PLS 232 Political Science Terms & Definitions - Chapter 1
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
World Politics
The study of how global actors' activities entail the exercise of influence to achieve and defend their goals and ideals, and how it affects the world at large
Mercator Projection
Classic Eurocentric view. Gerard Mercator mapped the without distorting direction which made distances deceptive as Europe was in the center of the world.
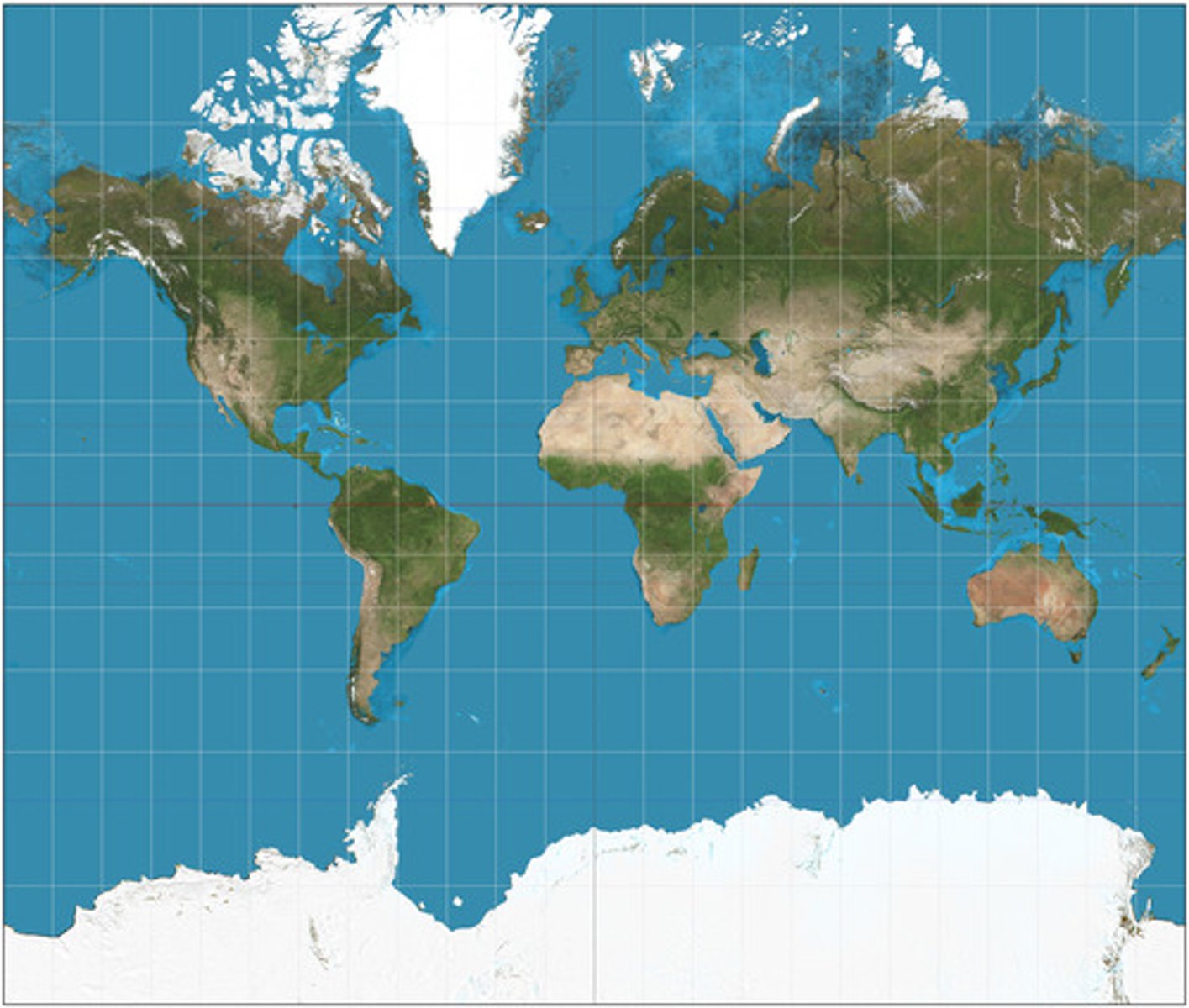
Peter's Projection
Each landmass appears in correct proportion to all the others, but it distorts shape and positions of landmasses. Draws attention to the Global South
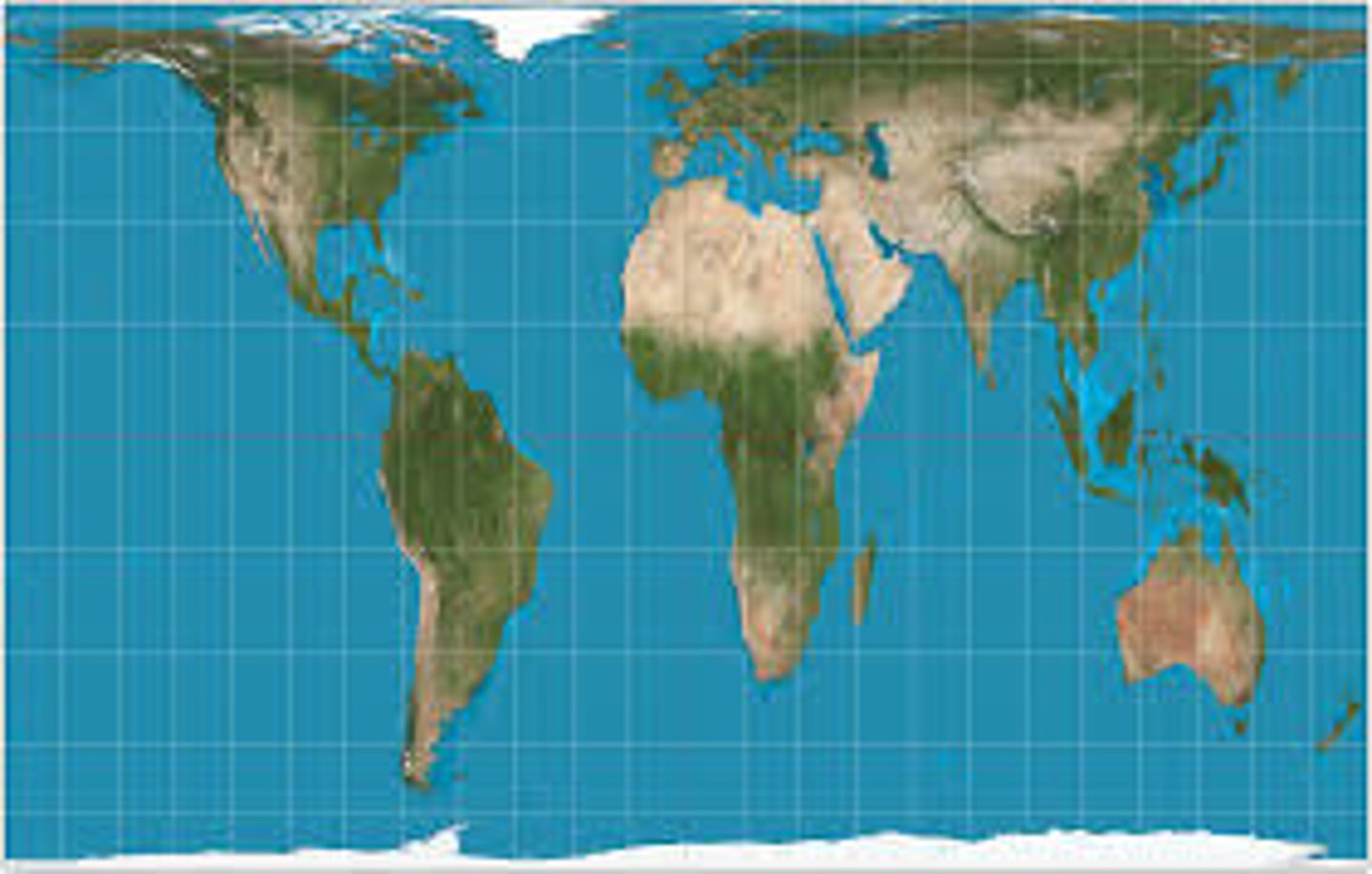
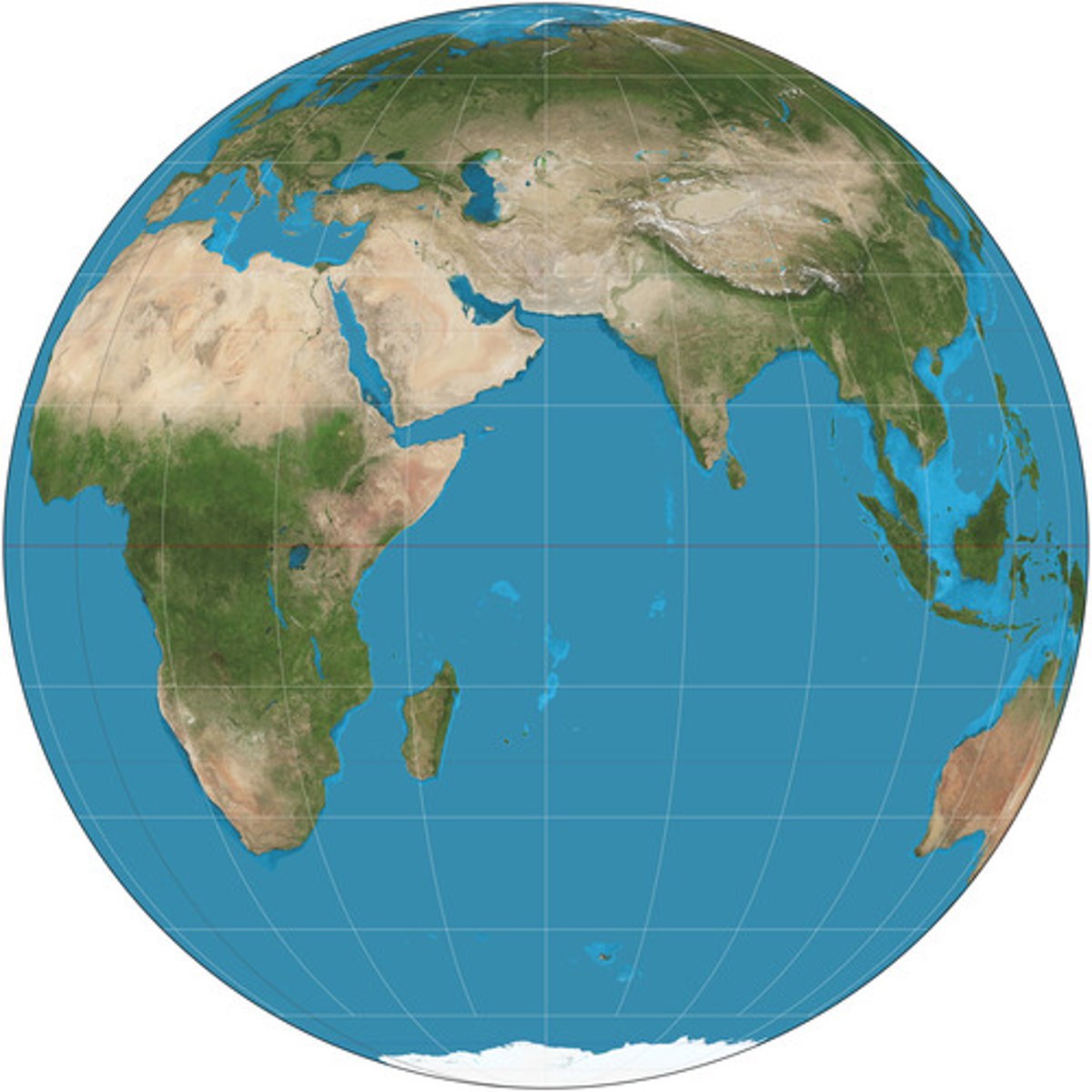
Orthographic Projection
Centers on mid-Atlantic. Uses rounded edges and distorts outer edges to give spherical perspective
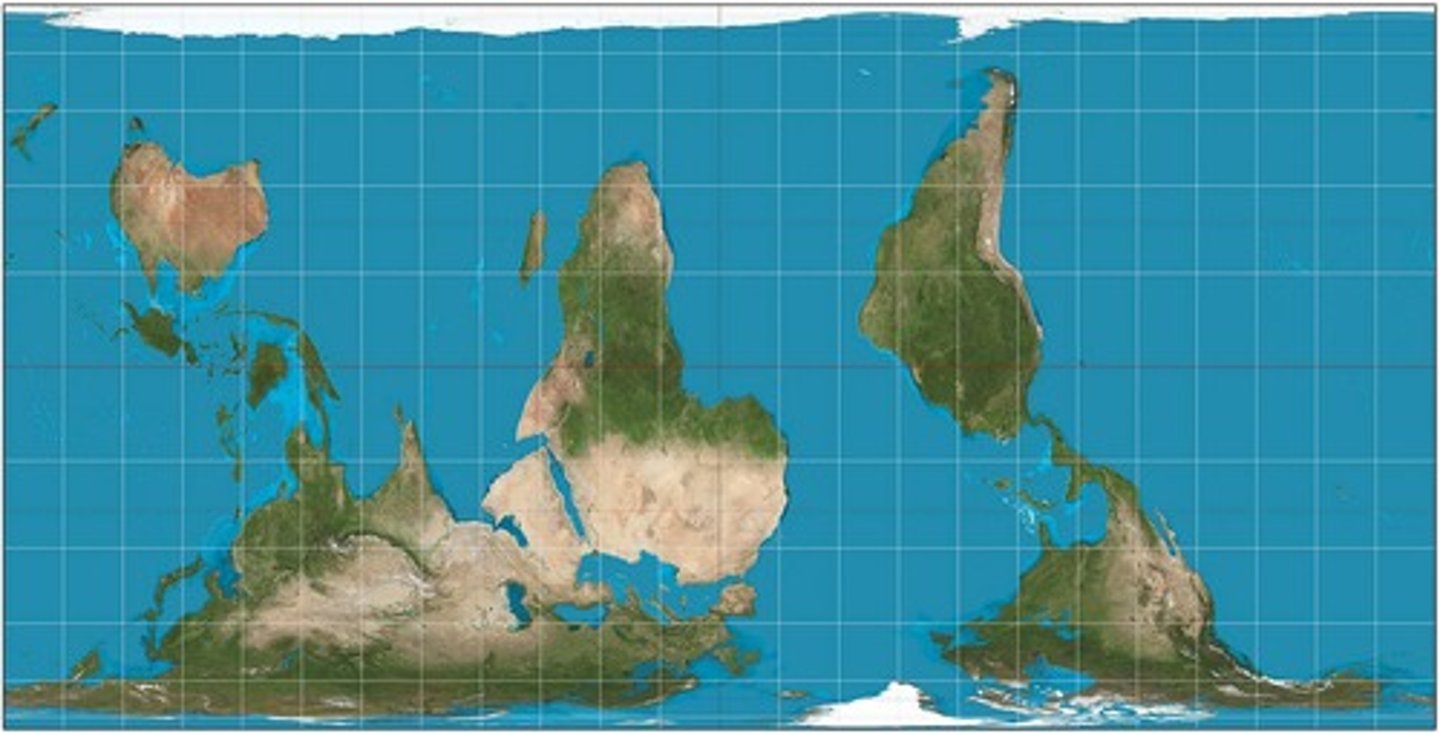
"Upside-Down" Projection
Global South positioned above Global North. Challenges Eurocentric conceptualization of the positions and globe's countries
Schematic Reasoning
The process of reasoning by which new information is interpreted according to a memory structure, a schema, which contains a network of generic scripts, metaphors, and simplified characterizations of observed objects and phenomena
Cognitive Dissonance
