Counseling Tool
what are the screening options for drug use?
NIDA Quick Screen
ASSIST
TAPS
what is TWEAK vs TWEAK (C)?
they are both screening for alcohol, but TWEAK (C) is for pregnant patients
intervention for alcohol use:
SBIRT approach
Cognitive behavioral strategies
Pharmacological options
intervention for drug use:
SBIRT approach
Cognitive behavioral strategies with high emphasis on relapse prevention
Pharmacological options
Testing for bloodborne pathogens
RFs of obesity:
Lack of physical exercise
Unhealthy eating habits
Low quality sleep
Stress
Health conditions
Genetics
Medications
environment
what measures do u use to screen for obesity?
BMI or waist circumference
who should be offered and/or referred to intensive, multicomponent behavioral interventions?
pts w BMI >30
RFs for unintentional injury:
Drowning (A leading cause of death for children): inability to swim, missing/ineffective fences, lack of supervision, location, not wearing life jackets, drinking alcohol or using prescription drugs
Transportation safety: Alcohol, drugs, distracted driving, risky driving, inexperienced driving, nighttime driving, rural vs urban driving
Older adult falls: medical conditions that affect vision, balance, sensation, postural hypotension, sarcopenia, medications, cluttered environment,
TBI and concussions: high-risk/collision sports, falls, lack of safety equipment, history of prior TBI
RFs for intentional injury:
Community: Perpetrators with low IQ, involvement with illicit substances, mental health diagnoses, exposure to violence, gang involvement, poor academic performance
Firearm: Perpetrators with violent history, violent victimization, drug/alcohol misuse, impaired cognition and poor judgment
Intimate partner: Victims of young age, low self esteem, low income, belief in strict gender roles, isolation
Sexual: Perpetrators with aggressive behaviors, early sexual initiation, exposure to sexually explicit media, strict gender roles
ages of abuse:
children <4yo, children w special needs, illness
elderly
which screening tools are used for injury & abuse?
HARK
HITS
screening for abdominal aortic aneurysms- age & what:
One-time screening with ultrasonography in men aged 65-75 who have ever smoked to R/O aaa
If aaa is <3cm, what should be done?
nothing, no rescreening
if aaa is 3-3.9cm, what should be done?
rescreen with ultrasonography every 2-3 years
if aaa 4-5.4cm, what should be done?
rescreen with ultrasonography or CT every 6-12 months.
Consider surgical consultation at 5 cm
if aaa >5.4cm, what should be done?
Surgical consultation for elective repair
what are the interventions for aaa?
Smoking cessation
Pharmacological
Surgical intervention
what is the primary prevention of lung cancer?
smoking prevention & cessation
what is the secondary prevention of lung cancer?
low dose CT at age 50-80yo with a 20+ pack year history
If havent smoked for 15 or more years, no need for screening