The general psychological tendency to deny discrepancies between one's preexisting beliefs (cognitions) and new information
Contradictory Tendencies in US Foreign Policy
Impulse to isolate itself (rejected membership in the League of Nations after WWII)
Determination to reform the world in its own image (aftermath of WWII gave rise to US globalist foreign policy, getting them involved nearly everywhere on every issue)
Mirror Images
The tendency of states and people in competitive interaction to perceive each other similarly - to see others the same hostile way others see them
Enduring Rivalries
Prolonged competition fueled by deep-seated mutual hatred that leads opposed actors to feud and fight over a long period of time without resolution of their conflict
"Thing that hurt, instruct"
Benjamin Franklin
Vietnam War caused many Americans to reject ideas about using military force in world politics
Defeat of the Third Reich forced German citizens to recognize the atrocities committed by Nazis and reevaluate their future
Human and financial losses in Iraq and Afghanistan led policy makers to reexamine their assumptions of "victory"
Actor
An individual group, state, or organization that plays a major role in world politics
State Sovereignty
A state's supreme authority to manage internal affairs and foreign relations
State
An independent legal entity with a government exercising exclusive control over the territory and population it governs
Nation
A collectivity whose people see themselves as members of the same group because they share the same ethnicity, culture, or language
Nation-state
An implied convergence between territorial states and the psychological identification of people within them
Ethnic Groups
People whose identity is primarily defined by their sense of sharing a common ancestral nationality, language, cultural heritage, and kinship
Intergovernmental Organizations (IGOs)
Institutions created and joined by states' government, which give them authority to make collective decisions to manage particular problems on the global agenda
Nongovernmental Organizations (NGOs)
Not-for-profit organizations of private citizens that function independent of any government and seek to support the public good. They may have consultative status with the United Nations and include professional associations, foundations, charities, or simply voluntary groups.
Level of Analysis
The different aspects of and agents in international affairs that may be stressed in interpreting and explaining global phenomena, depending on whether the analyst choose to focus on "wholes" (the complete global system and large collectives) or on "parts" (individual states or people)
State Level of Analysis
An analytical approach that emphasizes the impact of worldwide conditions on foreign policy behavior and human welfare
Transformation
A change in the characteristic pattern of interaction among the most active participants in world politics of such magnitude that it appears that one "global system" has replaced another
Systemic Level of Analysis
An analytical approach that emphasizes the impact of worldwide conditions on foreign policy behavior and human welfare
Global System
The predominant patterns of behaviors and beliefs that prevail internationally and define the major worldwide conditions that heavily influence human and state activities
Great Powers
The most powerful countries, militarily and economically, in the global system
Anarchy
A condition in which the units in the global system are subjected to few, if any, overarching institutions to regulate their conduct
Cycles
The periodic reemergence of conditions similar to those that existed previously
The Modern State System
Created in 1648 at Peace of Westphalia. Changed prior system of church governance, gave states sovereignty.
International Relations
The way global actors interact in their individual and collective efforts to modify existing global circumstances and how these interactions shape the ultimate trajectories of global trends
International Relations - The Field
Created in 1919 after WWI with the goal to understand war and help prevent it in the future